Cirrus Cloud on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
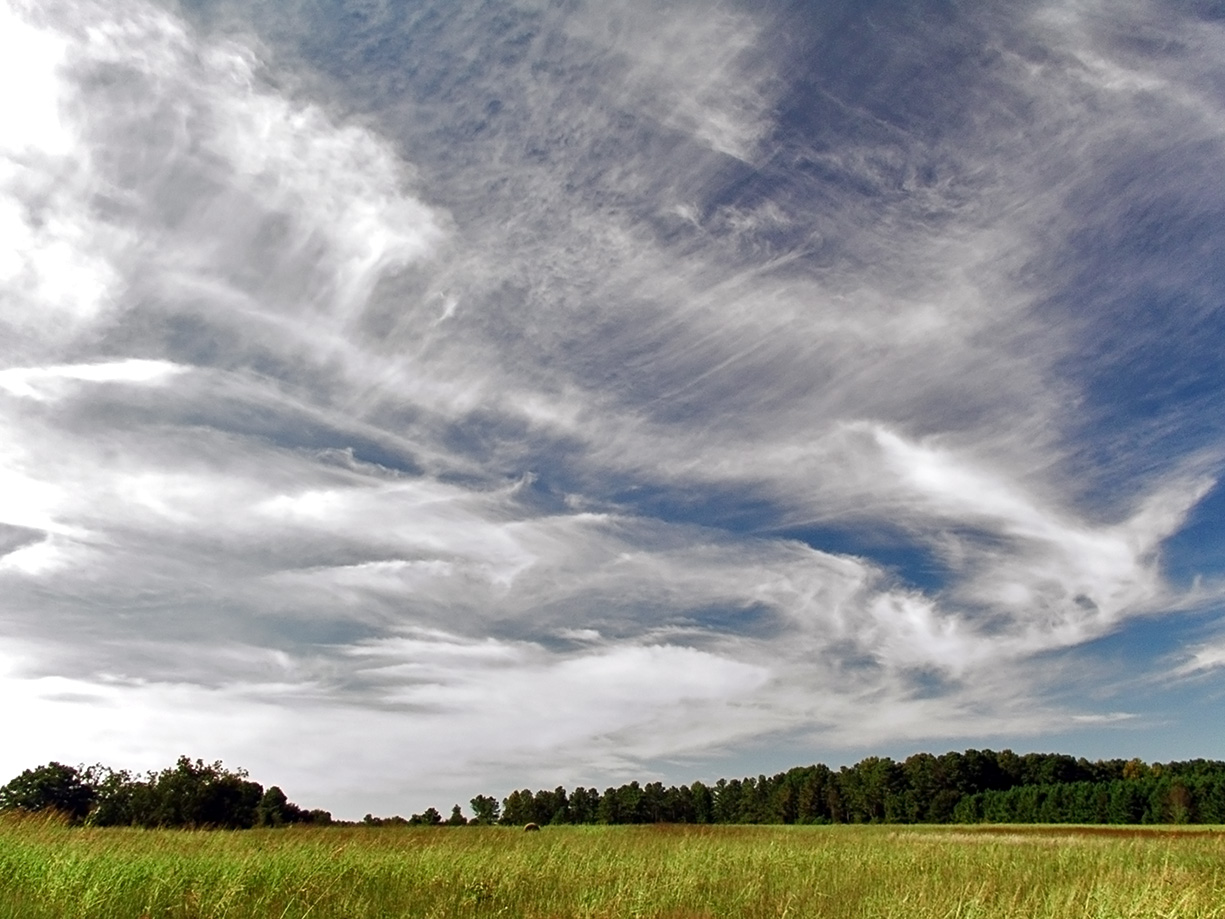 Cirrus ( cloud classification symbol: Ci) is a
Cirrus ( cloud classification symbol: Ci) is a
 Sheets of cirrus clouds commonly fan out from the eye walls of tropical cyclones. (The eye wall is the ring of storm clouds surrounding the eye of a tropical cyclone.) A large shield of cirrus and
Sheets of cirrus clouds commonly fan out from the eye walls of tropical cyclones. (The eye wall is the ring of storm clouds surrounding the eye of a tropical cyclone.) A large shield of cirrus and

 Random, isolated cirrus do not have any particular significance. A large number of cirrus clouds can be a sign of an approaching
Random, isolated cirrus do not have any particular significance. A large number of cirrus clouds can be a sign of an approaching
 Cirrus ( cloud classification symbol: Ci) is a
Cirrus ( cloud classification symbol: Ci) is a genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
of high cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may co ...
made of ice crystals
Ice crystals are solid ice exhibiting atomic ordering on various length scales and include hexagonal columns, hexagonal plates, dendritic crystals, and diamond dust.
Formation
The hugely symmetric shapes are due to depositional growth, na ...
. Cirrus clouds typically appear delicate and wispy with white strands. Cirrus are usually formed when warm, dry air rises, causing water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous pha ...
deposition onto rocky or metallic dust particles at high altitudes. Globally, they form anywhere between above sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised g ...
, with the higher elevations usually in the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
and the lower elevations in more polar regions
The polar regions, also called the frigid zones or polar zones, of Earth are the regions of the planet that surround its geographical poles (the North and South Poles), lying within the polar circles. These high latitudes are dominated by float ...
.
Cirrus clouds can form from the tops of thunderstorms
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are someti ...
and tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
s and sometimes predict the arrival of rain
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water f ...
or storms. Although they are a sign that rain and maybe storms are on the way, cirrus themselves drop no more than falling streaks of ice crystals. These crystals dissipate, melt, and evaporate as they fall through warmer and drier air and never reach ground. Cirrus clouds warm the earth, potentially contributing to climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
. A warming earth will likely produce more cirrus clouds, potentially resulting in a self-reinforcing loop.
Optical phenomena
Optical phenomena are any observable events that result from the interaction of light and matter.
All optics, optical phenomena coincide with Quantum mechanics, quantum phenomena. Common optical phenomena are often due to the interaction of ligh ...
, such as sun dog
A sun dog (or sundog) or mock sun, also called a parhelion (plural parhelia) in meteorology, is an atmospheric optical phenomenon that consists of a bright spot to one or both sides of the Sun. Two sun dogs often flank the Sun within a 22° ...
s and halos, can be produced by light interacting with ice crystals in cirrus clouds. There are two other high-level cirrus-like clouds called cirrostratus
Cirrostratus is a high-level, very thin, generally uniform ''stratiform'' genus-type of cloud. It is made out of ice-crystals, which are pieces of frozen water. It is difficult to detect and it can make halos. These are made when the cloud takes t ...
and cirrocumulus
Cirrocumulus is one of the three main genus-types of high-altitude tropospheric clouds, the other two being cirrus and cirrostratus. They usually occur at an altitude of . Like lower-altitude cumuliform and stratocumuliform clouds, cirrocumulus si ...
. Cirrostratus looks like a sheet of cloud, whereas cirrocumulus looks like a pattern of small cloud tufts. Unlike cirrus and cirrostratus, cirrocumulus clouds contain droplets of supercooled
Supercooling, also known as undercooling, is the process of lowering the temperature of a liquid or a gas below its melting point without it becoming a solid. It achieves this in the absence of a seed crystal or nucleus around which a crystal ...
(below freezing point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends ...
) water.
Cirrus clouds form in the atmospheres of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terr ...
, Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but ...
, Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
, Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus (mythology), Uranus (Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars (mythology), Mars), grandfather ...
, and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times ...
; and on Titan, one of Saturn's larger moons. Some of these extraterrestrial cirrus clouds are made of ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
or methane ice
Methane clathrate (CH4·5.75H2O) or (8CH4·46H2O), also called methane hydrate, hydromethane, methane ice, fire ice, natural gas hydrate, or gas hydrate, is a solid clathrate compound (more specifically, a clathrate hydrate) in which a large amou ...
, much like water ice in cirrus on Earth. Some interstellar cloud
An interstellar cloud is generally an accumulation of gas, plasma, and dust in our and other galaxies. Put differently, an interstellar cloud is a denser-than-average region of the interstellar medium, the matter and radiation that exists in t ...
s, made of grains of dust
Dust is made of fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in homes ...
smaller than a thousandth of a millimeter, are also called ''cirrus''.
Description
Cirrus are wispy clouds made of long strands of ice crystals that are described as feathery, hair-like, or layered in appearance. First defined scientifically byLuke Howard
Luke Howard, (28 November 1772 – 21 March 1864) was a British manufacturing chemist and an amateur meteorologist with broad interests in science. His lasting contribution to science is a nomenclature system for clouds, which he proposed i ...
in an 1803 paper, their name is derived from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
word ''cirrus'', meaning 'curl' or 'fringe'. They are transparent
Transparency, transparence or transparent most often refer to:
* Transparency (optics), the physical property of allowing the transmission of light through a material
They may also refer to:
Literal uses
* Transparency (photography), a still, ...
, meaning that the Sun can be seen through them. Ice crystals in the clouds cause them to usually appear white, but the rising or setting Sun can color them various shades of yellow or red. At dusk
Dusk occurs at the darkest stage of twilight, or at the very end of astronomical twilight after sunset and just before nightfall.''The Random House College Dictionary'', "dusk". At predusk, during early to intermediate stages of twilight, enou ...
, they can appear gray.
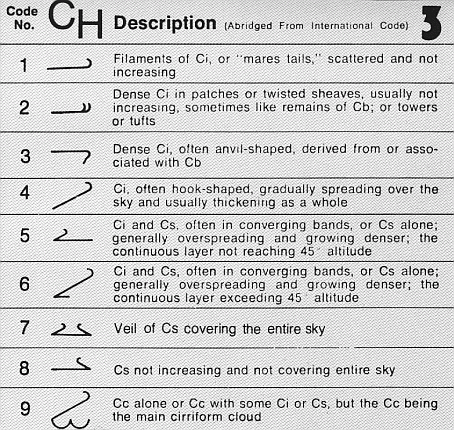
Cirrus comes in five visually-distinct species: castellanus
A castellanus (or castellatus) (from latin ''castellanus'', castle) is a cloud that displays at least in its upper part cumuliform protuberances having the shape of turrets that give a battlement, crenellated aspect. Some of these turrets are hig ...
, fibratus, floccus, spissatus, and uncinus:
* Cirrus castellanus has cumuliform tops caused by high-altitude convection rising up from the main cloud body;
* Cirrus fibratus looks striated and is the most common cirrus species;
* Cirrus floccus species looks like a series of tufts
Tufts University is a private research university on the border of Medford and Somerville, Massachusetts. It was founded in 1852 as Tufts College by Christian universalists who sought to provide a nonsectarian institution of higher learning. ...
;
* Cirrus spissatus is a particularly dense form of cirrus that often forms from thunderstorms.
* Cirrus uncinus clouds are hooked and are the form that is usually called mare's tails.
Each species is divided into up to four varieties: intortus, vertebratus, radiatus, and duplicatus:
* Intortus variety has an extremely contorted shape, with Kelvin–Helmholtz waves being a form of cirrus intortus that has been twisted into loops by layers of wind blowing at different speeds, called wind shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal ...
;
* Radiatus variety has large, radial bands of cirrus clouds that stretch across the sky;
* Vertebratus variety occurs when cirrus clouds are arranged side-by-side like ribs;
* Duplicatus variety occurs when cirrus clouds are arranged above one another in layers.
Cirrus clouds often produce hair-like filaments called fall streak
A fallstreak hole (also known as a cavum, hole punch cloud, punch hole cloud, skypunch, cloud canal or cloud hole) is a large gap, usually circular or elliptical, that can appear in cirrocumulus or altocumulus clouds. The holes are caused by super ...
s, made of heavier ice crystals that fall from the cloud. These are similar to the virga
In meteorology, a virga, also called a dry storm, is an observable :wikt:fallstreak, streak or Precipitation shaft, shaft of precipitation (meteorology), precipitation falling from a cloud that Evaporation, evaporates or Sublimation (phase t ...
produced in liquid–water clouds. The sizes and shapes of fall streaks are determined by the wind shear.
Cirrus cloud cover varies diurnally. During the day, cirrus cloud cover drops, and during the night, it increases. Based on CALIPSO
CALIPSO is a joint NASA (USA) and CNES (France) environmental satellite, built in the Cannes Mandelieu Space Center, which was launched atop a Delta II rocket on April 28, 2006. Its name stands for Cloud-Aerosol Lidar and Infrared Pathfinder Sate ...
satellite data, cirrus covers an average of 31% to 32% of the Earth's surface. Cirrus cloud cover varies wildly by location, with some parts of the tropics reaching up to 70% cirrus cloud cover. Polar regions, on the other hand, have significantly less cirrus cloud cover, with some areas having a yearly average of only around 10% coverage. These percentages treat clear days and nights, as well as days and nights with other cloud types, as lack of cirrus cloud cover.
Formation
Cirrus clouds are usually formed as warm, dry air rises, causing water vapor to undergo deposition onto rocky or metallic dust particles at high altitudes. The average cirrus cloud altitude increases aslatitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
decreases, but the altitude is always capped by the tropopause
The tropopause is the atmospheric boundary that demarcates the troposphere from the stratosphere; which are two of the five layers of the atmosphere of Earth. The tropopause is a thermodynamic gradient-stratification layer, that marks the end of ...
. These conditions commonly occur at the leading edge of a warm front
A warm front is a density discontinuity located at the leading edge of a homogeneous warm air mass, and is typically located on the equator-facing edge of an isotherm gradient. Warm fronts lie within broader troughs of low pressure than cold fro ...
. Because absolute humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity depen ...
is low at such high altitudes, this genus tends to be fairly transparent. Cirrus clouds can also form inside fallstreak hole
A fallstreak hole (also known as a cavum, hole punch cloud, punch hole cloud, skypunch, cloud canal or cloud hole) is a large gap, usually circular or elliptical, that can appear in cirrocumulus or altocumulus clouds. The holes are caused by super ...
s (also called "cavum").
At latitudes of 65° N or S, close to polar regions
The polar regions, also called the frigid zones or polar zones, of Earth are the regions of the planet that surround its geographical poles (the North and South Poles), lying within the polar circles. These high latitudes are dominated by float ...
, cirrus clouds form, on average, only above sea level. In temperate regions, at roughly 45° N or S, their average altitude increases to above sea level. In tropical regions
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred t ...
, at roughly 5° N or S, cirrus clouds form above sea level on average. Across the globe, cirrus clouds can form anywhere from above sea level. Cirrus clouds form with a vast range of thicknesses. They can be as little as from top to bottom to as thick as . Cirrus cloud thickness is usually somewhere between those two extremes, with an average thickness of .
The jet stream
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow, meandering thermal wind, air currents in the Atmosphere of Earth, atmospheres of some planets, including Earth. On Earth, the main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are west ...
, a high-level wind band, can stretch cirrus clouds long enough to cross continents. Jet streak
Jet, Jets, or The Jet(s) may refer to:
Aerospace
* Jet aircraft, an aircraft propelled by jet engines
** Jet airliner
** Jet engine
** Jet fuel
* Jet Airways, an Indian airline
* Wind Jet (ICAO: JET), an Italian airline
* Journey to Enceladu ...
s, bands of faster-moving air in the jet stream, can create arcs of cirrus cloud hundreds of kilometers long.
Cirrus cloud formation may be effected by organic aerosol
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or Human impact on the environment, anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog o ...
s (particles produced by plants) acting as additional nucleation
In thermodynamics, nucleation is the first step in the formation of either a new thermodynamic phase or structure via self-assembly or self-organization within a substance or mixture. Nucleation is typically defined to be the process that deter ...
points for ice crystal formation. However, research suggests that cirrus clouds more commonly form on rocky or metallic particles rather than on organic ones.
Tropical cyclones
 Sheets of cirrus clouds commonly fan out from the eye walls of tropical cyclones. (The eye wall is the ring of storm clouds surrounding the eye of a tropical cyclone.) A large shield of cirrus and
Sheets of cirrus clouds commonly fan out from the eye walls of tropical cyclones. (The eye wall is the ring of storm clouds surrounding the eye of a tropical cyclone.) A large shield of cirrus and cirrostratus
Cirrostratus is a high-level, very thin, generally uniform ''stratiform'' genus-type of cloud. It is made out of ice-crystals, which are pieces of frozen water. It is difficult to detect and it can make halos. These are made when the cloud takes t ...
typically accompanies the high altitude outflowing winds of tropical cyclones, and these can make the underlying bands of rain—and sometimes even the eye—difficult to detect in satellite photographs.
Thunderstorms
Thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are someti ...
s can form dense cirrus at their tops. As the cumulonimbus cloud in a thunderstorm grows vertically, the liquid water droplets freeze when the air temperature reaches the freezing point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends ...
. The anvil cloud
A cumulonimbus incus (Latin ''incus'', "anvil"), also known as an anvil cloud, is a cumulonimbus cloud which has reached the level of tropopause, stratospheric stability and has formed the characteristic flat, anvil-top shape. It signifies the ...
takes its shape because the temperature inversion
In meteorology, an inversion is a deviation from the normal change of an atmospheric property with altitude. It almost always refers to an inversion of the air temperature lapse rate, in which case it is called a temperature inversion. No ...
at the tropopause prevents the warm, moist air forming the thunderstorm from rising any higher, thus creating the flat top. In the tropics, these thunderstorms occasionally produce copious amounts of cirrus from their anvils. High-altitude winds commonly push this dense mat out into an anvil shape that stretches downwind
Windward () and leeward () are terms used to describe the direction of the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference ...
as much as several kilometers.
Individual cirrus cloud formations can be the remnants of anvil clouds formed by thunderstorms. In the dissipating stage of a cumulonimbus cloud, when the normal column rising up to the anvil has evaporated or dissipated, the mat of cirrus in the anvil is all that is left.
Contrails
Contrail
Contrails (; short for "condensation trails") or vapor trails are line-shaped clouds produced by aircraft engine exhaust or changes in air pressure, typically at aircraft cruising altitudes several miles above the Earth's surface. Contrails ar ...
s are an artificial type of cirrus cloud formed when water vapor from the exhaust of a jet engine
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine discharging a fast-moving jet of heated gas (usually air) that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition can include rocket, Pump-jet, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term ...
condenses on particles, which come from either the surrounding air or the exhaust itself, and freezes, leaving behind a visible trail. The exhaust can trigger the formation of cirrus by providing ice nuclei
An ice nucleus, also known as an ice nucleating particle (INP), is a particle which acts as the nucleus for the formation of an ice crystal in the atmosphere.
Ice Nucleation Mechanisms
There are a number of mechanisms of ice nucleation in the atm ...
when there is an insufficient naturally-occurring supply in the atmosphere. One of the environmental impacts of aviation is that persistent contrails can form into large mats of cirrus, and increased air traffic has been implicated as one possible cause of the increasing frequency and amount of cirrus in Earth's atmosphere.
Use in forecasting
 Random, isolated cirrus do not have any particular significance. A large number of cirrus clouds can be a sign of an approaching
Random, isolated cirrus do not have any particular significance. A large number of cirrus clouds can be a sign of an approaching frontal system
A weather front is a boundary separating air masses for which several characteristics differ, such as air density, wind, temperature, and humidity. Disturbed and unstable weather due to these differences often arises along the boundary. For ins ...
or upper air disturbance. The appearance of cirrus signals a change in weather—usually more stormy—in the near future. If the cloud is a ''cirrus castellanus
Cirrus castellanus or Cirrus castellatus is a species of cirrus cloud. Its name comes from the word ''castellanus'', which means ''of a fort'', ''of a castle'' in Latin. Like all cirrus, this species occurs at high altitudes. It appears as separat ...
'', there might be instability at the high altitude level. When the clouds deepen and spread, especially when they are of the ''cirrus radiatus'' variety or ''cirrus fibratus'' species, this usually indicates an approaching weather front. If it is a warm front, the cirrus clouds spread out into cirrostratus, which then thicken and lower into altocumulus
Altocumulus (From Latin ''Altus'', "high", ''cumulus'', "heaped") is a middle-altitude cloud genus that belongs mainly to the ''stratocumuliform'' physical category characterized by globular masses or rolls in layers or patches, the individual ele ...
and altostratus
Altostratus is a middle-altitude cloud genus made up of water droplets, ice crystals, or a mixture of the two. Altostratus clouds are formed when large masses of warm, moist air rise, causing water vapor to condense. Altostratus clouds are usual ...
. The next set of clouds are the rain-bearing nimbostratus cloud
A nimbostratus cloud is a multi-level, amorphous, nearly uniform and often dark grey cloud that usually produces continuous rain, snow or sleet but no lightning or thunder. When cirrus clouds precede a
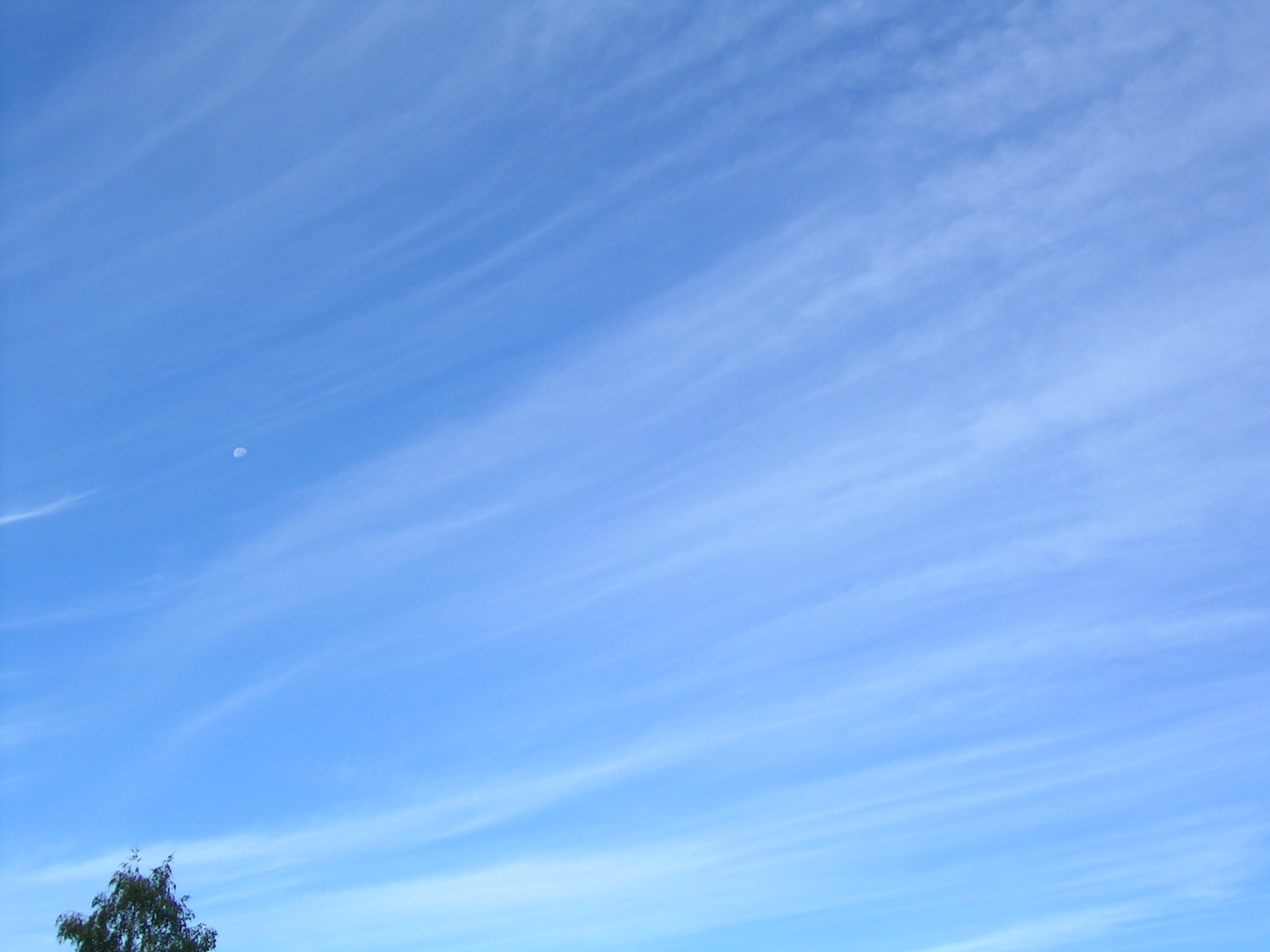 Scientists have studied the properties of cirrus using several different methods.
Scientists have studied the properties of cirrus using several different methods.
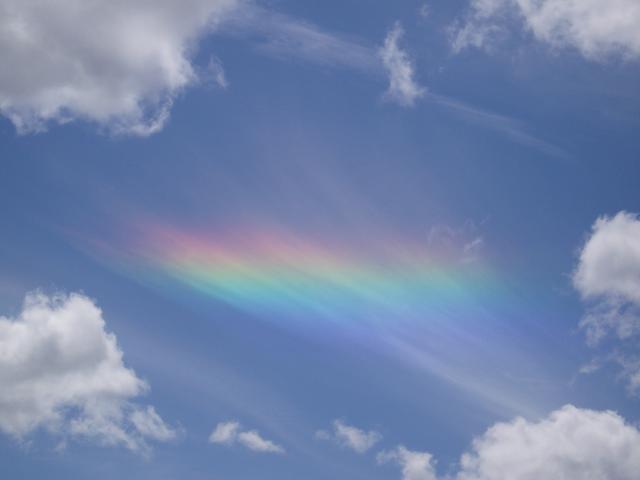 Cirrus clouds can produce several optical effects like halos around the Sun and Moon. Halos are caused by interaction of the light with hexagonal ice crystals present in the clouds which, depending on their shape and orientation, can result in a wide variety of white and colored rings, arcs and spots in the sky, including
Cirrus clouds can produce several optical effects like halos around the Sun and Moon. Halos are caused by interaction of the light with hexagonal ice crystals present in the clouds which, depending on their shape and orientation, can result in a wide variety of white and colored rings, arcs and spots in the sky, including
 Cirrus clouds are one of three different genera of high-level clouds, all of which are given the prefix "cirro-". The other two genera are
Cirrus clouds are one of three different genera of high-level clouds, all of which are given the prefix "cirro-". The other two genera are
cold front
A cold front is the leading edge of a cooler mass of air at ground level that replaces a warmer mass of air and lies within a pronounced surface trough of low pressure. It often forms behind an extratropical cyclone (to the west in the Norther ...
, squall line
A squall line, or more accurately a quasi-linear convective system (QLCS), is a line of thunderstorms, often forming along or ahead of a cold front. In the early 20th century, the term was used as a synonym for cold front (which often are accompa ...
or multicellular thunderstorm
A multicellular thunderstorm cluster is a thunderstorm that is composed of multiple cells, each being at a different stage in the life cycle of a thunderstorm. It appears as several anvils clustered together. A cell is an updraft/downdraft coupl ...
, it is because they are blown off the anvil, and the next to arrive are the cumulonimbus clouds. Kelvin-Helmholtz waves indicate extreme wind shear at high levels. When a jet streak creates a large arc of cirrus, weather conditions may be right for the development of winter storm
A winter storm is an event in which wind coincides with varieties of precipitation that only occur at freezing temperatures, such as snow, mixed snow and rain, or freezing rain. In temperate continental climates, these storms are not necessar ...
s.
Within the tropics, 36 hours prior to the center passage of a tropical cyclone, a veil of white cirrus clouds approaches from the direction of the cyclone. In the mid- to late-19th century, forecasters used these cirrus veils to predict the arrival of hurricanes. In the early 1870s the president of Belén College in Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.
, Father Benito Viñes, developed the first hurricane forecasting system; he mainly used the motion of these clouds in formulating his predictions. He would observe the clouds hourly from 4:00 am to 10:00 pm. After accumulating enough information, Viñes began accurately predicting the paths of hurricanes; he summarized his observations in his book ''Apuntes Relativos a los Huracanes de las Antilles'', published in English as ''Practical Hints in Regard to West Indian Hurricanes''.
Effects on climate
Cirrus clouds cover up to 25% of the Earth (up to 70% in the tropics at night) and have a net heating effect. When they are thin and translucent, the clouds efficiently absorb outgoinginfrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
radiation while only marginally reflecting the incoming sunlight. When cirrus clouds are thick, they reflect only around 9% of the incoming sunlight, but they prevent almost 50% of the outgoing infrared radiation from escaping, thus raising the temperature of the atmosphere beneath the clouds by an average of 10 °C (18 °F)—a process known as the greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when energy from a planet's host star goes through the planet's atmosphere and heats the planet's surface, but greenhouse gases in the atmosphere prevent some of the heat from returning directly ...
. Averaged worldwide, cloud formation results in a temperature loss of 5 °C (9 °F) at the earth's surface, mainly the result of stratocumulus cloud
A stratocumulus cloud, occasionally called a cumulostratus, belongs to a genus-type of clouds characterized by large dark, rounded masses, usually in groups, lines, or waves, the individual elements being larger than those in altocumulus, and the ...
s.
Cirrus clouds are likely becoming more common due to climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
. As their greenhouse effect is stronger than their reflection of sunlight, this would act as a self-reinforcing feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in the ...
. Metallic particles from human sources act as additional nucleation seeds, potentially increasing cirrus cloud cover and thus contributing further to climate change. Aircraft in the upper troposphere can create contrail cirrus clouds if local weather conditions are right. These contrails contribute to climate change.
Cirrus cloud thinning
Cirrus cloud thinning (CCT) is a proposed form of climate engineering. Cirrus clouds are high cold ice that, like other clouds, both reflect sunlight and absorb warming infrared radiation. However, they differ from other types of clouds in that, o ...
has been proposed as a possible geoengineering
Climate engineering (also called geoengineering) is a term used for both carbon dioxide removal (CDR) and solar radiation management (SRM), also called solar geoengineering, when applied at a planetary scale.IPCC (2022Chapter 1: Introduction and F ...
approach to reduce climate damage due to carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
. Cirrus cloud thinning would involve injecting particles into the upper troposphere to reduce the amount of cirrus clouds. The 2021 IPCC Assessment Report expressed low confidence in the cooling effect of cirrus cloud thinning, due to limited understanding.
Cloud properties
 Scientists have studied the properties of cirrus using several different methods.
Scientists have studied the properties of cirrus using several different methods. Lidar
Lidar (, also LIDAR, or LiDAR; sometimes LADAR) is a method for determining ranges (variable distance) by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected light to return to the receiver. It can also be ...
(laser-based radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, w ...
) gives highly accurate information on the cloud's altitude, length, and width. Balloon-carried hygrometer
A hair tension dial hygrometer with a nonlinear scale.
A hygrometer is an instrument used to measure the amount of water vapor in air, in soil, or in confined spaces. Humidity measurement instruments usually rely on measurements of some other qu ...
s measure the humidity of the cirrus cloud but are not accurate enough to measure the depth of the cloud. Radar units give information on the altitudes and thicknesses of cirrus clouds. Another data source is satellite measurements from the Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment
The Stratospheric Aerosol and Gas Experiment (SAGE) is a series of remote sensing satellite instruments used to study the chemical composition of Earth's atmosphere. Specifically, SAGE has been used to study the Earth's ozone layer and aerosols a ...
program. These satellites measure where infrared radiation
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
is absorbed in the atmosphere, and if it is absorbed at cirrus altitudes, then it is assumed that there are cirrus clouds in that location. NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research.
NASA was established in 1958, succeeding t ...
's Moderate-Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) is a satellite-based sensor used for earth and climate measurements. There are two MODIS sensors in Earth orbit: one on board the Terra (EOS AM) satellite, launched by NASA in 1999 ...
gives information on the cirrus cloud cover by measuring reflected infrared radiation of various specific frequencies during the day. During the night, it determines cirrus cover by detecting the Earth's infrared emissions. The cloud reflects this radiation back to the ground, thus enabling satellites to see the "shadow" it casts into space. Visual observations from aircraft or the ground provide additional information about cirrus clouds. Particle Analysis by Laser Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is use ...
(PALMS) is used to identify the type of nucleation seeds that spawned the ice crystals in a cirrus cloud.
Cirrus clouds have an average ice crystal concentration of 300,000 ice crystals per 10 cubic meters
The cubic metre (in Commonwealth English and international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures) or cubic meter (in American English) is the unit of volume in the International System of Units (SI). Its symbol is m ...
(270,000 ice crystals per 10 cubic yard
Cubic may refer to:
Science and mathematics
* Cube (algebra), "cubic" measurement
* Cube, a three-dimensional solid object bounded by six square faces, facets or sides, with three meeting at each vertex
** Cubic crystal system, a crystal system ...
s). The concentration ranges from as low as 1 ice crystal per 10 cubic meters to as high as 100 million ice crystals per 10 cubic meters (just under 1 ice crystal per 10 cubic yards to 77 million ice crystals per 10 cubic yards), a difference of eight orders of magnitude
An order of magnitude is an approximation of the logarithm of a value relative to some contextually understood reference value, usually 10, interpreted as the base of the logarithm and the representative of values of magnitude one. Logarithmic dis ...
. The size of each ice crystal is typically 0.25 millimeters, but they range from as short as 0.01 millimeters up to several millimeters. The ice crystals in contrails can be much smaller than those in naturally-occurring cirrus cloud, being around 0.001 millimeters to 0.1 millimeters in length.
In addition to forming in different sizes, the ice crystals in cirrus clouds can crystallize in different shapes: solid columns, hollow columns, plates, rosettes, and conglomerations of the various other types. The shape of the ice crystals is determined by the air temperature, atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, 7 ...
, and ice supersaturation
In physical chemistry, supersaturation occurs with a solution when the concentration of a solute exceeds the concentration specified by the value of solubility at equilibrium. Most commonly the term is applied to a solution of a solid in a liqu ...
(the amount by which the relative humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity depe ...
exceeds 100%). Cirrus in temperate regions typically have the various ice crystal shapes separated by type. The columns and plates concentrate near the top of the cloud, whereas the rosettes and conglomerations concentrate near the base. In the northern Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenla ...
region, cirrus clouds tend to be composed of only the columns, plates, and conglomerations, and these crystals tend to be at least four times larger than the minimum size. In Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ...
, cirrus are usually composed of only columns which are much longer than normal.
Cirrus clouds are usually colder than . At temperatures above , most cirrus clouds have relative humidities of roughly 100% (that is they are saturated). Cirrus can supersaturate, with relative humidities over ice that can exceed 200%. Below there are more of both undersaturated and supersaturated cirrus clouds. The more supersaturated clouds are probably young cirrus.
Optical phenomena
 Cirrus clouds can produce several optical effects like halos around the Sun and Moon. Halos are caused by interaction of the light with hexagonal ice crystals present in the clouds which, depending on their shape and orientation, can result in a wide variety of white and colored rings, arcs and spots in the sky, including
Cirrus clouds can produce several optical effects like halos around the Sun and Moon. Halos are caused by interaction of the light with hexagonal ice crystals present in the clouds which, depending on their shape and orientation, can result in a wide variety of white and colored rings, arcs and spots in the sky, including sun dog
A sun dog (or sundog) or mock sun, also called a parhelion (plural parhelia) in meteorology, is an atmospheric optical phenomenon that consists of a bright spot to one or both sides of the Sun. Two sun dogs often flank the Sun within a 22° ...
s, the 46° halo
A 46° halo is a rare atmospheric optical phenomenon that consists of a halo with an apparent radius of approximately 46° around the Sun. At solar elevations of 15–27°, 46° halos are often confused with the less rare and more colourful su ...
, the 22° halo
A 22° halo is an atmospheric optical phenomenon that consists of a halo with an apparent radius of approximately 22° around the Sun or Moon. When visible around the Moon, it is also known as a moon ring or winter halo. It forms as sunlight o ...
, and circumhorizontal arc
A circumhorizontal arc is an optical phenomenon that belongs to the family of ice halos formed by the refraction of sunlight or moonlight in plate-shaped ice crystals suspended in the atmosphere, typically in cirrus or cirrostratus clouds. In i ...
s. Circumhorizontal arcs are only visible when the Sun rises higher than 58° above the horizon, preventing observers at higher latitudes from ever being able to see them.
More rarely, cirrus clouds are capable of producing glories, more commonly associated with liquid water-based clouds such as stratus
Stratus may refer to:
Weather
*Stratus cloud, a cloud type
**Nimbostratus cloud, a cloud type
**Stratocumulus cloud, a cloud type
**Altostratus cloud, a cloud type
**Altostratus undulatus cloud, a cloud type
**Cirrostratus cloud, a cloud type
Mus ...
. A glory is a set of concentric, faintly-colored glowing rings that appear around the shadow of the observer, and are best observed from a high viewpoint or from a plane. Cirrus clouds only form glories when the constituent ice crystals are aspherical; researchers suggest that the ice crystals must be between 0.009 millimeters and 0.015 millimeters in length for a glory to appear.
Relation to other clouds
cirrocumulus
Cirrocumulus is one of the three main genus-types of high-altitude tropospheric clouds, the other two being cirrus and cirrostratus. They usually occur at an altitude of . Like lower-altitude cumuliform and stratocumuliform clouds, cirrocumulus si ...
and cirrostratus. High-level clouds usually form above . Cirrocumulus and cirrostratus are sometimes informally referred to as ''cirriform clouds'' because of their frequent association with cirrus.
In the intermediate range, from , are the mid-level clouds, which are given the prefix "alto-". They comprise two genera, altostratus
Altostratus is a middle-altitude cloud genus made up of water droplets, ice crystals, or a mixture of the two. Altostratus clouds are formed when large masses of warm, moist air rise, causing water vapor to condense. Altostratus clouds are usual ...
and altocumulus
Altocumulus (From Latin ''Altus'', "high", ''cumulus'', "heaped") is a middle-altitude cloud genus that belongs mainly to the ''stratocumuliform'' physical category characterized by globular masses or rolls in layers or patches, the individual ele ...
. These clouds are formed from ice crystals, supercooled water droplets, or liquid water droplets.
Low-level clouds usually form below and do not have a prefix. The two genera that are strictly low-level are stratus
Stratus may refer to:
Weather
*Stratus cloud, a cloud type
**Nimbostratus cloud, a cloud type
**Stratocumulus cloud, a cloud type
**Altostratus cloud, a cloud type
**Altostratus undulatus cloud, a cloud type
**Cirrostratus cloud, a cloud type
Mus ...
, and stratocumulus
A stratocumulus cloud, occasionally called a cumulostratus, belongs to a genus-type of clouds characterized by large dark, rounded masses, usually in groups, lines, or waves, the individual elements being larger than those in altocumulus, and the ...
. These clouds are composed of water droplets, except during winter when they are formed of supercooled water
Supercooling, also known as undercooling, is the process of lowering the temperature of a liquid or a gas below its melting point without it becoming a solid. It achieves this in the absence of a seed crystal or nucleus around which a crystal ...
droplets or ice crystals if the temperature at cloud level is below freezing. Three additional genera usually form in the low-altitude range, but may be based at higher levels under conditions of very low humidity. They are the genera cumulus
Cumulus clouds are clouds which have flat bases and are often described as "puffy", "cotton-like" or "fluffy" in appearance. Their name derives from the Latin ''cumulo-'', meaning ''heap'' or ''pile''. Cumulus clouds are low-level clouds, gener ...
, and cumulonimbus
Cumulonimbus (from Latin ''cumulus'', "heaped" and ''nimbus'', "rainstorm") is a dense, towering vertical cloud, typically forming from water vapor condensing in the lower troposphere that builds upward carried by powerful Buoyancy, buoyant air ...
, and nimbostratus
A nimbostratus cloud is a multi-level, amorphous, nearly uniform and often dark grey cloud that usually produces continuous rain, snow or sleet but no lightning or thunder.
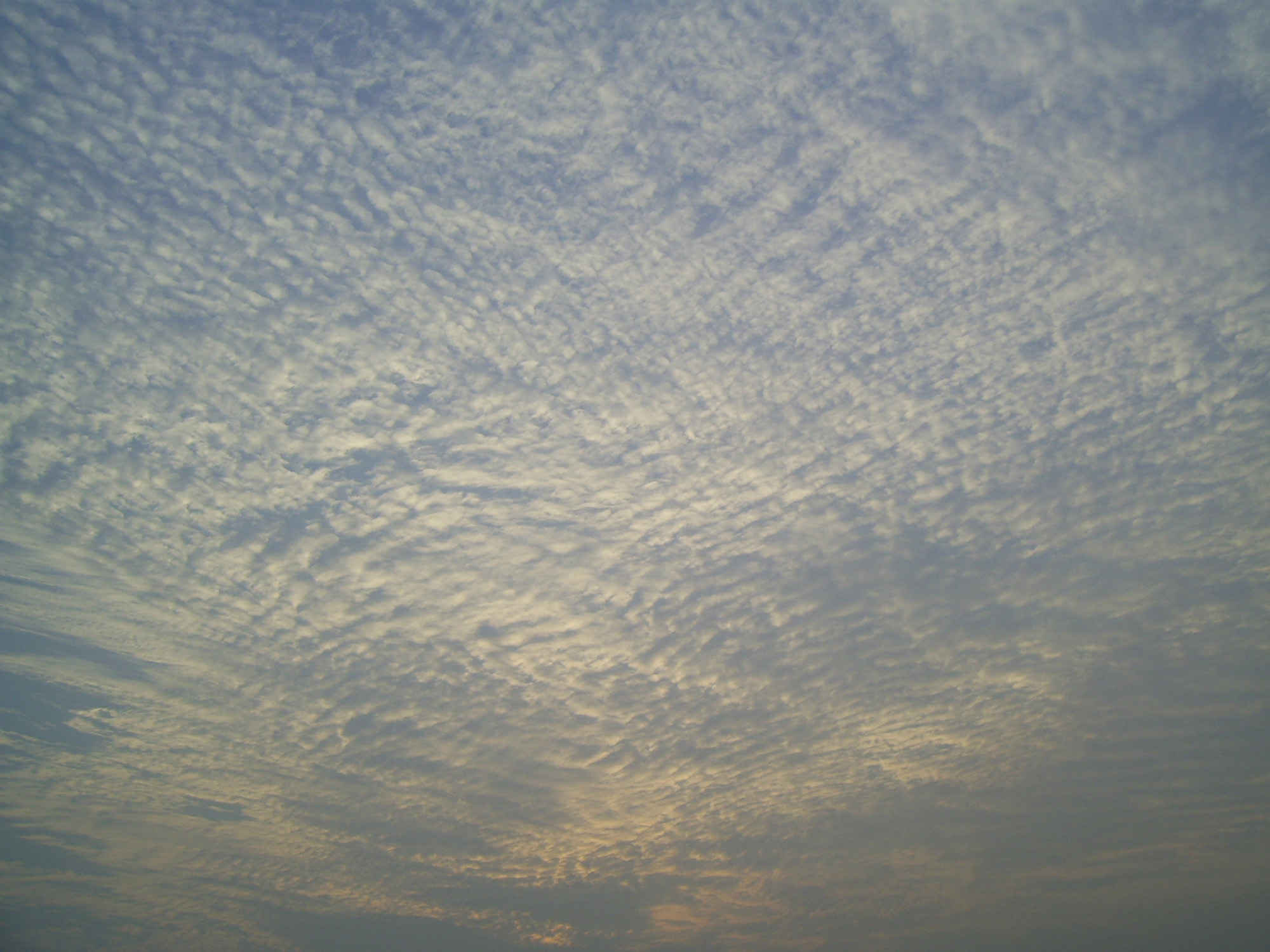 Cirrocumulus clouds form in sheets or patches and do not cast shadows. They commonly appear in regular, rippling patterns or in rows of clouds with clear areas between. Cirrocumulus are, like other members of the cumuliform category, formed via
Cirrocumulus clouds form in sheets or patches and do not cast shadows. They commonly appear in regular, rippling patterns or in rows of clouds with clear areas between. Cirrocumulus are, like other members of the cumuliform category, formed via
 Cirrostratus clouds can appear as a milky sheen in the sky or as a striated sheet. They are sometimes similar to altostratus and are distinguishable from the latter because the Sun or Moon is always clearly visible through transparent cirrostratus, in contrast to altostratus which tends to be opaque or translucent. Cirrostratus come in two species, ''fibratus'' and ''nebulosus''. The ice crystals in these clouds vary depending upon the height in the cloud. Towards the bottom, at temperatures of around , the crystals tend to be long, solid, hexagonal columns. Towards the top of the cloud, at temperatures of around , the predominant crystal types are thick, hexagonal plates and short, solid, hexagonal columns. These clouds commonly produce halos, and sometimes the halo is the only indication that such clouds are present. They are formed by warm, moist air being lifted slowly to a very high altitude. When a warm front approaches, cirrostratus clouds become thicker and descend forming altostratus clouds, and rain usually begins 12 to 24 hours later.
Cirrostratus clouds can appear as a milky sheen in the sky or as a striated sheet. They are sometimes similar to altostratus and are distinguishable from the latter because the Sun or Moon is always clearly visible through transparent cirrostratus, in contrast to altostratus which tends to be opaque or translucent. Cirrostratus come in two species, ''fibratus'' and ''nebulosus''. The ice crystals in these clouds vary depending upon the height in the cloud. Towards the bottom, at temperatures of around , the crystals tend to be long, solid, hexagonal columns. Towards the top of the cloud, at temperatures of around , the predominant crystal types are thick, hexagonal plates and short, solid, hexagonal columns. These clouds commonly produce halos, and sometimes the halo is the only indication that such clouds are present. They are formed by warm, moist air being lifted slowly to a very high altitude. When a warm front approaches, cirrostratus clouds become thicker and descend forming altostratus clouds, and rain usually begins 12 to 24 hours later.
 Cirrus clouds have been observed on several other planets. In 2008, the Martian Lander ''
Cirrus clouds have been observed on several other planets. In 2008, the Martian Lander ''
Cirrocumulus
 Cirrocumulus clouds form in sheets or patches and do not cast shadows. They commonly appear in regular, rippling patterns or in rows of clouds with clear areas between. Cirrocumulus are, like other members of the cumuliform category, formed via
Cirrocumulus clouds form in sheets or patches and do not cast shadows. They commonly appear in regular, rippling patterns or in rows of clouds with clear areas between. Cirrocumulus are, like other members of the cumuliform category, formed via convective
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convect ...
processes. Significant growth of these patches indicates high-altitude instability and can signal the approach of poorer weather. The ice crystals in the bottoms of cirrocumulus clouds tend to be in the form of hexagonal cylinders. They are not solid, but instead tend to have stepped funnels coming in from the ends. Towards the top of the cloud, these crystals have a tendency to clump together. These clouds do not last long, and they tend to change into cirrus because as the water vapor continues to deposit on the ice crystals, they eventually begin to fall, destroying the upward convection. The cloud then dissipates into cirrus. Cirrocumulus clouds come in four species: ''stratiformis'', ''lenticularis'', ''castellanus'', and ''floccus''. They are iridescent
Iridescence (also known as goniochromism) is the phenomenon of certain surfaces that appear to gradually change color as the angle of view or the angle of illumination changes. Examples of iridescence include soap bubbles, feathers, butterfl ...
when the constituent supercooled water droplets are all about the same size.
Cirrostratus
 Cirrostratus clouds can appear as a milky sheen in the sky or as a striated sheet. They are sometimes similar to altostratus and are distinguishable from the latter because the Sun or Moon is always clearly visible through transparent cirrostratus, in contrast to altostratus which tends to be opaque or translucent. Cirrostratus come in two species, ''fibratus'' and ''nebulosus''. The ice crystals in these clouds vary depending upon the height in the cloud. Towards the bottom, at temperatures of around , the crystals tend to be long, solid, hexagonal columns. Towards the top of the cloud, at temperatures of around , the predominant crystal types are thick, hexagonal plates and short, solid, hexagonal columns. These clouds commonly produce halos, and sometimes the halo is the only indication that such clouds are present. They are formed by warm, moist air being lifted slowly to a very high altitude. When a warm front approaches, cirrostratus clouds become thicker and descend forming altostratus clouds, and rain usually begins 12 to 24 hours later.
Cirrostratus clouds can appear as a milky sheen in the sky or as a striated sheet. They are sometimes similar to altostratus and are distinguishable from the latter because the Sun or Moon is always clearly visible through transparent cirrostratus, in contrast to altostratus which tends to be opaque or translucent. Cirrostratus come in two species, ''fibratus'' and ''nebulosus''. The ice crystals in these clouds vary depending upon the height in the cloud. Towards the bottom, at temperatures of around , the crystals tend to be long, solid, hexagonal columns. Towards the top of the cloud, at temperatures of around , the predominant crystal types are thick, hexagonal plates and short, solid, hexagonal columns. These clouds commonly produce halos, and sometimes the halo is the only indication that such clouds are present. They are formed by warm, moist air being lifted slowly to a very high altitude. When a warm front approaches, cirrostratus clouds become thicker and descend forming altostratus clouds, and rain usually begins 12 to 24 hours later.
Other planets
 Cirrus clouds have been observed on several other planets. In 2008, the Martian Lander ''
Cirrus clouds have been observed on several other planets. In 2008, the Martian Lander ''Phoenix
Phoenix most often refers to:
* Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore
* Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States
Phoenix may also refer to:
Mythology
Greek mythological figures
* Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ...
'' took a time-lapse
Time-lapse photography is a technique in which the frequency at which film frames are captured (the frame rate) is much lower than the frequency used to view the sequence. When played at normal speed, time appears to be moving faster and thus ...
photograph of a group of cirrus clouds moving across the Martian sky using lidar. Near the end of its mission, the Phoenix Lander detected more thin clouds close to the north pole of Mars. Over the course of several days, they thickened, lowered, and eventually began snowing. The total precipitation was only a few thousandths of a millimeter. James Whiteway from York University
York University (french: Université York), also known as YorkU or simply YU, is a public university, public research university in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is Canada's fourth-largest university, and it has approximately 55,700 students, 7,0 ...
concluded that "precipitation is a component of the artian
Artian ( fa, ارتيان, also Romanized as Artīān) is a village in Takab Rural District, in the Central District of Dargaz County, Razavi Khorasan Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 408, in 100 families.
See also
* Li ...
hydrologic cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly const ...
". These clouds formed during the Martian night in two layers, one around above ground and the other at surface level. They lasted through early morning before being burned away by the Sun. The crystals in these clouds were formed at a temperature of , and they were shaped roughly like ellipsoids 0.127 millimeters long and 0.042 millimeters wide.
On Jupiter, cirrus clouds are composed of ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
. When Jupiter's South Equatorial Belt disappeared, one hypothesis put forward by Glenn Orten was that a large quantity of ammonia cirrus clouds had formed above it, hiding it from view. NASA's Cassini probe Cassini may refer to:
People
* Cassini (surname)
* Oleg Cassini (1913-2006), American fashion designer
:Cassini family:
* Giovanni Domenico Cassini (1625–1712), Italian mathematician, astronomer, engineer, and astrologer
* Jacques Cassini (167 ...
detected these clouds on Saturn and thin water-ice cirrus on Saturn's moon Titan. Cirrus clouds composed of methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Eart ...
ice exist on Uranus. On Neptune, thin wispy clouds which could possibly be cirrus have been detected over the Great Dark Spot
The Great Dark Spot (also known as GDS-89, for Great Dark Spot, 1989) was one of a series of dark spots on Neptune similar in appearance to Jupiter's Great Red Spot. In 1989, GDS-89 was the first Great Dark Spot on Neptune to be observed by NASA ...
. As on Uranus, these are probably methane crystals.
Interstellar cirrus clouds are composed of tiny dust grains smaller than a micrometer Micrometer can mean:
* Micrometer (device), used for accurate measurements by means of a calibrated screw
* American spelling of micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; ...
and are therefore not true cirrus clouds, which are composed of frozen crystals. They range from a few light year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
s to dozens of light years across. While they are not technically cirrus clouds, the dust clouds are referred to as "cirrus" because of their similarity to the clouds on Earth. They emit infrared radiation, similar to the way cirrus clouds on Earth reflect heat being radiated out into space.
Notes
References
Footnotes Bibliography * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Authority control Cloud types