Chemnitz Oper 2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Chemnitz (; from 1953 to 1990: Karl-Marx-Stadt , ) is the third-largest city in the
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
of Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
after Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as wel ...
and Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label=Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth larg ...
. It is the 28th largest city of Germany as well as the fourth largest city in the area of former East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
after (East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
) Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitue ...
, Leipzig and Dresden. The city is part of the Central German Metropolitan Region
The Central German Metropolitan Region (german: Metropolregion Mitteldeutschland) is one of the officially established metropolitan regions in Germany. It is centered on the major cities of Leipzig and Halle, extending over Central German parts ...
, and lies in the middle of a string of cities sitting in the densely populated northern foreland of the Elster
Elster may refer to:
Places
* Black Elster (''Schwarze Elster''), a river in Germany
* White Elster (''Weiße Elster''), a river in Germany and the Czech Republic
** Elster Viaduct, a railway bridge over the White Elster
** Elster Viaduct (Pirk) ...
and Ore Mountains, stretching from Plauen
Plauen (; Czech language, Czech: ''Plavno'') is, with around 65,000 inhabitants, the fifth-largest city of Saxony, Germany after Leipzig, Dresden, Chemnitz and Zwickau, the second-largest city of the Vogtland after Gera, as well as the larges ...
in the southwest via Zwickau
Zwickau (; is, with around 87,500 inhabitants (2020), the fourth-largest city of Saxony after Leipzig, Dresden and Chemnitz and it is the seat of the Zwickau District. The West Saxon city is situated in the valley of the Zwickau Mulde (German: ' ...
, Chemnitz and Freiberg
Freiberg is a university and former mining town in Saxony, Germany. It is a so-called ''Große Kreisstadt'' (large county town) and the administrative centre of Mittelsachsen district.
Its historic town centre has been placed under heritage c ...
to Dresden in the northeast.
Located in the Ore Mountain Basin The Ore Mountain BasinCentral Saxon Hill Country to the north. The city stands on the
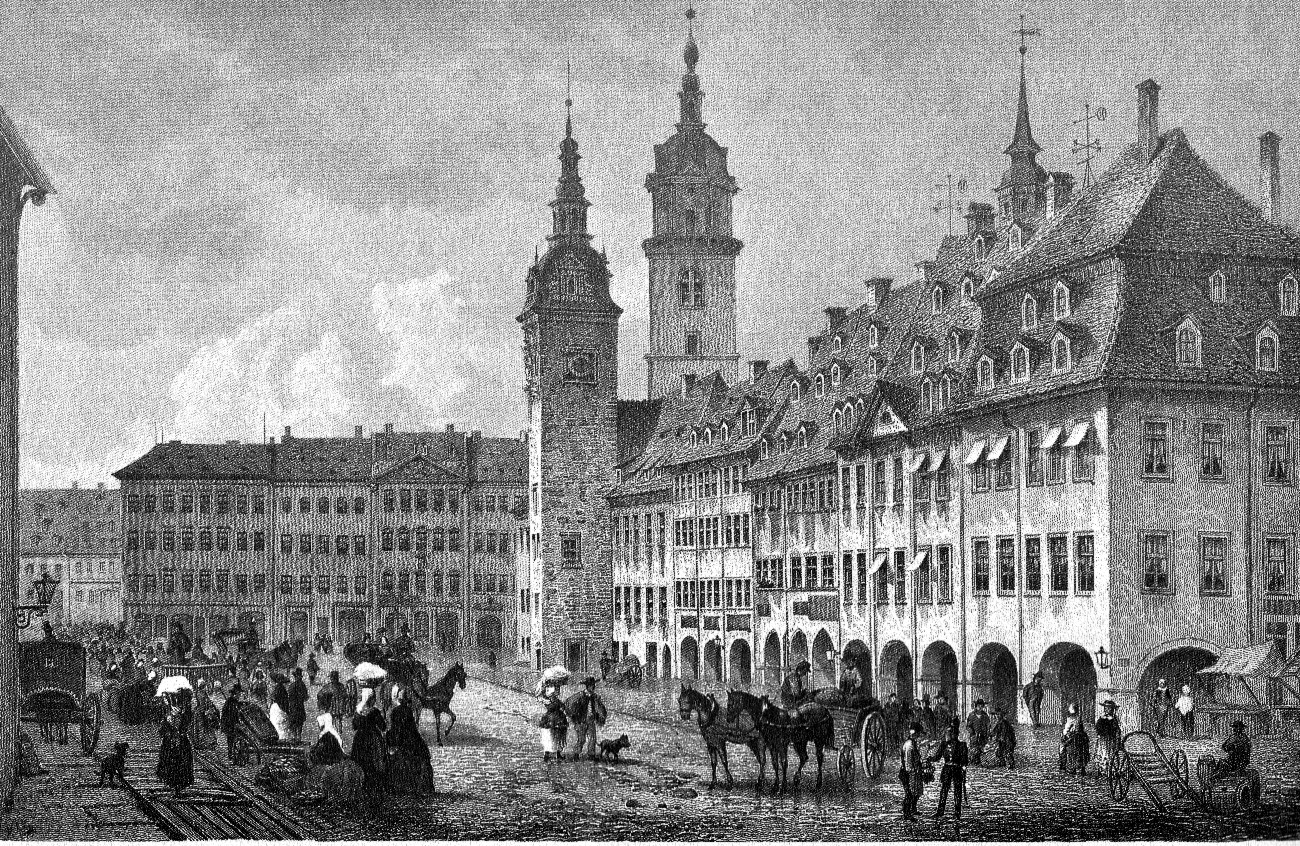
 After the dissolution of the Länder (states) in the GDR in 1952, Chemnitz became seat of a district (). On 10 May 1953, the city was renamed by decision of the East German government to after
After the dissolution of the Länder (states) in the GDR in 1952, Chemnitz became seat of a district (). On 10 May 1953, the city was renamed by decision of the East German government to after
 On 23 April 1990, a referendum on the future name of the city was held: 76% of the voters voted for the old name "". On 1 June 1990, the city was officially renamed.
After the
On 23 April 1990, a referendum on the future name of the city was held: 76% of the voters voted for the old name "". On 1 June 1990, the city was officially renamed.
After the
/ref> Large shopping centers were constructed on the city periphery to the early 1990s. Chemnitz is the only major German city whose centre was re-planned after 1990, similar to the reconstruction of several other German cities in the immediate post-war years. Plans for the recovery of a compressed city centre around the historic town hall in 1991 led to an urban design competition. This was announced internationally by the city and carried out with the help of the partner city of . The mooted project on an essentially unused area of the former city would be comparable in circumference with the in Berlin. Numerous internationally renowned architects such as , and provided designs for a new city centre. The mid-1990s began the development of the inner city brownfields around the town hall to a new town. In Chemnitz city more than 66,000 square meters of retail space have emerged. With the construction of office and commercial building on the construction site "B3" at the court, the last gap in 2010 was closed in city centre image. The intensive development included demolition of partially historically valuable buildings from the period and was controversial. Between 1990 and 2007 more than 250 buildings were leveled. In late August 2018 the city was the site of a series of
In late August 2018 the city was the site of a series of
File:Altes und Neues Rathaus am Chemnitzer Marktplatz 2015.jpg, Old and new city hall
File:Chemnitz, Roter Turm und Galerie Roter Turm.JPG, Red tower
File:Chemnitz Opernhaus 2002.jpg,
Image:Chemnitz stadtteilnummern.svg, left,
The city area does not include a unified, closed settlement area after numerous incorporations. The rural settlements of mainly eastern districts are separated from the settlement area of the Chemnitz city center, whereas this partly continues over the western city limits to Limbach-Oberfrohna and Hohenstein-Ernstthal.
Wahlen in Sachsen
 The most recent city council election was held on 26 May 2019, and the results were as follows:
! colspan=2, Party
! Votes
! %
! +/-
! Seats
! +/-
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Christian Democratic Union (CDU)
, 69,195
, 20.0
, 4.5
, 13
, 2
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left,
The most recent city council election was held on 26 May 2019, and the results were as follows:
! colspan=2, Party
! Votes
! %
! +/-
! Seats
! +/-
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Christian Democratic Union (CDU)
, 69,195
, 20.0
, 4.5
, 13
, 2
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left,
Wahlen in Sachsen
 Heavy destruction in World War II as well as post-war demolition to erect a truly socialist city centre left the city with a vast open space around its
Heavy destruction in World War II as well as post-war demolition to erect a truly socialist city centre left the city with a vast open space around its
File:VW factory Mosel-Zwickau (aka).jpg, is the largest employer in the Agglomeration.
File:Büro- und Wohnhaus der Deutschen Bundesbank - Filiale Chemnitz, Zschopauer Straße, 2015.jpg,
File:Anbau Dämmerung.jpg, The is the largest hospital in the former East German states and the second biggest employer in Chemnitz.
File:Kaufhaus Peek&Cloppenburg, Chemnitz, Neumarkt, 2015.jpg, Chemnitz is a shopping destination. Photo shows the Peek & Cloppenburg store in the city centre.
File:View from Klínovec northwards.JPG, Chemnitz is the centerpiece of tourism in the Ore Mountains.
 After German reunification Saxony faced a significant population decrease. Since 1988 Chemnitz has lost about 20 percent of its inhabitants. The city had a fertility rate of 1.64 in 2015.
Foreign population in Chemnitz by nationality as of 31 December 2019:
A large contributor to the city's foreign population is
After German reunification Saxony faced a significant population decrease. Since 1988 Chemnitz has lost about 20 percent of its inhabitants. The city had a fertility rate of 1.64 in 2015.
Foreign population in Chemnitz by nationality as of 31 December 2019:
A large contributor to the city's foreign population is
File:Hauptbahnhof Chemnitz und Bahnhofsvorplatz 2015.jpg, , the main train station of Chemnitz
File:Zentralhaltestelle Chemnitz, Innenstadt, 2015.jpg, Tram stop at at night
File:Trams at Chemnitz Hauptbahnhof - geo.hlipp.de - 5066.jpg, A tram in Chemnitz
File:Flugplatz Chemnitz-Jahnsdorf Edcj 2011.jpg, The small commercial airport

 * (basketball, men)
* (
* (basketball, men)
* (
Chemnitz River
The Chemnitz is a river in Saxony, Germany, a right tributary of the Zwickauer Mulde. It gave name to the city of Chemnitz, where it is formed by the smaller rivers Zwönitz and Würschnitz. It joins the Zwickauer Mulde near Wechselburg, south o ...
(progression: ), which is formed through the confluence of the rivers Zwönitz
Zwönitz () is a town in the district Erzgebirgskreis, in Saxony, Germany. It is situated 9 km south of Stollberg, and 24 km southwest of Chemnitz.
Parts of the town
Zwönitz consists of:
Population
* 1542 – 570
* 1697 – 741
...
and Würschnitz
The Würschnitz is a river of Saxony, Germany. At its confluence with the Zwönitz
Zwönitz () is a town in the district Erzgebirgskreis, in Saxony, Germany. It is situated 9 km south of Stollberg, and 24 km southwest of Chemnitz ...
in the borough of Altchemnitz.
The name of the city as well as the names of the rivers are of Slavic origin. Chemnitz is the third largest city in the Thuringian
Thuringian is an East Central German dialect group spoken in much of the modern German Free State of Thuringia north of the Rennsteig ridge, southwestern Saxony-Anhalt and adjacent territories of Hesse and Bavaria. It is close to Upper Saxon sp ...
-Upper Saxon
Upper Saxon (german: Obersächsisch, ; ) is an East Central German language spoken in much of the modern German state of Saxony and in adjacent parts of southeastern Saxony-Anhalt and eastern Thuringia. As of the early 21st century, it's mostl ...
dialect area after Leipzig and Dresden. The city's economy is based on the service sector
The tertiary sector of the economy, generally known as the service sector, is the third of the three economic sectors in the three-sector model (also known as the economic cycle). The others are the primary sector (raw materials) and the second ...
and manufacturing industry
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to a rang ...
. Chemnitz University of Technology
Chemnitz (; from 1953 to 1990: Karl-Marx-Stadt , ) is the third-largest city in the German state of Saxony after Leipzig and Dresden. It is the 28th largest city of Germany as well as the fourth largest city in the area of former East Germany a ...
has around 10,000 students.
Chemnitz will be the European Capital of Culture of 2025.
Etymology
Chemnitz is named after the riverChemnitz
Chemnitz (; from 1953 to 1990: Karl-Marx-Stadt , ) is the third-largest city in the German state of Saxony after Leipzig and Dresden. It is the 28th largest city of Germany as well as the fourth largest city in the area of former East Germany a ...
, a small tributary of the Zwickau Mulde
The Zwickauer Mulde () is a river in Saxony, Germany. It is the left tributary of the Mulde and in length.
The source of the river is in the Ore Mountains, near Schöneck, in the Vogtlandkreis. It runs northeast to Aue, then northwest to ...
. The word "Chemnitz" is from the Sorbian language
The Sorbian languages ( hsb, serbska rěč, dsb, serbska rěc) are the Upper Sorbian language and Lower Sorbian language, two closely related and partially mutually intelligible languages spoken by the Sorbs, a West Slavic ethno-cultural mino ...
( hsb, Kamjenica), and means "stony rook
Rook (''Corvus frugilegus'') is a bird of the corvid family. Rook or rooks may also refer to:
Games
*Rook (chess), a piece in chess
*Rook (card game), a trick-taking card game
Military
* Sukhoi Su-25 or Rook, a close air support aircraft
* USS ...
. The word is composed of the Slavic word meaning "stone" and the feminine suffix .
It is known in Czech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
* Czech, ...
as and in Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
as . There are many other towns named Kamienica or Kamenice in areas with past or present Slavic settlement.
History

Free imperial city
An early Slavic tribe's settlement was located at , and the first documented use of this name was in 1143, as the location of aBenedictine
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG
, caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal
, abbreviation = OSB
, formation =
, motto = (English: 'Pray and Work')
, foun ...
monastery around which a settlement grew. Around 1170, Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (german: link=no, Friedrich I, it, Federico I), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death 35 years later. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt on ...
granted this the rights of a free imperial city
In the Holy Roman Empire, the collective term free and imperial cities (german: Freie und Reichsstädte), briefly worded free imperial city (', la, urbs imperialis libera), was used from the fifteenth century to denote a self-ruling city that ...
. Kamienica was later Germanised as Chemnitz.
Meissen and Saxony
In 1307, the town became subordinate to theMargraviate of Meissen
The Margravate of Meissen (german: Markgrafschaft Meißen) was a medieval principality in the area of the modern German state of Saxony. It originally was a frontier march
In medieval Europe, a march or mark was, in broad terms, any kind of bor ...
, the predecessor of the Saxon state. In medieval times
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire an ...
, Chemnitz became a centre of textile production and trade. More than one third of the population worked in textile production. In 1356 the Margraviate was succeeded by the Electorate of Saxony
The Electorate of Saxony, also known as Electoral Saxony (German: or ), was a territory of the Holy Roman Empire from 1356–1806. It was centered around the cities of Dresden, Leipzig and Chemnitz.
In the Golden Bull of 1356, Emperor Charles ...
.
Geologist Georgius Agricola
Georgius Agricola (; born Georg Pawer or Georg Bauer; 24 March 1494 – 21 November 1555) was a German Humanist scholar, mineralogist and metallurgist. Born in the small town of Glauchau, in the Electorate of Saxony of the Holy Roman Empir ...
(1494-1555), author of several significant works on mining and metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sc ...
including the landmark treatise ''De Re Metallica'', became city physician
City physician (German: ; , , from Latin ) was a historical title in the Late Middle Ages for a physician appointed by the city council. The city physician was responsible for the health of the population, particularly the poor, and the sanitary ...
of Chemnitz in 1533 and lived here until his death in 1555. In 1546 he was elected a Burgher of Chemnitz and in the same year also was appointed Burgomaster (lord mayor), serving again in 1547, 1551, and 1553. In spite of having been a leading citizen of the city, when Agricola died in 1555 the Protestant Duke denied him burial in the city's cathedral due to Agricola's allegiance to his Roman Catholic faith. Agricola's friends arranged for his remains to be buried in more sympathetic Zeitz
Zeitz ( hsb, Žič) is a town in the Burgenlandkreis district, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated on the river White Elster, in the triangle of the federal states Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia and Saxony.
History
Zeitz was first recorded u ...
, approximately 50 km away. Chemnitz became a famous trading and textile manufacturing town.
In 1806, with the end of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
, the Electorate was renamed as the Kingdom of Saxony
The Kingdom of Saxony (german: Königreich Sachsen), lasting from 1806 to 1918, was an independent member of a number of historical confederacies in Napoleonic through post-Napoleonic Germany. The kingdom was formed from the Electorate of Saxon ...
, and this survived until the revolutions of 1918 which followed the Armistice ending the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
.
By the early 19th century, Chemnitz had become an industrial centre (sometimes called "the Saxon Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The t ...
", german: Sächsisches Manchester, ). Important industrial companies were founded by Richard Hartmann
Richard Hartmann (8 November 1809 – 16 December 1878) was a German engineering manufacturer.
Life
Hartmann was born on 8 November 1809 in Barr, Bas-Rhin, the son of a tawer (''Weissgerber'', a tanner of white leather). In his Alsace home ...
, Louis Schönherr and Johann von Zimmermann. Chemnitz became a centre of innovation in the kingdom of Saxony and later in Germany. In 1913, Chemnitz had a population of 320,000 and, like Leipzig and Dresden, was larger at that time than today. After losing inhabitants due to the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
Chemnitz grew rapidly again and reached its all-time peak of 360,250 inhabitants in 1930. Thereafter, growth was stalled by the world economic crisis.
Weimar Republic
As a working-class industrial city, Chemnitz was a powerful center of socialist political organization after the First World War. At the foundation of the German Communist Party the localIndependent Social Democratic Party of Germany
The Independent Social Democratic Party of Germany (german: Unabhängige Sozialdemokratische Partei Deutschlands, USPD) was a short-lived political party in Germany during the German Empire and the Weimar Republic. The organization was establish ...
voted by 1,000 votes to three to break from the party and join the Communist Party behind their local leaders, Fritz Heckert
Friedrich (Fritz) Carl Heckert (born 28 March 1884 in Chemnitz – died 7 April 1936 in Moscow) was a German politician, co-founder of the Spartacus League and the Communist Party of Germany and a leading member of the Communist International (Co ...
and Heinrich Brandler
Heinrich Brandler (3 July 1881 – 26 September 1967) was a German communist, trade unionist, politician, revolutionary activist, and political writer. Brandler is best remembered as the head of the Communist Party of Germany (KPD) during the party ...
. In March 1919 the German Communist Party had over 10,000 members in the
city of Chemnitz. Chemnitz was one of the big German industrial centers. Due to the export traffic a modern marshalling yard was erected 1929 in Chemnitz-Hilbersdorf. At that time it was a leading city in the European textile market. Auto Union
Auto Union AG, was an amalgamation of four German automobile manufacturers, founded in 1932 and established in 1936 in Chemnitz, Saxony. It is the immediate predecessor of Audi as it is known today.
As well as acting as an umbrella firm f ...
(today Audi) was founded 1932 in Chemnitz.
World War II
Allied bombing destroyed 41 per cent of the built-up area of Chemnitz during theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. Chemnitz contained factories that produced military hardware and a Flossenbürg forced labor
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, violence including death, or other forms of ex ...
subcamp (500 female inmates) for Astra-Werke AG. The oil refinery
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, lique ...
was a target for bombers during the Oil Campaign of World War II, and Operation Thunderclap attacks included the following raids:
* 14/15 February 1945: The first major raid on Chemnitz used 717 RAF
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and ...
bombers, but due to cloud cover most bombs fell over open countryside.
* 2/3–5 March: USAAF
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
bombers attacked the marshalling yards.
* 5 March: 760 RAF bombers attacked.
The headquarters of the auto manufacturer Auto Union
Auto Union AG, was an amalgamation of four German automobile manufacturers, founded in 1932 and established in 1936 in Chemnitz, Saxony. It is the immediate predecessor of Audi as it is known today.
As well as acting as an umbrella firm f ...
was based in Chemnitz from 1932 and its buildings were badly damaged. At the end of the war, the company's executives fled and relocated the company in Ingolstadt
Ingolstadt (, Austro-Bavarian: ) is an independent city on the Danube in Upper Bavaria with 139,553 inhabitants (as of June 30, 2022). Around half a million people live in the metropolitan area. Ingolstadt is the second largest city in Upper Bav ...
, Bavaria, where it evolved into Audi
Audi AG () is a German automotive manufacturer of luxury vehicles headquartered in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, Germany. As a subsidiary of its parent company, the Volkswagen Group, Audi produces vehicles in nine production facilities worldwide.
Th ...
, now a brand within the Volkswagen group.
The World War II bombings left most of the city in ruins and post-war
In Western usage, the phrase post-war era (or postwar era) usually refers to the time since the end of World War II. More broadly, a post-war period (or postwar period) is the interval immediately following the end of a war. A post-war period c ...
, the East German reconstruction included large low rise (and later high-rise ) housing. Some tourist sites were reconstructed during the East German
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
era and after German reunification
German reunification (german: link=no, Deutsche Wiedervereinigung) was the process of re-establishing Germany as a united and fully sovereign state, which took place between 2 May 1989 and 15 March 1991. The day of 3 October 1990 when the Ge ...
. The city was occupied by Soviet troops on 8 May 1945.
GDR
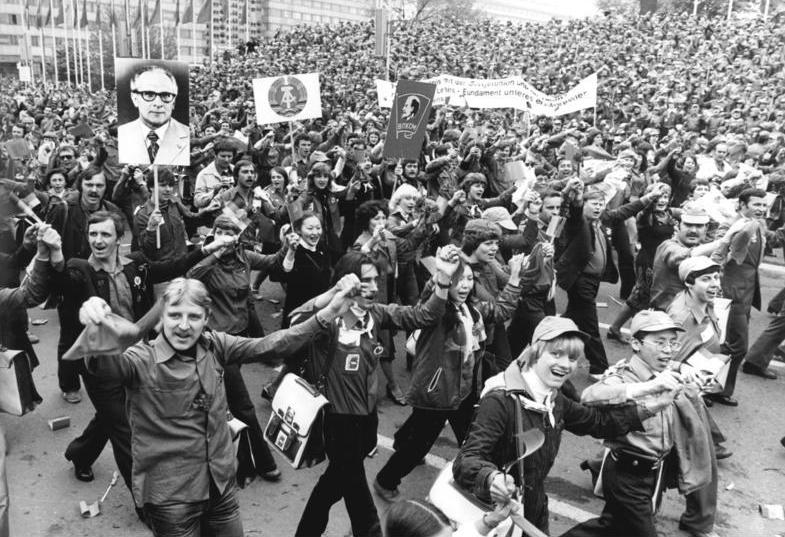
 After the dissolution of the Länder (states) in the GDR in 1952, Chemnitz became seat of a district (). On 10 May 1953, the city was renamed by decision of the East German government to after
After the dissolution of the Länder (states) in the GDR in 1952, Chemnitz became seat of a district (). On 10 May 1953, the city was renamed by decision of the East German government to after Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...
, in recognition of its industrial heritage and the Karl Marx Year
Karl Marx Year (german: Karl-Marx-Jahr) was a series of anniversaries of Karl Marx commemorated by East Germany in 1953, 1968, and 1983. The most prominent was in 1953, for the 70th anniversary of Marx's death, and included the renaming of Chemnitz ...
marking the 135th anniversary of his birth and the 70th anniversary of his death. GDR Prime Minister Otto Grotewohl
Otto Emil Franz Grotewohl (; 11 March 1894 – 21 September 1964) was a German politician who served as the first prime minister of the German Democratic Republic (GDR/East Germany) from its foundation in October 1949 until his death in Septembe ...
said:
After the city centre was destroyed in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the East German authorities attempted to rebuild it to symbolise the conceptions of urban development of a socialist city. The layout of the city centre at that time was rejected in favour of a new road network. However, the original plans were not completed. In addition, the rapid development of housing took priority over the preservation of old buildings. So in the 1960s and 1970s, both in the centre as well as the periphery, large areas were built in apartment-block style, for example . The old buildings of the period, which still existed in the Kassberg, and especially, were neglected and fell increasingly into dereliction.
After reunification
 On 23 April 1990, a referendum on the future name of the city was held: 76% of the voters voted for the old name "". On 1 June 1990, the city was officially renamed.
After the
On 23 April 1990, a referendum on the future name of the city was held: 76% of the voters voted for the old name "". On 1 June 1990, the city was officially renamed.
After the reunification of Germany
German reunification (german: link=no, Deutsche Wiedervereinigung) was the process of re-establishing Germany as a united and fully sovereign state, which took place between 2 May 1989 and 15 March 1991. The day of 3 October 1990 when the Ge ...
on 3 October 1990, the city of Chemnitz faced several difficult tasks. Many inhabitants migrated to the former West Germany and unemployment in the region increased sharply; in addition Chemnitz did not have adequate shopping facilities, but this was increasingly demanded."Kurzfassung zur Promotion des Dipl.-Pol. Alexander Bergmann zur Thematik 'Deutschlands jüngste Innenstadt – Rekonstruktion in Chemnitz verstehen'"/ref> Large shopping centers were constructed on the city periphery to the early 1990s. Chemnitz is the only major German city whose centre was re-planned after 1990, similar to the reconstruction of several other German cities in the immediate post-war years. Plans for the recovery of a compressed city centre around the historic town hall in 1991 led to an urban design competition. This was announced internationally by the city and carried out with the help of the partner city of . The mooted project on an essentially unused area of the former city would be comparable in circumference with the in Berlin. Numerous internationally renowned architects such as , and provided designs for a new city centre. The mid-1990s began the development of the inner city brownfields around the town hall to a new town. In Chemnitz city more than 66,000 square meters of retail space have emerged. With the construction of office and commercial building on the construction site "B3" at the court, the last gap in 2010 was closed in city centre image. The intensive development included demolition of partially historically valuable buildings from the period and was controversial. Between 1990 and 2007 more than 250 buildings were leveled.
 In late August 2018 the city was the site of a series of
In late August 2018 the city was the site of a series of protests
A protest (also called a demonstration, remonstration or remonstrance) is a public expression of objection, disapproval or dissent towards an idea or action, typically a political one.
Protests can be thought of as acts of coopera ...
that attracted at least 8,000 people. The protests were attended by far-right
Far-right politics, also referred to as the extreme right or right-wing extremism, are political beliefs and actions further to the right of the left–right political spectrum than the standard political right, particularly in terms of being ...
and Neo-Nazi
Neo-Nazism comprises the post–World War II militant, social, and political movements that seek to revive and reinstate Nazism, Nazi ideology. Neo-Nazis employ their ideology to promote hatred and Supremacism#Racial, racial supremacy (ofte ...
groups. News outlets reported about mob violence and riots. The protests started after two immigrants from the Middle East were arrested in connection with the murder of Daniel H., a 35 year old German man, the son of a German mother and a Cuban father, which had happened on 26 August. Violent clashes occurred between far-right protesters and far-left counter protesters, leading to injuries. The mobs outnumbered the local police presence. There were reports that rightist protesters chased down dark skinned bystanders and those that appeared to be foreigners on the streets before more police arrived and intervened. The riots were widely condemned by media outlets and politicians throughout Germany, and were "described as reminiscent of civil war and Nazi pogroms."
The reports of mob violence and riots were criticized as incorrect later on. The German language Swiss newspaper Neue Zürcher Zeitung
The ''Neue Zürcher Zeitung'' (''NZZ''; "New Journal of Zürich") is a Swiss, German-language daily newspaper, published by NZZ Mediengruppe in Zürich. The paper was founded in 1780. It was described as having a reputation as a high-quality ne ...
corrected its earlier reports, stating that there had evidently been no mob violence but there have been sporadic encroachments. Minister President of Saxony Michael Kretschmer came to the same conclusion: "there were no mobs and man hunts".
One week after the protests, a free "Concert against the Right" under the motto "We are more" (#wirsindmehr) attracted an audience of some 65,000 people. A one-minute silence commemorated the murdered Daniel H., the son of a German mother and a Cuban father. The concert itself has been criticized for far-left activities and violent song texts of some of the participating bands.
Culture and sights
The city won the bid to be one of the two European Capitals of Culture (in 2025) on 28 October 2020, beating Hanover, Hildesheim, Magdeburg and Nuremberg.Theater Chemnitz
Theater Chemnitz is the municipal theatre organization in Chemnitz, Germany. Performances of opera, ballet, plays, symphonic concerts, and puppet theatre take place in its three main venues: the Opernhaus Chemnitz (for opera, ballet and musical th ...
offers a variety of theatre: opera (opera house from 1909), plays, ballet and (puppets), and runs concerts by the orchestra Robert-Schumann-Philharmonie (founded 1832).
Tourist sights include the Kassberg neighborhood with 18th and 19th century buildings and the Karl Marx Monument
The Karl Marx Monument (german: Karl-Marx-Monument) is a 7.10m (23.29ft)-tall stylized head of Karl Marx in Chemnitz, Germany. The heavy-duty sculpture, together with the base platform, stand over 13 meters (42 feet) tall and weighs approximate ...
by Lev Kerbel
Lev Yefimovich Kerbel (russian: Лев Ефимович Кербель; – 14 August 2003) was a sculptor of Soviet realist works. Kerbel's creations included statues of Karl Marx, Vladimir Lenin, Yuri Gagarin, which were sent by Soviet Gove ...
, nicknamed (a Saxon dialect word for head) by the locals. Landmarks include the Old Town Hall with its Renaissance portal (15th century), the castle on the site of the former monastery, and the area around the opera house
An opera house is a theatre building used for performances of opera. It usually includes a stage, an orchestra pit, audience seating, and backstage facilities for costumes and building sets.
While some venues are constructed specifically for o ...
and the old university. The most conspicuous landmark is the red tower built in the late 12th or early 13th century as part of the city wall
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
.
The Chemnitz petrified forest
The Chemnitz petrified forest is a petrified forest in Chemnitz, Germany.
Most of the trunks are exhibited in the Museum of Natural History in Chemnitz inside of Kulturkaufhaus Tietz , including slices of trunks with polished edges. A small colle ...
is located in the courtyard of Kulturkaufhaus Tietz. It is one of the very few in existence, and dates back several million years (details shown in the Museum of Natural Sciences "Museum für Naturkunde Chemnitz", founded 1859). Also within the city limits, in the district of Rabenstein, is the smallest castle in Saxony, Rabenstein Castle.
The city has changed considerably since German reunification. Most of its industry is now gone and the core of the city has been rebuilt with many shops as well as huge shopping centres. Many of these shops are international brands, including Zara, H&M, Esprit, , Leiser Shoes, and Peek & Cloppenburg. The large (Red Tower) shopping centre is very popular with young people.
The Chemnitz Industrial Museum is an Anchor Point of ERIH, the European Route of Industrial Heritage
The European Route of Industrial Heritage (ERIH) is a tourist route of the most important industrial heritage sites in Europe. This is a tourism industry information initiative to present a network of industrial heritage sites across Europe. The a ...
. Additional unique industrial monuments are located at the "Schauplatz Eisenbahn" (Saxon Railway Museum and Museum of Technology Cable Running System) in Chemnitz-Hilbersdorf. The State Museum of Archaeology Chemnitz opened in 2014 and is located in the former Schocken Department Stores
Schocken Department Stores (Kaufhaus Schocken) was a chain of department stores in Germany before World War II. History
The company was founded by Simon Schocken (1874–1929) and Salman Schocken (1877–1959). After Simon had married into the ...
(architect: Erich Mendelsohn; opening of the department store: 1930).
The , formerly a bank, opened on 1 December 2007. , who lived in Munich, had a collection of some 2,500 pieces of modern art
Modern art includes artistic work produced during the period extending roughly from the 1860s to the 1970s, and denotes the styles and philosophies of the art produced during that era. The term is usually associated with art in which the tradi ...
, including many paintings and drawings by , and others.
The other great art museum in Chemnitz is located near central railway station, it is called "Museum am Theaterplatz" (erected 1909 as "König-Albert-Museum").
The is a municipal botanical garden
A botanical garden or botanic gardenThe terms ''botanic'' and ''botanical'' and ''garden'' or ''gardens'' are used more-or-less interchangeably, although the word ''botanic'' is generally reserved for the earlier, more traditional gardens, an ...
, and the is a non-profit garden specializing in arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenla ...
and alpine plant
Alpine plants are plants that grow in an alpine climate, which occurs at high elevation and above the tree line. There are many different plant species and taxa that grow as a plant community in these alpine tundra. These include perennial grasses, ...
s.
Near the city center is the "Villa Esche" located (Henry-van-de-Velde-museum). This historical house was built in 1902 in art-nouveau-style by van de Velde.
Image gallery
Chemnitz Opera
Theater Chemnitz is the municipal theatre organization in Chemnitz, Germany. Performances of opera, ballet, plays, symphonic concerts, and puppet theatre take place in its three main venues: the Opernhaus Chemnitz (for opera, ballet and musical t ...
at Opernplatz
File:St.-Petri-Kirche in Chemnitz (Barras).JPG, St. Petri church
File:Lutherkirche chemnitz.jpg, Lutheran church
File:Schlossteich und -kirche in Chemnitz (Hiroshi).JPG, Castle church over the Castle Lake
File:Hotel Mercure, Chemnitz, 2015.jpg, The Mercure Hotel, tallest building in Chemnitz
File:Chemnitz-Glaesernes-Kaufhaus.jpg, The Transparent department store
File:Chemnitz-Falkeplatz.jpg, View over at night
File:Castle Rabenstein 1 (aka).jpg,
File:Karl-Marx-Monument in Chemnitz.jpg, Bust of Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...
, the city's former namesake
File:Hauptgebäude der TU Chemnitz, 2015.jpg, Chemnitz University of Technology
Chemnitz (; from 1953 to 1990: Karl-Marx-Stadt , ) is the third-largest city in the German state of Saxony after Leipzig and Dresden. It is the 28th largest city of Germany as well as the fourth largest city in the area of former East Germany a ...
File:Blick zur Galerie Roter Turm und zum Hotel Mercure in Chemnitz 2015.jpg, View over the city halls and the inner city
File:Chemnitz-Kulturhaus.jpg,
File:Wasserschloss-Klaffenbach2.jpg, Watercastle
File:Chemnitz Stadtbad1.JPG,
File:Chemnitz-AmSchloss.jpg, Guest houses at Castle park
File:Der Versteinerte Wald von Chemnitz im Lichthof des Kulturkaufhaus DAStietz, 2015.jpg, Chemnitz petrified forest
The Chemnitz petrified forest is a petrified forest in Chemnitz, Germany.
Most of the trunks are exhibited in the Museum of Natural History in Chemnitz inside of Kulturkaufhaus Tietz , including slices of trunks with polished edges. A small colle ...
inside the
File:Chemnitz-Gunzenhauser-night.jpg, Gunzenhauser Museum
File:Kaufhaus Schocken in Chemnitz 2014.jpg, State Museum of Archaeology Chemnitz
Administrative divisions
The city of Chemnitz consists of 39 neighborhoods. The neighborhoods of Einsiedel, Euba, Grüna, Klaffenbach, Kleinolbersdorf-Altenhain, Mittelbach, Röhrsdorf and Wittgensdorf are at the same time localities within the meaning of Sections 65 to 68 of the Saxon Municipal Code. These neighborhoods came in the wake of the last incorporation wave after 1990 as formerly independent municipalities to the city of Chemnitz and therefore enjoy this special position compared to the other parts of the city. These localities each have a local council, which, depending on the number of inhabitants of the locality concerned, comprises between ten and sixteen members as well as a chairman of the same. The local councils are to hear important matters concerning the locality. A final decision is, however, incumbent on the city council of the city of Chemnitz. (PDF; 75 KB) The official identification of the districts by numbers is based on the following principle: Starting from the city center (neighborhoods Zentrum and Schloßchemnitz), all other parts of the city are assigned clockwise in ascending order the tenth place of their index, the one-digit is awarded in the direction of city periphery in ascending order.Politics
Mayor
The first freely elected mayor after German reunification was Dieter Noll of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU), who served from 1990 to 1991, followed by Joachim Pilz (CDU) until 1993. The mayor was originally chosen by the city council, but since 1994 has been directly elected. Peter Seifert of theSocial Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
For ...
(SPD) served from 1993 until 2006. Between 2006 and 2020 Barbara Ludwig (SPD) has served as mayor. Sven Schulze (SPD) was elected mayor in 2020.
The most recent mayoral election was held on 20 September 2020, with a runoff held on 11 October, and the results were as follows:
! rowspan=2 colspan=2, Candidate
! rowspan=2, Party
! colspan=2, First round
! colspan=2, Second round
, -
! Votes
! %
! Votes
! %
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Sven Schulze
, align=left, Social Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
For ...
, 22,241
, 23.1
, 31,749
, 34.9
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Almut Patt
, align=left, Christian Democratic Union
, 20,630
, 21.4
, 20,047
, 22.0
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Susanne Schaper
, align=left, The Left
, 14,584
, 15.1
, 14,668
, 16.1
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Ulrich Oehme
, align=left, Alternative for Germany
Alternative for Germany (german: link=no, Alternative für Deutschland, AfD; ) is a right-wing populist
*
*
*
*
*
*
* political party in Germany. AfD is known for its opposition to the European Union, as well as immigration to Germany. I ...
, 11,731
, 12.2
, 12,034
, 13.2
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Lars Faßmann
, align=left, Independent
Independent or Independents may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Artist groups
* Independents (artist group), a group of modernist painters based in the New Hope, Pennsylvania, area of the United States during the early 1930s
* Independ ...
, 11,470
, 11.9
, 12,515
, 13.8
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Volkmar Zschocke
, align=left, Alliance 90/The Greens
Alliance 90/The Greens (german: Bündnis 90/Die Grünen, ), often simply referred to as the Greens ( ), is a Green politics, green List of political parties in Germany, political party in Germany. It was formed in 1993 as the merger of The Greens ...
, 6,811
, 7.1
, align=center colspan=2, ''Withdrew''
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Matthias Eberlein
, align=left, Free Voters
Free Voters (german: Freie Wähler, FW or FWG) in Germany may belong to an association of people which participates in an election without having the status of a registered political party. Usually it involves a locally organized group of voters ...
, 3,394
, 3.5
, align=center colspan=2, ''Withdrew''
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Paul Vogel
, align=left, Die PARTEI
(''Party for Labour, Rule of Law, Animal Protection, Promotion of Elites and Grassroots Democratic Initiative''), or Die PARTEI (''The PARTY''), is a German political party. It was founded in 2004 by the editors of the German satirical magazi ...
, 1,527
, 1.6
, align=center colspan=2, ''Withdrew''
, -
! colspan=3, Valid votes
! 96,428
! 99.5
! 91,017
! 99.7
, -
! colspan=3, Invalid votes
! 489
! 0.5
! 285
! 0.3
, -
! colspan=3, Total
! 96,917
! 100.0
! 91,302
! 100.0
, -
! colspan=3, Electorate/voter turnout
! 194,952
! 49.7
! 194,850
! 46.9
, -
, colspan=7, SourceWahlen in Sachsen
City council
Alternative for Germany
Alternative for Germany (german: link=no, Alternative für Deutschland, AfD; ) is a right-wing populist
*
*
*
*
*
*
* political party in Germany. AfD is known for its opposition to the European Union, as well as immigration to Germany. I ...
(AfD)
, 62,053
, 17.9
, 12.3
, 11
, 8
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, The Left (Die Linke)
, 58,009
, 16.7
, 6.9
, 10
, 5
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Social Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
For ...
(SPD)
, 40,357
, 11.6
, 7.9
, 7
, 5
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Alliance 90/The Greens
Alliance 90/The Greens (german: Bündnis 90/Die Grünen, ), often simply referred to as the Greens ( ), is a Green politics, green List of political parties in Germany, political party in Germany. It was formed in 1993 as the merger of The Greens ...
(Grüne)
, 39,908
, 11.5
, 3.6
, 7
, 2
, -
,
, align=left, Pro Chemnitz/ German Social Union (PRO.DSU)
, 26,606
, 7.7
, 2.0
, 5
, 2
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Free Democratic Party (FDP)
, 25,623
, 7.4
, 1.9
, 4
, 1
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Die PARTEI
(''Party for Labour, Rule of Law, Animal Protection, Promotion of Elites and Grassroots Democratic Initiative''), or Die PARTEI (''The PARTY''), is a German political party. It was founded in 2004 by the editors of the German satirical magazi ...
(PARTEI)
, 10,260
, 3.0
, 2.4
, 1
, 1
, -
,
, align=left, People's Solidarity
People's Solidarity (german: Volkssolidarität) is an organisation for elderly people in the new states of Germany, founded 1945. It was one of many important non-parliamentary mass organisations in the former socialist country, East Germany. T ...
(Vosi)
, 7,862
, 2.3
, 0.8
, 1
, 1
, -
, bgcolor=,
, align=left, Pirate Party Germany
The Pirate Party Germany (german: Piratenpartei Deutschland), commonly known as Pirates (), is a political party in Germany founded in September 2006 at c-base. It states general agreement with the Swedish Piratpartiet as a party of the informat ...
(Piraten)
, 6,817
, 2.0
, 0.1
, 1
, ±0
, -
! colspan=2, Valid votes
! 118,548
! 98.5
!
!
!
, -
! colspan=2, Invalid votes
! 1,837
! 1.5
!
!
!
, -
! colspan=2, Total
! 120,385
! 100.0
!
! 60
! ±0
, -
! colspan=2, Electorate/voter turnout
! 196,515
! 61.3
! 17.2
!
!
, -
, colspan=7, SourceWahlen in Sachsen
Urban renewal
 Heavy destruction in World War II as well as post-war demolition to erect a truly socialist city centre left the city with a vast open space around its
Heavy destruction in World War II as well as post-war demolition to erect a truly socialist city centre left the city with a vast open space around its town hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
where once a vibrant city heart had been. Because of massive investment in out-of-town shopping right after reunification, it was not until 1999 that major building activity was started in the centre. Comparable to in Berlin, a whole new quarter of the city was constructed in recent years. New buildings include the department store
A department store is a retail establishment offering a wide range of consumer goods in different areas of the store, each area ("department") specializing in a product category. In modern major cities, the department store made a dramatic app ...
by , with a façade by and Peek & Cloppenburg clothing store by and Partner.
Economy
Chemnitz is the largest city of the urban area and is one of the most important economic areas of Germany's new federal states. Chemnitz had a GDP of €8.456 billion in 2016, with GDP per capita at €34,166. Since about 2000, the city's economy has recorded high annualGDP growth
Economic growth can be defined as the increase or improvement in the inflation-adjusted market value of the goods and services produced by an economy in a financial year. Statisticians conventionally measure such growth as the percent rate of ...
rates; Chemnitz is among the top ten German cities in terms of growth rate. The local and regional economic structure is characterized by medium-sized companies, with the heavy industrial sectors of mechanical engineering, metal processing, and vehicle manufacturing as the most significant industries.
About 100,000 people are employed, of whom about 46,000 commute from other municipalities. 16.3% of employees in Chemnitz have a university or college degree
An academic degree is a qualification awarded to students upon successful completion of a course of study in higher education, usually at a college or university. These institutions commonly offer degrees at various levels, usually including unde ...
, twice the average rate in Germany.
Image gallery
Demography
Chemnitz University of Technology
Chemnitz (; from 1953 to 1990: Karl-Marx-Stadt , ) is the third-largest city in the German state of Saxony after Leipzig and Dresden. It is the 28th largest city of Germany as well as the fourth largest city in the area of former East Germany a ...
. In 2017, out of its 10,482 students, 2712 were foreign students, which equals to about 25%, making Chemnitz the most internationalised of the three major universities of Saxony.
Languages
*Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety ...
* Chemnitz dialect
Chemnitz dialect is a distinct German dialect of the city of Chemnitz and an urban variety of Vorerzgebirgisch, a variant of Upper Saxon German.
Phonology
Consonants
* are bilabial, whereas are labiodental.
* are dental .
** is alveolar ...
, which is a variety of Upper Saxon German
Upper Saxon (german: Obersächsisch, ; ) is an East Central German language spoken in much of the modern German state of Saxony and in adjacent parts of southeastern Saxony-Anhalt and eastern Thuringia. As of the early 21st century, it's mostl ...
Transport

Roads
Chemnitz is linked to two motorways (s), A4 and A72 . Themotorway junction
In the field of road transport, an interchange (American English) or a grade-separated junction (British English) is a road junction that uses grade separations to allow for the movement of traffic between two or more roadways or highways, using ...
is situated in the northwestern area of the city. The motorway A72 between and Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as wel ...
is still under construction. Within the administrative area of Chemnitz there are eight motorway exits (). The A4 motorway is part of the European route E40
European route E40 is the longest European route, more than long, connecting Calais in France via Belgium, Germany, Poland, Ukraine, Russia, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, and Kyrgyzstan, with Ridder in Kazakhstan near the border with R ...
, one of the longest European E roads, connecting Chemnitz with the Asian Highway
The Asian Highway Network (AH), also known as the Great Asian Highway, is a cooperative project among countries in Asia and the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (ESCAP) to improve their connectivity via h ...
system to the east and France to the west.
Public transport
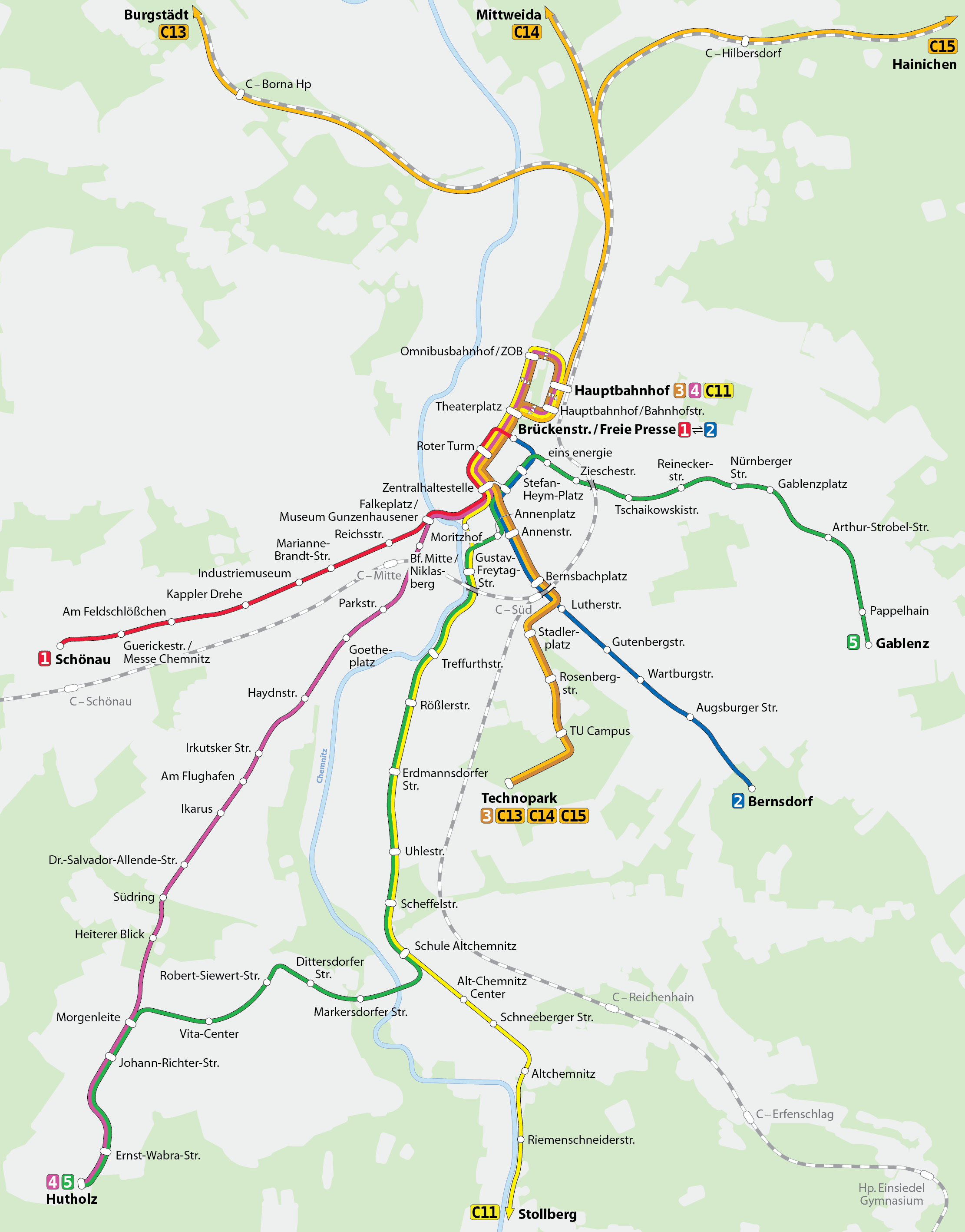
Public transport within Chemnitz is provided with tram and bus, as well as by the . Nowadays, the city and its surroundings are served by one line, five lines of the Chemnitz tramway network, 27 city bus lines, as well as several regional bus lines. At night, the city is served by two bus lines, two tram lines, and the line.Chemnitz Hauptbahnhof
Chemnitz Hauptbahnhof is the main railway station in Chemnitz in Germany.
Station building
The station has a combination of terminating and through platforms. Platform tracks 5 to 9 terminate and tracks 1 to 4 and 10 to 14 continue to the wes ...
is the main station for the city. In June 2022, an intercity connection from Chemnitz via Dresden and Berlin to Rostock-Warnemünde was established again for the first time since 2006. Prior to this, Chemnitz was for a long time the largest German city without a connection of long-distance intercity services. 2 RegionalExpress routes connected Chemnitz to the larger cities of Saxony (RE3 from Dresden Hbf via Chemnitz to Hof & RE6 to Leipzig Hbf). In addition, 4 RegionalBahn and 4 CityBahn routes also operate from the Hauptbahnhof.
The length of the tram, and bus networks is , and respectively. In August 2012, electro-diesel trams were ordered from , to support an expansion of the light rail network to , with new routes serving , and .
Airports
Three airports are near Chemnitz, including the twointernational airport
An international airport is an airport with customs and border control facilities enabling passengers to travel between countries around the world. International airports are usually larger than domestic airports and they must feature longer ...
s of Saxony in Dresden and Leipzig. Both Leipzig/Halle Airport
Leipzig/Halle Airport (German: ''Flughafen Leipzig/Halle'') is an international airport located in Schkeuditz, Saxony, Germany and serves both Leipzig, Saxony, and Halle, Saxony-Anhalt.
It is Germany's 14th largest airport by passengers and ...
and Dresden Airport
Dresden Airport is the international airport of Dresden, the state capital of Saxony, Germany. It is located in Klotzsche, a district of Dresden north of the city centre. It was formerly also known in German as ''Flughafen Dresden-Klotzsche''. ...
are about from Chemnitz and offer numerous continental as well as intercontinental flights.
Chemnitz also has a small commercial airport ( about south of the city. When its current upgrade is completed it will have an asphalt runway long and wide.
Sports

football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
)
* Chemnitzer PSV
Chemnitzer Polizeisportverein e.V. (commonly known as Chemnitzer PSV, or CPSV for short) is a German sports club in Chemnitz, Germany. Founded in 1920 as PSV Chemnitz, the club sees itself as their legal successor. With almost 2,000 members, C ...
(football, handball, volleyball)
* Chemcats Chemnitz (basketball, women)
* VfB Fortuna Chemnitz (football)
* (swimming)
* (swimming)
* (swimming, gymnastics, volleyball, skittles
Skittles may refer to:
* Skittles (confectionery), a brand of fruit-flavor chewy candy, distributed by Wm. Wrigley Jr. Company
*'' Skittles Commercial: The Broadway Musical''
* Skittles (sport), the game from which bowling originated
* Skittles (ch ...
)
* (ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an ice skating rink with lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two opposing teams use ice hock ...
, skater hockey)
* (tennis)
* Floor Fighters Chemnitz (floorball
Floorball is a type of floor hockey with five players and a goalkeeper in each team. Men and women play indoors with sticks and a plastic ball with holes. Matches are played in three twenty-minute periods. The sport of bandy also played a role ...
)
* (luge
A luge is a small one- or two-person sled on which one sleds supine (face up) and feet-first. A luger steers by using the calf muscles to flex the sled's runners or by exerting opposite shoulder pressure to the seat. Racing sleds weigh for s ...
)
* (figure skating
Figure skating is a sport in which individuals, pairs, or groups perform on figure skates on ice. It was the first winter sport to be included in the Olympic Games, when contested at the 1908 Olympics in London. The Olympic disciplines are me ...
, ice dancing
Ice dance (sometimes referred to as ice dancing) is a discipline of figure skating that historically draws from ballroom dancing. It joined the World Figure Skating Championships in 1952, and became a Winter Olympic Games medal sport in 1976. Ac ...
, curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns sliding ...
)
* Chemnitz Crusaders (American football
American football (referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada), also known as gridiron, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular field with goalposts at each end. The offense, the team with ...
)
* Tower Rugby Chemnitz (rugby
Rugby may refer to:
Sport
* Rugby football in many forms:
** Rugby league: 13 players per side
*** Masters Rugby League
*** Mod league
*** Rugby league nines
*** Rugby league sevens
*** Touch (sport)
*** Wheelchair rugby league
** Rugby union: 1 ...
)
* (football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
)
* (cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
)
Notable people
*Paul Oswald Ahnert
Paul Oswald Ahnert (22 November 1897 – 27 February 1989) was a German astronomer. He first became famous in Germany for publishing the ''"Kalender für Sternfreunde"'' from 1948 until 1988, an annual calendar of astronomical events. The mino ...
(1897–1989), astronomer
* Brigitte Ahrens (born 1945), pop singer
* Olaf Altmann
Olaf Altmann (born 1966) is a German scenic designer.
Born in Karl-Marx-Stadt (now Chemnitz), Altmann began his theatre career as a stage technician at the municipal theatre. There, he also designed his first stage design for a production of Hasko ...
(born 1960), scenic designer
* Mark Arndt (born 1941), Russian Orthodox Archbishop
* Michael Ballack
Michael Ballack (; born 26 September 1976) is a German former professional footballer. He is among the top goal scorers in the history of the German national team. Ballack wore the number 13 shirt for every team he has played for, except 1. FC ...
(born 1976), German footballer, former captain of Bayern Munich
Fußball-Club Bayern München e. V. (FCB, ), also known as FC Bayern (), Bayern Munich, or simply Bayern, is a German professional sports club based in Munich, Bavaria. It is best known for its professional men's football team, which pla ...
and Germany
* Veronika Bellmann
Veronika Maria Bellmann ( née Wächter; born 20 November 1960 in Chemnitz, ''then Karl-Marx-Stadt in East Germany'') is a German politician and member of the CDU.
She was Member of the German Bundestag for Mittelsachsen from 2002 until 202 ...
(born 1960), politician
* Fritz Bennewitz
Fritz Bennewitz (20 January 1926 – 13 September 1995) was a German theatre director.
Life
Bennewitz was born in Chemnitz. His father was a train driver: his mother worked as a seamstress.
Between 1950 and 1953 he was a student of German st ...
(1926–1995), theater director
* Gerd Böckmann
Gerd Böckmann (born 11 January 1944 in Chemnitz, Germany) is a German television actor.
Selected filmography Television
* ''Derrick'' - Season 2, Episode 10: ''"Kamillas junger Freund"'' (1975, TV)
* ''Derrick'' - Season 4, Episode 6: ''"Das Kuc ...
(born 1944), television actor and director
* Werner Bräunig (1934–1976), writer
* Marianne Brandt
Marianne Brandt (1 October 1893 – 18 June 1983) was a German painter, sculptor, photographer, metalsmith, and designer who studied at the Bauhaus art school in Weimar and later became head of the Bauhaus ''Metall-Werkstatt'' (Metal Workshop ...
(1893–1983), artist, designer
* Valery Bykovsky
Valery Fyodorovich Bykovsky (russian: Вале́рий Фёдорович Быко́вский; 2 August 1934 – 27 March 2019) was a Soviet cosmonaut who flew on three space flights: Vostok 5, Soyuz 22, and Soyuz 31. He was also backup for Vo ...
(1934–2019), Soviet cosmonaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member aboard a spacecraft. Although generally r ...
* C418
Daniel Rosenfeld (born 9 May 1989), better known by his stage/online name C418 (pronounced "see four eighteen"), is a German musician, producer and sound engineer, best known as the composer and sound designer for the sandbox video game ''Minec ...
(real name Daniel Rosenfeld, born 1989), music producer and sound engineer for ''Minecraft
''Minecraft'' is a sandbox game developed by Mojang Studios. The game was created by Markus "Notch" Persson in the Java programming language. Following several early private testing versions, it was first made public in May 2009 before being ...
'' and ''Stranger Things
''Stranger Things'' is an American science fiction horror drama television series created by the Duffer Brothers, who also serve as showrunners and are executive producers along with Shawn Levy and Dan Cohen. Produced by Monkey Massacre Prod ...
''
* Hans Carl von Carlowitz
Hans Carl von Carlowitz, originally ''Hannß Carl von Carlowitz'' (24 December 1645 - 3 March 1714), was a Saxon tax accountant and mining administrator. His book ''Sylvicultura oeconomica, oder haußwirthliche Nachricht und Naturmäßige Anweisu ...
(1645–1714), forest scientist
* Max Eckert-Greifendorff
Max Eckert (after 1934, Max Eckert-Greifendorff: 10 April 1868 in Chemnitz, Kingdom of Saxony – 26 December 1938, in Aachen) was a German geographer.
Biography
He received his education in Löbau and Berlin, and taught for some time at Löbau ...
(1868–1938), cartographer and professor
* Gerson Goldhaber
Gerson Goldhaber (February 20, 1924 – July 19, 2010) was a German-born American particle physicist and astrophysicist. He was one of the discoverers of the J/ψ meson which confirmed the existence of the charm quark. He worked at Lawrence Be ...
(1924–2010), American nuclear and astrophysicist
* Friedrich Goldmann
Friedrich Goldmann (27 April 1941 – 24 July 2009) was a German composer and conductor.
Life
Born on 27 April 1941 in Siegmar-Schönau (since July 1951 incorporated into Chemnitz), Goldmann's music education began in 1951 when he joined the Dr ...
(1941–2009), composer and conductor
* Johannes Hähle (1906–1944), military photographer
* Peter Härtling
Peter Härtling (; 13 November 1933 – 10 July 2017) was a German writer, poet, publisher and journalist. He received the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany for his major contribution to German literature.
Biography
Härtling wa ...
(born 1933), writer
* Frank Heinrich
Frank Heinrich (born 25 January 1964) is a German theologian, social pedagogue and politician of the Christian Democratic Union (CDU).
Background and education
Heinrich was born in Siegen. At the age of three he moved to the southern part of ...
(born 1964), politician, member of the Bundestag
The Bundestag (, "Federal Diet") is the German federal parliament. It is the only federal representative body that is directly elected by the German people. It is comparable to the United States House of Representatives or the House of Commons ...
* Stephan Hermlin
Stephan Hermlin (; 13 April 1915 – 6 April 1997), real name ''Rudolf Leder,'' was a German author. He wrote, among other things, stories, essays, translations, and lyric poetry and was one of the more well-known authors of former East Germany.
...
(1915–1997), writer
* Stefan Heym
Helmut Flieg or Hellmuth Fliegel (10 April 1913 – 16 December 2001) was a German writer, known by his pseudonym Stefan Heym (). He lived in the United States and trained at Camp Ritchie, making him one of the Ritchie Boys of World War II. In ...
(1913–2001), writer and member of the Bundestag of the PDS
* Christian Gottlob Heyne
Christian Gottlob Heyne (; 25 September 1729 – 14 July 1812) was a German classical scholar and archaeologist as well as long-time director of the Göttingen State and University Library. He was a member of the Göttingen School of History.
...
(1729–1812), classical scholar and archaeologist
* Sigmund Jähn
Sigmund Werner Paul Jähn (; 13 February 1937 – 21 September 2019) was a German cosmonaut and pilot who in 1978 became the first German to fly into space as part of the Soviet Union's Interkosmos programme.
Early life
Jähn was born on 13 Fe ...
(1937–2019), first German astronaut
An astronaut (from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'star', and (), meaning 'sailor') is a person trained, equipped, and deployed by a human spaceflight program to serve as a commander or crew member aboard a spacecraft. Although generally r ...
(Interkosmos
Interkosmos (russian: Интеркосмос) was a Soviet space program, designed to help the Soviet Union's allies with crewed and uncrewed space missions.
The program was formed in April 1967 in Moscow. All members of the program from USSR ...
flight of August 26, 1978)
* John Kluge
John Werner Kluge (; September 21, 1914September 7, 2010) was a German-American entrepreneur who became a television industry mogul in the United States. At one time he was the richest person in the U.S.
Early life and education
Kluge was bo ...
(1921–2010), German-American billionaire and media mogul
* Helga Lindner (born 1951), swimmer; Olympic
Olympic or Olympics may refer to
Sports
Competitions
* Olympic Games, international multi-sport event held since 1896
** Summer Olympic Games
** Winter Olympic Games
* Ancient Olympic Games, ancient multi-sport event held in Olympia, Greece b ...
silver medalist
* Max Littmann
Max Littmann (3 January 1862 – 20 September 1931) was a German architect.
Littmann was educated in the Gewerbeakademie Chemnitz and the Technische Hochschule Dresden. In 1885, he moved to Munich where he met Friedrich Thiersch and Gabriel ...
(1862–1931), architect
* Anja Mittag
Anja Mittag (; born 16 May 1985) is a German football coach and player who plays as a striker. Mittag is currently a player-coach for RB Leipzig.
In July 2020, Mittag announced that she will end her playing career after the women's Saxony Cup ...
(born 1985), footballer
A football player or footballer is a sportsperson who plays one of the different types of football. The main types of football are association football, American football, Canadian football, Australian rules football, Gaelic football, rugby ...
, World Champion 2007
* Frederick and William , founders of the Diamant bicycle brand
* Carsten Nicolai
Carsten Nicolai (18 September 1965), also known as Alva Noto, is a German musician and visual artist. He is a member of the music groups Diamond Version with Olaf Bender (Byetone), Signal with Frank Bretschneider and Olaf Bender, Cyclo with Ry ...
(born 1965), contemporary artist
* Frei Otto
Frei Paul Otto (; 31 May 1925 – 9 March 2015) was a German architect and structural engineer noted for his use of lightweight structures, in particular tensile and membrane structures, including the roof of the Olympic Stadium in Munich for ...
(1925–2015), architect, architectural theorist and professor of architecture, builder of the Munich Olympic Park
* Sylke Otto (born 1969), luge
A luge is a small one- or two-person sled on which one sleds supine (face up) and feet-first. A luger steers by using the calf muscles to flex the sled's runners or by exerting opposite shoulder pressure to the seat. Racing sleds weigh for s ...
* Siegfried Rapp
Siegfried Rapp (1915 - 1982) was a German pianist who lost his right arm during World War II and then focused on the left-hand repertoire. He is now mainly remembered for being the first to perform Prokofiev's Piano Concerto No. 4 for the Left Ha ...
(1917–1977), one-armed German pianist
* Frederick Emil Resche (1966–1946), U.S. Army brigadier general
* Frank Rost
Frank Rost (born 30 June 1973) is a German former professional footballer who played as a goalkeeper.
He comes from a sporting family background; his father Peter won a gold medal at the 1980 Olympic Games in handball, and his mother Christi ...
(born 1973), retired football goalkeeper
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
* Bruno Salzer (1859–1919), one of Chemnitz's leading entrepreneurs
* Aliona Savchenko, ice figure skater
* Helmut Schelsky
Helmut Schelsky (14 October 1912 – 24 February 1984), was a German sociologist, the most influential in post-World War II Germany, well into the 1970s.
Biography
Schelsky was born in Chemnitz, Saxony. He turned to social philosophy and even ...
(1912–1984), sociologist and university lecturer
* Karl Schmidt-Rottluff
Karl Schmidt-Rottluff (Karl Schmidt until 1905; 1 December 1884 – 10 August 1976) was a German expressionist painter and printmaker; he was one of the four founders of the artist group Die Brücke.
Life and work
Schmidt-Rottluff was born in ...
(1884–1976), painter and graphic artist of expressionism
* Maria Schüppel Maria Schüppel (1923 – 27 June 2011) was a German composer, educator, pianist and pioneering music therapist who composed works for lyre and voice, and experimented with electronic music.
Schüppel was born in Chemnitz. After her father’s ...
(1923-2011), composer and pioneering music therapist
* Matthias Schweighöfer
Matthias Schweighöfer (; born 11 March 1981) is a German actor, voice actor, film director, and producer.
Early life
Born in Anklam, Western Pomerania, Schweighöfer attended Berlin's renowned acting school Ernst Busch Academy of Dramatic Art ...
(born 1981), actor and film director
* Jörg Schüttauf
Jörg Schüttauf (born 26 December 1961) is a German actor. He studied at the Theaterhochschule Leipzig. Since 2002 he has starred in the Hessischer Rundfunk version of the popular television crime series ''Tatort''.
Filmography Film
* 1985: ''E ...
(born 1961), actor
* Nadja Stefanoff (born 1983), soprano
A soprano () is a type of classical female singing voice and has the highest vocal range of all voice types. The soprano's vocal range (using scientific pitch notation) is from approximately middle C (C4) = 261 Hz to "high A" (A5) = 880&n ...
* Matthias Steiner
Matthias Steiner (; born 25 August 1982 in Vienna) is a retired Austrian-German weightlifter, and Olympic gold medalist.
As a native Austrian, he competed for Austria internationally from 1998 to 2005, in European Championships, World Champions ...
(born 1982), German-Austrian weightlifter
Olympic weightlifting, or Olympic-style weightlifting (officially named Weightlifting), is a sport in which athletes compete in lifting a barbell loaded with weight plates from the ground to overhead, with each athlete trying to successfully lift ...
, Olympic
Olympic or Olympics may refer to
Sports
Competitions
* Olympic Games, international multi-sport event held since 1896
** Summer Olympic Games
** Winter Olympic Games
* Ancient Olympic Games, ancient multi-sport event held in Olympia, Greece b ...
gold medalist 2008
* Ingo Steuer
Ingo Steuer (born 1 November 1966) is a German pair skater and skating coach. With Mandy Wötzel, he is the 1998 Olympic bronze medalist, the 1997 World champion, the 1995 European champion, and a four-time German national champion. As a c ...
(born 1966), figure skater
* Robin Szolkowy
Robin Szolkowy (born 14 July 1979) is a retired German pair skater. With partner Aliona Savchenko, he is the 2010 and 2014 Olympic bronze medalist, a five-time World champion ( 2008, 2009, 2011, 2012, 2014), a four-time European champion ( ...
, ice figure skater
* Hans-Günther Thalheim
Hans-Günther Thalheim (5 May 1924 – 3 December 2018) was a German professor of German studies, German language and linguistics and of Literary sciences. He was also a writer and literary editor.
Life
Thalheim was born in Chemnitz, in the sou ...
(1924-2018), germanist and linguist
* Siegfried Vogel
Siegfried Vogel (born 6 March 1937) is a German operatic Voice type, bass. Based at the Staatsoper Berlin, he performed internationally at major opera houses and festivals, including the Salzburg Festival and the Bayreuth Festival. He began in Wol ...
(born 1937), operatic bass
* Kurt Wagner (1904–1989), German general
* Katarina Witt
Katarina Witt (, ; born 3 December 1965) is a German former figure skater. A two-time Olympic champion, Witt is regarded as one of the greatest ladies' singles figure skaters of all time. Her Laureus profile states "she is remembered most for h ...
(born 1965), figure skater
* Mandy Wötzel
Mandy Wötzel (born 21 July 1973) is a German former pair skater who represented East Germany and later Germany in international competition. With partner Ingo Steuer, she is the 1998 Olympic bronze medalist, the 1997 World champion, the 1995 ...
(born 1973), figure skater
* Klaus Wunderlich
Klaus Wunderlich (18 June 1931 – 28 October 1997) was a famous German easy listening organist.
Biography
Wunderlich was born in Chemnitz. He played the Hammond organ model C3 then mid 60s changed to model Hammond H100. Wunderlich also tri ...
(1931–1997), organist
An organist is a musician who plays any type of organ (music), organ. An organist may play organ repertoire, solo organ works, play with an musical ensemble, ensemble or orchestra, or accompany one or more singers or instrumentalist, instrumental ...
Twin towns – sister cities
Chemnitz is twinned with: *Tampere
Tampere ( , , ; sv, Tammerfors, ) is a city in the Pirkanmaa region, located in the western part of Finland. Tampere is the most populous inland city in the Nordic countries. It has a population of 244,029; the urban area has a population o ...
, Finland (1961)
* Ljubljana
Ljubljana (also known by other historical names) is the capital and largest city of Slovenia. It is the country's cultural, educational, economic, political and administrative center.
During antiquity, a Roman city called Emona stood in the ar ...
, Slovenia (1966)
* Arras
Arras ( , ; pcd, Aro; historical nl, Atrecht ) is the prefecture of the Pas-de-Calais Departments of France, department, which forms part of the regions of France, region of Hauts-de-France; before the regions of France#Reform and mergers of ...
, France (1967)
* Timbuktu
Timbuktu ( ; french: Tombouctou;
Koyra Chiini: ); tmh, label=Tuareg, script=Tfng, ⵜⵏⴱⴾⵜ, Tin Buqt a city in Mali, situated north of the Niger River. The town is the capital of the Tombouctou Region, one of the eight administrativ ...
, Mali (1968)
* Ústí nad Labem
Ústí nad Labem (, , ) is a city in the Czech Republic. It has about 92,000 inhabitants. It is the capital of its eponymous region and district. It is a major industrial centre and, besides being an active river port, is an important railway ju ...
, Czech Republic (1970)
* Łódź
Łódź, also rendered in English as Lodz, is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located approximately south-west of Warsaw. The city's coat of arms is an example of canti ...
, Poland (1972)
* Mulhouse
Mulhouse (; Alsatian language, Alsatian: or , ; ; meaning ''Mill (grinding), mill house'') is a city of the Haut-Rhin Departments of France, department, in the Grand Est Regions of France, region, eastern France, close to the France–Switzerl ...
, France (1981)
* Manchester
Manchester () is a city in Greater Manchester, England. It had a population of 552,000 in 2021. It is bordered by the Cheshire Plain to the south, the Pennines to the north and east, and the neighbouring city of Salford to the west. The t ...
, England, UK (1983)
* Volgograd
Volgograd ( rus, Волгогра́д, a=ru-Volgograd.ogg, p=vəɫɡɐˈɡrat), geographical renaming, formerly Tsaritsyn (russian: Цари́цын, Tsarítsyn, label=none; ) (1589–1925), and Stalingrad (russian: Сталингра́д, Stal ...
, Russia (1988)
* Düsseldorf
Düsseldorf ( , , ; often in English sources; Low Franconian and Ripuarian: ''Düsseldörp'' ; archaic nl, Dusseldorp ) is the capital city of North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous state of Germany. It is the second-largest city in th ...
, Germany (1988)
* Akron
Akron () is the fifth-largest city in the U.S. state of Ohio and is the county seat of Summit County. It is located on the western edge of the Glaciated Allegheny Plateau, about south of downtown Cleveland. As of the 2020 Census, the city prop ...
, United States (1997)
* Taiyuan
Taiyuan (; ; ; Mandarin pronunciation: ; also known as (), ()) is the capital and largest city of Shanxi Province, People's Republic of China. Taiyuan is the political, economic, cultural and international exchange center of Shanxi Province. ...
, China (1999)
See also
*2018 Chemnitz protests
The 2018 Chemnitz protests took place in Chemnitz, in the German state of Saxony. In the early morning of 26 August, after a festival celebrating the city's founding, a fight broke out resulting in the death of a German man and serious injuries ...
References
Bibliography
External links
* * * * {{Authority control Cities in Saxony Oil campaign of World War II