deoxycytidine kinase on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Deoxycytidine kinase (dCK) is an
 dCK is a
dCK is a
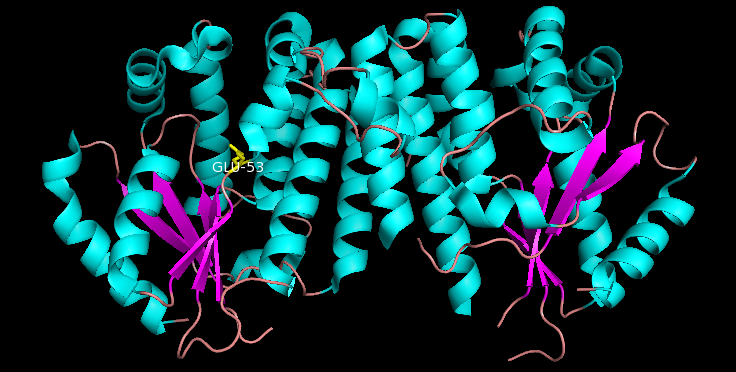
 Glu53 performs base catalysis to deprotonate the hydroxyl group, which allows the now nucleophilic oxygen from the nucleoside 5' hydroxyl group to attack the end of the phosphate chain (gamma phosphate) on the phosphoryl donor (e.g. ATP or UTP). This has deemed the "closed" conformation as the catalytically active conformation since it catalyzes the phosphoryl transfer between phosphoryl donors and receiving nucleosides. Similarly, "open" conformation is generally referred to as the catalytically inactive form since Glu53 is not in close proximity to nucleoside 5' hydroxyl group and will not catalyze the phosphoryl transfer.
Glu53 performs base catalysis to deprotonate the hydroxyl group, which allows the now nucleophilic oxygen from the nucleoside 5' hydroxyl group to attack the end of the phosphate chain (gamma phosphate) on the phosphoryl donor (e.g. ATP or UTP). This has deemed the "closed" conformation as the catalytically active conformation since it catalyzes the phosphoryl transfer between phosphoryl donors and receiving nucleosides. Similarly, "open" conformation is generally referred to as the catalytically inactive form since Glu53 is not in close proximity to nucleoside 5' hydroxyl group and will not catalyze the phosphoryl transfer.
monotherapy
have been observed to develop chemoresistance to the drug.
enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products ...
which is encoded by the ''DCK'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
in humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
. dCK predominantly phosphorylates deoxycytidine
Deoxycytidine is a deoxyribonucleoside, a component of deoxyribonucleic acid. It is similar to the ribonucleoside cytidine, but with one hydroxyl group removed from the C2' position.
Deoxycytidine can be phosphorylated at C5' of the deoxyribos ...
(dC) and converts dC into deoxycytidine monophosphate
Deoxycytidine monophosphate (dCMP), also known as deoxycytidylic acid or deoxycytidylate in its conjugate acid and conjugate base forms, respectively, is a deoxynucleotide, and one of the four monomers that make up DNA. In a DNA double helix, it ...
. dCK catalyzes one of the initial steps in the nucleoside salvage pathway and has the potential to phosphorylate other preformed nucleosides, specifically deoxyadenosine
Deoxyadenosine (symbol dA or dAdo) is a deoxyribonucleoside. It is a derivative of the nucleoside adenosine, differing from the latter by the replacement of a hydroxyl group (-OH) by hydrogen (-H) at the 2′ position of its ribose sugar moiety. ...
(dA) and deoxyguanosine
Deoxyguanosine is composed of the purine nucleobase guanine linked by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of deoxyribose. It is similar to guanosine, but with one hydroxyl group removed from the 2' position of the ribose sugar (making it deoxyribo ...
(dG), and convert them into their monophosphate forms. There has been recent biomedical research interest in investigating dCK's potential as a therapeutic target for different types of cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
.
Structure
 dCK is a
dCK is a homodimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has ...
where each monomer subunit consists of multiple alpha helices
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid located four residues ear ...
surrounding a beta sheet core. Each subunit includes a nucleotide donor binding site, nucleoside acceptor binding site, nucleotide base sensing loop (240-254 residues), insert region (12-15 residues) that connects helices 2 and 3. dCK has several different protein conformations but its conformation depends on the nucleoside or nucleotide it binds to. dCK can bind to ADP, ATP, UDP or UTP (phosphoryl group donors) but UDP/UTP binding changes the enzyme's conformation by rearranging the nucleotide base sensing loop as compared to the dCK's conformation when bound to ATP. This change in conformation when a specific phosphoryl donor is bound in the nucleotide binding site determines which nucleoside can bind in the nucleoside binding site. For example, it has been observed that when dCK binds to ADP, dCK takes on a "closed" conformation or more compact nucleoside binding site where glutamic acid 53 (Glu53) is brought into closer proximity to directly interact with the nucleoside's 5' hydroxyl group.
* One hypothesis for the functionality of the "open" conformation is that the "open" conformation may assist in the initial nucleoside binding and the release of the monophosphate product
Function
Deoxycytidine kinase (dCK) phosphorylates several deoxyribonucleosides and theirnucleoside analogue
Nucleoside analogues are nucleosides which contain a nucleic acid analogue and a sugar. Nucleotide analogs are nucleotides which contain a nucleic acid analogue, a sugar, and a phosphate group with one to three phosphates.
Nucleoside and nucl ...
s (a nucleoside with a sugar and a different nucleic acid base substitute or analogue that has unique properties when modified) using phosphate groups from ATP and UTP. More specifically, dCK adds the first phosphoryl group to preformed nucleosides and is usually the rate-limiting enzyme of the overall process of converting nucleosides to their deoxynucleoside triphosphate form, or nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecule ...
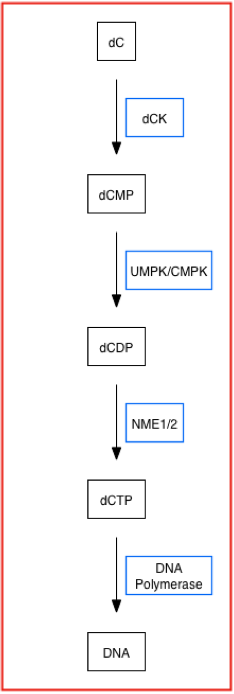
form, in the nucleoside salvage pathway. Below is a simplified pathway that displays dCK's role in synthesizing nucleotides using the nucleoside salvage pathway.
 Glu53 performs base catalysis to deprotonate the hydroxyl group, which allows the now nucleophilic oxygen from the nucleoside 5' hydroxyl group to attack the end of the phosphate chain (gamma phosphate) on the phosphoryl donor (e.g. ATP or UTP). This has deemed the "closed" conformation as the catalytically active conformation since it catalyzes the phosphoryl transfer between phosphoryl donors and receiving nucleosides. Similarly, "open" conformation is generally referred to as the catalytically inactive form since Glu53 is not in close proximity to nucleoside 5' hydroxyl group and will not catalyze the phosphoryl transfer.
Glu53 performs base catalysis to deprotonate the hydroxyl group, which allows the now nucleophilic oxygen from the nucleoside 5' hydroxyl group to attack the end of the phosphate chain (gamma phosphate) on the phosphoryl donor (e.g. ATP or UTP). This has deemed the "closed" conformation as the catalytically active conformation since it catalyzes the phosphoryl transfer between phosphoryl donors and receiving nucleosides. Similarly, "open" conformation is generally referred to as the catalytically inactive form since Glu53 is not in close proximity to nucleoside 5' hydroxyl group and will not catalyze the phosphoryl transfer.
Regulation
One method of to regulate both catalytic activity and substrate specificity is a post-translational modification on Serine 74, a residue in the insert region on each of the individual dCK subunits. Although serine 74 is far from dCK's active site, phosphorylation of serine 74 (Ser74) on dCK causes a change in enzyme conformation and influences enzyme kinetics. More specifically, phosphorylation of Ser74 favors dCK to adopt its open (inactive) conformation and allow dCK to become more competent in binding and releasing nucleosides but restricts dCK from transferring phosphoryl groups. dCK's closed (active) conformation allows dCK to transfer phosphoryl groups, but not bind or release nucleosides. The "open" and "closed" states refer to the nucleoside binding site on dCK.Nucleotide biosynthesis
dCK is a key enzyme in the nucleoside salvage pathway (NSP). More specifically, this pathway recycles preformed nucleosides from degrading DNA molecules to synthesize dNTPs for the cell. The nucleoside salvage pathway can act as an alternative path to produce nucleotides (dNTP's) in case of '' de novo'' pathway downregulation. That is, the salvage pathway (and thus dCK) is upregulated when the de novo pathway is downregulated or inhibited in order to compensate for the loss in nucleotide production. Both the ''de novo'' pathway (DNP) and the nucleoside salvage pathway (NSP) are anabolic pathways that produce deoxyribonucleotide triphosphates (dNTP's) or nucleotides, themonomer
In chemistry, a monomer ( ; '' mono-'', "one" + ''-mer'', "part") is a molecule that can react together with other monomer molecules to form a larger polymer chain or three-dimensional network in a process called polymerization.
Classification
...
s that make up DNA.
Therapeutic implications
Deficiency of dCK is associated with resistance to antiviral and anticancer chemotherapeutic agents. Conversely, increased deoxycytidine kinase activity is associated with increased activation of these agents to cytotoxic nucleoside triphosphate derivatives. dCK is clinically important because of its relationship to drug resistance and sensitivity. Manipulating dCK's enzymatic activity has been shown to have a strong correlation in sensitizing cells to the effects of other drugs (e.g. RNR inhibitors, gemcitabine) or treatments (e.g. ionizing radiation) and so more combination therapies are currently been studied to reduce biological resistance mechanisms and drug tolerance in patients. For example,gemcitabine
Gemcitabine, with brand names including Gemzar, is a chemotherapy medication. It treats cancers including testicular cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, and bladder cancer. It is administered by ...
is a FDA-approved pyrimidine nucleoside analogue and a dCK activity based prodrug that has been used to treat pancreatic, breast, bladder and non-small cell lung cancer. Mechanistically, dCK, which uptakes preformed nucleosides, adds the first phosphoryl group on dFdC (gemcitabine's original form as a deoxycytidine analog) to convert it into dFdCMP, its monophosphate form. Cytidylate kinase or UMP-CMP kinase then adds the second phosphoryl group to form dFdCDP (gemcitabine diphosphate form), which can inhibit ribonucleotide reductase. Nucleoside-diphosphate kinase or nucleoside kinase A adds the third phosphoryl group to form dFdCTP (gemcitabine triphosphate form) which is gemcitabine's active form which inhibits both deoxycytidylate deaminase and DNA polymerase. Although gemcitabine has widely used to treat solid tumors for over a decade, patients taking gemcitabine alonemonotherapy
have been observed to develop chemoresistance to the drug.
See also
*Nucleoside phosphorylase
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase, PNP, PNPase or inosine phosphorylase () is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''NP'' gene. It catalyzes the chemical reaction
:purine nucleoside + phosphate \rightleftharpoons purine + alpha-D-ribose 1- ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* {{Kinases EC 2.7.1