Circus Flaminius on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
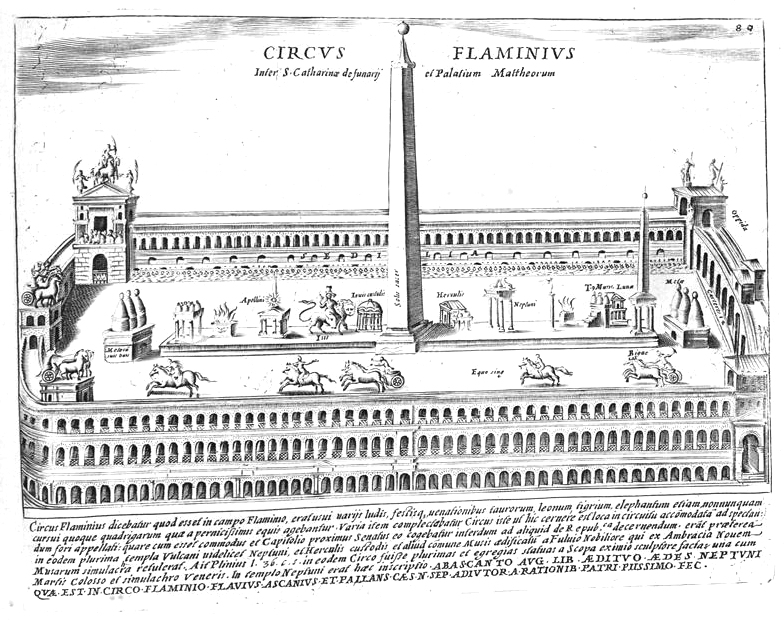 The Circus Flaminius was a large, circular area in
The Circus Flaminius was a large, circular area in
 The Circus Flaminius was a large, circular area in
The Circus Flaminius was a large, circular area in ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 B ...
, located in the southern end of the Campus Martius
The Campus Martius (Latin for the "Field of Mars", Italian ''Campo Marzio'') was a publicly owned area of ancient Rome about in extent. In the Middle Ages, it was the most populous area of Rome. The IV rione of Rome, Campo Marzio, which covers ...
near the Tiber River
The Tiber ( ; it, Tevere ; la, Tiberis) is the third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the Ri ...
. It contained a small race-track used for obscure games, and various other buildings and monuments. It was "built", or sectioned off, by Gaius Flaminius in 221 BC. After Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
divided the city into 14 administrative regions, the Circus Flaminius gave its name to Regio IX, which encompassed the Circus and all of the Campus Martius west of the Via Lata
The Via del Corso is a main street in the historical centre of Rome. It is straight in an area otherwise characterized by narrow meandering alleys and small piazzas. Considered a wide street in ancient times, the Corso is approximately 10 metres w ...
.
Topography and structures
In its early existence, the Circus was a loop, approximately 500 meters in length stretching across the Flaminian Fields (''Prata Flaminia'').Varro
Marcus Terentius Varro (; 116–27 BC) was a Roman polymath and a prolific author. He is regarded as ancient Rome's greatest scholar, and was described by Petrarch as "the third great light of Rome" (after Vergil and Cicero). He is sometimes calle ...
states that the actual Circus was built around the Fields, which were already a hallowed site for games by the time the Circus was laid in 220 BC. The '' ludi Taurei'' were hosted in the Fields since they were inaugurated by Rome's last king Lucius Tarquinius Superbus
Lucius Tarquinius Superbus (died 495 BC) was the legendary seventh and final king of Rome, reigning 25 years until the popular uprising that led to the establishment of the Roman Republic.Livy, ''ab urbe condita libri'', I He is commonly known ...
(d. 495 BC).
During the 2nd century BC, this broad space was encroached upon by buildings and monuments. The circus had no permanent seating, nor were there any permanent structures to mark the perimeter of the race track. By the early 3rd century AD, the only open space that remained was a small piazza in the center, no more than 300 meters long, where the ''ludi
''Ludi'' (Latin plural) were public games held for the benefit and entertainment of the Roman people (''populus Romanus''). ''Ludi'' were held in conjunction with, or sometimes as the major feature of, Roman religious festivals, and were also ...
'' (public games) had always been held.
There were many structures in the vicinity of the circus (“in circo Flaminio”). The Temple of Pietas lay on the edge of the Forum Holitorium
The Forum Holitorium ( it, Foro Olitorio; en, Vegetable-sellers' Market) is an archaeological area of Rome, Italy, on the slopes of the Capitoline Hill. It was "oddly located" outside the Porta Carmentalis in the Campus Martius, crowded between ...
to the southeast. The Temple of Mars was situated in the northwest. It is estimated that by 220 BC there were six temples, including one to Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
, in the Flaminian Fields. A theatre dedicated to Apollo was also set up in 179 BC, close to the temple of Apollo, and later rebuilt under the dictatorship of Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman people, Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caes ...
. The rebuilding of the theatre necessitated shortening the Circus itself, and required that several temples be destroyed.
The temple of Apollo "''in circo''" acquired special significance under Augustus, as a popular legend developed that he had been sired by the god while his mother Atia was visiting the temple. Augustus undertook myriad new constructions around the Circus, and probably had it paved for the first time. Most notably Augustus demolished the small theater dedicated to Apollo, as well as the temples of Diana and Pietas, to build the Theatre of Marcellus
The Theatre of Marcellus ( la, Theatrum Marcelli, it, Teatro di Marcello) is an ancient open-air theatre in Rome, Italy, built in the closing years of the Roman Republic. At the theatre, locals and visitors alike were able to watch performances o ...
on the eastern side of the Circus. Augustus also built the Porticus Octaviae
The Porticus Octaviae (Portico of Octavia; it, Portico di Ottavia) is an ancient structure in Rome. The colonnaded walks of the portico enclosed the temples of Jupiter Stator and Juno Regina, as well as a library. The structure was used as a fi ...
, which hemmed in the Circus on its northeastern side. Augustus' relation Lucius Marcius Phillipus restored the Temple of Hercules Musarum The Temple of Hercules Musarum (Latin: ''Aedes Herculis Musarum'') was a temple dedicated to Hercules in ancient Rome, near the Circus Flaminius.
The temple was built by Marcus Fulvius Nobilior, who conquered the Greek city of Ambracia in 189 BC. ...
with a surrounding portico that could be accessed from the Circus.
In AD 15, statues to the deified Augustus were erected, dedicated by C. Norbanus Flaccus. In the early Principate two monumental arches were added at the north and south ends of the Circus, the northern one dedicated to Germanicus
Germanicus Julius Caesar (24 May 15 BC – 10 October AD 19) was an ancient Roman general, known for his campaigns in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicus was born into an influential branch of the Patric ...
in the year of his death (19 CE), and the southern one to the stepson of Augustus, Drusus
Drusus may refer to:
* Claudius (Tiberius Claudius Drusus) (10 BC–AD 54), Roman emperor from 41 to 54
* Drusus Caesar (AD 8–33), adoptive grandson of Roman emperor Tiberius
* Drusus Julius Caesar (14 BC–AD 23), son of Roman emperor Tiberiu ...
.
Location
Beginning in the Renaissance, the Circus Flaminius was identified with the ancient arcades facing onto the ''Via delle Botteghe Oscure'' ("Street of Dark Shops"), so-called because in the middle ages the arcades had sheltered the workshops of artisans. This placed the Circus north of the ''porticus Phillipi'' between the Piazza Paganica and Piazza Margana. In the 1960s, this long-held identification was challenged by the joining of new fragments to theForma Urbis
The ''Forma Urbis Romae'' or Severan Marble Plan is a massive marble map of ancient Rome, created under the emperor Septimius Severus between 203 and 211. Matteo Cadario gives specific years of 205–208, noting that the map was based on pro ...
, which identified the arcades as in fact belonging to the Theatre of Balbus
Theatre of Balbus was an ancient Roman structure in the Campus Martius of Rome. It was built in 13 BC by proconsul Lucius Cornelius Balbus (minor), likely from the spoils of a military campaign by order of Augustus (Cassius Dio 54.18.2; Pliny the ...
and its connecting portico (the "Crypta Balbi" as the archaeological site is known). New excavations combined with the new configuration of the Marble Plan altered the understanding of where the Circus Flaminius was located, moving it southwest closer to the Tiber and placing it on a southeast-northwest axis.
A previously disregarded reference in the ''Mirabilia Urbis Romae
''Mirabilia Urbis Romae'' ("Marvels of the City of Rome") is a much-copied medieval Latin text that served generations of pilgrims and tourists as a guide to the city of Rome. The original, which was written by a canon of St Peter's, dates from ...
'' ("Circus Flammineus Ad Pontem Ludeorum"), which placed it near the Pons Fabricius
The Pons Fabricius ( it, Ponte Fabricio, "Fabrician Bridge") or Ponte dei Quattro Capi, is the oldest Roman bridge in Rome, Italy, still existing in its original state. Built in 62 BC, it spans half of the Tiber River, from the Campus Martiu ...
, and a fragment of the Marble Plan labelled "CIR FLAM" which fitted south of the Portico of Octavia, confirmed the Circus to be roughly located between the Tiber to the south and the Porticos of Octavia and Phillipus to the north, and hemmed in by the Theatre of Marcellus to the east.
Use
The Circus Flaminius was never meant to rival the much largerCircus Maximus
The Circus Maximus (Latin for "largest circus"; Italian: ''Circo Massimo'') is an ancient Roman chariot-racing stadium and mass entertainment venue in Rome, Italy. In the valley between the Aventine and Palatine hills, it was the first and l ...
, and, unlike the Circus Maximus, it was not just an entertainment venue. It almost certainly lacked a track designed for chariot racing
Chariot racing ( grc-gre, ἁρματοδρομία, harmatodromia, la, ludi circenses) was one of the most popular ancient Greek, Roman, and Byzantine sports. In Greece, chariot racing played an essential role in aristocratic funeral games from ...
. The only ''ludi'' held there were the Taurian Games
The Taurian Games (Latin ''Ludi Taurii'' or ''Ludi Taurei'', rarely Taurilia) were games ''(ludi)'' held in ancient Rome in honor of the ''di inferi'', the gods of the underworld. They were not part of a regularly scheduled religious festival on th ...
, which featured horseback racing around turning posts ''(metae)''. The obscure Taurian Games were held to propitiate the gods of the underworld ''(di inferi
The ''di inferi'' or ''dii inferi'' (Latin, "the gods below") were a shadowy collective of ancient Roman deities associated with death and the underworld. The epithet ''inferi'' is also given to the mysterious Manes, a collective of ancestral sp ...
)'', and seem to have been symbolically grounded in the site itself, as they were never moved to a different circus. Equestrian events were also associated with underworld deities in other rituals and festivals in the Campus Martius. Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
makes no mention of equestrian activities taking place in the Circus Flaminius. Valerius Maximus
Valerius Maximus () was a 1st-century Latin writer and author of a collection of historical anecdotes: ''Factorum ac dictorum memorabilium libri IX'' ("Nine books of memorable deeds and sayings", also known as ''De factis dictisque memorabilibus'' ...
, who is likely to be in error, is the only ancient source that claims the ''Ludi Plebeii
The Plebeian Games (Latin ''Ludi Plebeii'') were an ancient Roman religious festival held November 4–17. The games ''(ludi)'' included both theatrical performances ''(ludi scaenici)'' and athletic competitions for the purpose of entertaining the ...
'' ("Plebeian Games") were held there. In 2 BC, the circus was flooded for the slaughter of 36 crocodiles to commemorate the building of the Forum of Augustus
The Forum of Augustus ( la, Forum Augustum; it, Foro di Augusto) is one of the Imperial fora of Rome, Italy, built by Augustus (). It includes the Temple of Mars Ultor. The incomplete forum and its temple were inaugurated in 2 BC, 40 years after ...
.
The Circus also hosted ceremonies related to the Roman triumph
The Roman triumph (') was a civil religion, civil ceremony and Religion in ancient Rome, religious rite of ancient Rome, held to publicly celebrate and sanctify the success of a military commander who had led Roman forces to victory in the servi ...
, as the Flaminian Fields traditionally figured along the triumphal route towards Capitoline Hill. In 63 BC Lucius Licinius Lucullus celebrated his triumph in the Third Mithridatic War
The Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC), the last and longest of the three Mithridatic Wars, was fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman Republic. Both sides were joined by a great number of allies dragging the entire east of the ...
and exhibited his spoils in the Circus, including a solid gold statue of Mithridates. Augustus did the same when he exhibited the captured insignia of the enemy armies from his campaigns in Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see #Name, names in other languages) is one of the four historical region, historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of ...
in the northern part of the Circus.
According to Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''P ...
, the Dictator Sulla
Lucius Cornelius Sulla Felix (; 138–78 BC), commonly known as Sulla, was a Roman general and statesman. He won the first large-scale civil war in Roman history and became the first man of the Republic to seize power through force.
Sulla had ...
massacred 6,000 prisoners in the Circus Flaminius after the Battle of the Colline Gate
The Battle of the Colline Gate, fought on 1 November 82 BC, was the decisive battle of the civil war between Lucius Cornelius Sulla and the Marians, notably led by Carrinas and Damasippus. A large part of the Marians' forces were made of Ital ...
in 82 BC. Prisoners of war from the nearby town of Antemnae
Antemnae was a town and Roman colony of ancient Latium in Italy. It was situated two miles north of ancient Rome on a hill (now Monte Antenne) commanding the confluence of the Aniene and the Tiber. It lay west of the later Via Salaria and now l ...
were rounded up in the Circus and slaughtered while the Senate met in the adjacent Temple of Bellona; the screams which could be heard from the Temple were a way of intimidating the Senators.Plutarch, ''Parallel Lives''; XXX.II
The Circus Flaminius was also used as a market. Assemblies were often held within it. In 9 BC, it was the venue where Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pri ...
delivered the ''Laudatio'' of Drusus.
Later history
The buildings remained in use until the end of the fourth century, when the area was finally abandoned. In the middle ages the ruins of theStadium of Domitian
The Stadium of Domitian ( it, Stadio di Domiziano), also known as the ''Circus Agonalis'', was located to the north of the Campus Martius in Rome, Italy. The Stadium was commissioned around AD 80 by the Emperor Titus Flavius Domitianus as a gift t ...
(the Piazza Navona
Piazza Navona () is a public open space in Rome, Italy. It is built on the site of the Stadium of Domitian, built in the 1st century AD, and follows the form of the open space of the stadium. The ancient Romans went there to watch the '' agones' ...
) were often incorrectly identified as the Circus Flaminius. In the 16th century the "Castrum Aureum" ("golden camp") mentioned in a Papal Bull of Pope Celestin III in 1192, was also identified as the Circus.
In 1555, Pope Paul IV
Pope Paul IV, born Gian Pietro Carafa, C.R. ( la, Paulus IV; it, Paolo IV; 28 June 1476 – 18 August 1559) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 23 May 1555 to his death in August 1559. While serving as pap ...
formed the Jewish Ghetto
In the Jewish diaspora, a Jewish quarter (also known as jewry, ''juiverie'', ''Judengasse'', Jewynstreet, Jewtown, or proto-ghetto) is the area of a city traditionally inhabited by Jews. Jewish quarters, like the Jewish ghettos in Europe, were ...
in the area encompassing much of the former Circus Flaminius. The Great Synagogue of Rome
The Great Synagogue of Rome ( it, Tempio Maggiore di Roma) is the largest synagogue in Rome.
History
The Jewish community of Rome goes back to the 2nd century B.C when the Roman Republic had an alliance of sorts with Judea under the leadership ...
stands roughly where the southern end of the arena was located.
See also
*List of ancient monuments in Rome
This is a list of ancient monuments from Republican and Imperial periods in the city of Rome, Italy.
Amphitheaters
* Amphitheater of Caligula
* Amphitheatrum Castrense
* Amphitheater of Nero
* Amphitheater of Statilius Taurus
* Colosseum
Bath ...
Notes
Sources
* * *{{cite book , last = Humphrey , first = John , authorlink = , title = Roman Circuses: Arenas for Chariot Racing , publisher = Butler & Tanner Ltd. , year = 1986 , pages = 540–545 , isbn = 0-520-04921-7 Buildings and structures completed in the 3rd century BC Ancient Roman circuses in Rome Topography of the ancient city of Rome 3rd-century BC establishments in Italy