Climate change in Malaysia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 As of 2000, the largest sectoral contributor to
As of 2000, the largest sectoral contributor to 
 Existing environmental pressures on natural resources are expected to be exacerbated. Natural disasters already cause around $1.3 billion in damage annually, mostly due to flooding.
Temperatures rose by 0.14–0.25 °C per decade from 1970 to 2013. By 2090, they are projected to rise between an additional 0.8 °C and 3.11 °C depending on global emissions. There is little expected seasonal variation for temperature increase. However,
Existing environmental pressures on natural resources are expected to be exacerbated. Natural disasters already cause around $1.3 billion in damage annually, mostly due to flooding.
Temperatures rose by 0.14–0.25 °C per decade from 1970 to 2013. By 2090, they are projected to rise between an additional 0.8 °C and 3.11 °C depending on global emissions. There is little expected seasonal variation for temperature increase. However, 

Climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
is having a considerable impact in Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
. Increasing temperatures are likely to greatly increase the number of heatwave
A heat wave, or heatwave, is a period of excessively hot weather, which may be accompanied by high humidity, especially in oceanic climate countries. While definitions vary, a heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the ...
s occurring annually. Variations in precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
may increase the frequency of drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
s and floods
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrolog ...
in various local areas. Sea level rise
Globally, sea levels are rising due to human-caused climate change. Between 1901 and 2018, the globally averaged sea level rose by , or 1–2 mm per year on average.IPCC, 2019Summary for Policymakers InIPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cry ...
may inundate some coastal areas. These impacts are expected to have numerous environmental and socioeconomic effects, exacerbating existing environmental issues
Environmental issues are effects of human activity on the biophysical environment, most often of which are harmful effects that cause environmental degradation. Environmental protection is the practice of protecting the natural environment on t ...
and reinforcing inequality
Inequality may refer to:
Economics
* Attention inequality, unequal distribution of attention across users, groups of people, issues in etc. in attention economy
* Economic inequality, difference in economic well-being between population groups
* ...
.
Malaysia itself contributes emissions given its significant use of coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
and natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
. However, the use of hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to Electricity generation, produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by energy transformation, converting the Pot ...
has expanded in the 21st century, and other potential energy sources such as solar power
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic e ...
and biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
are being explored. The government anticipates the need to adapt in areas such as health and coastal defences, and has ratified the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (french: Accord de Paris), often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, Climate change a ...
.
Emissions
 As of 2000, the largest sectoral contributor to
As of 2000, the largest sectoral contributor to greenhouse gas emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions from human activities strengthen the greenhouse effect, contributing to climate change. Most is carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels: coal, oil, and natural gas. The largest emitters include coal in China and lar ...
was the energy sector
The energy industry is the totality of all of the industries involved in the production and sale of energy, including fuel extraction, manufacturing, refining and distribution. Modern society consumes large amounts of fuel, and the energy indust ...
, whose 58 million tonnes (Mt) of equivalent emissions made up 26% of the national total. This was followed by the transport sector with 36 Mt, or 16%. Other estimates put the energy sector as producing 55% of emissions in 2011, and 46% in 2013.
Fossil fuel
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels m ...
s remain the primary fuel for electricity generation. Demand for electricity grew 64% in the decade prior to 2017. In 2017, over 44% of electricity was produced from burning coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
, and 38% from natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
. The 17% produced through renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
came almost completely from hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to Electricity generation, produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by energy transformation, converting the Pot ...
, with other renewables producing just 0.5% of electricity. Coal usage has been increasing, overtaking natural gas usage in 2010. The percentage produced by natural gas has decreased from 57% in 1995, when coal produced only 9%. Most coal is imported, due to the high costs of mining domestic deposits. Much of this change is due to the amount of natural gas being used deliberately being maintained at its 2000 levels, leaving further demand to be taken up by coal as part of diversification. Natural gas production continued to increase, but was diverted to exports. At one point oil was a significant fuel for electricity generation, producing 21% of electricity in 1995, but as oil prices rose this decreased to 2% in 2010 and 0.6% in 2017.
Hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to Electricity generation, produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by energy transformation, converting the Pot ...
is concentrated in East Malaysia
East Malaysia (), or the Borneo States, also known as Malaysian Borneo, is the part of Malaysia on and near the island of Borneo, the world's third-largest island. Near the coast of Sabah is a small archipelago called Labuan. East Malaysia li ...
, although potential also exists in Perak
Perak () is a state of Malaysia on the west coast of the Malay Peninsula. Perak has land borders with the Malaysian states of Kedah to the north, Penang to the northwest, Kelantan and Pahang to the east, and Selangor to the south. Thailand's ...
and Pahang
Pahang (;Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , Pahang Hulu Malay: ''Paha'', Pahang Hilir Malay: ''Pahaeng'', Ulu Tembeling Malay: ''Pahaq)'' officially Pahang Darul Makmur with the Arabic honorific ''Darul Makmur'' (Jawi: , "The Abode of Tranquility") is a ...
. Despite the recent increase in coal use, no new coal capacity is expected under current plans, which instead target natural gas, and to a lesser extent solar and hydropower. and emissions decreased from 2010 to 2017, during a period of hydropower expansion, while the growth in emissions slowed.
Short-lived climate pollutants
The Climate and Clean Air Coalition to Reduce Short-Lived Climate Pollutants (CCAC) was launched by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and six countries—Bangladesh, Canada, Ghana, Mexico, Sweden, and the United States—on 16Februar ...
are related to high levels of air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types ...
in major cities.
Deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated d ...
, particularly for palm oil
Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil derived from the mesocarp (reddish pulp) of the fruit of the oil palms. The oil is used in food manufacturing, in beauty products, and as biofuel. Palm oil accounted for about 33% of global oils produced from ...
and natural rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and ...
production, is also a major contributor to the country's greenhouse gas emissions. A 2016 study estimated deforestation and land use change between 2010 and 2015 contributed to 22.1 million Mg annual CO2 emissions.
Impacts
 Existing environmental pressures on natural resources are expected to be exacerbated. Natural disasters already cause around $1.3 billion in damage annually, mostly due to flooding.
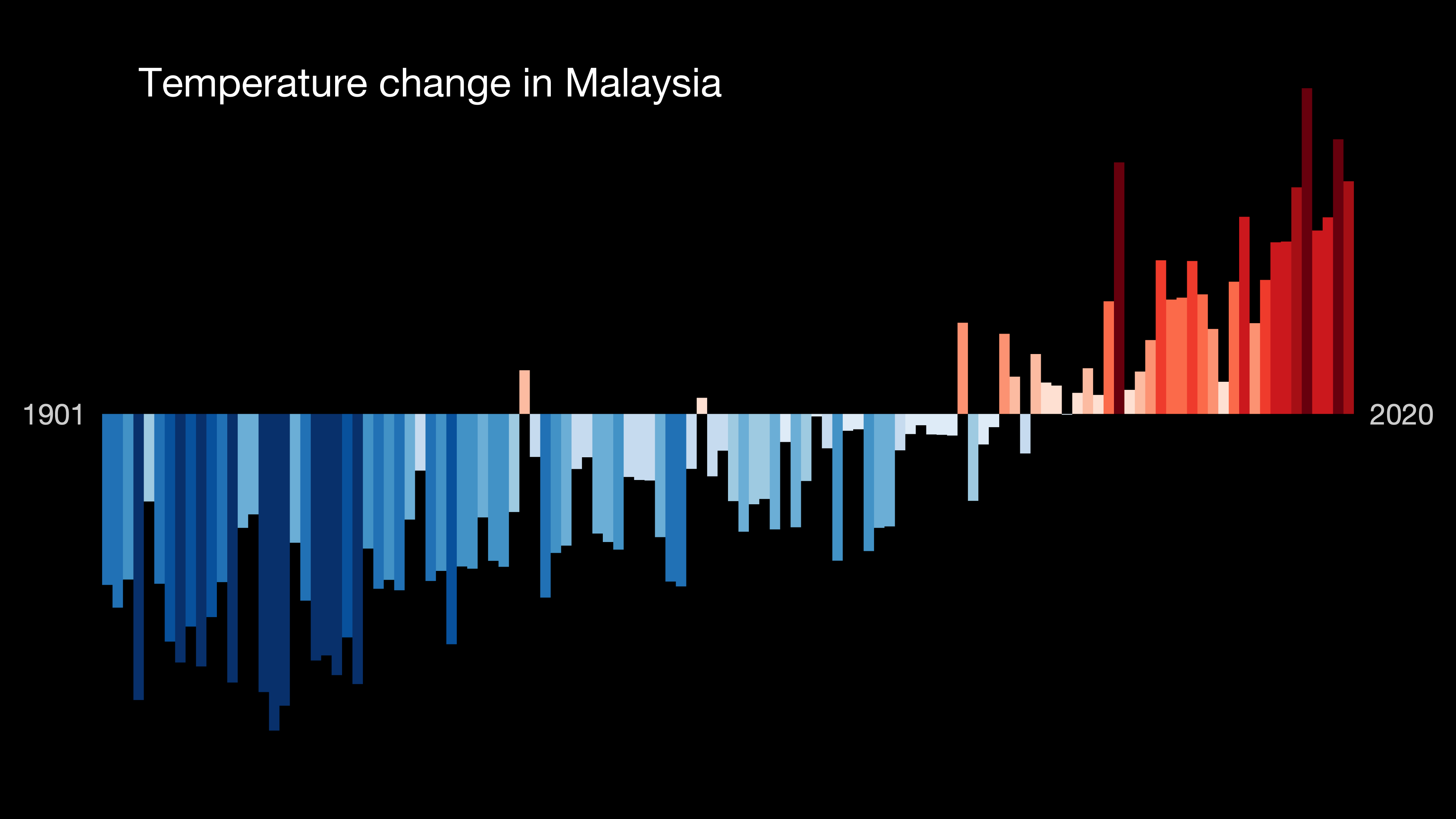
Temperatures rose by 0.14–0.25 °C per decade from 1970 to 2013. By 2090, they are projected to rise between an additional 0.8 °C and 3.11 °C depending on global emissions. There is little expected seasonal variation for temperature increase. However,
Existing environmental pressures on natural resources are expected to be exacerbated. Natural disasters already cause around $1.3 billion in damage annually, mostly due to flooding.
Temperatures rose by 0.14–0.25 °C per decade from 1970 to 2013. By 2090, they are projected to rise between an additional 0.8 °C and 3.11 °C depending on global emissions. There is little expected seasonal variation for temperature increase. However, heatwave
A heat wave, or heatwave, is a period of excessively hot weather, which may be accompanied by high humidity, especially in oceanic climate countries. While definitions vary, a heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the ...
s are expected to increase in frequency and intensity. Currently, a period of three days at the extreme high of expected temperatures has a 2% probability of occurring. Under high emissions scenarios, this will increase to 93%, reflecting the overall higher temperatures. Such high temperatures will worsen existing urban heat island
An urban heat island (UHI) is an urban or metropolitan area that is significantly warmer than its surrounding rural areas due to human activities. The temperature difference is usually larger at night than during the day, and is most apparen ...
s such as Kuala Lumpur
, anthem = '' Maju dan Sejahtera''
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, pushpin_map = Malaysia#Southeast Asia#Asia
, pushpin_map_caption =
, coordinates =
, su ...
, which can already reach temperatures higher than surrounding areas. Annual heat-related deaths among the elderly may go from less than 1 per 100,000 to 45 per 100,000 in high-emission scenarios. Coral bleaching
Coral bleaching is the process when corals become white due to various stressors, such as changes in temperature, light, or nutrients. Bleaching occurs when coral polyps expel the zooxanthellae (dinoflagellates that are commonly referred to as alg ...
is another expected effect, which will have both environmental and economic impacts.
A reliance on surface water leaves Malaysia vulnerable to precipitation changes, however models do not show significant expected changes, and Kelantan
Kelantan (; Jawi: ; Kelantanese Malay: ''Klate'') is a state in Malaysia. The capital is Kota Bharu and royal seat is Kubang Kerian. The honorific name of the state is ''Darul Naim'' (Jawi: ; "The Blissful Abode").
Kelantan is located in the ...
and Pahang
Pahang (;Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , Pahang Hulu Malay: ''Paha'', Pahang Hilir Malay: ''Pahaeng'', Ulu Tembeling Malay: ''Pahaq)'' officially Pahang Darul Makmur with the Arabic honorific ''Darul Makmur'' (Jawi: , "The Abode of Tranquility") is a ...
may see more water than they do at present. Rainfall is expected to increase, and more so in East Malaysia than Peninsular Malaysia. The precise magnitude of the increase varies between predictions, and between potential emissions scenarios. Under the scenarios predicting high levels of global emissions, the increase is expected to be around 12% above the current . Flooding, exacerbated by extreme rainfall events, is a present and growing risk. With no action taken, under a high emissions scenario floods may affect an average of 234,500 people annually between 2070 and 2100. Extreme rainfall events may deposit up to 32% more rain in 2090. In 2010, around 130,000 people in the country were exposed to potential 1-in-25-year flood events. Under high emissions, this will increase to 200,000 by 2030. Even in low emission scenarios, 1-in-100-year events are expected to become 1-in-25-year occurrences. Ecosystem degradation and the spread of urban areas have weakened natural flood resilience.
From 1993 to 2015, sea levels rose between and annually, depending on location. In the future, sea levels are expected to rise 0.4–0.7m, with East Malaysia being particularly vulnerable. Coastal agricultural areas are a noted area of risk, and current mangrove habitats may disappear by 2060. Such a rise will increase the impact of typhoon
A typhoon is a mature tropical cyclone that develops between 180° and 100°E in the Northern Hemisphere. This region is referred to as the Northwestern Pacific Basin, and is the most active tropical cyclone basin on Earth, accounting for a ...
s, which themselves may be increased in intensity. This brings risk to current ecotourism
Ecotourism is a form of tourism involving responsible travel (using sustainable transport) to natural areas, conserving the environment, and improving the well-being of the local people. Its purpose may be to educate the traveler, to provide funds ...
in coastal areas.

Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
is further threatened by droughts and floods
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrolog ...
. Rice yields may decline by 60%. Other potentially impacted products include rubber, palm oil, and cocoa. Annual drought probability, which currently lies at 4%, may increase to 9%. Such probability varies by locality, being most likely in Sabah
Sabah () is a States and federal territories of Malaysia, state of Malaysia located in northern Borneo, in the region of East Malaysia. Sabah borders the Malaysian state of Sarawak to the southwest and the North Kalimantan province of Indone ...
. Overall, precipitation changes will have a more significant impact on agriculture than temperature changes.
Communities most exposed to the impact of climate change are poorer, including those involved in manual labour, agriculture, and fisheries. The impacts of climate change are thus expected to reinforce existing inequality, both in impact and in the ability to adapt.
Mitigation
TheInternational Renewable Energy Agency
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) is an intergovernmental organization mandated to facilitate cooperation, advance knowledge, and promote the adoption and sustainable use of renewable energy. It is the first international organis ...
predicted in 2014 that Malaysia might reach just over 50% of its electricity production from renewables by 2030.
In 2021, the government announced the goal of reaching net zero emissions by 2050 in the Twelfth Malaysia Plan
The Twelfth Malaysia Plan ( Malay: ''Rancangan Malaysia Kedua Belas''), otherwise known as the 12th Malaysia Plan and abbreviated as "12MP", is a comprehensive blueprint prepared by the Economic Planning Unit (EPU) of the Prime Minister's Depart ...
. Prime Minister Ismail Sabri Yaakob
Dato' Sri Ismail Sabri bin Yaakob ( ms, اسماعيل صبري بن يعقوب, label= Jawi, script=arab, italic=unset; born 18 January 1960) is a Malaysian lawyer and politician who served as the 9th Prime Minister of Malaysia from August 2 ...
also said that Malaysia would not build any new coal power plants, would expand electric vehicle infrastructure
An electric vehicle charging network is an infrastructure system of charging stations to recharge electric vehicles. Many government, car manufacturers, and charging infrastructure providers sought to create networks. the largest fast-chargi ...
, and introduce a blue economic blueprint for coastal development.
An attempt to sell 2 million hectares of forest in Sabah as carbon offset
A carbon offset is a reduction or removal of emissions of carbon dioxide or other greenhouse gases made in order to compensate for emissions made elsewhere. Offsets are measured in tonnes of carbon dioxide-equivalent (CO2e). One ton of carbon ...
credits stalled in 2022 amid local opposition following a lack of consultation and questions as to where profits would go.
Adaptation
Climate resilience
Climate resilience is defined as the "capacity of social, economic and ecosystems to cope with a hazardous event or trend or disturbance".IPCC, 2022Summary for Policymakers .-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, M. Tignor, ...
measures were included in the Tenth and Eleventh Malaysia Plan
The Eleventh Malaysia Plan (11MP) ( Malay: ''Rancangan Malaysia ke-11'') 2016–2020 is Malaysia's five-year development plan towards realising the goal of Vision 2020. The preparation of the 11th Malaysia Plan is based on the National Developme ...
s. The government states it has invested in the health service in anticipation of an expected 144% increase in the population at risk of malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. S ...
, and expected increases in dengue
Dengue fever is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus. Symptoms typically begin three to fourteen days after infection. These may include a high fever, headache, vomiting, muscle and joint pains, and a characteristic ...
, diarrhoea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin wi ...
, and waterborne diseases
Waterborne diseases are conditions (meaning adverse effects on human health, such as death, disability, illness or disorders) caused by pathogenic micro-organisms that are transmitted in water. These diseases can be spread while bathing, washing ...
.
Adaptation measures such as improving dikes
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice
* Dikes, ...
would greatly reduce the impact of sea level rise on coastal communities within this century.
Policies
Malaysia ratified theUnited Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) established an international environmental treaty to combat "dangerous human interference with the climate system", in part by stabilizing greenhouse gas concentrations in th ...
in 1994, and the Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that (part ...
in 2002. A National Policy on Climate Change was enacted in 2009, along with a National Renewable Energy Policy. Around this time Malaysia pledged a 40% reduction in carbon intensity by 2020 compared to 2005, and the Renewable Energy Act was adopted in 2011 alongside the Sustainable Energy Development Authority Act.
In the late 20th century, energy policy centred around diversification for energy security
Energy security is the association between national security and the availability of natural resources for energy consumption. Access to (relatively) cheap energy has become essential to the functioning of modern economies. However, the uneven ...
. Renewable energy became more prominent in the 21st century, becoming part of official policy in the 2016–2020 Eleventh Malaysia Plan, alongside the 2016–2025 National Energy Efficiency Action Plan.
Malaysia ratified the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (french: Accord de Paris), often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, Climate change a ...
on 16 November 2016, while submitting its first Nationally Determined Contribution
A nationally determined contribution (NDC) or intended nationally determined contribution (INDC) is a non-binding national plan highlighting climate change mitigation, including climate-related targets for greenhouse gas emission reductions. These ...
. An Intended Nationally Determined Contribution had previously been submitted on 27 November 2015. The Second National Communication to the UNFCCC emphasises improved Water resource management
Water resources are natural resources of water that are potentially useful for humans, for example as a source of drinking water supply or irrigation water. 97% of the water on the Earth is Saline water, salt water and only three percent is fresh ...
.
In 2018, the government announced a target for 20% renewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
by 2025. Hydropower had grown from 5% of the energy mix in 2010 to 17% in 2017, matching much of the increased demand during that time. Solar power has become more used as its price has decreased, such as along the North–South Expressway. There is growing interest in biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
from agricultural waste.
Emission data collected by the Department of Environment is not publicly released.
See also
*Environmental issues in Malaysia
Malaysia faces several environmental issues. Malaysia's environment possesses megadiverse biological diversity, with globally significant endemism and biodiversity, but is threatened by several issues. Deforestation is a major issue in the countr ...
* Plug-in electric vehicles in Malaysia
, there were around 31,000 electric vehicles registered in Malaysia. , about 0.05% of new cars sold in Malaysia were electric.
Government policy
, electric vehicles are exempt from Malaysian road taxes.
, electric vehicles are exempt from all im ...
* Climate change in Indonesia
References
External links
* * * * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Climate Change in Malaysia Environmental issues in Malaysia