Digital Circuit Design on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Integrated circuit design, or IC design, is a sub-field of
Integrated circuit design, or IC design, is a sub-field of
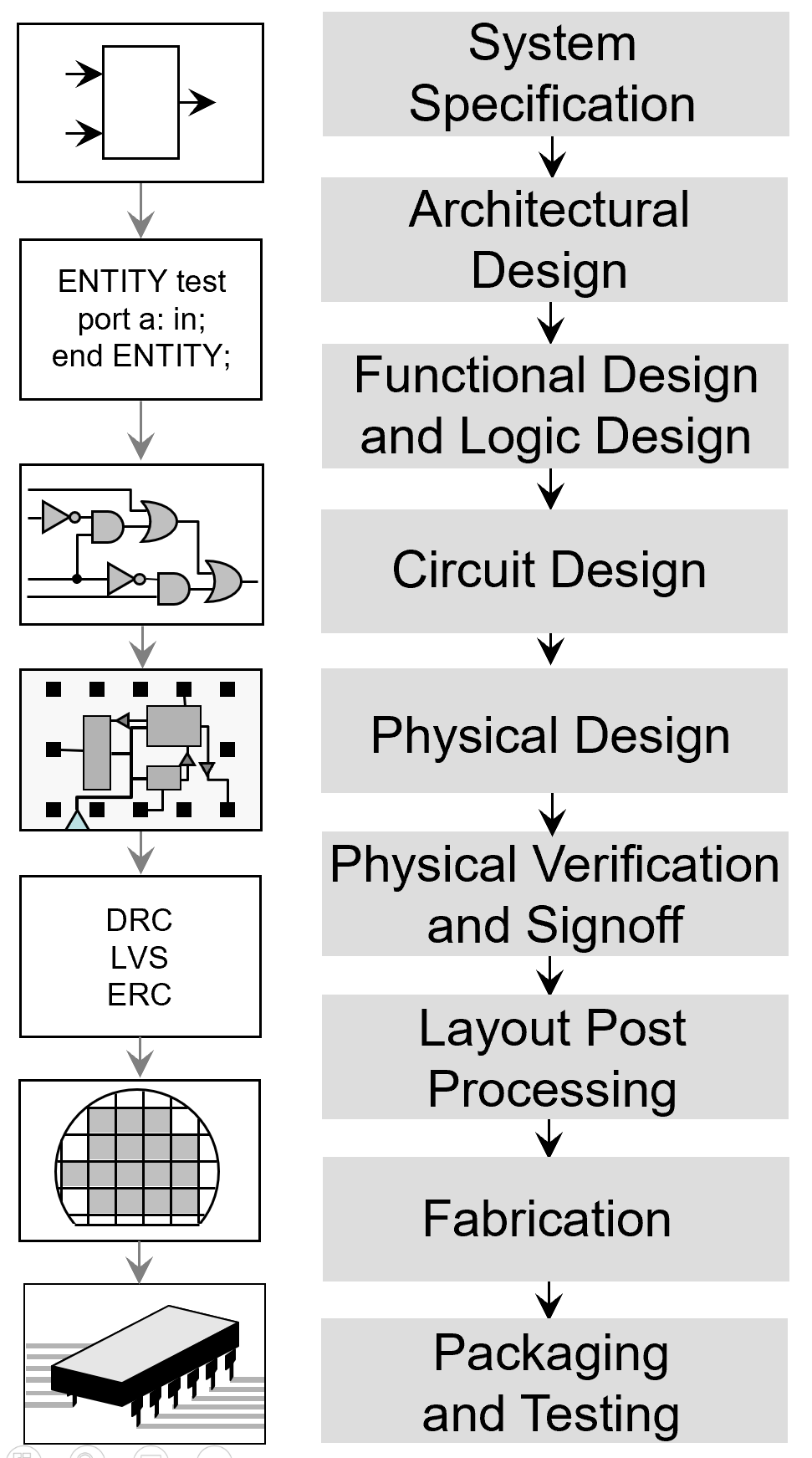 A typical IC design cycle involves several steps:
# System Specification
## Feasibility study and die size estimate
## Function analysis
# Architectural or System Level Design
#Logic Design
## Analogue Design, Simulation & Layout
## Digital Design & Simulation
## System Simulation, Emulation & Verification
# Circuit Design
##Digital design synthesis
## Design For Test and Automatic test pattern generation
##
A typical IC design cycle involves several steps:
# System Specification
## Feasibility study and die size estimate
## Function analysis
# Architectural or System Level Design
#Logic Design
## Analogue Design, Simulation & Layout
## Digital Design & Simulation
## System Simulation, Emulation & Verification
# Circuit Design
##Digital design synthesis
## Design For Test and Automatic test pattern generation
##
 RTL is only a behavioral model of the actual functionality of what the chip is supposed to operate under. It has no link to a physical aspect of how the chip would operate in real life at the materials, physics, and electrical engineering side. For this reason, the next step in the IC design process, physical design stage, is to map the RTL into actual geometric representations of all electronics devices, such as capacitors, resistors, logic gates, and transistors that will go on the chip.
The main steps of physical design are listed below. In practice there is not a straightforward progression - considerable iteration is required to ensure all objectives are met simultaneously. This is a difficult problem in its own right, called design closure.
* Logic synthesis: The RTL is mapped into a gate-level netlist in the target technology of the chip.
*
RTL is only a behavioral model of the actual functionality of what the chip is supposed to operate under. It has no link to a physical aspect of how the chip would operate in real life at the materials, physics, and electrical engineering side. For this reason, the next step in the IC design process, physical design stage, is to map the RTL into actual geometric representations of all electronics devices, such as capacitors, resistors, logic gates, and transistors that will go on the chip.
The main steps of physical design are listed below. In practice there is not a straightforward progression - considerable iteration is required to ensure all objectives are met simultaneously. This is a difficult problem in its own right, called design closure.
* Logic synthesis: The RTL is mapped into a gate-level netlist in the target technology of the chip.
*
 Integrated circuit design, or IC design, is a sub-field of
Integrated circuit design, or IC design, is a sub-field of electronics engineering
Electronics engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering which emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current f ...
, encompassing the particular logic and circuit design
The process of circuit design can cover systems ranging from complex electronic systems down to the individual transistors within an integrated circuit. One person can often do the design process without needing a planned or structured design ...
techniques required to design integrated circuits, or ICs. ICs consist of miniaturized electronic component
An electronic component is any basic discrete device or physical entity in an electronic system used to affect electrons or their associated fields. Electronic components are mostly industrial products, available in a singular form and are not ...
s built into an electrical network on a monolithic semiconductor substrate by photolithography
In integrated circuit manufacturing, photolithography or optical lithography is a general term used for techniques that use light to produce minutely patterned thin films of suitable materials over a substrate, such as a silicon wafer, to protect ...
.
IC design can be divided into the broad categories of digital
Digital usually refers to something using discrete digits, often binary digits.
Technology and computing Hardware
*Digital electronics, electronic circuits which operate using digital signals
**Digital camera, which captures and stores digital i ...
and analog
Analog or analogue may refer to:
Computing and electronics
* Analog signal, in which information is encoded in a continuous variable
** Analog device, an apparatus that operates on analog signals
*** Analog electronics, circuits which use analo ...
IC design. Digital IC design is to produce components such as microprocessors, FPGA
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term '' field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware de ...
s, memories ( RAM, ROM
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* R ...
, and flash) and digital ASIC
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC ) is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-efficien ...
s. Digital design focuses on logical correctness, maximizing circuit density, and placing circuits so that clock and timing signals are routed efficiently. Analog IC design also has specializations in power IC design and RF IC design. Analog IC design is used in the design of op-amp
An operational amplifier (often op amp or opamp) is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op amp produces an output potential (relative to c ...
s, linear regulators, phase locked loops, oscillator
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
s and active filters. Analog design is more concerned with the physics of the semiconductor devices such as gain, matching, power dissipation, and resistance. Fidelity of analog signal amplification and filtering is usually critical and as a result, analog ICs use larger area active devices than digital designs and are usually less dense in circuitry.
Modern ICs are enormously complicated. An average desktop computer chip, as of 2015, has over 1 billion transistors. The rules for what can and cannot be manufactured are also extremely complex. Common IC processes of 2015 have more than 500 rules. Furthermore, since the manufacturing process itself is not completely predictable, designers must account for its statistical
Statistics (from German: ''Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industria ...
nature. The complexity of modern IC design, as well as market pressure to produce designs rapidly, has led to the extensive use of automated design tools in the IC design process. In short, the design of an IC using EDA software is the design, test, and verification of the instructions that the IC is to carry out.
Fundamentals
Integrated circuit design involves the creation of electronic components, such as transistors,resistors
A resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to divide voltages, bias active el ...
, capacitors
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
The effect of a ...
and the interconnection of these components onto a piece of semiconductor, typically silicon. A method to isolate the individual components formed in the substrate
Substrate may refer to:
Physical layers
*Substrate (biology), the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the surface or medium on which an organism grows or is attached
** Substrate (locomotion), the surface over which an organism lo ...
is necessary since the substrate silicon is conductive and often forms an active region of the individual components. The two common methods are p-n junction isolation and dielectric isolation
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the mate ...
. Attention must be given to power dissipation of transistors and interconnect resistances and current density of the interconnect, contacts and vias since ICs contain very tiny devices compared to discrete components, where such concerns are less of an issue. Electromigration
Electromigration is the transport of material caused by the gradual movement of the ions in a conductor due to the momentum transfer between conducting electrons and diffusing metal atoms. The effect is important in applications where high direc ...
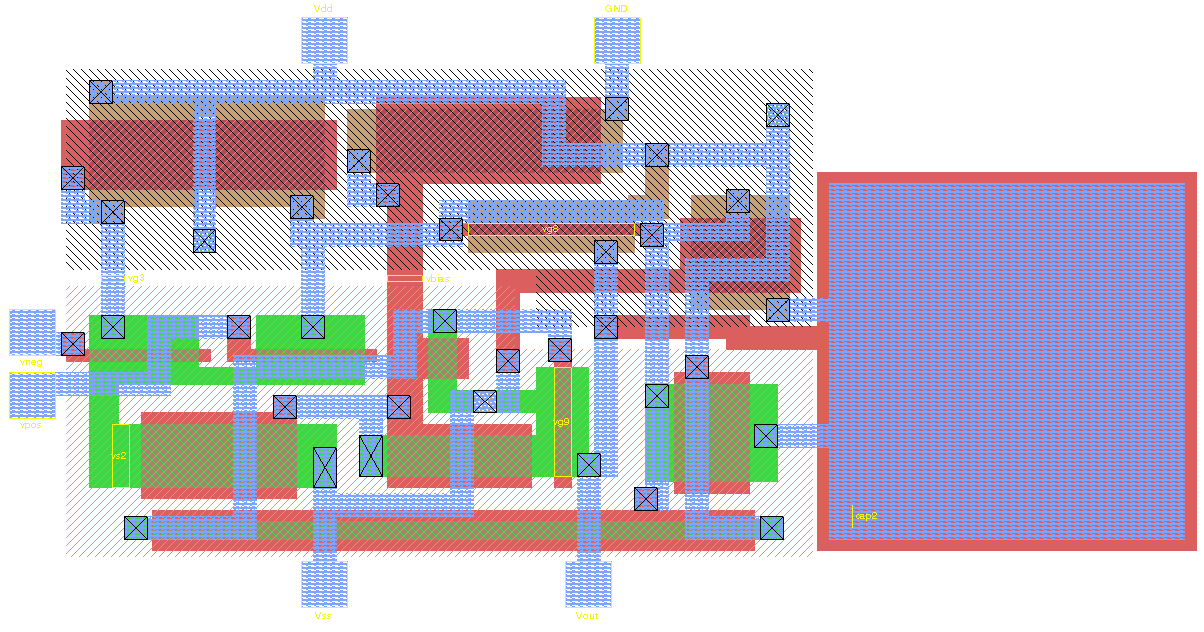
in metallic interconnect and ESD damage to the tiny components are also of concern. Finally, the physical layout of certain circuit subblocks is typically critical, in order to achieve the desired speed of operation, to segregate noisy portions of an IC from quiet portions, to balance the effects of heat generation across the IC, or to facilitate the placement of connections to circuitry outside the IC.
Design flow
 A typical IC design cycle involves several steps:
# System Specification
## Feasibility study and die size estimate
## Function analysis
# Architectural or System Level Design
#Logic Design
## Analogue Design, Simulation & Layout
## Digital Design & Simulation
## System Simulation, Emulation & Verification
# Circuit Design
##Digital design synthesis
## Design For Test and Automatic test pattern generation
##
A typical IC design cycle involves several steps:
# System Specification
## Feasibility study and die size estimate
## Function analysis
# Architectural or System Level Design
#Logic Design
## Analogue Design, Simulation & Layout
## Digital Design & Simulation
## System Simulation, Emulation & Verification
# Circuit Design
##Digital design synthesis
## Design For Test and Automatic test pattern generation
##Design for manufacturability (IC)
Design for manufacturability (also sometimes known as design for manufacturing or DFM) is the general engineering practice of designing products in such a way that they are easy to manufacture. The concept exists in almost all engineering discipli ...
# Physical Design
##Floorplanning
##Place and Route
##Parasitic Extraction
#Physical Verification & Signoff
A sign-on (or start-up in Commonwealth countries except Canada) is the beginning of operations for a radio or television station, generally at the start of each day. It is the opposite of a sign-off (or closedown in Commonwealth countries exce ...
##Static timing
##Co-simulation and timing
# Mask data preparation
Mask data preparation (MDP), also known as layout post processing, is the procedure of translating a file containing the intended set of polygons from an integrated circuit layout into set of instructions that a photomask writer can use to genera ...
(Layout Post Processing)
##Chip finishing with Tape out
##Reticle layout
##Layout-to-mask preparation
# Wafer fabrication
# Packaging
Packaging is the science, art and technology of enclosing or protecting products for distribution, storage, sale, and use. Packaging also refers to the process of designing, evaluating, and producing packages. Packaging can be described as a co ...
# Die test
##Post silicon validation {{no footnotes, date=July 2011
Post-silicon validation and debug is the last step in the development of a semiconductor integrated circuit.
Pre-silicon process
During the pre-silicon process, engineers test devices in a virtual environment with s ...
and integration
## Device characterization
## Tweak (if necessary)
# Chip Deployment
##Datasheet generation (of usually a Portable Document Format (PDF) file)
## Ramp up
## Production
## Yield Analysis / Warranty Analysis Reliability (semiconductor)
Reliability of semiconductor devices can be summarized as follows:
# Semiconductor devices are very sensitive to impurities and particles. Therefore, to manufacture these devices it is necessary to manage many processes while accurately controllin ...
##Failure analysis Failure analysis is the process of collecting and analyzing data to determine the cause of a failure, often with the goal of determining corrective actions or liability.
According to Bloch and Geitner, ”machinery failures reveal a reaction chain o ...
on any returns
## Plan for next generation chip using production information if possible
Summary
Roughly saying, digital IC design can be divided into three parts. * Electronic system-level design: This step creates the user functional specification. The user may use a variety of languages and tools to create this description. Examples include a C/ C++ model, VHDL, SystemC, SystemVerilog Transaction Level Models, Simulink and MATLAB. *RTL design: This step converts the user specification (what the user wants the chip to do) into a register transfer level (RTL) description. The RTL describes the exact behavior of the digital circuits on the chip, as well as the interconnections to inputs and outputs. * Physical circuit design: This step takes the RTL, and a library of available logic gates (standard cell
In semiconductor design, standard cell methodology is a method of designing application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) with mostly digital-logic features. Standard cell methodology is an example of design abstraction, whereby a low-level v ...
library), and creates a chip design. This step involves use of IC layout editor
An Integrated circuit layout editor or IC layout editor is an electronic design automation software tool that allows a user to digitize the shapes and patterns that form an integrated circuit. Typically the view will include the components (usual ...
, layout and floor planning, figuring out which gates to use, defining places for them, and wiring (clock timing synthesis, routing) them together.
Note that the second step, RTL design, is responsible for the chip doing the right thing. The third step, physical design, does not affect the functionality at all (if done correctly) but determines how fast the chip operates and how much it costs.
A standard cell normally represents a single logic gate. the use of standard cells allows the chip's design to be split into logical and physical levels. A fabless company would normally only work on the logical design of a chip, determining how cells are connected and the functionality of the chip, while following design rules from the foundry the chip will be made in, while the physical design of the chip, the cells themselves, are normally done by the foundry and it comprises the physics of the transistor device. Foundries supply libraries of standard cells to fabless companies for design purposes and to allow manufacturing of their designs using the foundry's facilities.
Design lifecycle
Theintegrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
(IC) development process starts with defining product requirements, progresses through architectural definition, implementation, bringup and finally production. The various phases of the integrated circuit development process are described below. Although the phases are presented here in a straightforward fashion, in reality there is iteration and these steps may occur multiple times.
Requirements
Before an architecture can be defined some high level product goals must be defined. The requirements are usually generated by a cross functional team that addresses market opportunity, customer needs, feasibility and much more. This phase should result in aproduct requirements document
A product requirements document (PRD) is a document containing all the requirements for a certain product.
It is written to allow people to understand ''what'' a product should do. A PRD should, however, generally avoid anticipating or defining ' ...
.
Architecture
The '' architecture'' defines the fundamental structure, goals and principles of the product. It defines high level concepts and the intrinsic value proposition of the product. Architecture teams take into account many variables and interface with many groups. People creating the architecture generally have a significant amount of experience dealing with systems in the area for which the architecture is being created. The work product of the architecture phase is an architectural specification.Micro-architecture
The micro-architecture is a step closer to the hardware. It implements the architecture and defines specific mechanisms and structures for achieving that implementation. The result of the micro-architecture phase is a micro-architecture specification which describes the methods used to implement the architecture.Implementation
In the implementation phase the design itself is created using the micro-architectural specification as the starting point. This involves low leveldefinition
A definition is a statement of the meaning of a term (a word, phrase, or other set of symbols). Definitions can be classified into two large categories: intensional definitions (which try to give the sense of a term), and extensional definitio ...
and partitioning, writing code
In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes shortened or secret, for communication through a communication ...
, entering schematics and verification. This phase ends with a design reaching tapeout.
Bringup
After a design is created, taped-out and manufactured, actual hardware, 'first silicon', is received which is taken into the lab where it goes through ''bringup''. Bringup is the process of powering, testing and characterizing the design in the lab. Numeroustests
Test(s), testing, or TEST may refer to:
* Test (assessment), an educational assessment intended to measure the respondents' knowledge or other abilities
Arts and entertainment
* ''Test'' (2013 film), an American film
* ''Test'' (2014 film), ...
are performed starting from very simple tests such as ensuring that the device will power on to much more complicated tests which try to stress the part in various ways. The result of the bringup phase is documentation of characterization data
Characterization or characterisation is the representation of persons (or other beings or creatures) in narrative and dramatic works. The term character development is sometimes used as a synonym. This representation may include direct methods l ...
(how well the part performs to spec) and errata (unexpected behavior).
Productization
Productization is the task of taking a design from engineering into mass production manufacturing. Although a design may have successfully met the specifications of the product in the lab during the bringup phase there are many challenges that product engineers face when trying to mass-produce those designs. The IC must be ramped up to production volumes with an acceptable yield. The goal of the productization phase is to reach mass production volumes at an acceptable cost.Sustaining
Once a design is mature and has reached mass production it must be sustained. The process must be continually monitored and problems dealt with quickly to avoid a significant impact on production volumes. The goal of sustaining is to maintain production volumes and continually reduce costs until the product reachesend of life End-of-life may refer to:
* End-of-life (product), a term used with respect to terminating the sale or support of goods and services
* End-of-life care, medical care for patients with terminal illnesses or conditions that have become advanced, prog ...
.
Design process
Microarchitecture and system-level design
The initial chip design process begins with system-level design and microarchitecture planning. Within IC design companies, management and often analytics will draft a proposal for a design team to start the design of a new chip to fit into an industry segment. Upper-level designers will meet at this stage to decide how the chip will operate functionally. This step is where an IC's functionality and design are decided. IC designers will map out the functional requirements, verification testbenches, and testing methodologies for the whole project, and will then turn the preliminary design into a system-level specification that can be simulated with simple models using languages like C++ and MATLAB and emulation tools. For pure and new designs, the system design stage is where anInstruction set
In computer science, an instruction set architecture (ISA), also called computer architecture, is an abstract model of a computer. A device that executes instructions described by that ISA, such as a central processing unit (CPU), is called an ' ...
and operation is planned out, and in most chips existing instruction sets are modified for newer functionality. Design at this stage is often statements such as ''encodes in the MP3 format'' or ''implements IEEE floating-point arithmetic
The IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic (IEEE 754) is a technical standard for floating-point arithmetic established in 1985 by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). The standard addressed many problems found in ...
''. At later stages in the design process, each of these innocent looking statements expands to hundreds of pages of textual documentation.
RTL design
Upon agreement of a system design, RTL designers then implement the functional models in a hardware description language like Verilog, SystemVerilog, or VHDL. Using digital design components like adders, shifters, and state machines as well as computer architecture concepts like pipelining, superscalar execution, and branch prediction, RTL designers will break a functional description into hardware models of components on the chip working together. Each of the simple statements described in the system design can easily turn into thousands of lines of RTL code, which is why it is extremely difficult to verify that the RTL will do the right thing in all the possible cases that the user may throw at it. To reduce the number of functionality bugs, a separate hardware verification group will take the RTL and design testbenches and systems to check that the RTL actually is performing the same steps under many different conditions, classified as the domain of functional verification. Many techniques are used, none of them perfect but all of them useful – extensive logic simulation, formal methods, hardware emulation,lint
Lint may refer to:
* Fibrous coat of thick hairs covering the seeds of the cotton plant
* Lint (material), an accumulation of fluffy fibers that collect on fabric
Places
* Lint, Belgium, a municipality located in Antwerp, Belgium
* Linț, a vill ...
-like code checking, code coverage, and so on.
A tiny error here can make the whole chip useless, or worse. The famous Pentium FDIV bug
The Pentium FDIV bug is a hardware bug affecting the floating-point unit (FPU) of the early Intel Pentium processors. Because of the bug, the processor would return incorrect binary floating point results when dividing certain pairs of high-pr ...
caused the results of a division to be wrong by at most 61 parts per million, in cases that occurred very infrequently. No one even noticed it until the chip had been in production for months. Yet Intel was forced to offer to replace, for free, every chip sold until they could fix the bug, at a cost of $475 million (US).
Physical design
 RTL is only a behavioral model of the actual functionality of what the chip is supposed to operate under. It has no link to a physical aspect of how the chip would operate in real life at the materials, physics, and electrical engineering side. For this reason, the next step in the IC design process, physical design stage, is to map the RTL into actual geometric representations of all electronics devices, such as capacitors, resistors, logic gates, and transistors that will go on the chip.
The main steps of physical design are listed below. In practice there is not a straightforward progression - considerable iteration is required to ensure all objectives are met simultaneously. This is a difficult problem in its own right, called design closure.
* Logic synthesis: The RTL is mapped into a gate-level netlist in the target technology of the chip.
*
RTL is only a behavioral model of the actual functionality of what the chip is supposed to operate under. It has no link to a physical aspect of how the chip would operate in real life at the materials, physics, and electrical engineering side. For this reason, the next step in the IC design process, physical design stage, is to map the RTL into actual geometric representations of all electronics devices, such as capacitors, resistors, logic gates, and transistors that will go on the chip.
The main steps of physical design are listed below. In practice there is not a straightforward progression - considerable iteration is required to ensure all objectives are met simultaneously. This is a difficult problem in its own right, called design closure.
* Logic synthesis: The RTL is mapped into a gate-level netlist in the target technology of the chip.
*Floorplanning
In electronic design automation, a floorplan of an integrated circuit is a schematics representation of tentative placement of its major functional blocks.
In modern electronic design process floorplans are created during the floorplanning de ...
: The RTL of the chip is assigned to gross regions of the chip, input/output (I/O) pins are assigned and large objects (arrays, cores, etc.) are placed.
* Placement: The gates in the netlist are assigned to nonoverlapping locations on the die area.
*Logic/placement refinement: Iterative logical and placement transformations to close performance and power constraints.
* Clock insertion: Clock signal wiring is (commonly, clock trees) introduced into the design.
*Routing
Routing is the process of selecting a path for traffic in a network or between or across multiple networks. Broadly, routing is performed in many types of networks, including circuit-switched networks, such as the public switched telephone netw ...
: The wires that connect the gates in the netlist are added.
*Postwiring optimization: Performance ( timing closure), noise (signal integrity
Signal integrity or SI is a set of measures of the quality of an electrical signal. In digital electronics, a stream of binary values is represented by a voltage (or current) waveform. However, digital signals are fundamentally analog in nature, ...
), and yield ( Design for manufacturability) violations are removed.
* Design for manufacturability: The design is modified, where possible, to make it as easy and efficient as possible to produce. This is achieved by adding extra vias or adding dummy metal/diffusion/poly layers wherever possible while complying to the design rules set by the foundry.
*Final checking: Since errors are expensive, time-consuming and hard to spot, extensive error checking is the rule, making sure the mapping to logic was done correctly, and checking that the manufacturing rules were followed faithfully.
*Chip finishing with Tapeout and mask generation: the design data is turned into photomasks in mask data preparation
Mask data preparation (MDP), also known as layout post processing, is the procedure of translating a file containing the intended set of polygons from an integrated circuit layout into set of instructions that a photomask writer can use to genera ...
.
Analog design
Before the advent of the microprocessor and software based design tools, analog ICs were designed using hand calculations and process kit parts. These ICs were low complexity circuits, for example,op-amp
An operational amplifier (often op amp or opamp) is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op amp produces an output potential (relative to c ...
s, usually involving no more than ten transistors and few connections. An iterative trial-and-error process and "overengineering" of device size was often necessary to achieve a manufacturable IC. Reuse of proven designs allowed progressively more complicated ICs to be built upon prior knowledge. When inexpensive computer processing became available in the 1970s, computer programs were written to simulate circuit designs with greater accuracy than practical by hand calculation. The first circuit simulator for analog ICs was called SPICE (Simulation Program with Integrated Circuits Emphasis). Computerized circuit simulation tools enable greater IC design complexity than hand calculations can achieve, making the design of analog ASIC
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC ) is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-efficien ...
s practical.
As many functional constraints must be considered in analog design, manual design is still widespread today. As a result, modern design flows for analog circuits are characterized by two different design styles – top-down and bottom-up. The top-down design style makes use of optimization-based tools similar to conventional digital flows. Bottom-up procedures re-use “expert knowledge” with the result of solutions previously conceived and captured in a procedural description, imitating an expert's decision. An example are cell generators, such as PCell
PCell stands for parameterized cell, a concept used widely in the automated design of analog integrated circuits. A PCell represents a part or a component of the circuit whose structure is dependent on one or more parameters. Hence, it is a cell ...
s.
Coping with variability
A challenge most critical to analog IC design involves the variability of the individual devices built on the semiconductor chip. Unlike board-level circuit design which permits the designer to select devices that have each been tested and binned according to value, the device values on an IC can vary widely which are uncontrollable by the designer. For example, some IC resistors can vary ±20% and β of an integratedBJT
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar t ...
can vary from 20 to 100. In the latest CMOS processes, β of vertical PNP transistors can even go below 1. To add to the design challenge, device properties often vary between each processed semiconductor wafer. Device properties can even vary significantly across each individual IC due to doping gradients. The underlying cause of this variability is that many semiconductor devices are highly sensitive to uncontrollable random variances in the process. Slight changes to the amount of diffusion time, uneven doping levels, etc. can have large effects on device properties.
Some design techniques used to reduce the effects of the device variation are:
* Using the ratios of resistors, which do match closely, rather than absolute resistor value.
* Using devices with matched geometrical shapes so they have matched variations.
* Making devices large so that statistical variations becomes an insignificant fraction of the overall device property.
* Segmenting large devices, such as resistors, into parts and interweaving them to cancel variations.
* Using common centroid
Common may refer to:
Places
* Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland
* Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts
* Cambridge Common, common land area in Cambridge, Massachusetts
* Clapham Common, originally com ...
device layout to cancel variations in devices which must match closely (such as the transistor differential pair of an op amp
An operational amplifier (often op amp or opamp) is a DC-coupled high- gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended output. In this configuration, an op amp produces an output potential (relative to ...
).
Vendors
The three largest companies sellingelectronic design automation
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing Electronics, electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools wo ...
tools are Synopsys, Cadence, and Mentor Graphics
Siemens EDA is a US-based electronic design automation (EDA) multinational corporation for electrical engineering and electronics, headquartered in Wilsonville, Oregon. Founded in 1981 as Mentor Graphics, the company was acquired by Siemens in ...
.
See also
* Electronic circuit design *Electronic design automation
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing Electronics, electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools wo ...
*Power network design (IC)
In the design of integrated circuits, power network design is the analysis and design of on-chip conductor networks that distribute electrical power on a chip. As in all engineering, this involves tradeoffs - the network must have adequate per ...
* Processor design
* IEEE Transactions on Computer-Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems
* Multi-project wafer service
*Standard cell
In semiconductor design, standard cell methodology is a method of designing application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) with mostly digital-logic features. Standard cell methodology is an example of design abstraction, whereby a low-level v ...
References
Further reading
*''Electronic Design Automation For Integrated Circuits Handbook'', by Lavagno, Martin, and Scheffer, {{ISBN, 0-8493-3096-3 A survey of the field ofelectronic design automation
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing Electronics, electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools wo ...
, one of the main enablers of modern IC design.
Integrated circuits
Electronic design
Electronic engineering