celtic fringe on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The Celtic nations are a cultural area and collection of geographical
The Celtic nations are a cultural area and collection of geographical
Newfoundland and Labrador Heritage website. There are virtually no known fluent speakers of Irish Gaelic in Newfoundland or Labrador today. Knowledge seems to be largely restricted to memorized passages, such as traditional tales and songs. Canadian Gaelic dialects of Scottish Gaelic are still spoken by Gaels in other parts of Atlantic Canada, primarily on
 The Celtic languages form a branch of the greater
The Celtic languages form a branch of the greater
 Formal cooperation between the Celtic nations is active in many contexts, including politics, languages, culture, music and sports:
The
Formal cooperation between the Celtic nations is active in many contexts, including politics, languages, culture, music and sports:
The
 During the
During the
 The
The
 In Celtic languages, England is usually referred to as "
In Celtic languages, England is usually referred to as "
 Most French people identify with the ancient
Most French people identify with the ancient
 After the partitioning of the British colony of Nova Scotia in 1784 New Brunswick was originally named New Ireland with the capital to be in Saint John.
Large swathes of the United States of America were subject to migration from Celtic peoples, or people from Celtic nations. Irish-speaking
After the partitioning of the British colony of Nova Scotia in 1784 New Brunswick was originally named New Ireland with the capital to be in Saint John.
Large swathes of the United States of America were subject to migration from Celtic peoples, or people from Celtic nations. Irish-speaking
Celtic League
{{DEFAULTSORT:Celtic Nations Cultural regions Geography of Northwestern Europe Linguistic regions of Europe
region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
s in Northwestern Europe
Northwestern Europe, or Northwest Europe, is a loosely defined subregion of Europe, overlapping Northern and Western Europe. The region can be defined both geographically and ethnographically.
Geographic definitions
Geographically, North ...
where the Celtic languages
The Celtic languages ( usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward ...
and cultural traits have survived. The term ''nation
A nation is a community of people formed on the basis of a combination of shared features such as language, history, ethnicity, culture and/or society. A nation is thus the collective identity of a group of people understood as defined by those ...
'' is used in its original sense to mean a people who share a common identity and culture and are identified with a traditional territory.
The six regions widely considered Celtic nations are Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period o ...
(''Breizh''), Cornwall (''Kernow''), Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
(''Éire''), the Isle of Man
)
, anthem = "O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europe ...
(''Mannin'', or ''Ellan Vannin''), Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to th ...
(''Alba''), and Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in 2 ...
(''Cymru''). In each of the six nations a Celtic language is spoken to some extent: Brittonic or Brythonic languages are spoken in Brittany ( Breton), Cornwall ( Cornish) and Wales ( Welsh), whilst Goidelic
The Goidelic or Gaelic languages ( ga, teangacha Gaelacha; gd, cànanan Goidhealach; gv, çhengaghyn Gaelgagh) form one of the two groups of Insular Celtic languages, the other being the Brittonic languages.
Goidelic languages historicall ...
or Gaelic languages are spoken in Scotland (Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as ...
), Ireland ( Irish), and the Isle of Man ( Manx).
Before the expansions of Ancient Rome and the Germanic and Slavic-speaking tribes, a significant part of Europe was dominated by Celtic-speaking cultures, leaving behind a legacy of Celtic cultural traits. Territories in north-western Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
—particularly northern Portugal, Galicia, Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensive ...
, León, and Cantabria (together historically referred to as Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia, northern Portugal, Asturias and Leon and the later Kingdom of Gallaecia. The Roman cities include ...
and Astures), covering north-central Portugal and northern Spain—are considered Celtic nations due to their culture and history. Unlike the others, however, no Celtic language has been spoken there in modern times.
Core nations
Each of the six nations has its ownCeltic language
The Celtic languages ( usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward ...
. In Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period o ...
, Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
, Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to th ...
, and Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in 2 ...
these have been spoken continuously through time, while Cornwall and the Isle of Man
)
, anthem = "O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europe ...
have languages that were spoken into modern times but later died as spoken community languages. In the latter two regions, however, language revitalisation
Language revitalization, also referred to as language revival or reversing language shift, is an attempt to halt or reverse the decline of a language or to revive an extinct one. Those involved can include linguists, cultural or community groups, o ...
movements have led to the adoption of these languages by adults and produced a number of native speakers.
Ireland, Wales, Brittany and Scotland contain areas where a Celtic language is used on a daily basis; in Ireland these areas are called the ''Gaeltacht
( , , ) are the districts of Ireland, individually or collectively, where the Irish government recognises that the Irish language is the predominant vernacular, or language of the home.
The ''Gaeltacht'' districts were first officially recog ...
''; in Wales '' Y Fro Gymraeg,'' Breizh-Izel (Lower Brittany) in western Brittany and Breizh-Uhel (Upper Brittany) in eastern Brittany. Generally these communities are in the west of their countries and in more isolated upland or island areas. Welsh, however, is much more widespread, with much of the north and west speaking it as a first language, or equally alongside English. Public signage is in dual languages throughout Wales and it is now a requirement to possess at least basic Welsh in order to be employed by the Welsh Government
, image =
, caption =
, date_established =
, country = Wales
, address =
, leader_title = First Minister ()
, appointed = First Minister approved by the Senedd, ceremonially appointed ...
. The term ''Gàidhealtachd
The (; English: ''Gaeldom'') usually refers to the Highlands and Islands of Scotland and especially the Scottish Gaelic-speaking culture of the area. The similar Irish language word refers, however, solely to Irish-speaking areas.
The term ...
'' historically distinguished the Gaelic-speaking areas of Scotland (the Highlands
Highland is a broad term for areas of higher elevation, such as a mountain range or mountainous plateau.
Highland, Highlands, or The Highlands, may also refer to:
Places Albania
* Dukagjin Highlands
Armenia
* Armenian Highlands
Australia
* So ...
and islands) from the Lowland
Upland and lowland are conditional descriptions of a plain based on elevation above sea level. In studies of the ecology of freshwater rivers, habitats are classified as upland or lowland.
Definitions
Upland and lowland are portions of ...
Scots (i.e. Anglo-Saxon-speaking) areas. More recently, this term has also been adopted as the Gaelic name of the Highland council area
Highland ( gd, A' Ghàidhealtachd, ; sco, Hieland) is a council area in the Scottish Highlands and is the largest local government area in the United Kingdom. It was the 7th most populous council area in Scotland at the 2011 census. It share ...
, which includes non-Gaelic speaking areas. Hence, more specific terms such as ''sgìre Ghàidhlig'' ("Gaelic-speaking area") are now used.
In Wales, the Welsh language
Welsh ( or ) is a Celtic language of the Brittonic subgroup that is native to the Welsh people. Welsh is spoken natively in Wales, by some in England, and in Y Wladfa (the Welsh colony in Chubut Province, Argentina). Historically, it has ...
is a core curriculum (compulsory) subject, which all pupils study. Additionally, 20% of schoolchildren in Wales attend Welsh medium schools, where they are taught entirely in the Welsh language. In the Republic of Ireland
Ireland ( ga, Éire ), also known as the Republic of Ireland (), is a country in north-western Europe consisting of 26 of the 32 counties of the island of Ireland. The capital and largest city is Dublin, on the eastern side of the island. ...
, all school children study Irish as one of the three core subjects until the end of secondary school, and 7.4% of primary school education is through Irish medium education, which is part of the Gaelscoil
A Gaelscoil (; plural: ''Gaelscoileanna'') is an Irish language-medium school in Ireland: the term refers especially to Irish-medium schools outside the Irish-speaking regions or Gaeltacht. Over 50,000 students attend Gaelscoileanna at primary an ...
movement. In the Isle of Man, there is one Manx-medium primary school, and all schoolchildren have the opportunity to learn Manx.
Other territories
Parts of the northern Iberian Peninsula, namely Galicia, Cantabria,Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensive ...
and Northern Portugal, also lay claim to this heritage. Musicians from Galicia and Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensive ...
have participated in Celtic music festivals, such as the Ortigueira's Festival of Celtic World in the village of Ortigueira
Ortigueira is a seaport and municipality in the province of A Coruña the autonomous community of Galicia in northwestern Spain. It belongs to the comarca of Ortegal. It is located on the northern slope of the Serra da Faladoira, the river Me ...
or the Breton Festival Interceltique de Lorient
__NOTOC__
The (French), Emvod Ar Gelted An Oriant (Breton) or Inter-Celtic Festival of Lorient in English, is an annual Celtic festival, located in the city of Lorient, Brittany, France. It was founded in 1971 by .
This annual festival takes ...
, which in 2013 celebrated the Year of Asturias, and in 2019 celebrated the Year of Galicia. Northern Portugal, part of ancient Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia, northern Portugal, Asturias and Leon and the later Kingdom of Gallaecia. The Roman cities include ...
(Galicia, Minho, Douro and Trás-os-Montes), also has traditions quite similar to Galicia. However, no Celtic language has been spoken in northern Iberia since probably the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
.Koch, John T. (2006). "Britonia". In John T. Koch, ''Celtic Culture: A Historical Encyclopedia''. Santa Barbara: ABC-CLIO, p. 291.
Irish was once widely spoken on the island of Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
, but had largely disappeared there by the early 20th century. Vestiges remain in some words found in Newfoundland English, such as scrob for "scratch", and sleveen for "rascal"Language: Irish GaelicNewfoundland and Labrador Heritage website. There are virtually no known fluent speakers of Irish Gaelic in Newfoundland or Labrador today. Knowledge seems to be largely restricted to memorized passages, such as traditional tales and songs. Canadian Gaelic dialects of Scottish Gaelic are still spoken by Gaels in other parts of Atlantic Canada, primarily on
Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (french: link=no, île du Cap-Breton, formerly '; gd, Ceap Breatainn or '; mic, Unamaꞌki) is an island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.
The island accounts for 18. ...
and adjacent areas of Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Engl ...
. In 2011, there were 1,275 Gaelic speakers in Nova Scotia, and 300 residents of the province considered a Gaelic language to be their "mother tongue".
Patagonian Welsh
Patagonian Welsh (Welsh: ''Cymraeg y Wladfa'') is a variety of the Welsh language spoken in Y Wladfa, the Welsh settlement in Patagonia, Chubut Province, Argentina. The decimal numeral system used in Modern Welsh originated in Patagonia in ...
is spoken principally in ''Y Wladfa
Y Wladfa (, "The Colony"), also occasionally Y Wladychfa Gymreig (, "The Welsh Settlement"), refers to the establishment of settlements by Welsh immigrants in Patagonia, beginning in 1865, mainly along the coast of the lower Chubut Valley. I ...
'' in the Chubut Province of Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and ...
, with sporadic speakers elsewhere in Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
. Estimates of the number of Welsh speakers range from 1,500 to 5,000.
Celtic languages
Indo-European
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutc ...
language family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in hi ...
. SIL Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' (stylized as ''Ethnoloɠue'') is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensiv ...
lists six living Celtic languages, of which four have retained a substantial number of native speakers. These are the Goidelic languages
The Goidelic or Gaelic languages ( ga, teangacha Gaelacha; gd, cànanan Goidhealach; gv, çhengaghyn Gaelgagh) form one of the two groups of Insular Celtic languages, the other being the Brittonic languages.
Goidelic languages historicall ...
(i.e. Irish and Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as ...
, which are both descended from Middle Irish
Middle Irish, sometimes called Middle Gaelic ( ga, An Mheán-Ghaeilge, gd, Meadhan-Ghàidhlig), is the Goidelic language which was spoken in Ireland, most of Scotland and the Isle of Man from AD; it is therefore a contemporary of late Old Eng ...
) and the Brittonic languages
The Brittonic languages (also Brythonic or British Celtic; cy, ieithoedd Brythonaidd/Prydeinig; kw, yethow brythonek/predennek; br, yezhoù predenek) form one of the two branches of the Insular Celtic language family; the other is Goidelic. ...
(i.e. Welsh and Breton, which are both descended from Common Brittonic
Common Brittonic ( cy, Brythoneg; kw, Brythonek; br, Predeneg), also known as British, Common Brythonic, or Proto-Brittonic, was a Celtic language spoken in Britain and Brittany.
It is a form of Insular Celtic, descended from Proto-Celtic, a ...
).
The other two, Cornish (a Brittonic language) and Manx (a Goidelic language), died in modern times with their presumed last native speakers in 1777
Events
January–March
* January 2 – American Revolutionary War – Battle of the Assunpink Creek: American general George Washington's army repulses a British attack by Lieutenant General Charles Cornwallis, in a secon ...
and 1974
Major events in 1974 include the aftermath of the 1973 oil crisis and the resignation of United States President Richard Nixon following the Watergate scandal. In the Middle East, the aftermath of the 1973 Yom Kippur War determined politics; f ...
respectively. For both these languages, however, revitalisation movements have led to the adoption of these languages by adults and children and produced some native speakers.
Taken together, there were roughly one million native speakers of Celtic languages as of the 2000s. In 2010, there were more than 1.4 million speakers of Celtic languages.
The chart below shows the population of each Celtic nation and the number of people in each nation who can speak Celtic languages. The total number of people living in the Celtic nations is 19,596,000 people and, of these, the total number of people who can speak the Celtic languages is approximately 2,818,000 or 14.3%.
Celtic identity
 Formal cooperation between the Celtic nations is active in many contexts, including politics, languages, culture, music and sports:
The
Formal cooperation between the Celtic nations is active in many contexts, including politics, languages, culture, music and sports:
The Celtic League
The Celtic League is a pan-Celtic organisation, founded in 1961, that aims to promote modern Celtic identity and culture in Ireland, Scotland, Wales, Brittany, Cornwall and the Isle of Man – referred to as the Celtic nations; it places p ...
is an inter-Celtic political organisation, which campaigns for the political, language, cultural and social rights, affecting one or more of the Celtic nations.
Established in 1917, the Celtic Congress
The International Celtic Congress ( br, Ar C'hendalc'h Keltiek, kw, An Guntelles Keltek, gv, Yn Cohaglym Celtiagh, gd, A' Chòmhdhail Cheilteach, ga, An Chomhdháil Cheilteach, cy, Y Gyngres Geltaidd) is a cultural organisation that seeks to ...
is a non-political organisation that seeks to promote Celtic culture and languages and to maintain intellectual contact and close cooperation between Celtic peoples.
Festivals celebrating the culture of the Celtic nations include the Festival Interceltique de Lorient
__NOTOC__
The (French), Emvod Ar Gelted An Oriant (Breton) or Inter-Celtic Festival of Lorient in English, is an annual Celtic festival, located in the city of Lorient, Brittany, France. It was founded in 1971 by .
This annual festival takes ...
(Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period o ...
), the Pan Celtic Festival (Ireland), CeltFest Cuba (Havana, Cuba), the National Celtic Festival ( Portarlington, Australia), the Celtic Media Festival
The Celtic Media Festival, formerly known as the Celtic Film and Television Festival, aims to promote the languages and cultures of the Celtic nations in film, on television, radio and new media. The festival is an annual three-day celebration ...
(showcasing film and television from the Celtic nations), and the Eisteddfod
In Welsh culture, an ''eisteddfod'' is an institution and festival with several ranked competitions, including in poetry and music.
The term ''eisteddfod'', which is formed from the Welsh morphemes: , meaning 'sit', and , meaning 'be', means, a ...
(Wales).
Inter-Celtic music festivals include Celtic Connections (Glasgow), and the Hebridean Celtic Festival
The Hebridean Celtic Festival (Scottish Gaelic: Fèis Cheilteach Innse Gall) or HebCelt is an international Scottish music festival, which takes place annually in Stornoway on Lewis, in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. Headliners to date inclu ...
(Stornoway). Due to immigration, a dialect of Scottish Gaelic ( Canadian Gaelic) is spoken by some on Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (french: link=no, île du Cap-Breton, formerly '; gd, Ceap Breatainn or '; mic, Unamaꞌki) is an island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.
The island accounts for 18. ...
in Nova Scotia, while a Welsh-speaking minority exists in the Chubut Province of Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
. Hence, for certain purposes—such as the Festival Interceltique de Lorient
__NOTOC__
The (French), Emvod Ar Gelted An Oriant (Breton) or Inter-Celtic Festival of Lorient in English, is an annual Celtic festival, located in the city of Lorient, Brittany, France. It was founded in 1971 by .
This annual festival takes ...
—Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia, northern Portugal, Asturias and Leon and the later Kingdom of Gallaecia. The Roman cities include ...
, Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensive ...
, and Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (french: link=no, île du Cap-Breton, formerly '; gd, Ceap Breatainn or '; mic, Unamaꞌki) is an island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.
The island accounts for 18. ...
in Nova Scotia are considered three of the ''nine'' Celtic nations.
Competitions are held between the Celtic nations in sports such as rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In its m ...
(Pro14
The United Rugby Championship (URC) is an annual rugby union competition involving professional teams from Ireland, Italy, Scotland, South Africa, and Wales. The current name was adopted in 2021 when the league expanded to include four South Af ...
—formerly known as the Celtic League), athletics (Celtic Cup) and association football (the Nations Cup—also known as the Celtic Cup).
The Republic of Ireland enjoyed a period of rapid economic growth between 1995 and 2007, leading to the use of the phrase Celtic Tiger to describe the country. Aspirations for Scotland to achieve a similar economic performance to that of Ireland led the Scotland First Minister
A first minister is any of a variety of leaders of government cabinets. The term literally has the same meaning as "prime minister" but is typically chosen to distinguish the office-holder from a superior prime minister. Currently the title of ' ...
Alex Salmond
Alexander Elliot Anderson Salmond (; born 31 December 1954) is a Scottish politician and economist who served as First Minister of Scotland from 2007 to 2014. A prominent figure on the Scottish nationalist movement, he has served as leader o ...
to set out his vision of a Celtic Lion economy for Scotland, in 2007.
Genetic studies
A Y-DNA study by an Oxford University research team in 2006 claimed that the majority of Britons, including many of the English, are descended from a group of tribes which arrived from Iberia around 5000 BC, before the spread of Celtic culture into western Europe. However, three major later genetic studies have largely invalidated these claims, instead showing thathaplogroup R1b
Haplogroup R1b (R-M343), previously known as Hg1 and Eu18, is a human Y-chromosome haplogroup.
It is the most frequently occurring paternal lineage in Western Europe, as well as some parts of Russia (e.g. the Bashkirs) and pockets of Central ...
in western Europe, most common in traditionally Celtic-speaking areas of Atlantic Europe like Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
and Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period o ...
, would have largely expanded in massive migrations from the Indo-European homeland
The Proto-Indo-European homeland (or Indo-European homeland) was the prehistoric linguistic homeland of the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE). From this region, its speakers migrated east and west, and went on to form the proto-communities of ...
, the Yamnaya culture
The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture (russian: Ямная культура, ua, Ямна культура lit. 'culture of pits'), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age arch ...
in the Pontic–Caspian steppe
The Pontic–Caspian steppe, formed by the Caspian steppe and the Pontic steppe, is the steppeland stretching from the northern shores of the Black Sea (the Pontus Euxinus of antiquity) to the northern area around the Caspian Sea. It extend ...
, during the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
along with carriers of Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Du ...
like proto-Celtic
Proto-Celtic, or Common Celtic, is the ancestral proto-language of all known Celtic languages, and a descendant of Proto-Indo-European. It is not attested in writing but has been partly reconstructed through the comparative method. Proto-Celtic ...
. Unlike previous studies, large sections of autosomal DNA were analyzed in addition to paternal Y-DNA
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or abs ...
markers. They detected an autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosomes ...
component present in modern Europeans which was not present in Neolithic or Mesolithic Europeans, and which would have been introduced into Europe with paternal lineages R1b and R1a, as well as the Indo-European languages. This genetic component, labelled as "Yamnaya" in the studies, then mixed to varying degrees with earlier Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymousl ...
hunter-gatherer or Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
farmer populations already existing in western Europe. Furthermore, a 2016 study also found that Bronze Age remains from Rathlin Island
Rathlin Island ( ga, Reachlainn, ; Local Irish dialect: ''Reachraidh'', ; Scots: ''Racherie'') is an island and civil parish off the coast of County Antrim (of which it is part) in Northern Ireland. It is Northern Ireland's northernmost point. ...
in Ireland dating to over 4,000 years ago were most genetically similar to modern Irish, Scottish and Welsh, and that the core of the genome of insular Celtic populations was established by this time.
In 2015 a genetic study of the United Kingdom showed that there is no unified 'Celtic' genetic identity compared to 'non-Celtic' areas. The 'Celtic' areas of the United Kingdom (Scotland, Northern Ireland, Wales and Cornwall) show the most genetic differences among each other. The data shows that Scottish and Cornish populations share greater genetic similarity with the English than they do with other 'Celtic' populations, with the Cornish in particular being genetically much closer to other English groups than they are to the Welsh or the Scots.
Terminology
The term ''Celtic nations'' derives from thelinguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of human language. It is called a scientific study because it entails a comprehensive, systematic, objective, and precise analysis of all aspects of language, particularly its nature and structure. Linguis ...
studies of the 16th century scholar George Buchanan
George Buchanan ( gd, Seòras Bochanan; February 1506 – 28 September 1582) was a Scottish historian and humanist scholar. According to historian Keith Brown, Buchanan was "the most profound intellectual sixteenth century Scotland produced." ...
and the polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
Edward Lhuyd
Edward Lhuyd FRS (; occasionally written Llwyd in line with modern Welsh orthography, 1660 – 30 June 1709) was a Welsh naturalist, botanist, linguist, geographer and antiquary. He is also named in a Latinate form as Eduardus Luidius.
Lif ...
. As Assistant Keeper and then Keeper of the Ashmolean Museum
The Ashmolean Museum of Art and Archaeology () on Beaumont Street, Oxford, England, is Britain's first public museum. Its first building was erected in 1678–1683 to house the cabinet of curiosities that Elias Ashmole gave to the University o ...
, Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
(1691–1709), Lhuyd travelled extensively in Great Britain, Ireland and Brittany in the late 17th and early 18th centuries. Noting the similarity between the languages of Brittany, Cornwall and Wales, which he called "P-Celtic
The Gallo-Brittonic languages, also known as the P-Celtic languages, are a subdivision of the Celtic languages of Ancient Gaul (both '' celtica'' and '' belgica'') and Celtic Britain, which share certain features. Besides common linguistic in ...
" or Brythonic, the languages of Ireland, the Isle of Man and Scotland, which he called "Q-Celtic
The Celtic languages ( usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward ...
" or Goidelic
The Goidelic or Gaelic languages ( ga, teangacha Gaelacha; gd, cànanan Goidhealach; gv, çhengaghyn Gaelgagh) form one of the two groups of Insular Celtic languages, the other being the Brittonic languages.
Goidelic languages historicall ...
, and between the two groups, Lhuyd published ''Archaeologia Britannica: an Account of the Languages, Histories and Customs of Great Britain, from Travels through Wales, Cornwall, Bas-Bretagne, Ireland and Scotland'' in 1707. His ''Archaeologia Britannica'' concluded that all six languages
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
derived from the same root. Lhuyd theorised that the root language descended from the languages
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
spoken by the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ap ...
tribes of Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during R ...
, whom Greek and Roman writers called Celt
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
ic. Having defined the languages of those areas as Celtic, the people living in them and speaking those languages became known as Celtic too. There is some dispute as to whether Lhuyd's theory is correct. Nevertheless, the term ''Celtic'' to describe the languages and peoples of Brittany, Cornwall and Wales, Ireland, the Isle of Man and Scotland was accepted from the 18th century and is widely used today.
These areas of Europe are sometimes referred to as the "Celt belt" or "Celtic fringe" because of their location generally on the western edges of the continent, and of the states they inhabit (e.g. Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period o ...
is in the northwest of France, Cornwall is in the south west of Great Britain, Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in 2 ...
in western Great Britain and the Gaelic-speaking parts of Ireland and Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to th ...
are in the west of those countries). Additionally, this region is known as the "Celtic Crescent" because of the near crescent
A crescent shape (, ) is a symbol or emblem used to represent the lunar phase in the first quarter (the "sickle moon"), or by extension a symbol representing the Moon itself.
In Hinduism, Lord Shiva is often shown wearing a crescent moon on hi ...
shaped position of the nations in Europe.
Endonyms and Celtic exonyms
The Celtic names for each nation in each language illustrate some of the similarity between the languages. Despite differences in orthography, there are many sound and lexical correspondences between the endonyms and exonyms used to refer to the Celtic nations.Territories of the ancient Celts
 During the
During the European Iron Age
In Europe, the Iron Age is the last stage of the prehistoric period and the first of the protohistoric periods,The Junior Encyclopædia Britannica: A reference library of general knowledge. (1897). Chicago: E.G. Melvin. (seriously? 1897 "Junio ...
, the ancient Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
extended their territory to most of Western and Central Europe and part of Eastern Europe and central Anatolia.
The Continental Celtic languages
The Continental Celtic languages are the now-extinct group of the Celtic languages that were spoken on the continent of Europe and in central Anatolia, as distinguished from the Insular Celtic languages of the British Isles and Brittany. ''Contine ...
were extinct by the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
, and the continental "Celtic cultural traits", such as oral traditions and practices like the visiting of sacred wells and springs, largely disappeared or, in some cases, were translated. Since they no longer have a living Celtic language, they are not included as 'Celtic nations'. Nonetheless, some of these countries have movements claiming a "Celtic identity".
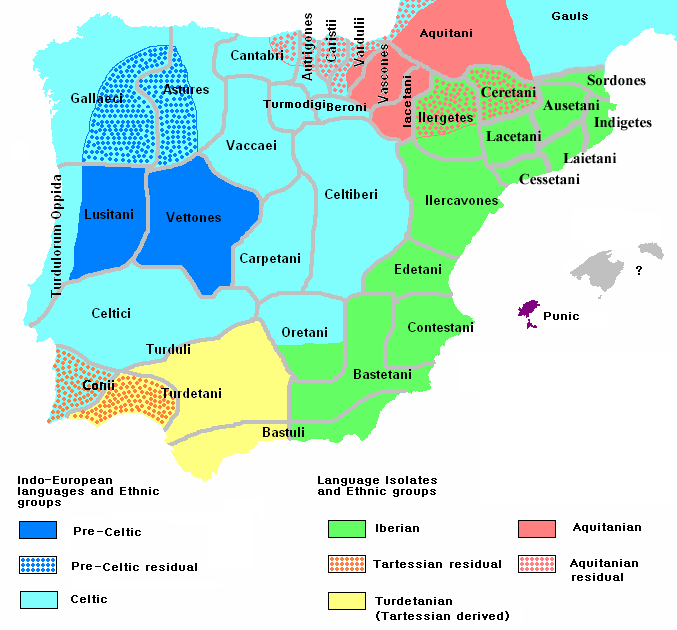
Iberian Peninsula
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
was an area heavily influenced by Celtic culture, particularly the ancient region of Gallaecia
Gallaecia, also known as Hispania Gallaecia, was the name of a Roman province in the north-west of Hispania, approximately present-day Galicia, northern Portugal, Asturias and Leon and the later Kingdom of Gallaecia. The Roman cities include ...
(about the modern region of Galicia and Braga, Viana do Castelo
Viana do Castelo () is a municipality and seat of the district of Viana do Castelo in the Norte Region of Portugal. The population in 2011 was 88,725, in an area of 319.02 km². The urbanized area of the municipality, comprising the city, ...
, Douro
The Douro (, , ; es, Duero ; la, Durius) is the highest-flow river of the Iberian Peninsula. It rises near Duruelo de la Sierra in Soria Province, central Spain, meanders south briefly then flows generally west through the north-west part o ...
, Porto
Porto or Oporto () is the second-largest city in Portugal, the capital of the Porto District, and one of the Iberian Peninsula's major urban areas. Porto city proper, which is the entire municipality of Porto, is small compared to its metropol ...
, and Bragança in Portugal) and the Asturian-Leonese region (Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensive ...
, León, Zamora and Salamanca
Salamanca () is a city in western Spain and is the capital of the Province of Salamanca in the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Castile and León. The city lies on several rolling hills by the Tormes River. Its Old City wa ...
in Spain). Only France and Britain have more ancient Celtic place names than Spain and Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a Sovereign state, country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southern Europe, Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes ...
combined (Cunliffe and Koch 2010 and 2012).
Some of the Celtic tribes recorded in these regions by the Romans were the Gallaeci, the Bracari The Bracari or Callaeci Bracari were an ancient Celtic tribe of Gallaecia, living in the northwest of modern Portugal, in the province of Minho, between the rivers Tâmega and Cávado. After the conquest of the region beginning in 136BC, the Rom ...
, the Astures, the Cantabri, the Celtici
]
The Celtici (in Portuguese language, Portuguese, Spanish, and Galician languages, ) were a Celtic tribe or group of tribes of the Iberian peninsula, inhabiting three definite areas: in what today are the regions of Alentejo and the Algarve i ...
, the Celtiberians, Celtiberi, the Tumorgogi, Albion and Cerbarci. The Lusitanians
The Lusitanians ( la, Lusitani) were an Indo-European speaking people living in the west of the Iberian Peninsula prior to its conquest by the Roman Republic and the subsequent incorporation of the territory into the Roman province of Lusitania. ...
are categorised by some as Celts, or at least Celticised, but there remain inscriptions in an apparently non-Celtic Lusitanian language
Lusitanian (so named after the Lusitani or Lusitanians) was an Indo-European Paleohispanic language. There has been support for either a connection with the ancient Italic languages or Celtic languages. It is known from only six sizeable inscri ...
. However, the language had clear affinities with the Gallaecian Celtic language. Modern-day Galicians
Galicians ( gl, galegos, es, gallegos, link=no) are a Celtic- Romance ethnic group from Spain that is closely related to the Portuguese people and has its historic homeland is Galicia, in the north-west of the Iberian Peninsula. Two Romanc ...
, Asturians
Asturians ( ast, asturianos) are a Celtic- Romance ethnic group native to the autonomous community of Asturias, in the North-West of the Iberian Peninsula.
Culture and society Heritage
Asturians are directly descended from the Astures, who wer ...
, Cantabrians and northern Portuguese claim a Celtic heritage or identity. Although the Celtic cultural traces are as difficult to analyse as in the other former Celtic countries of Europe, because of the extinction of Iberian Celtic languages in Roman times, Celtic heritage is attested in toponymics and language substratum, ancient texts, folklore and music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect ...
. At the end, late Celtic influence is also attributed to the fifth century Romano-Briton colony of Britonia
Britonia (which became Bretoña in Galician and Spanish) is the historical, apparently Latinized name of a Celtic settlement by Romano-Britons on the Iberian peninsula following the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain. The area is roughly analog ...
in Galicia.
Tenth century Middle Irish
Middle Irish, sometimes called Middle Gaelic ( ga, An Mheán-Ghaeilge, gd, Meadhan-Ghàidhlig), is the Goidelic language which was spoken in Ireland, most of Scotland and the Isle of Man from AD; it is therefore a contemporary of late Old Eng ...
mythical history Lebor Gabála Érenn
''Lebor Gabála Érenn'' (literally "The Book of the Taking of Ireland"), known in English as ''The Book of Invasions'', is a collection of poems and prose narratives in the Irish language intended to be a history of Ireland and the Irish fro ...
( ir, Leabhar Gabhála Éireann) credited Gallaecia as the point from where the Gallaic Celts sailed to conquer Ireland.
England
 In Celtic languages, England is usually referred to as "
In Celtic languages, England is usually referred to as "Saxon
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
-land" (''Sasana'', ''Pow Sows'', ''Bro-Saoz'' etc.), and in Welsh as ''Lloegr'' (though the Welsh translation of English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
also refers to the Saxon route: Saesneg, with the English people being referred to as "Saeson", or "Saes" in the singular). The mildly derogatory Scottish Gaelic term ''Sassenach
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
'' derives from this source. However, spoken Cumbric survived until approximately the 12th century, Cornish until the 18th century, and Welsh within the Welsh Marches
The Welsh Marches ( cy, Y Mers) is an imprecisely defined area along the border between England and Wales in the United Kingdom. The precise meaning of the term has varied at different periods.
The English term Welsh March (in Medieval Latin ...
, notably in Archenfield, now part of Herefordshire
Herefordshire () is a county in the West Midlands of England, governed by Herefordshire Council. It is bordered by Shropshire to the north, Worcestershire to the east, Gloucestershire to the south-east, and the Welsh counties of Monmouthsh ...
, until the 19th century. Both Cumbria and Cornwall were traditionally Brythonic in culture. Cornwall existed as an independent state for some time after the foundation of England, and Cumbria originally retained a great deal of autonomy within the Kingdom of Northumbria
la, Regnum Northanhymbrorum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of Northumbria
, common_name = Northumbria
, status = State
, status_text = Unified Anglian kingdom (before 876)North: Anglian kingdom (af ...
. The unification of the Anglian kingdom of Northumbria with the Cumbric kingdom of Cumbria came about due to a political marriage between the Northumbrian King Oswiu and Queen Riemmelth (''Rhiainfellt'' in Old Welsh
Old Welsh ( cy, Hen Gymraeg) is the stage of the Welsh language from about 800 AD until the early 12th century when it developed into Middle Welsh.Koch, p. 1757. The preceding period, from the time Welsh became distinct from Common Brittonic ...
), a then Princess of Rheged
Rheged () was one of the kingdoms of the ''Hen Ogledd'' ("Old North"), the Brittonic-speaking region of what is now Northern England and southern Scotland, during the post-Roman era and Early Middle Ages. It is recorded in several poetic an ...
.
Movements of population between different parts of Great Britain over the last two centuries, with industrial development and changes in living patterns such as the growth of second home ownership, have greatly modified the demographics of these areas, including the Isles of Scilly
The Isles of Scilly (; kw, Syllan, ', or ) is an archipelago off the southwestern tip of Cornwall, England. One of the islands, St Agnes, is the most southerly point in Britain, being over further south than the most southerly point of th ...
off the coast of Cornwall, although Cornwall in particular retains Celtic cultural features, and a Cornish self-government movement
Cornish nationalism is a cultural, political and social movement that seeks the recognition of Cornwall – the south-westernmost part of the island of Great Britain – as a nation distinct from England. It is usually based on three general ...
is well established.
Brythonic and Cumbric placenames are found throughout England but are more common in the West of England than the East, reaching their highest density in the traditionally Celtic areas of Cornwall, Cumbria and the areas of England bordering Wales. Name elements containing Brythonic topographic words occur in many areas of England, such as: ''caer'' 'fort', as in the Cumbrian city of Carlisle; ''pen'' 'hill' as in the Cumbrian town of Penrith and Pendle Hill in Lancashire; ''afon'' 'river' as in the Rivers
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wat ...
Avon in Warwickshire, Devon and Somerset; and ''mynydd'' 'mountain', as in Long Mynd in Shropshire. The name ' Cumbria' is derived from the same root as Cymru, the Welsh name for Wales, meaning 'the land of comrades'.
Formerly Gaulish regions
 Most French people identify with the ancient
Most French people identify with the ancient Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They spo ...
and are well aware that they were a people that spoke Celtic languages and lived Celtic ways of life. Nowadays, the popular nickname ''Gaulois'', "Gaulish people", is very often used to mean 'stock French people' to make the difference with the descendants of foreigners in France.
Walloons
Walloons (; french: Wallons ; wa, Walons) are a Gallo-Romance ethnic group living native to Wallonia and the immediate adjacent regions of France. Walloons primarily speak '' langues d'oïl'' such as Belgian French, Picard and Walloon. Wallo ...
occasionally characterise themselves as "Celts", mainly in opposition to the "Teutonic" Flemish
Flemish (''Vlaams'') is a Low Franconian dialect cluster of the Dutch language. It is sometimes referred to as Flemish Dutch (), Belgian Dutch ( ), or Southern Dutch (). Flemish is native to Flanders, a historical region in northern Belgium; ...
and "Latin" French identities.
Others think they are Belgian, that is to say Germano-Celtic people different from the Gaulish-Celtic French.
The ethnonym
An ethnonym () is a name applied to a given ethnic group. Ethnonyms can be divided into two categories: exonyms (whose name of the ethnic group has been created by another group of people) and autonyms, or endonyms (whose name is created and used ...
"Walloon" derives from a Germanic word meaning "foreign", cognate with the words "Welsh" and "Vlach
"Vlach" ( or ), also "Wallachian" (and many other variants), is a historical term and exonym used from the Middle Ages until the Modern Era to designate mainly Romanians but also Aromanians, Megleno-Romanians, Istro-Romanians and other Eastern ...
".
The name of Belgium, home country of the Walloon people, is cognate with the Celtic tribal names Belgae and (possibly) the Irish legendary Fir Bolg
In medieval Irish myth, the Fir Bolg (also spelt Firbolg and Fir Bholg) are the fourth group of people to settle in Ireland. They are descended from the Muintir Nemid, an earlier group who abandoned Ireland and went to different parts of Europe ...
.
Italian Peninsula
The Canegrate culture (13th century BC) may represent the first migratory wave of the proto-Celtic population from the northwest part of the Alps that, through the Alpine passes, had already penetrated and settled in the western Po valley betweenLake Maggiore
Lake Maggiore (, ; it, Lago Maggiore ; lmo, label=Western Lombard, Lagh Maggior; pms, Lagh Magior; literally 'Greater Lake') or Verbano (; la, Lacus Verbanus) is a large lake located on the south side of the Alps. It is the second largest la ...
and Lake Como
Lake Como ( it, Lago di Como , ; lmo, label=Western Lombard, Lagh de Còmm , ''Cómm'' or ''Cùmm'' ), also known as Lario (; after the la, Larius Lacus), is a lake of glacial origin in Lombardy, Italy. It has an area of , making it the thi ...
( Scamozzina culture). It has also been proposed that a more ancient proto-Celtic presence can be traced back to the beginning of the Middle Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
(16th–15th century BC), when North Westwern Italy appears closely linked regarding the production of bronze artifacts, including ornaments, to the western groups of the Tumulus culture
__NOTOC__
The Tumulus culture (German: ''Hügelgräberkultur'') dominated Central Europe during the Middle Bronze Age ( 1600 to 1300 BC).
It was the descendant of the Unetice culture. Its heartland was the area previously occupied by the U ...
(Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the ar ...
, 1600–1200 BC). La Tène cultural material appeared over a large area of mainland Italy, the southernmost example being the Celtic helmet from Canosa di Puglia
Canosa di Puglia, generally known simply as Canosa ( nap, label= Canosino, Canaus), is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Barletta-Andria-Trani, Apulia, southern Italy. It is located between Bari and Foggia, on the northwestern edge of the ...
.
Italy is home to the Lepontic, the oldest attested Celtic language (from the 6th century BC). Anciently spoken in Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
and in Northern-Central Italy, from the Alps
The Alps () ; german: Alpen ; it, Alpi ; rm, Alps ; sl, Alpe . are the highest and most extensive mountain range system that lies entirely in Europe, stretching approximately across seven Alpine countries (from west to east): France, Sw ...
to Umbria
it, Umbro (man) it, Umbra (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, ...
. According to the ''Recueil des Inscriptions Gauloises'', more than 760 Gaulish inscriptions have been found throughout present-day France—with the notable exception of Aquitaine
Aquitaine ( , , ; oc, Aquitània ; eu, Akitania; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Aguiéne''), archaic Guyenne or Guienne ( oc, Guiana), is a historical region of southwestern France and a former administrative region of the country. Since 1 Janua ...
—and in Italy, which testifies the importance of Celtic heritage in the peninsula.
The French- and Arpitan-speaking Aosta Valley
, Valdostan or Valdotainian it, Valdostano (man) it, Valdostana (woman)french: Valdôtain (man)french: Valdôtaine (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title = Official languages
, population_blank1 = Italian French
...
region in Italy also presents a claim of Celtic heritage.
The Northern League autonomist
Autonomism, also known as autonomist Marxism is an anti-capitalist left-wing political and social movement and theory. As a theoretical system, it first emerged in Italy in the 1960s from workerism (). Later, post-Marxist and anarchist tendenc ...
party often exalts what it claims are the Celtic roots of all Northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative region ...
or Padania
Padania (, also , ) is an alternative name and proposed independent state encompassing Northern Italy, derived from the name of the Po River (Latin ''Padus''), whose basin includes much of the region, centered on the Po Valley (), the major plain ...
.
Reportedly, Friuli
Friuli ( fur, Friûl, sl, Furlanija, german: Friaul) is an area of Northeast Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity containing 1,000,000 Friulians. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli Venezia Giuli ...
also has a claim to Celticity (recent studies have estimated that about 1/10 of Friulian words are of Celtic origin; also, a lot of typical Friulian traditions, dances, songs and mythology are remnants of the culture of Carnian tribes who lived in this area during the Roman age and the early Middle Ages. Some Friuli
Friuli ( fur, Friûl, sl, Furlanija, german: Friaul) is an area of Northeast Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity containing 1,000,000 Friulians. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli Venezia Giuli ...
ans consider themselves and their region as one of the Celtic Nations)
Central and Eastern European regions
Celtic tribes inhabited land in what is now southern Germany and Austria. Many scholars have associated the earliest Celtic peoples with theHallstatt culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western and Central European culture of Late Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe (Hallstatt C, Hallstatt D) from the 8th to 6th centuries ...
. The Boii
The Boii (Latin plural, singular ''Boius''; grc, Βόιοι) were a Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul (Northern Italy), Pannonia (Hungary), parts of Bavaria, in and around Bohemia (after whom the ...
, the Scordisci
The Scordisci ( el, Σκορδίσκοι) were a Celtic Iron Age cultural group centered in the territory of present-day Serbia, at the confluence of the Savus (Sava), Dravus (Drava), Margus (Morava) and Danube rivers. They were historically n ...
, and the Vindelici
The Vindelici (Gaulish: ) were a Gallic people dwelling around present-day Augsburg ( Bavaria) during the Iron Age and the Roman period.
Name
They are mentioned as by Horace (1st c. BC), as (; var. ) by Strabo (early 1st c. AD), as and ( ...
are some of the tribes that inhabited Central Europe, including what is now Slovakia, Serbia, Croatia, Poland and the Czech Republic as well as Germany and Austria. The Boii gave their name to Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohe ...
. The Boii founded a city on the site of modern Prague, and some of its ruins are now a tourist attraction. There are claims among modern Czechs that the Czech people are as much descendants of the Boii as they are from the later Slavic invaders (as well as the historical Germanic peoples of Czech lands). This claim may not only be political: according to a 2000 study by Semino, 35.6% of Czech males have y-chromosome haplogroup R1b, which is common among Celts but rare among Slavs.
Celts also founded Singidunum
Singidunum ( sr, Сингидунум/''Singidunum'') was an ancient city which later evolved into modern Belgrade, the capital of Serbia. The name is of Celtic origin, going back to the time when Celtic tribe Scordisci settled the area in the ...
near present-day Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; names in other languages) is the capital and largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers and the crossroads of the Pannonian Plain and the Balkan Peninsula. Nearly 1,166,763 m ...
, though the Celtic presence in modern-day Serbian regions is limited to the far north (mainly including the historically at least partially Hungarian Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capita ...
).
The modern-day capital of Turkey, Ankara
Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the capital of Turkey. Located in the central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5.1 million in its urban center and over 5.7 million in Ankara Province, mak ...
, was once the center of the Celtic culture in Central Anatolia, giving the name to the region—Galatia
Galatia (; grc, Γαλατία, ''Galatía'', "Gaul") was an ancient area in the highlands of central Anatolia, roughly corresponding to the provinces of Ankara and Eskişehir, in modern Turkey. Galatia was named after the Gauls from Thrace ( ...
.
The La Tène culture
The La Tène culture (; ) was a European Iron Age culture. It developed and flourished during the late Iron Age (from about 450 BC to the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC), succeeding the early Iron Age Hallstatt culture without any defi ...
—named for a region in modern Switzerland—succeeded the Halstatt era in much of central Europe.
Celtic diaspora
In other regions, people with a heritage from one of the Celtic nations also associate with the Celtic identity. In these areas, Celtic traditions and languages are significant components of local culture. These include the Permanent North American Gaeltacht in Tamworth, Ontario, Canada which is the only Irish Gaeltacht outside Ireland; the Chubut valley ofPatagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and ...
with Welsh-speaking Welsh Argentines (known as Y Wladfa
Y Wladfa (, "The Colony"), also occasionally Y Wladychfa Gymreig (, "The Welsh Settlement"), refers to the establishment of settlements by Welsh immigrants in Patagonia, beginning in 1865, mainly along the coast of the lower Chubut Valley. I ...
); Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (french: link=no, île du Cap-Breton, formerly '; gd, Ceap Breatainn or '; mic, Unamaꞌki) is an island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.
The island accounts for 18. ...
in Nova Scotia, with Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as ...
-speaking Scottish Canadians
Scottish Canadians are people of Scottish descent or heritage living in Canada. As the third-largest ethnic group in Canada and amongst the first Europeans to settle in the country, Scottish people have made a large impact on Canadian culture si ...
; and southeast Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
with traditionally Irish-speaking Irish Canadians
ga, Gael-Cheanadaigh
, image = Irish_Canadian_population_by_province.svg
, image_caption = Irish Canadians as percent of population by province/territory
, population = 4,627,00013.4% of the Canadian population (2016)
, po ...
. Also at one point in the 1900s there were well over 12,000 Gaelic Scots from the Isle of Lewis
The Isle of Lewis ( gd, Eilean Leòdhais) or simply Lewis ( gd, Leòdhas, ) is the northern part of Lewis and Harris, the largest island of the Western Isles or Outer Hebrides archipelago in Scotland. The two parts are frequently referred to as ...
living in the Eastern Townships
The Eastern Townships (french: Cantons de l'Est) is an historical administrative region in southeastern Quebec, Canada. It lies between the St. Lawrence Lowlands and the American border, and extends from Granby in the southwest, to Drummondv ...
of Quebec, Canada, with place names that still exist today recalling those inhabitants. Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
has a region known as "Little Cornwall" where tens of thousands of Cornish miners migrated to work the mines of Hidalgo
Hidalgo may refer to:
People
* Hidalgo (nobility), members of the Spanish nobility
* Hidalgo (surname)
Places
Mexico
* Hidalgo (state), in central Mexico
* Hidalgo, Coahuila, a town in the north Mexican state of Coahuila
* Hidalgo, Nuevo L ...
where today the Cornish legacy is very present in Pachuca
Pachuca (; ote, Nju̱nthe), formally known as Pachuca de Soto, is the capital and largest city of the Mexican state of Hidalgo. It is located in the south-central part of the state. Pachuca de Soto is also the name of the municipality of whi ...
and Real del Monte
Mineral del Monte, commonly called Real del Monte () or El Real, is a small mining town, and one of the 84 municipalities of Hidalgo, in the State of Hidalgo in east-central Mexico.
It is located at an altitude of . As of 2005, the municipal ...
. Mexico received migrants from Cornwall, Scotland, Ireland, Brittany, Galicia and Asturias and they celebrate their Celtic culture in this Celtic Corner of Mexico in Real del Monte-Pachuca "Little Cornwall" area, an area visited by the Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales ( cy, Tywysog Cymru, ; la, Princeps Cambriae/Walliae) is a title traditionally given to the heir apparent to the English and later British throne. Prior to the conquest by Edward I in the 13th century, it was used by the ruler ...
in 2014 to strengthen the cultural ties between Hidalgo and Cornwall.
Saint John, New Brunswick
Saint John is a seaport city of the Atlantic Ocean located on the Bay of Fundy in the province of New Brunswick, Canada. Saint John is the oldest incorporated city in Canada, established by royal charter on May 18, 1785, during the reign of Ki ...
has often been called "Canada's Irish City". In the years between 1815, when vast industrial changes began to disrupt the old life-styles in Europe, and Canadian Confederation in 1867, when immigration of that era passed its peak, more than 150,000 immigrants from Ireland flooded into Saint John. Those who came in the earlier period were largely tradesmen, and many stayed in Saint John, becoming the backbone of its builders. But when the Great Famine raged between 1845 and 1852, huge waves of Famine refugees flooded these shores. It is estimated that between 1845 and 1847, some 30,000 arrived, more people than were living in the city at the time. In 1847, dubbed "Black 47," one of the worst years of the Famine, some 16,000 immigrants, most of them from Ireland, arrived at Partridge Island, the immigration and quarantine station at the mouth of Saint John Harbour. However, thousands of Irish were living in New Brunswick prior to these events, mainly in Saint John.
 After the partitioning of the British colony of Nova Scotia in 1784 New Brunswick was originally named New Ireland with the capital to be in Saint John.
Large swathes of the United States of America were subject to migration from Celtic peoples, or people from Celtic nations. Irish-speaking
After the partitioning of the British colony of Nova Scotia in 1784 New Brunswick was originally named New Ireland with the capital to be in Saint John.
Large swathes of the United States of America were subject to migration from Celtic peoples, or people from Celtic nations. Irish-speaking Irish Catholic
Irish Catholics are an ethnoreligious group native to Ireland whose members are both Catholic and Irish. They have a large diaspora, which includes over 36 million American citizens and over 14 million British citizens (a quarter of the Briti ...
s congregated particularly in the East Coast cities of New York, Boston, and Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since ...
, and also in Pittsburgh
Pittsburgh ( ) is a city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, United States, and the county seat of Allegheny County. It is the most populous city in both Allegheny County and Western Pennsylvania, the second-most populous city in Pennsylv ...
and Chicago, while Scots and Ulster-Scots were particularly prominent in the Southern United States, including Appalachia
Appalachia () is a cultural region in the Eastern United States that stretches from the Southern Tier of New York State to northern Alabama and Georgia. While the Appalachian Mountains stretch from Belle Isle in Newfoundland and Labrador, C ...
although Appalachia also received regular Irish immigrants and immigrants from wales. Gaelic speaking Highland-Scots also migrated in concentrated numbers to the Cape Fear River area in North Carolina and the fortress-town of Darien, Georgia.
A legend that became popular during the Elizabethan era
The Elizabethan era is the epoch in the Tudor period of the history of England during the reign of Queen Elizabeth I (1558–1603). Historians often depict it as the golden age in English history. The symbol of Britannia (a female personif ...
claims that a Welsh prince named Madoc
Madoc ab Owain Gwynedd (also spelled Madog) was, according to folklore, a Welsh prince who sailed to America in 1170, over three hundred years before Christopher Columbus's voyage in 1492.
According to the story, he was a son of Owain Gwyned ...
established a colony in North America in the late 12th century. The story continues that the settlers merged with local Indian tribes, who preserved the Welsh language
Welsh ( or ) is a Celtic language of the Brittonic subgroup that is native to the Welsh people. Welsh is spoken natively in Wales, by some in England, and in Y Wladfa (the Welsh colony in Chubut Province, Argentina). Historically, it has ...
and the Christian religion
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
for hundreds of years. However, there is no contemporary evidence that Prince Madoc existed. An area of Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; (Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, Mary ...
known as the Welsh Tract was settled by Welsh Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's abili ...
, where the names of several towns still bear Welsh names, such as Bryn Mawr, the Lower
Lower may refer to:
*Lower (surname)
*Lower Township, New Jersey
*Lower Receiver (firearms)
*Lower Wick
Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is situated about five miles south west of Dursley, eigh ...
and Upper Gwynedd Townships, and Bala Cynwyd
Bala Cynwyd ( ) is a community in Lower Merion Township, Pennsylvania. It is located on the Philadelphia Main Line in Southeastern Pennsylvania, bordering the western edge of Philadelphia at U.S. Route 1 (City Avenue). It was originally two sepa ...
. In the 19th century, Welsh settlers arrived in the Chubut River valley of Patagonia, Argentina and established a colony called Y Wladfa
Y Wladfa (, "The Colony"), also occasionally Y Wladychfa Gymreig (, "The Welsh Settlement"), refers to the establishment of settlements by Welsh immigrants in Patagonia, beginning in 1865, mainly along the coast of the lower Chubut Valley. I ...
( es, link=no, Colonia Galesa). Today, the Welsh language and Welsh tea houses are common in several towns, many of which have Welsh names. Dolavon and Trelew
Trelew (, from cy, tref "town" and the name of the founder, Lewis Jones) is a city in the eastern part of the Chubut Province of Argentina. Located in Patagonia, the city is the largest and most populous in the low valley of the Chubut River, ...
are examples of Welsh towns.
In his autobiography, the South African poet Roy Campbell recalled his youth in the Dargle Valley, near the city of Pietermaritzburg
Pietermaritzburg (; Zulu: umGungundlovu) is the capital and second-largest city in the province of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. It was founded in 1838 and is currently governed by the Msunduzi Local Municipality. Its Zulu name umGungundlovu ...
, where people spoke only Gaelic and Zulu.
In New Zealand, the southern regions of Otago
Otago (, ; mi, Ōtākou ) is a region of New Zealand located in the southern half of the South Island administered by the Otago Regional Council. It has an area of approximately , making it the country's second largest local government reg ...
and Southland were settled by the Free Church of Scotland. Many of the place names in these two regions (such as the main cities of Dunedin and Invercargill
Invercargill ( , mi, Waihōpai is the southernmost and westernmost city in New Zealand, and one of the southernmost cities in the world. It is the commercial centre of the Southland region. The city lies in the heart of the wide expanse of ...
and the major river, the Clutha) have Scottish Gaelic names, and Celtic culture is still prominent in this area.
In addition to these, a number of people from Canada, the United States, Australia, South Africa and other parts of the former British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
have formed various Celtic societies over the years.
See also
*Anglo-Celtic
Anglo-Celtic people are descended primarily from British and Irish people. The concept is mainly relevant outside of Great Britain and Ireland, particularly in Australia, but is also used in Canada, the United States, New Zealand and South Africa, ...
* Breton nationalism
Breton nationalism ( Breton: ''roadelouriezh Brezhoneg'', French: ''nationalisme Breton'') is a form of regional nationalism associated with the region of Brittany in France. The political aspirations of Breton nationalists include the desire ...
* Celt
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
* Celtic Christianity
Celtic Christianity ( kw, Kristoneth; cy, Cristnogaeth; gd, Crìosdaidheachd; gv, Credjue Creestee/Creestiaght; ga, Críostaíocht/Críostúlacht; br, Kristeniezh; gl, Cristianismo celta) is a form of Christianity that was common, or held ...
* Celtic Revival
The Celtic Revival (also referred to as the Celtic Twilight) is a variety of movements and trends in the 19th, 20th and 21st centuries that see a renewed interest in aspects of Celtic culture. Artists and writers drew on the traditions of Gae ...
* Celtic art
Celtic art is associated with the peoples known as Celts; those who spoke the Celtic languages in Europe from pre-history through to the modern period, as well as the art of ancient peoples whose language is uncertain, but have cultural and styli ...
* Celtic fusion
* Celtic mythology
* Galician nationalism
Galician nationalism is a form of nationalism found mostly in Galicia, which asserts that Galicians are a nation and that promotes the cultural unity of Galicians. The political movement referred to as modern Galician nationalism was born at ...
* Germanic languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, Engl ...
* Irish nationalism
Irish nationalism is a nationalist political movement which, in its broadest sense, asserts that the people of Ireland should govern Ireland as a sovereign state. Since the mid-19th century, Irish nationalism has largely taken the form of cu ...
* Pan-Celticism
Pan-Celticism ( ga, Pan-Cheilteachas, Scottish Gaelic: ''Pan-Cheilteachas'', Breton: ''Pan-Keltaidd'', Welsh: ''Pan-Geltaidd,'' Cornish: ''Pan-Keltaidd,'' Manx: ''Pan-Cheltaghys''), also known as Celticism or Celtic nationalism is a politica ...
* Norse-Gaelic
* Romance-speaking Europe
Most languages of Europe belong to the Indo-European language family. Out of a total European population of 744 million as of 2018, some 94% are native speakers of an Indo-European language. Within Indo-European, the three largest phyla are Ro ...
* Scottish national identity
Scottish national identity is a term referring to the sense of national identity, as embodied in the shared and characteristic culture, languages and traditions, of the Scottish people.
Although the various dialects of Gaelic, the Scots ...
* Slavic Europe
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to:
Peoples
* Slavic peoples, an ethno-linguistic group living in Europe and Asia
** East Slavic peoples, eastern group of Slavic peoples
** South Slavic peoples, southern group of Slavic peoples
** West Sla ...
* Welsh nationalism
Welsh nationalism ( cy, Cenedlaetholdeb Cymreig) emphasises and celebrates the distinctiveness of Welsh culture and Wales as a nation or country. Welsh nationalism may also include calls for further autonomy or self determination which includes ...
References
Further reading
*External links
*Celtic League
{{DEFAULTSORT:Celtic Nations Cultural regions Geography of Northwestern Europe Linguistic regions of Europe