Decapitated Columbus Statue on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Decapitation or beheading is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and most other animals, since it deprives the brain of
Decapitation or beheading is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and most other animals, since it deprives the brain of



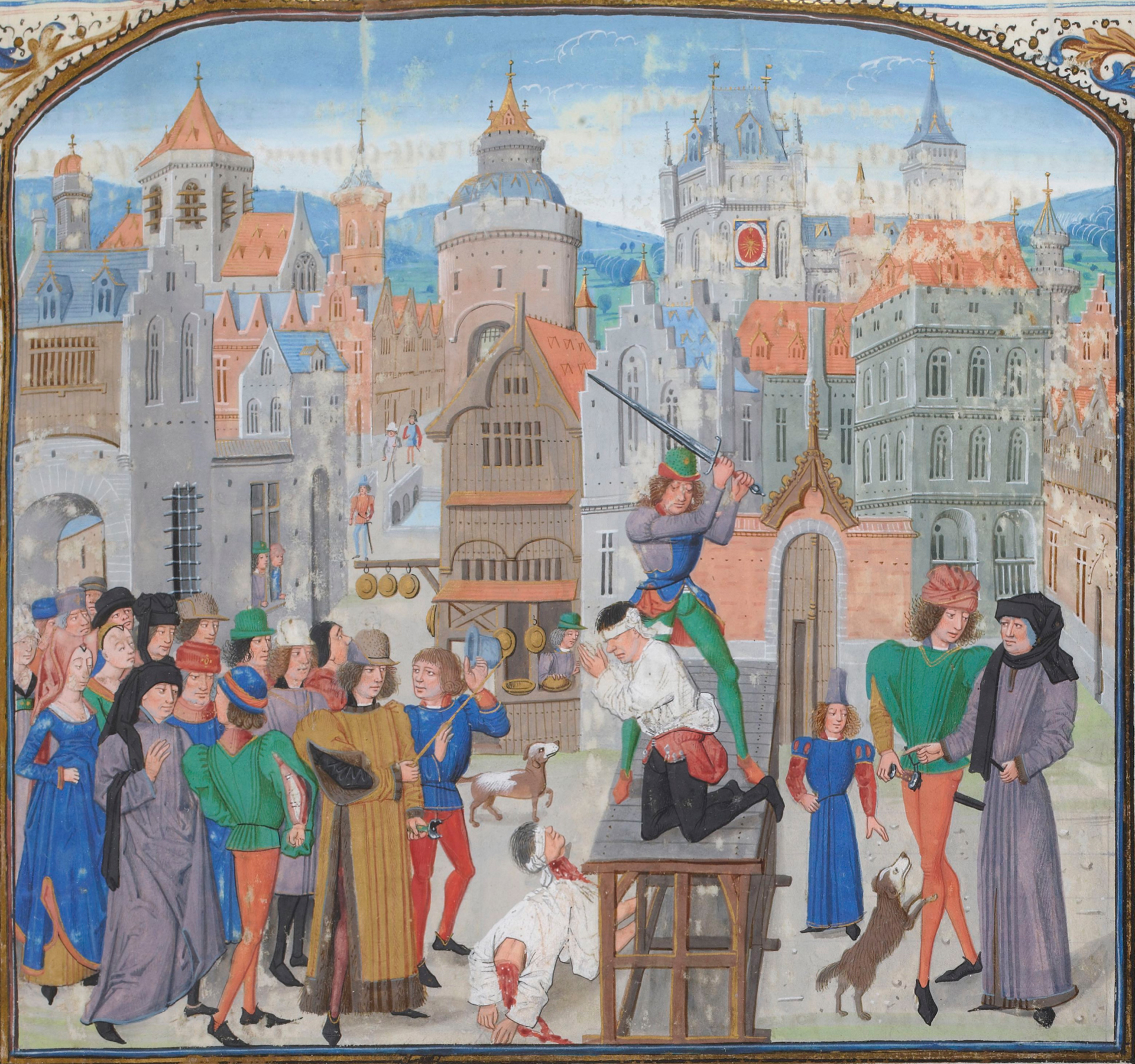
 Humans have practiced capital punishment by beheading for millennia. The Narmer Palette (c. 3000 BCE) shows the first known depiction of decapitated corpses. The terms "capital offence", "capital crime", "capital punishment", derive from the Latin ''caput'', "head", referring to the punishment for serious offences involving the forfeiture of the head; i.e. death by beheading.
Some cultures, such as ancient Rome and Greece, regarded decapitation as the most honorable form of death. In the Middle Ages, many European nations continued to reserve the method only for nobles and royalty. In France, the French Revolution made it the only legal method of execution for all criminals regardless of class, one of the period's many symbolic changes.
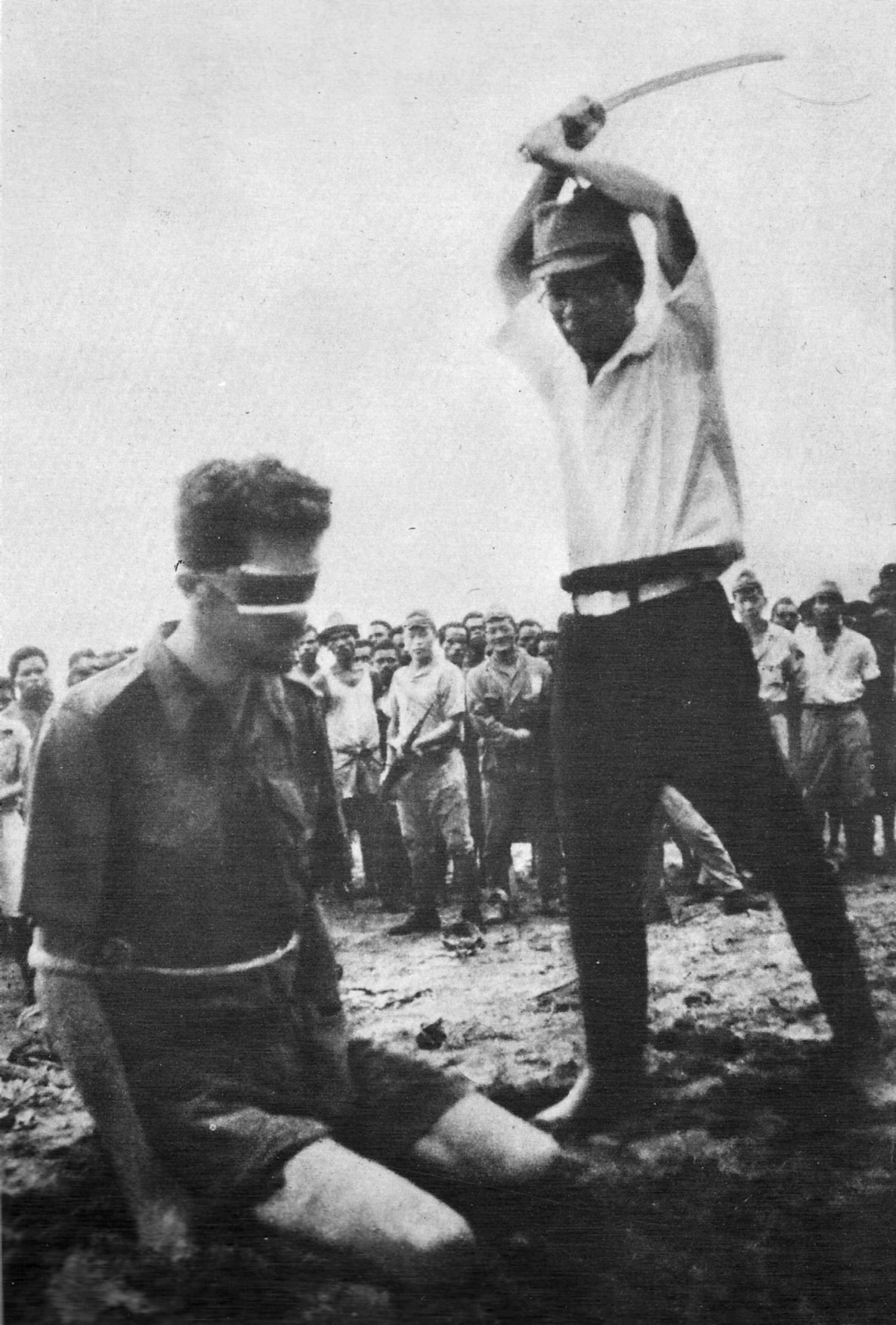
Others have regarded beheading as dishonorable and contemptuous, such as the Japanese troops who beheaded prisoners during World War II. In recent times, it has become associated with terrorism.
Humans have practiced capital punishment by beheading for millennia. The Narmer Palette (c. 3000 BCE) shows the first known depiction of decapitated corpses. The terms "capital offence", "capital crime", "capital punishment", derive from the Latin ''caput'', "head", referring to the punishment for serious offences involving the forfeiture of the head; i.e. death by beheading.
Some cultures, such as ancient Rome and Greece, regarded decapitation as the most honorable form of death. In the Middle Ages, many European nations continued to reserve the method only for nobles and royalty. In France, the French Revolution made it the only legal method of execution for all criminals regardless of class, one of the period's many symbolic changes.
Others have regarded beheading as dishonorable and contemptuous, such as the Japanese troops who beheaded prisoners during World War II. In recent times, it has become associated with terrorism.
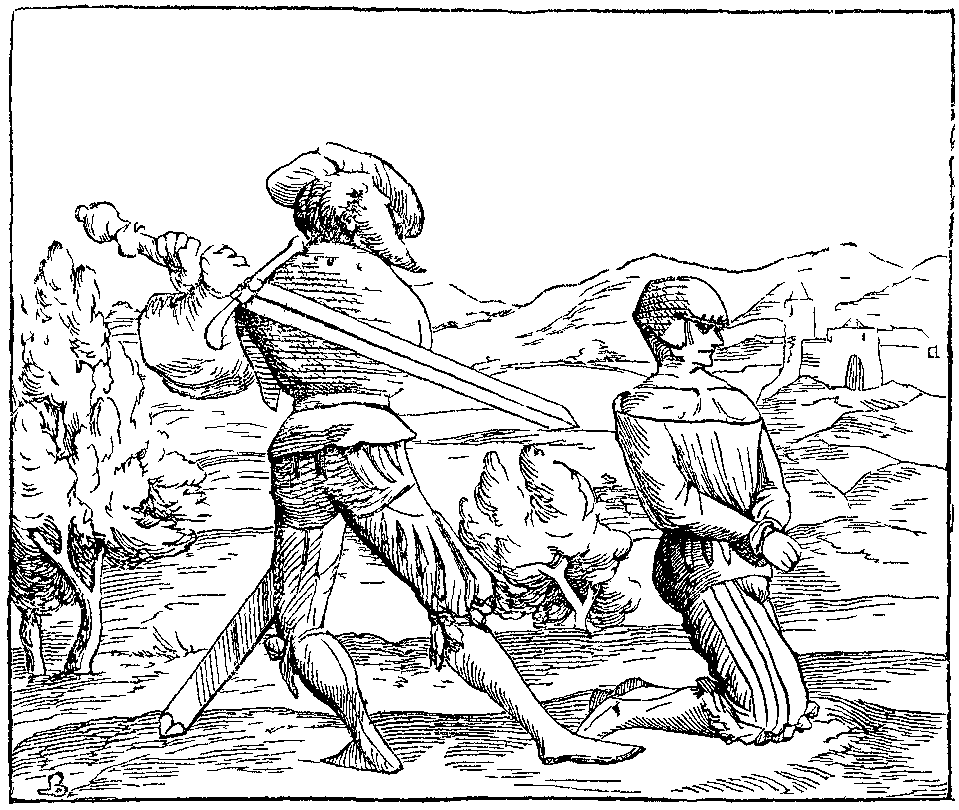
 To ensure that the blow would be fatal, executioners' swords usually were blade-heavy two-handed swords. Likewise, if an axe was used, it almost invariably was wielded with both hands. In England, a
To ensure that the blow would be fatal, executioners' swords usually were blade-heavy two-handed swords. Likewise, if an axe was used, it almost invariably was wielded with both hands. In England, a
 Many German states had used a guillotine-like device known as a ("falling axe") since the 17th and 18th centuries, and decapitation by guillotine was the usual means of execution in Germany until the abolition of the death penalty in West Germany in 1949. It was last used in communist East Germany in 1966.
In Nazi Germany, the was reserved for common criminals and people convicted of
Many German states had used a guillotine-like device known as a ("falling axe") since the 17th and 18th centuries, and decapitation by guillotine was the usual means of execution in Germany until the abolition of the death penalty in West Germany in 1949. It was last used in communist East Germany in 1966.
In Nazi Germany, the was reserved for common criminals and people convicted of 
 In traditional
In traditional
 In
In
 In British history, beheading was typically used for noblemen, while commoners would be hanged; eventually, hanging was adopted as the standard means of non-military executions. The last actual execution by beheading was of Simon Fraser, 11th Lord Lovat on 9 April 1747, while a number of convicts were beheaded posthumously up to the early 19th century. (Typically traitors were sentenced to be
In British history, beheading was typically used for noblemen, while commoners would be hanged; eventually, hanging was adopted as the standard means of non-military executions. The last actual execution by beheading was of Simon Fraser, 11th Lord Lovat on 9 April 1747, while a number of convicts were beheaded posthumously up to the early 19th century. (Typically traitors were sentenced to be
 The ancient Greeks and Romans regarded decapitation as a comparatively honorable form of execution for criminals. The traditional procedure, however, included first being tied to a stake and whipped with rods. Axes were used by the Romans, and later swords, which were considered a more honorable instrument of death. Those who could verify that they were Roman citizens were to be beheaded, rather than undergoing the much more horrific experience of crucifixion. In the Roman Republic of the early 1st century BC, it became the tradition for the severed heads of public enemies—such as the political opponents of Marius and
The ancient Greeks and Romans regarded decapitation as a comparatively honorable form of execution for criminals. The traditional procedure, however, included first being tied to a stake and whipped with rods. Axes were used by the Romans, and later swords, which were considered a more honorable instrument of death. Those who could verify that they were Roman citizens were to be beheaded, rather than undergoing the much more horrific experience of crucifixion. In the Roman Republic of the early 1st century BC, it became the tradition for the severed heads of public enemies—such as the political opponents of Marius and
 This trend of beheading and publicly displaying the decapitated bodies was started by the Los Zetas, a criminal group composed by former Mexican special forces operators, trained in the infamous ''US Army School of the Americas'', in torture techniques and psychological warfare.
This trend of beheading and publicly displaying the decapitated bodies was started by the Los Zetas, a criminal group composed by former Mexican special forces operators, trained in the infamous ''US Army School of the Americas'', in torture techniques and psychological warfare.
Crime Library
{{Capital punishment Execution methods Capital punishment Causes of death

 Decapitation or beheading is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and most other animals, since it deprives the brain of
Decapitation or beheading is the total separation of the head from the body. Such an injury is invariably fatal to humans and most other animals, since it deprives the brain of oxygenated blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the ci ...
, while all other organs are deprived of the involuntary functions that are needed for the body to function.
The term ''beheading'' refers to the act of deliberately decapitating a person, either as a means of murder or as an execution; it may be performed with an axe, sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
, knife, machete or by mechanical means such as a guillotine or chainsaw. An executioner who carries out executions by beheading is sometimes called a headsman. Accidental decapitation can be the result of an explosion, a car or industrial accident, improperly administered execution by hanging or other violent injury. Suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and s ...
by decapitation is rare but not unknown. The national laws of Saudi Arabia, Yemen, and Qatar permit beheading; however, in practice, Saudi Arabia is the only country that continues to behead its offenders regularly as a punishment for capital crimes.
Less commonly, decapitation can also refer to the removal of the head from a body
Body may refer to:
In science
* Physical body, an object in physics that represents a large amount, has mass or takes up space
* Body (biology), the physical material of an organism
* Body plan, the physical features shared by a group of anima ...
that is already dead. This might be done to take the head as a trophy
A trophy is a tangible, durable reminder of a specific achievement, and serves as a recognition or evidence of merit. Trophies are often awarded for sporting events, from youth sports to professional level athletics. In many sports medals (or, in ...
, for public display, to make the deceased more difficult to identify, for cryonics, or for other, more esoteric reasons.
Etymology
The word decapitation has its roots in the Late Latin word ''decapitare''. The meaning of the word ''decapitare'' can be discerned from its morphemes ''de-'' (down, from) + ''capit-'' (head). The past participle of ''decapitare'' is ''decapitatus'' which was used to create ''decapitationem'', the noun form of ''decapitatus'' in Medieval Latin. From the Medieval Latin form, ''decapitationem'', the French word ''décapitation'' was produced.History




 Humans have practiced capital punishment by beheading for millennia. The Narmer Palette (c. 3000 BCE) shows the first known depiction of decapitated corpses. The terms "capital offence", "capital crime", "capital punishment", derive from the Latin ''caput'', "head", referring to the punishment for serious offences involving the forfeiture of the head; i.e. death by beheading.
Some cultures, such as ancient Rome and Greece, regarded decapitation as the most honorable form of death. In the Middle Ages, many European nations continued to reserve the method only for nobles and royalty. In France, the French Revolution made it the only legal method of execution for all criminals regardless of class, one of the period's many symbolic changes.
Others have regarded beheading as dishonorable and contemptuous, such as the Japanese troops who beheaded prisoners during World War II. In recent times, it has become associated with terrorism.
Humans have practiced capital punishment by beheading for millennia. The Narmer Palette (c. 3000 BCE) shows the first known depiction of decapitated corpses. The terms "capital offence", "capital crime", "capital punishment", derive from the Latin ''caput'', "head", referring to the punishment for serious offences involving the forfeiture of the head; i.e. death by beheading.
Some cultures, such as ancient Rome and Greece, regarded decapitation as the most honorable form of death. In the Middle Ages, many European nations continued to reserve the method only for nobles and royalty. In France, the French Revolution made it the only legal method of execution for all criminals regardless of class, one of the period's many symbolic changes.
Others have regarded beheading as dishonorable and contemptuous, such as the Japanese troops who beheaded prisoners during World War II. In recent times, it has become associated with terrorism.
Physiological aspects
Pain
If a headsman's axe orsword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
is sharp and his aim is precise, decapitation is quick and thought to be a relatively painless form of death. If the instrument is blunt or the executioner is clumsy, repeated strokes might be required to sever the head, resulting in a prolonged and more painful death. Robert Devereux, 2nd Earl of Essex, and Mary, Queen of Scots required three strikes at their respective executions. The same could be said for the execution of Johann Friedrich Struensee, favorite of the Danish queen Caroline Matilda of Great Britain. Margaret Pole, 8th Countess of Salisbury, is said to have required up to 10 strokes before decapitation was achieved. This particular story may, however, be apocryphal, as highly divergent accounts exist. Historian and philosopher David Hume, for example, relates the following about her death: To ensure that the blow would be fatal, executioners' swords usually were blade-heavy two-handed swords. Likewise, if an axe was used, it almost invariably was wielded with both hands. In England, a
To ensure that the blow would be fatal, executioners' swords usually were blade-heavy two-handed swords. Likewise, if an axe was used, it almost invariably was wielded with both hands. In England, a bearded axe
A bearded axe, or Skeggøx (from Old Norse ''Skegg'', "beard", and ''øx'', "axe"), is any of various axes, used as a tool and weapon, as early as the 6th century AD. It is most commonly associated with Viking Age Scandinavians. The hook or "bea ...
was used for beheading, with the blade's edge extending downwards from the tip of the shaft.
Finland's official beheading axe resides today at the Museum of Crime in Vantaa. It is a broad-bladed two-handed axe. It was last used when murderer Tahvo Putkonen was executed in 1825, the last execution in peacetime in Finland.
Physiology of death by decapitation
Decapitation is quickly fatal to humans and most animals. Unconsciousness occurs within 10 seconds without circulating oxygenated blood ( brain ischemia). Cell death and irreversiblebrain damage
Neurotrauma, brain damage or brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating t ...
occurs after 3–6 minutes with no oxygen, due to excitotoxicity. Some anecdotes suggest more extended persistence of human consciousness after decapitation, but most doctors consider this unlikely and consider such accounts to be misapprehensions of reflexive twitching rather than deliberate movement, since deprivation of oxygen must cause nearly immediate coma and death (" onsciousness isprobably lost within 2–3 seconds, due to a rapid fall of intracranial perfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ or a tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion is measured as the rate at which blood is deliver ...
of blood").
A laboratory study testing for humane methods of euthanasia in awake animals used EEG monitoring to measure the time duration following decapitation for rats to become fully unconscious, unable to perceive distress and pain. It was estimated that this point was reached within 3–4 seconds, correlating closely with results found in other studies on rodents (2.7 seconds, and 3–6 seconds). The same study also suggested that the massive wave which can be recorded by EEG monitoring approximately one minute after decapitation ultimately reflects brain death. Other studies indicate that electrical activity in the brain has been demonstrated to persist for 13 to 14 seconds following decapitation (although it is disputed as to whether such activity implies that pain is perceived), and a 2010 study reported that decapitation of rats generated responses in EEG indices over a period of 10 seconds that have been linked to nociception
Nociception (also nocioception, from Latin ''nocere'' 'to harm or hurt') is the sensory nervous system's process of encoding noxious stimuli. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a painful stimulus, co ...
across a number of different species of animals, including rats.
Some animals (such as cockroaches) can survive decapitation and die not because of the loss of the head directly, but rather because of starvation
Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric energy intake, below the level needed to maintain an organism's life. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, dea ...
. A number of other animals, including snakes, and turtles, have also been known to survive for some time after being decapitated, as they have slower metabolisms and their nervous systems can continue to function at some capacity for a limited time even after connection to the brain is lost, responding to any nearby stimulus. In addition, the bodies of chickens and turtles may continue to move temporarily after decapitation.
Although head transplantation by the reattachment of blood vessels has seen some very limited success in animals, a fully functional reattachment of a severed human head (including repair of the spinal cord, muscles, and other critically important tissues) has not yet been achieved.
Technology
Guillotine
Early versions of the guillotine included the Halifax Gibbet, which was used in Halifax, England, from 1286 until the 17th century, and the " Maiden", employed in Edinburgh from the 16th through the 18th centuries. The modern form of the guillotine was invented shortly before the French Revolution with the aim of creating a quick and painless method of execution requiring little skill on the part of the operator. Decapitation by guillotine became a common mechanically assisted form of execution. The French observed a strict code of etiquette surrounding such executions. For example, a man named Legros, one of the assistants at the execution ofCharlotte Corday
Marie-Anne Charlotte de Corday d'Armont (27 July 1768 – 17 July 1793), known as Charlotte Corday (), was a figure of the French Revolution. In 1793, she was executed by guillotine for the assassination of Jacobin leader Jean-Paul Marat, who w ...
, was imprisoned for three months and dismissed for slapping the face of the victim after the blade had fallen in order to see whether any flicker of life remained. The guillotine was used in France during the French Revolution and remained the normal judicial method in both peacetime and wartime into the 1970s, although the firing squad was used in certain cases. France abolished the death penalty in 1981.
The guillotine was also used in Algeria before the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
relinquished control of it, as shown in Gillo Pontecorvo's film '' The Battle of Algiers''.
Another guillotine existed in Vatican City until recent years. It had been brought in by Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
's forces during the early 19th century; and, as of 1870, the pope still claimed the authority to use it. The Holy See has since abolished capital punishment within its own jurisdiction, and recent popes have condemned capital punishment wherever it is still practised.
 Many German states had used a guillotine-like device known as a ("falling axe") since the 17th and 18th centuries, and decapitation by guillotine was the usual means of execution in Germany until the abolition of the death penalty in West Germany in 1949. It was last used in communist East Germany in 1966.
In Nazi Germany, the was reserved for common criminals and people convicted of
Many German states had used a guillotine-like device known as a ("falling axe") since the 17th and 18th centuries, and decapitation by guillotine was the usual means of execution in Germany until the abolition of the death penalty in West Germany in 1949. It was last used in communist East Germany in 1966.
In Nazi Germany, the was reserved for common criminals and people convicted of political crime
In criminology
Criminology (from Latin , "accusation", and Ancient Greek , ''-logia'', from λόγος ''logos'' meaning: "word, reason") is the study of crime and deviant behaviour. Criminology is an interdisciplinary field in both the ...
s, including treason. Members of the White Rose resistance movement, a group of students in Munich that included siblings Sophie
Sophie is a version of the female given name Sophia, meaning "wise".
People with the name Born in the Middle Ages
* Sophie, Countess of Bar (c. 1004 or 1018–1093), sovereign Countess of Bar and lady of Mousson
* Sophie of Thuringia, Duchess o ...
and Hans Scholl
Hans Fritz Scholl (; 22 September 1918 – 22 February 1943) was, along with Alexander Schmorell, one of the two founding members of the White Rose resistance movement in Nazi Germany. The principal author of the resistance movement's ...
, were executed by decapitation.
Contrary to popular myth, executions were generally not conducted face-up, and chief executioner Johann Reichhart
Johann Reichhart (29 April 1893 – 26 April 1972) was a German state-appointed judicial executioner in Bavaria from 1924 to 1946. During the Nazi period, he executed numerous people who were sentenced to death for their resistance to the Germa ...
was insistent on maintaining "professional" protocol throughout the era, having administered the death penalty during the earlier Weimar Republic. Nonetheless, it is estimated that some 16,500 persons were guillotined in Germany and Austria between 1933 and 1945, a number that includes resistance fighter
A resistance movement is an organized effort by some portion of the civil population of a country to withstand the legally established government or an occupying power and to disrupt civil order and stability. It may seek to achieve its objectives ...
s both within Germany itself and in countries occupied by Nazi forces. As these resistance fighters were not part of any regular army, they were considered common criminals and were in many cases transported
''Transported'' is an Australian convict melodrama film directed by W. J. Lincoln. It is considered a lost film.
Plot
In England, Jessie Grey is about to marry Leonard Lincoln but the evil Harold Hawk tries to force her to marry him and she wou ...
to Germany for execution. Decapitation was considered a "dishonorable" death, in contrast to execution by firing squad.

Historical practices by nation
Africa
Congo
In the Democratic Republic of Congo, the conflict and ethnic massacre between local army andKamuina Nsapu
The Kamwina Nsapu rebellion, also spelled Kamuina Nsapu rebellion, was an uprising that took place in the Democratic Republic of the Congo between 2016 and 2019. It was instigated by the Kamwina Nsapu militia against state security forces in the ...
rebels has caused several deaths and atrocities such as rape and mutilation. One of them is decapitation, both a fearsome way to intimidate victims as well as an act that may include ritualistic elements. According to an UN report from Congolese refugees, they believed the Bana Mura Bana Mura is an armed militant group active in the Kasaï region of the Democratic Republic of Congo. It mostly recruits ethnic Chokwe, Pende, and Tetela, and is supported by the Congolese government. According to the United Nations, the group de ...
and Kamuina Nsapu militias have "magical powers" as a result of drinking the blood of decapitated victims, making them invincible. According to some reports, they indeed feed the blood from their victims' heads to younger members as an initiation rite, then they often burn the remains or sometimes consume these, committing cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
.
Besides the massive decapitations (like the beheading of 40 members of the State Police), a globally notorious case happened in March 2017 to Swedish politician Zaida Catalán
Zaida Catalán (6 October 1980 – March 2017) was a Swedish politician who was a member of the Green Party and leader of the Young Greens of Sweden between 2001 and 2005.
She was known for her work in activism including environmental issues, a ...
and American UN expert Michael Sharp, who were kidnapped and executed during a mission near the village of Ngombe in Kasaï Province
Kasaï is one of the 21 new provinces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo created in the 2015 repartitioning. Kasaï and Kasaï-Central provinces are the result of the dismemberment of the former Kasaï-Occidental province. Kasaï was for ...
. The UN was reportedly horrified when video footage of the executions surfaced in April that same year, where some grisly details led to assume ritual components of the beheading: the perpetrators first cut the hair of both victims, and then one of them beheaded Catalán only, because it would "increase his power", which may be linked to the fact that Congolese militias are particularly brutal in their acts of violence toward women and children.
In the trial that followed investigations after the bodies were discovered, and according to a testimony of a primary school teacher from Bunkonde, near the village of Moyo Musuila where the executions took place, he witnessed a teenage militant carrying the young woman's head, but despite the efforts of the investigation, the head was never found. According to a report published on 29 May 2019, the Monusco peacekeeping military mission led by Colonel Luis Mangini, in the search for the missing remains, arrived to a ritual place in Moyo Musila where "parts of bodies, hands and heads" were cut and used for rituals, where they lost track of the victim's head.
Asia
Azerbaijan
During the2016 Armenian–Azerbaijani clashes
The 2016 Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, also known as the Four-Day War,, IPA: ʰɑroɾjɑ pɑtɛɾɑzm az, Dördgünlük müharibə April War,; or April clashes, began along the Nagorno-Karabakh line of contact on 1 April 2016 with the Artsakh D ...
, reports emerged that Yazidi-Armenian serviceman Kyaram Sloyan was decapitated by Azerbaijani servicemen. Azerbaijan denied this.
Several reports of decapitation, along with other types of mutilation of Armenian POWs by Azerbaijani soldiers, emerged during the 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war
The Second Nagorno-Karabakh War was an armed conflict in 2020 that took place in the disputed region of Nagorno-Karabakh and Armenian-occupied territories surrounding Nagorno-Karabakh, the surrounding territories. It was a major escalation of ...
.
China
 In traditional
In traditional China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
, decapitation was considered a more severe form of punishment than strangulation, although strangulation caused more prolonged suffering. This was because in Confucian tradition, bodies were gifts from their parents, and so it was therefore disrespectful to their ancestors to return their bodies to the grave dismembered. The Chinese, however, had other punishments, such as dismembering the body into multiple pieces (similar to the English quartering). In addition, there was also a practice of cutting the body at the waist, which was a common method of execution before being abolished in the early Qing dynasty due to the lingering death it caused. In some tales, people did not die immediately after decapitation.
India
The British officer John Masters recorded in his autobiography that Pathans in British India during theAnglo-Afghan War
Anglo-Afghan War may refer to:
* British-Afghan Wars
** First Anglo-Afghan War
The First Anglo-Afghan War ( fa, جنگ اول افغان و انگلیس) was fought between the British Empire and the Emirate of Afghanistan, Emirate of Kabul fr ...
s would behead enemy soldiers who were captured, such as British and Sikh soldiers.
Japan

 In
In Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
, decapitation was a common punishment, sometimes for minor offences. Samurai were often allowed to decapitate soldiers who had fled from battle, as it was considered cowardly. Decapitation was historically performed as the second step in seppuku
, sometimes referred to as hara-kiri (, , a native Japanese kun reading), is a form of Japanese ritual suicide by disembowelment. It was originally reserved for samurai in their code of honour but was also practised by other Japanese people ...
(ritual suicide
Suicide is the act of intentionally causing one's own death. Mental disorders (including depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, personality disorders, anxiety disorders), physical disorders (such as chronic fatigue syndrome), and s ...
by disembowelment
Disembowelment or evisceration is the removal of some or all of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract (the bowels, or viscera), usually through a horizontal incision made across the abdominal area. Disembowelment may result from an accident ...
). After the victim had sliced his own abdomen open, another warrior would strike his head off from behind with a katana to hasten death and to reduce the suffering. The blow was expected to be precise enough to leave intact a small strip of skin at the front of the neck—to spare invited and honored guests the indelicacy of witnessing a severed head rolling about, or towards them; such an occurrence would have been considered inelegant and in bad taste. The sword was expected to be used upon the slightest sign that the practitioner might yield to pain and cry out—avoiding dishonor to him and to all partaking in the privilege of observing an honorable demise. As skill was involved, only the most trusted warrior was honored by taking part. In the late Sengoku period, decapitation was performed as soon as the person chosen to carry out seppuku had made the slightest wound to his abdomen.
Decapitation (without seppuku) was also considered a very severe and degrading form of punishment. One of the most brutal decapitations was that of (杉谷善住坊), who attempted to assassinate Oda Nobunaga
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' and one of the leading figures of the Sengoku period. He is regarded as the first "Great Unifier" of Japan.
Nobunaga was head of the very powerful Oda clan, and launched a war against other ''daimyō'' to unify ...
, a prominent '' daimyō'', in 1570. After being caught, Zenjubō was buried alive in the ground with only his head out, and the head was slowly sawn off with a bamboo saw by passers-by for several days (punishment by sawing; (). These unusual punishments were abolished in the early Meiji era. A similar scene is described in the last page of James Clavell's book ''Shōgun''.
Korea
Historically, decapitation had been the most common method of execution in Korea, until it was replaced by hanging in 1896. Professional executioners were called (망나니) and they were volunteered from death rows.Pakistan
Pakistan's government employs death by hanging for capital punishment. Since 2007, militants from Tehrek-e-Taliban Pakistan have used beheadings as a form of punishment for opponents, criminals and spies in the northwest region of Pakistan. Severed heads of opponents or government officials in Swat Valley were left on popular street corners in order to terrorize the local population. The beheadings have stopped in Swat since the military incursion and sweep-up that began in May 2009 and ended in June 2009. Three Sikhs were beheaded by the Taliban in Pakistan in 2010. Daniel Pearl was beheaded by his captors in the city of Karachi.Thailand
Historically, decapitation had been the main method of execution in Thailand, until it was replaced by shooting in 1934.Europe
Bosnia and Herzegovina
During the war in Bosnia and Herzegovina (1992–1995) there were a number of ritual beheadings of Serbs and Croats who were taken as prisoners of war bymujahedin
''Mujahideen'', or ''Mujahidin'' ( ar, مُجَاهِدِين, mujāhidīn), is the plural form of ''mujahid'' ( ar, مجاهد, mujāhid, strugglers or strivers or justice, right conduct, Godly rule, etc. doers of jihād), an Arabic term th ...
members of the Bosnian Army. At least one case is documented and proven in court by the ICTY
The International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY) was a body of the United Nations that was established to prosecute the war crimes that had been committed during the Yugoslav Wars and to try their perpetrators. The tribunal ...
where mujahedin, members of 3rd Corps of Army BiH, beheaded Bosnian Serb Dragan Popović.
Britain
 In British history, beheading was typically used for noblemen, while commoners would be hanged; eventually, hanging was adopted as the standard means of non-military executions. The last actual execution by beheading was of Simon Fraser, 11th Lord Lovat on 9 April 1747, while a number of convicts were beheaded posthumously up to the early 19th century. (Typically traitors were sentenced to be
In British history, beheading was typically used for noblemen, while commoners would be hanged; eventually, hanging was adopted as the standard means of non-military executions. The last actual execution by beheading was of Simon Fraser, 11th Lord Lovat on 9 April 1747, while a number of convicts were beheaded posthumously up to the early 19th century. (Typically traitors were sentenced to be hanged, drawn and quartered
To be hanged, drawn and quartered became a statutory penalty for men convicted of high treason in the Kingdom of England from 1352 under Edward III of England, King Edward III (1327–1377), although similar rituals are recorded during the rei ...
, a method which had already been discontinued.) Beheading was degraded to a secondary means of execution, including for treason, with the abolition of drawing and quartering in 1870 and finally abolished by the Statute Law (Repeals) Act 1973
The Statute Law (Repeals) Act 1973 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, which implemented recommendations contained in the fourth report on statute law revision, by the Law Commission and the Scottish Law Commission.
This Act was ...
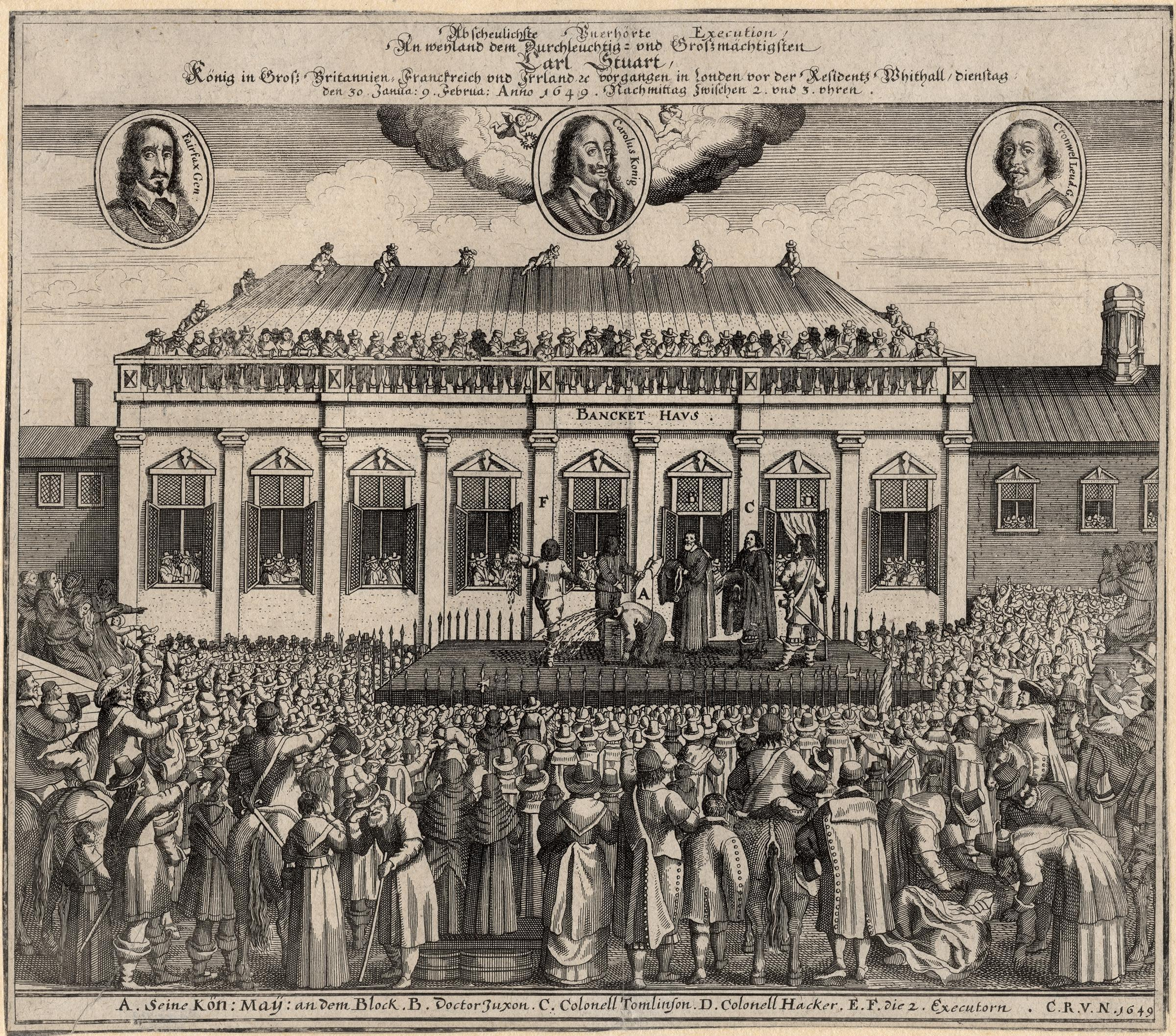
. One of the most notable executions by decapitation in Britain was that of King Charles I of England, who was beheaded outside the Banqueting House in Whitehall in 1649, after being captured by parliamentarians during the English Civil War and tried for treason.
Celts
The Celts of western Europe long pursued a "cult of the severed head", as evidenced by both Classical literary descriptions and archaeological contexts. This cult played a central role in their temples and religious practices and earned them a reputation ashead hunters
''Head Hunters'' is the twelfth studio album by American pianist and composer Herbie Hancock, released October 26, 1973, on Columbia Records. Recording sessions for the album took place in the evening at Wally Heider Studios and Different Fur T ...
among the Mediterranean peoples. Diodorus Siculus
Diodorus Siculus, or Diodorus of Sicily ( grc-gre, Διόδωρος ; 1st century BC), was an ancient Greek historian. He is known for writing the monumental universal history ''Bibliotheca historica'', in forty books, fifteen of which su ...
, in his 1st-century ''Historical Library
''Bibliotheca historica'' ( grc, Βιβλιοθήκη Ἱστορική, ) is a work of universal history by Diodorus Siculus. It consisted of forty books, which were divided into three sections. The first six books are geographical in theme, a ...
'' (5.29.4) wrote the following about Celtic head-hunting:
Both the Greeks and Romans found the Celtic decapitation practices shocking and the latter put an end to them when Celtic regions came under their control. However, Greeks and Romans both employed decapitation and other horrific tortures, highlighting a tendency to view practices as more shocking when carried out by an outside group, even if the practices are essentially similar.
According to Paul Jacobsthal, "Amongst the Celts the human head was venerated above all else, since the head was to the Celt the soul, centre of the emotions as well as of life itself, a symbol of divinity and of the powers of the other-world." Arguments for a Celtic cult of the severed head include the many sculptured representations of severed heads in La Tène carvings, and the surviving Celtic mythology, which is full of stories of the severed heads of heroes and the saints who carry their own severed heads, right down to ''Sir Gawain and the Green Knight'', where the Green Knight picks up his own severed head after Gawain has struck it off in a beheading game
The beheading game is a literary trope found in Irish mythology and medieval chivalric romance. The trope consists of a stranger who arrives at a royal court and challenges a hero to an exchange of blows: the hero may decapitate the stranger, bu ...
, just as Saint Denis carried his head to the top of Montmartre.Wilhelm, James J. "Sir Gawain and the Green Knight." The Romance of Arthur. Ed. Wilhelm, James J. New York: Garland Publishing, 1994. 399–465.
A further example of this regeneration after beheading lies in the tales of Connemara's Saint Féchín, who after being beheaded by Vikings carried his head to the Holy Well on Omey Island and on dipping it into the well placed it back upon his neck and was restored to full health.Charles-Edwards, ''Early Christian Ireland'', p. 467 n. 82.
Classical antiquity
 The ancient Greeks and Romans regarded decapitation as a comparatively honorable form of execution for criminals. The traditional procedure, however, included first being tied to a stake and whipped with rods. Axes were used by the Romans, and later swords, which were considered a more honorable instrument of death. Those who could verify that they were Roman citizens were to be beheaded, rather than undergoing the much more horrific experience of crucifixion. In the Roman Republic of the early 1st century BC, it became the tradition for the severed heads of public enemies—such as the political opponents of Marius and
The ancient Greeks and Romans regarded decapitation as a comparatively honorable form of execution for criminals. The traditional procedure, however, included first being tied to a stake and whipped with rods. Axes were used by the Romans, and later swords, which were considered a more honorable instrument of death. Those who could verify that they were Roman citizens were to be beheaded, rather than undergoing the much more horrific experience of crucifixion. In the Roman Republic of the early 1st century BC, it became the tradition for the severed heads of public enemies—such as the political opponents of Marius and Sulla
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix (; 138–78 BC), commonly known as Sulla, was a Roman general and statesman. He won the first large-scale civil war in Roman history and became the first man of the Republic to seize power through force.
Sulla had ...
, for example—to be publicly displayed on the Rostra in the Forum Romanum
The Roman Forum, also known by its Latin name Forum Romanum ( it, Foro Romano), is a rectangular forum (plaza) surrounded by the ruins of several important ancient government buildings at the center of the city of Rome. Citizens of the ancient ...
after execution. Perhaps the most famous such victim was Cicero who, on instructions from Mark Antony, had his hands (which had penned the '' Philippicae'' against Antony) and his head cut off and nailed up for display in this manner.
France
In France, until the abolition of capital punishment in 1981, the main method of execution had been by beheading by means of the guillotine. Other than a small number of military cases in which a firing squad was used (including that of Jean Bastien-Thiry), the guillotine was the only legal method of execution from 1791, when it was introduced by the Legislative Assembly during the last days of the kingdom French Revolution, until 1981. Before the revolution, beheading had typically been reserved for noblemen and carried out manually. In 1981, PresidentFrançois Mitterrand
François Marie Adrien Maurice Mitterrand (26 October 19168 January 1996) was President of France, serving under that position from 1981 to 1995, the longest time in office in the history of France. As First Secretary of the Socialist Party, he ...
abolished capital punishment and issued commutations for those whose sentences had not been carried out.
The first person executed by the guillotine in France was highwayman Nicolas Jacques Pelletier
Nicolas Jacques Pelletier (c. 175625 April 1792) was a French highwayman who was the first person to be executed by guillotine.
Robbery and subsequent sentencing
Pelletier routinely associated with a group of known criminals. On the night of 1 ...
in April 1792. The last execution was of murderer Hamida Djandoubi, in Marseilles, in 1977. Throughout its extensive overseas colonies and dependencies, the device was also used, including on St Pierre
Saint-Pierre (French, 'Saint Peter') may refer to:
Buildings and churches
* Church of Saint-Pierre, Caen, Normandy, France
* Saint-Pierre, Firminy, France, designed by Le Corbusier
* Saint-Pierre-le-Jeune Protestant Church, Strasbourg, France
...
in 1889 and on Martinique as late as 1965.
Germany
*Fritz Haarmann
Friedrich Heinrich Karl "Fritz" Haarmann (25 October 1879 – 15 April 1925) was a German serial killer, known as the Butcher of Hanover, the Vampire of Hanover and the Wolf Man, who committed the sexual assault, murder, mutilation and dismember ...
, a serial killer from Hannover who was sentenced to death for killing 27 young men, was decapitated in April 1925. He was nicknamed "The Butcher from Hannover" and was rumored to have sold his victims' flesh to his neighbor's restaurant.
* In July 1931, notorious serial killer Peter Kürten, known as "The Vampire of Düsseldorf", was executed on the guillotine in Cologne.
* On 1 August 1933, in Altona, Bruno Tesch
Bruno Emil Tesch (14 August 1890 – 16 May 1946) was a German chemist and entrepreneur. Together with Gerhard Peters and Walter Heerdt, he invented the insecticide Zyklon B. He was the owner of Tesch & Stabenow (called ''Testa''), a pest contro ...
and three others were beheaded. These were the first executions in Nazi Germany. The executions concerned the Altona Bloody Sunday
Altona Bloody Sunday (german: Altonaer Blutsonntag) is the name given to the events of 17 July 1932 when a recruitment march by the Nazi SA led to violent clashes between the police, the SA and supporters of the Communist Party of Germany ...
(''Altonaer Blutsonntag'') riot, an SA march on 17 July 1932 that turned violent and led to 18 people being shot dead.
* Marinus van der Lubbe by guillotine in 1934 after a show trial
A show trial is a public trial in which the judicial authorities have already determined the guilt or innocence of the defendant. The actual trial has as its only goal the presentation of both the accusation and the verdict to the public so th ...
in which he was found guilty of starting the Reichstag fire
The Reichstag fire (german: Reichstagsbrand, ) was an arson attack on the Reichstag building, home of the German parliament in Berlin, on Monday 27 February 1933, precisely four weeks after Nazi leader Adolf Hitler was sworn in as Chancellor of ...
.
* In February 1935 Benita von Falkenhayn
Benita Ursula von Falkenhayn, maiden name von Zollikofer-Altenklingen (14 August 1900 – 18 February 1935) was a German baroness who served as a spy for the Second Polish Republic.
Life
Falkenhayn was born in Berlin to the noble Zollikofer ...
and Renate von Natzmer
Renate von Natzmer (1898 in Borkow (Kreis Schlawe, Pomerania) – February 18, 1935 in Berlin) was a German noblewoman who worked for the army during the Weimar Republic and Third Reich. She also worked for Polish intelligence. In the early 1 ...
were beheaded with the axe and block in Berlin for espionage for Poland. Axe beheading was the only method of execution in Berlin until 1938, when it was decreed that all civil executions would henceforth be carried out by guillotine. However, the practice was continued in rare cases such as that of Olga Bancic
Olga Bancic (; born Golda Bancic; also known under her French '' nom de guerre'' Pierrette; 10 May 1912 – 10 May 1944) was a Jewish Romanian communist activist, known for her role in the French Resistance. A member of the FTP-MOI and Missak M ...
and Werner Seelenbinder
Werner Seelenbinder (2 August 1904 – 24 October 1944) was a German communist and wrestler.
Early years
Seelenbinder was born in Stettin, Pomerania (modern-day Poland), and became a wrestler after training as a joiner. He had connections with ...
in 1944. Beheading by guillotine survived in West Germany until 1949 and in East Germany until 1966.
* A group of three Catholic clergymen, Johannes Prassek, Eduard Müller and Hermann Lange, and an Evangelical Lutheran pastor, Karl Friedrich Stellbrink, were arrested following the bombing of Lübeck, tried by the People's Court in 1943 and sentenced to death by decapitation; all were beheaded on 10 November 1943, in the Hamburg prison at Holstenglacis. Stellbrink had explained the raid next morning in his Palm Sunday sermon as a "trial by ordeal", which the Nazi authorities interpreted to be an attack on their system of government and as such undermined morale and aided the enemy.
* In October 1944, Werner Seelenbinder
Werner Seelenbinder (2 August 1904 – 24 October 1944) was a German communist and wrestler.
Early years
Seelenbinder was born in Stettin, Pomerania (modern-day Poland), and became a wrestler after training as a joiner. He had connections with ...
was executed by manual beheading, the last legal use of the method (other than by guillotine) in both Europe and the rest of the Western world. Earlier the same year, Olga Bancic
Olga Bancic (; born Golda Bancic; also known under her French '' nom de guerre'' Pierrette; 10 May 1912 – 10 May 1944) was a Jewish Romanian communist activist, known for her role in the French Resistance. A member of the FTP-MOI and Missak M ...
had been executed by the same means.
* In February 1943, American academic Mildred Harnack
Mildred Elizabeth Harnack ( Fish; September 16, 1902 – February 16, 1943) was an American literary historian, translator, and member of the German resistance against the Nazi regime. After marrying Arvid Harnack, she moved to Germany in 192 ...
and the university students Hans Scholl
Hans Fritz Scholl (; 22 September 1918 – 22 February 1943) was, along with Alexander Schmorell, one of the two founding members of the White Rose resistance movement in Nazi Germany. The principal author of the resistance movement's ...
, Sophie Scholl, and Christoph Probst
Christoph Ananda Probst (6 November 1919 – 22 February 1943) was a German student of medicine and member of the White Rose (''Weiße Rose'') German resistance to Nazism, resistance group.
Early life
Probst was born in Murnau am Staffelsee. ...
of the White Rose protest movement, were all beheaded by the Nazi State. Four other members of the White Rose, an anti-Nazi group, were also executed by the People's Court later that same year. The anti-Nazi Helmuth Hübener was also decapitated by People's Court order.
* In 1966, former Auschwitz
Auschwitz concentration camp ( (); also or ) was a complex of over 40 concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) during World War II and the Holocaust. It con ...
doctor Horst Fischer was executed by the German Democratic Republic by guillotine, the last executed by this method outside France. Beheading was subsequently replaced by shooting in the neck.
Nordic countries
InNordic countries
The Nordic countries (also known as the Nordics or ''Norden''; literal translation, lit. 'the North') are a geographical and cultural region in Northern Europe and the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic. It includes the sovereign states of Denmar ...
, decapitation was the usual means of carrying out capital punishment. Noblemen were beheaded with a sword
A sword is an edged, bladed weapon intended for manual cutting or thrusting. Its blade, longer than a knife or dagger, is attached to a hilt and can be straight or curved. A thrusting sword tends to have a straighter blade with a pointed ti ...
, and commoners with an axe. The last executions by decapitation in Finland in 1825, Norway in 1876, Faroe Islands in 1609, and in Iceland in 1830 were carried out with axes. The same was the case in Denmark in 1892. Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
continued the practice for a few decades, executing its second to last criminal—mass murderer Johan Filip Nordlund
John Filip Nordlund (also known as "''Mälarmördaren''", "''Mordlund''", "''Svarte Filip''") (23 March 1875 – 10 December 1900) was a Swedish mass murderer, the second to last person to be executed in Sweden (after Alfred Ander in 1910) and ...
—by axe in 1900. It was replaced by the guillotine, which was used for the first and only time on Johan Alfred Ander in 1910.
The official beheading axe of Finland resides today in the Museum of Crime, Vantaa.
Spain
In Spain executions were carried out by various methods including strangulation by thegarrotte
A garrote or garrote vil (a Spanish word; alternative spellings include garotte and similar variants''Oxford English Dictionary'', 11th Ed: garrotte is normal British English spelling, with single r alternate. Article title is US English spellin ...
. In the 16th and 17th centuries, noblemen were sometimes executed by means of beheading. Examples include Anthony van Stralen, Lord of Merksem
Anthony van Stralen (1521 - executed, Vilvoorde, 24 September 1568), Lord of Merksem, Lord of Dambrugghe was a Mayor of Antwerp. Although he was Roman Catholic, he became a famous victim of the terror of the Duke of Alva.
Family
He was the son ...
, Lamoral, Count of Egmont
Lamoral, Count of Egmont, Prince of Gavere (18 November 1522 – 5 June 1568) was a general and statesman in the Spanish Netherlands just before the start of the Eighty Years' War, whose execution helped spark the national uprising that eventuall ...
and Philip de Montmorency, Count of Horn. They were tied to a chair on a scaffold. The executioner used a knife to cut the head from the body. It was considered to be a more honourable death if the executioner started with cutting the throat.
Middle East
Iran
Iran, since the 1979Islamic Revolution
The Iranian Revolution ( fa, انقلاب ایران, Enqelâb-e Irân, ), also known as the Islamic Revolution ( fa, انقلاب اسلامی, Enqelâb-e Eslâmī), was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dyna ...
, has alleged it uses beheading as one of the methods of punishment.
Iraq
Though not officially sanctioned, legal beheadings were carried out against at least 50 prostitutes and pimps under Saddam Hussein as late as 2000. Beheadings have emerged as another terror tactic especially in Iraq since 2003. Civilians have borne the brunt of the beheadings, although U.S. and Iraqi military personnel have also been targeted. After kidnapping the victim, the kidnappers typically make some sort of demand of the government of the hostage's nation and give a time limit for the demand to be carried out, often 72 hours. Beheading is often threatened if the government fails to heed the wishes of the hostage takers. Sometimes, the beheadings are videotaped and made available on the Internet. One of the most publicized of such executions was that of Nick Berg. Judicial execution is practiced in Iraq, but is generally carried out by hanging.Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia has a criminal justice system based onShari'ah
Sharia (; ar, شريعة, sharīʿa ) is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition. It is derived from the religious precepts of Islam and is based on the sacred scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran and the ...
law reflecting a particular state-sanctioned interpretation of Islam. Crimes such as rape, murder, apostasy, and sorcery are punishable by beheading. It is usually carried out publicly
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociological concept of the ''Öffentlichkei ...
by beheading with a sword.
A public beheading will typically take place around 9am. The convicted person is walked into the square and kneels in front of the executioner. The executioner uses a sword to remove the condemned person's head from his or her body at the neck with a single strike. After the convicted person is pronounced dead, a police official announces the crimes committed by the beheaded alleged criminal and the process is complete. The official might announce the same before the actual execution. This is the most common method of execution in Saudi Arabia.
According to Amnesty International
Amnesty International (also referred to as Amnesty or AI) is an international non-governmental organization focused on human rights, with its headquarters in the United Kingdom. The organization says it has more than ten million members and sup ...
, at least 79 people were executed in Saudi Arabia in 2013. Foreigners are not exempt, accounting for "almost half" of executions in 2013.
Syria
The Syrian government employs hanging as its method of capital punishment. However, the terrorist organisation known as the Islamic State, which controlled territory in much of eastern Syria, had regularly carried out beheadings of people. Syrian rebels attempting to overthrow the Syrian government have been implicated in beheadings too.North America
Mexico
Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla
Don (honorific), Don Miguel Gregorio Antonio Ignacio Hidalgo y Costilla y Gallaga Mandarte Villaseñor (8 May 1753 – 30 July 1811), more commonly known as Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla or Miguel Hidalgo (), was a Catholic priest, leader ...
, Ignacio Allende, José Mariano Jiménez
José Mariano Jiménez (August 18, 1781 – June 26, 1811) was a Mexican engineer and rebel officer active at the beginning of the Mexican War of Independence.
Mariano Jiménez was born in San Luis Potosí. He studied in the Colegio de Miner ...
and Juan Aldama were tried for treason, executed by firing squad and beheaded during the Mexican independence in 1811. Their heads were on display on the four corners of the Alhóndiga de Granaditas, in Guanajuato
Guanajuato (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guanajuato ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Guanajuato), is one of the 32 states that make up the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 46 municipalities and its capital city i ...
.
During the Mexican Drug War, some Mexican drug cartels turned to decapitation and beheading of rival cartel members as a method of intimidation.
 This trend of beheading and publicly displaying the decapitated bodies was started by the Los Zetas, a criminal group composed by former Mexican special forces operators, trained in the infamous ''US Army School of the Americas'', in torture techniques and psychological warfare.
This trend of beheading and publicly displaying the decapitated bodies was started by the Los Zetas, a criminal group composed by former Mexican special forces operators, trained in the infamous ''US Army School of the Americas'', in torture techniques and psychological warfare.
United States
The United States government has never employed beheading as a legal method of execution. However, beheading has sometimes been used in mutilations of the dead, particularly of black people like Nat Turner, who led a rebellion against slavery. When caught, he was publicly hanged, flayed, and beheaded. This was a technique used by many enslavers to discourage the "frequent bloody uprisings" that were carried out by "kidnapped Africans". While bodily dismemberment of various kinds was employed to instill terror, Dr. Erasmus D. Fenner noted postmortem decapitation was particularly effective. US soldiers have committed decapitations in various invasions and/or conquests, including of the Native Americans, the Philippines, Korea, and Vietnam. Regarding Vietnam, correspondent Michael Herr notes "thousands" of photo-albums made by US soldiers "all seemed to contain the same pictures": "the severed head shot, the head often resting on the chest of the dead man or being held up by a smiling Marine, or a lot of the heads, arranged in a row, with a burning cigarette in each of the mouths, the eyes open". Some of the victims were "very young". General George Patton IV, son of the famous WWII generalGeorge S. Patton
George Smith Patton Jr. (November 11, 1885 – December 21, 1945) was a general in the United States Army who commanded the Seventh United States Army in the Mediterranean Theater of World War II, and the Third United States Army in France ...
, was known for keeping "macabre souvenirs", such as "a Vietnamese skull that sat on his desk." Other Americans "hacked the heads off Vietnamese to keep, trade, or exchange for prizes offered by commanders."
As a terror tactic, "some American troops hacked the heads off... dead ietnameseand mounted them on pikes or poles".
Although the Utah Territory permitted a person sentenced to death to choose beheading as a means of execution, no person chose that option, and it was dropped when Utah became a state.
Notable people who have been beheaded
See also
*Atlanto-occipital dislocation Atlanto-occipital dislocation, orthopedic decapitation, or internal decapitation describes ligamentous separation of the spinal column from the skull base. It is possible for a human to survive such an injury; however, 70% of cases result in immedia ...
, where the skull is dislodged from the spine
Spine or spinal may refer to:
Science Biology
* Vertebral column, also known as the backbone
* Dendritic spine, a small membranous protrusion from a neuron's dendrite
* Thorns, spines, and prickles, needle-like structures in plants
* Spine (zoolog ...
; a generally, but not always, fatal injury.
* Beheading in Islam
* Beheading video
* Blood atonement
* Blood squirt
Blood squirt (blood spurt, blood spray, blood gush, or blood jet) is the effect when an artery is ruptured. Blood pressure causes the blood to bleed out at a rapid, intermittent rate in a spray or jet, coinciding with the pulse, rather than the s ...
, a result from a decapitation.
* Cephalophore, a martyred saint who supposedly carries his/her severed head.
* Chhinnamasta, a Hindu goddess who supposedly decapitates herself and holds her head in her hand.
* Cleveland Torso Murderer, a serial killer who decapitated some of his victims.
* Dismemberment
* François-Jean de la Barre
François-Jean Lefebvre de la Barre (12 September 17451 July 1766) was a young French nobleman. He was tortured and beheaded before his body was burnt on a pyre along with Voltaire's '' Philosophical Dictionary'' nailed to his torso. La Barre i ...
* Headhunting
* List of methods of capital punishment
* Mike the Headless Chicken
Mike the Headless Chicken (April 20, 1945March 17, 1947) was a male Wyandotte chicken that lived for 18 months after his head had been cut off. After the loss of his head, Mike achieved national fame until his death in March 1947. In Fruita, C ...
Notes
References
External links
Crime Library
{{Capital punishment Execution methods Capital punishment Causes of death