CMB Cold Spot on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
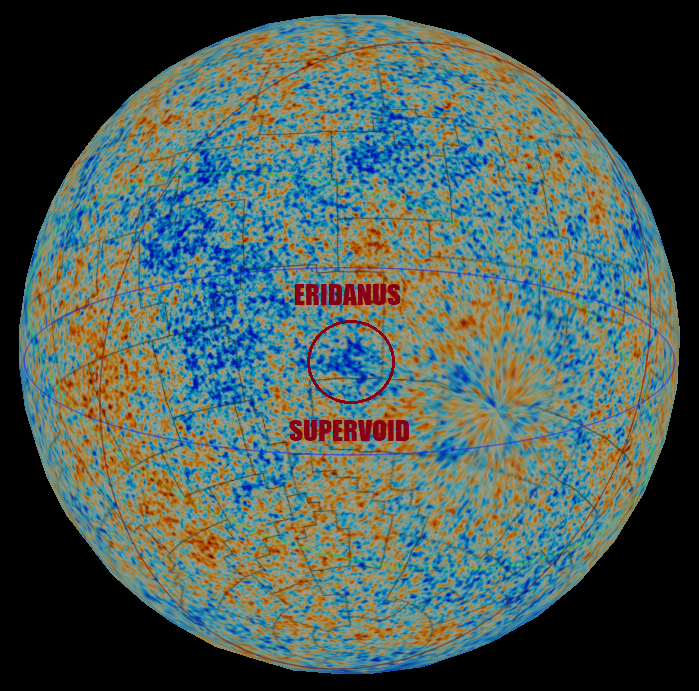 The CMB Cold Spot or WMAP Cold Spot is a region of the sky seen in
The CMB Cold Spot or WMAP Cold Spot is a region of the sky seen in
 In the first year of data recorded by the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), a region of sky in the constellation Eridanus was found to be cooler than the surrounding area. Subsequently, using the data gathered by WMAP over 3 years, the statistical significance of such a large, cool region was estimated. The probability of finding a deviation at least as high in
In the first year of data recorded by the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), a region of sky in the constellation Eridanus was found to be cooler than the surrounding area. Subsequently, using the data gathered by WMAP over 3 years, the statistical significance of such a large, cool region was estimated. The probability of finding a deviation at least as high in
 One possible explanation of the cold spot is a huge
One possible explanation of the cold spot is a huge
Great Void in Eridanus, (WMAP Cold Spot)
Daily Tech
Gaping "Hole" in the Sky Found, Experts Say
BBC News: Great 'cosmic nothingness' found
 The CMB Cold Spot or WMAP Cold Spot is a region of the sky seen in
The CMB Cold Spot or WMAP Cold Spot is a region of the sky seen in microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ran ...
s that has been found to be unusually large and cold relative to the expected properties of the cosmic microwave background radiation
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all space ...
(CMBR). The "Cold Spot" is approximately 70 µK (0.00007 K) colder than the average CMB temperature (approximately 2.7 K), whereas the root mean square
In mathematics and its applications, the root mean square of a set of numbers x_i (abbreviated as RMS, or rms and denoted in formulas as either x_\mathrm or \mathrm_x) is defined as the square root of the mean square (the arithmetic mean of the ...
of typical temperature variations is only 18 µK.After the dipole
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways:
*An electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple example of this system i ...
anisotropy, which is due to the Doppler shift
The Doppler effect or Doppler shift (or simply Doppler, when in context) is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who d ...
of the microwave background radiation due to our peculiar velocity
Peculiar motion or peculiar velocity refers to the velocity of an object relative to a ''rest frame'' — usually a frame in which the average velocity of some objects is zero.
Galactic astronomy
In galactic astronomy, peculiar motion refers to ...
relative to the comoving cosmic rest frame, has been subtracted out. This feature is consistent with the Earth moving at some 627 km/s towards the constellation Virgo
Virgo may refer to:
*Virgo (astrology), the sixth astrological sign of the zodiac
*Virgo (constellation), a constellation
*Virgo Cluster, a cluster of galaxies in the constellation Virgo
*Virgo Stellar Stream, remains of a dwarf galaxy
*Virgo Supe ...
. At some points, the "cold spot" is 140 µK colder than the average CMB temperature.
The radius of the "cold spot" subtends about 5°; it is centered at the galactic coordinate , (equatorial Equatorial may refer to something related to:
*Earth's equator
**the tropics, the Earth's equatorial region
**tropical climate
*the Celestial equator
** equatorial orbit
**equatorial coordinate system
** equatorial mount, of telescopes
* equatorial ...
: ''α'' = , ''δ'' = ). It is, therefore, in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere
The southern celestial hemisphere, also called the Southern Sky, is the southern half of the celestial sphere; that is, it lies south of the celestial equator. This arbitrary sphere, on which seemingly fixed stars form constellations, appears ...
, in the direction of the constellation Eridanus.
Typically, the largest fluctuations of the primordial CMB temperature occur on angular scales of about 1°. Thus a cold region as large as the "cold spot" appears very unlikely, given generally accepted theoretical models. Various alternative explanations exist, including a so-called Eridanus Supervoid or Great Void that may exist between us and the primordial CMB (foreground voids can cause cold spots against the CMB background). Such a void
Void may refer to:
Science, engineering, and technology
* Void (astronomy), the spaces between galaxy filaments that contain no galaxies
* Void (composites), a pore that remains unoccupied in a composite material
* Void, synonym for vacuum, a ...
would affect the observed CMB via the integrated Sachs–Wolfe effect, and would be one of the largest structures in the observable universe
The observable universe is a ball-shaped region of the universe comprising all matter that can be observed from Earth or its space-based telescopes and exploratory probes at the present time, because the electromagnetic radiation from these obj ...
. This would be an extremely large region of the universe, roughly 150 to 300 Mpc or 500 million to one billion light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
s across and 6 to 10 billion light years away, at redshift , containing a density of matter much smaller than the average density at that redshift.
Discovery and significance
 In the first year of data recorded by the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), a region of sky in the constellation Eridanus was found to be cooler than the surrounding area. Subsequently, using the data gathered by WMAP over 3 years, the statistical significance of such a large, cool region was estimated. The probability of finding a deviation at least as high in
In the first year of data recorded by the Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), a region of sky in the constellation Eridanus was found to be cooler than the surrounding area. Subsequently, using the data gathered by WMAP over 3 years, the statistical significance of such a large, cool region was estimated. The probability of finding a deviation at least as high in Gaussian
Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855) is the eponym of all of the topics listed below.
There are over 100 topics all named after this German mathematician and scientist, all in the fields of mathematics, physics, and astronomy. The English eponymo ...
simulations was found to be 1.85%. Thus it appears unlikely, but not impossible, that the cold spot was generated by the standard mechanism of quantum fluctuation
In quantum physics, a quantum fluctuation (also known as a vacuum state fluctuation or vacuum fluctuation) is the temporary random change in the amount of energy in a point in space, as prescribed by Werner Heisenberg's uncertainty principle. ...
s during cosmological inflation
In physical cosmology, cosmic inflation, cosmological inflation, or just inflation, is a theory of exponential expansion of space in the early universe. The inflationary epoch lasted from seconds after the conjectured Big Bang singularit ...
, which in most inflationary models gives rise to Gaussian statistics. The cold spot may also, as suggested in the references above, be a signal of non-Gaussian primordial fluctuations.
Some authors called into question the statistical significance of this cold spot.
In 2013, the CMB Cold Spot was also observed by the Planck
Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck (, ; 23 April 1858 – 4 October 1947) was a German theoretical physicist whose discovery of energy quanta won him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918.
Planck made many substantial contributions to theoretical p ...
satellite at similar significance, discarding the possibility of being caused by a systematic error
Observational error (or measurement error) is the difference between a measured value of a quantity and its true value.Dodge, Y. (2003) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', OUP. In statistics, an error is not necessarily a " mistak ...
of the WMAP satellite.
Possible causes other than primordial temperature fluctuation
The large 'cold spot' forms part of what has been called an 'axis of evil
The phrase "axis of evil" was first used by U.S. President George W. Bush and originally referred to Iran, Iraq, and North Korea. It was used in Bush's State of the Union address on January 29, 2002, less than five months after the 9/11 attac ...
' (so-called because it was unexpected to see a structure like this).
Supervoid
 One possible explanation of the cold spot is a huge
One possible explanation of the cold spot is a huge void
Void may refer to:
Science, engineering, and technology
* Void (astronomy), the spaces between galaxy filaments that contain no galaxies
* Void (composites), a pore that remains unoccupied in a composite material
* Void, synonym for vacuum, a ...
between us and the primordial CMB. A region cooler than surrounding sightlines can be observed if a large void is present, as such a void would cause an increased cancellation between the "late-time" integrated Sachs–Wolfe effect
The Sachs–Wolfe effect, named after Rainer K. Sachs and Arthur M. Wolfe, is a property of the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB), in which photons from the CMB are Gravitational redshift, gravitationally redshifted, causing the CMB spec ...
and the "ordinary" Sachs–Wolfe effect. This effect would be much smaller if dark energy
In physical cosmology and astronomy, dark energy is an unknown form of energy that affects the universe on the largest scales. The first observational evidence for its existence came from measurements of supernovas, which showed that the univer ...
were not stretching the void as photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always ...
s went through it.
*
''Rudnick et al''. found a dip in NVSS galaxy number counts in the direction of the Cold Spot, suggesting the presence of a large void. Since then, some additional works have cast doubt on the "supervoid" explanation. The correlation between the NVSS dip and the Cold Spot was found to be marginal using a more conservative statistical analysis. Also, a direct survey for galaxies in several one-degree-square fields within the Cold Spot found no evidence for a supervoid. However, the supervoid explanation has not been ruled out entirely; it remains intriguing, since supervoids do seem capable of affecting the CMB measurably.
A 2015 study shows the presence of a supervoid that has a diameter of 1.8 billion light year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
s and is centered at 3 billion light-years from our galaxy
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. ...
in the direction of the Cold Spot, likely being associated with it. This would make it the largest void detected, and one of the largest structures known.A claim by Szapudi ''et al'' states that the newly found void is the "largest structure ever identified by humanity". However, another source reports that the largest structure is the supercluster
A supercluster is a large group of smaller galaxy clusters or galaxy groups; they are among the largest known structures in the universe. The Milky Way is part of the Local Group galaxy group (which contains more than 54 galaxies), which in turn ...
corresponding to the NQ2-NQ4 GRB overdensity at 10 billion light years. Later measurements of the Sachs–Wolfe effect
The Sachs–Wolfe effect, named after Rainer K. Sachs and Arthur M. Wolfe, is a property of the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB), in which photons from the CMB are Gravitational redshift, gravitationally redshifted, causing the CMB spec ...
show too its likely existence.
Although large voids are known in the universe, a void would have to be exceptionally vast to explain the cold spot, perhaps 1,000 times larger in volume than expected typical voids. It would be 6 billion–10 billion light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 1012 ...
s away and nearly one billion light-years across, and would be perhaps even more improbable to occur in the large-scale structure than the WMAP cold spot would be in the primordial CMB.
A 2017 study reported surveys showing no evidence that associated voids in the line of sight could have caused the CMB Cold Spot and concluded that it may instead have a primordial origin.
One important thing to confirm or rule out the late time integrated Sachs–Wolfe effect is the mass profile of galaxies in the area as ISW effect is affected by the galaxy bias which depends on the mass profiles and types of galaxies.
In December 2021, the Dark Energy Survey
The Dark Energy Survey (DES) is an astronomical survey designed to constrain the properties of dark energy. It uses images taken in the near-ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared to measure the expansion of the universe using Type Ia supernov ...
(DES), analyzing their data, put forward more evidence for the correlation between the Eridanus supervoid and the CMB cold spot.
Cosmic texture
In late 2007, (''Cruz et al.'') argued that the Cold Spot could be due to a cosmic texture, a remnant of aphase transition
In chemistry, thermodynamics, and other related fields, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states of ...
in the early Universe.
Parallel universe
A controversial claim byLaura Mersini-Houghton
Laura Mersini-Houghton (''née'' Mersini) is an Albanian-American cosmologist and theoretical physicist, and professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. She is a proponent of the multiverse hypothesis and the author of a theor ...
is that it could be the imprint of another universe beyond our own, caused by quantum entanglement
Quantum entanglement is the phenomenon that occurs when a group of particles are generated, interact, or share spatial proximity in a way such that the quantum state of each particle of the group cannot be described independently of the state of ...
between universes before they were separated by cosmic inflation
In physical cosmology, cosmic inflation, cosmological inflation, or just inflation, is a theory of exponential expansion of space in the early universe. The inflationary epoch lasted from seconds after the conjectured Big Bang singularity ...
. Laura Mersini-Houghton said, "Standard cosmology cannot explain such a giant cosmic hole" and made the hypothesis that the WMAP cold spot is "… the unmistakable imprint of another universe beyond the edge of our own." If true, this provides the first empirical evidence
Empirical evidence for a proposition is evidence, i.e. what supports or counters this proposition, that is constituted by or accessible to sense experience or experimental procedure. Empirical evidence is of central importance to the sciences and ...
for a parallel universe (though theoretical models of parallel universes existed previously). It would also support string theory
In physics, string theory is a theoretical framework in which the point-like particles of particle physics are replaced by one-dimensional objects called strings. String theory describes how these strings propagate through space and interac ...
. The team claims that there are testable
Testability is a primary aspect of Science and the Scientific Method and is a property applying to an empirical hypothesis, involves two components:
#Falsifiability or defeasibility, which means that counterexamples to the hypothesis are logicall ...
consequences for its theory. If the parallel-universe theory is true, there will be a similar void in the Celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
's opposite hemisphere (which ''New Scientist'' reported to be in the Southern celestial hemisphere; the results of the New Mexico array study reported it as being in the Northern).
Other researchers have modeled the cold spot as potentially the result of cosmological bubble collisions, again before inflation.
A sophisticated computational analysis (using Kolmogorov complexity
In algorithmic information theory (a subfield of computer science and mathematics), the Kolmogorov complexity of an object, such as a piece of text, is the length of a shortest computer program (in a predetermined programming language) that produ ...
) has derived evidence for a north and a south cold spot in the satellite data: "...among the high randomness regions is the southern non-Gaussian anomaly, the Cold Spot, with a stratification expected for the voids. Existence of its counterpart, a Northern Cold Spot with almost identical randomness properties among other low-temperature regions is revealed."
These predictions and others were made prior to the measurements (see Laura Mersini). However, apart from the Southern Cold Spot, the varied statistical methods in general fail to confirm each other regarding a Northern Cold Spot. The 'K-map' used to detect the Northern Cold Spot was noted to have twice the measure of randomness measured in the standard model. The difference is speculated to be caused by the randomness introduced by voids (unaccounted-for voids were speculated to be the reason for the increased randomness above the standard model).
Sensitivity to finding method
The cold spot is mainly anomalous because it stands out compared to the relatively hot ring around it; it is not unusual if one only considers the size and coldness of the spot itself. More technically, its detection and significance depends on using a compensatedfilter
Filter, filtering or filters may refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Filter (software), a computer program to process a data stream
* Filter (video), a software component tha ...
like a Mexican hat wavelet
In mathematics and numerical analysis, the Ricker wavelet
:\psi(t) = \frac \left(1 - \left(\frac\right)^2 \right) e^
is the negative normalizing constant, normalized second derivative of a Gaussian function, i.e., up to scale and normalization, t ...
to find it.
See also
* CfA2 Great Wall *Cosmic microwave background
In Big Bang cosmology the cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation that is a remnant from an early stage of the universe, also known as "relic radiation". The CMB is faint cosmic background radiation filling all spac ...
* Dark flow
In astrophysics, dark flow is a theoretical non-random component of the peculiar velocity of galaxy clusters. The actual measured velocity is the sum of the velocity predicted by Hubble's Law plus a possible small and unexplained (or ''dark'') ...
* Great Attractor
The Great Attractor is a gravitational anomaly in intergalactic space and the apparent central gravitational point of the Laniakea Supercluster. The observed anomalies suggest a localized concentration of mass millions of times more massive than ...
* List of largest voids
* Sloan Great Wall
The Sloan Great Wall (SGW) is a cosmic structure formed by a giant wall of galaxies (a galaxy filament). Its discovery was announced from Princeton University on October 20, 2003, by J. Richard Gott III, Mario Jurić, and their colleagues, b ...
* South Pole Wall
The South Pole Wall (SPW or The South Pole Wall) is a massive cosmic structure formed by a giant wall of galaxies (a galaxy filament) that extends across at least 1.37 billion light-years of space, the nearest light (and consequently part) of w ...
* Void (astronomy)
Cosmic voids (also known as dark space) are vast spaces between filaments (the largest-scale structures in the universe), which contain very few or no galaxies. The cosmological evolution of the void regions differs drastically from the evolut ...
* Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe
Notes
References
External links
Great Void in Eridanus, (WMAP Cold Spot)
Daily Tech
Space.com
Space.com is an online publication focused on space exploration, astronomy, skywatching and entertainment, with editorial teams based in the United States and United Kingdom. The website offers live coverage of space missions, astronomical discov ...
, 2007-08-23
Gaping "Hole" in the Sky Found, Experts Say
National Geographic News
The National Geographic Society (NGS), headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States, is one of the largest non-profit scientific and educational organizations in the world.
Founded in 1888, its interests include geography, archaeology, and ...
BBC News: Great 'cosmic nothingness' found
BBC News
BBC News is an operational business division of the British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) responsible for the gathering and broadcasting of news and current affairs in the UK and around the world. The department is the world's largest broadca ...
, 2007-08-24
{{Portal bar, Astronomy, Stars, Spaceflight, Outer space, Solar System
Voids (astronomy)
Eridanus (constellation)
Cosmic background radiation
Astronomical objects discovered in 2001