Columbia River on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Columbia River (
 The Columbia enters
The Columbia enters  The
The
 When the
When the  The floodwaters rushed across eastern Washington, creating the
The floodwaters rushed across eastern Washington, creating the
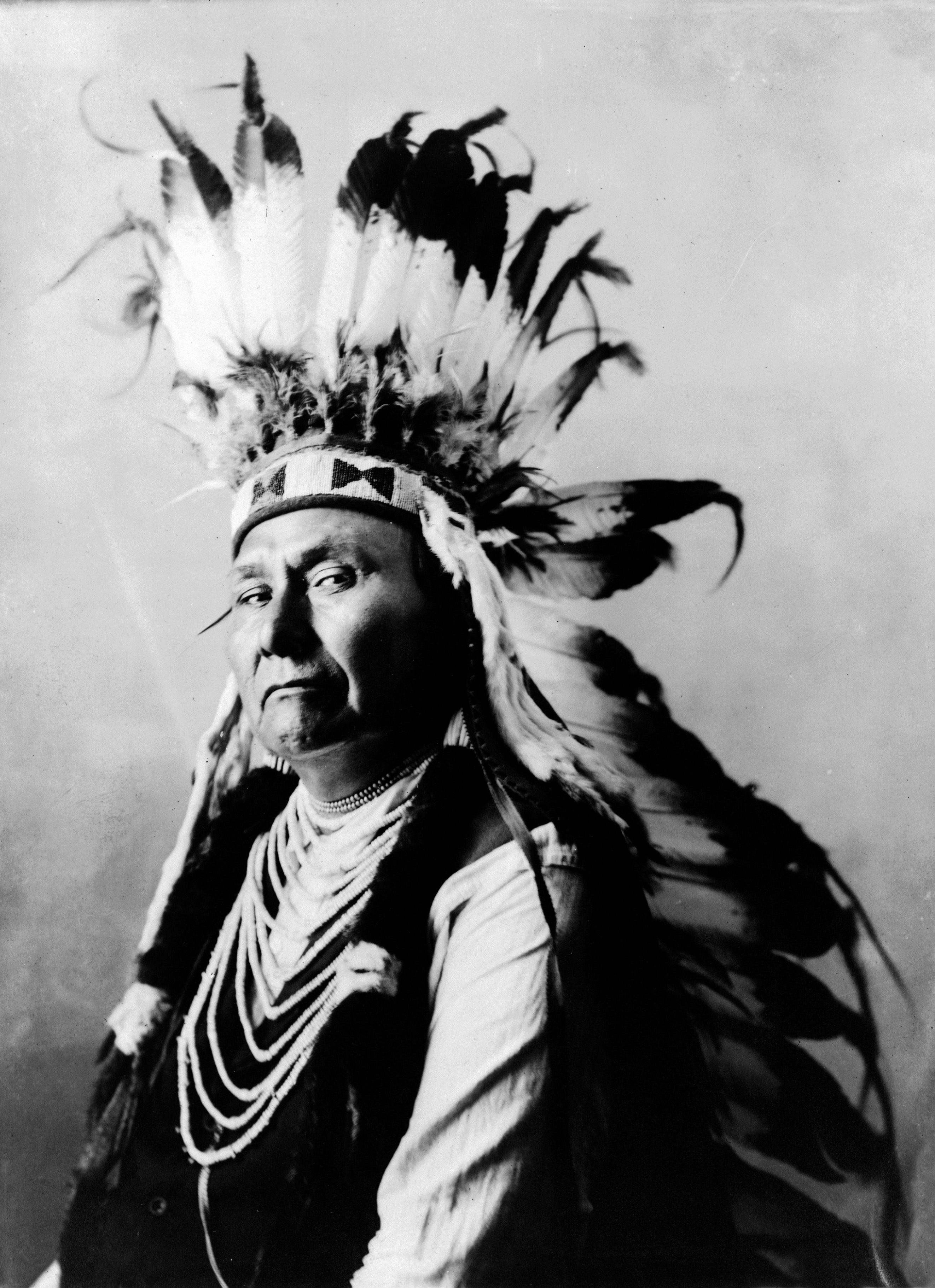 Humans have inhabited the Columbia's watershed for more than 15,000 years, with a transition to a sedentary lifestyle based mainly on salmon starting about 3,500 years ago. In 1962, archaeologists found evidence of human activity dating back 11,230 years at the
Humans have inhabited the Columbia's watershed for more than 15,000 years, with a transition to a sedentary lifestyle based mainly on salmon starting about 3,500 years ago. In 1962, archaeologists found evidence of human activity dating back 11,230 years at the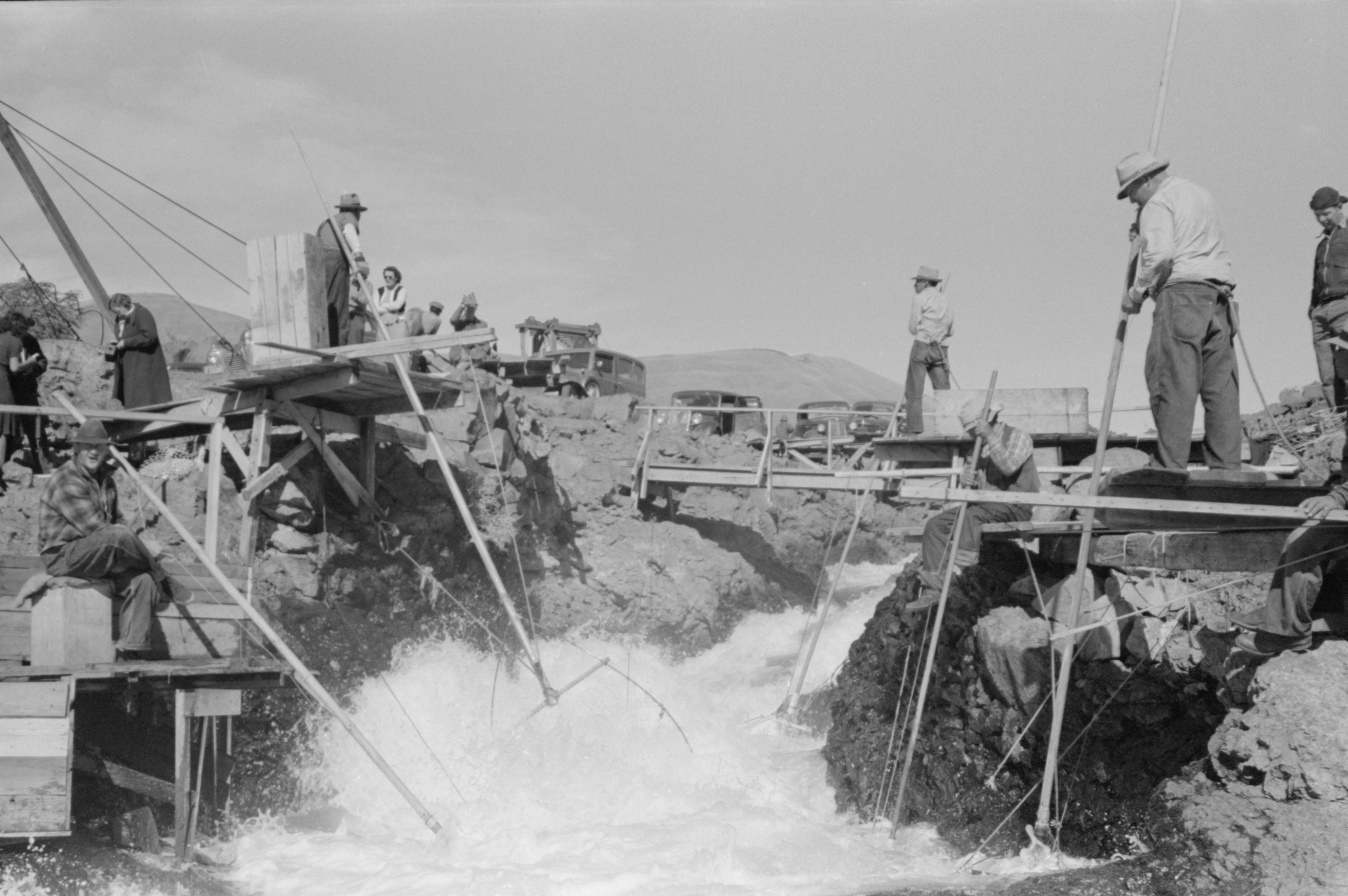  Fish were central to the culture of the region's natives, both as sustenance and as part of their religious beliefs. Natives drew fish from the Columbia at several major sites, which also served as trading posts.
Fish were central to the culture of the region's natives, both as sustenance and as part of their religious beliefs. Natives drew fish from the Columbia at several major sites, which also served as trading posts.
 Some historians believe that Japanese or Chinese vessels blown off course reached the Northwest Coast long before Europeans—possibly as early as 219
Some historians believe that Japanese or Chinese vessels blown off course reached the Northwest Coast long before Europeans—possibly as early as 219  On May 12, 1792, Gray returned south and crossed the Columbia Bar, becoming the first known explorer of European descent to enter the river. Gray's fur trading mission had been financed by
On May 12, 1792, Gray returned south and crossed the Columbia Bar, becoming the first known explorer of European descent to enter the river. Gray's fur trading mission had been financed by  Because the Columbia was at the same latitude as the headwaters of the Missouri River, there was some speculation that Gray and Vancouver had discovered the long-sought Northwest Passage. A 1798 British map showed a dotted line connecting the Columbia with the Missouri. When the American explorers Meriwether Lewis and
Because the Columbia was at the same latitude as the headwaters of the Missouri River, there was some speculation that Gray and Vancouver had discovered the long-sought Northwest Passage. A 1798 British map showed a dotted line connecting the Columbia with the Missouri. When the American explorers Meriwether Lewis and

 American captain Robert Gray and British captain George Vancouver, who explored the river in 1792, proved that it was possible to cross the Columbia Bar. Many of the challenges associated with that feat remain today; even with modern engineering alterations to the mouth of the river, the strong currents and shifting sandbar make it dangerous to pass between the river and the Pacific Ocean.
The use of
American captain Robert Gray and British captain George Vancouver, who explored the river in 1792, proved that it was possible to cross the Columbia Bar. Many of the challenges associated with that feat remain today; even with modern engineering alterations to the mouth of the river, the strong currents and shifting sandbar make it dangerous to pass between the river and the Pacific Ocean.
The use of
 Efforts to maintain and improve the navigation channel have continued to the present day. In 1990 a new round of studies examined the possibility of further dredging on the lower Columbia. The plans were controversial from the start because of economic and environmental concerns.
In 1999, Congress authorized deepening the channel between Portland and Astoria from , which will make it possible for large container and grain ships to reach Portland and Vancouver. The project has met opposition because of concerns about stirring up toxic sediment on the riverbed. Portland-based Northwest Environmental Advocates brought a lawsuit against the Army Corps of Engineers, but it was rejected by the Ninth U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals in August 2006. The project includes measures to mitigate environmental damage; for instance, the
Efforts to maintain and improve the navigation channel have continued to the present day. In 1990 a new round of studies examined the possibility of further dredging on the lower Columbia. The plans were controversial from the start because of economic and environmental concerns.
In 1999, Congress authorized deepening the channel between Portland and Astoria from , which will make it possible for large container and grain ships to reach Portland and Vancouver. The project has met opposition because of concerns about stirring up toxic sediment on the riverbed. Portland-based Northwest Environmental Advocates brought a lawsuit against the Army Corps of Engineers, but it was rejected by the Ninth U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals in August 2006. The project includes measures to mitigate environmental damage; for instance, the

 In 1902, the
In 1902, the
 The Bureau of Reclamation's Columbia Basin Project focused on the generally dry region of central Washington known as the Columbia Basin, which features rich loess soil. Several groups developed competing proposals, and in 1933, President Franklin D. Roosevelt authorized the Columbia Basin Project. The Grand Coulee Dam was the project's central component; upon completion, it pumped water up from the Columbia to fill the formerly dry Grand Coulee, forming Banks Lake. By 1935, the intended height of the dam was increased from a range between to , a height that would extend the lake impounded by the dam all the way to the Canada–US border; the project had grown from a local New Deal relief measure to a major national project.
The project's initial purpose was irrigation, but the onset of World War II created a high demand for electricity, mainly for aluminum production and for the development of
The Bureau of Reclamation's Columbia Basin Project focused on the generally dry region of central Washington known as the Columbia Basin, which features rich loess soil. Several groups developed competing proposals, and in 1933, President Franklin D. Roosevelt authorized the Columbia Basin Project. The Grand Coulee Dam was the project's central component; upon completion, it pumped water up from the Columbia to fill the formerly dry Grand Coulee, forming Banks Lake. By 1935, the intended height of the dam was increased from a range between to , a height that would extend the lake impounded by the dam all the way to the Canada–US border; the project had grown from a local New Deal relief measure to a major national project.
The project's initial purpose was irrigation, but the onset of World War II created a high demand for electricity, mainly for aluminum production and for the development of
 The largest of the 150 hydroelectric projects, the Grand Coulee Dam and the Chief Joseph Dam, are also the largest in the United States. As of 2017, Grand Coulee is the fifth largest hydroelectric plant in the world.
Inexpensive hydropower supported the location of a large aluminum industry in the region, because its Aluminium production, reduction from bauxite requires large amounts of electricity. Until 2000, the Northwestern United States produced up to 17 percent of the world's aluminum and 40 percent of the aluminum produced in the United States. The commoditization of power in the early 21st century, coupled with drought that reduced the generation capacity of the river, damaged the industry and by 2001, Columbia River aluminum producers had idled 80 percent of its production capacity. By 2003, the entire United States produced only 15 percent of the world's aluminum, and many smelters along the Columbia had gone dormant or out of business.
Power remains relatively inexpensive along the Columbia, and since the mid-2000 several global enterprises have moved server farm operations into the area to avail themselves of cheap power. Downriver of Grand Coulee, each dam's reservoir is closely regulated by the Bonneville Power Administration (BPA), the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, and various Washington public utility districts to ensure flow, flood control, and power generation objectives are met. Increasingly, hydro-power operations are required to meet standards under the US Endangered Species Act and other agreements to manage operations to minimize impacts on salmon and other fish, and some conservation and fishing groups support removing four dams on the lower Snake River, the largest tributary of the Columbia.
In 1941, the BPA hired Oklahoma folksinger Woody Guthrie to write songs for a documentary film promoting the benefits of hydropower. In the month he spent traveling the region Guthrie wrote The Columbia River Collection, 26 songs, which have become an important part of the cultural history of the region.
The largest of the 150 hydroelectric projects, the Grand Coulee Dam and the Chief Joseph Dam, are also the largest in the United States. As of 2017, Grand Coulee is the fifth largest hydroelectric plant in the world.
Inexpensive hydropower supported the location of a large aluminum industry in the region, because its Aluminium production, reduction from bauxite requires large amounts of electricity. Until 2000, the Northwestern United States produced up to 17 percent of the world's aluminum and 40 percent of the aluminum produced in the United States. The commoditization of power in the early 21st century, coupled with drought that reduced the generation capacity of the river, damaged the industry and by 2001, Columbia River aluminum producers had idled 80 percent of its production capacity. By 2003, the entire United States produced only 15 percent of the world's aluminum, and many smelters along the Columbia had gone dormant or out of business.
Power remains relatively inexpensive along the Columbia, and since the mid-2000 several global enterprises have moved server farm operations into the area to avail themselves of cheap power. Downriver of Grand Coulee, each dam's reservoir is closely regulated by the Bonneville Power Administration (BPA), the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, and various Washington public utility districts to ensure flow, flood control, and power generation objectives are met. Increasingly, hydro-power operations are required to meet standards under the US Endangered Species Act and other agreements to manage operations to minimize impacts on salmon and other fish, and some conservation and fishing groups support removing four dams on the lower Snake River, the largest tributary of the Columbia.
In 1941, the BPA hired Oklahoma folksinger Woody Guthrie to write songs for a documentary film promoting the benefits of hydropower. In the month he spent traveling the region Guthrie wrote The Columbia River Collection, 26 songs, which have become an important part of the cultural history of the region.
 The Columbia supports several species of
The Columbia supports several species of
 The nuclear reactors were decommissioned at the end of the Cold War, and the Hanford site is the focus of one of the world's largest environmental remediation, environmental cleanup, managed by the United States Department of Energy, Department of Energy under the oversight of the Washington Department of Ecology and the United States Environmental Protection Agency, Environmental Protection Agency. Nearby aquifers contain an estimated 270 billion US gallons (1 billion m3) of groundwater contaminated by high-level nuclear waste that has leaked out of Hanford's underground storage tanks. , 1 million US gallons (3,785 m3) of highly radioactive waste is traveling through groundwater toward the Columbia River. This waste is expected to reach the river in 12 to 50 years if cleanup does not proceed on schedule.
In addition to concerns about nuclear waste, numerous other pollutants are found in the river. These include chemical pesticides, bacteria, arsenic, dioxins, and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB).
Studies have also found significant levels of toxins in fish and the waters they inhabit within the basin. Accumulation of toxins in fish threatens the survival of fish species, and human consumption of these fish can lead to health problems. Water quality is also an important factor in the survival of other wildlife and plants that grow in the Columbia River drainage basin. The states, Indian tribes, and federal government are all engaged in efforts to restore and improve the water, land, and air quality of the Columbia River drainage basin and have committed to work together to enhance and accomplish critical ecosystem restoration efforts. A number of cleanup efforts are currently underway, including Superfund projects at Portland Harbor, Hanford, and Lake Roosevelt.
Timber industry activity further contaminates river water, for example in the increased sediment runoff that results from clearcutting, clearcuts. The Northwest Forest Plan, a piece of federal legislation from 1994, mandated that timber companies consider the environmental impacts of their practices on rivers like the Columbia.
On July 1, 2003, Christopher Swain of Portland, Oregon, became the first person to swim the Columbia River's entire length, in an effort to raise public awareness about the river's environmental health.
The nuclear reactors were decommissioned at the end of the Cold War, and the Hanford site is the focus of one of the world's largest environmental remediation, environmental cleanup, managed by the United States Department of Energy, Department of Energy under the oversight of the Washington Department of Ecology and the United States Environmental Protection Agency, Environmental Protection Agency. Nearby aquifers contain an estimated 270 billion US gallons (1 billion m3) of groundwater contaminated by high-level nuclear waste that has leaked out of Hanford's underground storage tanks. , 1 million US gallons (3,785 m3) of highly radioactive waste is traveling through groundwater toward the Columbia River. This waste is expected to reach the river in 12 to 50 years if cleanup does not proceed on schedule.
In addition to concerns about nuclear waste, numerous other pollutants are found in the river. These include chemical pesticides, bacteria, arsenic, dioxins, and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB).
Studies have also found significant levels of toxins in fish and the waters they inhabit within the basin. Accumulation of toxins in fish threatens the survival of fish species, and human consumption of these fish can lead to health problems. Water quality is also an important factor in the survival of other wildlife and plants that grow in the Columbia River drainage basin. The states, Indian tribes, and federal government are all engaged in efforts to restore and improve the water, land, and air quality of the Columbia River drainage basin and have committed to work together to enhance and accomplish critical ecosystem restoration efforts. A number of cleanup efforts are currently underway, including Superfund projects at Portland Harbor, Hanford, and Lake Roosevelt.
Timber industry activity further contaminates river water, for example in the increased sediment runoff that results from clearcutting, clearcuts. The Northwest Forest Plan, a piece of federal legislation from 1994, mandated that timber companies consider the environmental impacts of their practices on rivers like the Columbia.
On July 1, 2003, Christopher Swain of Portland, Oregon, became the first person to swim the Columbia River's entire length, in an effort to raise public awareness about the river's environmental health.
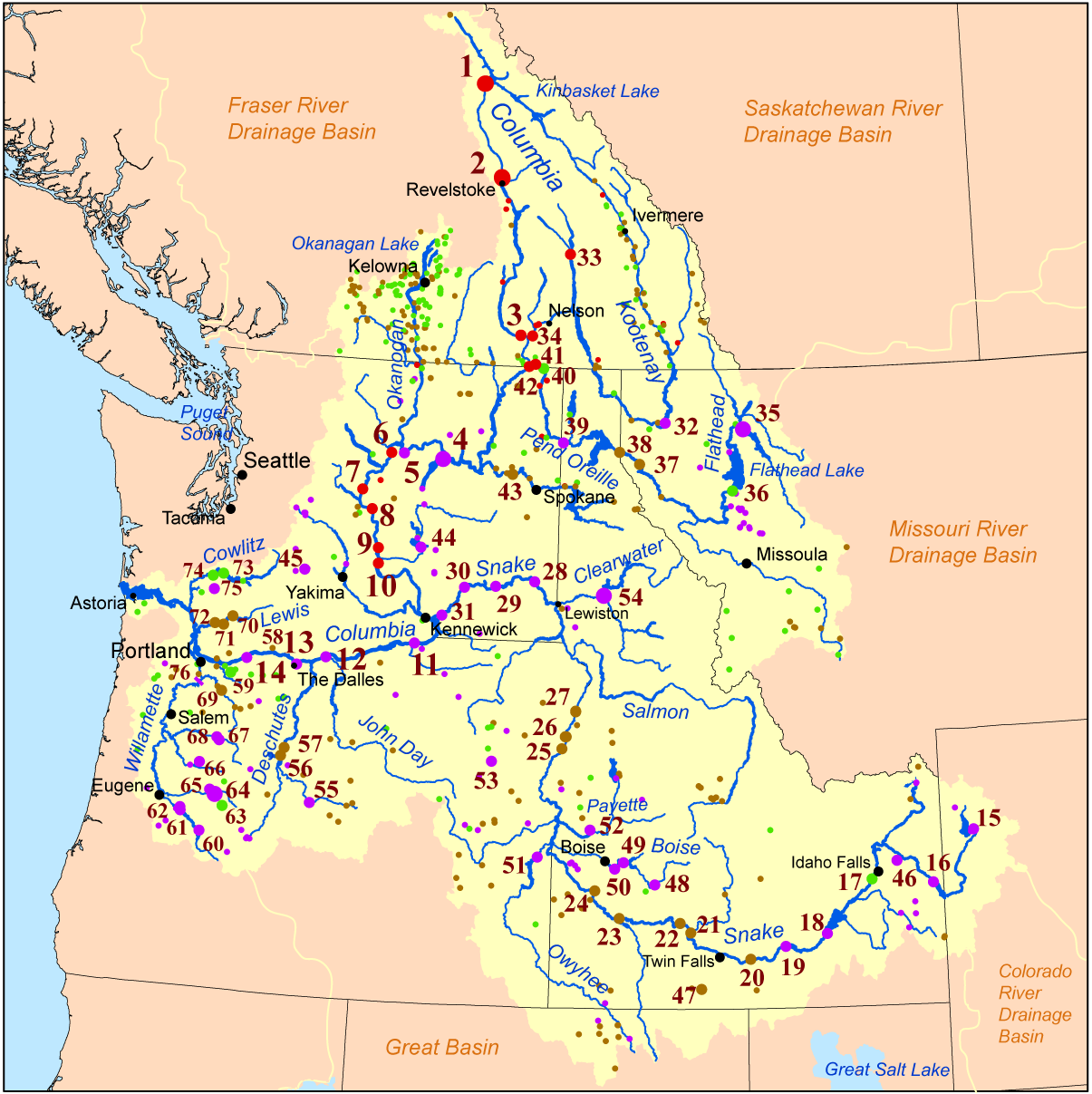
 Most of the Columbia's drainage basin (which, at , is about the size of France) lies roughly between the Rocky Mountains on the east and the Cascade Mountains on the west. In the United States and Canada the term watershed is often used to mean drainage basin. The term ''Columbia Basin'' is used to refer not only to the entire drainage basin but also to subsets of the river's full watershed, such as the relatively flat and unforested area in eastern Washington bounded by the Cascades, the Rocky Mountains, and the Blue Mountains. Within the watershed are diverse landforms including mountains, arid plateaus, river valleys, rolling uplands, and deep gorges. Grand Teton National Park lies in the watershed, as well as parts of Yellowstone National Park, Glacier National Park (U.S.), Glacier National Park, Mount Rainier National Park, and North Cascades National Park. Canadian National Parks in the watershed include Kootenay National Park, Yoho National Park, Glacier National Park (Canada), Glacier National Park, and Mount Revelstoke National Park. Hells Canyon, the deepest gorge in North America, and the Columbia Gorge are in the watershed. Vegetation varies widely, ranging from Tsuga heterophylla, western hemlock and Thuja plicata, western redcedar in the moist regions to sagebrush in the arid regions. The watershed provides habitat for 609 known fish and wildlife species, including the bull trout, bald eagle, gray wolf, grizzly bear, and Canada lynx.
The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) divides the waters of the Columbia and its tributaries into three freshwater ecoregions, naming them Columbia Glaciated, Columbia Unglaciated, and Upper Snake. The Columbia Glaciated ecoregion, making up about a third of the total watershed, lies in the north and was covered with ice sheets during the Pleistocene. The ecoregion includes the mainstem Columbia north of the Snake River and tributaries such as the Yakima, Okanagan, Pend Oreille, Clark Fork, and Kootenay rivers. The effects of glacier, glaciation include a number of large lakes and a relatively low diversity of freshwater fish. The Upper Snake ecoregion is defined as the Snake River watershed above Shoshone Falls, which totally blocks fish migration. This region has 14 species of fish, many of which are endemism, endemic. The Columbia Unglaciated ecoregion makes up the rest of the watershed. It includes the mainstem Columbia below the Snake River and tributaries such as the Salmon, John Day, Deschutes, and lower Snake Rivers. Of the three ecoregions it is the richest in terms of freshwater species diversity. There are 35 species of fish, of which four are endemic. There are also high levels of mollusk endemism.
In 2016, over eight million people lived within the Columbia's drainage basin. Of this total about 3.5 million people lived in Oregon, 2.1 million in Washington, 1.7 million in Idaho, half a million in British Columbia, and 0.4 million in Montana. Population in the watershed has been rising for many decades and is projected to rise to about 10 million by 2030. The highest population densities are found west of the Cascade Mountains along the Interstate 5, I-5 corridor, especially in the Portland-Vancouver urban area. High densities are also found around Spokane, Washington, and Boise, Idaho. Although much of the watershed is rural and sparsely populated, areas with recreational and scenic values are growing rapidly. The central Oregon county of Deschutes County, Oregon, Deschutes is the fastest-growing in the state. Populations have also been growing just east of the Cascades in central Washington around the city of Yakima, Washington, Yakima and the Tri-Cities area. Projections for the coming decades assume growth throughout the watershed, including the interior. The Canadian part of the Okanagan subbasin is also growing rapidly.
Climate varies greatly from place to place within the watershed. Elevation ranges from sea level at the river mouth to more than in the mountains, and temperatures vary with elevation. The highest peak is Mount Rainier, at . High elevations have cold winters and short cool summers; interior regions are subject to great temperature variability and severe droughts. Over some of the watershed, especially west of the Cascade Mountains, precipitation maximums occur in winter, when Pacific storms come ashore. Atmospheric conditions block the flow of moisture in summer, which is generally dry except for occasional thunderstorms in the interior. In some of the eastern parts of the watershed, especially shrub-steppe regions with Continental climate patterns, precipitation maximums occur in early summer. Annual precipitation varies from more than a year in the Cascades to less than in the interior. Much of the watershed gets less than a year.
Several major North American drainage basins and many minor ones share a common border with the Columbia River's drainage basin. To the east, in northern Wyoming and Montana, the Continental Divide separates the Columbia watershed from the Mississippi-Missouri watershed, which empties into the Gulf of Mexico. To the northeast, mostly along the southern border between British Columbia and Alberta, the Continental Divide separates the Columbia watershed from the Nelson River, Nelson-Lake Winnipeg-Saskatchewan River, Saskatchewan watershed, which empties into Hudson Bay. The Mississippi and Nelson watersheds are separated by the Laurentian Divide, which meets the Continental Divide at Triple Divide Peak (Montana), Triple Divide Peak near the headwaters of the Columbia's Flathead River tributary. This point marks the meeting of three of North America's main drainage patterns, to the Pacific Ocean, to Hudson Bay, and to the Atlantic Ocean via the Gulf of Mexico.
Further north along the Continental Divide, a short portion of the combined Continental and Laurentian divides separate the Columbia watershed from the MacKenzie River, MacKenzie-Slave River, Slave-Athabasca River, Athabasca watershed, which empties into the Arctic Ocean. The Nelson and Mackenzie watersheds are separated by a divide between streams flowing to the Arctic Ocean and those of the List of Hudson Bay rivers, Hudson Bay watershed. This divide meets the Continental Divide at Snow Dome (Canada), Snow Dome (also known as Dome), near the northernmost bend of the Columbia River.
To the southeast, in western Wyoming, another divide separates the Columbia watershed from the Colorado River, Colorado–Green River (Colorado River), Green watershed, which empties into the Gulf of California. The Columbia, Colorado, and Mississippi watersheds meet at Three Waters Mountain in the Wind River Range of . To the south, in Oregon, Nevada, Utah, Idaho, and Wyoming, the Columbia watershed is divided from the Great Basin, whose several watersheds are endorheic basin, endorheic, not emptying into any ocean but rather drying up or sinking into sumps. Great Basin watersheds that share a border with the Columbia watershed include Harney Basin, Humboldt River, and Great Salt Lake. The associated triple divide points are Commissary Ridge North, Wyoming, and Sproats Meadow Northwest, Oregon. To the north, mostly in British Columbia, the Columbia watershed borders the Fraser River watershed. To the west and southwest the Columbia watershed borders a number of smaller watersheds that drain to the Pacific Ocean, such as the Klamath River in Oregon and California and the Puget Sound Basin in Washington.
Most of the Columbia's drainage basin (which, at , is about the size of France) lies roughly between the Rocky Mountains on the east and the Cascade Mountains on the west. In the United States and Canada the term watershed is often used to mean drainage basin. The term ''Columbia Basin'' is used to refer not only to the entire drainage basin but also to subsets of the river's full watershed, such as the relatively flat and unforested area in eastern Washington bounded by the Cascades, the Rocky Mountains, and the Blue Mountains. Within the watershed are diverse landforms including mountains, arid plateaus, river valleys, rolling uplands, and deep gorges. Grand Teton National Park lies in the watershed, as well as parts of Yellowstone National Park, Glacier National Park (U.S.), Glacier National Park, Mount Rainier National Park, and North Cascades National Park. Canadian National Parks in the watershed include Kootenay National Park, Yoho National Park, Glacier National Park (Canada), Glacier National Park, and Mount Revelstoke National Park. Hells Canyon, the deepest gorge in North America, and the Columbia Gorge are in the watershed. Vegetation varies widely, ranging from Tsuga heterophylla, western hemlock and Thuja plicata, western redcedar in the moist regions to sagebrush in the arid regions. The watershed provides habitat for 609 known fish and wildlife species, including the bull trout, bald eagle, gray wolf, grizzly bear, and Canada lynx.
The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) divides the waters of the Columbia and its tributaries into three freshwater ecoregions, naming them Columbia Glaciated, Columbia Unglaciated, and Upper Snake. The Columbia Glaciated ecoregion, making up about a third of the total watershed, lies in the north and was covered with ice sheets during the Pleistocene. The ecoregion includes the mainstem Columbia north of the Snake River and tributaries such as the Yakima, Okanagan, Pend Oreille, Clark Fork, and Kootenay rivers. The effects of glacier, glaciation include a number of large lakes and a relatively low diversity of freshwater fish. The Upper Snake ecoregion is defined as the Snake River watershed above Shoshone Falls, which totally blocks fish migration. This region has 14 species of fish, many of which are endemism, endemic. The Columbia Unglaciated ecoregion makes up the rest of the watershed. It includes the mainstem Columbia below the Snake River and tributaries such as the Salmon, John Day, Deschutes, and lower Snake Rivers. Of the three ecoregions it is the richest in terms of freshwater species diversity. There are 35 species of fish, of which four are endemic. There are also high levels of mollusk endemism.
In 2016, over eight million people lived within the Columbia's drainage basin. Of this total about 3.5 million people lived in Oregon, 2.1 million in Washington, 1.7 million in Idaho, half a million in British Columbia, and 0.4 million in Montana. Population in the watershed has been rising for many decades and is projected to rise to about 10 million by 2030. The highest population densities are found west of the Cascade Mountains along the Interstate 5, I-5 corridor, especially in the Portland-Vancouver urban area. High densities are also found around Spokane, Washington, and Boise, Idaho. Although much of the watershed is rural and sparsely populated, areas with recreational and scenic values are growing rapidly. The central Oregon county of Deschutes County, Oregon, Deschutes is the fastest-growing in the state. Populations have also been growing just east of the Cascades in central Washington around the city of Yakima, Washington, Yakima and the Tri-Cities area. Projections for the coming decades assume growth throughout the watershed, including the interior. The Canadian part of the Okanagan subbasin is also growing rapidly.
Climate varies greatly from place to place within the watershed. Elevation ranges from sea level at the river mouth to more than in the mountains, and temperatures vary with elevation. The highest peak is Mount Rainier, at . High elevations have cold winters and short cool summers; interior regions are subject to great temperature variability and severe droughts. Over some of the watershed, especially west of the Cascade Mountains, precipitation maximums occur in winter, when Pacific storms come ashore. Atmospheric conditions block the flow of moisture in summer, which is generally dry except for occasional thunderstorms in the interior. In some of the eastern parts of the watershed, especially shrub-steppe regions with Continental climate patterns, precipitation maximums occur in early summer. Annual precipitation varies from more than a year in the Cascades to less than in the interior. Much of the watershed gets less than a year.
Several major North American drainage basins and many minor ones share a common border with the Columbia River's drainage basin. To the east, in northern Wyoming and Montana, the Continental Divide separates the Columbia watershed from the Mississippi-Missouri watershed, which empties into the Gulf of Mexico. To the northeast, mostly along the southern border between British Columbia and Alberta, the Continental Divide separates the Columbia watershed from the Nelson River, Nelson-Lake Winnipeg-Saskatchewan River, Saskatchewan watershed, which empties into Hudson Bay. The Mississippi and Nelson watersheds are separated by the Laurentian Divide, which meets the Continental Divide at Triple Divide Peak (Montana), Triple Divide Peak near the headwaters of the Columbia's Flathead River tributary. This point marks the meeting of three of North America's main drainage patterns, to the Pacific Ocean, to Hudson Bay, and to the Atlantic Ocean via the Gulf of Mexico.
Further north along the Continental Divide, a short portion of the combined Continental and Laurentian divides separate the Columbia watershed from the MacKenzie River, MacKenzie-Slave River, Slave-Athabasca River, Athabasca watershed, which empties into the Arctic Ocean. The Nelson and Mackenzie watersheds are separated by a divide between streams flowing to the Arctic Ocean and those of the List of Hudson Bay rivers, Hudson Bay watershed. This divide meets the Continental Divide at Snow Dome (Canada), Snow Dome (also known as Dome), near the northernmost bend of the Columbia River.
To the southeast, in western Wyoming, another divide separates the Columbia watershed from the Colorado River, Colorado–Green River (Colorado River), Green watershed, which empties into the Gulf of California. The Columbia, Colorado, and Mississippi watersheds meet at Three Waters Mountain in the Wind River Range of . To the south, in Oregon, Nevada, Utah, Idaho, and Wyoming, the Columbia watershed is divided from the Great Basin, whose several watersheds are endorheic basin, endorheic, not emptying into any ocean but rather drying up or sinking into sumps. Great Basin watersheds that share a border with the Columbia watershed include Harney Basin, Humboldt River, and Great Salt Lake. The associated triple divide points are Commissary Ridge North, Wyoming, and Sproats Meadow Northwest, Oregon. To the north, mostly in British Columbia, the Columbia watershed borders the Fraser River watershed. To the west and southwest the Columbia watershed borders a number of smaller watersheds that drain to the Pacific Ocean, such as the Klamath River in Oregon and California and the Puget Sound Basin in Washington.
 The Columbia receives more than 60 significant tributary, tributaries. The four largest that empty directly into the Columbia (measured either by discharge (hydrology), discharge or by size of watershed) are the Snake River (mostly in Idaho), the Willamette River (in northwest Oregon), the Kootenay River (mostly in British Columbia), and the Pend Oreille River (mostly in northern Washington and Idaho, also known as the lower part of the Clark Fork). Each of these four averages more than and drains an area of more than .
The Snake is by far the largest tributary. Its watershed of is larger than the state of Idaho. Its discharge is roughly a third of the Columbia's at the rivers' confluence but compared to the Columbia upstream of the confluence the Snake is longer (113%) and has a larger drainage basin (104%).
The Pend Oreille River system (including its main tributaries, the Clark Fork and Flathead rivers) is also similar in size to the Columbia at their confluence. Compared to the Columbia River above the two rivers' confluence, the Pend Oreille-Clark-Flathead is nearly as long (about 86%), its basin about three-fourths as large (76%), and its discharge over a third (37%).Calculated mainly with data from:
The Columbia receives more than 60 significant tributary, tributaries. The four largest that empty directly into the Columbia (measured either by discharge (hydrology), discharge or by size of watershed) are the Snake River (mostly in Idaho), the Willamette River (in northwest Oregon), the Kootenay River (mostly in British Columbia), and the Pend Oreille River (mostly in northern Washington and Idaho, also known as the lower part of the Clark Fork). Each of these four averages more than and drains an area of more than .
The Snake is by far the largest tributary. Its watershed of is larger than the state of Idaho. Its discharge is roughly a third of the Columbia's at the rivers' confluence but compared to the Columbia upstream of the confluence the Snake is longer (113%) and has a larger drainage basin (104%).
The Pend Oreille River system (including its main tributaries, the Clark Fork and Flathead rivers) is also similar in size to the Columbia at their confluence. Compared to the Columbia River above the two rivers' confluence, the Pend Oreille-Clark-Flathead is nearly as long (about 86%), its basin about three-fourths as large (76%), and its discharge over a third (37%).Calculated mainly with data from:

BC Hydro
Bibliography on Water Resources and International Law
Peace Palace Library * *
Columbia River
US Environmental Protection Agency
Columbia River Gorge National Scenic Area
from the US Forest Service
Columbia River Inter-Tribal Fish Commission
* * , dating to the 17th century
University of Washington Libraries Digital Collections – Tollman and Canaris Photographs
Photographs document the salmon fishing industry on the southern Washington coast and in the lower Columbia River around the year 1897 and offer insights about commercial salmon fishing and the techniques used at the beginning of the 20th century.
''National Geographic'' via Internet Archive {{Featured article Columbia River, Columbia River Gorge, Borders of Oregon Borders of Washington (state) Drainage basins of the Pacific Ocean International rivers of North America Rivers of Benton County, Washington Rivers of British Columbia Rivers of Chelan County, Washington Rivers of Clark County, Washington Rivers of Clatsop County, Oregon Rivers of Cowlitz County, Washington Rivers of Franklin County, Washington Rivers of Hood River County, Oregon Rivers of Multnomah County, Oregon Rivers of Oregon Rivers of Wasco County, Oregon Rivers of Washington (state) Rivers of Douglas County, Washington Rivers with fish ladders
Upper Chinook
Upper Chinook, endonym Kiksht, also known as Columbia Chinook, and Wasco-Wishram after its last surviving dialect, is a recently extinct language of the US Pacific Northwest. It had 69 speakers in 1990, of whom 7 were monolingual: five Wasco and ...
: ' or '; Sahaptin
The Sahaptin are a number of Native American tribes who speak dialects of the Sahaptin language. The Sahaptin tribes inhabited territory along the Columbia River and its tributaries in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. Sahaptin-s ...
: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect
Sinixt (''sn-selxcin'') is one of multiple distinct dialects of the Colville-Okanagan language. It is part of the Southern Interior Salish sub-grouping of the Salishan Language family. Traditionally spoken among the Sinixt People of the souther ...
'' '') is the largest river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
in the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Tho ...
region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
of British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
, Canada. It flows northwest and then south into the U.S. state of Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
, then turns west to form most of the border between Washington and the state of Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
before emptying into the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
. The river is long, and its largest tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainage ...
is the Snake River
The Snake River is a major river of the greater Pacific Northwest region in the United States. At long, it is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, in turn, the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean. The Snake ...
. Its drainage basin is roughly the size of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
and extends into seven US states and a Canadian province. The fourth-largest river in the United States by volume, the Columbia has the greatest flow of any North American river entering the Pacific. The Columbia has the 36th greatest discharge of any river in the world.
The Columbia and its tributaries have been central to the region's culture and economy for thousands of years. They have been used for transportation since ancient times, linking the region's many cultural groups. The river system hosts many species of anadromous
Fish migration is mass relocation by fish from one area or body of water to another. Many types of fish migrate on a regular basis, on time scales ranging from daily to annually or longer, and over distances ranging from a few metres to thousan ...
fish, which migrate between freshwater habitats and the saline waters of the Pacific Ocean. These fish—especially the salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the ...
species—provided the core subsistence for native peoples.
The first documented European discovery of the Columbia River occurred when Bruno de Heceta
Bruno de Heceta (Hezeta) y Dudagoitia (1743–1807) was a Spanish Basque explorer of the Pacific Northwest. Born in Bilbao of an old Basque family, he was sent by the Viceroy of New Spain, Antonio María Bucareli y Ursúa, to explore the area nort ...
sighted the river's mouth in 1775. On May 11, 1792, a private American ship, Columbia Rediviva, under Captain Robert Gray from Boston became the first non-indigenous vessel to enter the river. Later in 1792, William Robert Broughton
William Robert Broughton (22 March 176214 March 1821) was a British naval officer in the late 18th century. As a lieutenant in the Royal Navy, he commanded HMS ''Chatham'' as part of the Vancouver Expedition, a voyage of exploration through th ...
of the British Royal Navy commanding the HMS ''Chatham'' as part of the Vancouver Expedition
The Vancouver Expedition (1791–1795) was a four-and-a-half-year voyage of exploration and diplomacy, commanded by Captain George Vancouver of the Royal Navy. The British expedition circumnavigated the globe and made contact with five continen ...
, navigated past the Oregon Coast Range
The Oregon Coast Range, often called simply the Coast Range and sometimes the Pacific Coast Range, is a mountain range, in the Pacific Coast Ranges physiographic region, in the U.S. state of Oregon along the Pacific Ocean. This north-south ru ...
and 100 miles upriver oyages of the Columbia on the Northwest Coast. Frederic W. Howayo what is now Vancouver, Washington. In the following decades, fur-trading companies used the Columbia as a key transportation route. Overland explorers entered the Willamette Valley
The Willamette Valley ( ) is a long valley in Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. The Willamette River flows the entire length of the valley and is surrounded by mountains on three sides: the Cascade Range to the eas ...
through the scenic, but treacherous Columbia River Gorge
The Columbia River Gorge is a canyon of the Columbia River in the Pacific Northwest of the United States. Up to deep, the canyon stretches for over as the river winds westward through the Cascade Range, forming the boundary between the st ...
, and pioneers began to settle the valley in increasing numbers. Steamship
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships ...
s along the river linked communities and facilitated trade; the arrival of railroads in the late 19th century, many running along the river, supplemented these links.
Since the late 19th century, public
In public relations and communication science, publics are groups of individual people, and the public (a.k.a. the general public) is the totality of such groupings. This is a different concept to the sociological concept of the ''Öffentlichkei ...
and private sector
The private sector is the part of the economy, sometimes referred to as the citizen sector, which is owned by private groups, usually as a means of establishment for profit or non profit, rather than being owned by the government.
Employment
The ...
s have extensively developed the river. To aid ship and barge navigation, locks
Lock(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
*Lock and key, a mechanical device used to secure items of importance
*Lock (water navigation), a device for boats to transit between different levels of water, as in a canal
Arts and entertainment
* ''Lock ...
have been built along the lower Columbia and its tributaries, and dredging
Dredging is the excavation of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage, navigability, and commercial use; constructing da ...
has opened, maintained, and enlarged shipping channels. Since the early 20th century, dams
A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use ...
have been built across the river for power generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery ( transmission, distribution, etc.) to end users or its stor ...
, navigation
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, ...
, irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow Crop, crops, Landscape plant, landscape plants, and Lawn, lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,00 ...
, and flood control
Flood control methods are used to reduce or prevent the detrimental effects of flood waters."Flood Control", MSN Encarta, 2008 (see below: Further reading). Flood relief methods are used to reduce the effects of flood waters or high water level ...
. The 14 hydroelectric dams on the Columbia's main stem
In hydrology, a mainstem (or trunk) is "the primary downstream segment of a river, as contrasted to its tributaries". Water enters the mainstem from the river's drainage basin, the land area through which the mainstem and its tributaries flow.. A ...
and many more on its tributaries produce more than 44 percent of total U.S. hydroelectric generation. Production of nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced b ...
has taken place at two sites along the river. Plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibi ...
for nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
s was produced for decades at the Hanford Site
The Hanford Site is a decommissioned nuclear production complex operated by the United States federal government on the Columbia River in Benton County in the U.S. state of Washington. The site has been known by many names, including SiteW a ...
, which is now the most contaminated nuclear site in the United States. These developments have greatly altered river environments in the watershed, mainly through industrial pollution and barriers to fish migration
Fish migration is mass relocation by fish from one area or body of water to another. Many types of fish migrate on a regular basis, on time scales ranging from daily to annually or longer, and over distances ranging from a few metres to thousa ...
.
Course
The Columbia begins its journey in the southern Rocky Mountain Trench in British Columbia (BC).Columbia Lake
Columbia Lake is the primary lake at the headwaters of the Columbia River, in British Columbia, Canada. It is fed by several small tributaries. The village of Canal Flats is located at the south end of the lake.
Columbia Lake is a fresh water la ...
– above sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised g ...
– and the adjoining Columbia Wetlands form the river's headwaters
The headwaters of a river or stream is the farthest place in that river or stream from its estuary or downstream confluence with another river, as measured along the course of the river. It is also known as a river's source.
Definition
The ...
. The trench is a broad, deep, and long glacial valley
U-shaped valleys, also called trough valleys or glacial troughs, are formed by the process of glaciation. They are characteristic of mountain glaciation in particular. They have a characteristic U shape in cross-section, with steep, straight s ...
between the Canadian Rockies
The Canadian Rockies (french: Rocheuses canadiennes) or Canadian Rocky Mountains, comprising both the Alberta Rockies and the British Columbian Rockies, is the Canadian segment of the North American Rocky Mountains. It is the easternmost part ...
and the Columbia Mountains
The Columbia Mountains are a group of mountain ranges along the upper Columbia River in British Columbia, Montana, Idaho and Washington. The mountain range covers 135,952 km² (52,491 sq mi). The range is bounded by the Rocky Mountain Tre ...
in BC. For its first , the Columbia flows northwest along the trench through Windermere Lake and the town of Invermere
Invermere is a community in eastern British Columbia, Canada, near the border of Alberta. It is the hub of the Columbia Valley between Golden to the north and Cranbrook to the south. Invermere sits on the northwest shore of Windermere Lake an ...
, a region known in British Columbia as the Columbia Valley
The Columbia Valley is the name used for a region in the Rocky Mountain Trench near the headwaters of the Columbia River between the town of Golden and the Canal Flats. The main hub of the valley is the town of Invermere. Other towns include R ...
, then northwest to Golden
Golden means made of, or relating to gold.
Golden may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
*Golden, in the parish of Probus, Cornwall
* Golden Cap, Dorset
*Golden Square, Soho, London
*Golden Valley, a valley on the River Frome in Gloucestershi ...
and into Kinbasket Lake
Kinbasket Lake (or Kinbasket Reservoir) is a reservoir on the Columbia River in southeast British Columbia, north of the city of Revelstoke and the town of Golden. The reservoir was created by the construction of the Mica Dam. The lake includes t ...
. Rounding the northern end of the Selkirk Mountains, the river turns sharply south through a region known as the Big Bend Country
In the Canadian province of British Columbia, Big Bend Country is the region around the northernmost section of the Columbia River, which changes from a northwestward course along the Rocky Mountain Trench to curve around the northern end of the S ...
, passing through Revelstoke Lake
Lake Revelstoke or Revelstoke Lake or Revelstoke Lake Reservoir is an artificial lake on the Columbia River, north of the town of Revelstoke, British Columbia and south of Mica Creek. This lake is the reservoir formed by the Revelstoke Dam, whi ...
and the Arrow Lakes
The Arrow Lakes in British Columbia, Canada, divided into Upper Arrow Lake and Lower Arrow Lake, are widenings of the Columbia River. The lakes are situated between the Selkirk Mountains to the east and the Monashee Mountains to the west. Bea ...
. Revelstoke, the Big Bend, and the Columbia Valley combined are referred to in BC parlance as the Columbia Country
Columbia Country refers to the upper basin of the Columbia River in the Canadian province of British Columbia. It includes a smaller region known as the Columbia Valley, near the river's headwaters at Columbia Lake in the Rocky Mountain Trench, a ...
. Below the Arrow Lakes, the Columbia passes the cities of Castlegar, located at the Columbia's confluence
In geography, a confluence (also: ''conflux'') occurs where two or more flowing bodies of water join to form a single channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main stem); o ...
with the Kootenay River
The Kootenay or Kootenai river is a major river in the Northwest Plateau, in southeastern British Columbia, Canada, and northern Montana and Idaho in the United States. It is one of the uppermost major tributary, tributaries of the Columbia Ri ...
, and Trail
A trail, also known as a path or track, is an unpaved lane or small road usually passing through a natural area. In the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland, a path or footpath is the preferred term for a pedestrian or hiking trail. ...
, two major population centers of the West Kootenay
The Kootenays or Kootenay ( ) is a region of southeastern British Columbia. It takes its name from the Kootenay River, which in turn was named for the Kutenai First Nations people.
Boundaries
The Kootenays are more or less defined by the Koot ...
region. The Pend Oreille River
The Pend Oreille River ( ) is a tributary of the Columbia River, approximately long, in northern Idaho and northeastern Washington in the United States, as well as southeastern British Columbia in Canada. In its passage through British Columbi ...
joins the Columbia about north of the U.S.–Canada border.
 The Columbia enters
The Columbia enters eastern Washington
Eastern Washington is the region of the U.S. state of Washington located east of the Cascade Range. It contains the city of Spokane (the second largest city in the state), the Tri-Cities, the Columbia River and the Grand Coulee Dam, the Hanf ...
flowing south and turning to the west at the Spokane River
The Spokane River is a tributary of the Columbia River, approximately long, in northern Idaho and eastern Washington in the United States. It drains a low mountainous area east of the Columbia, passing through the Spokane Valley and the city of ...
confluence. It marks the southern and eastern borders of the Colville Indian Reservation
The Colville Indian Reservation is an Indian reservation in the northwest United States, in north central Washington, inhabited and managed by the Confederated Tribes of the Colville Reservation, which is federally recognized.
Established ...
and the western border of the Spokane Indian Reservation
The Spokan or Spokane people are a Native American Plateau tribe who inhabit the eastern portion of present-day Washington state and parts of northern Idaho in the United States of America.
The current Spokane Indian Reservation is located in ...
. The river turns south after the Okanogan River
The Okanogan River (known as the Okanagan River in Canada) is a tributary of the Columbia River, approximately 115 mi (185 km) long, in southern British Columbia and north central Washington. It drains a scenic plateau region called th ...
confluence, then southeasterly near the confluence with the Wenatchee River
The Wenatchee River is a river in the U.S. state of Washington, originating at Lake Wenatchee and flowing southeast for , emptying into the Columbia River immediately north of Wenatchee, Washington. On its way it passes the towns of Plain, Leave ...
in central Washington. This C‑shaped segment of the river is also known as the "Big Bend". During the Missoula Floods
The Missoula floods (also known as the Spokane floods or the Bretz floods or Bretz's floods) were cataclysmic glacial lake outburst floods that swept periodically across eastern Washington and down the Columbia River Gorge at the end of the las ...
10,000 to 15,000 years ago, much of the floodwater took a more direct route south, forming the ancient river bed known as the Grand Coulee
Grand Coulee is an ancient river bed in the U.S. state of Washington. This National Natural Landmark stretches for about 60 miles (100 km) southwest from Grand Coulee Dam to Soap Lake, being bisected by Dry Falls into the Upper and Lower ...
. After the floods, the river found its present course, and the Grand Coulee was left dry. The construction of the Grand Coulee Dam
Grand Coulee Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Washington, built to produce hydroelectric power and provide irrigation water. Constructed between 1933 and 1942, Grand Coulee originally had two powerh ...
in the mid-20th century impounded the river, forming Lake Roosevelt, from which water was pumped into the dry coulee
Coulee, or coulée ( or ) is a term applied rather loosely to different landforms, all of which refer to a kind of valley or drainage zone. The word ''coulee'' comes from the Canadian French ''coulée'', from French ''couler'' 'to flow'.
The ...
, forming the reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation.
Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including contro ...
of Banks Lake
Banks Lake is a long reservoir in central Washington in the United States.
Part of the Columbia Basin Project, Banks Lake occupies the northern portion of the Grand Coulee, a formerly dry coulee near the Columbia River, formed by the Missoula Fl ...
.
The river flows past The Gorge Amphitheatre
The Gorge Amphitheatre, originally known as Champs de Brionne Music Theatre, is an outdoor concert venue in Grant County, Washington, United States. It is situated near Columbia River in Central Washington, west of George. The venue is manage ...
, a prominent concert venue in the Northwest, then through Priest Rapids Dam
Priest Rapids Dam is a hydroelectric, concrete gravity dam; located on the Columbia River, between the Yakima Firing Range and the Hanford Nuclear Reservation, and bridges Yakima County and Grant County, in the U.S. state of Washington. The d ...
, and then through the Hanford Nuclear Reservation
The Hanford Site is a decommissioned nuclear production complex operated by the United States federal government on the Columbia River in Benton County in the U.S. state of Washington. The site has been known by many names, including SiteW a ...
. Entirely within the reservation is Hanford Reach
The Hanford Reach is a free-flowing section of the Columbia River, around long, in eastern Washington state. It is named after a large northward bend in the river's otherwise southbound course.
Hanford Reach is the only section of the Columbia i ...
, the only US stretch of the river that is completely free-flowing, unimpeded by dams, and not a tidal estuary
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environment ...
. The Snake River
The Snake River is a major river of the greater Pacific Northwest region in the United States. At long, it is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, in turn, the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean. The Snake ...
and Yakima River
The Yakima River is a tributary of the Columbia River in south central and eastern Washington state, named for the indigenous Yakama people. Lewis and Clark mention in their journals that the Chin-nâm pam (or the Lower Snake River Chamnapam ...
join the Columbia in the Tri-Cities population center. The Columbia makes a sharp bend to the west at the Washington–Oregon border. The river defines that border for the final of its journey.
 The
The Deschutes River Deschutes River may refer to:
*Deschutes River (Oregon)
The Deschutes River in central Oregon is a major tributary of the Columbia River. The river provides much of the drainage on the eastern side of the Cascade Range in Oregon, gathering many ...
joins the Columbia near The Dalles
The Dalles is the largest city of Wasco County, Oregon, United States. The population was 16,010 at the 2020 census, and it is the largest city on the Oregon side of the Columbia River between the Portland Metropolitan Area, and Hermiston ...
. Between The Dalles and Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
* Portland, Oregon, the largest city in the state of Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States
* Portland, Maine, the largest city in the state of Maine, in the New England region of the northeas ...
, the river cuts through the Cascade Range
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, ...
, forming the dramatic Columbia River Gorge
The Columbia River Gorge is a canyon of the Columbia River in the Pacific Northwest of the United States. Up to deep, the canyon stretches for over as the river winds westward through the Cascade Range, forming the boundary between the st ...
. No other rivers except for the Klamath Klamath may refer to:
Ethnic groups
*Klamath people, a Native American people of California and Oregon
**Klamath Tribes, a federally recognized group of tribes in Oregon
*Klamath language, spoken by the Klamath people
Places in the United States
* ...
and Pit River completely breach the Cascades—the other rivers that flow through the range also originate in or very near the mountains. The headwaters and upper course of the Pit River are on the Modoc Plateau
__NOTOC__
The Modoc Plateau lies in the northeast corner of California as well as parts of Oregon and Nevada. Nearly of the Modoc National Forest are on the plateau between the Medicine Lake Highlands in the west and the Warner Mountains in the ...
; downstream, the Pit cuts a canyon through the southern reaches of the Cascades. In contrast, the Columbia cuts through the range nearly a thousand miles from its source in the Rocky Mountains. The gorge is known for its strong and steady winds, scenic beauty, and its role as an important transportation link. The river continues west, bending sharply to the north-northwest near Portland and Vancouver, Washington
Vancouver is a city on the north bank of the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Washington, located in Clark County. Incorporated in 1857, Vancouver has a population of 190,915 as of the 2020 census, making it the fourth-largest city in Was ...
, at the Willamette River
The Willamette River ( ) is a major tributary of the Columbia River, accounting for 12 to 15 percent of the Columbia's flow. The Willamette's main stem is long, lying entirely in northwestern Oregon in the United States. Flowing northward b ...
confluence. Here the river slows considerably, dropping sediment that might otherwise form a river delta
A river delta is a landform shaped like a triangle, created by deposition (geology), deposition of sediment that is carried by a river and enters slower-moving or stagnant water. This occurs where a river enters an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, res ...
. Near Longview, Washington
Longview is a city in Cowlitz County, Washington, United States. It is the principal city of the Longview, Washington Metropolitan Statistical Area, which encompasses all of Cowlitz County. Longview's population was 37,818 at the time of the 2 ...
and the Cowlitz River
The Cowlitz River is a river in the state of Washington in the United States, a tributary of the Columbia River. Its tributaries drain a large region including the slopes of Mount Rainier, Mount Adams, and Mount St. Helens.
The Cowlitz has a d ...
confluence, the river turns west again. The Columbia empties into the Pacific Ocean just west of Astoria, Oregon, over the Columbia Bar, a shifting sandbar
In oceanography, geomorphology, and Earth science, geoscience, a shoal is a natural submerged ridge, bank (geography), bank, or bar that consists of, or is covered by, sand or other unconsolidated material and rises from the bed of a body o ...
that makes the river's mouth one of the most hazardous stretches of water to navigate in the world. Because of the danger and the many shipwrecks near the mouth, it acquired a reputation as the "Graveyard of Ships".
The Columbia drains an area of about . Its drainage basin covers nearly all of Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and Wyom ...
, large portions of British Columbia, Oregon, and Washington, ultimately all of Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
west of the Continental Divide
A continental divide is a drainage divide on a continent such that the drainage basin on one side of the divide feeds into one ocean or sea, and the basin on the other side either feeds into a different ocean or sea, or else is endorheic, not ...
, and small portions of Wyoming
Wyoming () is a U.S. state, state in the Mountain states, Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the south ...
, Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
, and Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
; the total area is similar to the size of France. Roughly of the river's length and 85 percent of its drainage basin are in the US. The Columbia is the twelfth-longest river and has the sixth-largest drainage basin in the United States. In Canada, where the Columbia flows for and drains , the river ranks 23rd in length, and the Canadian part of its basin ranks 13th in size among Canadian basins.
The Columbia shares its name with nearby places, such as British Columbia, as well as with landforms and bodies of water.
Discharge
With an average flow at the mouth of about , the Columbia is the largest river by discharge flowing into the Pacific from the Americas and is the fourth-largest by volume in the US. The average flow where the river crosses the international border between Canada and the United States is from a drainage basin of . This amounts to about 15 percent of the entire Columbia watershed. The Columbia's highest recorded flow, measured at The Dalles, was in June 1894, before the river was dammed. The lowest flow recorded at The Dalles was on April 16, 1968, and was caused by the initial closure of theJohn Day Dam
The John Day Dam is a concrete gravity run-of-the-river dam spanning the Columbia River in the northwestern United States. The dam features a navigation lock plus fish ladders on both sides. The John Day Lock has the highest lift (at ) of any U.S ...
, upstream. The Dalles is about from the mouth; the river at this point drains about or about 91 percent of the total watershed. Flow rates on the Columbia are affected by many large upstream reservoirs, many diversions for irrigation, and, on the lower stretches, reverse flow from the tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravity, gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide t ...
s of the Pacific Ocean. The National Ocean Service
The National Ocean Service (NOS) is an office within the U.S. Department of Commerce National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). It is responsible for preserving and enhancing the nation's coastal resources and ecosystems along the of ...
observes water levels at six tide gauge
A tide gauge is a device for measuring the change in sea level relative to a vertical datum.
It its also known as mareograph, marigraph, sea-level recorder and limnimeter.
When applied to freshwater continental water bodies, the instrument ma ...
s and issues tide forecasts for twenty-two additional locations along the river between the entrance at the North Jetty and the base of Bonneville Dam
Bonneville Lock and Dam consists of several run-of-the-river dam structures that together complete a span of the Columbia River between the U.S. states of Oregon and Washington at River Mile 146.1. The dam is located east of Portland, Oregon ...
, the head of tide
Head of tide, tidal limit or tidehead is the farthest point upstream where a river is affected by tidal fluctuations, or where the fluctuations are less than a certain amount. This applies to rivers which flow into tidal bodies such as oceans, ...
.
The Columbia River multiannual average discharge:
Geology
 When the
When the rift
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.
Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-grabe ...
ing of Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
, due to the process of plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
, pushed North America away from Europe and Africa and into the Panthalassic Ocean (ancestor to the modern Pacific Ocean), the Pacific Northwest was not part of the continent. As the North American continent moved westward, the Farallon Plate
The Farallon Plate was an ancient oceanic plate. It formed one of the three main plates of Panthalassa, alongside the Phoenix Plate and Izanagi Plate, which were connected by a triple junction. The Farallon Plate began subducting under the west ...
subducted
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
under its western margin. As the plate subducted, it carried along island arc
Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle alon ...
s which were accreted to the North American continent, resulting in the creation of the Pacific Northwest between 150 and 90 million years ago. The general outline of the Columbia Basin was not complete until between 60 and 40 million years ago, but it lay under a large inland sea later subject to uplift. Between 50 and 20 million years ago, from the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
through the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
eras, tremendous volcanic eruptions frequently modified much of the landscape traversed by the Columbia. The lower reaches of the ancestral river passed through a valley near where Mount Hood later arose. Carrying sediments from erosion and erupting volcanoes, it built a thick delta that underlies the foothills on the east side of the Coast Range near Vernonia
''Vernonia'' is a genus of about 350 species of forbs and shrubs in the Daisy family Asteraceae. Some species are known as ironweed. Some species are edible and of economic value. They are known for having intense purple flowers. There have been ...
in northwestern Oregon. Between 17 million and 6 million years ago, huge outpourings of flood basalt
A flood basalt (or plateau basalt) is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reac ...
lava covered the Columbia River Plateau
The Columbia Plateau is a geologic and geographic region that lies across parts of the U.S. states of Washington, Oregon, and Idaho. It is a wide flood basalt plateau between the Cascade Range and the Rocky Mountains, cut through by the Columbi ...
and forced the lower Columbia into its present course. The modern Cascade Range began to uplift 5 to 4 million years ago. Cutting through the uplifting mountains, the Columbia River significantly deepened the Columbia River Gorge.
The river and its drainage basin experienced some of the world's greatest known catastrophic floods toward the end of the last ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
. The periodic rupturing of ice dams at Glacial Lake Missoula
Lake Missoula was a prehistoric proglacial lake in western Montana that existed periodically at the end of the last ice age between 15,000 and 13,000 years ago. The lake measured about and contained about of water, half the volume of Lake Mic ...
resulted in the Missoula Floods, with discharges exceeding the combined flow of all the other rivers in the world, dozens of times over thousands of years. The exact number of floods is unknown, but geologists have documented at least 40; evidence suggests that they occurred between about 19,000 and 13,000 years ago.
 The floodwaters rushed across eastern Washington, creating the
The floodwaters rushed across eastern Washington, creating the channeled scablands
The Channeled Scablands are a relatively barren and soil-free region of interconnected relict and dry flood channels, coulees and cataracts eroded into Palouse loess and the typically flat-lying basalt flows that remain after cataclysmic floods ...
, which are a complex network of dry canyon-like channels, or coulees that are often braided
Braided is a musical group consisting of Casey LeBlanc, Ashley Leitão, and Amber Fleury, who all competed on the third season of '' Canadian Idol'' in 2005. They are the third music group to come from an Idol show in the world, after Young Div ...
and sharply gouged into the basalt rock underlying the region's deep topsoil. Numerous flat-topped butte
__NOTOC__
In geomorphology, a butte () is an isolated hill with steep, often vertical sides and a small, relatively flat top; buttes are smaller landforms than mesas, plateaus, and tablelands. The word ''butte'' comes from a French word mea ...
s with rich soil stand high above the chaotic scablands. Constrictions at several places caused the floodwaters to pool into large temporary lakes, such as Lake Lewis
Lake Lewis was a temporary lake in the Pacific Northwest region of North America, largely formed by the Missoula Floods in about the 14th millennium B.C.
Lake Lewis was formed when the restricted flow of waters from periodic cataclysmic floods f ...
, in which sediments were deposited. Water depths have been estimated at at Wallula Gap
Wallula Gap () is a large water gap of the Columbia River in the northwest United States in southeast Washington. It cuts through the Horse Heaven Hills basalt anticlines in the Columbia River Basin, just south of the confluence of the Wall ...
and over modern Portland, Oregon. Sediments were also deposited when the floodwaters slowed in the broad flats of the Quincy, Othello, and Pasco Basins. The floods' periodic inundation of the lower Columbia River Plateau deposited rich sediments; 21st-century farmers in the Willamette Valley "plow fields of fertile Montana soil and clays from Washington's Palouse".
Over the last several thousand years a series of large landslides have occurred on the north side of the Columbia River Gorge, sending massive amounts of debris south from Table Mountain
Table Mountain ( naq, Huriǂoaxa, lit= sea-emerging; af, Tafelberg) is a flat-topped mountain forming a prominent landmark overlooking the city of Cape Town in South Africa. It is a significant tourist attraction, with many visitors using the ...
and Greenleaf Peak
Greenleaf Peak is a mountain in the Cascade Range in the U.S. state of Washington, located on the north side of the Columbia River near Table Mountain, in the Columbia River Gorge. The peak lies within the Columbia River Gorge National Scenic ...
into the gorge near the present site of Bonneville Dam. The most recent and significant is known as the Bonneville Slide, which formed a massive earthen dam, filling of the river's length. Various studies have placed the date of the Bonneville Slide anywhere between 1060 and 1760 AD; the idea that the landslide debris present today was formed by more than one slide is relatively recent and may explain the large range of estimates. It has been suggested that if the later dates are accurate there may be a link with the 1700 Cascadia earthquake. The pile of debris resulting from the Bonneville Slide blocked the river until rising water finally washed away the sediment. It is not known how long it took the river to break through the barrier; estimates range from several months to several years. Much of the landslide's debris remained, forcing the river about south of its previous channel and forming the Cascade Rapids
The Cascades Rapids (sometimes called Cascade Falls or Cascades of the Columbia) were an area of rapids along North America's Columbia River, between the U.S. states of Washington and Oregon. Through a stretch approximately wide, the river ...
. In 1938, the construction of Bonneville Dam inundated the rapids as well as the remaining trees that could be used to refine the estimated date of the landslide.
In 1980, the eruption of Mount St. Helens deposited large amounts of sediment in the lower Columbia, temporarily reducing the depth of the shipping channel by .
Indigenous peoples
 Humans have inhabited the Columbia's watershed for more than 15,000 years, with a transition to a sedentary lifestyle based mainly on salmon starting about 3,500 years ago. In 1962, archaeologists found evidence of human activity dating back 11,230 years at the
Humans have inhabited the Columbia's watershed for more than 15,000 years, with a transition to a sedentary lifestyle based mainly on salmon starting about 3,500 years ago. In 1962, archaeologists found evidence of human activity dating back 11,230 years at the Marmes Rockshelter
The Marmes Rockshelter (also known as (45-FR-50)) is an archaeological site first excavated in 1962, near Lyons Ferry Park and the confluence of the Snake and Palouse Rivers, in Franklin County, southeastern Washington. This rockshelter is remar ...
, near the confluence of the Palouse
The Palouse ( ) is a distinct geographic region of the northwestern United States, encompassing parts of north central Idaho, southeastern Washington, and, by some definitions, parts of northeast Oregon. It is a major agricultural area, prima ...
and Snake rivers in eastern Washington. In 1996 the skeletal remains of a 9,000-year-old prehistoric man (dubbed Kennewick Man
Kennewick Man and Ancient One are the names generally given to the skeletal remains of a prehistoric Paleoamerican man found on a bank of the Columbia River in Kennewick, Washington, on July 28, 1996. It is one of the most complete ancient ...
) were found near Kennewick, Washington
Kennewick () is a city in Benton County in the U.S. state of Washington. It is located along the southwest bank of the Columbia River, just southeast of the confluence of the Columbia and Yakima rivers and across from the confluence of the ...
. The discovery rekindled debate in the scientific community over the origins of human habitation in North America and sparked a protracted controversy over whether the scientific or Native American community was entitled to possess and/or study the remains.
Many different Native Americans and First Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
peoples have a historical and continuing presence on the Columbia. South of the Canada–US border, the Colville, Spokane
Spokane ( ) is the largest city and county seat of Spokane County, Washington, United States. It is in eastern Washington, along the Spokane River, adjacent to the Selkirk Mountains, and west of the Rocky Mountain foothills, south of the Ca ...
, Coeur d'Alene, Yakama
The Yakama are a Native American tribe with nearly 10,851 members, based primarily in eastern Washington state.
Yakama people today are enrolled in the federally recognized tribe, the Confederated Tribes and Bands of the Yakama Nation. Their ...
, Nez Perce
The Nez Percé (; autonym in Nez Perce language: , meaning "we, the people") are an Indigenous people of the Plateau who are presumed to have lived on the Columbia River Plateau in the Pacific Northwest region for at least 11,500 years.Ames, K ...
, Cayuse, Palus
Palus may refer to:
* Palus, Maharashtra, a place in India
* 24194 Paľuš, a main belt asteroid, named for Pavel Paľuš (born 1936), Slovak astronomer
* Palus tribe, or Palouse people
* ''Palus'', a grade of gladiator
See also
* Palu (dis ...
, Umatilla, Cowlitz Cowlitz may refer to:
People
* Cowlitz people, an indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest
** Cowlitz language, member of the Tsamosan branch of the Coast Salish family of Salishan languages
* Cowlitz Indian Tribe, a federally recognized tribe of ...
, and the Confederated Tribes of Warm Springs live along the US stretch. Along the upper Snake River and Salmon River, the Shoshone Bannock
Bannock may mean:
* Bannock (food), a kind of bread, cooked on a stone or griddle
* Bannock (Indigenous American), various types of bread, usually prepared by pan-frying
* Bannock people, a Native American people of what is now southeastern Oregon ...
tribes are present. The Sinixt
The Sinixt"Sinixt Nation…" (also known as the Sin-Aikst or Sin Aikst,Reyes 2002, ''passim.'' "Senjextee", "Arrow Lakes Band", or — less commonly in recent decades — simply as "The Lakes") are a First Nations People. The Sinixt are ...
or Lakes people lived on the lower stretch of the Canadian portion, while above that the Shuswap people Shuswap may refer to:
* Secwepemc, an indigenous people in British Columbia, Canada, also known in English as the Shuswap
** Shuswap Nation Tribal Council, a multi-band regional organization of Secwepemc governments based in Kamloops, British Colu ...
(Secwepemc in their own language) reckon the whole of the upper Columbia east to the Rockies as part of their territory. The Canadian portion of the Columbia Basin outlines the traditional homelands of the Canadian Kootenay–Ktunaxa
The Kutenai ( ), also known as the Ktunaxa ( ; ), Ksanka ( ), Kootenay (in Canada) and Kootenai (in the United States), are an indigenous people of Canada and the United States. Kutenai bands live in southeastern British Columbia, northern ...
.
The Chinook tribe, which is not federally recognized
This is a list of federally recognized tribes in the contiguous United States of America. There are also federally recognized Alaska Native tribes. , 574 Indian tribes were legally recognized by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) of the United ...
, who live near the lower Columbia River, call it ' or ' in the Upper Chinook (Kiksht) language, and it is ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana'' to the Sahaptin (Ichishkíin Sɨ́nwit)-speaking peoples of its middle course in present-day Washington. The river is known as ' by the Sinixt people
The Sinixt"Sinixt Nation…" (also known as the Sin-Aikst or Sin Aikst,Reyes 2002, ''passim.'' "Senjextee", "Arrow Lakes Band", or — less commonly in recent decades — simply as "The Lakes") are a First Nations People. The Sinixt are ...
, who live in the area of the Arrow Lakes in the river's upper reaches in Canada. All three terms essentially mean "the big river".
Oral histories describe the formation and destruction of the Bridge of the Gods, a land bridge that connected the Oregon and Washington sides of the river in the Columbia River Gorge. The bridge, which aligns with geological records of the Bonneville Slide, was described in some stories as the result of a battle between gods, represented by Mount Adams and Mount Hood, in their competition for the affection of a goddess, represented by Mount St. Helens. Native American stories about the bridge differ in their details but agree in general that the bridge permitted increased interaction between tribes on the north and south sides of the river.
Horses, originally acquired from Spanish New Mexico
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
, spread widely via native trade networks, reaching the Shoshone of the Snake River Plain by 1700. The Nez Perce, Cayuse, and Flathead people acquired their first horses around 1730. Along with horses came aspects of the emerging plains culture, such as equestrian and horse training
Horse training refers to a variety of practices that teach horses to perform certain behaviors when commanded to do so by humans. Horses are trained to be manageable by humans for everyday care as well as for equestrian activities from horse ra ...
skills, greatly increased mobility, hunting efficiency, trade over long distances, intensified warfare, the linking of wealth and prestige to horses and war, and the rise of large and powerful tribal confederacies. The Nez Perce and Cayuse kept large herds and made annual long-distance trips to the Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
for bison hunting, adopted the plains culture to a significant degree, and became the main conduit through which horses and the plains culture diffused into the Columbia River region. Other peoples acquired horses and aspects of the plains culture unevenly. The Yakama, Umatilla, Palus, Spokane, and Coeur d'Alene maintained sizable herds of horses and adopted some of the plains cultural characteristics, but fishing and fish-related economies remained important. Less affected groups included the Molala
The Molala (also Molale, Molalla, Molele) are a people of the Plateau culture area in the Oregon Cascades and central Oregon, United States. They are one of the Confederated Tribes of the Grand Ronde Community of Oregon, with 141 of the 882 member ...
, Klickitat, Wenatchi
The Wenatchi people or Šnp̍əšqʷáw̉šəxʷi / Np̓əšqʷáw̓səxʷ ("People in the between") are Native Americans who originally lived near the confluence of the Columbia and Wenatchee Rivers in Central Washington state. They spoke Interio ...
, Okanagan, and Sinkiuse-Columbia
The Sinkiuse-Columbia are a Native American tribe so-called because of their former prominent association with the Columbia River. They belong to the inland division of the Salishan group, with their nearest relatives being the Wenatchis and M ...
peoples, who owned small numbers of horses and adopted few plains culture features. Some groups remained essentially unaffected, such as the Sanpoil and Nespelem people, whose culture remained centered on fishing.
Natives of the region encountered foreigners at several times and places during the 18th and 19th centuries. European and American vessels explored the coastal area around the mouth of the river in the late 18th century, trading with local natives. The contact would prove devastating to the Indian tribes; a large portion of their population was wiped out by a smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
epidemic. Canadian explorer Alexander Mackenzie crossed what is now interior British Columbia in 1793. From 1805 to 1807, the Lewis and Clark Expedition
The Lewis and Clark Expedition, also known as the Corps of Discovery Expedition, was the United States expedition to cross the newly acquired western portion of the country after the Louisiana Purchase. The Corps of Discovery was a select gro ...
entered the Oregon Country along the Clearwater Clearwater or Clear Water may refer to:
Places Canada
* Clear Water Academy, a private Catholic school located in Calgary, Alberta
* Clearwater (provincial electoral district), a former provincial electoral district in Alberta
* Clearwater, Briti ...
and Snake rivers, and encountered numerous small settlements of natives. Their records recount tales of hospitable traders who were not above stealing small items from the visitors. They also noted brass teakettles, a British musket, and other artifacts that had been obtained in trade with coastal tribes. From the earliest contact with westerners, the natives of the mid- and lower Columbia were not tribal, but instead congregated in social units no larger than a village, and more often at a family level; these units would shift with the season as people moved about, following the salmon catch up and down the river's tributaries.
Sparked by the 1847 Whitman Massacre
The Whitman massacre (also known as the Walla Walla massacre and referred to as the Tragedy at Waiilatpu by the National Park Service) was the killing of the Washington missionaries Marcus Whitman and his wife Narcissa, along with eleven others ...
, a number of violent battles were fought between American settlers and the region's natives. The subsequent Indian Wars, especially the Yakima War
The Yakima War (1855–1858), also referred to as the Yakima Native American War of 1855 or the Plateau War, was a conflict between the United States and the Yakama, a Sahaptian-speaking people of the Northwest Plateau, then part of Washington T ...
, decimated the native population and removed much land from native control. As years progressed, the right of natives to fish along the Columbia became the central issue of contention with the states, commercial fishers, and private property owners. The US Supreme Court upheld fishing rights in landmark cases in 1905 and 1918, as well as the 1974 case ''United States v. Washington
''United States v. Washington'', 384 F. Supp. 312 (W.D. Wash. 1974), aff'd, 520 F.2d 676 (9th Cir. 1975), commonly known as the Boldt Decision (from the name of the trial court judge, George Hugo Boldt), was a legal case in 1974 heard in t ...
'', commonly called the Boldt Decision.
 Fish were central to the culture of the region's natives, both as sustenance and as part of their religious beliefs. Natives drew fish from the Columbia at several major sites, which also served as trading posts.
Fish were central to the culture of the region's natives, both as sustenance and as part of their religious beliefs. Natives drew fish from the Columbia at several major sites, which also served as trading posts. Celilo Falls
Celilo Falls (Wyam, meaning "echo of falling water" or "sound of water upon the rocks," in several native languages) was a tribal fishing area on the Columbia River, just east of the Cascade Mountains, on what is today the border between the U.S. ...
, located east of the modern city of The Dalles, was a vital hub for trade and the interaction of different cultural groups, being used for fishing and trading for 11,000 years. Prior to contact with westerners, villages along this stretch may have at times had a population as great as 10,000. The site drew traders from as far away as the Great Plains.
The Cascades Rapids of the Columbia River Gorge, and Kettle Falls
Kettle Falls ( Salish: Shonitkwu, meaning "roaring or noisy waters", also Schwenetekoo translated as "Keep Sounding Water") was an ancient and important salmon fishing site on the upper reaches of the Columbia River, in what is today the U.S. ...
and Priest Rapids in eastern Washington, were also major fishing and trading sites.
In prehistoric times the Columbia's salmon and steelhead runs numbered an estimated annual average of 10 to 16 million fish. In comparison, the largest run since 1938 was in 1986, with 3.2 million fish entering the Columbia. The annual catch by natives has been estimated at . The most important and productive native fishing site was located at Celilo Falls, which was perhaps the most productive inland fishing site in North America. The falls were located at the border between Chinookan- and Sahaptian-speaking peoples and served as the center of an extensive trading network across the Pacific Plateau. Celilo was the oldest continuously inhabited community on the North American continent.
Salmon canneries established by white settlers beginning in 1866 had a strong negative impact on the salmon population, and in 1908 US President Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
observed that the salmon run
''Salmon Run'' is a 1982 video game for the Atari 8-bit family created by Bill Williams and distributed via the Atari Program Exchange. ''Salmon Run'' was the first game in Williams's career, followed by a string of successes noted for their o ...
s were but a fraction of what they had been 25 years prior.
As river development continued in the 20th century, each of these major fishing sites was flooded by a dam, beginning with Cascades Rapids in 1938. The development was accompanied by extensive negotiations between natives and US government agencies. The Confederated Tribes of Warm Springs, a coalition of various tribes, adopted a constitution and incorporated after the 1938 completion of the Bonneville Dam flooded Cascades Rapids; Still, in the 1930s, there were natives who lived along the river and fished year round, moving along with the fish's migration patterns throughout the seasons. The Yakama were slower to do so, organizing a formal government in 1944. In the 21st century, the Yakama, Nez Perce, Umatilla, and Warm Springs tribes all have treaty fishing rights along the Columbia and its tributaries.
In 1957 Celilo Falls was submerged by the construction of The Dalles Dam, and the native fishing community was displaced. The affected tribes received a $26.8 million settlement for the loss of Celilo and other fishing sites submerged by The Dalles Dam. The Confederated Tribes of Warm Springs used part of its $4 million settlement to establish the Kah-Nee-Ta
Kah-Nee-Ta Resort & Spa was a resort in central Oregon, United States, on the Warm Springs Indian Reservation, near the community of Warm Springs in Jefferson County. It closed on 5 September 2018, laying off all its employees. It is plann ...
resort south of Mount Hood.
New waves of explorers
 Some historians believe that Japanese or Chinese vessels blown off course reached the Northwest Coast long before Europeans—possibly as early as 219
Some historians believe that Japanese or Chinese vessels blown off course reached the Northwest Coast long before Europeans—possibly as early as 219 BCE
Common Era (CE) and Before the Common Era (BCE) are year notations for the Gregorian calendar (and its predecessor, the Julian calendar), the world's most widely used calendar era. Common Era and Before the Common Era are alternatives to the or ...
. Historian Derek Hayes claims that "It is a near certainty that Japanese or Chinese people arrived on the northwest coast long before any European." It is unknown whether they landed near the Columbia. Evidence exists that Spanish castaways reached the shore in 1679 and traded with the Clatsop
The Clatsop is a small tribe of Chinookan-speaking Native Americans in the Pacific Northwest of the United States. In the early 19th century they inhabited an area of the northwestern coast of present-day Oregon from the mouth of the Columbia R ...
; if these were the first Europeans to see the Columbia, they failed to send word home to Spain.
In the 18th century, there was strong interest in discovering a Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea route between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The eastern route along the Arc ...
that would permit navigation between the Atlantic (or inland North America) and the Pacific Ocean. Many ships in the area, especially those under Spanish and British command, searched the northwest coast for a large river that might connect to Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay ( crj, text=ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, translit=Wînipekw; crl, text=ᐐᓂᐹᒄ, translit=Wînipâkw; iu, text=ᑲᖏᖅᓱᐊᓗᒃ ᐃᓗᐊ, translit=Kangiqsualuk ilua or iu, text=ᑕᓯᐅᔭᕐᔪᐊᖅ, translit=Tasiujarjuaq; french: b ...
or the Missouri River. The first documented European discovery of the Columbia River was that of Bruno de Heceta
Bruno de Heceta (Hezeta) y Dudagoitia (1743–1807) was a Spanish Basque explorer of the Pacific Northwest. Born in Bilbao of an old Basque family, he was sent by the Viceroy of New Spain, Antonio María Bucareli y Ursúa, to explore the area nort ...
, who in 1775 sighted the river's mouth. On the advice of his officers, he did not explore it, as he was short-staffed and the current was strong. He considered it a bay, and called it '' Ensenada de Asunción'' (''Assumption
Assumption, in Christianity, refers to the Assumption of Mary, a belief in the taking up of the Virgin Mary into heaven.
Assumption may also refer to:
Places
* Assumption, Alberta, Canada
* Assumption, Illinois, United States
** Assumption Tow ...
Cove''). Later Spanish maps, based on his sighting, showed a river, labeled ''Río de San Roque'' (''The Saint Roch
Roch (lived c. 1348 – 15/16 August 1376/79 (traditionally c. 1295 – 16 August 1327, also called Rock in English, is a Catholic saint, a confessor whose death is commemorated on 16 August and 9 September in Italy; he is especially invoked a ...
River''), or an entrance, called ''Entrada de Hezeta'', named for Bruno de Hezeta, who sailed the region. Following Hezeta's reports, British maritime fur trader Captain John Meares
John Meares (c. 1756 – 1809) was an English navigator, explorer, and maritime fur trader, best known for his role in the Nootka Crisis, which brought Britain and Spain to the brink of war.
Career
Meares' father was Charles Meares, "formerly an ...
searched for the river in 1788 but concluded that it did not exist. He named Cape Disappointment for the non-existent river, not realizing the cape marks the northern edge of the river's mouth.
What happened next would form the basis for decades of both cooperation and dispute between British and American exploration of, and ownership claim to, the region. Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
commander George Vancouver sailed past the mouth in April 1792 and observed a change in the water's color, but he accepted Meares' report and continued on his journey northward. Later that month, Vancouver encountered the American captain Robert Gray at the Strait of Juan de Fuca
The Strait of Juan de Fuca (officially named Juan de Fuca Strait in Canada) is a body of water about long that is the Salish Sea's outlet to the Pacific Ocean. The international boundary between Canada and the United States runs down the centre ...
. Gray reported that he had seen the entrance to the Columbia and had spent nine days trying but failing to enter.
 On May 12, 1792, Gray returned south and crossed the Columbia Bar, becoming the first known explorer of European descent to enter the river. Gray's fur trading mission had been financed by
On May 12, 1792, Gray returned south and crossed the Columbia Bar, becoming the first known explorer of European descent to enter the river. Gray's fur trading mission had been financed by Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
merchants, who outfitted him with a private vessel named ''Columbia Rediviva
''Columbia Rediviva'' (commonly known as ''Columbia'') was a privately owned American ship under the command, first, of John Kendrick, and later Captain Robert Gray, best known for going to the Pacific Northwest for the maritime fur trade. ...
''; he named the river after the ship on May 18. Gray spent nine days trading near the mouth of the Columbia, then left without having gone beyond upstream. The farthest point reached was Grays Bay at the mouth of Grays River. Gray's discovery of the Columbia River was later used by the United States to support its claim to the Oregon Country, which was also claimed by Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
, Spain and other nations.
In October 1792, Vancouver sent Lieutenant William Robert Broughton
William Robert Broughton (22 March 176214 March 1821) was a British naval officer in the late 18th century. As a lieutenant in the Royal Navy, he commanded HMS ''Chatham'' as part of the Vancouver Expedition, a voyage of exploration through th ...
, his second-in-command, up the river. Broughton got as far as the Sandy River at the western end of the Columbia River Gorge, about upstream, sighting and naming Mount Hood. Broughton formally claimed the river, its drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, t ...
, and the nearby coast for Britain. In contrast, Gray had not made any formal claims on behalf of the United States.
 Because the Columbia was at the same latitude as the headwaters of the Missouri River, there was some speculation that Gray and Vancouver had discovered the long-sought Northwest Passage. A 1798 British map showed a dotted line connecting the Columbia with the Missouri. When the American explorers Meriwether Lewis and
Because the Columbia was at the same latitude as the headwaters of the Missouri River, there was some speculation that Gray and Vancouver had discovered the long-sought Northwest Passage. A 1798 British map showed a dotted line connecting the Columbia with the Missouri. When the American explorers Meriwether Lewis and William Clark
William Clark (August 1, 1770 – September 1, 1838) was an American explorer, soldier, Indian agent, and territorial governor. A native of Virginia, he grew up in pre-statehood Kentucky before later settling in what became the state of Misso ...
charted the vast, unmapped lands of the American West
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Far West, and the West) is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term ''the Wes ...
in their overland expedition (1803–1805), they found no passage between the rivers. After crossing the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
, Lewis and Clark built dugout canoe
A dugout canoe or simply dugout is a boat made from a hollowed tree. Other names for this type of boat are logboat and monoxylon. ''Monoxylon'' (''μονόξυλον'') (pl: ''monoxyla'') is Greek – ''mono-'' (single) + '' ξύλον xylon'' ( ...
s and paddled down the Snake River, reaching the Columbia near the present-day Tri-Cities, Washington. They explored a few miles upriver, as far as Bateman Island
Bateman Island is an island located on the Columbia River immediately east of the Yakima River Delta between the cities of Richland and Kennewick, Washington, in the United States. It is approximately long and wide () and is part of the city of ...
, before heading down the Columbia, concluding their journey at the river's mouth and establishing Fort Clatsop
Fort Clatsop was the encampment of the Lewis and Clark Expedition in the Oregon Country near the mouth of the Columbia River during the winter of 1805–1806. Located along the Lewis and Clark River at the north end of the Clatsop Plains approxi ...
, a short-lived establishment that was occupied for less than three months.
Canadian explorer David Thompson, of the North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what is present-day Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great weal ...
, spent the winter of 1807–08 at Kootanae House
Kootanae House, also spelled Kootenae House, was a North West Company fur trading post built by Jaco Finlay under the direction of David Thompson near present-day Invermere, British Columbia in 1807. It was abandoned in 1812. In 1808 Thompson rec ...
near the source of the Columbia at present-day Invermere, British Columbia. Over the next few years he explored much of the river and its northern tributaries. In 1811 he traveled down the Columbia to the Pacific Ocean, arriving at the mouth just after John Jacob Astor
John Jacob Astor (born Johann Jakob Astor; July 17, 1763 – March 29, 1848) was a German-American businessman, merchant, real estate mogul, and investor who made his fortune mainly in a fur trade monopoly, by History of opium in China, smuggl ...
's Pacific Fur Company
The Pacific Fur Company (PFC) was an American fur trade venture wholly owned and funded by John Jacob Astor that functioned from 1810 to 1813. It was based in the Pacific Northwest, an area contested over the decades between the United Kingdom o ...
had founded Astoria. On his return to the north, Thompson explored the one remaining part of the river he had not yet seen, becoming the first Euro-descended person to travel the entire length of the river.
In 1825, the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business di ...
(HBC) established Fort Vancouver
Fort Vancouver was a 19th century fur trading post that was the headquarters of the Hudson's Bay Company's Columbia Department, located in the Pacific Northwest. Named for Captain George Vancouver, the fort was located on the northern bank of th ...
on the bank of the Columbia, in what is now Vancouver, Washington, as the headquarters of the company's Columbia District
The Columbia District was a fur trading district in the Pacific Northwest region of British North America in the 19th century. Much of its territory overlapped with the disputed Oregon Country. It was explored by the North West Company betw ...
, which encompassed everything west of the Rocky Mountains, north of California, and south of Russian-claimed Alaska. Chief Factor
A factor is a type of trader who receives and sells goods on commission, called factorage. A factor is a mercantile fiduciary transacting business in his own name and not disclosing his principal. A factor differs from a commission merchant in ...
John McLoughlin, a physician who had been in the fur trade since 1804, was appointed superintendent of the Columbia District. The HBC reoriented its Columbia District operations toward the Pacific Ocean via the Columbia, which became the region's main trunk route. In the early 1840s Americans began to colonize the Oregon country in large numbers via the Oregon Trail
The Oregon Trail was a east–west, large-wheeled wagon route and emigrant trail in the United States that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon. The eastern part of the Oregon Trail spanned part of what is now the state of Kans ...
, despite the HBC's efforts to discourage American settlement in the region. For many the final leg of the journey involved travel down the lower Columbia River to Fort Vancouver. This part of the Oregon Trail, the treacherous stretch from The Dalles to below the Cascades, could not be traversed by horses or wagons (only watercraft, at great risk). This prompted the 1846 construction of the Barlow Road
The Barlow Road (at inception, Mount Hood Road) is a historic road in what is now the U.S. state of Oregon. It was built in 1846 by Sam Barlow and Philip Foster, with authorization of the Provisional Legislature of Oregon, and served as the la ...
.
In the Treaty of 1818
The Convention respecting fisheries, boundary and the restoration of slaves, also known as the London Convention, Anglo-American Convention of 1818, Convention of 1818, or simply the Treaty of 1818, is an international treaty signed in 1818 betw ...
the United States and Britain agreed that both nations were to enjoy equal rights in Oregon Country for 10 years. By 1828, when the so-called "joint occupation" was renewed for an indefinite period, it seemed probable that the lower Columbia River would in time become the border between the two nations. For years the Hudson's Bay Company successfully maintained control of the Columbia River and American attempts to gain a foothold were fended off. In the 1830s, American religious missions were established at several locations in the lower Columbia River region. In the 1840s a mass migration of American settlers undermined British control. The Hudson's Bay Company tried to maintain dominance by shifting from the fur trade, which was in decline, to exporting other goods such as salmon and lumber. Colonization schemes were attempted, but failed to match the scale of American settlement. Americans generally settled south of the Columbia, mainly in the Willamette Valley. The Hudson's Bay Company tried to establish settlements north of the river, but nearly all the British colonists moved south to the Willamette Valley. The hope that the British colonists might dilute the American presence in the valley failed in the face of the overwhelming number of American settlers. These developments rekindled the issue of "joint occupation" and the boundary dispute
A territorial dispute or boundary dispute is a disagreement over the possession or control of land between two or more political entities.
Context and definitions
Territorial disputes are often related to the possession of natural resources s ...
. While some British interests, especially the Hudson's Bay Company, fought for a boundary along the Columbia River, the Oregon Treaty
The Oregon Treaty is a treaty between the United Kingdom and the United States that was signed on June 15, 1846, in Washington, D.C. The treaty brought an end to the Oregon boundary dispute by settling competing American and British claims to t ...
of 1846 set the boundary at the 49th parallel. As part of the treaty, the British retained all areas north of the line while the U.S. acquired the south. The Columbia River became much of the border between the U.S. territories of Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
and Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
. Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
became a U.S. state in 1859, while Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
later entered into the Union in 1889.
By the turn of the 20th century, the difficulty of navigating the Columbia was seen as an impediment to the economic development of the Inland Empire region east of the Cascades. The dredging and dam building that followed would permanently alter the river, disrupting its natural flow but also providing electricity, irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow Crop, crops, Landscape plant, landscape plants, and Lawn, lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,00 ...
, navigability
A body of water, such as a river, canal or lake, is navigable if it is deep, wide and calm enough for a water vessel (e.g. boats) to pass safely. Such a navigable water is called a ''waterway'', and is preferably with few obstructions against di ...
and other benefits to the region.
Navigation

 American captain Robert Gray and British captain George Vancouver, who explored the river in 1792, proved that it was possible to cross the Columbia Bar. Many of the challenges associated with that feat remain today; even with modern engineering alterations to the mouth of the river, the strong currents and shifting sandbar make it dangerous to pass between the river and the Pacific Ocean.
The use of
American captain Robert Gray and British captain George Vancouver, who explored the river in 1792, proved that it was possible to cross the Columbia Bar. Many of the challenges associated with that feat remain today; even with modern engineering alterations to the mouth of the river, the strong currents and shifting sandbar make it dangerous to pass between the river and the Pacific Ocean.
The use of steamboat
A steamboat is a boat that is marine propulsion, propelled primarily by marine steam engine, steam power, typically driving propellers or Paddle steamer, paddlewheels. Steamboats sometimes use the ship prefix, prefix designation SS, S.S. or S/S ...
s along the river, beginning with the British '' Beaver'' in 1836 and followed by American vessels in 1850, contributed to the rapid settlement and economic development of the region. Steamboats operated in several distinct stretches of the river: on its lower reaches, from the Pacific Ocean to Cascades Rapids; from the Cascades to the Dalles-Celilo Falls; from Celilo to Priests Rapids; on the Wenatchee Reach of eastern Washington; on British Columbia's Arrow Lakes; and on tributaries like the Willamette, the Snake and Kootenay Lake. The boats, initially powered by burning wood, carried passengers and freight throughout the region for many years. Early railroads served to connect steamboat lines interrupted by waterfalls on the river's lower reaches. In the 1880s, railroads maintained by companies such as the Oregon Railroad and Navigation Company
The Oregon Railroad and Navigation Company (OR&N) was a railroad that operated a rail network of running east from Portland, Oregon, United States, to northeastern Oregon, northeastern Washington, and northern Idaho. It operated from 1896 as a ...
began to supplement steamboat operations as the major transportation links along the river.
Opening the passage to Lewiston
As early as 1881, industrialists proposed altering the natural channel of the Columbia to improve navigation. Changes to the river over the years have included the construction ofjetties
A jetty is a structure that projects from land out into water. A jetty may serve as a breakwater, as a walkway, or both; or, in pairs, as a means of constricting a channel. The term derives from the French word ', "thrown", signifying somet ...
at the river's mouth, dredging
Dredging is the excavation of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage, navigability, and commercial use; constructing da ...
, and the construction of canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flow un ...
s and navigation locks. Today, ocean freighters can travel upriver as far as Portland and Vancouver, and barges can reach as far inland as Lewiston, Idaho.
The shifting Columbia Bar makes passage between the river and the Pacific Ocean difficult and dangerous, and numerous rapids along the river hinder navigation. ''Pacific Graveyard,'' a 1964 book by James A. Gibbs, describes the many shipwrecks near the mouth of the Columbia. Jetties, first constructed in 1886, extend the river's channel into the ocean. Strong currents and the shifting sandbar remain a threat to ships entering the river and necessitate continuous maintenance of the jetties.
In 1891, the Columbia was dredged to enhance shipping. The channel between the ocean and Portland and Vancouver was deepened from to . ''The Columbian
''The Columbian'' is a daily newspaper serving the Vancouver, Washington, and Clark County, Washington area. The paper was published for its first decade (1890–1900) as a four-page daily that was meant as a counterweight to the local Republi ...
'' called for the channel to be deepened to as early as 1905, but that depth was not attained until 1976.
Cascade Locks and Canal
The Cascade Locks and Canal was a navigation project on the Columbia River between the U.S. states of Oregon and Washington, completed in 1896. It allowed the steamboats of the Columbia River to bypass the Cascades Rapids, and thereby opened a pas ...
were first constructed in 1896 around the Cascades Rapids, enabling boats to travel safely through the Columbia River Gorge. The Celilo Canal
Celilo Canal was a canal connecting two points of the Columbia River between the states of Oregon and Washington, U.S. just east of The Dalles.
In the natural state of the Columbia River, there was an stretch from The Dalles to Celilo Falls that ...
, bypassing Celilo Falls, opened to river traffic in 1915. In the mid-20th century, the construction of dams along the length of the river submerged the rapids beneath a series of reservoirs. An extensive system of locks allowed ships and barges to pass easily from one reservoir to the next. A navigation channel reaching to Lewiston, Idaho, along the Columbia and Snake rivers, was completed in 1975. Among the main commodities are wheat and other grains, mainly for export. As of 2016, the Columbia ranked third, behind the Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
and Paraná rivers, among the world's largest export corridors for grain.
The 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens caused mudslides in the area, which reduced the Columbia's depth by for a stretch, disrupting Portland's economy.
Deeper shipping channel
US Army Corps of Engineers
, colors =
, anniversaries = 16 June (Organization Day)
, battles =
, battles_label = Wars
, website =
, commander1 = ...
must restore 12 times the area of wetland damaged by the project. In early 2006, the Corps spilled of hydraulic oil into the Columbia, drawing further criticism from environmental organizations.
Work on the project began in 2005 and concluded in 2010. The project's cost is estimated at $150 million. The federal government is paying 65 percent, Oregon and Washington are paying $27 million each, and six local ports are also contributing to the cost.
Dams

 In 1902, the
In 1902, the United States Bureau of Reclamation
The Bureau of Reclamation, and formerly the United States Reclamation Service, is a federal agency under the U.S. Department of the Interior, which oversees water resource management, specifically as it applies to the oversight and opera ...
was established to aid in the economic development
In the economics study of the public sector, economic and social development is the process by which the economic well-being and quality of life of a nation, region, local community, or an individual are improved according to targeted goals and ...
of arid western states
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
. One of its major undertakings was building Grand Coulee Dam to provide irrigation for the of the Columbia Basin Project
The Columbia Basin Project (or CBP) in Central Washington, United States, is the irrigation network that the Grand Coulee Dam makes possible. It is the largest water reclamation project in the United States, supplying irrigation water to over of ...
in central Washington. With the onset of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the focus of dam construction shifted to production of hydroelectricity. Irrigation efforts resumed after the war.
River development occurred within the structure of the 1909 International Boundary Waters Treaty between the US and Canada. The United States Congress passed the Rivers and Harbors Act#List of later acts, Rivers and Harbors Act of 1925, which directed the Army Corps of Engineers and the Federal Power Commission to explore the development of the nation's rivers. This prompted agencies to conduct the first formal financial analysis of hydroelectric development; the reports produced by various agencies were presented in House Document 308. Those reports, and subsequent related reports, are referred to as 308 Reports.
In the late 1920s, political forces in the Northwestern United States generally favored private development of hydroelectric dams along the Columbia. But the overwhelming victories of gubernatorial candidate George W. Joseph in the Oregon gubernatorial election, 1930, 1930 Republican primary, and later his law partner Julius Meier, were understood to demonstrate strong public support for public ownership of dams. In 1933, President Franklin D. Roosevelt signed a bill that enabled the construction of the Bonneville and Grand Coulee dams as public works projects. The legislation was attributed to the efforts of Oregon Senator Charles McNary, Washington Senator Clarence Dill, and Oregon Congressman Charles Martin (Oregon politician), Charles Martin, among others.
In 1948, 1948 Columbia River flood, floods swept through the Columbia watershed, destroying Vanport, Oregon, Vanport, then the second largest city in Oregon, and impacting cities as far north as Trail, British Columbia. The flooding prompted the United States Congress to pass the Flood Control Act of 1950, authorizing the federal development of additional dams and other flood control
Flood control methods are used to reduce or prevent the detrimental effects of flood waters."Flood Control", MSN Encarta, 2008 (see below: Further reading). Flood relief methods are used to reduce the effects of flood waters or high water level ...
mechanisms. By that time local communities had become wary of federal hydroelectric projects, and sought local control of new developments; a public utility district in Grant County, Washington, ultimately began construction of the dam at Priest Rapids.
In the 1960s, the United States and Canada signed the Columbia River Treaty, which focused on flood control and the maximization of downstream power generation. Canada agreed to build dams and provide reservoir storage, and the United States agreed to deliver to Canada one-half of the increase in US downstream power benefits as estimated five years in advance. Canada's obligation was met by building three dams (two on the Columbia, and one on the Duncan River (British Columbia), Duncan River), the last of which was completed in 1973.
Today the main stem of the Columbia River has 14 dams, of which three are in Canada and 11 in the US. Four mainstem dams and four lower Snake River dams contain navigation locks to allow ship and barge passage from the ocean as far as Lewiston, Idaho. The river system as a whole has more than 400 dams for hydroelectricity and irrigation. The dams address a variety of demands, including flood control, navigation, stream flow regulation, storage and delivery of stored waters, land reclamation, reclamation of public lands and Indian reservations, and the generation of hydroelectric power.
The larger U.S. dams are owned and operated by the federal government (some by the Army Corps of Engineers and some by the Bureau of Reclamation), while the smaller dams are operated by public utility districts, and private power companies. The federally operated system is known as the Federal Columbia River Power System, which includes 31 dams on the Columbia and its List of tributaries of the Columbia River, tributaries. The system has altered the seasonal flow of the river in order to meet higher electricity demands during the winter. At the beginning of the 20th century, roughly 75 percent of the Columbia's flow occurred in the summer, between April and September. By 1980, the summer proportion had been lowered to about 50 percent, essentially eliminating the seasonal pattern.
The installation of dams dramatically altered the landscape and ecosystem of the river. At one time, the Columbia was one of the top salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the ...
-producing river systems in the world. Previously active fishing sites, such as Celilo Falls in the eastern Columbia River Gorge, have exhibited a sharp decline in fishing along the Columbia in the last century, and salmon populations have been dramatically reduced. Fish ladders have been installed at some dam sites to help the fish journey to spawning waters. Chief Joseph Dam has no fish ladders and completely blocks fish migration to the upper half of the Columbia River system.
Irrigation
 The Bureau of Reclamation's Columbia Basin Project focused on the generally dry region of central Washington known as the Columbia Basin, which features rich loess soil. Several groups developed competing proposals, and in 1933, President Franklin D. Roosevelt authorized the Columbia Basin Project. The Grand Coulee Dam was the project's central component; upon completion, it pumped water up from the Columbia to fill the formerly dry Grand Coulee, forming Banks Lake. By 1935, the intended height of the dam was increased from a range between to , a height that would extend the lake impounded by the dam all the way to the Canada–US border; the project had grown from a local New Deal relief measure to a major national project.
The project's initial purpose was irrigation, but the onset of World War II created a high demand for electricity, mainly for aluminum production and for the development of
The Bureau of Reclamation's Columbia Basin Project focused on the generally dry region of central Washington known as the Columbia Basin, which features rich loess soil. Several groups developed competing proposals, and in 1933, President Franklin D. Roosevelt authorized the Columbia Basin Project. The Grand Coulee Dam was the project's central component; upon completion, it pumped water up from the Columbia to fill the formerly dry Grand Coulee, forming Banks Lake. By 1935, the intended height of the dam was increased from a range between to , a height that would extend the lake impounded by the dam all the way to the Canada–US border; the project had grown from a local New Deal relief measure to a major national project.
The project's initial purpose was irrigation, but the onset of World War II created a high demand for electricity, mainly for aluminum production and for the development of nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
s at the Hanford Site. Irrigation began in 1951. The project provides water to more than of fertile but arid land in central Washington, transforming the region into a major agricultural center. Important crops include orchard fruit, potatoes, alfalfa, mentha, mint, beans, beets, and wine grapes.
Since 1750, the Columbia has experienced six multi-year droughts. The longest, lasting 12 years in the mid‑19th century, reduced the river's flow to 20 percent below average. Scientists have expressed concern that a similar drought would have grave consequences in a region so dependent on the Columbia. In 1992–1993, a lesser drought affected farmers, hydroelectric power producers, shippers, and wildlife managers.
Many farmers in central Washington build dams on their property for irrigation and to control frost on their crops. The Washington Department of Ecology, using new techniques involving aerial photographs, estimated there may be as many as a hundred such dams in the area, most of which are illegal. Six such dams have failed in recent years, causing hundreds of thousands of dollars of damage to crops and public roads. Fourteen farms in the area have gone through the permitting process to build such dams legally.
Hydroelectricity
The Columbia's heavy flow and large elevation drop over a short distance, , give it tremendous capacity for hydroelectricity generation. In comparison, theMississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
drops less than . The Columbia alone possesses one-third of the United States's hydroelectric potential. In 2012, the river and its tributaries accounted for 29 Gigawatt, GW of hydroelectric generating capacity, contributing 44 percent of the total hydroelectric generation in the nation.
 The largest of the 150 hydroelectric projects, the Grand Coulee Dam and the Chief Joseph Dam, are also the largest in the United States. As of 2017, Grand Coulee is the fifth largest hydroelectric plant in the world.
Inexpensive hydropower supported the location of a large aluminum industry in the region, because its Aluminium production, reduction from bauxite requires large amounts of electricity. Until 2000, the Northwestern United States produced up to 17 percent of the world's aluminum and 40 percent of the aluminum produced in the United States. The commoditization of power in the early 21st century, coupled with drought that reduced the generation capacity of the river, damaged the industry and by 2001, Columbia River aluminum producers had idled 80 percent of its production capacity. By 2003, the entire United States produced only 15 percent of the world's aluminum, and many smelters along the Columbia had gone dormant or out of business.
Power remains relatively inexpensive along the Columbia, and since the mid-2000 several global enterprises have moved server farm operations into the area to avail themselves of cheap power. Downriver of Grand Coulee, each dam's reservoir is closely regulated by the Bonneville Power Administration (BPA), the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, and various Washington public utility districts to ensure flow, flood control, and power generation objectives are met. Increasingly, hydro-power operations are required to meet standards under the US Endangered Species Act and other agreements to manage operations to minimize impacts on salmon and other fish, and some conservation and fishing groups support removing four dams on the lower Snake River, the largest tributary of the Columbia.
In 1941, the BPA hired Oklahoma folksinger Woody Guthrie to write songs for a documentary film promoting the benefits of hydropower. In the month he spent traveling the region Guthrie wrote The Columbia River Collection, 26 songs, which have become an important part of the cultural history of the region.
The largest of the 150 hydroelectric projects, the Grand Coulee Dam and the Chief Joseph Dam, are also the largest in the United States. As of 2017, Grand Coulee is the fifth largest hydroelectric plant in the world.
Inexpensive hydropower supported the location of a large aluminum industry in the region, because its Aluminium production, reduction from bauxite requires large amounts of electricity. Until 2000, the Northwestern United States produced up to 17 percent of the world's aluminum and 40 percent of the aluminum produced in the United States. The commoditization of power in the early 21st century, coupled with drought that reduced the generation capacity of the river, damaged the industry and by 2001, Columbia River aluminum producers had idled 80 percent of its production capacity. By 2003, the entire United States produced only 15 percent of the world's aluminum, and many smelters along the Columbia had gone dormant or out of business.
Power remains relatively inexpensive along the Columbia, and since the mid-2000 several global enterprises have moved server farm operations into the area to avail themselves of cheap power. Downriver of Grand Coulee, each dam's reservoir is closely regulated by the Bonneville Power Administration (BPA), the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, and various Washington public utility districts to ensure flow, flood control, and power generation objectives are met. Increasingly, hydro-power operations are required to meet standards under the US Endangered Species Act and other agreements to manage operations to minimize impacts on salmon and other fish, and some conservation and fishing groups support removing four dams on the lower Snake River, the largest tributary of the Columbia.
In 1941, the BPA hired Oklahoma folksinger Woody Guthrie to write songs for a documentary film promoting the benefits of hydropower. In the month he spent traveling the region Guthrie wrote The Columbia River Collection, 26 songs, which have become an important part of the cultural history of the region.
Ecology and environment
Fish migration
 The Columbia supports several species of
The Columbia supports several species of anadromous
Fish migration is mass relocation by fish from one area or body of water to another. Many types of fish migrate on a regular basis, on time scales ranging from daily to annually or longer, and over distances ranging from a few metres to thousan ...
fish that migrate between the Pacific Ocean and fresh water tributaries of the river. Sockeye salmon, Coho salmon, Coho and Chinook salmon, Chinook (also known as "king") salmon, and Rainbow trout, steelhead, all of the genus ''Oncorhynchus'', are ocean fish that migrate up the rivers at the end of their life cycles to spawn. White sturgeon, which take 15 to 25 years to mature, typically migrate between the ocean and the upstream habitat several times during their lives.
Salmon populations declined dramatically after the establishment of salmon cannery, canneries in 1867. In 1879 it was reported that 545,450 salmon, with an average weight of were caught (in a recent season) and mainly canned for export to England. A can weighing could be sold for penny (British pre-decimal coin), 8d or 9d. By 1908, there was widespread concern about the decline of salmon and sturgeon. In that year, the people of Oregon passed two laws under their newly instituted program of Oregon System, citizens' initiatives limiting fishing on the Columbia and other rivers. Then in 1948, another initiative banned the use of seine fishing, seine nets (devices already used by Native Americans, and refined by later settlers) altogether.
Dams interrupt the migration of anadromous fish. Salmon and steelhead return to the streams in which they were born to spawn; where dams prevent their return, entire populations of salmon die. Some of the Columbia and Snake River dams employ fish ladders, which are effective to varying degrees at allowing these fish to travel upstream. Another problem exists for the juvenile salmon headed downstream to the ocean. Previously, this journey would have taken two to three weeks. With river currents slowed by the dams, and the Columbia converted from wild river to a series of slackwater pools, the journey can take several months, which increases the mortality rate. In some cases, the Army Corps of Engineers transports juvenile fish downstream by truck or river barge. The Chief Joseph Dam and several dams on the Columbia's tributaries entirely block migration, and there are no migrating fish on the river above these dams. Sturgeon have different migration habits and can survive without ever visiting the ocean. In many upstream areas cut off from the ocean by dams, sturgeon simply live upstream of the dam.
Not all fish have suffered from the modifications to the river; the northern pikeminnow (formerly known as the ''squawfish'') thrives in the warmer, slower water created by the dams. Research in the mid-1980s found that juvenile salmon were suffering substantially from the predatory pikeminnow, and in 1990, in the interest of protecting salmon, a "bounty" program was established to reward anglers for catching pikeminnow.
In 1994, the salmon catch was smaller than usual in the rivers of Oregon, Washington, and British Columbia, causing concern among commercial fishermen, government agencies, and tribal leaders. US government intervention, to which the states of Alaska, Idaho, and Oregon objected, included an 11-day closure of an Alaska fishery. In April 1994 the U.S. Regional Fishery Management Councils, Pacific Fisheries Management Council unanimously approved the strictest regulations in 18 years, banning all commercial salmon fishing for that year from Cape Falcon, Oregon, Cape Falcon north to the Canada–US border. In the winter of 1994, the return of coho salmon far exceeded expectations, which was attributed in part to the fishing ban.
Also in 1994, United States Secretary of the Interior Bruce Babbitt first proposed the removal of several Pacific Northwest dams because of their impact on salmon spawning. The Northwest Power and Conservation Council, Northwest Power Planning Council approved a plan that provided more water for fish and less for electricity, irrigation, and transportation. Environmental advocates have called for the removal of certain dams in the Columbia system in the years since. Of the 227 major dams in the Columbia River drainage basin, the four Washington dams on the lower Snake River are often identified for removal, for example in an ongoing lawsuit concerning a Presidency of George W. Bush, Bush administration plan for salmon recovery. These dams and reservoirs limit the recovery of upriver salmon runs to Idaho's Salmon and Clearwater rivers. Historically, the Snake produced over 1.5 million spring and summer Chinook salmon, a number that has dwindled to several thousand in recent years. Idaho Power, Idaho Power Company's Hells Canyon dams have no fish ladders (and do not pass juvenile salmon downstream), and thus allow no steelhead or salmon to migrate above Hells Canyon. In 2007, the destruction of the Bull Run Hydroelectric Project, Marmot Dam on the Sandy River was the first dam removal in the system. Other Columbia Basin dams that have been removed include Condit Hydroelectric Project, Condit Dam on Washington's White Salmon River, and the Milltown Dam on the Clark Fork (river), Clark Fork in Montana.
Pollution
In southeastern Washington, a stretch of the river passes through theHanford Site
The Hanford Site is a decommissioned nuclear production complex operated by the United States federal government on the Columbia River in Benton County in the U.S. state of Washington. The site has been known by many names, including SiteW a ...
, established in 1943 as part of the Manhattan Project. The site served as a plutonium production complex, with nine nuclear reactors and related facilities along the banks of the river. From 1944 to 1971, pump systems drew cooling water from the river and, after treating this water for use by the reactors, returned it to the river. Before being released back into the river, the used water was held in large tanks known as retention basins for up to six hours. Longer-lived isotopes were not affected by this retention, and several becquerel, terabecquerels entered the river every day. By 1957, the eight plutonium production reactors at Hanford dumped a daily average of 50,000 Curie (unit), curies of radioactive material into the Columbia. These releases were kept secret by the federal government until the release of declassified documents in the late 1980s. Radiation was measured downstream as far west as the Washington and Oregon coasts.
 The nuclear reactors were decommissioned at the end of the Cold War, and the Hanford site is the focus of one of the world's largest environmental remediation, environmental cleanup, managed by the United States Department of Energy, Department of Energy under the oversight of the Washington Department of Ecology and the United States Environmental Protection Agency, Environmental Protection Agency. Nearby aquifers contain an estimated 270 billion US gallons (1 billion m3) of groundwater contaminated by high-level nuclear waste that has leaked out of Hanford's underground storage tanks. , 1 million US gallons (3,785 m3) of highly radioactive waste is traveling through groundwater toward the Columbia River. This waste is expected to reach the river in 12 to 50 years if cleanup does not proceed on schedule.
In addition to concerns about nuclear waste, numerous other pollutants are found in the river. These include chemical pesticides, bacteria, arsenic, dioxins, and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB).
Studies have also found significant levels of toxins in fish and the waters they inhabit within the basin. Accumulation of toxins in fish threatens the survival of fish species, and human consumption of these fish can lead to health problems. Water quality is also an important factor in the survival of other wildlife and plants that grow in the Columbia River drainage basin. The states, Indian tribes, and federal government are all engaged in efforts to restore and improve the water, land, and air quality of the Columbia River drainage basin and have committed to work together to enhance and accomplish critical ecosystem restoration efforts. A number of cleanup efforts are currently underway, including Superfund projects at Portland Harbor, Hanford, and Lake Roosevelt.
Timber industry activity further contaminates river water, for example in the increased sediment runoff that results from clearcutting, clearcuts. The Northwest Forest Plan, a piece of federal legislation from 1994, mandated that timber companies consider the environmental impacts of their practices on rivers like the Columbia.
On July 1, 2003, Christopher Swain of Portland, Oregon, became the first person to swim the Columbia River's entire length, in an effort to raise public awareness about the river's environmental health.
The nuclear reactors were decommissioned at the end of the Cold War, and the Hanford site is the focus of one of the world's largest environmental remediation, environmental cleanup, managed by the United States Department of Energy, Department of Energy under the oversight of the Washington Department of Ecology and the United States Environmental Protection Agency, Environmental Protection Agency. Nearby aquifers contain an estimated 270 billion US gallons (1 billion m3) of groundwater contaminated by high-level nuclear waste that has leaked out of Hanford's underground storage tanks. , 1 million US gallons (3,785 m3) of highly radioactive waste is traveling through groundwater toward the Columbia River. This waste is expected to reach the river in 12 to 50 years if cleanup does not proceed on schedule.
In addition to concerns about nuclear waste, numerous other pollutants are found in the river. These include chemical pesticides, bacteria, arsenic, dioxins, and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB).
Studies have also found significant levels of toxins in fish and the waters they inhabit within the basin. Accumulation of toxins in fish threatens the survival of fish species, and human consumption of these fish can lead to health problems. Water quality is also an important factor in the survival of other wildlife and plants that grow in the Columbia River drainage basin. The states, Indian tribes, and federal government are all engaged in efforts to restore and improve the water, land, and air quality of the Columbia River drainage basin and have committed to work together to enhance and accomplish critical ecosystem restoration efforts. A number of cleanup efforts are currently underway, including Superfund projects at Portland Harbor, Hanford, and Lake Roosevelt.
Timber industry activity further contaminates river water, for example in the increased sediment runoff that results from clearcutting, clearcuts. The Northwest Forest Plan, a piece of federal legislation from 1994, mandated that timber companies consider the environmental impacts of their practices on rivers like the Columbia.
On July 1, 2003, Christopher Swain of Portland, Oregon, became the first person to swim the Columbia River's entire length, in an effort to raise public awareness about the river's environmental health.
Nutrient cycle
Both natural and Human impact on the environment, anthropogenic processes are involved in the nutrient cycle, cycling of nutrients in the Columbia River basin. Natural processes in the system include Estuary, estuarine mixing of fresh and ocean waters, and climate variability patterns such as the Pacific Decadal Oscillation and the El Niño–Southern Oscillation, El Nino Southern Oscillation (both climatic cycles that affect the amount of regional snowpack and river discharge). Natural sources of nutrients in the Columbia River include weathering, leaf litter,salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the ...
carcasses, runoff from its Tributary, tributaries, and Estuarine water circulation, ocean estuary exchange. Major anthropogenic impacts to nutrients in the basin are due to fertilizers from agriculture, sewage systems, logging, and the construction of dams.
Nutrients dynamics vary in the river basin from the River source, headwaters to the main river and dams, to finally reaching the Columbia River Estuary, Columbia River estuary and ocean. Upstream in the headwaters, salmon run
''Salmon Run'' is a 1982 video game for the Atari 8-bit family created by Bill Williams and distributed via the Atari Program Exchange. ''Salmon Run'' was the first game in Williams's career, followed by a string of successes noted for their o ...
s are the main source of nutrients. Dams along the river impact nutrient cycling by increasing Residence time (fluid dynamics), residence time of nutrients, and reducing the transport of silicate to the estuary, which directly impacts diatoms, a type of phytoplankton. The dams are also a barrier to salmon migration, and can increase the amount of methane locally produced. The Columbia River estuary exports high rates of nutrients into the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
; with the exception of nitrogen, which is delivered into the estuary by ocean upwelling sources.
Watershed
 Most of the Columbia's drainage basin (which, at , is about the size of France) lies roughly between the Rocky Mountains on the east and the Cascade Mountains on the west. In the United States and Canada the term watershed is often used to mean drainage basin. The term ''Columbia Basin'' is used to refer not only to the entire drainage basin but also to subsets of the river's full watershed, such as the relatively flat and unforested area in eastern Washington bounded by the Cascades, the Rocky Mountains, and the Blue Mountains. Within the watershed are diverse landforms including mountains, arid plateaus, river valleys, rolling uplands, and deep gorges. Grand Teton National Park lies in the watershed, as well as parts of Yellowstone National Park, Glacier National Park (U.S.), Glacier National Park, Mount Rainier National Park, and North Cascades National Park. Canadian National Parks in the watershed include Kootenay National Park, Yoho National Park, Glacier National Park (Canada), Glacier National Park, and Mount Revelstoke National Park. Hells Canyon, the deepest gorge in North America, and the Columbia Gorge are in the watershed. Vegetation varies widely, ranging from Tsuga heterophylla, western hemlock and Thuja plicata, western redcedar in the moist regions to sagebrush in the arid regions. The watershed provides habitat for 609 known fish and wildlife species, including the bull trout, bald eagle, gray wolf, grizzly bear, and Canada lynx.
The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) divides the waters of the Columbia and its tributaries into three freshwater ecoregions, naming them Columbia Glaciated, Columbia Unglaciated, and Upper Snake. The Columbia Glaciated ecoregion, making up about a third of the total watershed, lies in the north and was covered with ice sheets during the Pleistocene. The ecoregion includes the mainstem Columbia north of the Snake River and tributaries such as the Yakima, Okanagan, Pend Oreille, Clark Fork, and Kootenay rivers. The effects of glacier, glaciation include a number of large lakes and a relatively low diversity of freshwater fish. The Upper Snake ecoregion is defined as the Snake River watershed above Shoshone Falls, which totally blocks fish migration. This region has 14 species of fish, many of which are endemism, endemic. The Columbia Unglaciated ecoregion makes up the rest of the watershed. It includes the mainstem Columbia below the Snake River and tributaries such as the Salmon, John Day, Deschutes, and lower Snake Rivers. Of the three ecoregions it is the richest in terms of freshwater species diversity. There are 35 species of fish, of which four are endemic. There are also high levels of mollusk endemism.
In 2016, over eight million people lived within the Columbia's drainage basin. Of this total about 3.5 million people lived in Oregon, 2.1 million in Washington, 1.7 million in Idaho, half a million in British Columbia, and 0.4 million in Montana. Population in the watershed has been rising for many decades and is projected to rise to about 10 million by 2030. The highest population densities are found west of the Cascade Mountains along the Interstate 5, I-5 corridor, especially in the Portland-Vancouver urban area. High densities are also found around Spokane, Washington, and Boise, Idaho. Although much of the watershed is rural and sparsely populated, areas with recreational and scenic values are growing rapidly. The central Oregon county of Deschutes County, Oregon, Deschutes is the fastest-growing in the state. Populations have also been growing just east of the Cascades in central Washington around the city of Yakima, Washington, Yakima and the Tri-Cities area. Projections for the coming decades assume growth throughout the watershed, including the interior. The Canadian part of the Okanagan subbasin is also growing rapidly.
Climate varies greatly from place to place within the watershed. Elevation ranges from sea level at the river mouth to more than in the mountains, and temperatures vary with elevation. The highest peak is Mount Rainier, at . High elevations have cold winters and short cool summers; interior regions are subject to great temperature variability and severe droughts. Over some of the watershed, especially west of the Cascade Mountains, precipitation maximums occur in winter, when Pacific storms come ashore. Atmospheric conditions block the flow of moisture in summer, which is generally dry except for occasional thunderstorms in the interior. In some of the eastern parts of the watershed, especially shrub-steppe regions with Continental climate patterns, precipitation maximums occur in early summer. Annual precipitation varies from more than a year in the Cascades to less than in the interior. Much of the watershed gets less than a year.
Several major North American drainage basins and many minor ones share a common border with the Columbia River's drainage basin. To the east, in northern Wyoming and Montana, the Continental Divide separates the Columbia watershed from the Mississippi-Missouri watershed, which empties into the Gulf of Mexico. To the northeast, mostly along the southern border between British Columbia and Alberta, the Continental Divide separates the Columbia watershed from the Nelson River, Nelson-Lake Winnipeg-Saskatchewan River, Saskatchewan watershed, which empties into Hudson Bay. The Mississippi and Nelson watersheds are separated by the Laurentian Divide, which meets the Continental Divide at Triple Divide Peak (Montana), Triple Divide Peak near the headwaters of the Columbia's Flathead River tributary. This point marks the meeting of three of North America's main drainage patterns, to the Pacific Ocean, to Hudson Bay, and to the Atlantic Ocean via the Gulf of Mexico.
Further north along the Continental Divide, a short portion of the combined Continental and Laurentian divides separate the Columbia watershed from the MacKenzie River, MacKenzie-Slave River, Slave-Athabasca River, Athabasca watershed, which empties into the Arctic Ocean. The Nelson and Mackenzie watersheds are separated by a divide between streams flowing to the Arctic Ocean and those of the List of Hudson Bay rivers, Hudson Bay watershed. This divide meets the Continental Divide at Snow Dome (Canada), Snow Dome (also known as Dome), near the northernmost bend of the Columbia River.
To the southeast, in western Wyoming, another divide separates the Columbia watershed from the Colorado River, Colorado–Green River (Colorado River), Green watershed, which empties into the Gulf of California. The Columbia, Colorado, and Mississippi watersheds meet at Three Waters Mountain in the Wind River Range of . To the south, in Oregon, Nevada, Utah, Idaho, and Wyoming, the Columbia watershed is divided from the Great Basin, whose several watersheds are endorheic basin, endorheic, not emptying into any ocean but rather drying up or sinking into sumps. Great Basin watersheds that share a border with the Columbia watershed include Harney Basin, Humboldt River, and Great Salt Lake. The associated triple divide points are Commissary Ridge North, Wyoming, and Sproats Meadow Northwest, Oregon. To the north, mostly in British Columbia, the Columbia watershed borders the Fraser River watershed. To the west and southwest the Columbia watershed borders a number of smaller watersheds that drain to the Pacific Ocean, such as the Klamath River in Oregon and California and the Puget Sound Basin in Washington.
Most of the Columbia's drainage basin (which, at , is about the size of France) lies roughly between the Rocky Mountains on the east and the Cascade Mountains on the west. In the United States and Canada the term watershed is often used to mean drainage basin. The term ''Columbia Basin'' is used to refer not only to the entire drainage basin but also to subsets of the river's full watershed, such as the relatively flat and unforested area in eastern Washington bounded by the Cascades, the Rocky Mountains, and the Blue Mountains. Within the watershed are diverse landforms including mountains, arid plateaus, river valleys, rolling uplands, and deep gorges. Grand Teton National Park lies in the watershed, as well as parts of Yellowstone National Park, Glacier National Park (U.S.), Glacier National Park, Mount Rainier National Park, and North Cascades National Park. Canadian National Parks in the watershed include Kootenay National Park, Yoho National Park, Glacier National Park (Canada), Glacier National Park, and Mount Revelstoke National Park. Hells Canyon, the deepest gorge in North America, and the Columbia Gorge are in the watershed. Vegetation varies widely, ranging from Tsuga heterophylla, western hemlock and Thuja plicata, western redcedar in the moist regions to sagebrush in the arid regions. The watershed provides habitat for 609 known fish and wildlife species, including the bull trout, bald eagle, gray wolf, grizzly bear, and Canada lynx.
The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) divides the waters of the Columbia and its tributaries into three freshwater ecoregions, naming them Columbia Glaciated, Columbia Unglaciated, and Upper Snake. The Columbia Glaciated ecoregion, making up about a third of the total watershed, lies in the north and was covered with ice sheets during the Pleistocene. The ecoregion includes the mainstem Columbia north of the Snake River and tributaries such as the Yakima, Okanagan, Pend Oreille, Clark Fork, and Kootenay rivers. The effects of glacier, glaciation include a number of large lakes and a relatively low diversity of freshwater fish. The Upper Snake ecoregion is defined as the Snake River watershed above Shoshone Falls, which totally blocks fish migration. This region has 14 species of fish, many of which are endemism, endemic. The Columbia Unglaciated ecoregion makes up the rest of the watershed. It includes the mainstem Columbia below the Snake River and tributaries such as the Salmon, John Day, Deschutes, and lower Snake Rivers. Of the three ecoregions it is the richest in terms of freshwater species diversity. There are 35 species of fish, of which four are endemic. There are also high levels of mollusk endemism.
In 2016, over eight million people lived within the Columbia's drainage basin. Of this total about 3.5 million people lived in Oregon, 2.1 million in Washington, 1.7 million in Idaho, half a million in British Columbia, and 0.4 million in Montana. Population in the watershed has been rising for many decades and is projected to rise to about 10 million by 2030. The highest population densities are found west of the Cascade Mountains along the Interstate 5, I-5 corridor, especially in the Portland-Vancouver urban area. High densities are also found around Spokane, Washington, and Boise, Idaho. Although much of the watershed is rural and sparsely populated, areas with recreational and scenic values are growing rapidly. The central Oregon county of Deschutes County, Oregon, Deschutes is the fastest-growing in the state. Populations have also been growing just east of the Cascades in central Washington around the city of Yakima, Washington, Yakima and the Tri-Cities area. Projections for the coming decades assume growth throughout the watershed, including the interior. The Canadian part of the Okanagan subbasin is also growing rapidly.
Climate varies greatly from place to place within the watershed. Elevation ranges from sea level at the river mouth to more than in the mountains, and temperatures vary with elevation. The highest peak is Mount Rainier, at . High elevations have cold winters and short cool summers; interior regions are subject to great temperature variability and severe droughts. Over some of the watershed, especially west of the Cascade Mountains, precipitation maximums occur in winter, when Pacific storms come ashore. Atmospheric conditions block the flow of moisture in summer, which is generally dry except for occasional thunderstorms in the interior. In some of the eastern parts of the watershed, especially shrub-steppe regions with Continental climate patterns, precipitation maximums occur in early summer. Annual precipitation varies from more than a year in the Cascades to less than in the interior. Much of the watershed gets less than a year.
Several major North American drainage basins and many minor ones share a common border with the Columbia River's drainage basin. To the east, in northern Wyoming and Montana, the Continental Divide separates the Columbia watershed from the Mississippi-Missouri watershed, which empties into the Gulf of Mexico. To the northeast, mostly along the southern border between British Columbia and Alberta, the Continental Divide separates the Columbia watershed from the Nelson River, Nelson-Lake Winnipeg-Saskatchewan River, Saskatchewan watershed, which empties into Hudson Bay. The Mississippi and Nelson watersheds are separated by the Laurentian Divide, which meets the Continental Divide at Triple Divide Peak (Montana), Triple Divide Peak near the headwaters of the Columbia's Flathead River tributary. This point marks the meeting of three of North America's main drainage patterns, to the Pacific Ocean, to Hudson Bay, and to the Atlantic Ocean via the Gulf of Mexico.
Further north along the Continental Divide, a short portion of the combined Continental and Laurentian divides separate the Columbia watershed from the MacKenzie River, MacKenzie-Slave River, Slave-Athabasca River, Athabasca watershed, which empties into the Arctic Ocean. The Nelson and Mackenzie watersheds are separated by a divide between streams flowing to the Arctic Ocean and those of the List of Hudson Bay rivers, Hudson Bay watershed. This divide meets the Continental Divide at Snow Dome (Canada), Snow Dome (also known as Dome), near the northernmost bend of the Columbia River.
To the southeast, in western Wyoming, another divide separates the Columbia watershed from the Colorado River, Colorado–Green River (Colorado River), Green watershed, which empties into the Gulf of California. The Columbia, Colorado, and Mississippi watersheds meet at Three Waters Mountain in the Wind River Range of . To the south, in Oregon, Nevada, Utah, Idaho, and Wyoming, the Columbia watershed is divided from the Great Basin, whose several watersheds are endorheic basin, endorheic, not emptying into any ocean but rather drying up or sinking into sumps. Great Basin watersheds that share a border with the Columbia watershed include Harney Basin, Humboldt River, and Great Salt Lake. The associated triple divide points are Commissary Ridge North, Wyoming, and Sproats Meadow Northwest, Oregon. To the north, mostly in British Columbia, the Columbia watershed borders the Fraser River watershed. To the west and southwest the Columbia watershed borders a number of smaller watersheds that drain to the Pacific Ocean, such as the Klamath River in Oregon and California and the Puget Sound Basin in Washington.
Major tributaries
 The Columbia receives more than 60 significant tributary, tributaries. The four largest that empty directly into the Columbia (measured either by discharge (hydrology), discharge or by size of watershed) are the Snake River (mostly in Idaho), the Willamette River (in northwest Oregon), the Kootenay River (mostly in British Columbia), and the Pend Oreille River (mostly in northern Washington and Idaho, also known as the lower part of the Clark Fork). Each of these four averages more than and drains an area of more than .
The Snake is by far the largest tributary. Its watershed of is larger than the state of Idaho. Its discharge is roughly a third of the Columbia's at the rivers' confluence but compared to the Columbia upstream of the confluence the Snake is longer (113%) and has a larger drainage basin (104%).
The Pend Oreille River system (including its main tributaries, the Clark Fork and Flathead rivers) is also similar in size to the Columbia at their confluence. Compared to the Columbia River above the two rivers' confluence, the Pend Oreille-Clark-Flathead is nearly as long (about 86%), its basin about three-fourths as large (76%), and its discharge over a third (37%).Calculated mainly with data from:
The Columbia receives more than 60 significant tributary, tributaries. The four largest that empty directly into the Columbia (measured either by discharge (hydrology), discharge or by size of watershed) are the Snake River (mostly in Idaho), the Willamette River (in northwest Oregon), the Kootenay River (mostly in British Columbia), and the Pend Oreille River (mostly in northern Washington and Idaho, also known as the lower part of the Clark Fork). Each of these four averages more than and drains an area of more than .
The Snake is by far the largest tributary. Its watershed of is larger than the state of Idaho. Its discharge is roughly a third of the Columbia's at the rivers' confluence but compared to the Columbia upstream of the confluence the Snake is longer (113%) and has a larger drainage basin (104%).
The Pend Oreille River system (including its main tributaries, the Clark Fork and Flathead rivers) is also similar in size to the Columbia at their confluence. Compared to the Columbia River above the two rivers' confluence, the Pend Oreille-Clark-Flathead is nearly as long (about 86%), its basin about three-fourths as large (76%), and its discharge over a third (37%).Calculated mainly with data from:

See also
* Columbia Park (Kennewick, Washington), a recreational area * Columbia River Estuary * Columbia River Maritime Museum, Astoria, Oregon * Empire Builder, an Amtrak rail line that follows the river from Portland to Pasco, Washington * Estella Mine, an abandoned mine with a view of the Columbia River Valley * Historic Columbia River Highway, a scenic highway on the Oregon side * List of crossings of the Columbia River * List of dams in the Columbia River watershed * List of longest rivers of Canada * List of longest rivers of the United States (by main stem) * List of longest streams of Oregon * Lists of ecoregions in List of ecoregions in North America (CEC), North America and List of ecoregions in Oregon, Oregon * Lists of rivers of List of rivers of British Columbia, British Columbia, List of rivers of Oregon, Oregon, and List of rivers of Washington, Washington * Okanagan Trail, a historic trail that followed the Columbia and Okanagan rivers * Robert Gray's Columbia River expeditionNotes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * (see s:en:The Columbia River: Its History, Its Myths, Its Scenery, Its Commerce, here for full online transcription) * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
BC Hydro
Bibliography on Water Resources and International Law
Peace Palace Library * *
Columbia River
US Environmental Protection Agency
Columbia River Gorge National Scenic Area
from the US Forest Service
Columbia River Inter-Tribal Fish Commission
* * , dating to the 17th century
University of Washington Libraries Digital Collections – Tollman and Canaris Photographs
Photographs document the salmon fishing industry on the southern Washington coast and in the lower Columbia River around the year 1897 and offer insights about commercial salmon fishing and the techniques used at the beginning of the 20th century.
''National Geographic'' via Internet Archive {{Featured article Columbia River, Columbia River Gorge, Borders of Oregon Borders of Washington (state) Drainage basins of the Pacific Ocean International rivers of North America Rivers of Benton County, Washington Rivers of British Columbia Rivers of Chelan County, Washington Rivers of Clark County, Washington Rivers of Clatsop County, Oregon Rivers of Cowlitz County, Washington Rivers of Franklin County, Washington Rivers of Hood River County, Oregon Rivers of Multnomah County, Oregon Rivers of Oregon Rivers of Wasco County, Oregon Rivers of Washington (state) Rivers of Douglas County, Washington Rivers with fish ladders