Dakota (fossil) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Dakota (specimen NDGS 2000) is the nickname given to an important ''
Dakota (specimen NDGS 2000) is the nickname given to an important ''
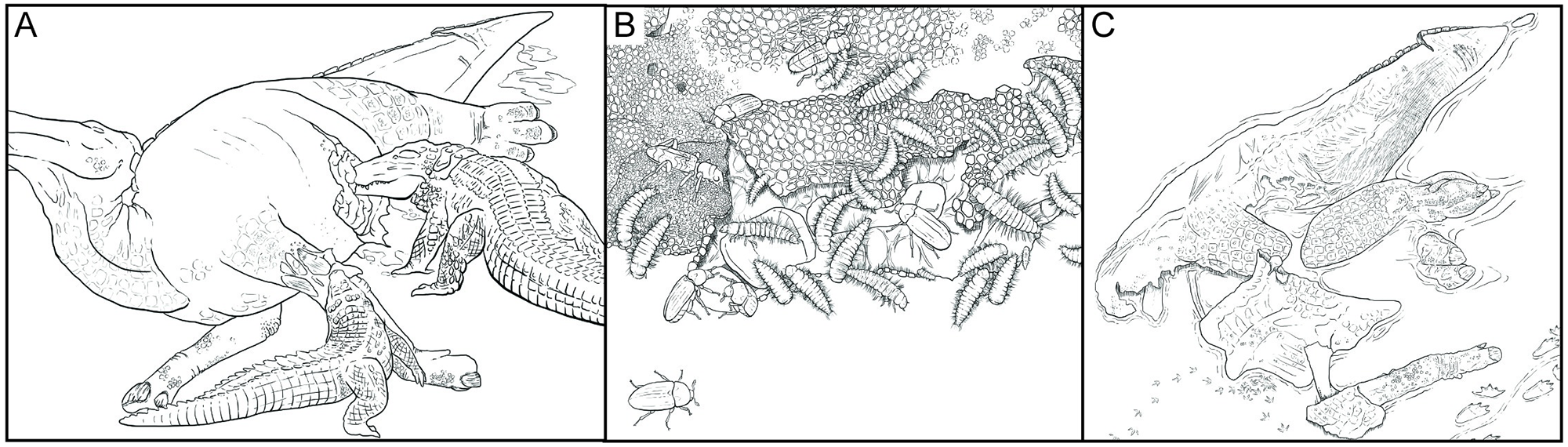 Dinosaur fossils with Dakota's degree of preservation are extremely rare because many different factors must come together to allow it to occur. The carcass first must escape
Dinosaur fossils with Dakota's degree of preservation are extremely rare because many different factors must come together to allow it to occur. The carcass first must escape
 Dakota (specimen NDGS 2000) is the nickname given to an important ''
Dakota (specimen NDGS 2000) is the nickname given to an important ''Edmontosaurus
''Edmontosaurus'' ( ) (meaning "lizard from Edmonton") is a genus of hadrosaurid (duck-billed) dinosaur. It contains two known species: ''Edmontosaurus regalis'' and ''Edmontosaurus annectens''. Fossils of ''E. regalis'' have been found in rocks ...
'' fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
found in the Hell Creek Formation in North Dakota
North Dakota () is a U.S. state in the Upper Midwest, named after the Native Americans in the United States, indigenous Dakota people, Dakota Sioux. North Dakota is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north a ...
. It is about 67 million years old, placing it in the Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval from ...
, the last stage of the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
period. It was about 12 m (40 ft) long and weighed about 7-8 tons.
The fossil is unusual and scientifically valuable because soft tissue including skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have diffe ...
and muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
have been fossilized, giving researchers the rare opportunity to study more than bone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provid ...
s, as with most vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, ...
fossils. Preliminary research results indicate that hadrosaurs had heavier tails and were able to run faster than was previously thought.
Discovery and analysis
Dakota was first discovered by paleontology studentTyler Lyson
Tyler R. Lyson (born 1982 or 1983) is an American paleontologist. He is the discoverer of the dinosaur fossil Dakota, a fossilized mummified hadrosaur. He has done significant research on the evolution of turtles and on the rise of mammals after th ...
on his family's North Dakota property in 1999 while he was a high school student, but he did not investigate the site in detail until 2004, when he discovered the soft tissue preservation. Lyson teamed with British paleontologist Phillip Manning, and the site was excavated in summer 2006.
Manning's team used a large-scale CT scan
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
ner, provided by NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...
and the Boeing Company, to generate high-resolution scans of the preserved muscles and tendons of the rear legs. Because the intervertebral disc
An intervertebral disc (or intervertebral fibrocartilage) lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold t ...
s which space out the spinal column of the tail have been fossilized, researchers have been able to calculate its length more accurately. The preservation of its muscles and tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability ...
s allow the calculation of its mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementar ...
. The results indicate the dinosaur could likely have run at , faster than the estimated top speed of '' Tyrannosaurus rex'', at .
The well-preserved integument has retained its texture, and researchers have mapped it in three dimensions. The scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number w ...
are of different sizes, and researchers speculate that their pattern may reflect the animal's coloration in life. For example, areas of an arm's joints are textured in what resembles a striped pattern. This fossil's examination was the subject of ''Dino Autopsy'', a documentary aired on National Geographic Channel
National Geographic (formerly National Geographic Channel; abbreviated and trademarked as Nat Geo or Nat Geo TV) is an American pay television television network, network and flagship (broadcasting), flagship channel owned by the National Geograp ...
on December 9, 2007.
The specimen was previously housed at the Marmarth Research Foundation
Marmarth ( ) is the largest city in Slope County in the U.S. State of North Dakota with a population of 101 as of 2020 census. It is situated in the southwestern part of Slope County, along the Bowman County line in the southwestern part of No ...
(MRF) under the catalog number MRF-3, but now it is permanently part of the collection of the North Dakota Geological Survey located at the State of North Dakota
North Dakota () is a U.S. state in the Upper Midwest, named after the indigenous Dakota Sioux. North Dakota is bordered by the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba to the north and by the U.S. states of Minnesota to the east, South ...
, under the specimen number/catalogue NDGS 2000.
Taphonomy
 Dinosaur fossils with Dakota's degree of preservation are extremely rare because many different factors must come together to allow it to occur. The carcass first must escape
Dinosaur fossils with Dakota's degree of preservation are extremely rare because many different factors must come together to allow it to occur. The carcass first must escape scavenger
Scavengers are animals that consume dead organisms that have died from causes other than predation or have been killed by other predators. While scavenging generally refers to carnivores feeding on carrion, it is also a herbivorous feeding b ...
s as well as degradation by the elements. The soft tissue must then be mineralized before it decomposes. Finally, as with all fossils, the mineralized body must escape destruction by geological forces over millions of years. News reports have referred to Dakota as " mummified"; however, it is actually a fossil of a mummified dinosaur, where the animal's dried tissues have been transformed to rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
through fossilization.
Stephanie K. Drumheller and team in 2022 proposed that Dakota was exceptionally preserved because of several identified scavenging marks to the carcass, which helped to escape the gases, fluids, and microbes that develop during decomposition. This may have likely allowed soft tissues to withstand the weeks and/or months required for desiccation
Desiccation () is the state of extreme dryness, or the process of extreme drying. A desiccant is a hygroscopic (attracts and holds water) substance that induces or sustains such a state in its local vicinity in a moderately sealed container.
...
prior to burial and eventual fossilization
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in ...
.
See also
*Timeline of hadrosaur research
A timeline is a display of a list of events in chronological order. It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labelled with dates paralleling it, and usually contemporaneous events.
Timelines can use any suitable scale representin ...
* Edmontosaurus mummy AMNH 5060
The ''Edmontosaurus'' mummy AMNH 5060 is an exceptionally well-preserved fossil of a dinosaur in the collection of the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH). Discovered in 1908 in the United States near Lusk, Wyoming, it was the first dinos ...
* Edmontosaurus mummy SMF R 4036
* Dueling Dinosaurs
The Dueling Dinosaurs or Montana Dueling Dinosaurs is a fossil specimen originating from the Hell Creek Formation of Montana. It consists of the fossilized skeletons of a tyrannosaur (generally considered a juvenile ''Tyrannosaurus, Tyrannosaurus ...
References
External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Dakota (Fossil) 1999 in paleontology Cretaceous fossil record Dinosaur fossils Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of North America Paleontology in North Dakota Saurolophines