Charles V of France on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Charles V (21 January 1338 – 16 September 1380), called the Wise (french: le Sage; la, Sapiens), was
 Charles was crowned
Charles was crowned
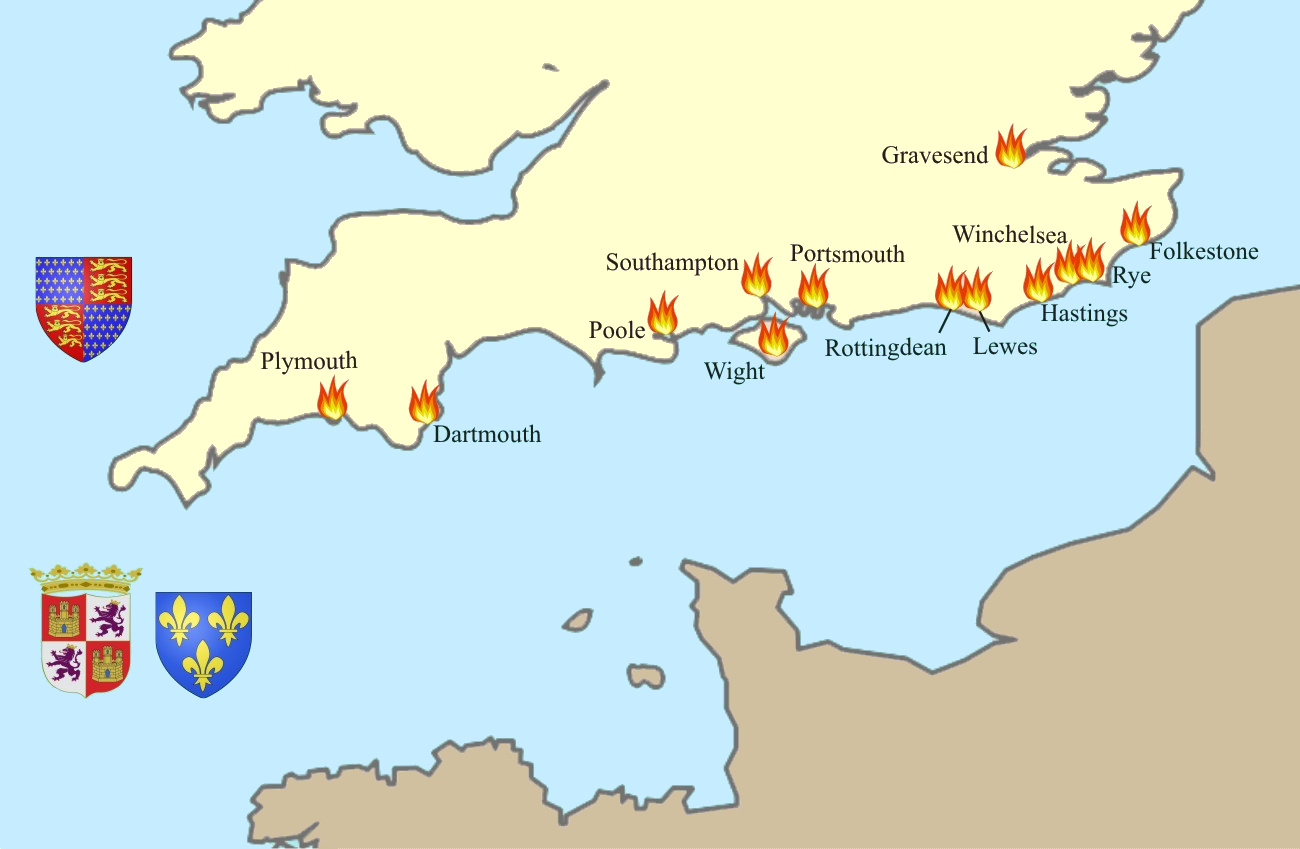 After the Castillan campaign, the Black Prince was invalid and heavily in debt. His rule in
After the Castillan campaign, the Black Prince was invalid and heavily in debt. His rule in
 Charles' reputation was of great significance for posterity, especially as his conception of governance was one that courtiers wished his successors could follow. Christine de Pizan's biography, commissioned by
Charles' reputation was of great significance for posterity, especially as his conception of governance was one that courtiers wished his successors could follow. Christine de Pizan's biography, commissioned by
King of France
France was ruled by monarchs from the establishment of the Kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions.
Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I () as the first ...
from 1364 to his death in 1380. His reign marked an early high point for France during the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, ...
, with his armies recovering much of the territory held by the English, and successfully reversed the military losses of his predecessors.
Charles became regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy ...
of France when his father John II John II may refer to:
People
* John Cicero, Elector of Brandenburg (1455–1499)
* John II Casimir Vasa of Poland (1609–1672)
* John II Comyn, Lord of Badenoch (died 1302)
* John II Doukas of Thessaly (1303–1318)
* John II Komnenos (1087–1 ...
was captured by the English at the Battle of Poitiers
The Battle of Poitiers was fought on 19September 1356 between a French army commanded by King JohnII and an Anglo- Gascon force under Edward, the Black Prince, during the Hundred Years' War. It took place in western France, south of Poi ...
in 1356. To pay for the defense of the kingdom, Charles raised taxes. As a result, he faced hostility from the nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy (class), aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below Royal family, royalty. Nobility has often been an Estates of the realm, estate of the realm with many e ...
, led by Charles the Bad
Charles II (10 October 1332 – 1 January 1387), called Charles the Bad, was King of Navarre 1349–1387 and Count of Évreux 1343–1387.
Besides the Pyrenean Kingdom of Navarre, Charles had extensive lands in Normandy, inherited from his fathe ...
, King of Navarre
This is a list of the kings and queens of kingdom of Pamplona, Pamplona, later kingdom of Navarre, Navarre. Pamplona was the primary name of the kingdom until its union with Kingdom of Aragon, Aragon (1076–1134). However, the territorial desig ...
; the opposition of the French bourgeoisie
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. They ...
, which was channeled through the Estates-General led by Étienne Marcel
Étienne Marcel (between 1302 and 131031 July 1358) was provost of the merchants of Paris under King John II of France, called John the Good (Jean le Bon). He distinguished himself in the defence of the small craftsmen and guildsmen who made u ...
; and with a peasant revolt known as the Jacquerie
The Jacquerie () was a popular revolt by peasants that took place in northern France in the early summer of 1358 during the Hundred Years' War. The revolt was centred in the valley of the Oise north of Paris and was suppressed after a few week ...
. Charles overcame all of these rebellions, but in order to liberate his father, he had to conclude the Treaty of Brétigny
The Treaty of Brétigny was a treaty, drafted on 8 May 1360 and ratified on 24 October 1360, between Kings Edward III of England and John II of France. In retrospect, it is seen as having marked the end of the first phase of the Hundred Years' ...
in 1360, in which he abandoned large portions of south-western France to Edward III of England
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring ro ...
and agreed to pay a huge ransom.
Charles became king in 1364. With the help of talented advisers, his skillful management of the kingdom allowed him to replenish the royal treasury and to restore the prestige of the House of Valois. He established the first permanent army paid with regular wages, which liberated the French populace from the companies of routiers
Routiers () were mercenary soldiers of the Middle Ages. Their particular distinction from other paid soldiers of the time was that they were organised into bands (''rutta'' or ''routes''). The term is first used in the 12th century but is partic ...
who regularly plundered the country when not employed. Led by Bertrand du Guesclin
Bertrand du Guesclin ( br, Beltram Gwesklin; 1320 – 13 July 1380), nicknamed "The Eagle of Brittany" or "The Black Dog of Brocéliande", was a Breton knight and an important military commander on the French side during the Hundred Years' W ...
, the French Army
The French Army, officially known as the Land Army (french: Armée de Terre, ), is the land-based and largest component of the French Armed Forces. It is responsible to the Government of France, along with the other components of the Armed For ...
was able to turn the tide of the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, ...
to Charles' advantage, and by the end of Charles' reign, they had reconquered almost all the territories ceded to the English in 1360. Furthermore, the French fleet, led by Jean de Vienne
Jean de Vienne (1341 – 25 September 1396) was a French knight, general and Admiral of France during the Hundred Years' War.
Early life
Jean de Vienne was born at Dole, in what is now Franche-Comté. As a nobleman, he started his military car ...
, managed to attack the English coast for the first time since the beginning of the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, ...
.
Charles V died in 1380. He was succeeded by his son Charles VI, whose disastrous reign allowed the English to regain control of large parts of France.
Biography
Early life
Charles was born at theChâteau de Vincennes
The Château de Vincennes () is a former fortress and royal residence next to the town of Vincennes, on the eastern edge of Paris, alongside the Bois de Vincennes. It was largely built between 1361 and 1369, and was a preferred residence, after ...
outside of Paris, the son of Prince John and Princess Bonne of France. He was educated at court with other boys of his age with whom he would remain close throughout his life: his uncle Philip, Duke of Orléans (only two years older than himself), his three brothers Louis Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
Derived or associated terms
* Lewis ( ...
, John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
, and Philip
Philip, also Phillip, is a male given name, derived from the Greek (''Philippos'', lit. "horse-loving" or "fond of horses"), from a compound of (''philos'', "dear", "loved", "loving") and (''hippos'', "horse"). Prominent Philips who popularize ...
, Louis of Bourbon, Edward
Edward is an English given name. It is derived from the Anglo-Saxon name ''Ēadweard'', composed of the elements '' ēad'' "wealth, fortune; prosperous" and '' weard'' "guardian, protector”.
History
The name Edward was very popular in Anglo-Sa ...
and Robert
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' ( non, Hróðr) "fame, glory, honou ...
of Bar
Bar or BAR may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bar (establishment), selling alcoholic beverages
* Candy bar
* Chocolate bar
Science and technology
* Bar (river morphology), a deposit of sediment
* Bar (tropical cyclone), a layer of cloud
* Bar (u ...
, Godfrey of Brabant, Louis I, Count of Étampes, Louis of Évreux, brother of Charles the Bad
Charles II (10 October 1332 – 1 January 1387), called Charles the Bad, was King of Navarre 1349–1387 and Count of Évreux 1343–1387.
Besides the Pyrenean Kingdom of Navarre, Charles had extensive lands in Normandy, inherited from his fathe ...
, John
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Secon ...
and Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*k ...
of Artois
Artois ( ; ; nl, Artesië; English adjective: ''Artesian'') is a region of northern France. Its territory covers an area of about 4,000 km2 and it has a population of about one million. Its principal cities are Arras (Dutch: ''Atrecht'') ...
, Charles of Alençon, and Philip of Rouvres.
The future king was highly intelligent but physically weak, with pale skin and a thin, ill-proportioned body. This made a sharp contrast to his father, who was tall, strong and sandy-haired.
First Dauphin of the French Royal House
Humbert II, Dauphin of Viennois, ruined due to his inability to raise taxes after a crusade in the Middle East, and childless after the death of his only son, decided to sell the Dauphiné, which was a fief of theHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
. Neither the pope nor the emperor wanted to buy and the transaction was concluded with Charles' grandfather, the reigning King Philip VI.
Under the Treaty of Romans, the Dauphiné of Viennois was to be held by a son of the future king John the Good. So it was Charles, the eldest son of the latter, who became the first Dauphin. At the age of twelve, he was suddenly vested power while in Grenoble
lat, Gratianopolis
, commune status = Prefecture and commune
, image = Panorama grenoble.png
, image size =
, caption = From upper left: Panorama of the city, Grenoble’s cable cars, place Saint- ...
(10 December 1349 to March 1350). A few days after his arrival, the people of Grenoble were invited to the Place Notre-Dame, where a platform was erected. Young Charles took his place next to Bishop John of Chissé and received the oath of allegiance of the people. In exchange, he publicly promised to respect the community charter and confirmed the liberties and franchises of Humbert II, which were summed up in a solemn statute before he signed his abdication and granted a last amnesty to all prisoners, except those facing the penalty of death.
On 8 April 1350 at Tain-l'Hermitage
Tain-l'Hermitage (; oc, Tinh de l'Ermitatge or ), commonly known as Tain, is a commune in the French department of Drôme, southeastern France.
Geography
It is located on the left bank of the river Rhône, opposite Tournon-sur-Rhône, which is l ...
, the Dauphin married his cousin Joanna of Bourbon
Joanna of Bourbon (''Jeanne de Bourbon''; 3 February 1338 – 6 February 1378) was Queen of France by marriage to King Charles V. She acted as his political adviser and was appointed potential regent in case of a minor regency.
Life
Early ...
at the age of 12. The prior approval of the pope was obtained for this consanguineous
Consanguinity ("blood relation", from Latin '' consanguinitas'') is the characteristic of having a kinship with another person (being descended from a common ancestor).
Many jurisdictions have laws prohibiting people who are related by blood fro ...
marriage (both were descended from Charles of Valois
Charles of Valois (12 March 1270 – 16 December 1325), the fourth son of King Philip III of France and Isabella of Aragon, was a member of the House of Capet and founder of the House of Valois, whose rule over France would start in 1 ...
). The marriage was delayed by the death of his mother Bonne of Luxembourg
Bonne of Luxemburg or Jutta of Luxemburg (20 May 131511 September 1349), was born Jutta (Judith), the second daughter of King John of Bohemia, and his first wife, Elisabeth of Bohemia. She was the first wife of King John II of France; however, as ...
and his grandmother Joan the Lame, swept away by the plague (he no longer saw them after he left for the Dauphiné). The dauphin himself had been seriously ill from August to December 1349. Gatherings were limited to slow the spread of the plague then raging in Europe, so the marriage took place in private.
The control of Dauphiné was valuable to the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. ...
, because it occupied the Rhône
The Rhône ( , ; wae, Rotten ; frp, Rôno ; oc, Ròse ) is a major river in France and Switzerland, rising in the Alps and flowing west and south through Lake Geneva and southeastern France before discharging into the Mediterranean Sea. At Ar ...
Valley, a major trade route between the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the e ...
and northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other g ...
since ancient times, putting them in direct contact with Avignon
Avignon (, ; ; oc, Avinhon, label=Provençal dialect, Provençal or , ; la, Avenio) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Vaucluse Departments of France, department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region of So ...
, a papal territory and diplomatic center of medieval Europe
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
. Despite his young age, the dauphin applied to be recognized by his subjects, interceding to stop a war raging between two vassal families, and gaining experience that was very useful to him.
Mission in Normandy
Charles was recalled toParis
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
at the death of his grandfather Philip VI and participated in the coronation of his father John the Good on 26 September 1350 in Reims
Reims ( , , ; also spelled Rheims in English) is the most populous city in the French department of Marne, and the 12th most populous city in France. The city lies northeast of Paris on the Vesle river, a tributary of the Aisne.
Founded by ...
. The legitimacy of John the Good, and that of the Valois in general, was not unanimous. His father, Philip VI, had lost all credibility with the disasters of Crécy, Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's prefecture is its third-largest city of Arras. Th ...
, the ravages of the plague, and the monetary changes needed to support the royal finances. The royal clan had to cope with opposition from all sides in the kingdom.
The first of these was led by Charles II of Navarre
Charles II (10 October 1332 – 1 January 1387), called Charles the Bad, was King of Navarre 1349–1387 and Count of Évreux 1343–1387.
Besides the Pyrenean Kingdom of Navarre, Charles had extensive lands in Normandy, inherited from his fathe ...
, called "the Bad", whose mother Joan II of Navarre
Joan II (french: Jeanne; 28 January 1312 – 6 October 1349) was Queen of Navarre from 1328 until her death. She was the only surviving child of Louis X of France, King of France and Navarre, and Margaret of Burgundy. Joan's paternity was dubiou ...
had renounced the crown of France for that of Navarre in 1328. Charles II of Navarre was the eldest of a powerful lineage. Ambitious of attaining the crown of France, he managed to gather around him the malcontents. He was supported by his relatives and allies: the House of Boulogne
Boulogne-sur-Mer (; pcd, Boulonne-su-Mér; nl, Bonen; la, Gesoriacum or ''Bononia''), often called just Boulogne (, ), is a coastal city in Northern France. It is a sub-prefecture of the department of Pas-de-Calais. Boulogne lies on the ...
(and their kin in Auvergne
Auvergne (; ; oc, label=Occitan, Auvèrnhe or ) is a former administrative region in central France, comprising the four departments of Allier, Puy-de-Dôme, Cantal and Haute-Loire. Since 1 January 2016, it has been part of the new region Auverg ...
), the barons of Champagne
Champagne (, ) is a sparkling wine originated and produced in the Champagne wine region of France under the rules of the appellation, that demand specific vineyard practices, sourcing of grapes exclusively from designated places within it, spe ...
loyal to Joan II of Navarre (heir of Champagne
Champagne (, ) is a sparkling wine originated and produced in the Champagne wine region of France under the rules of the appellation, that demand specific vineyard practices, sourcing of grapes exclusively from designated places within it, spe ...
, had it not merged into the crown of France
France was ruled by monarchs from the establishment of the Kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions.
Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I () as the firs ...
), and by the followers of Robert of Artois
Robert I (25 September 1216 – 8 February 1250), called the Good, was the first Count of Artois. He was the fifth (and second surviving) son of King Louis VIII of France and Blanche of Castile.
Life
He received Artois as an appanage, in accordan ...
, driven from the kingdom by Philip VI. He also had the support of the University of Paris
, image_name = Coat of arms of the University of Paris.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of Arms
, latin_name = Universitas magistrorum et scholarium Parisiensis
, motto = ''Hic et ubique terrarum'' (Latin)
, mottoeng = Here and a ...
and the northwestern merchants where the cross-Channel
Channel, channels, channeling, etc., may refer to:
Geography
* Channel (geography), in physical geography, a landform consisting of the outline (banks) of the path of a narrow body of water.
Australia
* Channel Country, region of outback Austral ...
trade was vital.
A brilliant orator, and accustomed to a monarchy controlled by the Cortes of Navarre
Cortes, Cortés, Cortês, Corts, or Cortès may refer to:
People
* Cortes (surname), including a list of people with the name
** Hernán Cortés (1485–1547), a Spanish conquistador
Places
* Cortes, Navarre, a village in the South border of ...
(the equivalent of the States General), Charles the Bad championed the reform of a state considered too arbitrary, leaving no voice to the nobility or the cities (John the Good governed with a circle of favorites and officers sometimes of humble extraction). Unlike his father, Charles V thought that a king must have the approval of his subjects and must listen to their advice. This view allowed him to approach the Norman nobles and the reformists, and thus Charles of Navarre.
The power of Navarre was such that, on 8 January 1354, he murdered with impunity his rival Charles de la Cerda (the king's favourite), and openly avowed this crime. He even obtained, through the Treaty of Mantes, territorial concessions and sovereignty by threatening to make an alliance with the English. But in Avignon, the English and French were negotiating a peace that would prevent Charles of Navarre from counting on the support of Edward III. He therefore concluded a treaty with the English in which the Kingdom of France would be partitioned between them. An English landing was planned for the end of the truce, which would expire on 24 June 1355.
King John ordered the Dauphin in March 1355 to organize the defense of Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
, which required raising the necessary taxes. The task was difficult because of the growing influence of Charles the Bad, who had acquired a status similar to that of a "Duke" under the Treaty of Mantes. He was likely to ally with Edward III and could at any time open the gateway to Normandy to the English. The Dauphin avoided war by reconciling Navarre with the king, which was sealed with a ceremony at the court on 24 September 1355. Edward III was offended at the latest betrayal of Charles of Navarre, and the promised landing did not occur.
Regency and the uprising of the Third Estate
King John was considered by many as a rash ruler, much in the same style as the feudal kings who came before which by then was becoming outdated, who alienated his nobles through arbitrary justice and elevated associates that were sometimes considered questionable. After a three-year break, theHundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, ...
with England resumed in 1355, with Edward, The Black Prince
Edward of Woodstock, known to history as the Black Prince (15 June 1330 – 8 June 1376), was the eldest son of King Edward III of England, and the heir apparent to the English throne. He died before his father and so his son, Richard II, su ...
, leading an English-Gascon army in a violent raid across southwestern France. After checking an English incursion into Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
, John led an army of about 16,000 men to the south, crossing the Loire river
The Loire (, also ; ; oc, Léger, ; la, Liger) is the longest river in France and the 171st longest in the world. With a length of , it drains , more than a fifth of France's land, while its average discharge is only half that of the Rhôn ...
in September 1356 with the goal of outflanking the Prince's 8,000 soldiers at Poitiers
Poitiers (, , , ; Poitevin: ''Poetàe'') is a city on the River Clain in west-central France. It is a commune and the capital of the Vienne department and the historical centre of Poitou. In 2017 it had a population of 88,291. Its agglomerat ...
. Rejecting advice from one captain to surround and starve the Prince, a tactic Edward feared, John attacked the strong enemy position. In the subsequent Battle of Poitiers
The Battle of Poitiers was fought on 19September 1356 between a French army commanded by King JohnII and an Anglo- Gascon force under Edward, the Black Prince, during the Hundred Years' War. It took place in western France, south of Poi ...
(19 September 1356), English archery all but annihilated the French cavalry, and John was captured. Charles led a battalion at Poitiers that withdrew early in the struggle; whether the order came from John (as he later claimed), or whether Charles himself ordered the withdrawal, is unclear.
The outcome of the battle left many embittered with the nobility. Popular opinion accused the nobles of betraying the king, while Charles and his brothers escaped blame – he was received with honor upon his return to Paris. The Dauphin summoned the Estates-General in October to seek money for the defense of the country. Furious at what they saw as poor management, many of those assembled organized into a body led by Étienne Marcel
Étienne Marcel (between 1302 and 131031 July 1358) was provost of the merchants of Paris under King John II of France, called John the Good (Jean le Bon). He distinguished himself in the defence of the small craftsmen and guildsmen who made u ...
, the Provost of Merchants (a title roughly equivalent to Mayor of Paris
The Mayor of Paris (french: Maire de Paris) is the chief executive of Paris, the capital and largest city in France. The officeholder is responsible for the administration and management of the city, submits proposals and recommendations to the C ...
today). Marcel demanded the dismissal of seven royal ministers, their replacement by a Council of 28 made up of nobles
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristi ...
, clergy
Clergy are formal leaders within established religions. Their roles and functions vary in different religious traditions, but usually involve presiding over specific rituals and teaching their religion's doctrines and practices. Some of the ter ...
and bourgeois
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. They ...
, and the release of Charles the Bad, who had been imprisoned by John for the murder of his constable. The Dauphin refused the demands, dismissed the Estates-General, and left Paris.
A contest of wills ensued. In an attempt to raise money, Charles tried to devalue the currency; Marcel ordered strikes, and the Dauphin was forced to cancel his plans and recall the Estates in February 1357. The Third Estate
The estates of the realm, or three estates, were the broad orders of social hierarchy used in Christendom (Christian Europe) from the Middle Ages to early modern Europe. Different systems for dividing society members into estates developed and ...
presented the Dauphin with a Grand Ordinance, a list of 61 articles that would have given the Estates-General the right to approve all future taxes, assemble at their own volition, and elect a Council of 36 (with 12 members from each Estate) to advise the king. Charles eventually signed the ordinance, but his dismissed councillors took news of the document to King John, imprisoned in Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( , ; Gascon oc, Bordèu ; eu, Bordele; it, Bordò; es, Burdeos) is a port city on the river Garonne in the Gironde department, Southwestern France. It is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the prefectur ...
. The King renounced the ordinance before being taken to England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
by Prince Edward.
Charles made a royal progress through the country that summer, winning support from the provinces, and winning Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S ...
back. Marcel, meanwhile, enlisted Charles the Bad, who asserted that his claim to the throne of France was at least as good as that of King Edward III of England
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring ro ...
, who had used his claim
His or HIS may refer to:
Computing
* Hightech Information System, a Hong Kong graphics card company
* Honeywell Information Systems
* Hybrid intelligent system
* Microsoft Host Integration Server
Education
* Hangzhou International School, in ...
as the pretext for initiating the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French Crown, ...
.
Marcel used the murder of a citizen seeking sanctuary in Paris to make an attack close to the Dauphin. Summoning a group of tradesmen, the Provost marched at the head of an army of 3,000, entered the royal palace, and had the crowd murder two of the Dauphin's marshals before his eyes. Charles, horrified, momentarily pacified the crowd, but sent his family away and left the capital as quickly as he could. Marcel's action destroyed support for the Third Estate among the nobles, and the Provost's subsequent backing of the Jacquerie
The Jacquerie () was a popular revolt by peasants that took place in northern France in the early summer of 1358 during the Hundred Years' War. The revolt was centred in the valley of the Oise north of Paris and was suppressed after a few week ...
undermined his support from the towns. He was murdered by a mob on 31 July 1358. Charles was able to recover Paris the following month and later issued a general amnesty for all, except close associates of Marcel.
Treaty of Brétigny
John's capture gave the English the edge in peace negotiations following theBattle of Poitiers
The Battle of Poitiers was fought on 19September 1356 between a French army commanded by King JohnII and an Anglo- Gascon force under Edward, the Black Prince, during the Hundred Years' War. It took place in western France, south of Poi ...
. The King signed the Treaty of London in 1359 that ceded most of western France to England and imposed a ruinous ransom of 4 million ''écus'' on the country. The Dauphin (backed by his councillors and the Estates General) rejected the treaty, and English King Edward invaded France later that year. Edward reached Reims
Reims ( , , ; also spelled Rheims in English) is the most populous city in the French department of Marne, and the 12th most populous city in France. The city lies northeast of Paris on the Vesle river, a tributary of the Aisne.
Founded by ...
in December and Paris in March, but Charles forbade his soldiers from direct confrontation with the English, relying on improved municipal fortifications made to Paris by Marcel. He would later rebuild the wall on the Left Bank (''Rive gauche''), and he built a new wall on the Right Bank (''Rive droite'') that extended to a new fortification called the Bastille
The Bastille (, ) was a fortress in Paris, known formally as the Bastille Saint-Antoine. It played an important role in the internal conflicts of France and for most of its history was used as a state prison by the kings of France. It was sto ...
. Edward pillaged and raided the countryside but could not bring the French to a decisive battle, so he eventually agreed to reduce his terms. This non-confrontational strategy would prove extremely beneficial to France during Charles' reign.
The Treaty of Brétigny
The Treaty of Brétigny was a treaty, drafted on 8 May 1360 and ratified on 24 October 1360, between Kings Edward III of England and John II of France. In retrospect, it is seen as having marked the end of the first phase of the Hundred Years' ...
, signed on 8 May 1360, ceded a third of western France (mostly in Aquitaine
Aquitaine ( , , ; oc, Aquitània ; eu, Akitania; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne ( oc, Guiana), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former administrative region of the country. Since 1 January ...
and Gascony
Gascony (; french: Gascogne ; oc, Gasconha ; eu, Gaskoinia) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part o ...
) to the English and lowered the King's ransom to 3 million ''écus''. King John was released the following October. His second son, Louis of Anjou, took his place as a hostage.
Though his father had regained his freedom, Charles suffered a great personal tragedy at nearly the same time. His three-year-old daughter Joan and infant daughter Bonne died within two months of each other late in 1360; at their double funeral, the Dauphin was said to be "so sorrowful as never before he had been." Charles himself had been severely ill, with his hair and nails falling out; some suggest the symptoms are those of arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, but ...
poisoning.
John proved as ineffective at ruling upon his return to France as he had before his capture. When Louis of Anjou escaped from English custody, John announced he had no choice but to return to captivity himself. He arrived in London in January 1364, became ill, and died in April.
King of France
Accession and first acts
 Charles was crowned
Charles was crowned King of France
France was ruled by monarchs from the establishment of the Kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions.
Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I () as the first ...
in 1364 at the Cathedral of Reims
, image = Reims Kathedrale.jpg
, imagealt = Facade, looking northeast
, caption = Façade of the cathedral, looking northeast
, pushpin map = France
, pushpin map alt = Location within France
, ...
. The new king was highly intelligent, but closed-mouthed and secretive, with sharp eyes, a long nose and a pale, grave manner. He suffered from gout
Gout ( ) is a form of inflammatory arthritis characterized by recurrent attacks of a red, tender, hot and swollen joint, caused by deposition of monosodium urate monohydrate crystals. Pain typically comes on rapidly, reaching maximal intensit ...
in the right hand and an abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends b ...
in his left arm, possibly a side-effect of an attempted poisoning in 1359. Doctors were able to treat the wound but told him that if it ever dried up, he would die within 15 days. His manner may have concealed a more emotional side; his marriage to Joan of Bourbon was considered very strong, and he made no attempt to hide his grief at her funeral or those of his children, five of whom predeceased him.
His reign was dominated by the war with the English and two major problems: recovering the territories ceded at Brétigny and ridding the land of the ''Tard-Venus'' (French for "latecomers"), mercenary companies that turned to robbery and pillage after the treaty was signed. In achieving these aims, Charles turned to a minor noble from Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo language, Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, Historical region, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known ...
named Bertrand du Guesclin
Bertrand du Guesclin ( br, Beltram Gwesklin; 1320 – 13 July 1380), nicknamed "The Eagle of Brittany" or "The Black Dog of Brocéliande", was a Breton knight and an important military commander on the French side during the Hundred Years' W ...
. Nicknamed "the Black Dog of Brocéliande
Brocéliande, earlier known as Brécheliant and Brécilien, is a legendary enchanted forest that had a reputation in the medieval European imagination as a place of magic and mystery. Brocéliande is featured in several medieval texts, mostly r ...
", du Guesclin fought the English during the Breton War of Succession
The War of the Breton Succession (, ) was a conflict between the Counts of Blois and the Montforts of Brittany for control of the Sovereign Duchy of Brittany, then a fief of the Kingdom of France. It was fought between 1341 and 12 April ...
and was an expert in guerrilla warfare
Guerrilla warfare is a form of irregular warfare in which small groups of combatants, such as paramilitary personnel, armed civilians, or Irregular military, irregulars, use military tactics including ambushes, sabotage, Raid (military), raids ...
. Du Guesclin also defeated Charles II of Navarre
Charles II (10 October 1332 – 1 January 1387), called Charles the Bad, was King of Navarre 1349–1387 and Count of Évreux 1343–1387.
Besides the Pyrenean Kingdom of Navarre, Charles had extensive lands in Normandy, inherited from his fathe ...
at the Battle of Cocherel
The Battle of Cocherel was a battle fought on 16 May 1364 between the forces of Charles V of France and the forces of Charles II of Navarre (known as ''Charles the Bad''), over the succession to the dukedom of Burgundy.Wagner. Encyclopedia o ...
in 1364 and eliminated his threat to Paris.
In order to lure the ''Tard-Venus'' out of France, Charles first hired them for an attempted crusade into Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
, but their reputation for brigandage preceded them, and the citizens of Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label=Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label=Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the Eu ...
refused to let them cross the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
on their journey. Charles next sent the mercenary companies (under the leadership of du Guesclin) to fight in a civil war in Castile between King Peter the Cruel and his illegitimate half-brother Henry
Henry may refer to:
People
*Henry (given name)
* Henry (surname)
* Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry
Royalty
* Portuguese royalty
** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal
** Henry, Count of Portugal, ...
. Peter had English backing, while Henry was supported by the French.
Du Guesclin and his men were able to drive Peter out of Castile in 1365 after the capture of the fortresses of Magallón
Magallón is a Spanish municipality, in the province of Saragossa, autonomous community of Aragon. It has an area of 78.61 km², with a population of 1221 inhabitants (INE
INE, Ine or ine may refer to:
Institutions
* Institut für Nuklear ...
and Briviesca
Briviesca is a municipality and a Spanish city located in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, head of the judicial district of Briviesca, capital of the comarca of La Bureba and province of Burgos, autonomous community of Castile and León. Acco ...
and the capital Burgos
Burgos () is a city in Spain located in the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is the capital and most populated municipality of the province of Burgos.
Burgos is situated in the north of the Iberian Peninsula, on the confluence of t ...
. The Black Prince
Edward of Woodstock, known to history as the Black Prince (15 June 1330 – 8 June 1376), was the eldest son of King Edward III of England, and the heir apparent to the English throne. He died before his father and so his son, Richard II, suc ...
, now serving as his father's viceroy in southwestern France, took up Peter's cause. At the Battle of Nájera
The Battle of Nájera, also known as the Battle of Navarrete, was fought on 3 April 1367 to the northeast of Nájera, in the province of La Rioja, Castile. It was an episode of the first Castilian Civil War which confronted King Peter of Casti ...
in April 1367, the English defeated Henry's army. Du Guesclin was captured after a memorable resistance and ransomed by Charles V, who considered him invaluable. The Black Prince, affected by dysentery
Dysentery (UK pronunciation: , US: ), historically known as the bloody flux, is a type of gastroenteritis that results in bloody diarrhea. Other symptoms may include fever, abdominal pain, and a feeling of incomplete defecation. Complications ...
, soon withdrew his support from Peter. The English army suffered badly during the retreat. Four English soldiers out of five died during the Castillan Campaign. In 1369, du Guesclin renewed the attack against Peter, defeating him at the decisive Battle of Montiel
The Battle of Montiel was a battle fought on 14 March 1369 between the Franco-Castilian forces supporting Henry of Trastámara and the Granadian-Castilian forces supporting the reigning Peter of Castile.
Background
In 1366 there was a civil war ...
. Henry stabbed the captive Peter to death in du Guesclin's tent, thereby gaining the throne of Castile. Bertrand was made Duke of Molina, and the Franco-Castillan alliance was sealed. Charles V could now resume the war against England under favorable conditions.
War resumes
 After the Castillan campaign, the Black Prince was invalid and heavily in debt. His rule in
After the Castillan campaign, the Black Prince was invalid and heavily in debt. His rule in Gascony
Gascony (; french: Gascogne ; oc, Gasconha ; eu, Gaskoinia) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part o ...
became increasingly autocratic. Nobles from Gascony petitioned Charles for aid, and when the Black Prince refused to answer a summons to Paris to answer the charges, Charles judged him disloyal and declared war in May 1369.
Instead of seeking a major battle, as his predecessors had done, Charles chose a strategy of attrition
Attrition warfare is a military strategy consisting of belligerent attempts to win a war by wearing down the enemy to the point of collapse through continuous losses in military personnel, personnel and materiel. The word ''attrition'' comes fro ...
, spreading the fighting at every point possible. The French and Castillan navies destroyed an English fleet at La Rochelle
La Rochelle (, , ; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''La Rochéle''; oc, La Rochèla ) is a city on the west coast of France and a seaport on the Bay of Biscay, a part of the Atlantic Ocean. It is the capital of the Charente-Maritime department. With ...
in 1372. Then, du Guesclin launched destructive raids against the coasts of England, naval reprisals to the English chevauchées. Bertrand du Guesclin, appointed Constable of France
The Constable of France (french: Connétable de France, from Latin for 'count of the stables') was lieutenant to the King of France, the first of the original five Great Officers of the Crown (along with seneschal, chamberlain, butler, and ...
in 1370, beat back a major English offensive in northern France with an unnerving combination of raid
Raid, RAID or Raids may refer to:
Attack
* Raid (military), a sudden attack behind the enemy's lines without the intention of holding ground
* Corporate raid, a type of hostile takeover in business
* Panty raid, a prankish raid by male college ...
s, siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition warfare, attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity con ...
s, and pitched battle
A pitched battle or set-piece battle is a battle in which opposing forces each anticipate the setting of the battle, and each chooses to commit to it. Either side may have the option to disengage before the battle starts or shortly thereafter. A ...
s. He notably crushed Robert Knolles
Sir Robert Knolles or Knollys ( – 15 August 1407; aged 81-82) was an important English knight of the Hundred Years' War, who, operating with the tacit support of the crown, succeeded in taking the only two major French cities, other tha ...
at the Battle of Pontvallain
The Battle of Pontvallain, part of the Hundred Years' War, took place in the Sarthe region of north-west France on 4 December 1370, when a French army under Bertrand du Guesclin heavily defeated an English force which had broken away from ...
.
Most of the major English leaders were killed in a few months and the Black Prince fled to England, where he died in 1376. By 1375, Charles recovered much of the English territories in France except Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's prefecture is its third-largest city of Arras. Th ...
and Gascony
Gascony (; french: Gascogne ; oc, Gasconha ; eu, Gaskoinia) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part o ...
, effectively nullifying the Treaty of Brétigny
The Treaty of Brétigny was a treaty, drafted on 8 May 1360 and ratified on 24 October 1360, between Kings Edward III of England and John II of France. In retrospect, it is seen as having marked the end of the first phase of the Hundred Years' ...
.
Papal schism
In 1376,Pope Gregory XI
Pope Gregory XI ( la, Gregorius, born Pierre Roger de Beaufort; c. 1329 – 27 March 1378) was head of the Catholic Church from 30 December 1370 to his death in March 1378. He was the seventh and last Avignon pope and the most recent French pop ...
, fearing a loss of the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
, decided to move his court back to Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
after nearly 70 years in Avignon
Avignon (, ; ; oc, Avinhon, label=Provençal dialect, Provençal or , ; la, Avenio) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Vaucluse Departments of France, department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region of So ...
. Charles, hoping to maintain French influence over the papacy
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
, tried to persuade Pope Gregory to remain in France, arguing that "Rome is wherever the Pope happens to be." Gregory refused.
The Pope died in March 1378. When cardinals gathered to elect a successor, a Roman mob, concerned that the predominantly French College of Cardinals
The College of Cardinals, or more formally the Sacred College of Cardinals, is the body of all cardinals of the Catholic Church. its current membership is , of whom are eligible to vote in a conclave to elect a new pope. Cardinals are appoi ...
would elect a French pope who would bring the papacy back to Avignon, surrounded the Vatican
Vatican may refer to:
Vatican City, the city-state ruled by the pope in Rome, including St. Peter's Basilica, Sistine Chapel, Vatican Museum
The Holy See
* The Holy See, the governing body of the Catholic Church and sovereign entity recognized ...
and demanded the election of a Roman. On 9 April, the cardinals elected Bartolomeo Prigamo, Archbishop of Bari, and a commoner by birth, as Pope Urban VI
Pope Urban VI ( la, Urbanus VI; it, Urbano VI; c. 1318 – 15 October 1389), born Bartolomeo Prignano (), was head of the Catholic Church from 8 April 1378 to his death in October 1389. He was the most recent pope to be elected from outside the ...
. The new pope quickly alienated his cardinals by criticising their vices, limiting the areas where they could receive income and even rising to strike one cardinal before a second restrained him. The French cardinals left Rome that summer and declared Urban's election invalid because of mob intimidation (a reason that had not been cited at the time of the election) and elected Cardinal Robert of Geneva as Pope Clement VII
Pope Clement VII ( la, Clemens VII; it, Clemente VII; born Giulio de' Medici; 26 May 1478 – 25 September 1534) was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 19 November 1523 to his death on 25 September 1534. Deemed "the ...
that September.
The French cardinals quickly moved to get Charles' support. The theology faculty of the University of Paris
, image_name = Coat of arms of the University of Paris.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of Arms
, latin_name = Universitas magistrorum et scholarium Parisiensis
, motto = ''Hic et ubique terrarum'' (Latin)
, mottoeng = Here and a ...
advised Charles not to make a hasty decision, but he recognised Clement as Pope in November and forbade any obedience to Urban. Charles' support allowed Clement to survive as pope and led to the Papal Schism, which would divide Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
for nearly 40 years.
Death
Charles' last years were spent in the consolidation ofNormandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
(and the neutralisation of Charles of Navarre). Peace negotiations with the English continued unsuccessfully. The taxes he had levied to support his wars against the English caused deep disaffection among the working classes.
The abscess on the King's left arm dried up in early September 1380 and Charles prepared to die. On his deathbed, perhaps fearful for his soul, Charles announced the abolition of the hearth tax
A hearth tax was a property tax in certain countries during the medieval and early modern period, levied on each hearth, thus by proxy on wealth. It was calculated based on the number of hearths, or fireplaces, within a municipal area and is cons ...
, the foundation of the government's finances. The ordinance would have been impossible to carry out, but its terms were known, and the government's refusal to reduce any of the other taxes on the people sparked the Maillotin revolt in 1381.
The King died on 16 September 1380 and was succeeded by his 11-year-old son, Charles VI. He is buried in the Basilica of St Denis, about five miles north of Paris.
Legacy
 Charles' reputation was of great significance for posterity, especially as his conception of governance was one that courtiers wished his successors could follow. Christine de Pizan's biography, commissioned by
Charles' reputation was of great significance for posterity, especially as his conception of governance was one that courtiers wished his successors could follow. Christine de Pizan's biography, commissioned by Philip the Bold
Philip II the Bold (; ; 17 January 1342 – 27 April 1404) was Duke of Burgundy and '' jure uxoris'' Count of Flanders, Artois and Burgundy. He was the fourth and youngest son of King John II of France and Bonne of Luxembourg.
Philip II was ...
, Duke of Burgundy
Duke of Burgundy (french: duc de Bourgogne) was a title used by the rulers of the Duchy of Burgundy, from its establishment in 843 to its annexation by France in 1477, and later by Holy Roman Emperors and Kings of Spain from the House of Habsburg ...
, in 1404, is a source of most of the intimate details of the king's life of which we are aware, but also provides a moral example for his successors. It draws heavily on the work of Nicole Oresme
Nicole Oresme (; c. 1320–1325 – 11 July 1382), also known as Nicolas Oresme, Nicholas Oresme, or Nicolas d'Oresme, was a French philosopher of the later Middle Ages. He wrote influential works on economics, mathematics, physics, astrology an ...
(who translated Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
's moral works into French) and Giles of Rome
Giles of Rome O.S.A. (Latin: ''Aegidius Romanus''; Italian: ''Egidio Colonna''; c. 1243 – 22 December 1316), was a Medieval philosopher and Scholastic theologian and a friar of the Order of St Augustine, who was also appointed to the ...
. Philippe de Mézières
Philippe de Mézières (c. 1327 – May 29, 1405), a French soldier and author, was born at the chateau of Mézières in Picardy.
Period of soldiering (1344–1358)
Philippe belonged to the poorer nobility. At first, he served under Luchino Visc ...
, in his allegorical "Songe du Vieil Pèlerin," attempts to persuade the dauphin (later King Charles VI) to follow the example of his wise father, notably in piety, though also to pursue reforming zeal in all policy considerations.
Of great importance to Charles V's cultural program was his vast library, housed in his expanded Louvre Palace
The Louvre Palace (french: link=no, Palais du Louvre, ), often referred to simply as the Louvre, is an iconic French palace located on the Rive Droite, Right Bank of the Seine in Paris, occupying a vast expanse of land between the Tuileries Ga ...
, and described in great detail by the nineteenth-century French historian Leopold Delisle
Leopold may refer to:
People
* Leopold (given name)
* Leopold (surname)
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional characters
* Leopold (The Simpsons), Leopold (''The Simpsons''), Superintendent Chalmers' assistant on ''The Simpsons''
* Leopold B ...
. Containing over 1,200 volumes, it was symbolic of the authority and magnificence of the royal person, but also of his concern with government for the common good
In philosophy, economics, and political science, the common good (also commonwealth, general welfare, or public benefit) is either what is shared and beneficial for all or most members of a given community, or alternatively, what is achieved by c ...
. Charles was keen to collect copies of works in French, in order that his counsellors had access to them. Perhaps the most significant ones commissioned for the library were those of Nicole Oresme, who translated Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
's ''Politics
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies ...
'', ''Ethics
Ethics or moral philosophy is a branch of philosophy that "involves systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong behavior".''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' The field of ethics, along with aesthetics, concerns m ...
'', and ''Economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and intera ...
'' into eloquent French for the first time (an earlier attempt had been made at the ''Politics'', but the manuscript is now lost). If the ''Politics'' and ''Economics'' served as a manual for government, then the ''Ethics'' advised the king on how to be a good man.
Other important works commissioned for the royal library were the anonymous legal treatise "Songe du Vergier," greatly inspired by the debates of Philip IV's jurists with Pope Boniface VIII
Pope Boniface VIII ( la, Bonifatius PP. VIII; born Benedetto Caetani, c. 1230 – 11 October 1303) was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 24 December 1294 to his death in 1303. The Caetani, Caetani family was of b ...
, the translations of Raol de Presles, which included St. Augustine's ''City of God'', and the ''Grandes Chroniques de France
The ''Grandes Chroniques de France'' is a vernacular royal compilation of the history of France, most manuscripts of which are luxury copies that are heavily illuminated. Copies were produced between the thirteenth and fifteenth centuries, the ...
'' edited in 1377 to emphasise the vassal
A vassal or liege subject is a person regarded as having a mutual obligation to a lord or monarch, in the context of the feudal system in medieval Europe. While the subordinate party is called a vassal, the dominant party is called a suzerain. W ...
age of Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring r ...
.
Charles' kingship placed great emphasis on both royal ceremony and scientific political theory
Political philosophy or political theory is the philosophical study of government, addressing questions about the nature, scope, and legitimacy of public agents and institutions and the relationships between them. Its topics include politics, l ...
, and to contemporaries and posterity his lifestyle at once embodied the reflective life advised by Aristotle and the model of French kingship derived from St. Louis
St. Louis () is the second-largest city in Missouri, United States. It sits near the confluence of the Mississippi and the Missouri Rivers. In 2020, the city proper had a population of 301,578, while the bi-state metropolitan area, which e ...
, Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first Holy ...
, and Clovis which he had illustrated in his ''Coronation Book'' of 1364, now in the British Library
The British Library is the national library of the United Kingdom and is one of the largest libraries in the world. It is estimated to contain between 170 and 200 million items from many countries. As a legal deposit library, the British ...
.
Charles V was also a builder king, and he created or rebuilt several significant buildings in the late 14th century style including the Bastille
The Bastille (, ) was a fortress in Paris, known formally as the Bastille Saint-Antoine. It played an important role in the internal conflicts of France and for most of its history was used as a state prison by the kings of France. It was sto ...
, the Louvre Palace
The Louvre Palace (french: link=no, Palais du Louvre, ), often referred to simply as the Louvre, is an iconic French palace located on the Rive Droite, Right Bank of the Seine in Paris, occupying a vast expanse of land between the Tuileries Ga ...
, Château de Vincennes
The Château de Vincennes () is a former fortress and royal residence next to the town of Vincennes, on the eastern edge of Paris, alongside the Bois de Vincennes. It was largely built between 1361 and 1369, and was a preferred residence, after ...
, and Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye
The Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye () is a former royal palace in the commune of Saint-Germain-en-Laye, in the ''département'' of Yvelines, about 19 km west of Paris, France. Today, it houses the ''musée d'Archéologie nationale'' (Nati ...
, which were widely copied by the nobility of the day.
While he was in many ways a typical medieval king, Charles V has been praised by historians for his pragmatism, which led to the recovery of the territories lost at Brétigny.
His successes, however, proved ephemeral. Charles' brothers, who dominated the regency council that ruled in the king's name until 1388, quarrelled among themselves and divided the government. Charles VI, meanwhile, preferred tournaments to the duties of kingship, and his descent into madness in 1392 put his uncles back in power. By 1419, the country was divided between Armagnac
Armagnac (, ) is a distinctive kind of brandy produced in the Armagnac region in Gascony, southwest France. It is distilled from wine usually made from a blend of grapes including Baco 22A, Colombard, Folle blanche and Ugni blanc, traditionally ...
and Burgundian factions and Henry V Henry V may refer to:
People
* Henry V, Duke of Bavaria (died 1026)
* Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor (1081/86–1125)
* Henry V, Duke of Carinthia (died 1161)
* Henry V, Count Palatine of the Rhine (c. 1173–1227)
* Henry V, Count of Luxembourg (121 ...
was conquering the northern part of France. The hard-won victories of Charles V had been lost through the venality of his successors.
Ancestors
Marriage and issue
On 8 April 1350 Charles marriedJoanna of Bourbon
Joanna of Bourbon (''Jeanne de Bourbon''; 3 February 1338 – 6 February 1378) was Queen of France by marriage to King Charles V. She acted as his political adviser and was appointed potential regent in case of a minor regency.
Life
Early ...
(3 February 1338 – 4 February 1378), leaving:
# Joanna (end September 1357 – 21 October 1360, Saint Antoine-des-Champs Abbey, Paris), interred at Saint-Antoine-des-Champs Abbey
Saint-Antoine-des-Champs Abbey was a convent in what is now the 12th arrondissement of Paris. The faubourg Saint-Antoine developed around it. It later became the hôpital Saint-Antoine.
History
Middle Ages
Renaissance and Enlightenment
Conver ...
.
# Bonne (1358 – 7 November 1360, Palais Royal, Paris), interred beside her older sister.
# Joanna (Château de Vincennes
The Château de Vincennes () is a former fortress and royal residence next to the town of Vincennes, on the eastern edge of Paris, alongside the Bois de Vincennes. It was largely built between 1361 and 1369, and was a preferred residence, after ...
, 6 June 1366 – 21 December 1366, Hôtel de Saint-Pol, Paris), interred at Saint Denis Basilica
The Basilica of Saint-Denis (french: Basilique royale de Saint-Denis, links=no, now formally known as the ) is a large former medieval abbey church and present cathedral in the commune of Saint-Denis, a northern suburb of Paris. The building ...
.
# Charles VI (3 December 1368 – 22 October 1422), King of France.
# Marie (Paris, 27 February 1370 – June 1377, Paris).
# Louis Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
Derived or associated terms
* Lewis ( ...
(13 March 1372 – 23 November 1407), Duke of Orléans.
# Isabella (Paris, 24 July 1373 – 23 February 1378, Paris).
# John (1374/76 – died young).
# Catherine
Katherine, also spelled Catherine, and other variations are feminine names. They are popular in Christian countries because of their derivation from the name of one of the first Christian saints, Catherine of Alexandria.
In the early Christ ...
(Paris, 4 February 1378 – November 1388, buried at Abbaye De Maubuisson, France), m. John of Berry, Count of Montpensier
The French lordship of Montpensier (named after the village of Montpensier, département of Puy-de-Dôme), located in historical Auvergne, became a countship in the 14th century.
It changed hands from the House of Thiern, to the House of Be ...
(son of John, Duke of Berry
John of Berry or John the Magnificent (French: ''Jean de Berry'', ; 30 November 1340 – 15 June 1416) was Duke of Berry and Auvergne and Count of Poitiers and Montpensier. He was Regent of France during the minority of his nephew 1380-1388 ...
).
With Biette de Cassinel, he had:
# Jean de Montagu (Paris, ca.1350 – 17 October 1409, Paris).
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * , - , - , - {{DEFAULTSORT:Charles 05 of France 1338 births 1380 deaths 14th-century kings of France 14th-century Dukes of Normandy Burials at the Basilica of Saint-Denis Ancien Régime Dauphins of France Dauphins of Viennois House of Valois Infectious disease deaths in France Male Shakespearean characters People from Vincennes People of the Hundred Years' War 1360s in France 1370s in France 1380s in France 14th-century French people 14th-century peers of France Sons of kings