Development (sonata form) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Sonata form (also ''sonata-allegro form'' or ''first movement form'') is a musical structure generally consisting of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation. It has been used widely since the middle of the 18th century (the early Classical period).
While it is typically used in the first
Sonata form (also ''sonata-allegro form'' or ''first movement form'') is a musical structure generally consisting of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation. It has been used widely since the middle of the 18th century (the early Classical period).
While it is typically used in the first
 According to the ''
According to the ''

 Sonata form (also ''sonata-allegro form'' or ''first movement form'') is a musical structure generally consisting of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation. It has been used widely since the middle of the 18th century (the early Classical period).
While it is typically used in the first
Sonata form (also ''sonata-allegro form'' or ''first movement form'') is a musical structure generally consisting of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation. It has been used widely since the middle of the 18th century (the early Classical period).
While it is typically used in the first movement
Movement may refer to:
Common uses
* Movement (clockwork), the internal mechanism of a timepiece
* Motion, commonly referred to as movement
Arts, entertainment, and media
Literature
* "Movement" (short story), a short story by Nancy Fu ...
of multi-movement pieces, it is sometimes used in subsequent movements as well—particularly the final movement. The teaching of sonata form in music theory rests on a standard definition and a series of hypotheses about the underlying reasons for the durability and variety of the form—a definition that arose in the second quarter of the 19th century. There is little disagreement that on the largest level, the form consists of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation; however, beneath this general structure, sonata form is difficult to pin down to a single model.
The standard definition focuses on the thematic and harmonic organization of tonal materials that are presented in an exposition
Exposition (also the French for exhibition) may refer to:
*Universal exposition or World's Fair
*Expository writing
**Exposition (narrative)
*Exposition (music)
*Trade fair
* ''Exposition'' (album), the debut album by the band Wax on Radio
*Exposi ...
, elaborated and contrasted in a development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development hell, when a project is stuck in development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
*Development (music), the process thematic material is reshaped
* Photograph ...
and then resolved harmonically and thematically in a recapitulation. In addition, the standard definition recognizes that an introduction
Introduction, The Introduction, Intro, or The Intro may refer to:
General use
* Introduction (music), an opening section of a piece of music
* Introduction (writing), a beginning section to a book, article or essay which states its purpose and g ...
and a coda
Coda or CODA may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* Movie coda, a post-credits scene
* ''Coda'' (1987 film), an Australian horror film about a serial killer, made for television
*''Coda'', a 2017 American experimental film from Na ...
may be present. Each of the sections is often further divided or characterized by the particular means by which it accomplishes its function in the form.
After its establishment, the sonata form became the most common form in the first movement of works entitled "sonata
Sonata (; Italian: , pl. ''sonate''; from Latin and Italian: ''sonare'' rchaic Italian; replaced in the modern language by ''suonare'' "to sound"), in music, literally means a piece ''played'' as opposed to a cantata (Latin and Italian ''cant ...
", as well as other long works of classical music, including the symphony
A symphony is an extended musical composition in Western classical music, most often for orchestra. Although the term has had many meanings from its origins in the ancient Greek era, by the late 18th century the word had taken on the meaning com ...
, concerto
A concerto (; plural ''concertos'', or ''concerti'' from the Italian plural) is, from the late Baroque era, mostly understood as an instrumental composition, written for one or more soloists accompanied by an orchestra or other ensemble. The typi ...
, string quartet
The term string quartet can refer to either a type of musical composition or a group of four people who play them. Many composers from the mid-18th century onwards wrote string quartets. The associated musical ensemble consists of two violinists ...
, and so on. Accordingly, there is a large body of theory on what unifies and distinguishes practice in the sonata form, both within and between eras. Even works that do not adhere to the standard description of a sonata form often present analogous structures or can be analyzed as elaborations or expansions of the standard description of sonata form.
Defining 'sonata form'
 According to the ''
According to the ''Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians
''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' is an encyclopedic dictionary of music and musicians. Along with the German-language ''Die Musik in Geschichte und Gegenwart'', it is one of the largest reference works on the history and theo ...
'', sonata form is "the most important principle of musical form, or formal type, from the Classical period well into the 20th century
The 20th (twentieth) century began on
January 1, 1901 ( MCMI), and ended on December 31, 2000 ( MM). The 20th century was dominated by significant events that defined the modern era: Spanish flu pandemic, World War I and World War II, nuclear ...
". As a formal model it is usually best exemplified in the first movements of multi-movement works from this period, whether orchestra
An orchestra (; ) is a large instrumental ensemble typical of classical music, which combines instruments from different families.
There are typically four main sections of instruments:
* bowed string instruments, such as the violin, viola, c ...
l or chamber
Chamber or the chamber may refer to:
In government and organizations
* Chamber of commerce, an organization of business owners to promote commercial interests
*Legislative chamber, in politics
* Debate chamber, the space or room that houses delib ...
, and has, thus, been referred to frequently as "first-movement form" or "sonata-allegro form" (since the typical first movement in a three- or four-movement cycle will be in allegro tempo). However, as what Grove, following Charles Rosen
Charles Welles Rosen (May 5, 1927December 9, 2012) was an American pianist and writer on music. He is remembered for his career as a concert pianist, for his recordings, and for his many writings, notable among them the book ''The Classical Sty ...
, calls a "principle"—a typical approach to shaping a large piece of instrumental
An instrumental is a recording normally without any vocals, although it might include some inarticulate vocals, such as shouted backup vocals in a big band setting. Through semantic widening, a broader sense of the word song may refer to instru ...
music—it can be seen to be active in a much greater variety of pieces and genres
Genre () is any form or type of communication in any mode (written, spoken, digital, artistic, etc.) with socially-agreed-upon conventions developed over time. In popular usage, it normally describes a category of literature, music, or other for ...
, from minuet
A minuet (; also spelled menuet) is a social dance of French origin for two people, usually in time. The English word was adapted from the Italian ''minuetto'' and the French ''menuet''.
The term also describes the musical form that accompa ...
to concerto
A concerto (; plural ''concertos'', or ''concerti'' from the Italian plural) is, from the late Baroque era, mostly understood as an instrumental composition, written for one or more soloists accompanied by an orchestra or other ensemble. The typi ...
to sonata-rondo. It also carries with it expressive and stylistic connotations: "sonata style"—for Donald Tovey
Sir Donald Francis Tovey (17 July 187510 July 1940) was a British musical analyst, musicologist, writer on music, composer, conductor and pianist. He had been best known for his '' Essays in Musical Analysis'' and his editions of works by Bach ...
and other theorists of his time—was characterized by drama, dynamism, and a "psychological" approach to theme and expression.
Although the Italian term ''sonata
Sonata (; Italian: , pl. ''sonate''; from Latin and Italian: ''sonare'' rchaic Italian; replaced in the modern language by ''suonare'' "to sound"), in music, literally means a piece ''played'' as opposed to a cantata (Latin and Italian ''cant ...
'' often refers to a piece in sonata form, it is important to separate the two. As the title for a single-movement piece of instrumental music—the past participle of ''suonare'', "to sound", as opposed to ''cantata
A cantata (; ; literally "sung", past participle feminine singular of the Italian verb ''cantare'', "to sing") is a vocal composition with an instrumental accompaniment, typically in several movements, often involving a choir.
The meaning of ...
'', the past participle of ''cantare'', "to sing"—"sonata" covers many pieces from the Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
and mid-18th century that are not "in sonata form". Conversely, in the late 18th century or "Classical" period, the title "sonata" is typically given to a work composed of three or four movements. Nonetheless, this multi-movement sequence is not what is meant by sonata form, which refers to the structure of an individual movement.
The definition of sonata form in terms of musical elements sits uneasily between two historical eras. Although the late 18th century witnessed the most exemplary achievements in the form, above all from Joseph Haydn
Franz Joseph Haydn ( , ; 31 March 173231 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of chamber music such as the string quartet and piano trio. His contributions ...
and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 17565 December 1791), baptised as Joannes Chrysostomus Wolfgangus Theophilus Mozart, was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition r ...
, a compositional theory of the time did not use the term "sonata form". Perhaps the most extensive contemporary description of the sonata-form type of movement may have been given by the theorist Heinrich Christoph Koch
Heinrich Christoph Koch (10 October 1749 – 19 March 1816) was a German music theorist, musical lexicographer and composer. In his lifetime, his music dictionary was widely distributed in Germany and Denmark; today his theory of form and syntax ...
in 1793: like earlier German theorists and unlike many of the descriptions of the form we are used to today, he defined it in terms of the movement's plan of modulation
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the ''carrier signal'', with a separate signal called the ''modulation signal'' that typically contains informatio ...
and principal cadences
In Western musical theory, a cadence (Latin ''cadentia'', "a falling") is the end of a phrase in which the melody or harmony creates a sense of full or partial resolution, especially in music of the 16th century onwards.Don Michael Randel (1999) ...
, without saying a great deal about the treatment of themes. Seen in this way, sonata form was closest to binary form
Binary form is a musical form in 2 related sections, both of which are usually repeated. Binary is also a structure used to choreograph dance. In music this is usually performed as A-A-B-B.
Binary form was popular during the Baroque period, of ...
, out of which it probably developed.
The model of the form that is often taught currently tends to be more thematically differentiated. It was originally promulgated by Anton Reicha
Anton (Antonín, Antoine) Joseph Reicha (Rejcha) (26 February 1770 – 28 May 1836) was a Czech-born, Bavarian-educated, later naturalized French composer and music theorist. A contemporary and lifelong friend of Beethoven, he is now best reme ...
in ''Traité de haute composition musicale'' in 1826, by Adolf Bernhard Marx
Friedrich Heinrich Adolf Bernhard Marx . B. Marx(15 May 1795, Halle – 17 May 1866, Berlin) was a German music theorist, critic, and musicologist.
Life
Marx was the son of a Jewish doctor in Halle who, though a member of the congregation, was ...
in ''Die Lehre von der musikalischen Komposition'' in 1845, and by Carl Czerny
Carl Czerny (; 21 February 1791 – 15 July 1857) was an Austrian composer, teacher, and pianist of Czech origin whose music spanned the late Classical and early Romantic eras. His vast musical production amounted to over a thousand works and ...
in 1848. Marx may be the originator of the term "sonata form". This model was derived from the study and criticism of Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. Beethoven remains one of the most admired composers in the history of Western music; his works rank amongst the most performed of the classical ...
's piano
The piano is a stringed keyboard instrument in which the strings are struck by wooden hammers that are coated with a softer material (modern hammers are covered with dense wool felt; some early pianos used leather). It is played using a keyboa ...
sonatas.
Definition as a formal model
A sonata-allegro movement is divided into sections. Each section is felt to perform specific functions in themusical argument A musical argument is a means of creating tension through the relation of expressive content and musical form:
Experimental musics may use process or indeterminacy rather than argument.LaBelle (2006), p.7.
The musical argument may be character ...
.
* It may begin with an ''introduction
Introduction, The Introduction, Intro, or The Intro may refer to:
General use
* Introduction (music), an opening section of a piece of music
* Introduction (writing), a beginning section to a book, article or essay which states its purpose and g ...
'', which is, in general, slower than the main movement.
* The first required section is the ''exposition
Exposition (also the French for exhibition) may refer to:
*Universal exposition or World's Fair
*Expository writing
**Exposition (narrative)
*Exposition (music)
*Trade fair
* ''Exposition'' (album), the debut album by the band Wax on Radio
*Exposi ...
''. The exposition presents the primary thematic material for the movement: one or two themes or theme groups, often in contrasting styles and in opposing keys
Key or The Key may refer to:
Common meanings
* Key (cryptography), a piece of information that controls the operation of a cryptography algorithm
* Key (lock), device used to control access to places or facilities restricted by a lock
* Key (map ...
, connected by a modulating transition. The exposition typically concludes with a closing theme, a ''codetta
In music, a coda () (Italian for "tail", plural ''code'') is a passage that brings a piece (or a movement) to an end. It may be as simple as a few measures, or as complex as an entire section.
In classical music
The presence of a coda as a st ...
'', or both.
* The exposition is followed by the ''development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development hell, when a project is stuck in development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
*Development (music), the process thematic material is reshaped
* Photograph ...
'' where the harmonic
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'', the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the ''1st harmonic'', the ...
and textural possibilities of the thematic material are explored.
* The development then re-transitions back to the '' recapitulation'' where the thematic material returns in the tonic key, and for the recapitulation to complete the musical argument, material that has not been stated in the tonic key is "resolved" by being played, in whole or in part, in the tonic.
* The movement may conclude with a ''coda
Coda or CODA may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* Movie coda, a post-credits scene
* ''Coda'' (1987 film), an Australian horror film about a serial killer, made for television
*''Coda'', a 2017 American experimental film from Na ...
'', beyond the final cadence of the recapitulation.
The term 'sonata form' is controversial and has been called misleading by scholars and composers almost from its inception. Its originators implied that there was a set template to which Classical and Romantic composers aspired, or should aspire. However, sonata form is currently viewed as a model for musical analysis, rather than compositional practice. Although the descriptions on this page could be considered an adequate analysis of many first-movement structures, there are enough variations that theorists such as Charles Rosen
Charles Welles Rosen (May 5, 1927December 9, 2012) was an American pianist and writer on music. He is remembered for his career as a concert pianist, for his recordings, and for his many writings, notable among them the book ''The Classical Sty ...
have felt them to warrant the plural in 'sonata forms'.
These variations include, but are not limited to:
*a monothematic exposition, where the same material is presented in different keys, often used by Haydn
Franz Joseph Haydn ( , ; 31 March 173231 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of chamber music such as the string quartet and piano trio. His contributions to musical form have led ...
;
*a 'third subject group' in a different key than the other two, used by Schubert
Franz Peter Schubert (; 31 January 179719 November 1828) was an Austrian composer of the late Classical and early Romantic eras. Despite his short lifetime, Schubert left behind a vast ''oeuvre'', including more than 600 secular vocal wor ...
(e.g. in the String Quintet, D. 956), and Bruckner's Symphony No. 4;
*the first subject recapitulated in the 'wrong' key, often the subdominant
In music, the subdominant is the fourth tonal degree () of the diatonic scale. It is so called because it is the same distance ''below'' the tonic as the dominant is ''above'' the tonicin other words, the tonic is the dominant of the subdomina ...
, as in Mozart's Piano Sonata No. 16 in C, K. 545 and Schubert's Symphony No. 5;
*the second subject group recapitulated in a key other than the tonic, as in Richard Strauss
Richard Georg Strauss (; 11 June 1864 – 8 September 1949) was a German composer, conductor, pianist, and violinist. Considered a leading composer of the late Romantic and early modern eras, he has been described as a successor of Richard Wag ...
's Symphony No. 2;
*and an extended coda section that pursues developmental, rather than concluding, processes, often found in Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. Beethoven remains one of the most admired composers in the history of Western music; his works rank amongst the most performed of the classical ...
's middle-period works, such as his Symphony No. 3.
Through the Romantic period, formal distortions and variations become so widespread (Mahler
Gustav Mahler (; 7 July 1860 – 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and the modernism ...
, Elgar
Sir Edward William Elgar, 1st Baronet, (; 2 June 1857 – 23 February 1934) was an English composer, many of whose works have entered the British and international classical concert repertoire. Among his best-known compositions are orchestr ...
and Sibelius
Jean Sibelius ( ; ; born Johan Julius Christian Sibelius; 8 December 186520 September 1957) was a Finnish composer of the late Romantic and early-modern periods. He is widely regarded as his country's greatest composer, and his music is often ...
among others are cited and studied by James Hepokoski
James Arnold Hepokoski (born 20 December 1946) is an American musicologist. He is best known for his work with Warren Darcy on developing sonata theory, first fully explained in their 2006 book ''Elements of Sonata Theory''.
Life and career
Jam ...
) that 'sonata form' as it is outlined here is not adequate to describe the complex musical structures that it is often applied to.
In the context of the many late-Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
extended binary forms that bear similarities to sonata form, sonata form can be distinguished by the following three characteristics:
* a separate development section including a retransition
* the simultaneous return of the first subject group and the tonic
* a full (or close to full) recapitulation of the second subject group
Outline of sonata form
The standard description of the sonata form is:Introduction
The ''introduction'' section is optional, or may be reduced to a minimum. If it is extended, it is, in general, slower than the main section and frequently focuses on thedominant key
In music, the dominant is the fifth scale degree () of the diatonic scale. It is called the ''dominant'' because it is second in importance to the first scale degree, the tonic. In the movable do solfège system, the dominant note is sung as "So( ...
. It may or may not contain material that is later stated in the exposition. The introduction increases the weight of the movement (such as the famous dissonant introduction to Mozart's "Dissonance" Quartet, K. 465), and also permits the composer to begin the exposition with a theme that would be too light to start on its own, as in Haydn's Symphony No. 103 ("The Drumroll") and Beethoven's Quintet for Piano and Winds Op. 16. The introduction usually is not included in the exposition repeat: the ''Pathétique'' is a possible counterexample. Much later, Chopin's Piano Sonata No. 2 (Op. 35) is a clear example where the introduction is also included.
On occasion, the material of introduction reappears in its original tempo later in the movement. Often, this occurs as late as the coda, as in Mozart's String Quintet in D major, K. 593, Haydn's "Drumroll" Symphony, Beethoven's Piano Sonata No. 8 ("Pathétique"), or Schubert's Symphony No. 9 ("Great"). Sometimes it can appear earlier: it occurs at the beginning of the development in the ''Pathétique'' Sonata, and at the beginning of the recapitulation of Schubert's Symphony No. 1.
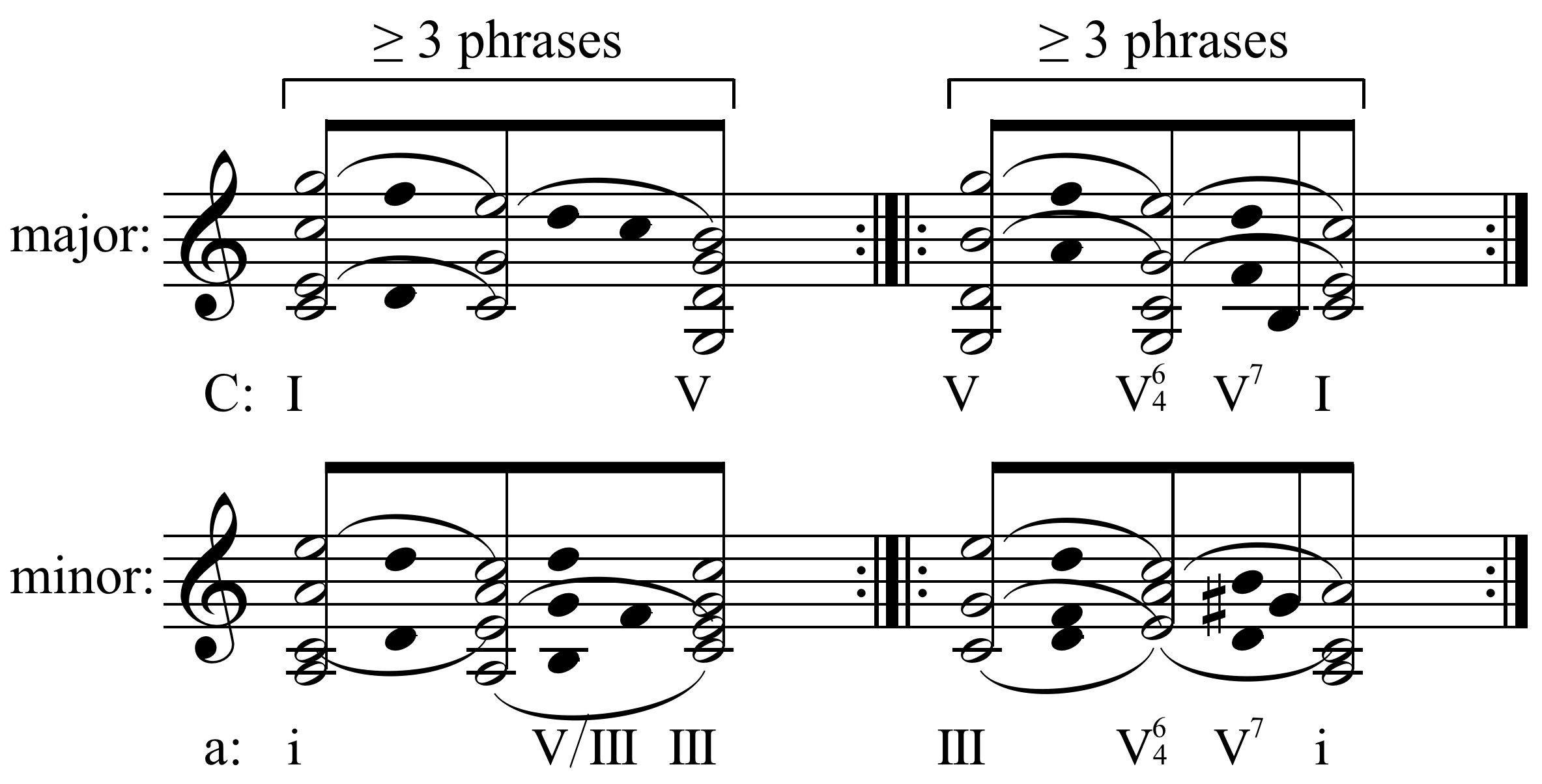
Exposition
The primary thematic material for the movement is presented in the exposition. This section can be further divided into several sections. The same section in most sonata form movements has prominent harmonic and thematic parallelisms (although in some works from the 19th century and onward, some of these parallelisms are subject to considerable exceptions), which include: * ''First subject group'', ''P'' (Prime) – this consists of one or more themes, all of them in the tonic key. Although some pieces are written differently, most follow this form. *'' Transition'', ''T'' – in this section the composer modulates from the key of the first subject to the key of the second. If the first group is in a major key, the second group will usually be in the dominant key. However, if the first group is in minor key, the second group will usually be therelative major
In music, relative keys are the major and minor scales that have the same key signatures (enharmonically equivalent), meaning that they share all the same notes but are arranged in a different order of whole steps and half steps. A pair of major an ...
.
*''Second subject group'', ''S'' – one or more themes in a different key from the first group. The material of the second group is often different in rhythm or mood from that of the first group (frequently, it is more lyrical).
*''Codetta
In music, a coda () (Italian for "tail", plural ''code'') is a passage that brings a piece (or a movement) to an end. It may be as simple as a few measures, or as complex as an entire section.
In classical music
The presence of a coda as a st ...
'', ''K'' – the purpose of this is to bring the exposition section to a close with a perfect cadence
In Western musical theory, a cadence (Latin ''cadentia'', "a falling") is the end of a phrase in which the melody or harmony creates a sense of full or partial resolution, especially in music of the 16th century onwards.Don Michael Randel (1999) ...
in the same key as the second group. It is not always used, and some works end the exposition on the second subject group.
The exposition is commonly repeated, particularly in classical works, and more likely in solo or chamber works than for concerti. Often, though not always, the last measure or measures of the exposition are slightly different between the repeats, one to point back to the tonic, where the exposition began, and the second to point towards the development.
Development
In general, the development starts in the same key as the exposition ended, and may move through many different keys during its course. It will usually consist of one or more themes from the exposition altered and on occasion juxtaposed and may include new material or themes—though exactly what is acceptable practice is a point of contention. Alterations include taking material through distant keys, breaking down of themes and sequencing of motifs, and so forth. The development varies greatly in length from piece to piece and from time period to time period, sometimes being relatively short compared to the exposition (e.g., the first movement of '' Eine kleine Nachtmusik'') and in other cases quite long and detailed (e.g., the first movement of the "Eroica" Symphony). Developments in the Classical era are typically shorter due to how much composers of that era valued symmetry, unlike the more expressive Romantic era in which development sections gain a much greater importance. However, it almost always shows a greater degree of tonal, harmonic, andrhythm
Rhythm (from Greek , ''rhythmos'', "any regular recurring motion, symmetry") generally means a " movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions". This general meaning of regular recu ...
ic instability than the other sections. In a few cases, usually in late Classical and early Romantic concertos, the development section consists of or ends with another exposition, often in the relative minor of the tonic key.
At the end, the music will usually return to the tonic key in preparation of the recapitulation. (On occasion, it will actually return to the sub-dominant key and then proceed with the same transition as in the exposition.) The transition from the development to the recapitulation is a crucial moment in the work. The last part of the development section is called the ': It prepares for the return of the first subject group in the tonic.
Exceptions include the first movement of Brahms
Johannes Brahms (; 7 May 1833 – 3 April 1897) was a German composer, pianist, and conductor of the mid-Romantic period. Born in Hamburg into a Lutheran family, he spent much of his professional life in Vienna. He is sometimes grouped with ...
's Piano Sonata No. 1. The general key of the movement is C major, and it would then follow that the retransition should stress the dominant seventh chord
In music theory, a dominant seventh chord, or major minor seventh chord, is a seventh chord, usually built on the fifth degree of the major scale, and composed of a root, major third, perfect fifth, and minor seventh. Thus it is a major triad tog ...
on G. Instead, it builds in strength over the dominant seventh chord on C, as if the music were proceeding to F major, only to take up immediately the first theme in C major. Another exception is the fourth movement of Schubert
Franz Peter Schubert (; 31 January 179719 November 1828) was an Austrian composer of the late Classical and early Romantic eras. Despite his short lifetime, Schubert left behind a vast ''oeuvre'', including more than 600 secular vocal wor ...
's Symphony No. 9. The home key of the movement is C major. The retransition prolongates over the dominant chord on G, but suddenly takes up the first theme in the flattened mediant E major
E major (or the key of E) is a major scale based on E, consisting of the pitches E, F, G, A, B, C, and D. Its key signature has four sharps. Its relative minor is C-sharp minor and its parallel minor is E minor. Its enharmonic equivalent, ...
.
A particularly common exception is for the dominant to be substituted with the dominant of the relative minor key: one example is the first movement of Haydn's String Quartet in E major, Op. 54 No. 3.
Occasionally, the retransition can begin with a false recapitulation, in which the opening material of the first theme group is presented before the development has completed. The surprise that ensues when the music continues to modulate toward the tonic can be used for either comic or dramatic effect.