Derbyshire Rifle Volunteers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Derbyshire ( ) is a ceremonial county in the
 Burial mounds of Neolithic settlers are also situated throughout the county. These chambered tombs were designed for collective burial and are mostly located in the central Derbyshire region. There are tombs at
Burial mounds of Neolithic settlers are also situated throughout the county. These chambered tombs were designed for collective burial and are mostly located in the central Derbyshire region. There are tombs at
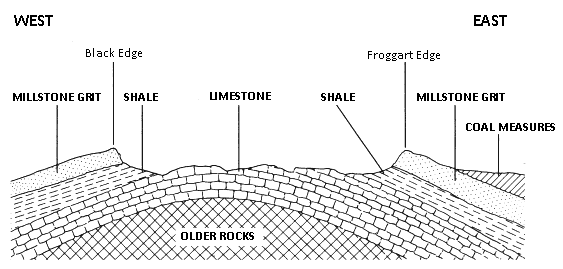 Younger still are the sandstones, shales and coal deposits found on the eastern flank of Derbyshire, forming the coal measures, which are of Westphalian age. All these rock layers disappear south of a line drawn between Ashbourne and Derby under layers of clays and sandstones ( Mercia Mudstone Group and Sherwood Sandstones) of Permo-Triassic age. Small amounts of carboniferous limestones, gritstones and coal measures reappear in the far south of Derbyshire from Ticknall (limestone) to
Younger still are the sandstones, shales and coal deposits found on the eastern flank of Derbyshire, forming the coal measures, which are of Westphalian age. All these rock layers disappear south of a line drawn between Ashbourne and Derby under layers of clays and sandstones ( Mercia Mudstone Group and Sherwood Sandstones) of Permo-Triassic age. Small amounts of carboniferous limestones, gritstones and coal measures reappear in the far south of Derbyshire from Ticknall (limestone) to
 As well as the protections afforded to the Peak District area under national and local policies, there are several
As well as the protections afforded to the Peak District area under national and local policies, there are several
 The Dark Peak is marked by heathlands, bogs, gritstone edges and acid grasslands containing relatively few species, with plants such as heather (''Calluna vulgaris''), crowberry (''Empetrum nigrum''), bilberry (''Vaccinium myrtillus'') and hare's-tail cotton grass (''Eriophorum vaginatum'') being dominant on the high moors. The dales of the White Peak are known for habitats such as calcareous grassland, ash woodlands and rock outcrops in all of which a much greater richness of lime-loving species occurs than elsewhere in the county. These include various orchids (such as early purple orchid (''Orchis mascula''), dark-red helleborine (''Epipactis atrorubens'') and
The Dark Peak is marked by heathlands, bogs, gritstone edges and acid grasslands containing relatively few species, with plants such as heather (''Calluna vulgaris''), crowberry (''Empetrum nigrum''), bilberry (''Vaccinium myrtillus'') and hare's-tail cotton grass (''Eriophorum vaginatum'') being dominant on the high moors. The dales of the White Peak are known for habitats such as calcareous grassland, ash woodlands and rock outcrops in all of which a much greater richness of lime-loving species occurs than elsewhere in the county. These include various orchids (such as early purple orchid (''Orchis mascula''), dark-red helleborine (''Epipactis atrorubens'') and
 Derbyshire has a mixture of a rural economy in the west, with a former coal-mining economy in the north-east (Bolsover district), the Erewash Valley around Ilkeston and in the south around Swadlincote. The rural landscape varies from arable farmland in the flatlands to the south of Derby, to upland pasture and
Derbyshire has a mixture of a rural economy in the west, with a former coal-mining economy in the north-east (Bolsover district), the Erewash Valley around Ilkeston and in the south around Swadlincote. The rural landscape varies from arable farmland in the flatlands to the south of Derby, to upland pasture and  Derbyshire's relative remoteness in the late 18th century and an abundance of fast-flowing streams led to a proliferation of the use of hydropower at the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, following the mills pioneered by
Derbyshire's relative remoteness in the late 18th century and an abundance of fast-flowing streams led to a proliferation of the use of hydropower at the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, following the mills pioneered by
 The county is divided into eleven constituencies for the election of members of parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons. As of December 2019, nine constituencies are represented by Conservative MPs, whilst the remaining two are represented by Labour MPs.
The results of the
The county is divided into eleven constituencies for the election of members of parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons. As of December 2019, nine constituencies are represented by Conservative MPs, whilst the remaining two are represented by Labour MPs.
The results of the  Derbyshire has a three-tier local government since the local government reorganisation in 1974. It has a county council based in Matlock and eight district councils and since 1997, a unitary authority area of the City of Derby. Derby remains part of Derbyshire only for ceremonial purposes.
Derbyshire has become fractionally smaller during government reorganisation over the years. The Sheffield suburbs Woodseats, Beauchief, Handsworth, Woodhouse, Norton, Mosborough, Totley, Bradway and Dore were previously parts of the county, but were lost to Sheffield between 1900 and 1933; Mosborough was transferred in 1967. However, Derbyshire gained part of the
Derbyshire has a three-tier local government since the local government reorganisation in 1974. It has a county council based in Matlock and eight district councils and since 1997, a unitary authority area of the City of Derby. Derby remains part of Derbyshire only for ceremonial purposes.
Derbyshire has become fractionally smaller during government reorganisation over the years. The Sheffield suburbs Woodseats, Beauchief, Handsworth, Woodhouse, Norton, Mosborough, Totley, Bradway and Dore were previously parts of the county, but were lost to Sheffield between 1900 and 1933; Mosborough was transferred in 1967. However, Derbyshire gained part of the  Although Derbyshire is in the
Although Derbyshire is in the
 Derbyshire has a
Derbyshire has a
 The county of Derbyshire has many attractions for tourists and local people. It offers Peak District scenery such as Mam Tor and Kinder Scout, and more urban attractions such as
The county of Derbyshire has many attractions for tourists and local people. It offers Peak District scenery such as Mam Tor and Kinder Scout, and more urban attractions such as
 As part of a 2002 marketing campaign, the plant conservation charity Plantlife chose the Jacob's-ladder as the county flower.
In September 2006, a proposal for a county flag was introduced, largely on the initiative of BBC Radio Derby. It consists of a white-bordered dark green cross encompassing a golden Tudor rose (a historical symbol of the county) all set in a blue field. The blue field represents the many waters of the county, its rivers and reservoirs, while the cross is green to mark the great areas of countryside. The flag was subsequently registered with the Flag Institute in September 2008.
In 2015, BBC Radio Derby commissioned a Derbyshire anthem entitled "Our Derbyshire", including lyrics suggested by its listeners. It received its first performance on 17 September 2015 at Derby Cathedral.
As part of a 2002 marketing campaign, the plant conservation charity Plantlife chose the Jacob's-ladder as the county flower.
In September 2006, a proposal for a county flag was introduced, largely on the initiative of BBC Radio Derby. It consists of a white-bordered dark green cross encompassing a golden Tudor rose (a historical symbol of the county) all set in a blue field. The blue field represents the many waters of the county, its rivers and reservoirs, while the cross is green to mark the great areas of countryside. The flag was subsequently registered with the Flag Institute in September 2008.
In 2015, BBC Radio Derby commissioned a Derbyshire anthem entitled "Our Derbyshire", including lyrics suggested by its listeners. It received its first performance on 17 September 2015 at Derby Cathedral.
"Derbyshire on TV and Film"
, BBC Derby, 27 September 2014, retrieved 20 August 2015.
* Alderwasley: '' Stig of the Dump''
* Ashbourne and Vernon Street in Derby: '' Nanny''
* Chesterfield: The twisted spire of Church of St Mary and All Saints, Chesterfield, was made famous by its use in the opening credits of the 1966–1971 ecclesiastical BBC TV sitcom '' All Gas and Gaiters'', featuring Derek Nimmo.
* Hadfield: '' The League of Gentlemen''
*
Derbyshire Heritage - derbyshireheritage.co.ukartsderbyshire.org.uk – Derby and Derbyshire arts guide
English Heritage and Derbyshire County Council *
Flora of Derbyshire
– Maps and information on vascular plant distribution
Images of Derbyshire
at the
East Midlands
The East Midlands is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It comprises the eastern half of the area traditionally known as the Midlands. It consists of Leicestershire, Derbyshire, Li ...
, England. It includes much of the Peak District National Park, the southern end of the Pennine range of hills and part of the National Forest
A state forest or national forest is a forest that is administered or protected by some agency of a sovereign or federated state, or territory.
Background
The precise application of the terms vary by jurisdiction. For example:
* In Australia ...
. It borders Greater Manchester to the north-west, West Yorkshire to the north, South Yorkshire to the north-east, Nottinghamshire to the east, Leicestershire
Leicestershire ( ; postal abbreviation Leics.) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the East Midlands, England. The county borders Nottinghamshire to the north, Lincolnshire to the north-east, Rutland to the east, Northamptonshire t ...
to the south-east, Staffordshire
Staffordshire (; postal abbreviation Staffs.) is a landlocked county in the West Midlands region of England. It borders Cheshire to the northwest, Derbyshire and Leicestershire to the east, Warwickshire to the southeast, the West Midlands Cou ...
to the west and south-west and Cheshire
Cheshire ( ) is a ceremonial and historic county in North West England, bordered by Wales to the west, Merseyside and Greater Manchester to the north, Derbyshire to the east, and Staffordshire and Shropshire to the south. Cheshire's county t ...
to the west.
Kinder Scout, at , is the highest point and Trent Meadows, where the River Trent leaves Derbyshire, the lowest at . The north–south River Derwent is the longest river at . In 2003, the Ordnance Survey named Church Flatts Farm at Coton in the Elms, near Swadlincote
Swadlincote is a former mining town in the district of South Derbyshire, England, lying within The National Forest area. It borders the counties of Leicestershire and Staffordshire, south-east of Burton upon Trent and north-west of Ashby-de ...
, as Britain's furthest point from the sea. Derby is a unitary authority area
A unitary authority is a local government, local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the ...
, but remains part of the ceremonial county
The counties and areas for the purposes of the lieutenancies, also referred to as the lieutenancy areas of England and informally known as ceremonial counties, are areas of England to which lords-lieutenant are appointed. Legally, the areas i ...
. The county was a lot larger than its present coverage, it once extended to the boundaries of the City of Sheffield district in South Yorkshire where it covered the suburbs such as Mosborough, Owlthorpe, Jordanthorpe, Totley, Dore and Abbeydale.
History
The area that is now Derbyshire was first visited, probably briefly, by humans 200,000 years ago during the Aveleyinterglacial
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene in ...
, as shown by a Middle Paleolithic
The Middle Paleolithic (or Middle Palaeolithic) is the second subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age as it is understood in Europe, Africa and Asia. The term Middle Stone Age is used as an equivalent or a synonym for the Middle Paleoli ...
Acheulean hand axe found near Hopton. Further occupation came with the Upper Paleolithic and Neolithic periods of the Stone Age when Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
hunter-gatherers roamed the hilly tundra.
Evidence of these nomadic tribes has been found in limestone caves located on the Nottinghamshire border. Deposits left in the caves date the occupancy at around 12,000 to 7,000 BCE.Pevsner, p. 22.
 Burial mounds of Neolithic settlers are also situated throughout the county. These chambered tombs were designed for collective burial and are mostly located in the central Derbyshire region. There are tombs at
Burial mounds of Neolithic settlers are also situated throughout the county. These chambered tombs were designed for collective burial and are mostly located in the central Derbyshire region. There are tombs at Minninglow
Minninglow (or Minning Low) is a hill in the Peak District National Park in Derbyshire, located within the White Peak area at grid reference . Within the clump of trees crowning the hill are a Neolithic chambered tomb and two Bronze Age bowl bar ...
and Five Wells that date back to between 2000 and 2500 BCE. Three miles west of Youlgreave lies the Neolithic henge monument
There are three related types of Neolithic earthwork that are all sometimes loosely called henges. The essential characteristic of all three is that they feature a ring-shaped bank and ditch, with the ditch inside the bank. Because the internal ...
of Arbor Low, which has been dated to 2500 BCE. It is not until the Bronze Age that real signs of agriculture and settlement are found in the county. In the moors of the Peak District signs of clearance, arable fields and hut circles were found after archaeological investigation. However this area and another settlement at Swarkestone
Swarkestone is a village and civil parish in the South Derbyshire district of Derbyshire, England. The population at the 2011 Census was 187.
Swarkestone has a very old village church, a full cricket pitch, a plant nursery/ garden centre and re ...
are all that have been found.Smith, p. 8.
During the Roman conquest of Britain
The Roman conquest of Britain refers to the conquest of the island of Britain by occupying Roman forces. It began in earnest in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius, and was largely completed in the southern half of Britain by 87 when the Staneg ...
, the invaders were attracted to Derbyshire for its lead ore in the limestone hills of the area. They settled throughout the county, with forts built near Brough in the Hope Valley and near Glossop. Later they settled round Buxton, famed for its warm springs, and set up a fort near modern-day Derby in an area now known as Little Chester.
Several kings of Mercia are buried in the Repton area.
Following the Norman Conquest, much of the county was subject to the forest laws
A royal forest, occasionally known as a kingswood (), is an area of land with different definitions in England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland. The term ''forest'' in the ordinary modern understanding refers to an area of wooded land; however, the ...
. To the northwest was the Forest of High Peak under the custodianship of William Peverel and his descendants. The rest of the county was bestowed upon Henry de Ferrers, a part of it becoming Duffield Frith. In time the whole area was given to the Duchy of Lancaster. Meanwhile, the Forest of East Derbyshire covered the whole county to the east of the River Derwent from the reign of Henry II to that of Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vassal o ...
.
Geography
Derbyshire mostly consists of upland terrain, especially in the northern and central parts of the county. The southern foothills and uplands of thePennines
The Pennines (), also known as the Pennine Chain or Pennine Hills, are a range of uplands running between three regions of Northern England: North West England on the west, North East England and Yorkshire and the Humber on the east. Commo ...
extend from the north of the Trent Valley throughout the Peak District and into the north of the county, reaching the county's highest point at Kinder Scout. The southern and eastern parts of the county are relatively low-lying from the Trent Valley and southwards, and east of the Pennines. The main rivers in the county are the River Derwent and the River Dove which both join the River Trent in the south. The River Derwent rises in the moorland of Bleaklow and flows throughout the Peak District and county for the majority of its course, while the River Dove rises in Axe Edge Moor and forms a boundary between Derbyshire and Staffordshire
Staffordshire (; postal abbreviation Staffs.) is a landlocked county in the West Midlands region of England. It borders Cheshire to the northwest, Derbyshire and Leicestershire to the east, Warwickshire to the southeast, the West Midlands Cou ...
for most of its length.
Landscape character
The varied landscapes within Derbyshire have been formed mainly as a consequence of the underlying geology, but also by the way the land has been managed and shaped by human activity. The county contains 11 discrete landscape types, known as National Character Areas, which have been described in detail by Natural England and further refined, mapped and described by Derbyshire County Council and the Peak District National Park. The 11 National Character Areas found within Derbyshire are: * Dark Peak *White Peak
The White Peak, also known as the Low Peak, is a limestone plateau that forms the central and southern part of the Peak District in England. It is mostly between and above sea-level and is enclosed by the higher altitude Dark Peak (also kno ...
*South West Peak
*Derbyshire Peak Fringe and Lower Derwent
*Nottinghamshire, Derbyshire and Yorkshire Coalfield
*Southern Magnesian Limestone
*Needwood and South Derbyshire Claylands
*Trent Valley Washlands
*Melbourne Parklands
* Leicestershire & South Derbyshire Coalfield
*Mease/Sence Lowlands
Geology
Derbyshire's solid geology can be split into two very different halves. The oldest rocks occur in the northern, more upland half of the county, and are mostly ofCarboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, million years ago. The name ''Carbonifero ...
age, comprising limestones, gritstone
Gritstone or grit is a hard, coarse-grained, siliceous sandstone. This term is especially applied to such sandstones that are quarried for building material. British gritstone was used for millstones to mill flour, to grind wood into pulp for pa ...
s, sandstones and shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especial ...
s. In its north-east corner to the east of Bolsover, there are also Magnesian Limestone rocks of Permian age. In contrast, the southern and more lowland half of Derbyshire contains much softer rocks, mainly mudstone
Mudstone, a type of mudrock, is a fine-grained sedimentary rock whose original constituents were clays or muds. Mudstone is distinguished from '' shale'' by its lack of fissility (parallel layering).Blatt, H., and R.J. Tracy, 1996, ''Petrology. ...
s and sandstones of Permo-Triassic age, which create gentler, more rolling landscapes with few rock outcrops. Across both regions can be found drift deposits of Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
age – mainly terrace and river gravel deposits and boulder clays. Landslip features are found on unstable layers of sandstones and shales, with Mam Tor and Alport Castles being the best-known. Cemented screes and tufa deposits occur very rarely in the limestone dales and rivers, whilst cave systems have been created naturally in the limestone since Pleistocene times. A recently discovered cave chamber near Castleton, named Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
, is the deepest shaft and biggest chamber of any cave in Britain.
The oldest rocks are Lower Carboniferous limestones of Dinantian age, which form the core of the White Peak within the Peak District National Park. Because northern Derbyshire is effectively an uplifted dome of rock layers that have subsequently eroded to expose older rocks in the centre of the Derbyshire Dome
The Derbyshire Dome is a geological formation across mid-Derbyshire in England.
The White Peak area of the Peak District is named after the limestone plateau landscape of the 'Derbyshire Dome' anticline. The plateau is generally between 200m a ...
, these are encircled by progressively younger limestone rocks, until they in turn give way on three sides to Upper Carboniferous shales, gritstones and sandstones of Namurian age.
 Younger still are the sandstones, shales and coal deposits found on the eastern flank of Derbyshire, forming the coal measures, which are of Westphalian age. All these rock layers disappear south of a line drawn between Ashbourne and Derby under layers of clays and sandstones ( Mercia Mudstone Group and Sherwood Sandstones) of Permo-Triassic age. Small amounts of carboniferous limestones, gritstones and coal measures reappear in the far south of Derbyshire from Ticknall (limestone) to
Younger still are the sandstones, shales and coal deposits found on the eastern flank of Derbyshire, forming the coal measures, which are of Westphalian age. All these rock layers disappear south of a line drawn between Ashbourne and Derby under layers of clays and sandstones ( Mercia Mudstone Group and Sherwood Sandstones) of Permo-Triassic age. Small amounts of carboniferous limestones, gritstones and coal measures reappear in the far south of Derbyshire from Ticknall (limestone) to Swadlincote
Swadlincote is a former mining town in the district of South Derbyshire, England, lying within The National Forest area. It borders the counties of Leicestershire and Staffordshire, south-east of Burton upon Trent and north-west of Ashby-de ...
(coal measures).
Some areas of the White Peak exhibit contemporaneous basalt flows (e.g. Ravens Tor at Millers Dale), as well as subsequent dolerite sill intrusion at a much later stage (e.g. near Tideswell Dale), whilst mineralisation of the carboniferous limestone in a subsequent period created extensive lead and fluorite deposits which have formed a significant part of Derbyshire's economy, as did coal mining. Lead mining has been important here since Roman Times. The more recent river gravels of the Trent valley remain a significant extractive industry today in south Derbyshire, as does the mining of limestone rock in central and northern parts of the county. Coarse sandstones were once extensively quarried both for local building materials and for the production of gritstone grinding wheels for use in mills, and both former industries have left their mark on the Derbyshire landscape.
Green belts
green belts
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a co ...
within the county, aimed at preserving the landscape surrounding main urban areas. There are four such areas, the first three being portions of much larger green belts that extend outside the county and surround large conurbations:
Ecology
Due to its central location in England and altitude range from 27 metres in the south to 636 metres in the north, Derbyshire contains many species at the edge of their UK distribution ranges. Some species with a predominantly northern British distribution are at the southern limit of their range, whilst others with a more southern distribution are at their northern limit in Derbyshire. As climate change progresses, a number of sensitive species are now being seen to be either expanding or contracting their range as a result. For the purposes of protecting and recording the county's most important habitats, Derbyshire has been split into two regions, each with its own Biodiversity Action Plan (BAP), based around National Character Areas. The Peak District BAP includes all of Derbyshire's uplands of the Dark Peak, South-West Peak and White Peak, including an area of limestone beyond the national park boundary. The remaining areas are monitored and recorded in the Lowland Derbyshire Biodiversity Action Plan, which subdivides the landscape into eight smaller Action Areas. The Derbyshire Biological Records Centre was formerly based at Derby Museum and Art Gallery, but since 2011 has been managed by Derbyshire Wildlife Trust. Two of Englands 48Local Nature Partnership Local Nature Partnerships (LNPs) are partnerships of a broad range of influential organisations, businesses and people, and from a range of sectors, charged by government with the task of bringing about improvements in their local natural environmen ...
s (LNP) also cover Derbyshire; these are the Peak District LNP and the Lowland Derbyshire & Nottinghamshire LNP.
Botany
Since 2002, the county flower for Derbyshire has been Jacob's-ladder (''Polemonium caeruleum''), a relatively rare species, and characteristic of certain limestone dales in the White Peak. Derbyshire is known to have contained 1,919 separate taxa of vascular plants (including species, hybrids and micro-species) since modern recording began, of which 1,133 are known to be either native or archaeophyte, the remainder being non-native species. These comprise 336 established species, 433 casuals and 17 unassigned. It is known that 34 species of plants once native here have been lost from Derbyshire (i.e. become locally extinct) since modern plant recording began in the 17th century. Derbyshire contains two endemic vascular plants, found nowhere else in the world: '' Rubus durescens'', a bramble occurring in central Derbyshire, and Derby hawkweed (''Hieracium naviense
''Hieracium naviense'' is a very rare species of hawkweed which has been given the common name of Derby hawkweed.
It is a native perennial plant of limestone cliffs, first discovered in Derbyshire, England, at the Winnats Pass (SK1382) by J.N. ...
''), still known only from Winnats Pass. One endemic species of moss, Derbyshire Feather Moss, occurs in one small 3-metre patch in just one Derbyshire limestone dale, its sole world location intentionally kept confidential.
The distribution and status of vascular plants in Derbyshire have been recorded over the last 120 years in a series of four major botanical works, each by different authors between 1889 and 2015, all entitled ''The Flora of Derbyshire''. Plant recording is mainly undertaken locally by volunteers from the Derbyshire Flora Group, and by staff at Derbyshire Wildlife Trust and the Peak District National Park.
 The Dark Peak is marked by heathlands, bogs, gritstone edges and acid grasslands containing relatively few species, with plants such as heather (''Calluna vulgaris''), crowberry (''Empetrum nigrum''), bilberry (''Vaccinium myrtillus'') and hare's-tail cotton grass (''Eriophorum vaginatum'') being dominant on the high moors. The dales of the White Peak are known for habitats such as calcareous grassland, ash woodlands and rock outcrops in all of which a much greater richness of lime-loving species occurs than elsewhere in the county. These include various orchids (such as early purple orchid (''Orchis mascula''), dark-red helleborine (''Epipactis atrorubens'') and
The Dark Peak is marked by heathlands, bogs, gritstone edges and acid grasslands containing relatively few species, with plants such as heather (''Calluna vulgaris''), crowberry (''Empetrum nigrum''), bilberry (''Vaccinium myrtillus'') and hare's-tail cotton grass (''Eriophorum vaginatum'') being dominant on the high moors. The dales of the White Peak are known for habitats such as calcareous grassland, ash woodlands and rock outcrops in all of which a much greater richness of lime-loving species occurs than elsewhere in the county. These include various orchids (such as early purple orchid (''Orchis mascula''), dark-red helleborine (''Epipactis atrorubens'') and fly orchid
''Ophrys insectifera'', the fly orchid, is a species of orchid and the type species of the genus ''Ophrys''. It is remarkable as an example of the use of sexually deceptive pollination and floral mimicry, as well as a highly selective and highly ...
(''Ophrys insectifera'')), common rockrose (''Helianthemum nummularium''), spring cinquefoil
''Potentilla neumanniana'', the spring cinquefoil or spotted cinquefoil, is a perennial flowering plant in the rose family (Rosaceae). It may grow up to the height of 5–15 cm.
It was first scientifically described by H.G.L. Reichenbach ...
(''Helianthemum nummularium'') and grass of parnassus
The genus ''Parnassia'', also known as grass of Parnassus or bog-stars, are plants now placed in the family Celastraceae, formerly classified in Parnassiaceae or Saxifragaceae. The plants occur in arctic and alpine habitats, as well as in dune ...
(''Parnassia palustris''). Specialised communities of plants occur on former lead workings, where typical metallophyte species include spring sandwort (''Minuartia verna''), alpine penny-cress (''Thlaspi caerulescens'') (both known locally in Derbyshire as Leadwort), as well as mountain pansy (''Viola lutea'') and moonwort (''Botrychium lunaria'').
In 2015 Derbyshire contained 304 vascular plant species now designated as of international, national or local conservation concern, for their rarity or recent declines, and collectively listed as Derbyshire Red Data plants. Work on recording and publishing a bryophyte flora for Derbyshire still continues: by 2012 a total of 518 bryophyte species had been recorded for the county.
Botanical recording in the UK predominantly uses the unchanging vice-county
A vice-county (vice county or biological vice-county) is a geographical division of the British Isles used for the purposes of biological recording and other scientific data-gathering. It is sometimes called a Watsonian vice-county as vice-co ...
boundary system, which results in a slightly different map of Derbyshire from the modern geographic county.
Zoology
A number of specialist organisations protect, promote and monitor records of individual animal groups across Derbyshire. The main ones are Derbyshire Ornithological Society; Derbyshire Mammal Group; Derbyshire Bat Group, Derbyshire Amphibian and Reptile Group, and the Derbyshire & Nottingham Entomological Society. All maintain databases of wildlife sightings, whilst some such as the Derbyshire Ornithological Society provide alerts of rare sightings on their websites or social media pages and also publish major works describing the status and distribution of species.Economy
moorland
Moorland or moor is a type of habitat found in upland areas in temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands and montane grasslands and shrublands biomes, characterised by low-growing vegetation on acidic soils. Moorland, nowadays, generally ...
in the high gritstone
Gritstone or grit is a hard, coarse-grained, siliceous sandstone. This term is especially applied to such sandstones that are quarried for building material. British gritstone was used for millstones to mill flour, to grind wood into pulp for pa ...
uplands of the southern Pennines.
Derbyshire is rich in natural mineral resources such as lead, iron, coal, and limestone, which have been exploited over a long period. Lead, for example, has been mined since Roman times. The limestone outcrops in the central area led to the establishment of large quarries to supply the industries of surrounding towns with lime for building and steelmaking, and latterly in the 20th-century cement manufacture. The Industrial Revolution also increased demand for building stone, and in the late 19th and early 20th-century, the arrival of the railways led to a large number of stone quarries being established. This industry has left its mark on the countryside, but is still a major industry: a lot of the stone is supplied as crushed stone for road building and concrete manufacture, and is moved by rail.
 Derbyshire's relative remoteness in the late 18th century and an abundance of fast-flowing streams led to a proliferation of the use of hydropower at the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, following the mills pioneered by
Derbyshire's relative remoteness in the late 18th century and an abundance of fast-flowing streams led to a proliferation of the use of hydropower at the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, following the mills pioneered by Richard Arkwright
Sir Richard Arkwright (23 December 1732 – 3 August 1792) was an English inventor and a leading entrepreneur during the early Industrial Revolution. He is credited as the driving force behind the development of the spinning frame, known as t ...
. Derbyshire has been said to be the home of the Industrial Revolution, and part of the Derwent Valley has been given World Heritage status in acknowledgement of this historic importance.
Nationally famous companies in Derbyshire include Rolls-Royce, one of the world's leading aerospace companies, based since before World War I in Derby, Thorntons just south of Alfreton and Toyota, who have one of the UK's largest car manufacturing plants at Burnaston. Ashbourne Water used to be bottled in Buxton by Nestlé Waters UK until 2006 and Buxton Water still is.
Derbyshire is one of only three counties permitted to make cheese that is labelled as Stilton cheese
Stilton is an English cheese, produced in two varieties: Blue, which has '' Penicillium roqueforti'' added to generate a characteristic smell and taste, and White, which does not. Both have been granted the status of a protected designation of o ...
. The others are Leicestershire
Leicestershire ( ; postal abbreviation Leics.) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the East Midlands, England. The county borders Nottinghamshire to the north, Lincolnshire to the north-east, Rutland to the east, Northamptonshire t ...
and Nottinghamshire. The smallest of six companies making this product is Hartington Creamery at Pikehall. As of March 2021, Hartington Stilton was marketing within the UK but also exporting to the US, EU and Canada. The company director told the BBC that they had "a surge in interest and consumer sales from the US".
Governance
2019 United Kingdom general election
The 2019 United Kingdom general election was held on Thursday, 12 December 2019. It resulted in the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party receiving a Landslide victory, landslide majority of 80 seats. The Conservatives made a net gain of 4 ...
in Derbyshire (including the city of Derby) are as follows:
 Derbyshire has a three-tier local government since the local government reorganisation in 1974. It has a county council based in Matlock and eight district councils and since 1997, a unitary authority area of the City of Derby. Derby remains part of Derbyshire only for ceremonial purposes.
Derbyshire has become fractionally smaller during government reorganisation over the years. The Sheffield suburbs Woodseats, Beauchief, Handsworth, Woodhouse, Norton, Mosborough, Totley, Bradway and Dore were previously parts of the county, but were lost to Sheffield between 1900 and 1933; Mosborough was transferred in 1967. However, Derbyshire gained part of the
Derbyshire has a three-tier local government since the local government reorganisation in 1974. It has a county council based in Matlock and eight district councils and since 1997, a unitary authority area of the City of Derby. Derby remains part of Derbyshire only for ceremonial purposes.
Derbyshire has become fractionally smaller during government reorganisation over the years. The Sheffield suburbs Woodseats, Beauchief, Handsworth, Woodhouse, Norton, Mosborough, Totley, Bradway and Dore were previously parts of the county, but were lost to Sheffield between 1900 and 1933; Mosborough was transferred in 1967. However, Derbyshire gained part of the Longdendale
Longdendale is a valley in the Peak District of England, north of Glossop and southwest of Holmfirth. The name means "long wooded valley" and the valley is mostly in the counties of Derbyshire and Greater Manchester.
Geography
The eastern part ...
valley and Tintwistle from Cheshire in 1974. The current area of the geographic/ceremonial county of Derbyshire is only 4.7 square kilometres less than it was over 100 years ago.
At the third tier are the parish councils, which do not cover all areas. The eight district councils in Derbyshire and the unitary authority of Derby are shown in the map above.
These district councils are responsible for local planning and building control, local roads, council housing
Public housing in the United Kingdom, also known as council estates, council housing, or social housing, provided the majority of rented accommodation until 2011 when the number of households in private rental housing surpassed the number in so ...
, environmental health, markets and fairs, refuse collection and recycling, cemeteries and crematoria, leisure services, parks, and tourism. Education, social services, libraries, main roads, public transport, policing and fire services, trading standards, waste disposal and strategic planning are the responsibility of the County Council.
 Although Derbyshire is in the
Although Derbyshire is in the East Midlands
The East Midlands is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. It comprises the eastern half of the area traditionally known as the Midlands. It consists of Leicestershire, Derbyshire, Li ...
, some parts, such as High Peak (which incorporated former areas of Cheshire
Cheshire ( ) is a ceremonial and historic county in North West England, bordered by Wales to the west, Merseyside and Greater Manchester to the north, Derbyshire to the east, and Staffordshire and Shropshire to the south. Cheshire's county t ...
after boundary changes in 1974), are closer to the northern cities of Manchester and Sheffield and these receive services more affiliated with northern England; for example, the North West Ambulance Service, Granada Television
ITV Granada, formerly known as Granada Television, is the ITV franchisee for the North West of England and Isle of Man. From 1956 to 1968 it broadcast to both the north west and Yorkshire but only on weekdays as ABC Weekend Television was it ...
and United Utilities serve the Glossop area and the NHS Trusts here are governed by the Greater Manchester Health Authority. Outside the main city of Derby, the largest town in the county is Chesterfield.
Derbyshire is also part of multiple combined authorities
A combined authority is a type of local government institution introduced in England outside Greater London by the Local Democracy, Economic Development and Construction Act 2009. Combined authorities are created voluntarily and allow a group ...
. High Peak is not part of Greater Manchester Combined Authority but is connected to the county both by rail and sharing a close area with Tameside at Glossop and Hadfield. The Erewash, Amber Valley and Derby districts are part of the D2N2 partnership with neighbouring Nottinghamshire. The Derbyshire Dales, Bolsover, North East Derbyshire and Chesterfield districts are part of the South Yorkshire Mayoral Combined Authority (as non constituent members).
Education
The Derbyshire school system is comprehensive with no selective schools. The independent sector includes Repton School,Trent College
Trent College is a co-educational independent day and boarding school located in Long Eaton, Derbyshire between Nottingham and Derby, Derbyshire, Derby. Founded in 1868 as a local ’middle class alternative’ to the more famous Public school ( ...
and The Elms School
Trent College is a co-educational independent day and boarding school located in Long Eaton, Derbyshire between Nottingham and Derby. Founded in 1868 as a local ’middle class alternative’ to the more famous public schools, it is now a coeduc ...
.
Settlements
There are several towns in the county, with Derby the largest and most populous. At the time of the 2011 census, a population of 770,600 lived in the county with 248,752 (32%) living in Derby. The table below shows all towns with over 10,000 inhabitants.Historic areas
Some settlements which were historically part of the county now fall under the counties of Greater Manchester, Leicestershire, South Yorkshire, andStaffordshire
Staffordshire (; postal abbreviation Staffs.) is a landlocked county in the West Midlands region of England. It borders Cheshire to the northwest, Derbyshire and Leicestershire to the east, Warwickshire to the southeast, the West Midlands Cou ...
:
Television
Because of the size of the county, southern parts of Derbyshire such as Derby, Matlock, Ashbourne andBakewell
Bakewell is a market town and civil parish in the Derbyshire Dales district of Derbyshire, England, known also for its local Bakewell pudding. It lies on the River Wye, about 13 miles (21 km) south-west of Sheffield. In the 2011 census, ...
are covered by BBC East Midlands
BBC East Midlands is the BBC English Region covering Derbyshire (except High Peak, North East Derbyshire and the northern areas of the Derbyshire Dales), Leicestershire, Nottinghamshire (except Bassetlaw), Rutland, southern parts of South Kes ...
and ITV Central in Nottingham, broadcast from Waltham. Northeast Derbyshire, Chesterfield, the eastern High Peak ( Hope Valley) and northern area of the Derbyshire Dales ( Tideswell and Hathersage) are covered by BBC Yorkshire from Emley Moor, with its ''Look North
''BBC Look North'' is a name used by the BBC for its regional news programmes in three regions in the North of England:
*''BBC Look North'' for the BBC North East and Cumbria region
*''BBC Look North'' for the BBC Yorkshire region
*''BBC Look No ...
'' from Leeds. The western area of the High Peak (Buxton, Glossop, New Mills and Chapel-en-le-Frith) are covered by BBC North West from Winter Hill and Granada Television
ITV Granada, formerly known as Granada Television, is the ITV franchisee for the North West of England and Isle of Man. From 1956 to 1968 it broadcast to both the north west and Yorkshire but only on weekdays as ABC Weekend Television was it ...
, both based in Salford.
Sport
Derbyshire has oneFootball League
The English Football League (EFL) is a league of professional football clubs from England and Wales. Founded in 1888 as the Football League, the league is the oldest such competition in the world. It was the top-level football league in Engla ...
team, Derby County, which plays in EFL League One
The English Football League One (often referred to as League One for short or Sky Bet League One for sponsorship purposes, and known as the Football League One from 2004 until 2016) is the second-highest division of the English Football Leag ...
, the third tier of English football. The next highest-placed team is Chesterfield, which participates in the National League, the fifth tier of English football. There are also many non-league teams playing throughout the county, most notably Alfreton Town, which plays in the National League North. The county is currently home to the world's oldest football club, Sheffield F.C., which plays in Dronfield in north-east Derbyshire. Glossop
Glossop is a market town in the Borough of High Peak, Derbyshire, England. It is located east of Manchester, north-west of Sheffield and north of the county town, Matlock. Glossop lies near Derbyshire's borders with Cheshire, Greater Manches ...
was the smallest town in the country to have a football team in the top tier of English football, Glossop North End
Glossop North End Association Football Club is a football club in Glossop, Derbyshire, England, which compete in the . Their home ground is Surrey Street, which has a capacity of 1,301 (200 seated, 1,101 standing). The club play in blue, and ar ...
.
cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
team based at the County Cricket Ground. Derbyshire County Cricket Club
Derbyshire County Cricket Club is one of eighteen first-class county clubs within the domestic cricket structure of England and Wales. It represents the historic county of Derbyshire. Its limited overs team is called the Derbyshire Falcons ...
currently plays in Division Two of the County Championship. There are also rugby league clubs based in the north of the county, the North Derbyshire Chargers and in Derby (Derby City RLFC). The county has numerous rugby union clubs, including Derby, Chesterfield Panthers, Matlock, Ilkeston, Ashbourne, Bakewell and Amber Valley.
The county is a popular area for a variety of recreational sports such as rock climbing
Rock climbing is a sport in which participants climb up, across, or down natural rock formations. The goal is to reach the summit of a formation or the endpoint of a usually pre-defined route without falling. Rock climbing is a physically and ...
, hill walking, hang gliding, caving, sailing on its many reservoirs, and cycling along the many miles of disused rail tracks that have been turned into cycle trails, such as the Monsal Trail and High Peak Trail
The High Peak Trail is a trail for walkers, cyclists and horse riders in the Peak District of England. Running from Dowlow , near Buxton, to High Peak Junction, Cromford , it follows the trackbed of the former Cromford and High Peak Rai ...
.
The town of Ashbourne in Derbyshire is known for its Royal Shrovetide Football
The Royal Shrovetide Football Match is a " medieval football" game played annually on Shrove Tuesday and Ash Wednesday in the town of Ashbourne in Derbyshire, England. Shrovetide ball games have been played in England since at least the 12th ...
, described as a "medieval football game", played annually on Shrove Tuesday and Ash Wednesday
Ash Wednesday is a holy day of prayer and fasting in many Western Christian denominations. It is preceded by Shrove Tuesday and falls on the first day of Lent (the six weeks of penitence before Easter). It is observed by Catholics in the Rom ...
.
Derbyshire is host to one of the only community Muggle quidditch teams in the country, known as Derby Union Quidditch Club. The Club recruits players from the age of 16 upwards from all over Derby, and has representatives from most local sixth forms and the University of Derby. The team has competed against both the Leeds Griffins and the Leicester Lovegoods in the past and is part of the vibrant UK quidditch scene. It is also an official International Quidditch Association team.
Local attractions
 The county of Derbyshire has many attractions for tourists and local people. It offers Peak District scenery such as Mam Tor and Kinder Scout, and more urban attractions such as
The county of Derbyshire has many attractions for tourists and local people. It offers Peak District scenery such as Mam Tor and Kinder Scout, and more urban attractions such as Bakewell
Bakewell is a market town and civil parish in the Derbyshire Dales district of Derbyshire, England, known also for its local Bakewell pudding. It lies on the River Wye, about 13 miles (21 km) south-west of Sheffield. In the 2011 census, ...
, Buxton and Derby. Such places include Bolsover Castle, Castleton, Chatsworth House
Chatsworth House is a stately home in the Derbyshire Dales, north-east of Bakewell and west of Chesterfield, Derbyshire, Chesterfield, England. The seat of the Duke of Devonshire, it has belonged to the House of Cavendish, Cavendish family sin ...
, National Tramway Museum at Crich, Peak Rail steam railway, Midland Railway steam railway, Dovedale, Haddon Hall, the Heights of Abraham and Matlock Bath.
In the north of the county, three large reservoirs, Howden, Derwent and Ladybower, were built in the early part of the 20th century to supply the rapidly growing populations of Sheffield, Derby and Leicester
Leicester ( ) is a city status in the United Kingdom, city, Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority and the county town of Leicestershire in the East Midlands of England. It is the largest settlement in the East Midlands.
The city l ...
with drinking water. The moorland catchment area around these is part of the Peak District National Park and extensively used for leisure pursuits such as walking and cycling.
There are many properties and lands in the care of the National Trust that are open to the public, such as Calke Abbey, Hardwick Hall, High Peak Estate, Ilam Park, Kedleston Hall, Longshaw Estate near Hathersage, and Sudbury Hall on the Staffordshire
Staffordshire (; postal abbreviation Staffs.) is a landlocked county in the West Midlands region of England. It borders Cheshire to the northwest, Derbyshire and Leicestershire to the east, Warwickshire to the southeast, the West Midlands Cou ...
border.
Notable gardens in Derbyshire include the formal ones in 17th–18th-century French style at Melbourne Hall south of Derby, the listed garden at Renishaw Hall near Eckington, Lea Rhododendron Gardens near Matlock, the Royal Horticultural Society recommended Bluebell Arboretum near Swadlincote
Swadlincote is a former mining town in the district of South Derbyshire, England, lying within The National Forest area. It borders the counties of Leicestershire and Staffordshire, south-east of Burton upon Trent and north-west of Ashby-de ...
, and the extensive gardens at Chatsworth House.
Ardotalia, also known as Melandra, or Melandra Castle, is an ancient Roman fort built in the north-west of the county. The ruins and foundations are open free of charge to the public.
County emblems
Demographics
In 1801 the population was 147,481 According to theUK Census 2001
A nationwide census, known as Census 2001, was conducted in the United Kingdom on Sunday, 29 April 2001. This was the 20th UK census and recorded a resident population of 58,789,194.
The 2001 UK census was organised by the Office for National ...
there were 956,301 people spread over the county's 254,615 hectares. This was estimated to have risen to 990,400 in 2006.
The county's population grew by 3.0 per cent from 1991 to 2001 which is around 21,100 people. This figure is higher than the national average of 2.65 per cent, but lower than the East Midlands average of 4.0 per cent. The county as a whole has an average population density of 2.9 people per hectare, making it less densely populated than England as a whole.
The density varies throughout the county, with the lowest being in the region of Derbyshire Dales at 0.88 per hectare, and the highest outside the main cities in the region of Erewash, which has 10.04 people per hectare.
In literature and popular culture
InJane Austen
Jane Austen (; 16 December 1775 – 18 July 1817) was an English novelist known primarily for her six major novels, which interpret, critique, and comment upon the British landed gentry at the end of the 18th century. Austen's plots of ...
's novel ''Pride and Prejudice
''Pride and Prejudice'' is an 1813 novel of manners by Jane Austen. The novel follows the character development of Elizabeth Bennet, the dynamic protagonist of the book who learns about the repercussions of hasty judgments and comes to appreci ...
'', Pemberley, the country house of Fitzwilliam Darcy, is in Derbyshire. Chatsworth House
Chatsworth House is a stately home in the Derbyshire Dales, north-east of Bakewell and west of Chesterfield, Derbyshire, Chesterfield, England. The seat of the Duke of Devonshire, it has belonged to the House of Cavendish, Cavendish family sin ...
in Derbyshire is named as one of the estates Elizabeth Bennet visits before arriving at Pemberley. In the 2005 film adaptation of the novel, Chatsworth House itself represents Pemberley. In one scene characters discuss visits to Matlock and Dovedale.
Sir Walter Scott's 1823 novel '' Peveril of the Peak'' is partly set in Derbyshire.
The events of Tom Stoppard's play '' Arcadia'' take place in the fictional country house of Sidley Park in Derbyshire.
Georgette Heyer's detective/romance novel '' The Toll-Gate'' is set in 1817 around a fictional toll-gate in Derbyshire.
The 1969 film '' Women in Love'' by Ken Russell
Henry Kenneth Alfred Russell (3 July 1927 – 27 November 2011) was a British film director, known for his pioneering work in television and film and for his flamboyant and controversial style. His films in the main were liberal adaptation ...
had scenes filmed in and around Elvaston Castle, notably the Greco-Roman wrestling scene, which was filmed in the castle's Great Hall.
The 1986 film '' Lady Jane'' by Trevor Nunn, starring Helena Bonham Carter and Cary Elwes, has scenes filmed at Haddon Hall.
The 1987 film '' The Princess Bride'' by Rob Reiner, starring Robin Wright and Cary Elwes, was partly filmed in Derbyshire. It included scenes at Haddon Hall and in the White Peak
The White Peak, also known as the Low Peak, is a limestone plateau that forms the central and southern part of the Peak District in England. It is mostly between and above sea-level and is enclosed by the higher altitude Dark Peak (also kno ...
and Dark Peak.
The 1988 film '' The Lair of the White Worm'' by Ken Russell, starring Hugh Grant, was filmed in Derbyshire. The opening title sequence is of Thor's Cave in the Manifold
In mathematics, a manifold is a topological space that locally resembles Euclidean space near each point. More precisely, an n-dimensional manifold, or ''n-manifold'' for short, is a topological space with the property that each point has a n ...
valley.
The 2008 film '' The Duchess'' includes scenes filmed at Chatsworth House
Chatsworth House is a stately home in the Derbyshire Dales, north-east of Bakewell and west of Chesterfield, Derbyshire, Chesterfield, England. The seat of the Duke of Devonshire, it has belonged to the House of Cavendish, Cavendish family sin ...
and at Kedleston Hall.
The 1993–2002 TV series '' Peak Practice'' was set in Crich and Fritchley, except for the twelfth and final series, and originally starred Kevin Whately and Amanda Burton. In 2003 an unrelated and less successful medical TV drama, ''Sweet Medicine
''Sweet Medicine'' is an ITV (TV network), ITV drama series from 2003 about a family doctor's office, doctor's surgery in the Peak District of central England. Intended as a replacement for the hit medical drama ''Peak Practice'', it was not a s ...
'', was mostly filmed in the historic market town of Wirksworth.
Other Derbyshire locations in which British TV scenes have been filmed include:, BBC Derby, 27 September 2014, retrieved 20 August 2015.
The Peak District
The Peak District is an upland area in England at the southern end of the Pennines. Mostly in Derbyshire, it extends into Cheshire, Greater Manchester, Staffordshire, West Yorkshire and South Yorkshire. It includes the Dark Peak, where moorla ...
is the scene of a series of four crime novels of the 21st century by Sarah Ward: ''Bitter Chill'' (2015), ''The Shrouded Path'' (2020), ''A Deadly Thaw'' and ''A Patient Fury''.
* Repton and especially Repton School: '' Goodbye, Mr. Chips'' (in both 1939
This year also marks the start of the Second World War, the largest and deadliest conflict in human history.
Events
Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix.
January
* January 1
** Third Reich
*** Jews are forbidden to ...
and 1983 versions)
* Shirebrook: '' The Full Monty''
* Wingfield Manor: 1980s BBC TV series of '' The Chronicles of Narnia''
See also
*Custos Rotulorum of Derbyshire
This is a list of people who have served as Custos Rotulorum of Derbyshire.
* Sir John Vernon bef. 1544 – aft. 1544
* Sir Francis Leke bef. 1547 – bef. 1580
* Sir John Manners 1580–1611
* George Manners bef. 1617–1617 ...
– Keepers of the Rolls
* Derbyshire (UK Parliament constituency)
* Derbyshire Police and Crime Commissioner
* High Sheriff of Derbyshire
* History of Derbyshire
* Lord Lieutenant of Derbyshire
References
Further reading
* * * * * * *External links
Derbyshire Heritage - derbyshireheritage.co.uk
English Heritage and Derbyshire County Council *
Flora of Derbyshire
– Maps and information on vascular plant distribution
Images of Derbyshire
at the
Historic England Archive
The Historic England Archive is the public archive of Historic England, located in The Engine House on Fire Fly Avenue in Swindon, formerly part of the Swindon Works of the Great Western Railway.
It is a public archive of architectural and arch ...
{{Authority control
East Midlands
Non-metropolitan counties
Counties of England established in antiquity