Cromorne on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
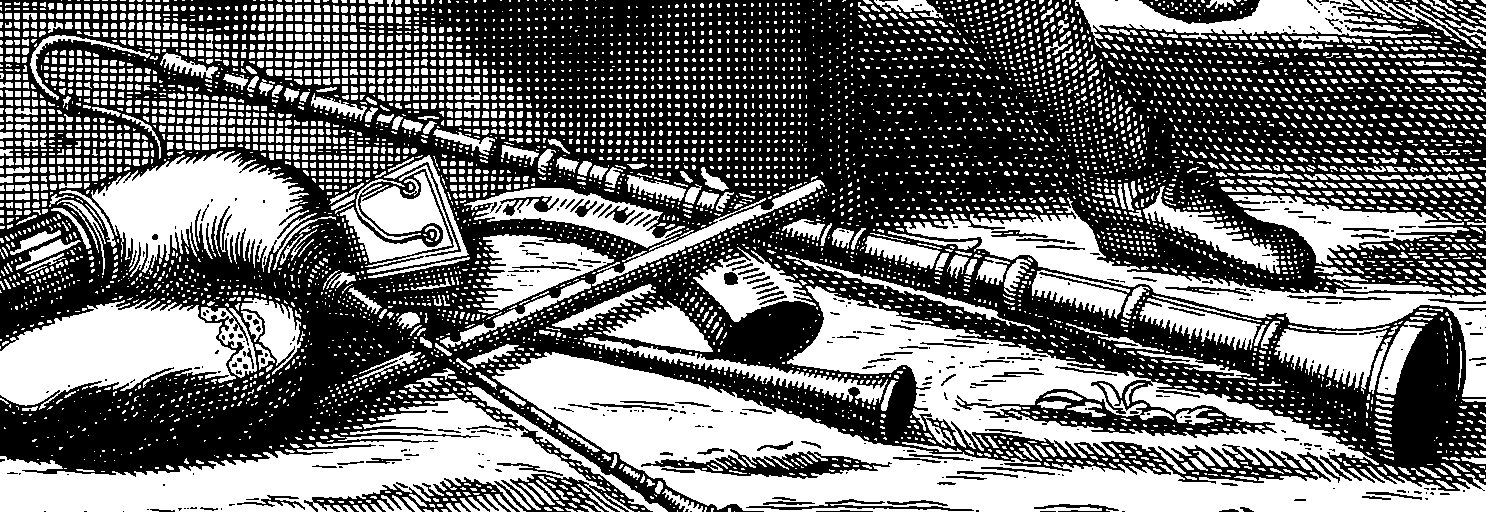 Cromorne is a French
Cromorne is a French
 Cromorne is a French
Cromorne is a French woodwind
Woodwind instruments are a family of musical instruments within the greater category of wind instruments. Common examples include flute, clarinet, oboe, bassoon, and saxophone. There are two main types of woodwind instruments: flutes and reed ...
reed instrument
Reed aerophones is one of the categories of musical instruments found in the Hornbostel-Sachs system of musical instrument classification. In order to produce sound with these Aerophones the player's breath is directed against a lamella or pair of ...
of uncertain identity, used in the early Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including t ...
period in French court music. The name is sometimes confused with the similar-sounding name crumhorn
The crumhorn is a double reed instrument of the woodwind family, most commonly used during the Renaissance period. In modern times, particularly since the 1960s, there has been a revival of interest in early music, and crumhorns are being play ...
, a musical woodwind instrument probably of different design, called "tournebout" by French theorists in the 17th century.
Crumhorn
By contrast, thecrumhorn
The crumhorn is a double reed instrument of the woodwind family, most commonly used during the Renaissance period. In modern times, particularly since the 1960s, there has been a revival of interest in early music, and crumhorns are being play ...
(also known by names including ''crum horn'', ''crumm horn'', ''Krummhorn'', ''Krummpfeife'', ''Kumbhorn'', ''cornamuto torto'', and ''piva torto'') is a capped double-reed instrument usually shaped like a letter "J" and possessing a rather small melodic range spanning a ninth (i.e. just over an octave) unless extended downward by keys or by the technique of underblowing, which increases the range by a perfect fifth. However, this instrument was apparently little used in England—despite listings in the inventories of Henry VIII and the earls of Arundel at Nonsuch House, and mention in a poem by Sir William Leighton, they are conspicuously absent from inventories and other documents of English town waits—or France and was called a "tournebout" by French theorists including Mersenne
Marin Mersenne, OM (also known as Marinus Mersennus or ''le Père'' Mersenne; ; 8 September 1588 – 1 September 1648) was a French polymath whose works touched a wide variety of fields. He is perhaps best known today among mathematicians for ...
(1636), Pierre Trichet (ca 1640), and even as late as Diderot
Denis Diderot (; ; 5 October 171331 July 1784) was a French philosopher, art critic, and writer, best known for serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the ''Encyclopédie'' along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. He was a prominen ...
(1767).
References
Sources * * *Further reading
* {{Double reed Woodwind instruments Early musical instruments