Celje on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
)
, pushpin_map = Slovenia
, pushpin_label_position = left
, pushpin_map_caption = Location of the city of Celje in Slovenia
, coordinates =
, subdivision_type =
 Once the area was incorporated in the
Once the area was incorporated in the 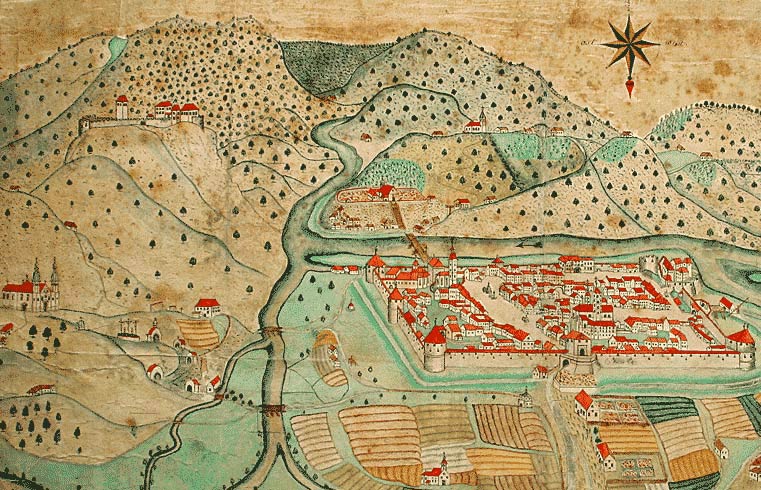 After the Counts of Celje died out in 1456, the region was inherited by the
After the Counts of Celje died out in 1456, the region was inherited by the
 The
The
 Postal number: SI-3000 (from 1991). (Old one: 63000 (between 1945–1991)).
Postal number: SI-3000 (from 1991). (Old one: 63000 (between 1945–1991)).
Motnikar, Barbara Šket, & Andrej Gosar. 2012. Obituaries: Janez Lapajne, 1937–2012. ''IASPEI Newsletter'' (June/July): 4.
*
File:The Celje Ceiling (stropna freska, Stara grofija).jpg, The Celje Ceiling from the Old's Counts Mansion (17th century)
File:SLO-Celje08-2.JPG, Stane Street, with the
Celje on Geopedia
* *
CeljeCafe.com unofficial website
{{Authority control Cities and towns in Styria (Slovenia) Populated places in the City Municipality of Celje Noricum
Country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while the ...
, subdivision_name =
, subdivision_type1 = Traditional region
, subdivision_name1 = Styria
Styria (german: Steiermark ; Serbo-Croatian and sl, ; hu, Stájerország) is a state (''Bundesland'') in the southeast of Austria. With an area of , Styria is the second largest state of Austria, after Lower Austria. Styria is bordered to ...
, subdivision_type2 = Statistical region
, subdivision_name2 = Savinja
The Savinja () is a river in northeast Slovenia which flows mostly in the Upper and Lower Savinja Valley ( sl, Zgornja in Spodnja Savinjska dolina) and through the cities of Celje and Laško. The Savinja is the main river of the Savinja Alps (Sl ...
, subdivision_type3 = Municipality
A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate.
The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go ...
, subdivision_name3 = Celje
, established_title = Town rights
, established_date = 11 April 1451
, founder =
, named_for =
, parts_type = Districts & local communities
, parts_style = list
, p1 =
, p2 =
, government_type =
, government_footnotes =
, leader_title = Mayor
, leader_name = Matija Kovač
, unit_pref = Metric
, area_footnotes =
, area_total_km2 = 22.7
, elevation_footnotes =
, elevation_m = 238
, elevation_max_m =
, elevation_min_m =
, population_footnotes =
, population_total = 37872
, population_as_of = 2020
, population_density_km2 = auto
, population_blank1_title = Municipality
, population_blank1 = 50,039
, population_note =
, timezone = CET
CET or cet may refer to:
Places
* Cet, Albania
* Cet, standard astronomical abbreviation for the constellation Cetus
* Colchester Town railway station (National Rail code CET), in Colchester, England
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Comcast En ...
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST = CEST CEST or cest may refer to:
* Central European Summer Time (UTC+2), daylight saving time observed in the central European time zone
* Cognitive-Experiential Self-Theory
* Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer, a subset of Magnetization transfer in ...
, utc_offset_DST = +2
, postal_code_type = Postal code
A postal code (also known locally in various English-speaking countries throughout the world as a postcode, post code, PIN or ZIP Code) is a series of letters or digits or both, sometimes including spaces or punctuation, included in a postal a ...
, postal_code = 3000
, area_code = 03
, blank_name = Climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologic ...
, blank_info = Cfb
, registration_plate = CE
, website =
, footnotes = Source: Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia
The Statistical Office of the Republic of Slovenia (SURS) ( Slovene: ''Statistični urad Republike Slovenije'', ''SURS'') is an independent Slovenian state institution in charge of official statistical surveying. It reports directly to the prime mi ...
, census of 2002.
, official_name =
Celje (, german: Cilli, ) is the fourth-largest city in Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
. It is a regional center of the traditional Slovenian region of Styria
Styria (german: Steiermark ; Serbo-Croatian and sl, ; hu, Stájerország) is a state (''Bundesland'') in the southeast of Austria. With an area of , Styria is the second largest state of Austria, after Lower Austria. Styria is bordered to ...
and the administrative seat of the City Municipality of Celje
The City Municipality of Celje (; sl, Mestna občina Celje) is one of twelve city municipalities in Slovenia. Its seat is the city of Celje, a regional center of Styria.
Settlements
In addition to the municipal seat of Celje, the municipalit ...
( sl, Mestna občina Celje). The town of Celje is located below Upper Celje Castle () at the confluence
In geography, a confluence (also: ''conflux'') occurs where two or more flowing bodies of water join to form a single channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main stem); o ...
of the Savinja
The Savinja () is a river in northeast Slovenia which flows mostly in the Upper and Lower Savinja Valley ( sl, Zgornja in Spodnja Savinjska dolina) and through the cities of Celje and Laško. The Savinja is the main river of the Savinja Alps (Sl ...
, Hudinja, Ložnica
The Ložnica () is a river in Slovenia, a left tributary of the Savinja in Celje
)
, pushpin_map = Slovenia
, pushpin_label_position = left
, pushpin_map_caption = Location of the city of Celje in Slov ...
, and Voglajna
The Voglajna () is a river in Styria, Slovenia. The river is long (including its source river, the Ločnica), and its catchment area is . Its source is Lake Slivnica ( sl, Slivniško jezero) near Slivnica pri Celju. It passes Šentjur, the ruins ...
rivers in the lower Savinja Valley
The Savinja () is a river in northeast Slovenia which flows mostly in the Upper and Lower Savinja Valley ( sl, Zgornja in Spodnja Savinjska dolina) and through the cities of Celje and Laško. The Savinja is the main river of the Savinja Alps (Sl ...
, and at the crossing of the roads connecting Ljubljana
Ljubljana (also known by other historical names) is the capital and largest city of Slovenia. It is the country's cultural, educational, economic, political and administrative center.
During antiquity, a Roman city called Emona stood in the ar ...
, Maribor
Maribor ( , , , ; also known by other #Name, historical names) is the second-largest city in Slovenia and the largest city of the traditional region of Styria (Slovenia), Lower Styria. It is also the seat of the City Municipality of Maribor, th ...
, Velenje
Velenje (; german: Wöllan''Leksikon občin kraljestev in dežel zastopanih v državnem zboru,'' vol. 4: ''Štajersko''. 1904. Vienna: C. Kr. Dvorna in Državna Tiskarna, p. 272.) is Slovenia's sixth-largest city, and the seat of the Municipality ...
, and the Central Sava Valley
The Central Sava Valley ( sl, Zasavje) is a valley in the Sava Hills and a geographic region along the Sava in central Slovenia, now constituting the Central Sava Statistical Region. The region consists of three municipalities: Zagorje ob Savi, ...
. It lies above mean sea level
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. ...
(MSL).
Name
Celje was known as ''Celeia'' during theRoman period
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
. Early attestations of the name during or following Slavic settlement include ''Cylia'' in 452, ''ecclesiae Celejanae'' in 579, ''Zellia'' in 824, ''in Cilia'' in 1310, ''Cilli'' in 1311, and ''Celee'' in 1575. The proto-Slovene name ''*Ceľe'' or ''*Celьje'', from which modern Slovene ''Celje'' developed, was borrowed from Vulgar Latin
Vulgar Latin, also known as Popular or Colloquial Latin, is the range of non-formal Register (sociolinguistics), registers of Latin spoken from the Crisis of the Roman Republic, Late Roman Republic onward. Through time, Vulgar Latin would evolve ...
''Celeae''. The name is of pre-Roman origin and its further etymology is unclear. In the local Slovene dialect, Celje is called ''Cjele'' or ''Cele''. In German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
it is called ''Cilli'', and it is known in Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
as ''Cilli'' or ''Celie''.
History
Early history
The first settlement in the area of Celje appeared during theHallstatt
Hallstatt ( , , ) is a small town in the district of Gmunden, in the Austrian state of Upper Austria. Situated between the southwestern shore of Hallstätter See and the steep slopes of the Dachstein massif, the town lies in the Salzkammergut ...
era. The settlement was known in the Celtic times and to Ancient Greek historians as ''Kelea''; findings suggest that Celt
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
s coined Noric money in the region.
 Once the area was incorporated in the
Once the area was incorporated in the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
in 15 BC, it was known as ''Civitas Celeia
)
, pushpin_map = Slovenia
, pushpin_label_position = left
, pushpin_map_caption = Location of the city of Celje in Slovenia
, coordinates =
, subdivision_type = Cou ...
''. It received municipal rights
Town privileges or borough rights were important features of European towns during most of the second millennium. The city law customary in Central Europe probably dates back to Italian models, which in turn were oriented towards the tradition ...
in AD 45 under the name ''municipium Claudia Celeia'' during the reign of the Roman Emperor Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusu ...
(41-54). Records suggest that the town was rich and densely populated, secured with the walls and towers, containing multi-storied marble palaces, wide squares, and streets. It was called ''Troia secunda'', the second; or small Troy
Troy ( el, Τροία and Latin: Troia, Hittite language, Hittite: 𒋫𒊒𒄿𒊭 ''Truwiša'') or Ilion ( el, Ίλιον and Latin: Ilium, Hittite language, Hittite: 𒃾𒇻𒊭 ''Wiluša'') was an ancient city located at Hisarlik in prese ...
. A Roman road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Re ...
through Celeia led from Aquileia
Aquileia / / / / ;Bilingual name of ''Aquileja – Oglej'' in: vec, Aquiłeja / ; Slovenian: ''Oglej''), group=pron is an ancient Roman city in Italy, at the head of the Adriatic at the edge of the lagoons, about from the sea, on the river N ...
(Sln. ''Oglej'') to Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
. Celeia soon became a flourishing Roman colony
A Roman (plural ) was originally a Roman outpost established in conquered territory to secure it. Eventually, however, the term came to denote the highest status of a Roman city. It is also the origin of the modern term ''colony''.
Characteri ...
, and many great buildings were constructed, such as the temple of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terr ...
, which was known across the Empire. Celeia was incorporated into Aquileia ca. 320 under the Roman Emperor Constantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
(272-337).
The city was razed by Slavic tribes
This is a list of Slavic peoples and Slavic tribes reported in Late Antiquity and in the Middle Ages, that is, before the year AD 1500.
Ancestors
*Proto-Indo-Europeans (Proto-Indo-European speakers)
** Proto-Balto-Slavs (common ancestors of B ...
during the Migration period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman ...
of the 5th and 6th centuries, but was rebuilt in the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
. The first mention of Celje in the Middle Ages was under the name of ''Cylie'' in Wolfhold von Admont's Chronicle, which was written between 1122 and 1137. The town was the seat of the Counts of Celje
The Counts of Celje ( sl, Celjski grofje) or the Counts of Cilli (german: Grafen von Cilli; hu, cillei grófok) were the most influential late medieval noble dynasty on the territory of present-day Slovenia. Risen as vassals of the Habsburg dukes ...
from 1341 to 1456 It acquired market-town status in the first half of the 14th century and town privileges
Town privileges or borough rights were important features of European towns during most of the second millennium. The city law customary in Central Europe probably dates back to Italian models, which in turn were oriented towards the traditio ...
from Count Frederick II on 11 April 1451.
Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
s of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
and administered by the Duchy of Styria. The city wall
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or earthworks to extensive military fortifications with towers, bastions and gates ...
s and defensive moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch, either dry or filled with water, that is dug and surrounds a castle, fortification, building or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. In some places moats evolved into more extensive ...
were built in 1473. The town defended itself against Turks
Turk or Turks may refer to:
Communities and ethnic groups
* Turkic peoples, a collection of ethnic groups who speak Turkic languages
* Turkish people, or the Turks, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
* Turkish citizen, a citizen of the Republic ...
and in 1515 during great Slovene peasant revolt
The Slovene Peasant Revolt ( sl, slovenski kmečki upor, german: Windischer Bauernbund) took place in 1515 and was the largest peasant revolt in the Slovene Lands. It engulfed most of what is now Slovenia as well as a significant portion of the pr ...
against peasants, who had taken Old Castle.
Many local nobles converted to Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
during the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
, but the region was converted back to Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
during the Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) a ...
. Celje became part of the Habsburgs' Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
during the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
. In 1867, after the defeat of Austria in the Austro-Prussian War
The Austro-Prussian War, also by many variant names such as Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), (; "German war of brothers") and by a variety of other names, was fought in 186 ...
, the town became part of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
.
19th century
The first service on theVienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
-Trieste
Trieste ( , ; sl, Trst ; german: Triest ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital city, and largest city, of the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, one of two autonomous regions which are not subdivided into provi ...
railway line
Rail terminology is a form of technical terminology. The difference between the American term ''railroad'' and the international term ''railway'' (used by the International Union of Railways and English-speaking countries outside the United Sta ...
came through Celje on 27 April 1846. In 1895, Celje secondary school, established in 1808, began to teach in Slovene.
At the end of the 19th century and in the early 20th century, Celje was a center of German nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the State (polity), state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a in-group and out-group, group of peo ...
which had repercussions for Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( sl, Slovenci ), are a South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia, and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovene as their n ...
. The 1910 census showed that 66.8% of the population was German. A symbol of this was the German Cultural Center (german: Deutsches Haus), built in 1906 and opened on 15 May 1907, today it is Celje Hall ( sl, Celjski dom). The centuries-old German name of the town, ''Cilli'', sounded no longer German enough to some German residents, the form ''Celle'' being preferred by many.
Population growth was steady during this period. In 1900, Celje had 6,743 inhabitants and by 1924 this had grown to 7,750. The National Hall
National Hall is a former venue in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, located at 1222–24 Market Street, between Twelfth and Thirteenth Streets. It was one of the most popular venues in the city, site of concerts, lectures, meetings, and political spee ...
(''Narodni dom''), which hosts the Mayors Office and Town Council today, was built in 1896. The first telephone
A telephone is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into e ...
line was installed in 1902 and the city received electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt, one joule per second. Standard prefixes apply to watts as with other SI units: thousands, millions and billions o ...
in 1913.
Slovene and German ethnic nationalism
Ethnic nationalism, also known as ethnonationalism, is a form of nationalism wherein the nation and nationality are defined in terms of ethnicity, with emphasis on an ethnocentric (and in some cases an ethnocratic) approach to various politi ...
increased during the 19th and early 20th centuries. With the collapse of Austria-Hungary in 1918 as a result of World War I, Celje became part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
(later known as Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
). During this period, the town experienced a rapid industrialization and a substantial growth in population.
Second World War
Celje was occupied byNazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
in April 1941. The Gestapo
The (), abbreviated Gestapo (; ), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.
The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Prussia into one organi ...
arrived in Celje on 16 April 1941 and were followed three days later by SS leader Heinrich Himmler
Heinrich Luitpold Himmler (; 7 October 1900 – 23 May 1945) was of the (Protection Squadron; SS), and a leading member of the Nazi Party of Germany. Himmler was one of the most powerful men in Nazi Germany and a main architect of th ...
, who inspected ''Stari pisker'' prison. During the war the city suffered from allied
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
bombing, aimed at important communication lines and military installations. The National Hall
National Hall is a former venue in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, located at 1222–24 Market Street, between Twelfth and Thirteenth Streets. It was one of the most popular venues in the city, site of concerts, lectures, meetings, and political spee ...
was severely damaged.
The toll of the war on the city was heavy. The city (including nearby towns) had a pre-war population of 20,000 and lost 575 people during the war, mostly between the ages of 20 and 30. More than 1,500 people were deported to Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
or into the German interior of the Third Reich
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
. Around 300 people were interned and around 1,000 people imprisoned in Celje's prisons. An unknown number of citizens were forcibly conscripted into the German army. Around 600 "stolen children" were taken to Nazi Germany for Germanization
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In ling ...
. A monument in Celje called ''Vojna in mir'' (War and Peace) by the sculptor Jakob Savinšek
Jakob Savinšek (4 February 1922 – 17 August 1961) was a Slovene sculptor, illustrator, and poet.
Life
Savinšek was born in the Upper Carniolan town of Kamnik, then part of the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (now in Slovenia ...
, commemorates the World War II era.
After the end of the war, the remaining German-speaking portion of the populace was expelled. Anti-tank trenches
A trench is a type of excavation or in the ground that is generally deeper than it is wide (as opposed to a wider gully, or ditch), and narrow compared with its length (as opposed to a simple hole or pit).
In geology, trenches result from erosi ...
and other sites were used to create 25 mass graves in Celje Mass graves in Celje were created in Celje, Slovenia, after the Second World War, from 1945 to 1956. The 11 known mass graves in Celje itself and 14 in the immediate vicinity include some of the largest mass graves in Slovenia.
Background
After the ...
and its immediate surroundings and were filled with Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
n, Serbian, and Slovenian militia members that had collaborated with the Germans, as well as ethnic German civilians from Celje and surrounding areas.
Independent Slovenia
Celje became part of independent Slovenia following theTen-Day War
The Ten-Day War ( sl, desetdnevna vojna), or the Slovenian War of Independence (), was a brief armed conflict that followed Slovenia's declaration of independence from Yugoslavia on 25 June 1991. It was fought between the separatists of the ...
in 1991. On 7 April 2006, Celje became the seat of a new Diocese of Celje
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Celje ( la, Dioecesis Celeiensis; sl, Škofija Celje) is a diocese located in the city of Celje in the Ecclesiastical province of Maribor in Slovenia.
History
* April 7, 2006: Established as Diocese of Celje from t ...
, created by Pope Benedict XVI
Pope Benedict XVI ( la, Benedictus XVI; it, Benedetto XVI; german: link=no, Benedikt XVI.; born Joseph Aloisius Ratzinger, , on 16 April 1927) is a retired prelate of the Catholic church who served as the head of the Church and the sovereign ...
within the Archdiocese of Maribor.
Sights
The town's tourist sights include a Grayfriars' monastery founded in 1241 and apalace
A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence, or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name palātium, for Palatine Hill in Rome which ...
from the 16th century.
The parish church, dating from the 14th century, with its beautiful Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
chapel, is an interesting specimen of medieval architecture. The so-called German church, in Romanesque style, belonged to the monastery, which was closed in 1808. The throne of the counts of Cilli is preserved here, and also the tombs of several members of the family.
Geography
Climate
Celje has a warm-summerhumid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
''Dfb'').
Symbols
coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central ele ...
of Celje are based on the coat of arms of the Counts of Celje
The Counts of Celje ( sl, Celjski grofje) or the Counts of Cilli (german: Grafen von Cilli; hu, cillei grófok) were the most influential late medieval noble dynasty on the territory of present-day Slovenia. Risen as vassals of the Habsburg dukes ...
.
The coat-of-arms of Celje was selected for the national arms immediately after World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
in 1918, when Slovenia together with Croatia and Serbia formed the original Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
(later Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, Југославија ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, Југославија ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, Югославия, translit=Juhoslavija ...
). A similar coat of arms was integrated into the Slovenian national arms in 1991.
Districts and local communities
The city of Celje is divided into 10 districts (''mestne četrti'') and the municipality 9 local communities (''krajevne skupnosti''): ''Districts'' *Center
Center or centre may refer to:
Mathematics
*Center (geometry), the middle of an object
* Center (algebra), used in various contexts
** Center (group theory)
** Center (ring theory)
* Graph center, the set of all vertices of minimum eccentrici ...
* Dečkovo Naselje
* Dolgo Polje
* Gaberje
* Hudinja
* Karel Destovnik Kajuh
Karel Destovnik, pen name and nom de guerre Kajuh (Slovene convention: ''Karel Destovnik – Kajuh'', 13 December 1922 – 22 February 1944) was a Slovenian poet, translator, resistance fighter, and Yugoslav people's hero.
Life and work
Ka ...
* Lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
* Nova Vas
* Savinja
The Savinja () is a river in northeast Slovenia which flows mostly in the Upper and Lower Savinja Valley ( sl, Zgornja in Spodnja Savinjska dolina) and through the cities of Celje and Laško. The Savinja is the main river of the Savinja Alps (Sl ...
* Slavko Šlander
Slavko Šlander, nom de guerre Aleš (20 June 1909 – 24 August 1941), was a Slovene communist, Partisan, and people's hero.
He was born in Dolenja Vas near Prebold, Duchy of Styria, Austria-Hungary (now part of Slovenia). Due to being e ...
''Local communities''
* Aljažev Hrib
* Ljubečna
Ljubečna () is a settlement in the City Municipality of Celje in eastern Slovenia. It is an urbanized settlement on the northeastern outskirts of Celje. The area is part of the traditional region of Lower Styria, Styria. It is now included with th ...
* Medlog
Medlog () is a settlement in the City Municipality of Celje in eastern Slovenia. It lies on the western outskirts of Celje. The grass runway of Celje Airport is located in the western part of the settlement. The area is part of the traditional reg ...
* Ostrožno
* Pod Gradom
* Škofja Vas
* Šmartno v Rožni Dolini
* Teharje
Teharje () is a settlement in the City Municipality of Celje in eastern Slovenia. It lies on the right bank of the Voglajna River on the eastern outskirts of Celje. The area is part of the traditional region of Styria. It is now included with t ...
* Trnovlje
Demographics
In 1991 the population consisted of: *Slovenians
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( sl, Slovenci ), are a South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia, and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovene as th ...
: 33,434 (82.1%)
* Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
: 1,864 (4.6%)
* Croats
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic, G ...
: 1,687 (4.1%)
* ethnic Muslims
Muslims ( Serbo-Croatian Latin and sl, Muslimani, Serbo-Croatian Cyrillic and mk, Муслимани) is a designation for a Serbo-Croatian speaking Muslims, inhabiting mostly the territory of the former Yugoslav republics. The term, adopted ...
: 466 (1.1%)
* Yugoslavs
Yugoslavs or Yugoslavians ( Bosnian and Croatian: ''Jugoslaveni'', Serbian and Macedonian ''Jugosloveni''/Југословени; sl, Jugoslovani) is an identity that was originally designed to refer to a united South Slavic people. It has b ...
: 405 (1%)
* Albanians
The Albanians (; sq, Shqiptarët ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Balkan Peninsula who share a common Albanian ancestry, culture, history and language. They primarily live in Albania, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Se ...
: 189
* Macedonians: 140
* Montenegrins
Montenegrins ( cnr, Црногорци, Crnogorci, or ; lit. "Black Mountain People") are a South Slavic ethnic group that share a common Montenegrin culture, history, and language, identified with the country of Montenegro.
Genetics
Accordi ...
: 93
* Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Urali ...
: 41
* Others: 82
* Unknown: 1,972 (4.8%)
* Undeclared: 249
* Regionally declared: 88
Town of Celje has 37,490 citizens as of 2002:
Municipality:
* Male: 22,744;
* Female: 24,816;
* Households: 18,410;
* Mean number of household members: 2.6;
* Apartments: 19,578;
* Buildings with apartments: 8,090.
The Celje annual municipal festival is held on April 11.
Education
Celje does not have its own university, although some college-level education has been established in the city. * The Faculty ofLogistics
Logistics is generally the detailed organization and implementation of a complex operation. In a general business sense, logistics manages the flow of goods between the point of origin and the point of consumption to meet the requirements of ...
, formally part of the University of Maribor
The University of Maribor ( sl, Univerza v Mariboru) is Slovenia's second-largest university, established in 1975 in Maribor, Slovenia. It currently has 17 faculties.
History
The university's roots reach back to 1859, when a theological semin ...
, was established in Celje in 2005.
* International School for Social and Business Studies
* Faculty of Commercial and Business Sciences
* UP Faculty of Management
Law and government
Mayor
The current mayor of Celje is Bojan Šrot.Vice mayors
The current mayors of Celje are Breda Arnšek and Vladimir Ljubek.Courts
In Celje there are three courts of general jurisdiction: * Celje Higher Court; * Celje District Court; * Celje Local Court. In addition to that there are also Celje Labour Court for resolving labour law disputes and an external department of Administrative Court for resolving disputes arising from administrative procedures.Communications
 Postal number: SI-3000 (from 1991). (Old one: 63000 (between 1945–1991)).
Postal number: SI-3000 (from 1991). (Old one: 63000 (between 1945–1991)).
Twin cities and friendship towns
Celje is twinned with *Grevenbroich
Grevenbroich () is a town in the Rhein-Kreis Neuss, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is situated on the river Erft, approximately 15 km southwest of Neuss and 15 km southeast of Mönchengladbach. Cologne and Düsseldorf are in a 30 ...
, Germany, since 1986
* Singen, Germany, since 1990
* Slavonski Brod
Slavonski Brod (), commonly shortened to simply Brod, is a city in eastern Croatia, near the border with Bosnia and Herzegovina. Being one of the principal cities in the historical regions of Slavonia and Posavina, Slavonski Brod was the 7th large ...
, Croatia, since 2010
* Doboj
Doboj ( sr-cyrl, Добој, ) is a city located in Republika Srpska, an entity of Bosnia and Herzegovina. It is situated on the banks of Bosna river, in the northern region of the Republika Srpska. As of 2013, it has a population of 71,441 ...
, Bosnia and Hercegovina, since 1965
* Pánd
Pánd is a village in Pest county, Hungary.
Location
Pánd is located between the towns of Káva and Tápióbicske along the minor road connecting Nagykáta and Monor. It is almost entirely located in the valleys of Őr Hill and Dobos Hill. ...
, Hungary, since 1998
Celje has friendship agreements with:
* Budva
Budva ( cnr, Будва, or ) is a Montenegrin town on the Adriatic Sea. It has 19,218 inhabitants, and it is the centre of Budva Municipality. The coastal area around Budva, called the Budva riviera, is the center of Montenegrin tourism, kn ...
, Montenegro
* Cherepovets, Russia
* Ćuprija
Ćuprija (Serbian Cyrillic: Ћуприја, ) is a town and municipality located in the Pomoravlje District of central Serbia. The population of the town is 19,380, while the municipality has 30,645 inhabitants.
History
The Romans founded the ...
, Serbia
* Graz
Graz (; sl, Gradec) is the capital city of the Austrian state of Styria and second-largest city in Austria after Vienna. As of 1 January 2021, it had a population of 331,562 (294,236 of whom had principal-residence status). In 2018, the popul ...
, Austria
* Spittal an der Drau
Spittal an der Drau is a town in the western part of the Austrian federal state of Carinthia. It is the administrative centre of Spittal an der Drau District, Austria's second largest district (''Bezirk'') by area.
Geography
The town is located o ...
, Austria
Notable residents and people born in Celje
*Anna of Celje
Anna of Cilli or Anne of Celje (1386 – 21 May 1416) was Queen of Poland (1402–1416). She was the second wife of Jogaila (Władysław II Jagiełło), King of Poland and Supreme Duke of Lithuania (reigned 1387–1434). Their marriage was po ...
(1381–1416), second wife of Jogaila, king of Poland and grand duke of Lithuania
* Lenore Aubert
Lenore Aubert (born Eleonore Maria Leisner, April 18, 1913The book ''Women in Horror Films, 1940s'' says that Aubert was born "on April 18, 1913 (although 1918 was given in publicity)." – July 31, 1993) was a model and Hollywood actress best ...
(1918–1993), Hollywood actress and model
* Barbara of Celje (1390/1395–1451), second wife of Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor
* (1915–2001), film actress
* Gregor Cankar
Gregor Cankar (born 25 January 1975 in Celje) is a Slovenian track and field athlete competing in long jump who won the bronze medal at the 1999 World Championships in Athletics. He finished sixth at the 1996 Summer Olympics
The 1996 Summer ...
(born 1975), athlete
* Jolanda Čeplak
Jolanda Batagelj (previously known as Jolanda Čeplak until 2002, born Jolanda Steblovnik on September 12, 1976) is a Slovenian middle distance athlete. She was born in Celje and lived in Velenje until briefly moving to Monaco. She ...
(born 1976), athlete
* Anica Černej
Anica Černej (3 April 1900, in Čadram, Oplotnica – 3 May 1944, in Neubrandenburg) was a Slovenes, Slovene author and poet.
Career
Černej worked at college of education in Ljubljana, where her main interests were social and pedagogical subjec ...
(1900–1944), poet, author, and schoolmistress
* Janez Drnovšek
Janez Drnovšek (; 17 May 1950 – 23 February 2008) was a Slovenian liberal politician, President of the Presidency of Yugoslavia (1989–1990), Prime Minister of Slovenia (1992–2002, with a short break in 2000) and President of Slovenia (2 ...
(1950–2008), politician, statesman, and third president of Slovenia
The president of Slovenia, officially the president of the Republic of Slovenia ( sl, Predsednik Republike Slovenije), is the head of state of the Republic of Slovenia. The position was established on 23 December 1991 when the National Assembly p ...
* Janez Drozg
Janez Drozg (April 4, 1933 – November 10, 2005) was a Slovene television and film director from Celje. Alongside his work with TV Ljubljana which dominated much of his career, he also directed features films such as ''Boj na požiralniku'' i ...
(1933–2005), television director
* Dejan Glavnik (born 1975), Slovenian extreme cyclist
* (born 1964), singer
* Bojan Gorišek (born 1962), pianist
* Hermann II of Celje (1365–1435), Count of Celje, Ortenburg and Seger
* Andrej Hieng
Andrej Hieng (17 February 1925 – 17 January 2000) was a Slovene language, Slovene writer, playwright and theatre director.
Hieng was born in Ljubljana in 1925. He studied at the Academy for Theatre, Radio, Film and Television, Academy of ...
(1925–2000), writer, playwright, screenwriter and dramaturgist
* (1943–2015), critic, essayist, theatrologist and dramaturgist
* Romana Jordan Cizelj
Romana Jordan (born 8 January 1966) is a Slovenian politician and physicist, currently serving as Member of the European Parliament (MEP). She is a member of the Slovenian Democratic Party, which is part of the European People's Party, and sits ...
(born 1966), physicist and politician
* Boban Jović
Boban Jović (born 25 June 1991) is a retired Slovenian footballer who played as a defender.
Club career
Jović started playing football at his local club Šampion, but moved to Aluminij in his teens. Even though he was playing in Slovenian ...
(born 1991), footballer
* Jelko Kacin
Jelko Kacin (born 26 November 1955) is a Slovenian politician.
During the Slovenian Independence War, he was the Secretary of Information of Slovenia. He founded the Slovenian Press Agency on 3 June 1991 and the war (also called the Ten-Day War ...
(born 1955), politician
* Alma Karlin (1889–1950), traveller, author, poet, and collector
* Margareta of Celje
Margaret of Celje (german: Margareta, pl, Małgorzata; 1411 – 22 July 1480) was a noblewoman member of the Slovenian House of Celje and by marriage Duchess of both half Głogów and Ścinawa.
She was the only child of Herman III, Count of Celj ...
(1411–1480), noblewoman member of the House of Celje, duchess of Głogów
Głogów (; german: Glogau, links=no, rarely , cs, Hlohov, szl, Głogōw) is a city in western Poland. It is the county seat of Głogów County, in Lower Silesian Voivodeship (since 1999), and was previously in Legnica Voivodeship (1975–199 ...
and Ścinawa
Ścinawa (german: Steinau an der Oder, links=no) is a town and municipality on the Oder river in the Lower Silesian region of Poland. The Ścinawa train station is a key gateway for travel throughout the region, connecting major destinations su ...
.
* Margit Korondi (born 1932), gymnast, Olympic champion
* (1937–2012), geophysicist and seismologist*
Janez Lapajne
Janez Lapajne (; born 24 June 1967 in Celje, Slovenia, grew up in Ljubljana, Slovenia is a Slovenian film director, producer, writer, editor and production designer.
The son of geophysicist , he graduated in film directing from the University o ...
(born 1967), film director
* Marianne Elisabeth Lloyd-Dolbey
Datin Marianne Elisabeth Lloyd-Dolbey (18 October 1919, in Drešinja Vas, Kingdom of Yugoslavia – 10 October 1994, in Celje, Slovenia) was a personal secretary to Sultan of Brunei Omar Ali Saifuddien III.
Early life and education
Mari ...
(1919-1994), personal secretary to the Brunei sultan Omar Ali Saifuddien III
Sultan Sir Omar Ali Saifuddien Sa'adul Khairi Waddien ( Jawi: ; 23 September 1914 – 7 September 1986) was the 28th Sultan of Brunei, reigning from 4 June 1950 until his abdication from the throne on 5 October 1967.
He was also Brunei's fir ...
* Janko Orožen
Janko Orožen (; 10 December 1891 – 30 September 1989)Šlebinger, Janko. 1935. "Orožen Janko." ''Slovenski biografski leksikon'', vol. 6: Mrkun–Peterlin. Ljubljana: Zadružna gospodarska banka. was a Slovene historian and schoolteacher.
Li ...
(1891–1989), historian, honorary citizen
* Oto Pestner
Oto Pestner (born January 4, 1956 in Celje) is a politician and one of the most prominent singers and composers of popular music from Slovenia. Until 2008, he was the leader of the Slovene vocal group New Swing Quartet.
From 1986 to 1991 and in 1 ...
(born 1956), musician and singer
* Milan Pogačnik
Milan Pogačnik (born 30 August 1946) is a Slovenian politician. Between November 2008 and March 2010, he served as the Minister of Agriculture, Forestry and Nutrition of Slovenia.
Biography
Pogačnik was born in Celje, then part of the People's ...
(born 1946), politician
* Lucija Polavder
Lucija Polavder (born 15 December 1984 in Celje)Factfile of Lucija Polavder
on Judo ...
(born 1984), judoka
* (1914–1947), worker, victim of the communist regime
* Fran Roš (1898–1976), writer, poet, playwright, honorary citizen
* on Judo ...
Johann Gabriel Seidl
Johann Gabriel Seidl (21 June 1804 – 18 July 1875)
was an Austrian archeologist, poet, storyteller and dramatist. He wrote the lyrics to "Gott erhalte, Gott beschütze unsern Kaiser, unser Land!" This was the 1854 version of the Austrian ...
(1804–1875), archeologist, poet, storyteller and dramatist
* Bina Štampe Žmavc (born 1952), poet and author
* Tina Trstenjak (born 1990), judoka, Olympic champion
* Beno Udrih
Beno Udrih (born July 5, 1982) is a Slovenian former professional basketball player who serves as a player development coach for the New Orleans Pelicans. He previously played in the NBA for the San Antonio Spurs, Sacramento Kings, Milwaukee Buck ...
(born 1982), basketball player
* Bogumil Vošnjak
Bogumil Vošnjak, also known as Bogomil Vošnjak (9 September 1882 – 18 June 1955), was a Slovene and Yugoslav jurist, politician, diplomat, author, and legal historian. He often wrote under the pseudonym Illyricus.
Biography
He was bor ...
(1882–1955), scholar, politician, diplomat
* Urška Žolnir
Urška Žolnir (born 9 October 1981) is a Slovenian retired judoka and a politician. She's a member of Judo Club Sankaku Celje.
She won the bronze medal in the half-middleweight (–63 kg) division at the 2004 Summer Olympics and gold me ...
(born 1981), judoka, Olympic champion
Gallery
cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denomination ...
in the background
File:Postcard of Celje (58).jpg, An old postcard of the railway station in front, Celje Hall on the right, and the Iron Court (''Železni dvor'', ''Eisenhof'') on the far left
File:SLO-Celje23.JPG, The National Hall
National Hall is a former venue in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, located at 1222–24 Market Street, between Twelfth and Thirteenth Streets. It was one of the most popular venues in the city, site of concerts, lectures, meetings, and political spee ...
(''Narodni dom''), today the town hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
, (Jan Vladimír Hráský
Jan Vladimír Hráský (1857–1939) was a Czech architect, builder, engineer, and hydrologist.
Hrásky is known in Slovenia as an original author of building in Neo-Renaissance style of Carniolan Provincial Manor in Ljubljana (1899–1902), w ...
, 1895–1896)
File:Celje Celjski dom 001.jpg, The Celje Hall (''Celjski dom''), (Peter Paul Brang
Peter Paul Brang (1852–1925) was a Viennese architect who worked in what are today the Czech Republic and Slovenia, as well as in Bulgaria and Romania.
Some of his works include the City Baths in Liberec (1901–1902) and Ústí nad Labem (1905 ...
, 1905–1906)
File:SLO-Celje19.JPG, The Celje Water Tower, part of the town walls, built after 1451
File:Celjski grad.JPG, Upper Celje Castle, viewed from the banks of the Savinja
The Savinja () is a river in northeast Slovenia which flows mostly in the Upper and Lower Savinja Valley ( sl, Zgornja in Spodnja Savinjska dolina) and through the cities of Celje and Laško. The Savinja is the main river of the Savinja Alps (Sl ...
River in Pečovnik toward the northeast
File:View over Celje from the Old town.JPG, View over Celje from Old town castle
References
External links
*Celje on Geopedia
* *
CeljeCafe.com unofficial website
{{Authority control Cities and towns in Styria (Slovenia) Populated places in the City Municipality of Celje Noricum