|
Temple Of Hercules Musarum
The Temple of Hercules Musarum (Latin: ''Aedes Herculis Musarum'') was a temple dedicated to Hercules in ancient Rome, near the Circus Flaminius. The temple was built by Marcus Fulvius Nobilior, who conquered the Greek city of Ambracia in 189 BC. It was probably completed and dedicated during his triumph in 187 BC. The epithet 'Musarum' means 'of the Muses' and refers to Nobilior's discovery that Hercules was known in Greece as 'Musagetes' or 'leader of the Muses'. The temple contained copies of the fasti and statues taken from Ambracia, including statues of the Muses. The Portico of Metellus was later built near the temple. In 29 BC, Lucius Marcius Philippus restored the temple and built a portico around it, later known as the ''Porticus Philippi'' or Portico of Philippus. Part of the temple's floorplan is known from a fragment (number 33) of the 3rd century Forma Urbis Romae The ''Forma Urbis Romae'' or Severan Marble Plan is a massive marble map of ancient Rome, created ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hercules
Hercules (, ) is the Roman equivalent of the Greek divine hero Heracles, son of Jupiter and the mortal Alcmena. In classical mythology, Hercules is famous for his strength and for his numerous far-ranging adventures. The Romans adapted the Greek hero's iconography and myths for their literature and art under the name ''Hercules''. In later Western art and literature and in popular culture, ''Hercules'' is more commonly used than ''Heracles'' as the name of the hero. Hercules is a multifaceted figure with contradictory characteristics, which enabled later artists and writers to pick and choose how to represent him. This article provides an introduction to representations of Hercules in the later tradition. Mythology Birth and early life In Roman mythology, although Hercules was seen as the champion of the weak and a great protector, his personal problems started at birth. Juno sent two witches to prevent the birth, but they were tricked by one of Alcmene's servants and sent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC–476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian Peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually dominated the Italian Peninsula, assimilated the Greek culture of southern Italy ( Magna Grecia) and the Etruscan culture and acquired an Empire that took in much of Europe and the lands and peoples surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. It was among the largest empires in the ancient world, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly 20% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
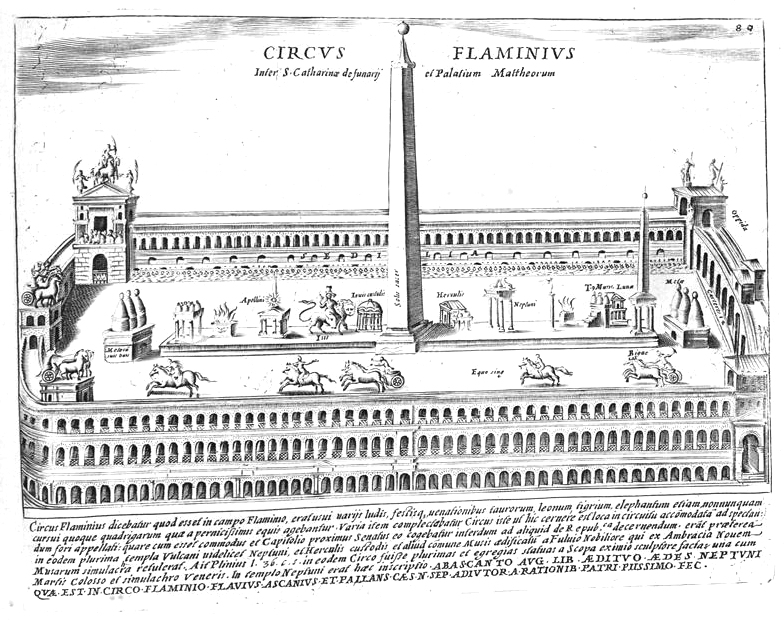
Circus Flaminius
The Circus Flaminius was a large, circular area in ancient Rome, located in the southern end of the Campus Martius near the Tiber River. It contained a small race-track used for obscure games, and various other buildings and monuments. It was "built", or sectioned off, by Gaius Flaminius in 221 BC. After Augustus divided the city into 14 administrative regions, the Circus Flaminius gave its name to Regio IX, which encompassed the Circus and all of the Campus Martius west of the Via Lata. Topography and structures In its early existence, the Circus was a loop, approximately 500 meters in length stretching across the Flaminian Fields (''Prata Flaminia''). Varro states that the actual Circus was built around the Fields, which were already a hallowed site for games by the time the Circus was laid in 220 BC. The '' ludi Taurei'' were hosted in the Fields since they were inaugurated by Rome's last king Lucius Tarquinius Superbus (d. 495 BC). During the 2nd century BC, this broad spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Fulvius Nobilior (consul 189 BC)
Marcus Fulvius Nobilior was a Roman general. He started his political career as curule aedile in 195 BC. When he was praetor (193 BC) he served with distinction in Spain, and as consul in 189 BC he completely broke the power of the Aetolian League. On his return to Rome, Nobilior celebrated a triumph (of which full details are given by Livy) remarkable for the magnificence of the spoils exhibited. On his Aetolian campaign he was accompanied by the poet Ennius, who made the capture of Ambracia, at which he was present, the subject of one of his plays. For this Nobilior was strongly opposed by Cato the Censor, on the ground that he had compromised his dignity as a Roman general. In 179 BC he was appointed censor together with Marcus Aemilius Lepidus. He restored the temple of Hercules and the Muses in the Circus Flaminius, placed in it a list of Fasti drawn up by himself, and endeavoured to make the Roman calendar more generally known.Macrobius ''Saturnalia'' 1.12.16 He was a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambracia
Ambracia (; grc-gre, Ἀμβρακία, occasionally , ''Ampracia'') was a city of ancient Greece on the site of modern Arta. It was captured by the Corinthians in 625 BC and was situated about from the Ambracian Gulf, on a bend of the navigable river Arachthos (or Aratthus), in the midst of a fertile wooded plain. History Ambracia was founded between 650 and 625 BC by Gorgus, son of the Corinthian tyrant Cypselus, at which time its economy was based on farmlands, fishing, timber for shipbuilding, and the exportation of the produce of Epirus. After the expulsion of Gorgus's son Periander its government developed into a strong democracy. The early policy of Ambracia was determined by its loyalty to Corinth (for which it probably served as an entrepot in the Epirus trade), and its consequent aversion to Corcyra (as Ambracia participated on the Corinthian side at the Battle of Sybota, which took place in 433 BC between the rebellious Corinthian colony of Corcyra (modern Corfu) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muses
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, the Muses ( grc, Μοῦσαι, Moûsai, el, Μούσες, Múses) are the inspirational goddesses of literature, science, and the arts. They were considered the source of the knowledge embodied in the poetry, lyric songs, and myths that were related orally for centuries in ancient Greek culture. Melete, Aoede, and Mneme are the original Boeotian Muses, and Calliope, Clio, Erato, Euterpe, Melpomene, Polyhymnia, Terpsichore, Thalia, and Urania are the nine Olympian Muses. In modern figurative usage, a Muse may be a source of artistic inspiration. Etymology The word ''Muses'' ( grc, Μοῦσαι, Moûsai) perhaps came from the o-grade of the Proto-Indo-European root (the basic meaning of which is 'put in mind' in verb formations with transitive function and 'have in mind' in those with intransitive function), or from root ('to tower, mountain') since all the most important cult-centres of the Muses were on mountains or hills. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasti
In ancient Rome, the ''fasti'' (Latin plural) were chronological or calendar-based lists, or other diachronic records or plans of official and religiously sanctioned events. After Rome's decline, the word ''fasti'' continued to be used for similar records in Christian Europe and later Western culture. Public business, including the official business of the Roman state, had to be transacted on ''dies fasti'', "allowed days". The ''fasti'' were the records of this business. In addition to the word's general sense, there were ''fasti'' that recorded specific kinds of events, such as the ''fasti triumphales'', lists of triumphs celebrated by Roman generals. The divisions of time used in the ''fasti'' were based on the Roman calendar. The yearly records of the ''fasti'' encouraged the writing of history in the form of chronological ''annales'', "annals," which in turn influenced the development of Roman historiography. Etymology ''Fasti'' is the plural of the Latin adjective ''fast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portico Of Metellus
The Porticus Octaviae (Portico of Octavia; it, Portico di Ottavia) is an ancient structure in Rome. The colonnaded walks of the portico enclosed the temples of Jupiter Stator and Juno Regina, as well as a library. The structure was used as a fish market from the medieval period up to the end of 19th century. History The structure was built by Augustus in the name of his sister, Octavia Minor, sometime after 27 BC, in place of the Porticus Metelli. The colonnaded walks of the portico enclosed the temples of Jupiter Stator and Juno Regina, next to the Theater of Marcellus. It burned in 80 AD and was restored, probably by Domitian, and again after a second fire in 203 AD by Septimius Severus and Caracalla. It was adorned with foreign marble and contained many famous works of art, enumerated in Pliny's '' Natural History''. The structure was damaged by an earthquake in 442 AD, when two of the destroyed columns were replaced with an archway which still stands. A church was bui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Marcius Philippus (consul 56 BC)
Lucius Marcius Philippus (born before 102 BC) was a politician and senator in the late Roman republic. He was governor of Syria from 61 to 60 and later served in the consulship of 56 BC. He was also step-father of the emperor Augustus. Biography and was the son of the consul in 91 BC and censor in 86 BC of the same name. He also had a brother, Quintus, who served as proconsul in Cilicia from 47 to 46 BC. His first known office was that of praetor in the year 62 BC. After the organisation of Roman Syria, carved out as a province from the Selucid Empire by Pompey in 64 BC, it was governed by two propraetorian governors. Philippus was one of them. He succeeded Marcus Aemilius Scaurus, who had governed the province as Pompey's ''proquaestor pro praetore''; Phillipus served there two years, from 61 through 60 BC. Consulship In 56 BC, he entered office as consul with Gnaeus Cornelius Lentulus Marcellinus as his colleague. Before th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forma Urbis Romae
The ''Forma Urbis Romae'' or Severan Marble Plan is a massive marble map of ancient Rome, created under the emperor Septimius Severus between 203 and 211. Matteo Cadario gives specific years of 205–208, noting that the map was based on property records. It originally measured 18 m (60 ft) wide by 13 m (45 ft) high and was carved into 150 Proconnesian marble slabs mounted on an interior wall of the Temple of Peace. Created at a scale of approximately 1 to 240 (Cadario states 1:260 to 1:270), the map was detailed enough to show the floor plans of nearly every temple, bath, and '' insula'' in the central Roman city. The boundaries of the plan were decided based on the available space on the marble, instead of by geographical or political borders as modern maps usually are. The map was oriented with south at the top. On the map are names and plans of public buildings, streets, and private homes. The creators used signs and details like columns and stairca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temples In The Campus Martius
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples are called Mandir), Buddhism, Sikhism (whose temples are called gurudwara), Jainism (whose temples are sometimes called derasar), Islam (whose temples are called mosques), Judaism (whose temples are called synagogues), Zoroastrianism (whose temples are sometimes called Agiary), the Baha'i Faith (which are often simply referred to as Baha'i House of Worship), Taoism (which are sometimes called Daoguan), Shinto (which are sometimes called Jinja), Confucianism (which are sometimes called the Temple of Confucius), and ancient religions such as the Ancient Egyptian religion and the Ancient Greek religion. The form and function of temples are thus very variable, though they are often considered by believers to be, in some sense, the "house" of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
180s BC Establishments
Eighteen or 18 may refer to: * 18 (number), the natural number following 17 and preceding 19 * one of the years 18 BC, AD 18, 1918, 2018 Film, television and entertainment * ''18'' (film), a 1993 Taiwanese experimental film based on the short story ''God's Dice'' * ''Eighteen'' (film), a 2005 Canadian dramatic feature film * 18 (British Board of Film Classification), a film rating in the United Kingdom, also used in Ireland by the Irish Film Classification Office * 18 (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the ''Dragon Ball'' franchise * "Eighteen", a 2006 episode of the animated television series ''12 oz. Mouse'' Music Albums * ''18'' (Moby album), 2002 * ''18'' (Nana Kitade album), 2005 * '' 18...'', 2009 debut album by G.E.M. Songs * "18" (5 Seconds of Summer song), from their 2014 eponymous debut album * "18" (One Direction song), from their 2014 studio album ''Four'' * "18", by Anarbor from their 2013 studio album '' Burnout'' * "I'm Eighteen", by Alice Cooper commonly r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |