DEPDC5 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
DEPDC5 (or DEP domain-containing 5) is a human




 One study on patients with hepatocellular carcinoma found higher DEPDC5 expression in
One study on patients with hepatocellular carcinoma found higher DEPDC5 expression in
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
of poorly understood function but has been associated with cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
in several studies. It is encoded by a gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
of the same name, located on chromosome 22
Chromosome 22 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in human cells. Humans normally have two copies of chromosome 22 in each cell. Chromosome 22 is the second smallest human chromosome, spanning about 49 million DNA base pairs and representing b ...
.
Function
The function of DEPDC5 is not yet known, but it has been implicated in intracellular signal transduction based on homology between the DEP domains of DEPDC5 and Dishevelled-1 (DVL1
Segment polarity protein dishevelled homolog DVL-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DVL1'' gene.
Function
DVL1, the human homolog of the Drosophila dishevelled gene (dsh) encodes a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein that regulates cell ...
).
Mutations in this gene have been associated to cases of focal epilepsy
Focal seizures (also called partial seizures and localized seizures) are seizures which affect initially only one hemisphere of the brain. The brain is divided into two hemispheres, each consisting of four lobes – the frontal, temporal, parie ...
(doi:10.1038/ng.2601).
Gene
In ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
'', the DEPDC5 gene has been localized to the long arm of chromosome 22, 22q12.2-q12.3, between the PRRL14 and YWHAH
14-3-3 protein eta also referred to as 14-3-3η is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''YWHAH'' gene.
Function
This gene product belongs to the 14-3-3 family of proteins that are normally intracellular in nature and help to mediate si ...
genes. The clinical relevance of this gene includes an intronic SNP (rs1012068) that has been associated with a 2-fold hepatocellular carcinoma-risk increase.

Structure
Domains

DEP
TheDEP domain
In molecular biology, the DEP domain (Dishevelled, Egl-10 and Pleckstrin domain) is a globular protein domain of about 80 amino acids that is found in over 50 proteins involved in G-protein signalling pathways. It was named after the three protei ...
derives its name from the proteins Dishevelled
Dishevelled (Dsh) is a family of proteins involved in canonical and non-canonical Wnt signalling pathways. Dsh (Dvl in mammals) is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein that acts directly downstream of frizzled receptors. It takes its name from its initi ...
, Egl-10 and Pleckstrin
Pleckstrin is a protein found in platelets. The name derives from platelet and leukocyte C kinase substrate and the KSTR string of amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional grou ...
, each of which contain a variant of this domain. It spans 82 residues and is 343 amino acids from the C-terminus. A SWISS-MODEL predicts two beta sheets
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a gen ...
and three alpha helices
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid located four residues ear ...
contained within the domain.
While its exact function is not known, the DEPDC5 DEP domain has the highest structural similarity to the DEP domain of DVL1 when performing a CBLAST at NCBI
The National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) is part of the United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), a branch of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It is approved and funded by the government of the United States. The ...
. The alignment scores an Evalue of 1.00e-08 and indicates 30% identity between the DEP domains of the two proteins. In DVL1, the DEP domain is involved in localization of the protein to the plasma membrane as part of the Wnt signaling pathway
The Wnt signaling pathways are a group of signal transduction pathways which begin with proteins that pass signals into a cell through cell surface receptors. The name Wnt is a portmanteau created from the names Wingless and Int-1. Wnt signaling ...
.
DUF 3608
The DUF 3608 domain sits 99 amino acids from the N-terminus and itself spans 280 amino acids. PELE predicts at least one beta sheet and two alpha helices within this domain. It also contains 26 highly conserved residues and several post-translation modifications. Both occurrences are addressed later in this article. Evidence for the function of DUF 3608 has been uncovered in theyeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are estimated to constit ...
homolog
In biology, homology is similarity due to shared ancestry between a pair of structures or genes in different taxa. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the wings of bats and birds, the arms of prima ...
Iml1p. Imlp1's DUF 3608 is thought to aid in binding to two protein partners, Npr2
Natriuretic peptide receptor B/guanylate cyclase B (atrionatriuretic peptide receptor B), also known as NPR2, is an atrial natriuretic peptide receptor. In humans it is encoded by the NPR2 gene.
A mutation of the NPR2 gene can result in dispropo ...
and Npr3. Together, these three proteins form the Iml1-Npr2-Npr3 complex and are involved in "non-nitrogen starvation" autophagy regulation. The researchers who uncovered this propose renaming DUF 3608 to RANS (Required for Autophagy induced under Non-nitrogen Starvation conditions).
Secondary Structure
Based on unanimous consensus by the secondary structure prediction tool PELE, DEPDC5 contains at least ten alpha helices and nine beta sheets. The locations of these secondary structures are illustrated in the image below: red highlights are alpha helices and blue highlights are beta sheets.Homology
Orthologs
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
are the most distantly related organisms to contain a protein orthologous
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a s ...
to human DEPDC5, including ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have b ...
'' and '' Albugo laibachii''. In the fungi, the protein name is Iml1p, or vacuolar membrane-associated protein Iml1. Name deviations in other organisms include CG12090 (''Drosophila
''Drosophila'' () is a genus of flies, belonging to the family Drosophilidae, whose members are often called "small fruit flies" or (less frequently) pomace flies, vinegar flies, or wine flies, a reference to the characteristic of many speci ...
'') and AGAP007010 (mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "li ...
). Conservation is high between humans and other vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with c ...
species, ranging from 74% identity in cichlids
Cichlids are fish from the family Cichlidae in the order Cichliformes. Cichlids were traditionally classed in a suborder, the Labroidei, along with the wrasses ( Labridae), in the order Perciformes, but molecular studies have contradicted th ...
to 99% identity in chimpanzees
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative th ...
.
The following table summarizes an analysis of 20 proteins orthologous to human DEPDC5.
30 residues have been conserved since animals and fungi diverged, with 26 of these located in the DUF 3608 domain. The following multiple sequence alignment
Multiple sequence alignment (MSA) may refer to the process or the result of sequence alignment of three or more biological sequences, generally protein, DNA, or RNA. In many cases, the input set of query sequences are assumed to have an evolutio ...
illustrates this conservation of the DUF domain; representatives from invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
and fungal clades
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
are aligned to the human DUF 3608 with completely conserved residues colored green.

Paralogs
There are no known human DEPDC5paralogs
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a sp ...
, but there are 64 human proteins containing a homologous DEP domain. There are also no identified paralogs for the yeast protein Iml1, the most distantly related ortholog of human DEPDC5.
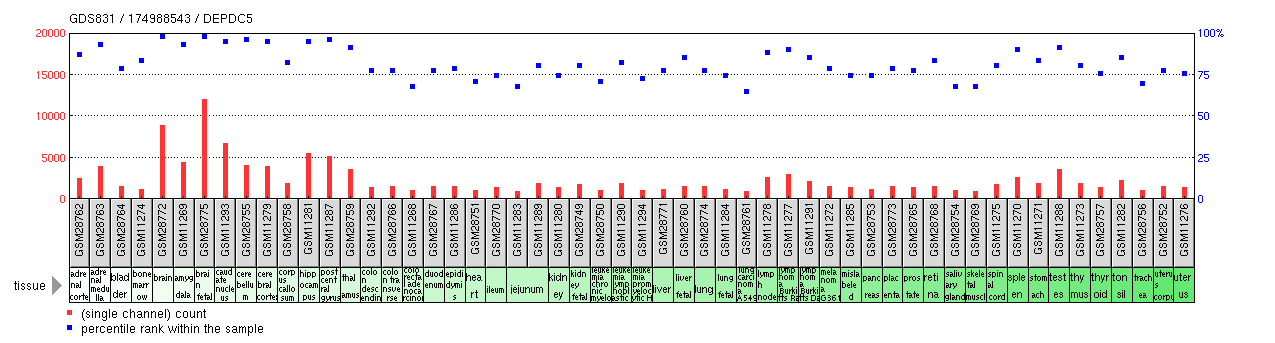
Expression
DEPDC5 expression has been characterized as ubiquitous in human tissue byRT-PCR
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of RNA into DNA (in this context called complementary DNA or cDNA) and amplification of specific DNA targets using polymerase ch ...
analysis and in DNA microarray studies as displayed in the chart below.
 One study on patients with hepatocellular carcinoma found higher DEPDC5 expression in
One study on patients with hepatocellular carcinoma found higher DEPDC5 expression in tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
tissue than in non-tumor tissue. Conversely, a homozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mo ...
deletion of three genes, one being DEPDC5, was found in two glioblastoma
Glioblastoma, previously known as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), is one of the most aggressive types of cancer that begin within the brain. Initially, signs and symptoms of glioblastoma are nonspecific. They may include headaches, personality ...
cases. Other expression anomalies include zero expression in MDA-MB-231
Scientists study the behaviour of isolated cells grown in the laboratory for insights into how cells function in the body in health and disease. Experiments using cell culture
Cell culture or tissue culture is the process by which cells are ...
breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a r ...
cell line and low expression in P116 (ZAP70
ZAP-70 (Zeta-chain-associated protein kinase 70) is a protein normally expressed near the surface membrane of lymphocytes (T cells, natural killer cells, and a subset of B cells). It is most prominently known to be recruited upon antigen binding to ...
negative) cell line.
Post-translational Modifications
The followingpost-translational modifications
Post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. This process occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. Proteins are synthesized by ribosom ...
were predicted with the proteomic tools compiled at ExPASy and PhosphoSite Plus for the human DEPDC5 protein.
Interaction
DEPDC5 may possibly interact with the proteasome subunit PSMA3 as evidenced by coimmunoprecipitation and the transcription factorMYC
''Myc'' is a family of regulator genes and proto-oncogenes that code for transcription factors. The ''Myc'' family consists of three related human genes: ''c-myc'' (MYC), ''l-myc'' ( MYCL), and ''n-myc'' (MYCN). ''c-myc'' (also sometimes refe ...
. DEPDC5 is in the "GATOR1" complex with NPRL2 and NPRL3.
References
{{Reflist