|
Floods In Malaysia
Floods in Malaysia are one of the most regular natural disasters affecting the country, which occurs nearly every year especially during the monsoon season. The coasts of peninsular Malaysia are the most prone to flooding especially during the northeast monsoon season from October to March. Notable floods * 10 December 1969 – Kluang flood. * January 1971 – Kuala Lumpur hit by flash floods. * 2 March 2006 – Shah Alam hit by flash floods. * 19 December 2006 – Several parts of Johor state including Muar, Johor Bahru, Skudai and Segamat were hit by flash floods. * 10 January 2007 – Several parts of Johor were hit by flash floods again. * 10 June 2007 – Kuala Lumpur hit by flash floods, worst since 10 June 2003. * December 2007 – Several parts of East Coast of Peninsula including Kelantan, Terengganu, Pahang and Johor were hit by flash floods. * November 2010 – Kedah and Perlis flooded due to heavy rainfall after a tropical depression. * December 2014 – Northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terengganu
Terengganu (; Terengganu Malay: ''Tranung'', Jawi: ), formerly spelled Trengganu or Tringganu, is a sultanate and constitutive state of federal Malaysia. The state is also known by its Arabic honorific, ''Dāru l- Īmān'' ("Abode of Faith"). The coastal city of Kuala Terengganu, which stands at the mouth of the broad Terengganu River, is both the state and royal capital as well as the largest city in Terengganu. There are many islands located close to the coast of Terengganu state, such as Perhentian Islands and Redang Island. Etymology There are several theories on the origin of the name "Terengganu". One theory attributes the name's origin to ''terang ganu'', Malay for 'bright rainbow'. Another story, said to have been originally narrated by the ninth Sultan of Terengganu, Baginda Omar, tells of a party of hunters from Pahang roving and hunting in the area of what is now southern Terengganu. One of the hunters spotted a big animal fang lying on the ground. A fellow part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
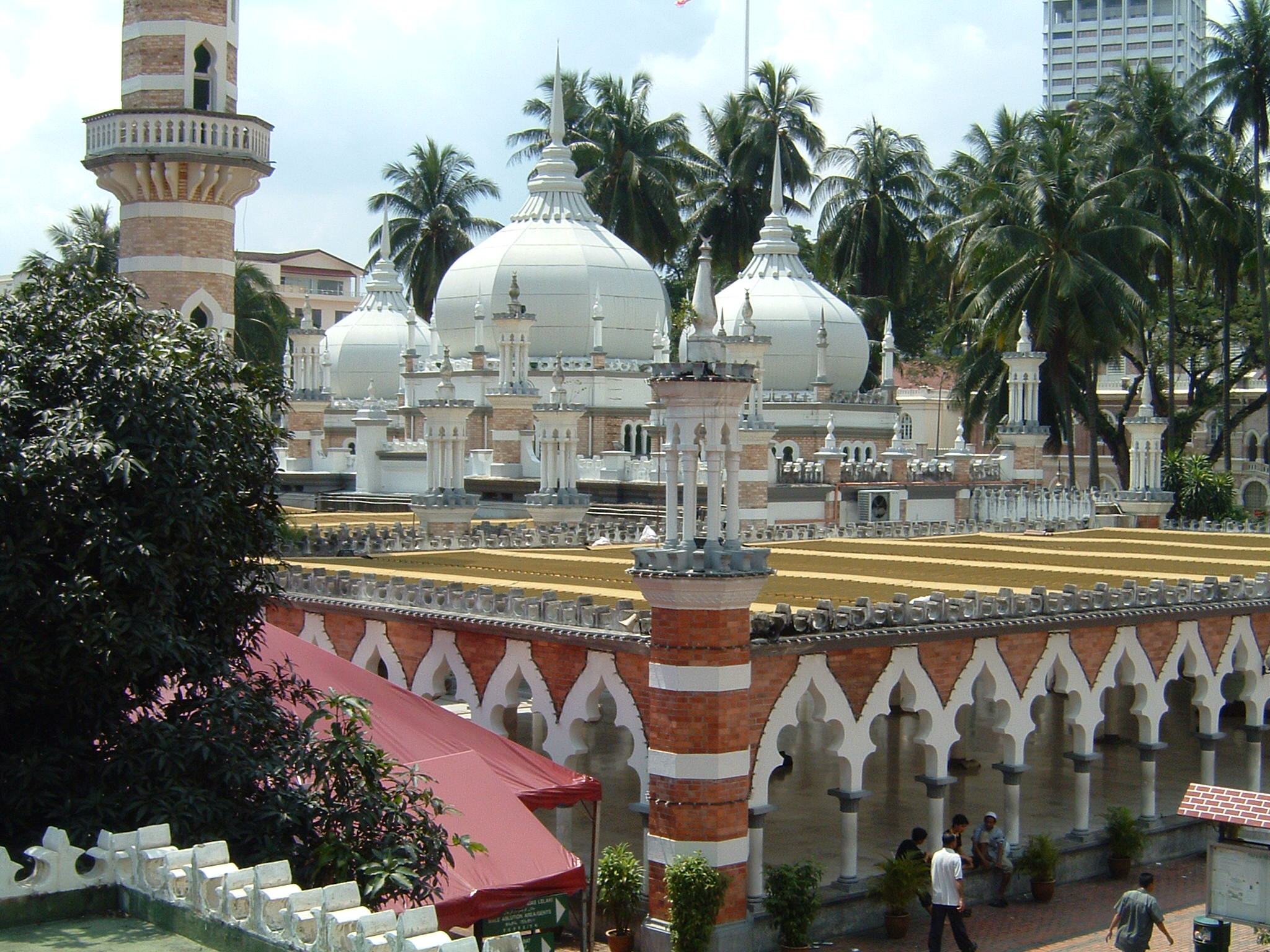
Masjid Jamek
Jamek Mosque, officially Sultan Abdul Samad Jamek Mosque ( ms, Masjid Jamek Sultan Abdul Samad) is one of the oldest mosques in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. It is located at the confluence of the Klang and Gombak River and may be accessed via Jalan Tun Perak. The mosque was designed by Arthur Benison Hubback, and built in 1909. The name "Jamek" is the Malay equivalent of the Arabic word ''jāmiʿ'' () meaning a place where people congregate to worship. It is also referred to as "Friday Mosque" by the locals. History The mosque was built on the location of an old Malay burial place at the confluence of Klang and Gombak River and named Jamek Mosque. A couple of mosques previously existed in the Java Street and Malay Street area serving the Malay communities, but Jamek Mosque was the first large mosque to be built in Kuala Lumpur. The foundation stone of the mosque was laid by the Sultan of Selangor, Sultan Sir Alaeddin Sulaiman Shah on 23 March 1908, and the Sultan officiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
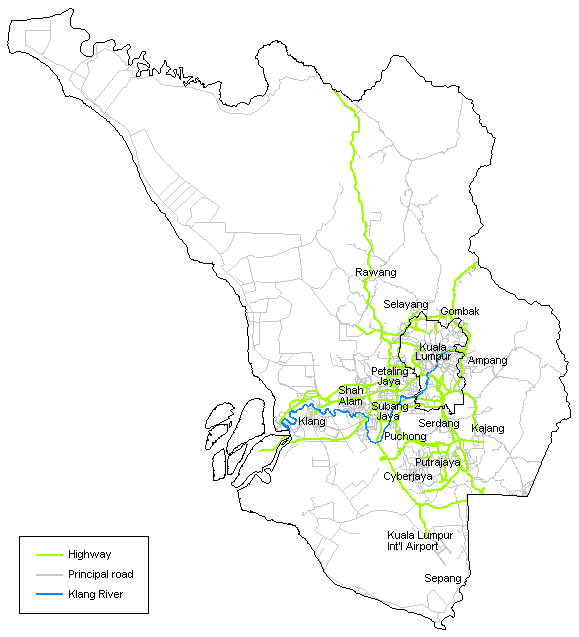
Klang Valley
Klang Valley ( ms, Lembah Klang; zh, 巴生谷; ) is an urban conglomeration in Malaysia that is centered in the federal territories of Kuala Lumpur and Putrajaya, and includes its adjoining cities and towns in the state of Selangor. It is conterminous with Greater Kuala Lumpur, although there are variations between the two. The Klang Valley is geographically delineated by the Titiwangsa Mountains to the north and east and the Strait of Malacca to the west. It extends to Rawang in the northwest, Semenyih in the southeast, and Klang and Port Klang in the southwest. The conurbation is the heartland of Malaysia's industry and commerce. As of 2020, the Klang Valley is home to roughly 8 million people. Origin The valley is named after the Klang River, the principal river that flows through it that starts at Klang Gates Quartz Ridge in Gombak and flows into the Straits of Malacca in Port Klang, The river is closely linked to the early development of the area as a cluster of tin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klang River
The Klang River ( ms, Sungai Klang) is a river which flows through Kuala Lumpur and Selangor in Malaysia and eventually flows into the Straits of Malacca. It is approximately in length and drains a basin of about . The Klang River has 11 major tributaries. Because the river flows through Klang Valley, which is a heavily populated area of more than four million people, it is considerably polluted, because of deep siltation caused by human waste from informal settlers of the riverbank and even from some business establishments without septic tanks or sewage treatment plants and by soil carried by mudflows from mountains. Heavy development has narrowed certain stretches of the river to the point that it resembles a large storm drain in some places. This contributes to flash floods in Kuala Lumpur, especially after heavy rain. Course , The Klang River originates from the Klang Gates Quartz Ridge in Gombak, near the border with Pahang, northeast of Kuala Lumpur. It is joine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extreme Weather
Extreme weather or extreme climate events includes unexpected, unusual, severe, or unseasonal weather; weather at the extremes of the historical distribution—the range that has been seen in the past. Often, extreme events are based on a location's recorded weather history and defined as lying in the most unusual ten percent. The main types of extreme weather include heat waves, cold waves and tropical cyclones. The effects of extreme weather events are seen in rising economic costs, loss of human lives, droughts, floods, landslides and changes in ecosystems. There is evidence to suggest that climate change is increasing the periodicity and intensity of some extreme weather events. Confidence in the attribution of extreme weather and other events to anthropogenic climate change is highest in changes in frequency or magnitude of extreme heat and cold events with some confidence in increases in heavy precipitation and increases in the intensity of droughts. Current evidence and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
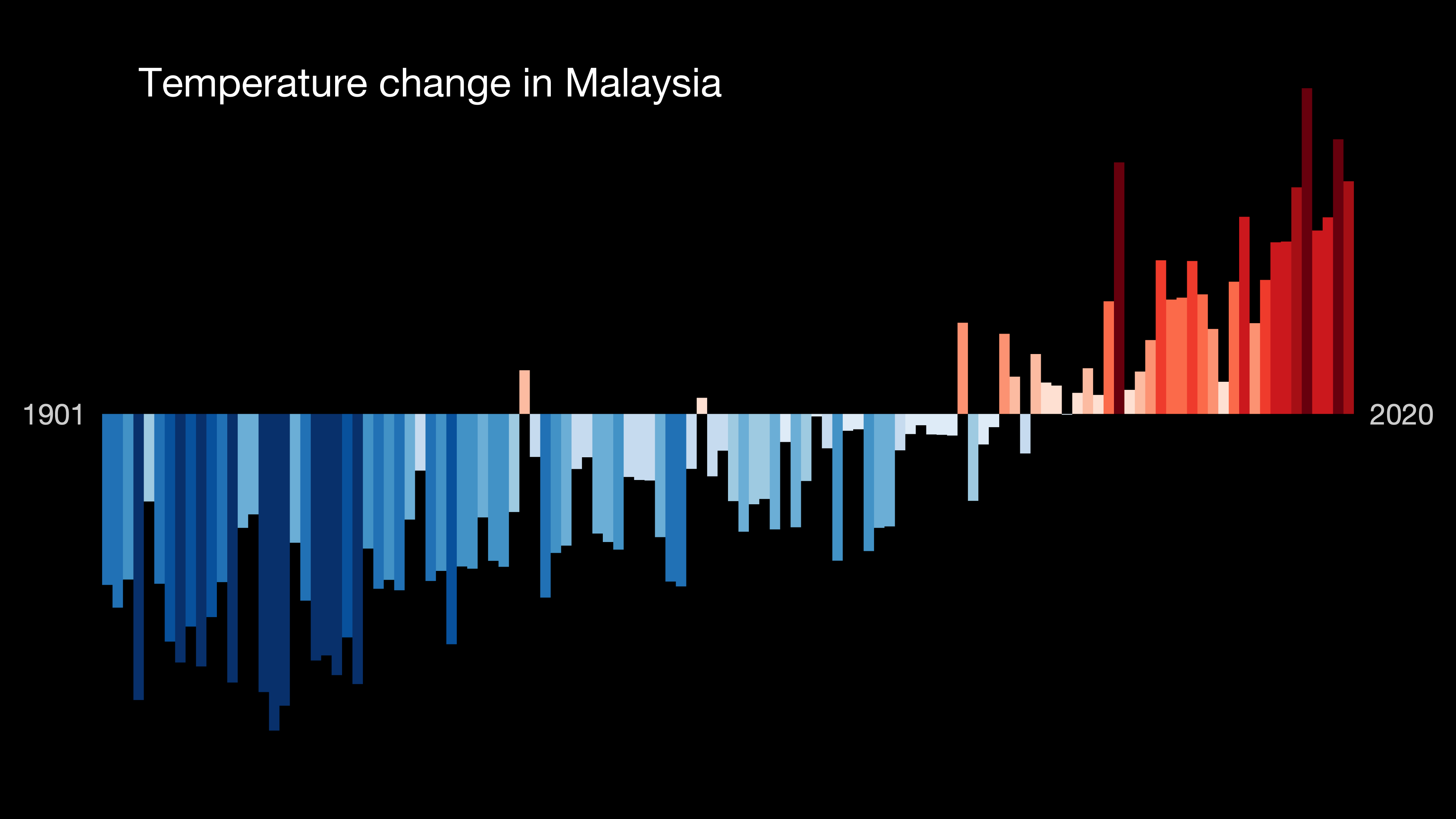
Climate Change In Malaysia
Climate change is having a considerable impact in Malaysia. Increasing temperatures are likely to greatly increase the number of heatwaves occurring annually. Variations in precipitation may increase the frequency of droughts and Floods in Malaysia, floods in various local areas. Sea level rise may inundate some coastal areas. These impacts are expected to have numerous environmental and socioeconomic effects, exacerbating existing Environmental issues in Malaysia, environmental issues and reinforcing Income inequality in Malaysia, inequality. Malaysia itself contributes emissions given its significant use of coal and natural gas. However, the use of hydropower has expanded in the 21st century, and other potential energy sources such as solar power and biomass are being explored. The government anticipates the need to adapt in areas such as health and coastal defences, and has ratified the Paris Agreement. Emissions As of 2000, the largest sectoral contributor to greenhouse gas e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wet Season
The wet season (sometimes called the Rainy season) is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. It is the time of year where the majority of a country's or region's annual precipitation occurs. Generally, the season lasts at least a month. The term ''green season'' is also sometimes used as a euphemism by tourist authorities. Areas with wet seasons are dispersed across portions of the tropics and subtropics. Under the Köppen climate classification, for tropical climates, a wet season month is defined as a month where average precipitation is or more. In contrast to areas with savanna climates and monsoon regimes, Mediterranean climates have wet winters and dry summers. Dry and rainy months are characteristic of tropical seasonal forests: in contrast to tropical rainforests, which do not have dry or wet seasons, since their rainfall is equally distributed throughout the year.Elisabeth M. Benders-Hyde (2003)World Climates.Blue Planet Biomes. Retr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscillation of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) between its limits to the north and south of the equator. Usually, the term monsoon is used to refer to the rainy phase of a seasonally changing pattern, although technically there is also a dry phase. The term is also sometimes used to describe locally heavy but short-term rains. The major monsoon systems of the world consist of the West African, Asia–Australian, the North American, and South American monsoons. The term was first used in English in British India and neighboring countries to refer to the big seasonal winds blowing from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea in the southwest bringing heavy rainfall to the area. Etymology The etymology of the word monsoon is not wholl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 Pacific Typhoon Season
The 2021 Pacific typhoon season was the second consecutive to have below-average tropical cyclone activity, with twenty-two named storms, and was the least active since 2011. Nine became typhoons, and five of those intensified into super typhoons. This low activity was caused by a strong La Niña that had persisted from the previous year. The season's first named storm, Dujuan, developed on February 16, while the last named storm, Rai, dissipated on December 21. The season's first typhoon, Surigae, reached typhoon status on April 16. It became the first super typhoon of the year on the next day, also becoming the strongest tropical cyclone in 2021. Surigae was also the most powerful tropical cyclone on record in the Northern Hemisphere for the month of April. Typhoons In-fa and Rai are responsible for more than half of the total damage this season, adding up to a combined total of $2.017 billion. The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean to the north of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021–2022 Malaysian Floods
On 16 December 2021, a tropical depression made landfall on the eastern coast of Peninsular Malaysia, bringing torrential downpours throughout the peninsula for three days. The resulting floods affected eight states across the peninsula, and left at least 54 dead and 2 missing. During its furthest extent, it caused the concurrent displacement of more than 71,000 residents, and have affected over 125,000 people overall. Declared by government officials as a " once in a century" disaster, it is the worst flood in the country in terms of displaced residents since the 2014–2015 Malaysia floods. It has also been historically compared with the 1971 Kuala Lumpur floods. It is the deadliest tropical cyclone-related disaster to hit Malaysia since Tropical Storm Greg of 1996, which killed 238 people and left 102 more missing. Record-high precipitations were measured at weather stations at Selangor and Kuala Lumpur. Widespread damages were reported in the states of Selangor and Pahang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2020–2021 Malaysian Floods
2020–2021 Malaysian floods is an event when several states in Malaysia were flooded in late 2020 and early 2021. Floods caused about tens of thousands of people to be evacuated to evacuation centers. The floods also claimed several lives, causing almost all types of land transport in the areas affected by the floods to be cut off. Affected areas The floods affected part of Peninsular Malaysia. Pahang and Johor are the states most severely affected by the floods this time. Other states involved are Terengganu, Kelantan, Selangor and Perak. Floods also occurred in Beaufort, Sabah. Cause of flooding Heavy rains for several days in a row were caused by the Northeast Monsoon Winds that hit the South China Sea, across Peninsular Malaysia. Heavy rains also hit Thailand, and also caused severe flooding there. Damage Large floods have affected land transport in the affected states. There was a landslide in Bukit Fraser, Pahang. The East Coast expressways is closed from any vehicle st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |