Discrete Tomography on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Discrete tomography
Herman, G. T. and Kuba, A., Discrete Tomography: Foundations, Algorithms, and Applications, Birkhäuser Boston, 1999
Herman, G. T. and Kuba, A., Advances in Discrete Tomography and Its Applications, Birkhäuser Boston, 2007
focuses on the problem of reconstruction of binary images (or finite subsets of the
Discrete tomography
Herman, G. T. and Kuba, A., Discrete Tomography: Foundations, Algorithms, and Applications, Birkhäuser Boston, 1999
Herman, G. T. and Kuba, A., Advances in Discrete Tomography and Its Applications, Birkhäuser Boston, 2007
focuses on the problem of reconstruction of binary images (or finite subsets of the
Algebraic aspects of discrete tomography
J. reine angew. Math. 534 (2001), 119-128.A. Alpers, R. Tijdeman, The Two-Dimensional Prouhet-Tarry-Escott Problem, Journal of Number Theory, 123 (2), pp. 403-412, 200
discrete mathematics,S. Brunetti, A. Del Lungo, P. Gritzmann, S. de Vries
On the reconstruction of binary and permutation matrices under (binary) tomographic constraints
Theoret. Comput. Sci. 406 (2008), no. 1-2, 63-71.A. Alpers, P. Gritzmann, On Stability, Error Correction, and Noise Compensation in Discrete Tomography, SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics 20 (1), pp. 227-239, 200
/ref>P. Gritzmann, B. Langfeld, On the index of Siegel grids and its application to the tomography of quasicrystals. European J. Combin. 29 (2008), no. 8, 1894-1909.
On the computational complexity of reconstructing lattice sets from their X-rays
Discrete Math. 202 (1999), no. 1-3, 45-71.C. Dürr, F. Guiñez, M. Matamala
Reconstructing 3-Colored Grids from Horizontal and Vertical Projections Is NP-hard
ESA 2009: 776-787. and
A theorem on flows in networks
Pacific J. Math. 7 (1957), 1073-1082.E. Barcucci, S. Brunetti, A. Del Lungo, M. Nivat
Reconstruction of lattice sets from their horizontal, vertical and diagonal X-rays
Discrete Mathematics 241(1-3): 65-78 (2001). In fact, a number of discrete tomography problems were first discussed as combinatorial problems. In 1957,
Stability and Instability in Discrete Tomography
Lecture Notes in Computer Science 2243; Digital and Image Geometry (Advanced Lectures), G. Bertrand, A. Imiya, R. Klette (Eds.), pp. 175-186, Springer-Verlag, 2001.A. Alpers, S. Brunetti
On the Stability of Reconstructing Lattice Sets from X-rays Along Two Directions
Lecture Notes in Computer Science 3429; Digital Geometry for Computer Imagery, E. Andres, G. Damiand, P. Lienhardt (Eds.), pp. 92-103, Springer-Verlag, 2005.B. van Dalen
Stability results for uniquely determined sets from two directions in discrete tomography
Discrete Mathematics 309(12): 3905-3916 (2009). *Coloring a grid using colors with the restriction that each row and each column has a specific number of cells of each color is known as the −atom problem in the discrete tomography community. The problem is NP-hard for , see. For further results see.
Approximating binary images from discrete X-rays
SIAM J. Optim. 11 (2000), no. 2, 522-546. for approximation guarantees), and
L. Rodek, H.F. Poulsen, E. Knudsen, G.T. Herman
A stochastic algorithm for reconstruction of grain maps of moderately deformed specimens based on X-ray diffraction
Journal of Applied Crystallography 40:313-321, 2007.K. J. Batenburg, J. Sijbers, H. F. Poulsen, and E. Knudsen, "DART: A Robust Algorithm for Fast Reconstruction of 3D Grain Maps", Journal of Applied Crystallography, vol. 43, pp. 1464-1473, 2010 A form of discrete tomography also forms the basis of
Euro DT (a Discrete Tomography Wiki site for researchers)Tomography applet by Christoph DürrPhD thesis on discrete tomography (2012): Tomographic segmentation and discrete tomography for quantitative analysis of transmission tomography data
{{Authority control Applied mathematics Digital geometry
 Discrete tomography
Herman, G. T. and Kuba, A., Discrete Tomography: Foundations, Algorithms, and Applications, Birkhäuser Boston, 1999
Herman, G. T. and Kuba, A., Advances in Discrete Tomography and Its Applications, Birkhäuser Boston, 2007
focuses on the problem of reconstruction of binary images (or finite subsets of the
Discrete tomography
Herman, G. T. and Kuba, A., Discrete Tomography: Foundations, Algorithms, and Applications, Birkhäuser Boston, 1999
Herman, G. T. and Kuba, A., Advances in Discrete Tomography and Its Applications, Birkhäuser Boston, 2007
focuses on the problem of reconstruction of binary images (or finite subsets of the integer lattice
In mathematics, the -dimensional integer lattice (or cubic lattice), denoted , is the lattice in the Euclidean space whose lattice points are -tuples of integers. The two-dimensional integer lattice is also called the square lattice, or grid ...
) from a small number of their projection
Projection, projections or projective may refer to:
Physics
* Projection (physics), the action/process of light, heat, or sound reflecting from a surface to another in a different direction
* The display of images by a projector
Optics, graphic ...
s.
In general, tomography
Tomography is imaging by sections or sectioning that uses any kind of penetrating wave. The method is used in radiology, archaeology, biology, atmospheric science, geophysics, oceanography, plasma physics, materials science, astrophysics, quantu ...
deals with the problem of determining shape and dimensional information of an object from a set of projections. From the mathematical point of view, the object corresponds to a function
Function or functionality may refer to:
Computing
* Function key, a type of key on computer keyboards
* Function model, a structured representation of processes in a system
* Function object or functor or functionoid, a concept of object-oriente ...
and the problem posed is to reconstruct this function from its integral
In mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented i ...
s or sums over subsets of its domain
Domain may refer to:
Mathematics
*Domain of a function, the set of input values for which the (total) function is defined
**Domain of definition of a partial function
**Natural domain of a partial function
**Domain of holomorphy of a function
* Do ...
. In general, the tomographic inversion problem may be continuous or discrete. In continuous tomography both the
domain and the range of the function are continuous and line integrals are used. In discrete tomography the domain of the function may be either discrete or continuous, and the range of the function is a finite set of real, usually nonnegative numbers. In continuous tomography when a large number of projections is available, accurate reconstructions can be made by many different algorithms.
It is typical for discrete tomography that only a few projections (line sums) are used. In this case, conventional techniques all fail. A special case of discrete tomography deals with the problem of the reconstruction of
a binary image from a small number of projections. The name ''discrete tomography'' is due to Larry Shepp, who organized the first meeting devoted to this topic (DIMACS
The Center for Discrete Mathematics and Theoretical Computer Science (DIMACS) is a collaboration between Rutgers University, Princeton University, and the research firms AT&T, Bell Labs, Applied Communication Sciences, and NEC. It was founded in ...
Mini-Symposium on Discrete Tomography, September 19, 1994, Rutgers University
Rutgers University (; RU), officially Rutgers, The State University of New Jersey, is a Public university, public land-grant research university consisting of four campuses in New Jersey. Chartered in 1766, Rutgers was originally called Queen's ...
).
Theory
Discrete tomography has strong connections with other mathematical fields, such asnumber theory
Number theory (or arithmetic or higher arithmetic in older usage) is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers and arithmetic function, integer-valued functions. German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777� ...
,R.J. Gardner, P. Gritzmann, Discrete tomography: determination of finite sets by X-rays, Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 349 (1997), no. 6, 2271-2295.L. Hajdu, R. TijdemanAlgebraic aspects of discrete tomography
J. reine angew. Math. 534 (2001), 119-128.A. Alpers, R. Tijdeman, The Two-Dimensional Prouhet-Tarry-Escott Problem, Journal of Number Theory, 123 (2), pp. 403-412, 200
discrete mathematics,S. Brunetti, A. Del Lungo, P. Gritzmann, S. de Vries
On the reconstruction of binary and permutation matrices under (binary) tomographic constraints
Theoret. Comput. Sci. 406 (2008), no. 1-2, 63-71.A. Alpers, P. Gritzmann, On Stability, Error Correction, and Noise Compensation in Discrete Tomography, SIAM Journal on Discrete Mathematics 20 (1), pp. 227-239, 200
/ref>P. Gritzmann, B. Langfeld, On the index of Siegel grids and its application to the tomography of quasicrystals. European J. Combin. 29 (2008), no. 8, 1894-1909.
computational complexity theory
In theoretical computer science and mathematics, computational complexity theory focuses on classifying computational problems according to their resource usage, and relating these classes to each other. A computational problem is a task solved by ...
R.J. Gardner, P. Gritzmann, D. PrangenbergOn the computational complexity of reconstructing lattice sets from their X-rays
Discrete Math. 202 (1999), no. 1-3, 45-71.C. Dürr, F. Guiñez, M. Matamala
Reconstructing 3-Colored Grids from Horizontal and Vertical Projections Is NP-hard
ESA 2009: 776-787. and
combinatorics
Combinatorics is an area of mathematics primarily concerned with counting, both as a means and an end in obtaining results, and certain properties of finite structures. It is closely related to many other areas of mathematics and has many appl ...
.H.J. Ryser, Matrices of zeros and ones, Bull. Amer. Math. Soc. 66 1960 442-464.D. GaleA theorem on flows in networks
Pacific J. Math. 7 (1957), 1073-1082.E. Barcucci, S. Brunetti, A. Del Lungo, M. Nivat
Reconstruction of lattice sets from their horizontal, vertical and diagonal X-rays
Discrete Mathematics 241(1-3): 65-78 (2001). In fact, a number of discrete tomography problems were first discussed as combinatorial problems. In 1957,
H. J. Ryser
Herbert John Ryser (July 28, 1923 – July 12, 1985) was a professor of mathematics, widely regarded as one of the major figures in combinatorics in the 20th century.David Gale
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
found the same consistency conditions, but in connection with the network flow problem. Another result of Ryser's is the definition of the switching operation by which discrete sets having the same projections can be transformed into each other.
The problem of reconstructing a binary image from a small number of projections generally leads to a large number of solutions. It is desirable to limit the class of possible solutions to only those that are typical of the class of the images which contains the image being reconstructed by using a priori information, such as convexity or connectedness.
Theorems
* Reconstructing (finite) planar lattice sets from their 1-dimensional X-rays is anNP-hard
In computational complexity theory, NP-hardness ( non-deterministic polynomial-time hardness) is the defining property of a class of problems that are informally "at least as hard as the hardest problems in NP". A simple example of an NP-hard pr ...
problem if the X-rays are taken from lattice directions (for the problem is in P).
*The reconstruction problem is highly unstable for (meaning that a small perturbation of the X-rays may lead to completely different reconstructions) and stable for , see.A. Alpers, P. Gritzmann, L. ThorensStability and Instability in Discrete Tomography
Lecture Notes in Computer Science 2243; Digital and Image Geometry (Advanced Lectures), G. Bertrand, A. Imiya, R. Klette (Eds.), pp. 175-186, Springer-Verlag, 2001.A. Alpers, S. Brunetti
On the Stability of Reconstructing Lattice Sets from X-rays Along Two Directions
Lecture Notes in Computer Science 3429; Digital Geometry for Computer Imagery, E. Andres, G. Damiand, P. Lienhardt (Eds.), pp. 92-103, Springer-Verlag, 2005.B. van Dalen
Stability results for uniquely determined sets from two directions in discrete tomography
Discrete Mathematics 309(12): 3905-3916 (2009). *Coloring a grid using colors with the restriction that each row and each column has a specific number of cells of each color is known as the −atom problem in the discrete tomography community. The problem is NP-hard for , see. For further results see.
Algorithms
Among the reconstruction methods one can find algebraic reconstruction techniques (e.g., DART or K. J. Batenburg, and J. Sijbers, "Generic iterative subset algorithms for discrete tomography", Discrete Applied Mathematics, vol. 157, no. 3, pp. 438-451, 2009),greedy algorithm
A greedy algorithm is any algorithm that follows the problem-solving heuristic of making the locally optimal choice at each stage. In many problems, a greedy strategy does not produce an optimal solution, but a greedy heuristic can yield locally ...
s (see P. Gritzmann, S. de Vries, M. WiegelmannApproximating binary images from discrete X-rays
SIAM J. Optim. 11 (2000), no. 2, 522-546. for approximation guarantees), and
Monte Carlo algorithm
In computing, a Monte Carlo algorithm is a randomized algorithm whose output may be incorrect with a certain (typically small) probability. Two examples of such algorithms are Karger–Stein algorithm and Monte Carlo algorithm for minimum Feedba ...
s.
Applications
Various algorithms have been applied inimage processing
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ...
,
Batenburg, Joost; Sijbers, Jan - DART: A practical reconstruction algorithm for discrete tomography - In: IEEE transactions on image processing, Vol. 20, Nr. 9, p. 2542-2553, (2011).
medicine
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care pract ...
,
three-dimensional statistical data security problems, computer
tomograph assisted engineering and design, electron microscopy
S. Bals, K. J. Batenburg, J. Verbeeck, J. Sijbers and G. Van Tendeloo, "Quantitative 3D reconstruction of catalyst particles for bamboo-like carbon-nanotubes", Nano Letters, Vol. 7, Nr. 12, p. 3669-3674, (2007)
Batenburg J., S. Bals, Sijbers J., C. Kubel, P.A. Midgley, J.C. Hernandez, U. Kaiser, E.R. Encina, E.A. Coronado and G. Van Tendeloo, "3D imaging of nanomaterials by discrete tomography", Ultramicroscopy, Vol. 109, p. 730-740, (2009)
and materials science, including the 3DXRD microscope.A. Alpers, H.F. Poulsen, E. Knudsen, G.T. Herman, A Discrete Tomography Algorithm for Improving the Quality of 3DXRD Grain Maps, Journal of Applied Crystallography 39, pp. 582-588, 200L. Rodek, H.F. Poulsen, E. Knudsen, G.T. Herman
A stochastic algorithm for reconstruction of grain maps of moderately deformed specimens based on X-ray diffraction
Journal of Applied Crystallography 40:313-321, 2007.K. J. Batenburg, J. Sijbers, H. F. Poulsen, and E. Knudsen, "DART: A Robust Algorithm for Fast Reconstruction of 3D Grain Maps", Journal of Applied Crystallography, vol. 43, pp. 1464-1473, 2010 A form of discrete tomography also forms the basis of
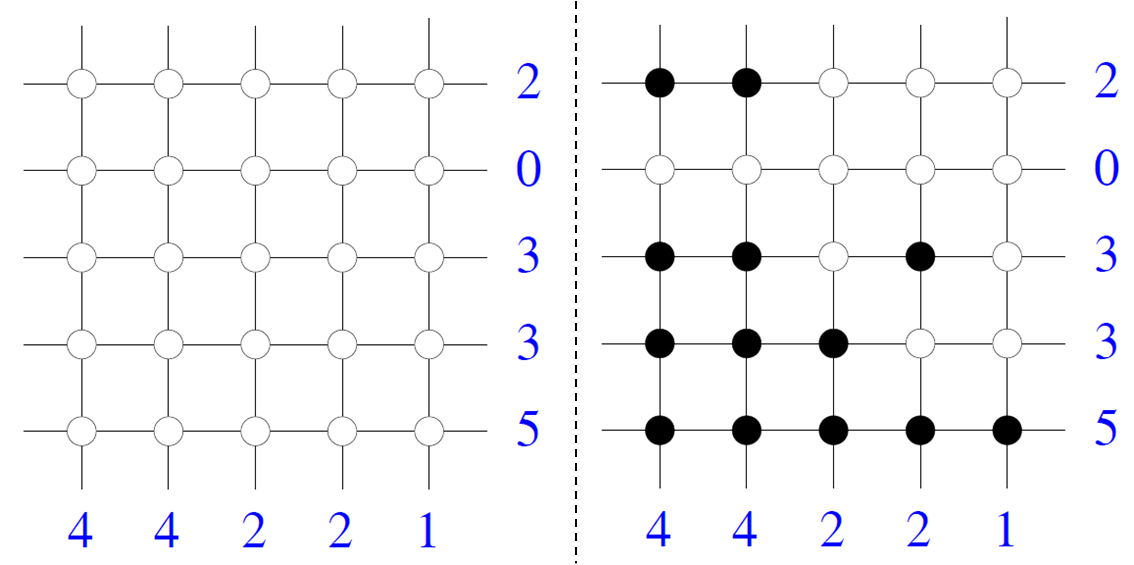
nonogram
Nonograms, also known as Hanjie, Paint by Numbers, Picross, Griddlers, and Pic-a-Pix, and by various other names, are picture logic puzzles in which cells in a grid must be colored or left blank according to numbers at the side of the grid to r ...
s, a type of logic puzzle
A logic puzzle is a puzzle deriving from the mathematics, mathematical field of deductive reasoning, deduction.
History
The logic puzzle was first produced by Charles Lutwidge Dodgson, who is better known under his pen name Lewis Carroll, the au ...
in which information about the rows and columns of a digital image is used to reconstruct the image.
See also
* Geometric tomographyReferences
External links
Euro DT (a Discrete Tomography Wiki site for researchers)
{{Authority control Applied mathematics Digital geometry