Cyprus Post on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cyprus ; tr, Kıbrıs (), officially the Republic of Cyprus,, , lit: Republic of Cyprus is an
 The earliest attested reference to ''Cyprus'' is the 15th century BC
The earliest attested reference to ''Cyprus'' is the 15th century BC

 Cyprus is at a strategic location in the Middle East. It was ruled by the
Cyprus is at a strategic location in the Middle East. It was ruled by the
/ref> The Kingdoms of Cyprus enjoyed special privileges and a semi-autonomous status, but they were still considered vassal subjects of the Great King. The island was conquered by

 When the
When the
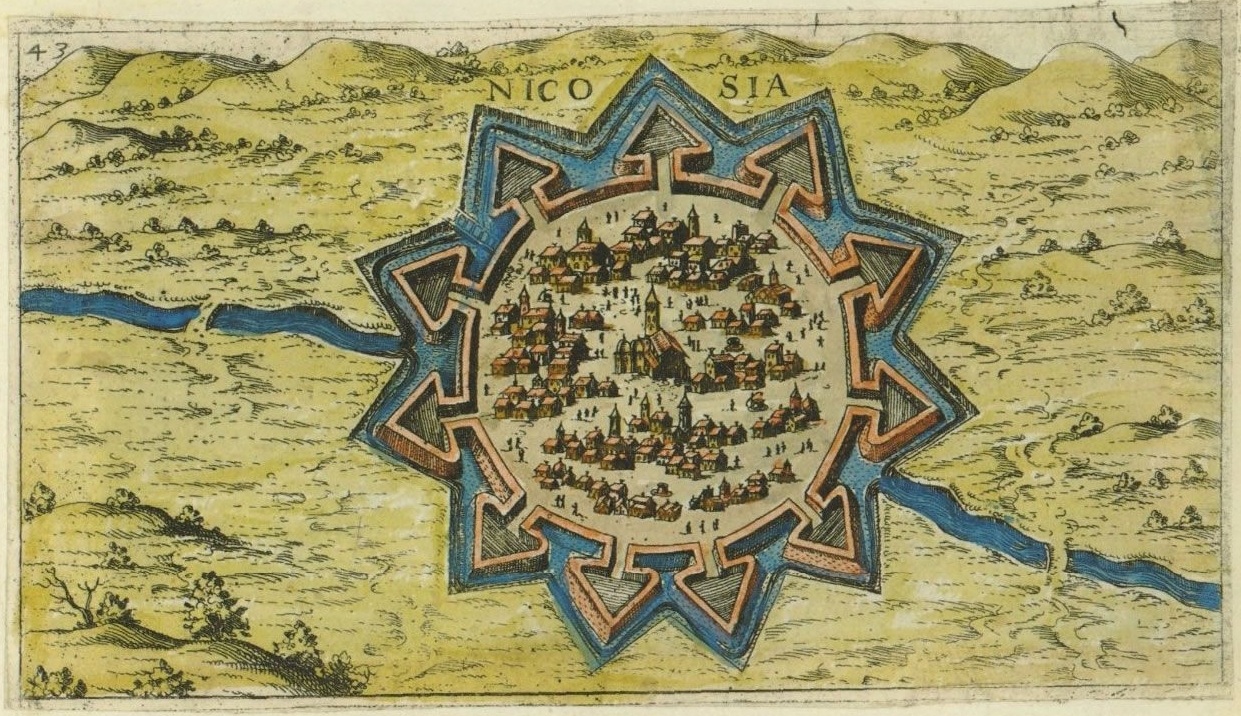
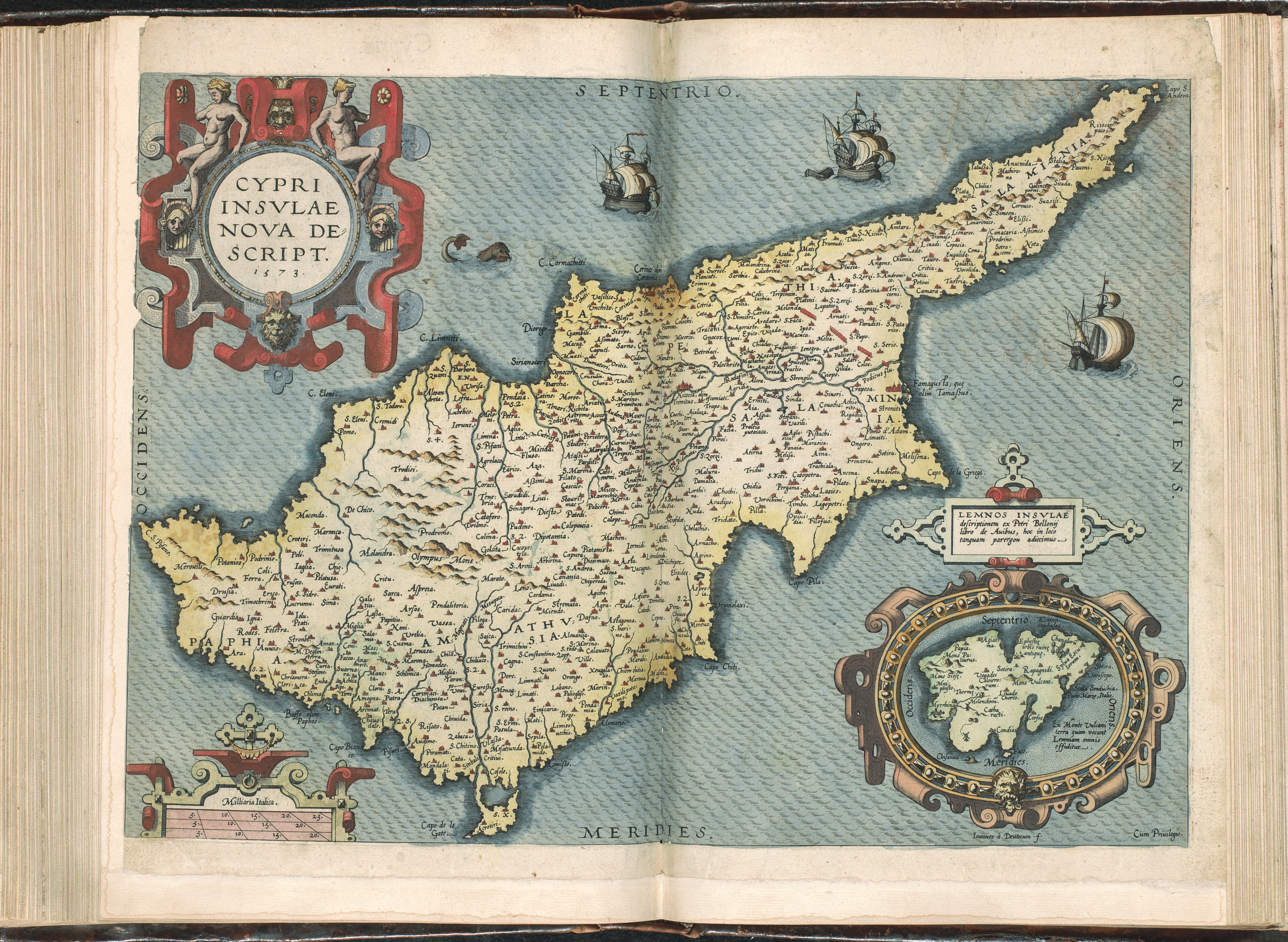 In 1570, a full-scale Ottoman assault with 60,000 troops brought the island under Ottoman control, despite stiff resistance by the inhabitants of Nicosia and Famagusta. Ottoman forces capturing Cyprus
In 1570, a full-scale Ottoman assault with 60,000 troops brought the island under Ottoman control, despite stiff resistance by the inhabitants of Nicosia and Famagusta. Ottoman forces capturing Cyprus  The Ottomans abolished the
The Ottomans abolished the
, ''U.S. Library of Congress'' The ratio of Muslims to Christians fluctuated throughout the period of Ottoman domination. In 1777–78, 47,000 Muslims constituted a majority over the island's 37,000 Christians. By 1872, the population of the island had risen to 144,000, comprising 44,000 Muslims and 100,000 Christians. The Muslim population included numerous crypto-Christians, including the Linobambaki, a crypto-Catholic community that arose due to religious persecution of the Catholic community by the Ottoman authorities; this community would assimilate into the Turkish Cypriot community during British rule. As soon as the
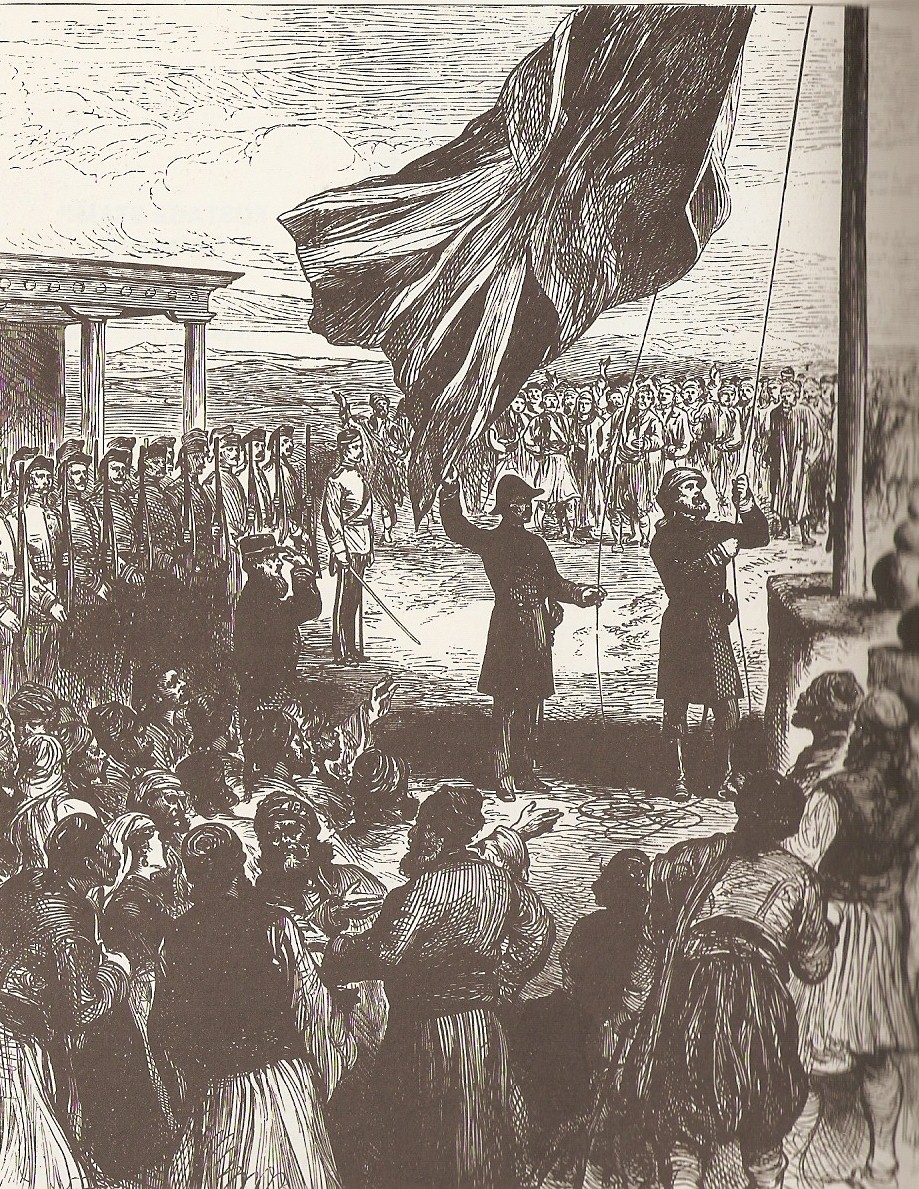 In the aftermath of the
In the aftermath of the  The island would serve Britain as a key military base for its colonial routes. By 1906, when the Famagusta harbour was completed, Cyprus was a strategic naval outpost overlooking the
The island would serve Britain as a key military base for its colonial routes. By 1906, when the Famagusta harbour was completed, Cyprus was a strategic naval outpost overlooking the  Initially, the Turkish Cypriots favoured the continuation of the British rule. However, they were alarmed by the Greek Cypriot calls for ''enosis'', as they saw the union of
Initially, the Turkish Cypriots favoured the continuation of the British rule. However, they were alarmed by the Greek Cypriot calls for ''enosis'', as they saw the union of
 On 16 August 1960, Cyprus attained independence after the
On 16 August 1960, Cyprus attained independence after the
, Library of Congress, Washington, DC, 1991. The UK retained the two
, Library of Congress, Washington, DC, 1991. Tensions were heightened when Cypriot President Archbishop Makarios III called for constitutional changes, which were rejected by Turkey and opposed by Turkish Cypriots. Intercommunal violence erupted on 21 December 1963, when two Turkish Cypriots were killed at an incident involving the Greek Cypriot police. The violence resulted in the death of 364 Turkish and 174 Greek Cypriots,Oberling, Pierre. ''The road to Bellapais'' (1982), Social Science Monographs
p. 120
"According to official records, 364 Turkish Cypriots and 174 Greek Cypriots were killed during the 1963–1964 crisis." destruction of 109 Turkish Cypriot or mixed villages and displacement of 25,000–30,000 Turkish Cypriots. The crisis resulted in the end of the Turkish Cypriot involvement in the administration and their claiming that it had lost its legitimacy; the nature of this event is still controversial. In some areas, Greek Cypriots prevented Turkish Cypriots from travelling and entering government buildings, while some Turkish Cypriots willingly withdrew due to the calls of the Turkish Cypriot administration. Turkish Cypriots started living in
(click on Historical review) The crisis of 1963–64 brought further intercommunal violence between the two communities, displaced more than 25,000 Turkish Cypriots into
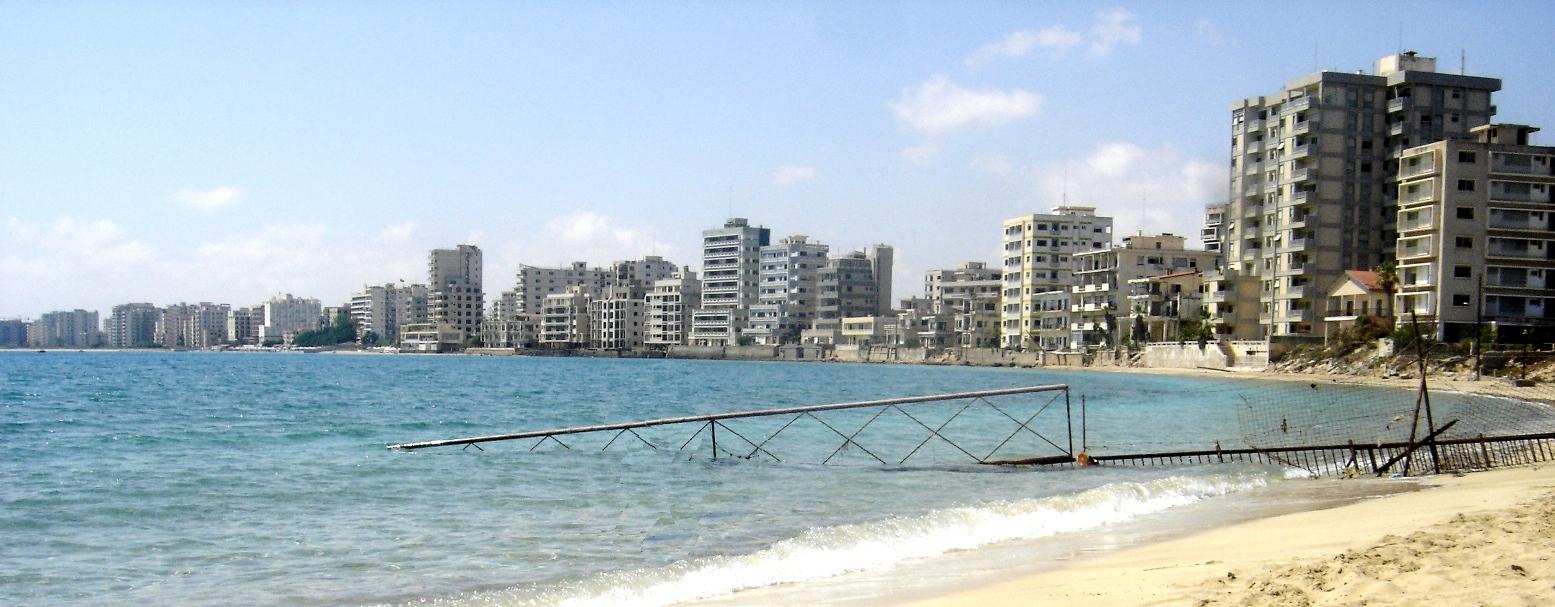 On 15 July 1974, the
On 15 July 1974, the
 After the restoration of constitutional order and the return of Archbishop Makarios III to Cyprus in December 1974, Turkish troops remained, occupying the northeastern portion of the island. In 1983, the Turkish Cypriot parliament, led by the Turkish Cypriot leader
After the restoration of constitutional order and the return of Archbishop Makarios III to Cyprus in December 1974, Turkish troops remained, occupying the northeastern portion of the island. In 1983, the Turkish Cypriot parliament, led by the Turkish Cypriot leader

 Cyprus is the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after the Italian islands of
Cyprus is the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after the Italian islands of
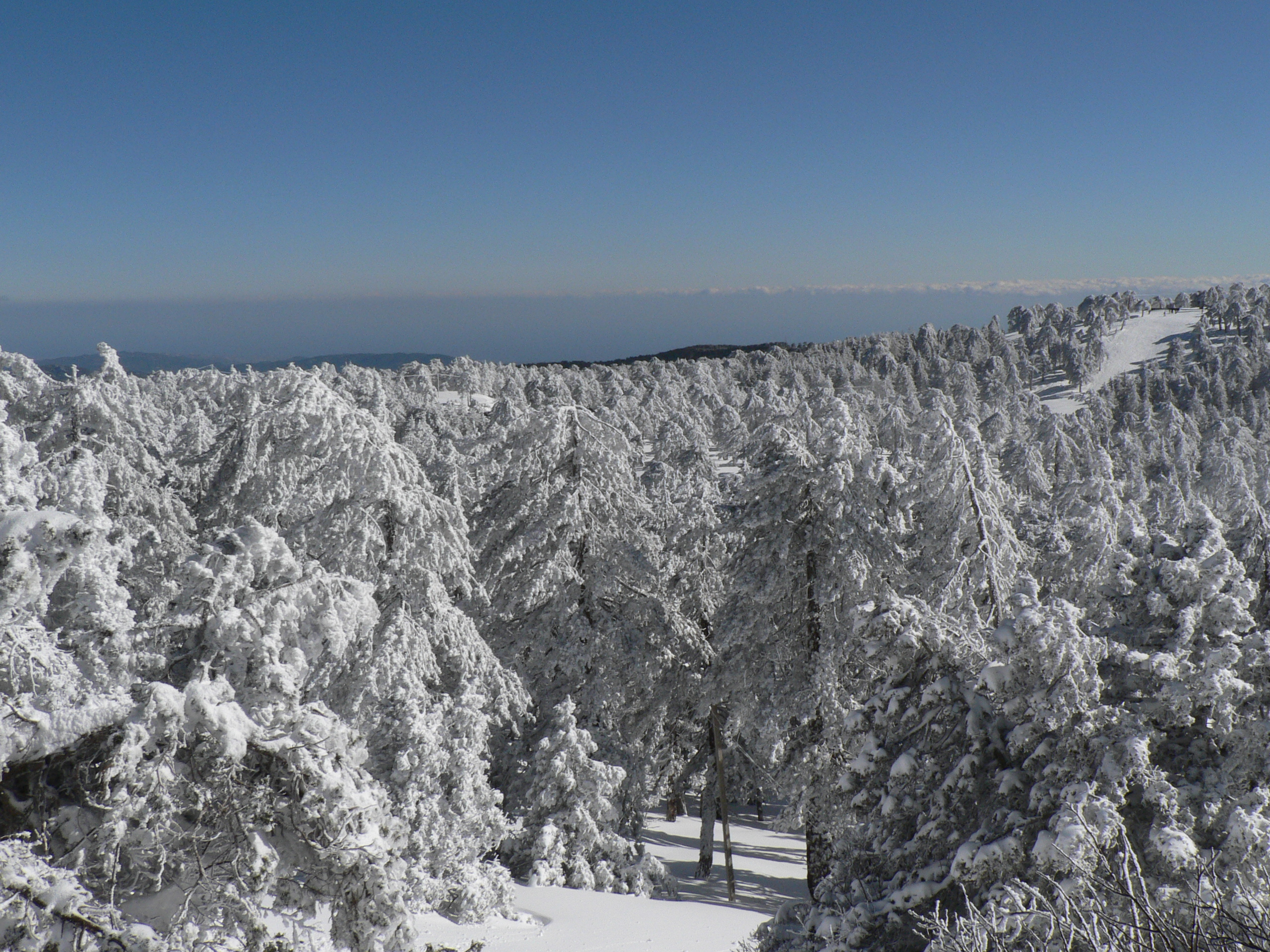 Cyprus has a Subtropics, subtropical climate – Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean and Semi-arid climate, semi-arid type (in the north-eastern part of the island) – Köppen climate classifications ''Csa'' and ''BSh'', with very mild winters (on the coast) and warm to hot summers. Snow is possible only in the Troodos Mountains in the central part of island. Rain occurs mainly in winter, with summer being generally dry.
Cyprus has one of the warmest climates in the Mediterranean part of the European Union. The average annual temperature on the coast is around during the day and at night. Generally, summers last about eight months, beginning in April with average temperatures of during the day and at night, and ending in November with average temperatures of during the day and at night, although in the remaining four months temperatures sometimes exceed .
Among all cities in the Mediterranean part of the European Union, Limassol has one of the warmest winters, in the period January – February average temperature is during the day and at night, in other coastal locations in Cyprus is generally during the day and at night. During March, Limassol has average temperatures of during the day and at night, in other coastal locations in Cyprus is generally during the day and at night.
The middle of summer is hot – in July and August on the coast the average temperature is usually around during the day and around at night (inland, in the highlands average temperature exceeds ) while in the June and September on the coast the average temperature is usually around during the day and around at night in Limassol, while is usually around during the day and around at night in Paphos. Large fluctuations in temperature are rare. Inland temperatures are more extreme, with colder winters and hotter summers compared with the coast of the island.
Average annual temperature of sea is , from in February to in August (depending on the location). In total 7 months – from May to November – the average sea temperature exceeds .
Sunshine hours on the coast are around 3,200 per year, from an average of 5–6 hours of sunshine per day in December to an average of 12–13 hours in July. This is about double that of cities in the northern half of Europe; for comparison, London receives about 1,540 per year. In December, London receives about 50 hours of sunshine while coastal locations in Cyprus about 180 hours (almost as much as in May in London).
Cyprus has a Subtropics, subtropical climate – Mediterranean climate, Mediterranean and Semi-arid climate, semi-arid type (in the north-eastern part of the island) – Köppen climate classifications ''Csa'' and ''BSh'', with very mild winters (on the coast) and warm to hot summers. Snow is possible only in the Troodos Mountains in the central part of island. Rain occurs mainly in winter, with summer being generally dry.
Cyprus has one of the warmest climates in the Mediterranean part of the European Union. The average annual temperature on the coast is around during the day and at night. Generally, summers last about eight months, beginning in April with average temperatures of during the day and at night, and ending in November with average temperatures of during the day and at night, although in the remaining four months temperatures sometimes exceed .
Among all cities in the Mediterranean part of the European Union, Limassol has one of the warmest winters, in the period January – February average temperature is during the day and at night, in other coastal locations in Cyprus is generally during the day and at night. During March, Limassol has average temperatures of during the day and at night, in other coastal locations in Cyprus is generally during the day and at night.
The middle of summer is hot – in July and August on the coast the average temperature is usually around during the day and around at night (inland, in the highlands average temperature exceeds ) while in the June and September on the coast the average temperature is usually around during the day and around at night in Limassol, while is usually around during the day and around at night in Paphos. Large fluctuations in temperature are rare. Inland temperatures are more extreme, with colder winters and hotter summers compared with the coast of the island.
Average annual temperature of sea is , from in February to in August (depending on the location). In total 7 months – from May to November – the average sea temperature exceeds .
Sunshine hours on the coast are around 3,200 per year, from an average of 5–6 hours of sunshine per day in December to an average of 12–13 hours in July. This is about double that of cities in the northern half of Europe; for comparison, London receives about 1,540 per year. In December, London receives about 50 hours of sunshine while coastal locations in Cyprus about 180 hours (almost as much as in May in London).
 Cyprus suffers from a chronic shortage of water. The country relies heavily on rain to provide household water, but in the past 30 years average yearly precipitation has decreased. Between 2001 and 2004, exceptionally heavy annual rainfall pushed water reserves up, with supply exceeding demand, allowing total storage in the island's reservoirs to rise to an all-time high by the start of 2005.
However, since then demand has increased annually – a result of local population growth, foreigners moving to Cyprus and the number of visiting tourists – while supply has fallen as a result of more frequent droughts.
Dams remain the principal source of water both for domestic and agricultural use; Cyprus has a total of 107 dams (plus one currently under construction) and reservoirs, with a total water storage capacity of about . Water desalination plants are gradually being constructed to deal with recent years of prolonged drought.
The Government has invested heavily in the creation of water desalination plants which have supplied almost 50 per cent of domestic water since 2001. Efforts have also been made to raise public awareness of the situation and to encourage domestic water users to take more responsibility for the conservation of this increasingly scarce commodity.
Turkey has built a water pipeline under the Mediterranean Sea from Anamur on its southern coast to the northern coast of Cyprus, to supply Northern Cyprus with potable and irrigation water ''(see Northern Cyprus Water Supply Project)''.
Cyprus suffers from a chronic shortage of water. The country relies heavily on rain to provide household water, but in the past 30 years average yearly precipitation has decreased. Between 2001 and 2004, exceptionally heavy annual rainfall pushed water reserves up, with supply exceeding demand, allowing total storage in the island's reservoirs to rise to an all-time high by the start of 2005.
However, since then demand has increased annually – a result of local population growth, foreigners moving to Cyprus and the number of visiting tourists – while supply has fallen as a result of more frequent droughts.
Dams remain the principal source of water both for domestic and agricultural use; Cyprus has a total of 107 dams (plus one currently under construction) and reservoirs, with a total water storage capacity of about . Water desalination plants are gradually being constructed to deal with recent years of prolonged drought.
The Government has invested heavily in the creation of water desalination plants which have supplied almost 50 per cent of domestic water since 2001. Efforts have also been made to raise public awareness of the situation and to encourage domestic water users to take more responsibility for the conservation of this increasingly scarce commodity.
Turkey has built a water pipeline under the Mediterranean Sea from Anamur on its southern coast to the northern coast of Cyprus, to supply Northern Cyprus with potable and irrigation water ''(see Northern Cyprus Water Supply Project)''.
 Cyprus is a presidential republic. The head of state and of the government is elected by a process of universal suffrage for a five-year term. Executive power is exercised by the government with legislative power vested in the House of Representatives whilst the Judiciary is independent of both the executive and the legislature.
The 1960 Constitution provided for a presidential system of government with independent executive, legislative and judicial branches as well as a complex system of checks and balances including a weighted power-sharing ratio designed to protect the interests of the Turkish Cypriots. The executive was led by a Greek Cypriot president and a Turkish Cypriot vice-president elected by their respective communities for five-year terms and each possessing a right of veto over certain types of legislation and executive decisions. Legislative power rested on the House of Representatives who were also elected on the basis of separate voters' rolls.
Cyprus is a presidential republic. The head of state and of the government is elected by a process of universal suffrage for a five-year term. Executive power is exercised by the government with legislative power vested in the House of Representatives whilst the Judiciary is independent of both the executive and the legislature.
The 1960 Constitution provided for a presidential system of government with independent executive, legislative and judicial branches as well as a complex system of checks and balances including a weighted power-sharing ratio designed to protect the interests of the Turkish Cypriots. The executive was led by a Greek Cypriot president and a Turkish Cypriot vice-president elected by their respective communities for five-year terms and each possessing a right of veto over certain types of legislation and executive decisions. Legislative power rested on the House of Representatives who were also elected on the basis of separate voters' rolls.
 Since 1965, following clashes between the two communities, the Turkish Cypriot seats in the House remain vacant. In 1974 Cyprus was divided de facto when the Turkish army occupied the northern third of the island. The Turkish Cypriots subsequently declared independence in 1983 as the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus but were recognised only by Turkey. In 1985 the TRNC adopted a constitution and held its first elections. The United Nations recognises the sovereignty of the Republic of Cyprus over the entire island of Cyprus.
The House of Representatives currently has 59 members elected for a five-year term, 56 members by proportional representation and three observer members representing the Armenians in Cyprus, Armenian, Roman Catholicism in Cyprus, Latin and Maronites in Cyprus, Maronite minorities. 24 seats are allocated to the Turkish people, Turkish community but remain vacant since 1964. The political environment is dominated by the communist Progressive Party of Working People, AKEL, the liberal conservative Democratic Rally, the centrism, centrist Democratic Party (Cyprus), Democratic Party, the social democracy, social-democratic Movement for Social Democracy, EDEK and the centrist European Party (Cyprus), EURO.KO.
In 2008, Dimitris Christofias became the country's first Communist head of state. Due to his involvement in the 2012–13 Cypriot financial crisis, Christofias did not run for re-election in 2013. The Presidential election in 2013 resulted in Democratic Rally candidate Nicos Anastasiades winning 57.48% of the vote. As a result, Anastasiades was sworn in on and has been president since 28 February 2013. Anastasiades was re-elected with 56% of the vote in the Cypriot presidential election, 2018, 2018 presidential election.
Since 1965, following clashes between the two communities, the Turkish Cypriot seats in the House remain vacant. In 1974 Cyprus was divided de facto when the Turkish army occupied the northern third of the island. The Turkish Cypriots subsequently declared independence in 1983 as the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus but were recognised only by Turkey. In 1985 the TRNC adopted a constitution and held its first elections. The United Nations recognises the sovereignty of the Republic of Cyprus over the entire island of Cyprus.
The House of Representatives currently has 59 members elected for a five-year term, 56 members by proportional representation and three observer members representing the Armenians in Cyprus, Armenian, Roman Catholicism in Cyprus, Latin and Maronites in Cyprus, Maronite minorities. 24 seats are allocated to the Turkish people, Turkish community but remain vacant since 1964. The political environment is dominated by the communist Progressive Party of Working People, AKEL, the liberal conservative Democratic Rally, the centrism, centrist Democratic Party (Cyprus), Democratic Party, the social democracy, social-democratic Movement for Social Democracy, EDEK and the centrist European Party (Cyprus), EURO.KO.
In 2008, Dimitris Christofias became the country's first Communist head of state. Due to his involvement in the 2012–13 Cypriot financial crisis, Christofias did not run for re-election in 2013. The Presidential election in 2013 resulted in Democratic Rally candidate Nicos Anastasiades winning 57.48% of the vote. As a result, Anastasiades was sworn in on and has been president since 28 February 2013. Anastasiades was re-elected with 56% of the vote in the Cypriot presidential election, 2018, 2018 presidential election.
 Cyprus has four exclaves, all in territory that belongs to the Akrotiri and Dhekelia, British Sovereign Base Area of Dhekelia. The first two are the villages of Ormidhia and Xylotymvou. The third is the Dhekelia Power Station, which is divided by a British road into two parts. The northern part is the Electricity Authority of Cyprus, EAC refugee settlement. The southern part, even though located by the sea, is also an exclave because it has no
Cyprus has four exclaves, all in territory that belongs to the Akrotiri and Dhekelia, British Sovereign Base Area of Dhekelia. The first two are the villages of Ormidhia and Xylotymvou. The third is the Dhekelia Power Station, which is divided by a British road into two parts. The northern part is the Electricity Authority of Cyprus, EAC refugee settlement. The southern part, even though located by the sea, is also an exclave because it has no
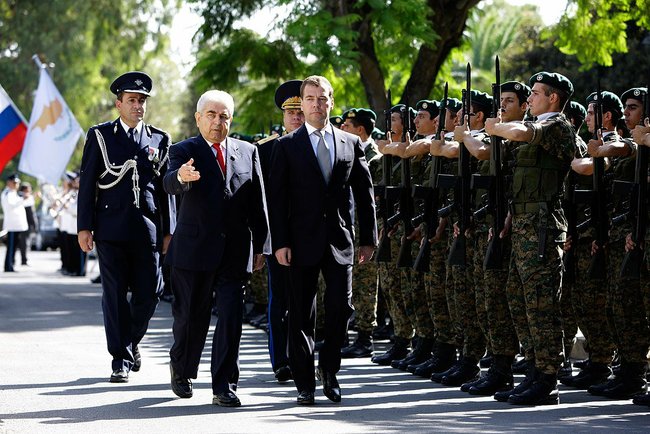 The Cypriot National Guard is the main military institution of the Republic of Cyprus. It is a combined arms force, with land, air and naval elements. Historically all men were required to spend 24 months serving in the National Guard after their 17th birthday, but in 2016 this period of compulsory service was reduced to 14 months.
Annually, approximately 10,000 persons are trained in recruit centres. Depending on their awarded speciality the conscript recruits are then transferred to speciality training camps or to operational units.
While until 2016 the armed forces were mainly conscript based, since then a large Professional Enlisted institution has been adopted (ΣΥΟΠ), which combined with the reduction of conscript service produces an approximate 3:1 ratio between conscript and professional enlisted.
The Cypriot National Guard is the main military institution of the Republic of Cyprus. It is a combined arms force, with land, air and naval elements. Historically all men were required to spend 24 months serving in the National Guard after their 17th birthday, but in 2016 this period of compulsory service was reduced to 14 months.
Annually, approximately 10,000 persons are trained in recruit centres. Depending on their awarded speciality the conscript recruits are then transferred to speciality training camps or to operational units.
While until 2016 the armed forces were mainly conscript based, since then a large Professional Enlisted institution has been adopted (ΣΥΟΠ), which combined with the reduction of conscript service produces an approximate 3:1 ratio between conscript and professional enlisted.
 The Cyprus Police (Greek: , tr, Kıbrıs Polisi) is the only National Police Service of the Republic of Cyprus and is under the Ministry of Justice and Public Order since 1993.Cyprus Government Web Portal
In "Freedom in the World 2011", Freedom House rated Cyprus as "free". In January 2011, the Report of the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights on the question of Human Rights in Cyprus noted that the ongoing division of Cyprus continues to affect human rights throughout the island "including freedom of movement, human rights pertaining to the question of missing persons, discrimination, the right to life, freedom of religion, and economic, social and cultural rights". The constant focus on the division of the island can sometimes mask other human rights issues.
In 2014, Turkey was ordered by the European Court of Human Rights to pay well over $100m in compensation to Cyprus for the invasion; Ankara announced that it would ignore the judgment. In 2014, a group of Cypriot refugees and a European parliamentarian, later joined by the Cypriot government, filed a complaint to the International Court of Justice, accusing Turkey of violating the Geneva Conventions by directly or indirectly transferring Turkish settlers in Northern Cyprus, its civilian population into occupied territory. Other violations of the Geneva and the Hague Conventions—both ratified by Turkey—amount to what archaeologist Sophocles Hadjisavvas called "the organized destruction of Greek and Christian heritage in the north". These violations include looting of cultural treasures, deliberate destruction of churches, neglect of works of art, and altering the names of important historical sites, which was condemned by the International Council on Monuments and Sites. Hadjisavvas has asserted that these actions are motivated by a Turkish policy of erasing the Greek presence in Northern Cyprus within a framework of ethnic cleansing. But some perpetrators are just motivated by greed and are seeking profit. Quote on p. 129: "the deliberate destruction of [Greek] heritage as an instrument toward the obliteration of an identity of a people in the framework of ethnic cleansing." Art law expert Alessandro Chechi has classified the connection of cultural heritage destruction to ethnic cleansing as the "Greek Cypriot viewpoint", which he reports as having been dismissed by two Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe, PACE reports. Chechi asserts joint Greek and Turkish Cypriot responsibility for the destruction of cultural heritage in Cyprus, noting the destruction of Turkish Cypriot heritage in the hands of Greek Cypriot extremists.
The Cyprus Police (Greek: , tr, Kıbrıs Polisi) is the only National Police Service of the Republic of Cyprus and is under the Ministry of Justice and Public Order since 1993.Cyprus Government Web Portal
In "Freedom in the World 2011", Freedom House rated Cyprus as "free". In January 2011, the Report of the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights on the question of Human Rights in Cyprus noted that the ongoing division of Cyprus continues to affect human rights throughout the island "including freedom of movement, human rights pertaining to the question of missing persons, discrimination, the right to life, freedom of religion, and economic, social and cultural rights". The constant focus on the division of the island can sometimes mask other human rights issues.
In 2014, Turkey was ordered by the European Court of Human Rights to pay well over $100m in compensation to Cyprus for the invasion; Ankara announced that it would ignore the judgment. In 2014, a group of Cypriot refugees and a European parliamentarian, later joined by the Cypriot government, filed a complaint to the International Court of Justice, accusing Turkey of violating the Geneva Conventions by directly or indirectly transferring Turkish settlers in Northern Cyprus, its civilian population into occupied territory. Other violations of the Geneva and the Hague Conventions—both ratified by Turkey—amount to what archaeologist Sophocles Hadjisavvas called "the organized destruction of Greek and Christian heritage in the north". These violations include looting of cultural treasures, deliberate destruction of churches, neglect of works of art, and altering the names of important historical sites, which was condemned by the International Council on Monuments and Sites. Hadjisavvas has asserted that these actions are motivated by a Turkish policy of erasing the Greek presence in Northern Cyprus within a framework of ethnic cleansing. But some perpetrators are just motivated by greed and are seeking profit. Quote on p. 129: "the deliberate destruction of [Greek] heritage as an instrument toward the obliteration of an identity of a people in the framework of ethnic cleansing." Art law expert Alessandro Chechi has classified the connection of cultural heritage destruction to ethnic cleansing as the "Greek Cypriot viewpoint", which he reports as having been dismissed by two Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe, PACE reports. Chechi asserts joint Greek and Turkish Cypriot responsibility for the destruction of cultural heritage in Cyprus, noting the destruction of Turkish Cypriot heritage in the hands of Greek Cypriot extremists.

 In the early 21st century the Cypriot economy has diversified and become prosperous. However, in 2012 it became affected by the European sovereign-debt crisis, Eurozone financial and banking crisis. In June 2012, the Cypriot government announced it would need € in foreign aid to support the Cyprus Popular Bank, and this was followed by Fitch Group, Fitch downgrading Cyprus's credit rating to junk status. Fitch said Cyprus would need an additional € to support its banks and the downgrade was mainly due to the exposure of Bank of Cyprus, Cyprus Popular Bank and Hellenic Bank, Cyprus's three largest banks, to the Greek government-debt crisis, Greek financial crisis.
In the early 21st century the Cypriot economy has diversified and become prosperous. However, in 2012 it became affected by the European sovereign-debt crisis, Eurozone financial and banking crisis. In June 2012, the Cypriot government announced it would need € in foreign aid to support the Cyprus Popular Bank, and this was followed by Fitch Group, Fitch downgrading Cyprus's credit rating to junk status. Fitch said Cyprus would need an additional € to support its banks and the downgrade was mainly due to the exposure of Bank of Cyprus, Cyprus Popular Bank and Hellenic Bank, Cyprus's three largest banks, to the Greek government-debt crisis, Greek financial crisis.
 The 2012–2013 Cypriot financial crisis led to an agreement with the Eurogroup in March 2013 to split the country's second largest bank, the Cyprus Popular Bank (also known as Laiki Bank), into a "bad" bank which would be wound down over time and a "good" bank which would be absorbed by the Bank of Cyprus. In return for a €10 billion bailout from the European Commission, the European Central Bank and the International Monetary Fund, often referred to as the "troika", the Cypriot government was required to impose a significant haircut (finance), haircut on deposit insurance, uninsured deposits, a large proportion of which were held by wealthy Russians who used Cyprus as a tax haven. Insured deposits of €100,000 or less were not affected.
The 2012–2013 Cypriot financial crisis led to an agreement with the Eurogroup in March 2013 to split the country's second largest bank, the Cyprus Popular Bank (also known as Laiki Bank), into a "bad" bank which would be wound down over time and a "good" bank which would be absorbed by the Bank of Cyprus. In return for a €10 billion bailout from the European Commission, the European Central Bank and the International Monetary Fund, often referred to as the "troika", the Cypriot government was required to impose a significant haircut (finance), haircut on deposit insurance, uninsured deposits, a large proportion of which were held by wealthy Russians who used Cyprus as a tax haven. Insured deposits of €100,000 or less were not affected.
 According to the 2017 International Monetary Fund estimates, its List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, per capita GDP (adjusted for purchasing power parity, purchasing power) at international dollar, $36,442 is below the average of the European Union. Cyprus has been sought as a base for several offshore businesses for its low tax rates. Tourism, financial services and shipping are significant parts of the economy. Economic policy of the Cyprus government has focused on meeting the criteria for admission to the European Union. The Cypriot government adopted the euro as the national currency on 1 January 2008.
Cyprus is the last EU member fully isolated from energy interconnections and it is expected that it will be connected to European network via EuroAsia Interconnector, 2000 MW high-voltage direct current, HVDC submarine power cable, undersea power cable. EuroAsia Interconnector will connect Greek, Cypriot, and Israeli power grids. It is a leading Project of Common Interest of the
According to the 2017 International Monetary Fund estimates, its List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, per capita GDP (adjusted for purchasing power parity, purchasing power) at international dollar, $36,442 is below the average of the European Union. Cyprus has been sought as a base for several offshore businesses for its low tax rates. Tourism, financial services and shipping are significant parts of the economy. Economic policy of the Cyprus government has focused on meeting the criteria for admission to the European Union. The Cypriot government adopted the euro as the national currency on 1 January 2008.
Cyprus is the last EU member fully isolated from energy interconnections and it is expected that it will be connected to European network via EuroAsia Interconnector, 2000 MW high-voltage direct current, HVDC submarine power cable, undersea power cable. EuroAsia Interconnector will connect Greek, Cypriot, and Israeli power grids. It is a leading Project of Common Interest of the
 Available modes of transport are by road, sea and air. Of the of roads in the Republic of Cyprus in 1998, were paved, and were unpaved. In 1996 the Turkish-occupied area had a similar ratio of paved to unpaved, with approximately of paved road and unpaved. Cyprus is one of only three EU nations in which vehicles drive on the Right- and left-hand traffic, left-hand side of the road, a remnant of British colonisation (the others being Ireland and Malta). Roads and motorways in Cyprus, A series of motorways runs along the coast from Paphos east to Ayia Napa, with two motorways running inland to Nicosia, one from Limassol and one from Larnaca.
Per capita private car ownership is the 29th-highest in the world. There were approximately 344,000 privately owned vehicles, and a total of 517,000 registered motor vehicles in the Republic of Cyprus in 2006. In 2006, plans were announced to improve and expand bus services and other public transport throughout Cyprus, with the financial backing of the
Available modes of transport are by road, sea and air. Of the of roads in the Republic of Cyprus in 1998, were paved, and were unpaved. In 1996 the Turkish-occupied area had a similar ratio of paved to unpaved, with approximately of paved road and unpaved. Cyprus is one of only three EU nations in which vehicles drive on the Right- and left-hand traffic, left-hand side of the road, a remnant of British colonisation (the others being Ireland and Malta). Roads and motorways in Cyprus, A series of motorways runs along the coast from Paphos east to Ayia Napa, with two motorways running inland to Nicosia, one from Limassol and one from Larnaca.
Per capita private car ownership is the 29th-highest in the world. There were approximately 344,000 privately owned vehicles, and a total of 517,000 registered motor vehicles in the Republic of Cyprus in 2006. In 2006, plans were announced to improve and expand bus services and other public transport throughout Cyprus, with the financial backing of the

 According to the CIA World Factbook, in 2001
According to the CIA World Factbook, in 2001
Main Results of the 2001 Census. Retrieved 29 February 2009. 94.8% of the population were Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox, 0.9% Armenian religion in Cyprus, Armenians and Maronite Church, Maronites, 1.5% Roman Catholics, 1.0% Church of England, and 0.6% Muslims. There is also a History of the Jews in Cyprus, Jewish community on Cyprus. The remaining 1.3% adhered to other religious denominations or did not state their religion.
 Cyprus has two official languages, Greek and Turkish language, Turkish. Armenian language, Armenian and Cypriot Maronite Arabic are recognised as minority languages. Although without official status, English is widely spoken and it features widely on road signs, public notices, and in advertisements, etc. English was the sole official language during British colonial rule and the lingua franca until 1960, and continued to be used (de facto) in courts of law until 1989 and in legislation until 1996. 80.4% of Cypriots are proficient in the English language as a second language. Russian is widely spoken among the country's minorities, residents and citizens of post-Soviet countries, and Pontic Greeks. Russian, after English and Greek, is the third language used on many signs of shops and restaurants, particularly in Limassol and Paphos. In addition to these languages, 12% speak French and 5% speak German.Europeans and their Languages
Cyprus has two official languages, Greek and Turkish language, Turkish. Armenian language, Armenian and Cypriot Maronite Arabic are recognised as minority languages. Although without official status, English is widely spoken and it features widely on road signs, public notices, and in advertisements, etc. English was the sole official language during British colonial rule and the lingua franca until 1960, and continued to be used (de facto) in courts of law until 1989 and in legislation until 1996. 80.4% of Cypriots are proficient in the English language as a second language. Russian is widely spoken among the country's minorities, residents and citizens of post-Soviet countries, and Pontic Greeks. Russian, after English and Greek, is the third language used on many signs of shops and restaurants, particularly in Limassol and Paphos. In addition to these languages, 12% speak French and 5% speak German.Europeans and their Languages
, Eurobarometer, European Commission, 2006. The everyday spoken language of Greek Cypriots is Cypriot Greek and that of Turkish Cypriots is Cypriot Turkish. These vernaculars both differ from their standard language, standard registers significantly.
 Greek Cypriots and Turkish Cypriots share a lot in common in their culture due to cultural exchanges but also have differences. Several traditional food (such as souvla and halloumi) and beverages are similar, as well as expressions and ways of life. Hospitality and buying or offering food and drinks for guests or others are common among both. In both communities, music, dance and art are integral parts of social life and many artistic, verbal and nonverbal expressions, traditional dances such as tsifteteli, similarities in dance costumes and importance placed on social activities are shared between the communities. However, the two communities have distinct religions and religious cultures, with the Greek Cypriots traditionally being Church of Cyprus, Greek Orthodox and Turkish Cypriots traditionally being Sunni Muslims, which has partly hindered cultural exchange. Greek Cypriots have influences from Greece and Christianity, while Turkish Cypriots have influences from Turkey and Islam.
The Limassol Carnival Festival is an annual carnival which is held at
Greek Cypriots and Turkish Cypriots share a lot in common in their culture due to cultural exchanges but also have differences. Several traditional food (such as souvla and halloumi) and beverages are similar, as well as expressions and ways of life. Hospitality and buying or offering food and drinks for guests or others are common among both. In both communities, music, dance and art are integral parts of social life and many artistic, verbal and nonverbal expressions, traditional dances such as tsifteteli, similarities in dance costumes and importance placed on social activities are shared between the communities. However, the two communities have distinct religions and religious cultures, with the Greek Cypriots traditionally being Church of Cyprus, Greek Orthodox and Turkish Cypriots traditionally being Sunni Muslims, which has partly hindered cultural exchange. Greek Cypriots have influences from Greece and Christianity, while Turkish Cypriots have influences from Turkey and Islam.
The Limassol Carnival Festival is an annual carnival which is held at
 The art history of Cyprus can be said to stretch back up to 10,000 years, following the discovery of a series of Chalcolithic period carved figures in the villages of Khoirokoitia and Lempa (Lemba), Lempa. The island is the home to numerous examples of high quality religious icon painting from the Cyprus in the Middle Ages, Middle Ages as well as List of painted churches in Cyprus, many painted churches. Cypriot architecture was heavily influenced by French Gothic architecture, French Gothic and Italian renaissance architecture, renaissance introduced in the island during the era of Latin domination (1191–1571).
A well known traditional art that dates at least from the 14th century is the Lefkara lace (also known as "Lefkaratika", which originates from the village Pano Lefkara, Lefkara. Lefkara lace is recognised as an intangible cultural heritage (ICH) by Unesco, and it is characterised by distinct design patterns, and its intricate, time-consuming production process. A genuine Lefkara lace with full embroidery can take typically hundreds of hours to be made, and that is why it is usually priced quite high. Another local form of art that originated from Lefkara is the production of Cypriot Filigree (locally known as ''Trifourenio''), a type of jewellery that is made with twisted threads of silver. In Lefkara village there is government funded centre named Lefkara Handicraft Centre the mission of which is to educate and teach the art of making the embroidery and silver jewellery. There's also the Museum of Traditional Embroidery and Silversmithing located in the village which has large collection of local handmade art.
In modern times Cypriot art history begins with the painter Vassilis Vryonides (1883–1958) who studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Venice. Arguably the two founding fathers of modern Cypriot art were Adamantios Diamantis (1900–1994) who studied at London's Royal College of Art and
Christopheros Savva (1924–1968) who also studied in London, at Saint Martin's School of Art. In 1960, Savva founded, together with Welsh artist Glyn Hughes, Apophasis [Decision], the first independent cultural centre of the newly established Republic of Cyprus. In 1968, Savva was among the artists representing Cyprus in its inaugural Pavilion at the 34th Venice Biennale. English Cypriot Artis
The art history of Cyprus can be said to stretch back up to 10,000 years, following the discovery of a series of Chalcolithic period carved figures in the villages of Khoirokoitia and Lempa (Lemba), Lempa. The island is the home to numerous examples of high quality religious icon painting from the Cyprus in the Middle Ages, Middle Ages as well as List of painted churches in Cyprus, many painted churches. Cypriot architecture was heavily influenced by French Gothic architecture, French Gothic and Italian renaissance architecture, renaissance introduced in the island during the era of Latin domination (1191–1571).
A well known traditional art that dates at least from the 14th century is the Lefkara lace (also known as "Lefkaratika", which originates from the village Pano Lefkara, Lefkara. Lefkara lace is recognised as an intangible cultural heritage (ICH) by Unesco, and it is characterised by distinct design patterns, and its intricate, time-consuming production process. A genuine Lefkara lace with full embroidery can take typically hundreds of hours to be made, and that is why it is usually priced quite high. Another local form of art that originated from Lefkara is the production of Cypriot Filigree (locally known as ''Trifourenio''), a type of jewellery that is made with twisted threads of silver. In Lefkara village there is government funded centre named Lefkara Handicraft Centre the mission of which is to educate and teach the art of making the embroidery and silver jewellery. There's also the Museum of Traditional Embroidery and Silversmithing located in the village which has large collection of local handmade art.
In modern times Cypriot art history begins with the painter Vassilis Vryonides (1883–1958) who studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Venice. Arguably the two founding fathers of modern Cypriot art were Adamantios Diamantis (1900–1994) who studied at London's Royal College of Art and
Christopheros Savva (1924–1968) who also studied in London, at Saint Martin's School of Art. In 1960, Savva founded, together with Welsh artist Glyn Hughes, Apophasis [Decision], the first independent cultural centre of the newly established Republic of Cyprus. In 1968, Savva was among the artists representing Cyprus in its inaugural Pavilion at the 34th Venice Biennale. English Cypriot Artis
Glyn HUGHES
1931–2014. In many ways these two artists set the template for subsequent Cypriot art and both their artistic styles and the patterns of their education remain influential to this day. In particular the majority of Cypriot artists still train in England while others train at art schools in Greece and local art institutions such as the Cyprus College of Art, University of Nicosia and the Frederick Institute of Technology. One of the features of Cypriot art is a tendency towards figurative painting although conceptual art is being rigorously promoted by a number of art "institutions" and most notably the Nicosia Municipal Art Centre. Municipal art galleries exist in all the main towns and there is a large and lively commercial art scene. Cyprus was due to host the international art festival Manifesta in 2006 but this was cancelled at the last minute following a dispute between the Dutch organisers of Manifesta and the Cyprus Ministry of Education and Culture over the location of some of the Manifesta events in the Turkish sector of the capital
 The traditional folk music of Cyprus has several common elements with Music of Greece, Greek, Music of Turkey, Turkish, and Arabic Music, all of which have descended from Byzantine music, including Greek Cypriot and Turkish Cypriot dances such as the ''sousta'', ''syrtos'', ''zeibekikos'', ''tatsia'', and ''karsilamas'' as well as the Middle Eastern-inspired ''tsifteteli'' and ''arapies''. There is also a form of musical poetry known as ''chattista'' which is often performed at traditional feasts and celebrations. The instruments commonly associated with Cyprus folk music are the violin ("fkiolin"), lute ("laouto"), Cyprus flute (fipple flute, ''pithkiavlin''), oud ("outi"), kanonaki and percussions (including the "drum, tamboutsia"). Composers associated with traditional Cypriot music include Solon Michaelides, Marios Tokas, Evagoras Karageorgis and Savvas Salides. Among musicians is also the acclaimed pianist Cyprien Katsaris, composer Andreas G. Orphanides, and composer and artistic director of the European Capital of Culture initiative Marios Joannou Elia.
Popular music in Cyprus is generally influenced by the Greek ''Laïka'' scene; artists who play in this genre include international Music recording sales certification, platinum star Anna Vissi, Evridiki, and Sarbel. Hip hop music, Hip hop and R&B have been supported by the emergence of Cypriot rap and the urban music scene at Ayia Napa, while in the last years the reggae scene is growing, especially through the participation of many Cypriot artists at the annual Reggae Sunjam festival. Is also noted Cypriot rock music and ''Éntekhno'' rock is often associated with artists such as Michalis Hatzigiannis and Alkinoos Ioannidis. Heavy metal music, Metal also has a small following in Cyprus represented by bands such as Armageddon (rev.16:16), Blynd, Winter's Verge, Methysos and Quadraphonic.
The traditional folk music of Cyprus has several common elements with Music of Greece, Greek, Music of Turkey, Turkish, and Arabic Music, all of which have descended from Byzantine music, including Greek Cypriot and Turkish Cypriot dances such as the ''sousta'', ''syrtos'', ''zeibekikos'', ''tatsia'', and ''karsilamas'' as well as the Middle Eastern-inspired ''tsifteteli'' and ''arapies''. There is also a form of musical poetry known as ''chattista'' which is often performed at traditional feasts and celebrations. The instruments commonly associated with Cyprus folk music are the violin ("fkiolin"), lute ("laouto"), Cyprus flute (fipple flute, ''pithkiavlin''), oud ("outi"), kanonaki and percussions (including the "drum, tamboutsia"). Composers associated with traditional Cypriot music include Solon Michaelides, Marios Tokas, Evagoras Karageorgis and Savvas Salides. Among musicians is also the acclaimed pianist Cyprien Katsaris, composer Andreas G. Orphanides, and composer and artistic director of the European Capital of Culture initiative Marios Joannou Elia.
Popular music in Cyprus is generally influenced by the Greek ''Laïka'' scene; artists who play in this genre include international Music recording sales certification, platinum star Anna Vissi, Evridiki, and Sarbel. Hip hop music, Hip hop and R&B have been supported by the emergence of Cypriot rap and the urban music scene at Ayia Napa, while in the last years the reggae scene is growing, especially through the participation of many Cypriot artists at the annual Reggae Sunjam festival. Is also noted Cypriot rock music and ''Éntekhno'' rock is often associated with artists such as Michalis Hatzigiannis and Alkinoos Ioannidis. Heavy metal music, Metal also has a small following in Cyprus represented by bands such as Armageddon (rev.16:16), Blynd, Winter's Verge, Methysos and Quadraphonic.
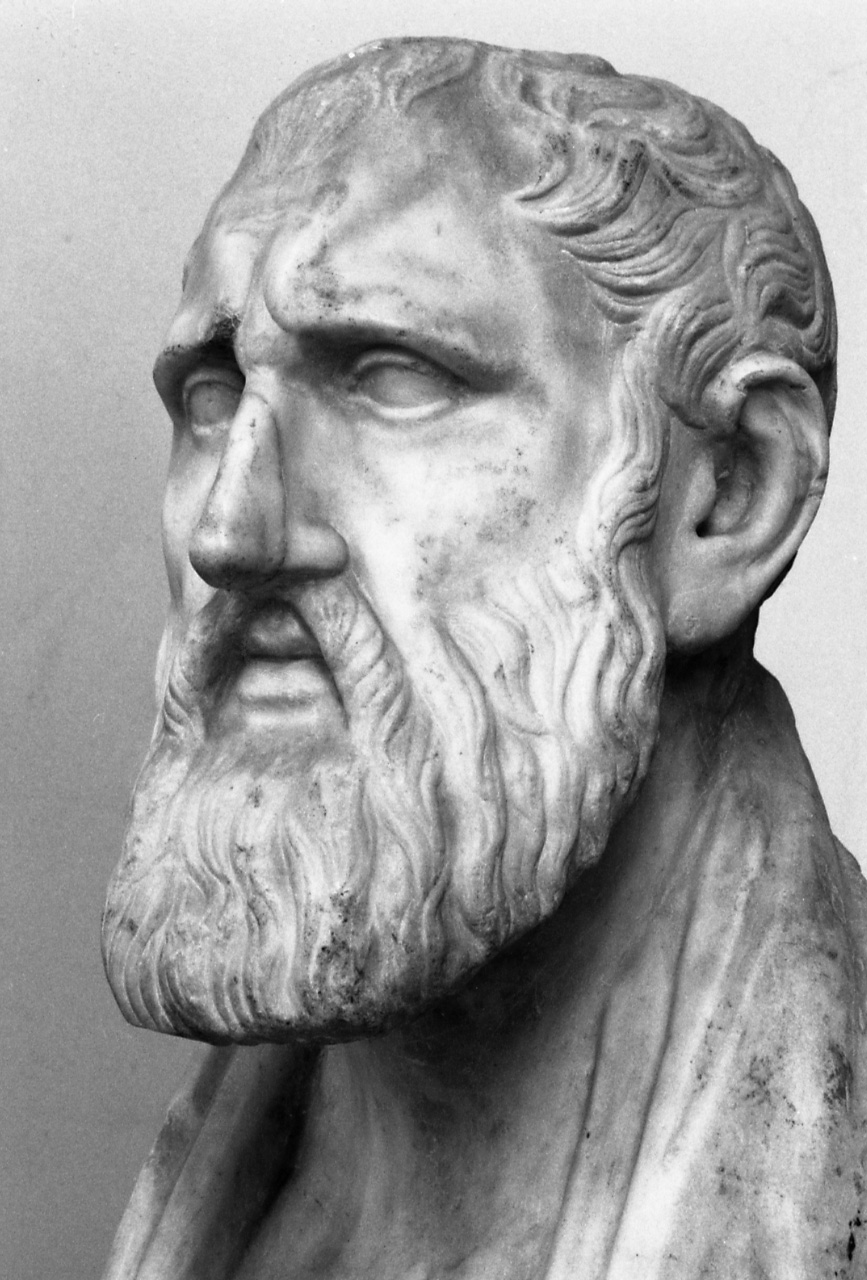 Literary production of the antiquity includes the ''Cypria'', an epic poetry, epic poem, probably composed in the late 7th century BC and attributed to Stasinus. The ''Cypria'' is one of the first specimens of Greek and European poetry. The Cypriot Zeno of Citium was the founder of the Stoic school of philosophy.
Epic poetry, notably the "acritic songs", flourished during Middle Ages. Two chronicles, one written by Leontios Machairas and the other by Georgios Boustronios, cover the entire Middle Ages until the end of Frankish rule (4th century–1489). Poèmes d'amour written in medieval Greek Cypriot date back from the 16th century. Some of them are actual translations of poems written by Petrarch, Bembo, Ariosto and G. Sannazzaro. Many Cypriot scholars fled Cyprus at troubled times such as Ioannis Kigalas (c. 1622–1687) who migrated from Cyprus to Italy in the 17th century, several of his works have survived in books of other scholars.
Literary production of the antiquity includes the ''Cypria'', an epic poetry, epic poem, probably composed in the late 7th century BC and attributed to Stasinus. The ''Cypria'' is one of the first specimens of Greek and European poetry. The Cypriot Zeno of Citium was the founder of the Stoic school of philosophy.
Epic poetry, notably the "acritic songs", flourished during Middle Ages. Two chronicles, one written by Leontios Machairas and the other by Georgios Boustronios, cover the entire Middle Ages until the end of Frankish rule (4th century–1489). Poèmes d'amour written in medieval Greek Cypriot date back from the 16th century. Some of them are actual translations of poems written by Petrarch, Bembo, Ariosto and G. Sannazzaro. Many Cypriot scholars fled Cyprus at troubled times such as Ioannis Kigalas (c. 1622–1687) who migrated from Cyprus to Italy in the 17th century, several of his works have survived in books of other scholars.
 Hasan Hilmi Efendi, a Turkish Cypriot poet, was rewarded by the Ottoman sultan Mahmud II and said to be the "sultan of the poems".
Modern Greek Cypriot literary figures include the poet and writer Kostas Montis, poet Kyriakos Charalambides, poet Michalis Pasiardis, writer Nicos Nicolaides, Stylianos Atteshlis, Altheides, Loukis Akritas and Demetris Th. Gotsis. Dimitris Lipertis, Vasilis Michaelides and Pavlos Liasides are folk poets who wrote poems mainly in the Cypriot Greek, Cypriot-Greek dialect. Among leading Turkish Cypriot writers are Osman Türkay, twice nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature, Özker Yaşın, Neriman Cahit, Urkiye Mine Balman, Mehmet Yaşın and Neşe Yaşın.
There is an increasingly strong presence of both temporary and permanent emigre Cypriot writers in world literature, as well as writings by second and third -generation Cypriot writers born or raised abroad, often writing in English. This includes writers such as Michael Paraskos and Stephanos Stephanides.
Examples of Cyprus in foreign literature include the works of Shakespeare, with most of the play ''Othello'' by William Shakespeare set on the island of Cyprus. British writer Lawrence Durrell lived in Cyprus from 1952 until 1956, during his time working for the British colonial government on the island, and wrote the book ''Bitter Lemons'' about his time in Cyprus which won the second Duff Cooper Prize in 1957.
Hasan Hilmi Efendi, a Turkish Cypriot poet, was rewarded by the Ottoman sultan Mahmud II and said to be the "sultan of the poems".
Modern Greek Cypriot literary figures include the poet and writer Kostas Montis, poet Kyriakos Charalambides, poet Michalis Pasiardis, writer Nicos Nicolaides, Stylianos Atteshlis, Altheides, Loukis Akritas and Demetris Th. Gotsis. Dimitris Lipertis, Vasilis Michaelides and Pavlos Liasides are folk poets who wrote poems mainly in the Cypriot Greek, Cypriot-Greek dialect. Among leading Turkish Cypriot writers are Osman Türkay, twice nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature, Özker Yaşın, Neriman Cahit, Urkiye Mine Balman, Mehmet Yaşın and Neşe Yaşın.
There is an increasingly strong presence of both temporary and permanent emigre Cypriot writers in world literature, as well as writings by second and third -generation Cypriot writers born or raised abroad, often writing in English. This includes writers such as Michael Paraskos and Stephanos Stephanides.
Examples of Cyprus in foreign literature include the works of Shakespeare, with most of the play ''Othello'' by William Shakespeare set on the island of Cyprus. British writer Lawrence Durrell lived in Cyprus from 1952 until 1956, during his time working for the British colonial government on the island, and wrote the book ''Bitter Lemons'' about his time in Cyprus which won the second Duff Cooper Prize in 1957.
''Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 2012'', Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor, U.S. Department of State, 22 March 2013. Retrieved 7 January 2014. Local television companies in Cyprus include the state owned Cyprus Broadcasting Corporation which runs two television channels. In addition on the Greek side of the island there are the private channels ANT1 Cyprus, Plus TV, Mega Channel, Sigma TV, Nimonia TV (NTV) and New Extra. In Northern Cyprus, the local channels are Bayrak, BRT, the Turkish Cypriot equivalent to the Cyprus Broadcasting Corporation, and a number of private channels. The majority of local arts and cultural programming is produced by the Cyprus Broadcasting Corporation and BRT, with local arts documentaries, review programmes and filmed drama series.
 During the medieval period, under the French Lusignan monarchs of Cyprus an elaborate form of courtly cuisine developed, fusing French, Byzantine and Middle Eastern forms. The Lusignan kings were known for importing Syrian cooks to Cyprus, and it has been suggested that one of the key routes for the importation of Middle Eastern recipes into France and other Western European countries, such as blancmange, was via the Lusignan Kingdom of Cyprus. These recipes became known in the West as ''vyands de Chypre'', or foods of Cyprus, and the food historian William Woys Weaver has identified over one hundred of them in English, French, Italian and German recipe books of the Middle Ages. One that became particularly popular across Europe in the medieval and early modern periods was a stew made with chicken or fish called ''malmonia'', which in English became mawmeny.
Another example of a Cypriot food ingredient entering the Western European canon is the cauliflower, still popular and used in a variety of ways on the island today, which was associated with Cyprus from the early Middle Ages. Writing in the 12th and 13th centuries the Arab botanists Ibn al-'Awwam and Ibn al-Baitar claimed the vegetable had its origins in Cyprus, and this association with the island was echoed in Western Europe, where cauliflowers were originally known as Cyprus cabbage or ''Cyprus colewart''. There was also a long and extensive trade in cauliflower seeds from Cyprus, until well into the sixteenth century.
Although much of the Lusignan food culture was lost after the fall of Cyprus to the Ottomans in 1571, a number of dishes that would have been familiar to the Lusignans survive today, including various forms of tahini and houmous, zalatina, skordalia and pickled wild song birds called ambelopoulia. Ambelopoulia, which is today highly controversial, and illegal, was exported in vast quantities from Cyprus during the Lusignan and Venetian periods, particularly to Italy and France. In 1533 the English traveller to Cyprus, John Locke, claimed to have seen the pickled wild birds packed into large jars, or which 1200 jars were exported from Cyprus annually.
Also familiar to the Lusignans would have been Halloumi cheese, which some food writers today claim originated in Cyprus during the Byzantine period although the name of the cheese itself is thought by academics to be of Arabic origin.P. Papademas, "Halloumi Cheese" in A.Y. Tamime (ed.), ''Brined Cheeses'' (Oxford: Blackwell Publishing, 2006) p.117 There is no surviving written documentary evidence of the cheese being associated with Cyprus before the year 1554, when the Italian historian Florio Bustron wrote of a sheep-milk cheese from Cyprus he called ''calumi''. Halloumi (Hellim) is commonly served sliced, grilled, fried and sometimes fresh, as an appetiser or meze dish.
During the medieval period, under the French Lusignan monarchs of Cyprus an elaborate form of courtly cuisine developed, fusing French, Byzantine and Middle Eastern forms. The Lusignan kings were known for importing Syrian cooks to Cyprus, and it has been suggested that one of the key routes for the importation of Middle Eastern recipes into France and other Western European countries, such as blancmange, was via the Lusignan Kingdom of Cyprus. These recipes became known in the West as ''vyands de Chypre'', or foods of Cyprus, and the food historian William Woys Weaver has identified over one hundred of them in English, French, Italian and German recipe books of the Middle Ages. One that became particularly popular across Europe in the medieval and early modern periods was a stew made with chicken or fish called ''malmonia'', which in English became mawmeny.
Another example of a Cypriot food ingredient entering the Western European canon is the cauliflower, still popular and used in a variety of ways on the island today, which was associated with Cyprus from the early Middle Ages. Writing in the 12th and 13th centuries the Arab botanists Ibn al-'Awwam and Ibn al-Baitar claimed the vegetable had its origins in Cyprus, and this association with the island was echoed in Western Europe, where cauliflowers were originally known as Cyprus cabbage or ''Cyprus colewart''. There was also a long and extensive trade in cauliflower seeds from Cyprus, until well into the sixteenth century.
Although much of the Lusignan food culture was lost after the fall of Cyprus to the Ottomans in 1571, a number of dishes that would have been familiar to the Lusignans survive today, including various forms of tahini and houmous, zalatina, skordalia and pickled wild song birds called ambelopoulia. Ambelopoulia, which is today highly controversial, and illegal, was exported in vast quantities from Cyprus during the Lusignan and Venetian periods, particularly to Italy and France. In 1533 the English traveller to Cyprus, John Locke, claimed to have seen the pickled wild birds packed into large jars, or which 1200 jars were exported from Cyprus annually.
Also familiar to the Lusignans would have been Halloumi cheese, which some food writers today claim originated in Cyprus during the Byzantine period although the name of the cheese itself is thought by academics to be of Arabic origin.P. Papademas, "Halloumi Cheese" in A.Y. Tamime (ed.), ''Brined Cheeses'' (Oxford: Blackwell Publishing, 2006) p.117 There is no surviving written documentary evidence of the cheese being associated with Cyprus before the year 1554, when the Italian historian Florio Bustron wrote of a sheep-milk cheese from Cyprus he called ''calumi''. Halloumi (Hellim) is commonly served sliced, grilled, fried and sometimes fresh, as an appetiser or meze dish.

 Seafood and fish dishes include squid, octopus, red mullet, and European seabass, sea bass. Cucumber and tomato are used widely in salads. Common vegetable preparations include potatoes in olive oil and parsley, pickled cauliflower and beets, asparagus and taro. Other traditional delicacies are meat marinated in dried coriander seeds and wine, and eventually dried and smoked, such as ''lountza'' (smoked pork loin), charcoal-grilled lamb, souvlaki (pork and chicken cooked over charcoal), and sheftalia (minced meat wrapped in mesentery). ''Pourgouri'' (bulgur, cracked wheat) is the traditional source of carbohydrate other than bread, and is used to make the delicacy Kibbeh, koubes.
Fresh vegetables and fruits are common ingredients. Frequently used vegetables include courgettes, green peppers, okra, green beans, artichokes, carrots, tomatoes, cucumbers, lettuce and grape leaves, and pulses such as beans, broad beans, peas, black-eyed beans, chick-peas and lentils. The most common fruits and nuts are pears, apples, grapes, oranges, mandarin orange, mandarines, nectarines, medlar, blackberries, cherry, strawberries, figs, watermelon, melon, avocado, lemon, pistachio, almond, chestnut, walnut, and hazelnut.
Cyprus is also well known for its desserts, including ''lokum'' (also known as Turkish delight) and Soutzoukos.Cyprus villagers make giant sweet
Seafood and fish dishes include squid, octopus, red mullet, and European seabass, sea bass. Cucumber and tomato are used widely in salads. Common vegetable preparations include potatoes in olive oil and parsley, pickled cauliflower and beets, asparagus and taro. Other traditional delicacies are meat marinated in dried coriander seeds and wine, and eventually dried and smoked, such as ''lountza'' (smoked pork loin), charcoal-grilled lamb, souvlaki (pork and chicken cooked over charcoal), and sheftalia (minced meat wrapped in mesentery). ''Pourgouri'' (bulgur, cracked wheat) is the traditional source of carbohydrate other than bread, and is used to make the delicacy Kibbeh, koubes.
Fresh vegetables and fruits are common ingredients. Frequently used vegetables include courgettes, green peppers, okra, green beans, artichokes, carrots, tomatoes, cucumbers, lettuce and grape leaves, and pulses such as beans, broad beans, peas, black-eyed beans, chick-peas and lentils. The most common fruits and nuts are pears, apples, grapes, oranges, mandarin orange, mandarines, nectarines, medlar, blackberries, cherry, strawberries, figs, watermelon, melon, avocado, lemon, pistachio, almond, chestnut, walnut, and hazelnut.
Cyprus is also well known for its desserts, including ''lokum'' (also known as Turkish delight) and Soutzoukos.Cyprus villagers make giant sweet
, ''BBC News'', 18 October 2004 This island has Protected geographical indications in the European Union#General regime, protected geographical indication (PGI) for its ''lokum'' produced in the village of Geroskipou.
 Sport governing bodies include the Cyprus Football Association, Cyprus Basketball Federation, Cyprus Volleyball Federation, Cyprus Automobile Association, Cyprus Badminton Federation, Cyprus Cricket Association, Cyprus Rugby Federation and the Cyprus Pool Association.
Notable sports teams in the Cyprus leagues include APOEL FC, Anorthosis Famagusta FC, AC Omonia, AEL Lemesos, Apollon Limassol FC, Apollon FC, Nea Salamis Famagusta FC, Olympiakos Nicosia, AEK Larnaca FC, AEL Limassol B.C., Keravnos B.C. and Apollon Limassol B.C. Stadiums or sports venues include the GSP Stadium (the largest in the Republic of Cyprus-controlled areas), Tsirion Stadium (second largest), Neo GSZ Stadium, Antonis Papadopoulos Stadium, Ammochostos Stadium and Makario Stadium.
In the 2008–09 season, Anorthosis Famagusta FC was the first Cypriot team to qualify for the UEFA Champions League Group stage. Next season, APOEL FC qualified for the UEFA Champions League group stage, and reached the last 8 of the 2011–12 UEFA Champions League after finishing top of its group and beating French Olympique Lyonnais in the Round of 16.
The Cyprus national rugby union team known as ''The Moufflons'' currently holds the record for most consecutive international wins, which is especially notable as the Cyprus Rugby Federation was only formed in 2006.
Tennis player Marcos Baghdatis was ranked 8th in the world, was a finalist at the Australian Open, and reached the The Championships, Wimbledon, Wimbledon semi-final, all in 2006. High jumper Kyriakos Ioannou achieved a jump of 2.35 m at the 11th IAAF World Championships in Athletics in Osaka, Japan, in 2007, winning the bronze medal. He has been ranked third in the world. In motorsports, Tio Ellinas is a successful race car driver, currently racing in the GP3 Series for Marussia Manor Motorsport. There is also mixed martial artist Costas Philippou, who competes in the Ultimate Fighting Championship promotion's middleweight division. Costas holds a 6–3 record in UFC bouts, and recently defeated "The Monsoon" Lorenz Larkin by a knockout in the first round.
Also notable for a Mediterranean island, the siblings Christopher Papamichalopoulos, Christopher and Sophia Papamichalopoulou qualified for the 2010 Winter Olympics in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. They were the only athletes who managed to qualify and thus represented Cyprus at the 2010 Winter Olympics.
The country's first ever Olympic medal, a silver medal, was won by the sailor Pavlos Kontides, at the 2012 Summer Olympics in the Sailing at the 2012 Summer Olympics – Men's Laser class, Men's Laser class.
Sport governing bodies include the Cyprus Football Association, Cyprus Basketball Federation, Cyprus Volleyball Federation, Cyprus Automobile Association, Cyprus Badminton Federation, Cyprus Cricket Association, Cyprus Rugby Federation and the Cyprus Pool Association.
Notable sports teams in the Cyprus leagues include APOEL FC, Anorthosis Famagusta FC, AC Omonia, AEL Lemesos, Apollon Limassol FC, Apollon FC, Nea Salamis Famagusta FC, Olympiakos Nicosia, AEK Larnaca FC, AEL Limassol B.C., Keravnos B.C. and Apollon Limassol B.C. Stadiums or sports venues include the GSP Stadium (the largest in the Republic of Cyprus-controlled areas), Tsirion Stadium (second largest), Neo GSZ Stadium, Antonis Papadopoulos Stadium, Ammochostos Stadium and Makario Stadium.
In the 2008–09 season, Anorthosis Famagusta FC was the first Cypriot team to qualify for the UEFA Champions League Group stage. Next season, APOEL FC qualified for the UEFA Champions League group stage, and reached the last 8 of the 2011–12 UEFA Champions League after finishing top of its group and beating French Olympique Lyonnais in the Round of 16.
The Cyprus national rugby union team known as ''The Moufflons'' currently holds the record for most consecutive international wins, which is especially notable as the Cyprus Rugby Federation was only formed in 2006.
Tennis player Marcos Baghdatis was ranked 8th in the world, was a finalist at the Australian Open, and reached the The Championships, Wimbledon, Wimbledon semi-final, all in 2006. High jumper Kyriakos Ioannou achieved a jump of 2.35 m at the 11th IAAF World Championships in Athletics in Osaka, Japan, in 2007, winning the bronze medal. He has been ranked third in the world. In motorsports, Tio Ellinas is a successful race car driver, currently racing in the GP3 Series for Marussia Manor Motorsport. There is also mixed martial artist Costas Philippou, who competes in the Ultimate Fighting Championship promotion's middleweight division. Costas holds a 6–3 record in UFC bouts, and recently defeated "The Monsoon" Lorenz Larkin by a knockout in the first round.
Also notable for a Mediterranean island, the siblings Christopher Papamichalopoulos, Christopher and Sophia Papamichalopoulou qualified for the 2010 Winter Olympics in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. They were the only athletes who managed to qualify and thus represented Cyprus at the 2010 Winter Olympics.
The country's first ever Olympic medal, a silver medal, was won by the sailor Pavlos Kontides, at the 2012 Summer Olympics in the Sailing at the 2012 Summer Olympics – Men's Laser class, Men's Laser class.
excerpt
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Sacopoulo, Marina (1966). ''Chypre d'aujourd'hui''. Paris: G.-P. Maisonneuve et Larose. 406 p., ill. with b&w photos. and fold. maps. * *
Cyprus
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Timeline of Cyprus by BBC
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs''
Cyprus
information from the United States Department of State includes Background Notes, Country Study and major reports *
Cyprus profile
from the BBC News
The UN in Cyprus
Cypriot Pottery, Bryn Mawr College Art and Artifact Collections
''The Cesnola collection of Cypriot art : stone sculpture''
a fully digitised text from The Metropolitan Museum of Art libraries * http://cypernochkreta.dinstudio.se Government
Cyprus High Commission Trade Centre – London
Republic of Cyprus – English Language
Press and Information Office – Ministry of Interior
Annan Plan
Tourism
Read about Cyprus on visitcyprus.com
– the official travel portal for Cyprus
Cyprus informational portal and open platform for contribution of Cyprus-related content
– www.Cyprus.com * Official publications
* [http://www.moi.gov.cy/moi/pio/pio.nsf/All/BD477C55623013C5C2256D740027CF98?OpenDocument Legal Issues arising from certain population transfers and displacements on the territory of the Republic of Cyprus in the period since 20 July 1974]
Address to Cypriots by President Papadopoulos (FULL TEXT)
Official Cyprus Government Web Site
Embassy of Greece, USA – Cyprus: Geographical and Historical Background
{{coord, 35, N, 33, E, type:country_region:CY_scale:2500000_source:GNS , display=title Cyprus, Republics in the Commonwealth of Nations Eastern Mediterranean International islands Island countries Islands of Asia Islands of Europe Mediterranean islands Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the European Union Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean Member states of the United Nations Middle Eastern countries Near Eastern countries Southeastern European countries Southern European countries Western Asian countries States and territories established in 1960 Countries in Asia Countries in Europe Greek-speaking countries and territories Turkish-speaking countries and territories Countries of Europe with multiple official languages
island country
An island country, island state or an island nation is a country whose primary territory consists of one or more islands or parts of islands. Approximately 25% of all independent countries are island countries. Island countries are historically ...
located south of the Anatolian Peninsula
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The reg ...
in the eastern Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
. Its continental position is disputed; while it is geographically in Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
, its cultural ties and geopolitics are overwhelmingly Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern regions of Europe, region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countrie ...
an. Cyprus is the third-largest and third-most populous island in the Mediterranean. It is located north of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
, east of Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
, south of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
, and west of Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus li ...
and Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
. Its capital and largest city is Nicosia
Nicosia ( ; el, Λευκωσία, Lefkosía ; tr, Lefkoşa ; hy, Նիկոսիա, romanized: ''Nikosia''; Cypriot Arabic: Nikusiya) is the largest city, capital, and seat of government of Cyprus. It is located near the centre of the Mesaor ...
. The northeast portion of the island is ''de facto'' governed by the self-declared Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus ( tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs), officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC; tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti, ''KKTC''), is a ''de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the island of Cyprus. Recog ...
, which was established after the 1974 invasion and which is recognised as a country only by Turkey.
The earliest known human activity on the island dates to around the 10th millennium BC
The 10th millennium BC spanned the years 10,000 BC to 9001 BC (c. 12 ka to c. 11 ka). It marks the beginning of the transition from the Palaeolithic to the Neolithic via the interim Mesolithic ( Northern Europe and Western Europe) and Epip ...
. Archaeological remains include the well-preserved ruins from the Hellenistic period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 3 ...
such as Salamis and Kourion
Kourion ( grc, Koύριov; la, Curium) was an important ancient Greek city-state on the southwestern coast of Cyprus. In the twelfth century BCE, after the collapse of the Mycenaean palaces, Greek settlers from Argos arrived on this site.
I ...
, and Cyprus is home to some of the oldest water wells in the world. Cyprus was settled by Mycenaean Greeks
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in Ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainland ...
in two waves in the 2nd millennium BC. As a strategic location in the Eastern Mediterranean
Eastern Mediterranean is a loose definition of the eastern approximate half, or third, of the Mediterranean Sea, often defined as the countries around the Levantine Sea.
It typically embraces all of that sea's coastal zones, referring to communi ...
, it was subsequently occupied by several major powers
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power in ...
, including the empires of the Assyrians, Egyptians
Egyptians ( arz, المَصرِيُون, translit=al-Maṣriyyūn, ; arz, المَصرِيِين, translit=al-Maṣriyyīn, ; cop, ⲣⲉⲙⲛ̀ⲭⲏⲙⲓ, remenkhēmi) are an ethnic group native to the Nile, Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian ...
and Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
, from whom the island was seized in 333 BC by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
. Subsequent rule by Ptolemaic Egypt, the Classical and Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
s for a short period, the French Lusignan dynasty
The House of Lusignan ( ; ) was a royal house of French origin, which at various times ruled several principalities in Europe and the Levant, including the kingdoms of Jerusalem, Cyprus, and Armenia, from the 12th through the 15th centuries du ...
and the Venetians was followed by over three centuries of Ottoman rule
Ottoman is the Turkish spelling of the Arabic masculine given name Uthman ( ar, عُثْمان, ‘uthmān). It may refer to:
Governments and dynasties
* Ottoman Caliphate, an Islamic caliphate from 1517 to 1924
* Ottoman Empire, in existence fro ...
between 1571 and 1878 (''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally ...
'' until 1914).
Cyprus was placed under the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
's administration based on the Cyprus Convention
The Cyprus Convention of 4 June 1878 was a secret agreement reached between Great Britain and the Ottoman Empire which granted administrative control of Cyprus to Britain (see British Cyprus), in exchange for its support of the Ottomans during ...
in 1878 and was formally annexed by the UK in 1914. The future of the island became a matter of disagreement between the two prominent ethnic communities, Greek Cypriots
Greek Cypriots or Cypriot Greeks ( el, Ελληνοκύπριοι, Ellinokýprioi, tr, Kıbrıs Rumları) are the ethnic Greek population of Cyprus, forming the island's largest ethnolinguistic community. According to the 2011 census, 659,115 r ...
, who made up 77% of the population in 1960, and Turkish Cypriots
Turkish Cypriots or Cypriot Turks ( tr, Kıbrıs Türkleri or ''Kıbrıslı Türkler''; el, Τουρκοκύπριοι, Tourkokýprioi) are ethnic Turks originating from Cyprus. Following the Ottoman conquest of the island in 1571, about 30,00 ...
, who made up 18% of the population. From the 19th century onwards, the Greek Cypriot population pursued ''enosis
''Enosis'' ( el, Ένωσις, , "union") is the movement of various Greek communities that live outside Greece for incorporation of the regions that they inhabit into the Greek state. The idea is related to the Megali Idea, an irredentist conc ...
'', union with Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
, which became a Greek national policy in the 1950s. The Turkish Cypriot population initially advocated the continuation of the British rule, then demanded the annexation of the island to Turkey, and in the 1950s, together with Turkey, established a policy of '' taksim'', the partition of Cyprus and the creation of a Turkish polity in the north.
Following nationalist violence in the 1950s, Cyprus was granted independence in 1960. The crisis of 1963–64 brought further intercommunal violence between the two communities, displaced more than 25,000 Turkish Cypriots into enclaves
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
and brought the end of Turkish Cypriot representation in the republic. On 15 July 1974, a coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
was staged by Greek Cypriot nationalists and elements of the Greek military junta
The Greek junta or Regime of the Colonels, . Also known within Greece as just the Junta ( el, η Χούντα, i Choúnta, links=no, ), the Dictatorship ( el, η Δικτατορία, i Diktatoría, links=no, ) or the Seven Years ( el, η Ε ...
in an attempt at ''enosis''. This action precipitated the Turkish invasion of Cyprus
The Turkish invasion of Cyprus began on 20 July 1974 and progressed in two phases over the following month. Taking place upon a background of Cypriot intercommunal violence, intercommunal violence between Greek Cypriots, Greek and Turkish ...
on 20 July, which led to the capture of the present-day territory of Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus ( tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs), officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC; tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti, ''KKTC''), is a ''de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the Geography of Cyprus, isl ...
and the displacement
Displacement may refer to:
Physical sciences
Mathematics and Physics
*Displacement (geometry), is the difference between the final and initial position of a point trajectory (for instance, the center of mass of a moving object). The actual path ...
of over 150,000 Greek Cypriots and 50,000 Turkish Cypriots. A separate Turkish Cypriot state in the north was established by unilateral declaration in 1983; the move was widely condemned by the international community
The international community is an imprecise phrase used in geopolitics and international relations to refer to a broad group of people and governments of the world.
As a rhetorical term
Aside from its use as a general descriptor, the term is ...
, with Turkey alone recognising the new state. These events and the resulting political situation are matters of a continuing dispute.
Cyprus is a major tourist destination in the Mediterranean. With an advanced, high-income economy
A high-income economy is defined by the World Bank as a nation with a gross national income per capita of US$12,696 or more in 2020, calculated using the Atlas method. While the term "high-income" is often used interchangeably with " First Worl ...
and a very high Human Development Index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, whi ...
, the Republic of Cyprus has been a member of the Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
since 1961 and was a founding member of the Non-Aligned Movement
The Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) is a forum of 120 countries that are not formally aligned with or against any major power bloc. After the United Nations, it is the largest grouping of states worldwide.
The movement originated in the aftermath o ...
until it joined the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
on 1 May 2004. On 1 January 2008, the Republic of Cyprus joined the eurozone
The euro area, commonly called eurozone (EZ), is a currency union of 19 member states of the European Union (EU) that have adopted the euro (€) as their primary currency and sole legal tender, and have thus fully implemented EMU policies ...
.
Etymology
 The earliest attested reference to ''Cyprus'' is the 15th century BC
The earliest attested reference to ''Cyprus'' is the 15th century BC Mycenaean Greek
Mycenaean Greek is the most ancient attested form of the Greek language, on the Greek mainland and Crete in Mycenaean Greece (16th to 12th centuries BC), before the hypothesised Dorian invasion, often cited as the ''terminus ad quem'' for the ...
, ''ku-pi-ri-jo'', meaning "Cypriot" (Greek: ), written in Linear B
Linear B was a syllabic script used for writing in Mycenaean Greek, the earliest attested form of Greek. The script predates the Greek alphabet by several centuries. The oldest Mycenaean writing dates to about 1400 BC. It is descended from ...
syllabic script.
The classical Greek form of the name is (''Kýpros'').
The etymology of the name is unknown.
Suggestions include:
* the Greek word for the Mediterranean cypress tree (''Cupressus sempervirens
''Cupressus sempervirens'', the Mediterranean cypress (also known as Italian cypress, Tuscan cypress, Persian cypress, or pencil pine), is a species of cypress native to the eastern Mediterranean region, in northeast Libya, southern Albania, sou ...
''), κυπάρισσος (''kypárissos'')
* the Greek name of the henna tree (''Lawsonia alba''), κύπρος (''kýpros'')
* an Eteocypriot
Eteocypriot is an extinct pre-Indo-European language that was spoken in Cyprus by the pre-Hellenic population until the Iron Age. The name means "true" or "original Cypriot" parallel to Eteocretan, both of which names are used by modern scholars ...
word for copper. It has been suggested, for example, that it has roots in the Sumerian word for copper (''zubar'') or for bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
(''kubar''), from the large deposits of copper ore found on the island.
Through overseas trade, the island has given its name to the Classical Latin
Classical Latin is the form of Literary Latin recognized as a literary standard by writers of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. It was used from 75 BC to the 3rd century AD, when it developed into Late Latin. In some later periods ...
word for copper through the phrase ''aes Cyprium'', "metal of Cyprus", later shortened to ''Cuprum''. R. S. P. Beekes, ''Etymological Dictionary of Greek'', Brill, 2009, p. 805 (''s.v.'' "Κύπρος").
The standard demonym
A demonym (; ) or gentilic () is a word that identifies a group of people (inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place (hamlet, village, town, city, region, province, ...
relating to Cyprus or its people or culture is ''Cypriot
Cypriot (in older sources often "Cypriote") refers to someone or something of, from, or related to the country of Cyprus.
* Cypriot people, or of Cypriot descent; this includes:
**Armenian Cypriots
**Greek Cypriots
**Maronite Cypriots
**Turkish C ...
''. The terms ''Cypriote'' and ''Cyprian'' (later a personal name) are also used, though less frequently.
The state's official name in Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
literally translates to "Cypriot Republic" in English, but this translation is not used officially; "Republic of Cyprus" is used instead.
History

Prehistoric and Ancient Cyprus
The earliest confirmed site of human activity on Cyprus isAetokremnos
Aetokremnos is a rock shelter near Limassol on the southern coast of Cyprus. It is situated on a steep cliff site c. above the Mediterranean sea. The name means ''"Cliff of the eagles"'' in Greek. Around have been excavated and out of the four l ...
, situated on the south coast, indicating that hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
s were active on the island from around 10,000 BC, with settled village communities
The study of village communities has become one of the fundamental methods of discussing the ancient history of institutions.
Wales
Frederic Seebohm has called our attention to the interesting surveys of Welsh tracts of country made in the ...
dating from 8200 BC. The arrival of the first humans correlates with the extinction of the 75 cm high Cyprus dwarf hippopotamus and 1 metre tall Cyprus dwarf elephant, the only large mammals native to the island. Water well
A well is an excavation or structure created in the ground by digging, driving, or drilling to access liquid resources, usually water. The oldest and most common kind of well is a water well, to access groundwater in underground aquifers. Th ...
s discovered by archaeologist
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
s in western Cyprus are believed to be among the oldest in the world, dated at 9,000 to 10,500 years old.
Remains of an 8-month-old cat were discovered buried with a human body at a separate Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
site in Cyprus. The grave is estimated to be 9,500 years old (7500 BC), predating ancient Egyptian civilisation and pushing back the earliest known feline-human association significantly. The remarkably well-preserved Neolithic village of Khirokitia
Khirokitia (sometimes spelled Choirokoitia; el, Χοιροκοιτία , suggested meaning ''Pig-cradle'', from 'pig, boar' + 'place of origin, cradle'; tr, Hirokitya) is an archaeological site on the island of Cyprus dating from the Neolit ...
is a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
, dating to approximately 6800 BC.
During the Late Bronze Age, the island experienced two waves of Greek settlement.Thomas, Carol G. and Conant, Craig: ''The Trojan War'', pp. 121–122. Greenwood Publishing Group, 2005. , 9780313325267. The first wave consisted of Mycenaean Greek
Mycenaean Greek is the most ancient attested form of the Greek language, on the Greek mainland and Crete in Mycenaean Greece (16th to 12th centuries BC), before the hypothesised Dorian invasion, often cited as the ''terminus ad quem'' for the ...
traders, who started visiting Cyprus around 1400 BC. A major wave of Greek settlement is believed to have taken place following the Late Bronze Age collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a time of widespread societal collapse during the 12th century BC, between c. 1200 and 1150. The collapse affected a large area of the Eastern Mediterranean (North Africa and Southeast Europe) and the Near East ...
of Mycenaean Greece from 1100 to 1050 BC, with the island's predominantly Greek character dating from this period. The first recorded name of a Cypriot king is ''Kushmeshusha'', as appears on letters sent to Ugarit in the 13th century BCE. Cyprus occupies an important role in Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical co ...
, being the birthplace of Aphrodite
Aphrodite ( ; grc-gre, Ἀφροδίτη, Aphrodítē; , , ) is an ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, and procreation. She was syncretized with the Roman goddess . Aphrodite's major symbols include ...
and Adonis
In Greek mythology, Adonis, ; derived from the Canaanite word ''ʼadōn'', meaning "lord". R. S. P. Beekes, ''Etymological Dictionary of Greek'', Brill, 2009, p. 23. was the mortal lover of the goddess Aphrodite.
One day, Adonis was gored by ...
, and home to King Cinyras, Teucer
In Greek mythology, Teucer (), also Teucrus, Teucros or Teucris ( grc, Τεῦκρος, Teûkros), was the son of King Telamon of Salamis Island and his second wife Hesione, daughter of King Laomedon of Troy. He fought alongside his half-bro ...
and Pygmalion
Pygmalion or Pigmalion may refer to:
Mythology
* Pygmalion (mythology), a sculptor who fell in love with his statue
Stage
* ''Pigmalion'' (opera), a 1745 opera by Jean-Philippe Rameau
* ''Pygmalion'' (Rousseau), a 1762 melodrama by Jean-Jacques ...
. Literary evidence suggests an early Phoenician presence at Kition
Kition (Egyptian language, Egyptian: ; Phoenician language, Phoenician: , , or , ; Ancient Greek: , ; Latin: ) was a petty kingdom, city-kingdom on the southern coast of Cyprus (in present-day Larnaca). According to the text on the plaque clos ...
, which was under Tyrian Tyrian may refer to the following:
* Tyrian, an adjective for Tyre, a city in the South Governorate of Lebanon
* ''Tyrian'' (video game), an arcade-style shooter video game by Epic MegaGames
* Tyrian purple, a colour
* Tyrian, a person who worsh ...
rule at the beginning of the 10th century BC. Some Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their histor ...
n merchants who were believed to come from Tyre colonised
Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territory. When ...
the area and expanded the political influence of Kition. After c. 850 BC, the sanctuaries t the Kathari site
T, or t, is the twentieth Letter (alphabet), letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabe ...
were rebuilt and reused by the Phoenicians. Cyprus is at a strategic location in the Middle East. It was ruled by the
Cyprus is at a strategic location in the Middle East. It was ruled by the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
for a century starting in 708 BC, before a brief spell under Egyptian rule and eventually Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
rule in 545 BC. The Cypriots, led by Onesilus
Onesilus or Onesilos ( el, Ὀνήσιλος, "useful one"; died 497 BC) was the brother of king Gorgos (Gorgus) of the Greek city-state of Salamis on the island of Cyprus. He is known only through the work of Herodotus (''Histories'', V.104–115 ...
, king of Salamis, joined their fellow Greeks in the Ionia
Ionia () was an ancient region on the western coast of Anatolia, to the south of present-day Izmir. It consisted of the northernmost territories of the Ionian League of Greek settlements. Never a unified state, it was named after the Ionian ...
n cities during the unsuccessful Ionian Revolt
The Ionian Revolt, and associated revolts in Aeolis, Doris, Cyprus and Caria, were military rebellions by several Greek regions of Asia Minor against Persian rule, lasting from 499 BC to 493 BC. At the heart of the rebellion was the dissatisf ...
in 499 BC against the Achaemenids. The revolt was suppressed, but Cyprus managed to maintain a high degree of autonomy and remained inclined towards the Greek world.
During the whole period of the Persian rule, there is a continuity in the reign of the Cypriot kings and during their rebellions they were crushed by Persian rulers from Asia Minor, which is an indication that the Cypriots were ruling the island with directly regulated relations with the Great King and there wasn't a Persian satrap.ALEXANDER_THE_GREAT_AND_THE_KINGDOMS_OF_CYPRUS_A_RECONSIDERATION ALEXANDER THE GREAT AND THE KINGDOMS OF CYPRUS -- A RECONSIDERATION/ref> The Kingdoms of Cyprus enjoyed special privileges and a semi-autonomous status, but they were still considered vassal subjects of the Great King. The island was conquered by
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
in 333 BC and Cypriot navy helped Alexander during the Siege of Tyre (332 BC)
The Siege of Tyre was orchestrated by Alexander the Great in 332 BC during his campaigns against the Persians. The Macedonian army was unable to capture the city, which was a strategic coastal base on the Mediterranean Sea, through convention ...
. Cypriot fleet were also sent to help Amphoterus (admiral)
Amphoterus (Greek: ) the brother of Craterus, was appointed by Alexander the Great commander of the fleet in the Hellespont in 333 BC. Amphoterus' appointment recognized his successful attempts to subdue the islands between Greece and Asia which h ...
. In addition, Alexander had two Cypriot generals Stasander and Stasanor Stasanor ( grc, Στασάνωρ; lived 4th century BC) was a native of Soli in Cyprus, who held a distinguished position among the officers of Alexander the Great.
Stasanor, officer of Alexander
Stasanor probably entered the service of Alexander ...
both from the Soli and later both became satraps in Alexander's empire.
Following Alexander's death, the division of his empire, and the subsequent Wars of the Diadochi
The Wars of the Diadochi ( grc, Πόλεμοι τῶν Διαδόχων, '), or Wars of Alexander's Successors, were a series of conflicts that were fought between the generals of Alexander the Great, known as the Diadochi, over who would rule h ...
, Cyprus became part of the Hellenistic empire
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 3 ...
of Ptolemaic Egypt. It was during this period that the island was fully Hellenized
Hellenization (other British spelling Hellenisation) or Hellenism is the adoption of Greek culture, religion, language and identity by non-Greeks. In the ancient period, colonization often led to the Hellenization of indigenous peoples; in th ...
. In 58 BC Cyprus was acquired by the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Kin ...
.
Roman Cyprus
Middle Ages

 When the
When the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
was divided into Eastern and Western parts in 286, Cyprus became part of the East Roman Empire (also called the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
), and would remain so for some 900 years. Under Byzantine rule, the Greek orientation that had been prominent since antiquity developed the strong Hellenistic-Christian character that continues to be a hallmark of the Greek Cypriot community.
Beginning in 649, Cyprus endured several attacks launched by raiders from the Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is eq ...
, which continued for the next 300 years. Many were quick piratical raids, but others were large-scale attacks in which many Cypriots were slaughtered and great wealth carried off or destroyed. There are no Byzantine churches which survive from this period; thousands of people were killed, and many cities – such as Salamis – were destroyed and never rebuilt. Byzantine rule was restored in 965, when Emperor Nikephoros II Phokas
Nikephoros II Phokas (; – 11 December 969), Latinized Nicephorus II Phocas, was Byzantine emperor from 963 to 969. His career, not uniformly successful in matters of statecraft or of war, nonetheless included brilliant military exploits whi ...
scored decisive victories on land and sea.
In 1156 Raynald of Châtillon
Raynald of Châtillon (french: Renaud; 11254 July 1187), also known as Reynald or Reginald, was a Crusader knight of French origin but also Prince of Antioch from 1153 to 1160 or 1161, and Lord of Oultrejordain from 1175 until his death. He wa ...
and Thoros II of Armenia
Thoros II, Prince of Armenia, also known as Toros II the Great ( hy, Թորոս Բ) or Thoros II the Great, (unknown – February 6, 1169) was the sixth Lord of Armenian Cilicia from the Rubenid dynasty from 1144/1145–1169. Referred to as the � ...
brutally sacked Cyprus over a period of three weeks, stealing so much plunder and capturing so many of the leading citizens and their families for ransom, that the island took generations to recover. Several Greek priests were mutilated and sent away to Constantinople.
In 1185 Isaac Komnenos, a member of the Byzantine imperial family, took over Cyprus and declared it independent of the Empire. In 1191, during the Third Crusade
The Third Crusade (1189–1192) was an attempt by three European monarchs of Western Christianity (Philip II of France, Richard I of England and Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor) to reconquer the Holy Land following the capture of Jerusalem by ...
, Richard I of England
Richard I (8 September 1157 – 6 April 1199) was King of England from 1189 until his death in 1199. He also ruled as Duke of Normandy, Aquitaine and Gascony, Lord of Cyprus, and Count of Poitiers, Anjou, Maine, and Nantes, and was ...
captured the island from Isaac. He used it as a major supply base that was relatively safe from the Saracen
upright 1.5, Late 15th-century German woodcut depicting Saracens
Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek and Latin writings, to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Romans as Arabia Pe ...
s. A year later Richard sold the island to the Knights Templar
, colors = White mantle with a red cross
, colors_label = Attire
, march =
, mascot = Two knights riding a single horse
, equipment ...
, who, following a bloody revolt, in turn sold it to Guy of Lusignan
Guy of Lusignan (c. 1150 – 18 July 1194) was a French Poitevin knight, son of Hugh VIII of Lusignan and as such born of the House of Lusignan. He was king of Jerusalem from 1186 to 1192 by right of marriage to Sibylla of Jerusalem, and King o ...
. His brother and successor Aimery was recognised as King of Cyprus
The Kingdom of Cyprus (french: Royaume de Chypre, la, Regnum Cypri) was a state that existed between 1192 and 1489. It was ruled by the French House of Lusignan. It comprised not only the island of Cyprus, but it also had a foothold on the Anat ...
by Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry VI (German: ''Heinrich VI.''; November 1165 – 28 September 1197), a member of the Hohenstaufen dynasty, was King of Germany ( King of the Romans) from 1169 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1191 until his death. From 1194 he was also King of S ...
.
Following the death in 1473 of James II, the last Lusignan king, the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia, ...
assumed control of the island, while the late king's Venetian widow, Queen Catherine Cornaro
Catherine Cornaro ( el, Αικατερίνη Κορνάρο, vec, Catarina Corner) (25 November 1454 – 10 July 1510) was the last monarch of the Kingdom of Cyprus, also holding the titles of the Queen of Jerusalem and Armenia. She was queen ...
, reigned as figurehead. Venice formally annexed the Kingdom of Cyprus
The Kingdom of Cyprus (french: Royaume de Chypre, la, Regnum Cypri) was a state that existed between 1192 and 1489. It was ruled by the French House of Lusignan. It comprised not only the island of Cyprus, but it also had a foothold on the Anat ...
in 1489, following the abdication of Catherine. The Venetians fortified Nicosia
Nicosia ( ; el, Λευκωσία, Lefkosía ; tr, Lefkoşa ; hy, Նիկոսիա, romanized: ''Nikosia''; Cypriot Arabic: Nikusiya) is the largest city, capital, and seat of government of Cyprus. It is located near the centre of the Mesaor ...
by building the Walls of Nicosia
The Walls of Nicosia, also known as the Venetian Walls, are a series of defensive walls which surround Nicosia the capital city of Cyprus. The first city walls were built in the Middle Ages, but they were completely rebuilt in the mid-16th cent ...
, and used it as an important commercial hub. Throughout Venetian rule, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
frequently raided Cyprus. In 1539 the Ottomans destroyed Limassol
Limassol (; el, Λεμεσός, Lemesós ; tr, Limasol or ) is a city on the southern coast of Cyprus and capital of the district with the same name. Limassol is the second largest urban area in Cyprus after Nicosia, with an urban population ...
and so fearing the worst, the Venetians also fortified Famagusta
Famagusta ( , ; el, Αμμόχωστος, Ammóchostos, ; tr, Gazimağusa or ) is a city on the east coast of Geography of Cyprus, Cyprus. It is located east of Nicosia District, Nicosia and possesses the deepest harbour of the island. Duri ...
and Kyrenia
Kyrenia ( el, Κερύνεια ; tr, Girne ) is a city on the northern coast of Cyprus, noted for its historic harbour and castle. It is under the ''de facto'' control of Northern Cyprus.
While there is evidence showing that the wider region ...
.
Although the Lusignan French aristocracy remained the dominant social class in Cyprus throughout the medieval period, the former assumption that Greeks were treated only as serfs on the island is no longer considered by academics to be accurate. It is now accepted that the medieval period saw increasing numbers of Greek Cypriots elevated to the upper classes, a growing Greek middle ranks, and the Lusignan royal household even marrying Greeks. This included King John II of Cyprus
John II or III of Cyprus (16 May 1418 – 28 July 1458) was the King of Cyprus and Armenian Cilicia, Armenia and also titular King of Jerusalem from 1432 to 1458. He was previously a titular Prince of Antioch.
History
Born 16 May 1418 in Nicos ...
who married Helena Palaiologina
Helena Palaiologina ( el, ; 3 February 1428 – 11 April 1458) was a Byzantine princess of the Palaiologos family, who became Queen of Cyprus and Armenia, titular Queen consort of Jerusalem, and Princess of Antioch through her marriage to King ...
.
Cyprus under the Ottoman Empire
 In 1570, a full-scale Ottoman assault with 60,000 troops brought the island under Ottoman control, despite stiff resistance by the inhabitants of Nicosia and Famagusta. Ottoman forces capturing Cyprus
In 1570, a full-scale Ottoman assault with 60,000 troops brought the island under Ottoman control, despite stiff resistance by the inhabitants of Nicosia and Famagusta. Ottoman forces capturing Cyprus massacred
A massacre is the killing of a large number of people or animals, especially those who are not involved in any fighting or have no way of defending themselves. A massacre is generally considered to be morally unacceptable, especially when per ...
many Greek and Armenian Christian inhabitants. The previous Latin elite were destroyed and the first significant demographic change since antiquity took place with the formation of a Muslim community. Soldiers who fought in the conquest settled on the island and Turkish peasants and craftsmen were brought to the island from Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
. This new community also included banished Anatolian tribes, "undesirable" persons and members of various "troublesome" Muslim sects, as well as a number of new converts on the island.
 The Ottomans abolished the
The Ottomans abolished the feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in Middle Ages, medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a wa ...
system previously in place and applied the millet system
In the Ottoman Empire, a millet (; ar, مِلَّة) was an independent court of law pertaining to "personal law" under which a confessional community (a group abiding by the laws of Muslim Sharia, Christian Canon law, or Jewish Halakha) was ...
to Cyprus, under which non-Muslim peoples were governed by their own religious authorities. In a reversal from the days of Latin rule, the head of the Church of Cyprus
The Church of Cyprus ( el, Ἐκκλησία τῆς Κύπρου, translit=Ekklisia tis Kyprou; tr, Kıbrıs Kilisesi) is one of the autocephalous Greek Orthodox churches that together with other Eastern Orthodox churches form the communio ...
was invested as leader of the Greek Cypriot population and acted as mediator between Christian Greek Cypriots and the Ottoman authorities. This status ensured that the Church of Cyprus was in a position to end the constant encroachments of the Roman Catholic Church. Ottoman rule of Cyprus was at times indifferent, at times oppressive, depending on the temperaments of the sultans and local officials, and the island began over 250 years of economic decline.Cyprus – Ottoman Rule, ''U.S. Library of Congress'' The ratio of Muslims to Christians fluctuated throughout the period of Ottoman domination. In 1777–78, 47,000 Muslims constituted a majority over the island's 37,000 Christians. By 1872, the population of the island had risen to 144,000, comprising 44,000 Muslims and 100,000 Christians. The Muslim population included numerous crypto-Christians, including the Linobambaki, a crypto-Catholic community that arose due to religious persecution of the Catholic community by the Ottoman authorities; this community would assimilate into the Turkish Cypriot community during British rule. As soon as the
Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. The Greeks were later assisted by ...
broke out in 1821, several Greek Cypriots left for Greece to join the Greek forces. In response, the Ottoman governor of Cyprus arrested and executed 486 prominent Greek Cypriots, including the Archbishop of Cyprus, Kyprianos
Archbishop Kyprianos of Cyprus ( el, Αρχιεπίσκοπος Κύπρου Κυπριανός) was the head of the Cypriot Orthodox Church in the early 19th century at the time that the Greek War of Independence broke out.
Kyprianos was born i ...
, and four other bishops. In 1828, modern Greece's first president Ioannis Kapodistrias
Count Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias (10 or 11 February 1776 – 9 October 1831), sometimes anglicized as John Capodistrias ( el, Κόμης Ιωάννης Αντώνιος Καποδίστριας, Komis Ioannis Antonios Kapodistrias; russian: � ...
called for union of Cyprus with Greece, and numerous minor uprisings took place. Reaction to Ottoman misrule led to uprisings by both Greek and Turkish Cypriots, although none were successful. After centuries of neglect by the Ottoman Empire, the poverty of most of the people and the ever-present tax collectors fuelled Greek nationalism, and by the 20th century the idea of ''enosis
''Enosis'' ( el, Ένωσις, , "union") is the movement of various Greek communities that live outside Greece for incorporation of the regions that they inhabit into the Greek state. The idea is related to the Megali Idea, an irredentist conc ...
'', or union, with newly independent Greece was firmly rooted among Greek Cypriots.
Under Ottoman rule, numeracy, school enrolment and literacy rates were all low. They persisted some time after Ottoman rule ended, and then increased rapidly during the twentieth century.
Cyprus under the British Empire
 In the aftermath of the
In the aftermath of the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878)
The Russo-Turkish War of 1877–1878 ( tr, 93 Harbi, lit=War of ’93, named for the year 1293 in the Islamic calendar; russian: Русско-турецкая война, Russko-turetskaya voyna, "Russian–Turkish war") was a conflict between th ...
and the Congress of Berlin
The Congress of Berlin (13 June – 13 July 1878) was a diplomatic conference to reorganise the states in the Balkan Peninsula after the Russo-Turkish War of 1877–78, which had been won by Russia against the Ottoman Empire. Represented at th ...
, Cyprus was leased
A lease is a contractual arrangement calling for the user (referred to as the ''lessee'') to pay the owner (referred to as the ''lessor'') for the use of an asset. Property, buildings and vehicles are common assets that are leased. Industrial ...
to the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
which de facto took over its administration in 1878 (though, in terms of sovereignty, Cyprus remained a ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally ...
'' Ottoman territory until 5 November 1914, together with Egypt and Sudan) in exchange for guarantees that Britain would use the island as a base to protect the Ottoman Empire against possible Russian aggression.
 The island would serve Britain as a key military base for its colonial routes. By 1906, when the Famagusta harbour was completed, Cyprus was a strategic naval outpost overlooking the
The island would serve Britain as a key military base for its colonial routes. By 1906, when the Famagusta harbour was completed, Cyprus was a strategic naval outpost overlooking the Suez Canal
The Suez Canal ( arz, قَنَاةُ ٱلسُّوَيْسِ, ') is an artificial sea-level waterway in Egypt, connecting the Mediterranean Sea to the Red Sea through the Isthmus of Suez and dividing Africa and Asia. The long canal is a popular ...
, the crucial main route to India which was then Britain's most important overseas possession. Following the outbreak of the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
and the decision of the Ottoman Empire to join the war on the side of the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
, on 5 November 1914 the British Empire formally annexed Cyprus and declared the Ottoman '' Khedivate'' of Egypt and Sudan a ''Sultanate'' and British protectorate.
In 1915, Britain offered Cyprus to Greece, ruled by King Constantine I of Greece
Constantine I ( el, Κωνσταντίνος Αʹ, ''Konstantínos I''; – 11 January 1923) was King of Greece from 18 March 1913 to 11 June 1917 and from 19 December 1920 to 27 September 1922. He was commander-in-chief of the Hellenic Army ...
, on condition that Greece join the war on the side of the British. The offer was declined. In 1923, under the Treaty of Lausanne
The Treaty of Lausanne (french: Traité de Lausanne) was a peace treaty negotiated during the Lausanne Conference of 1922–23 and signed in the Palais de Rumine, Lausanne, Switzerland, on 24 July 1923. The treaty officially settled the conflic ...
, the nascent Turkish republic relinquished any claim to Cyprus, and in 1925 it was declared a British crown colony
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Counci ...
. During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, many Greek and Turkish Cypriots enlisted in the Cyprus Regiment.
The Greek Cypriot population, meanwhile, had become hopeful that the British administration would lead to ''enosis''. The idea of ''enosis'' was historically part of the ''Megali Idea
The Megali Idea ( el, Μεγάλη Ιδέα, Megáli Idéa, Great Idea) is a nationalist and irredentist concept that expresses the goal of reviving the Byzantine Empire, by establishing a Greek state, which would include the large Greek popul ...
'', a greater political ambition of a Greek state encompassing the territories with Greek inhabitants in the former Ottoman Empire, including Cyprus and Asia Minor
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The re ...
with a capital in Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
, and was actively pursued by the Cypriot Orthodox Church
The Church of Cyprus ( el, Ἐκκλησία τῆς Κύπρου, translit=Ekklisia tis Kyprou; tr, Kıbrıs Kilisesi) is one of the autocephalous Greek Orthodox churches that together with other Eastern Orthodox churches form the communion ...
, which had its members educated in Greece. These religious officials, together with Greek military officers and professionals, some of whom still pursued the ''Megali Idea
The Megali Idea ( el, Μεγάλη Ιδέα, Megáli Idéa, Great Idea) is a nationalist and irredentist concept that expresses the goal of reviving the Byzantine Empire, by establishing a Greek state, which would include the large Greek popul ...
'', would later found the guerrilla organisation ''Ethniki Organosis Kyprion Agoniston'' or National Organisation of Cypriot Fighters (EOKA
The Ethniki Organosis Kyprion Agoniston (EOKA; ; el, Εθνική Οργάνωσις Κυπρίων Αγωνιστών, lit=National Organisation of Cypriot Fighters) was a Greek Cypriot
Greek Cypriots or Cypriot Greeks ( el, Ελληνο� ...
). The Greek Cypriots viewed the island as historically Greek and believed that union with Greece was a natural right. In the 1950s, the pursuit of ''enosis'' became a part of the Greek national policy.
 Initially, the Turkish Cypriots favoured the continuation of the British rule. However, they were alarmed by the Greek Cypriot calls for ''enosis'', as they saw the union of
Initially, the Turkish Cypriots favoured the continuation of the British rule. However, they were alarmed by the Greek Cypriot calls for ''enosis'', as they saw the union of Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and ...
with Greece, which led to the exodus of Cretan Turks
The Cretan Muslims ( el, Τουρκοκρητικοί or , or ; tr, Giritli, , or ; ar, أتراك كريت) or Cretan Turks were the Muslim inhabitants of the island of Crete. Their descendants settled principally in Turkey, the Dodecanese ...
, as a precedent to be avoided, and they took a pro-partition stance in response to the militant activity of EOKA. The Turkish Cypriots also viewed themselves as a distinct ethnic group of the island and believed in their having a separate right to self-determination
The right of a people to self-determination is a cardinal principle in modern international law (commonly regarded as a ''jus cogens'' rule), binding, as such, on the United Nations as authoritative interpretation of the Charter's norms. It stat ...
from Greek Cypriots. Meanwhile, in the 1950s, Turkish leader Menderes considered Cyprus an "extension of Anatolia", rejected the partition of Cyprus along ethnic lines and favoured the annexation of the whole island to Turkey. Nationalistic slogans centred on the idea that "Cyprus is Turkish" and the ruling party declared Cyprus to be a part of the Turkish homeland that was vital to its security. Upon realising that the fact that the Turkish Cypriot population was only 20% of the islanders made annexation unfeasible, the national policy was changed to favour partition. The slogan "Partition or Death" was frequently used in Turkish Cypriot and Turkish protests starting in the late 1950s and continuing throughout the 1960s. Although after the Zürich and London conferences Turkey seemed to accept the existence of the Cypriot state and to distance itself from its policy of favouring the partition of the island, the goal of the Turkish and Turkish Cypriot leaders remained that of creating an independent Turkish state in the northern part of the island.
In January 1950, the Church of Cyprus organised a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
under the supervision of clerics and with no Turkish Cypriot participation, where 96% of the participating Greek Cypriots voted in favour of ''enosis'', The Greeks were 80.2% of the total island' s population at the time ( census 1946). Restricted autonomy under a constitution was proposed by the British administration but eventually rejected. In 1955 the EOKA organisation was founded, seeking union with Greece through armed struggle. At the same time the Turkish Resistance Organisation
The Turkish Resistance Organisation ( tr, Türk Mukavemet Teşkilatı, TMT) was a Turkish Cypriot pro- taksim paramilitary organisation formed by Rauf Denktaş and Turkish military officer Rıza Vuruşkan in 1958 as an organisation to counter the ...
(TMT), calling for Taksim, or partition, was established by the Turkish Cypriots as a counterweight. British officials also tolerated the creation of the Turkish underground organisation T.M.T. The Secretary of State for the Colonies in a letter dated 15 July 1958 had advised the Governor of Cyprus not to act against T.M.T despite its illegal actions so as not to harm British relations with the Turkish government.
Independence and inter-communal violence
When Cyprus was placed under theUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
's administration based on the Cyprus Convention
The Cyprus Convention of 4 June 1878 was a secret agreement reached between Great Britain and the Ottoman Empire which granted administrative control of Cyprus to Britain (see British Cyprus), in exchange for its support of the Ottomans during ...
in 1878 and was formally annexed by the UK in 1914. The future of the island became a matter of disagreement between the two prominent ethnic communities, Greek Cypriots
Greek Cypriots or Cypriot Greeks ( el, Ελληνοκύπριοι, Ellinokýprioi, tr, Kıbrıs Rumları) are the ethnic Greek population of Cyprus, forming the island's largest ethnolinguistic community. According to the 2011 census, 659,115 r ...
, who made up 77% of the population in 1960, and Turkish Cypriots
Turkish Cypriots or Cypriot Turks ( tr, Kıbrıs Türkleri or ''Kıbrıslı Türkler''; el, Τουρκοκύπριοι, Tourkokýprioi) are ethnic Turks originating from Cyprus. Following the Ottoman conquest of the island in 1571, about 30,00 ...
, who made up 18% of the population. From the 19th century onwards, the Greek Cypriot population pursued ''enosis
''Enosis'' ( el, Ένωσις, , "union") is the movement of various Greek communities that live outside Greece for incorporation of the regions that they inhabit into the Greek state. The idea is related to the Megali Idea, an irredentist conc ...
'', union with Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
, which became a Greek national policy in the 1950s. The Turkish Cypriot population initially advocated the continuation of the British rule, then demanded the annexation of the island to Turkey, and in the 1950s, together with Turkey, established a policy of '' taksim'', the partition of Cyprus and the creation of a Turkish polity in the north. On 16 August 1960, Cyprus attained independence after the
On 16 August 1960, Cyprus attained independence after the Zürich and London Agreement
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich ...
between the United Kingdom, Greece and Turkey. Cyprus had a total population of 573,566; of whom 442,138 (77.1%) were Greeks, 104,320 (18.2%) Turks, and 27,108 (4.7%) others.Eric Solsten, ed. ''Cyprus: A Country Study'', Library of Congress, Washington, DC, 1991. The UK retained the two
Sovereign Base Areas
Akrotiri and Dhekelia, officially the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia (SBA),, ''Periochés Kyríarchon Váseon Akrotiríou ke Dekélias''; tr, Ağrotur ve Dikelya İngiliz Egemen Üs Bölgeleri is a British Overseas Territory ...
of Akrotiri and Dhekelia
Akrotiri and Dhekelia, officially the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia (SBA),, ''Periochés Kyríarchon Váseon Akrotiríou ke Dekélias''; tr, Ağrotur ve Dikelya İngiliz Egemen Üs Bölgeleri is a British Overseas Territory o ...
, while government posts and public offices were allocated by ethnic quotas, giving the minority Turkish Cypriots a permanent veto, 30% in parliament and administration, and granting the three mother-states guarantor rights.
However, the division of power as foreseen by the constitution soon resulted in legal impasses and discontent on both sides, and nationalist militants started training again, with the military support of Greece and Turkey respectively. The Greek Cypriot leadership believed that the rights given to Turkish Cypriots under the 1960 constitution were too extensive and designed the Akritas plan
The Akritas plan ( el, Σχέδιο Ακρίτας), was an inside document of the Greek Cypriot secret organisation of EOK (mostly known as Akritas organisation) that was authored in 1963 and was revealed to the public in 1966. It entailed the we ...
, which was aimed at reforming the constitution in favour of Greek Cypriots, persuading the international community about the correctness of the changes and violently subjugating Turkish Cypriots in a few days should they not accept the plan.Eric Solsten, ed. ''Cyprus: A Country Study'', Library of Congress, Washington, DC, 1991. Tensions were heightened when Cypriot President Archbishop Makarios III called for constitutional changes, which were rejected by Turkey and opposed by Turkish Cypriots. Intercommunal violence erupted on 21 December 1963, when two Turkish Cypriots were killed at an incident involving the Greek Cypriot police. The violence resulted in the death of 364 Turkish and 174 Greek Cypriots,Oberling, Pierre. ''The road to Bellapais'' (1982), Social Science Monographs
p. 120
"According to official records, 364 Turkish Cypriots and 174 Greek Cypriots were killed during the 1963–1964 crisis." destruction of 109 Turkish Cypriot or mixed villages and displacement of 25,000–30,000 Turkish Cypriots. The crisis resulted in the end of the Turkish Cypriot involvement in the administration and their claiming that it had lost its legitimacy; the nature of this event is still controversial. In some areas, Greek Cypriots prevented Turkish Cypriots from travelling and entering government buildings, while some Turkish Cypriots willingly withdrew due to the calls of the Turkish Cypriot administration. Turkish Cypriots started living in
enclaves
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
. The republic's structure was changed, unilaterally, by Makarios, and Nicosia was divided by the Green Line, with the deployment of UNFICYP troops.
In 1964, Turkey threatened to invade Cyprus in response to the continuing Cypriot intercommunal violence
Several distinct periods of Cypriot intercommunal violence involving the two main ethnic communities, Greek Cypriots and Turkish Cypriots, marked mid-20th century Cyprus. These included the Cyprus Emergency of 1955–59 during British rule, the ...
, but this was stopped by a strongly worded telegram from the US President Lyndon B. Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
on 5 June, warning that the US would not stand beside Turkey in case of a consequential Soviet invasion of Turkish territory. Meanwhile, by 1964, ''enosis'' was a Greek policy and would not be abandoned; Makarios and the Greek prime minister Georgios Papandreou
Georgios Papandreou ( ''Geórgios Papandréou''; 13 February 1888 – 1 November 1968) was a Greek politician, the founder of the Papandreou political dynasty. He served three terms as prime minister of Greece (1944–1945, 1963, 1964–196 ...
agreed that ''enosis'' should be the ultimate aim and King Constantine
Constantine most often refers to:
* Constantine the Great, Roman emperor from 306 to 337, also known as Constantine I
*Constantine, Algeria, a city in Algeria
Constantine may also refer to:
People
* Constantine (name), a masculine given name ...
wished Cyprus "a speedy union with the mother country". Greece dispatched 10,000 troops to Cyprus to counter a possible Turkish invasion.
Following nationalist violence in the 1950s, Cyprus was granted independence in 1960.Cyprus date of independence(click on Historical review) The crisis of 1963–64 brought further intercommunal violence between the two communities, displaced more than 25,000 Turkish Cypriots into
enclaves
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
and brought the end of Turkish Cypriot representation in the republic. On 15 July 1974, a coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
was staged by Greek Cypriot nationalists and elements of the Greek military junta
The Greek junta or Regime of the Colonels, . Also known within Greece as just the Junta ( el, η Χούντα, i Choúnta, links=no, ), the Dictatorship ( el, η Δικτατορία, i Diktatoría, links=no, ) or the Seven Years ( el, η Ε ...
in an attempt at ''enosis''. This action precipitated the Turkish invasion of Cyprus
The Turkish invasion of Cyprus began on 20 July 1974 and progressed in two phases over the following month. Taking place upon a background of Cypriot intercommunal violence, intercommunal violence between Greek Cypriots, Greek and Turkish ...
on 20 July, which led to the capture of the present-day territory of Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus ( tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs), officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC; tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti, ''KKTC''), is a ''de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the Geography of Cyprus, isl ...
and the displacement
Displacement may refer to:
Physical sciences
Mathematics and Physics
*Displacement (geometry), is the difference between the final and initial position of a point trajectory (for instance, the center of mass of a moving object). The actual path ...
of over 150,000 Greek Cypriots and 50,000 Turkish Cypriots. A separate Turkish Cypriot state in the north was established by unilateral declaration in 1983; the move was widely condemned by the international community
The international community is an imprecise phrase used in geopolitics and international relations to refer to a broad group of people and governments of the world.
As a rhetorical term
Aside from its use as a general descriptor, the term is ...
, with Turkey alone recognising the new state. These events and the resulting political situation are matters of a continuing dispute.
1974 coup d'état, invasion, and division
Greek military junta
The Greek junta or Regime of the Colonels, . Also known within Greece as just the Junta ( el, η Χούντα, i Choúnta, links=no, ), the Dictatorship ( el, η Δικτατορία, i Diktatoría, links=no, ) or the Seven Years ( el, η Ε ...
under Dimitrios Ioannides
Dimitrios Ioannidis ( el, Δημήτριος Ιωαννίδης ; 13 March 1923 – 16 August 2010), also known as Dimitris Ioannidis and as The Invisible Dictator, was a Greek military officer and one of the leading figures in the junta that r ...
carried out a coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
in Cyprus, to unite the island with Greece. The coup ousted president Makarios III and replaced him with pro-enosis
''Enosis'' ( el, Ένωσις, , "union") is the movement of various Greek communities that live outside Greece for incorporation of the regions that they inhabit into the Greek state. The idea is related to the Megali Idea, an irredentist conc ...
nationalist Nikos Sampson
Nikos Sampson (born Nikos Georgiadis, el, Νίκος Γεωργιάδης; 16 December 1935 – 9 May 2001) was the ''de facto'' president of Cyprus who succeeded Archbishop Makarios, appointed as the president of Cyprus by the Greek military ...
. In response to the coup, five days later, on 20 July 1974, the Turkish army invaded the island, citing a right to intervene to restore the constitutional order from the 1960 Treaty of Guarantee. This justification has been rejected by the United Nations and the international community.
The Turkish air force began bombing Greek positions in Cyprus, and hundreds of paratroopers
A paratrooper is a military parachutist—someone trained to parachute into a military operation, and usually functioning as part of an airborne force. Military parachutists (troops) and parachutes were first used on a large scale during Worl ...
were dropped in the area between Nicosia and Kyrenia, where well-armed Turkish Cypriot enclaves had been long-established; while off the Kyrenia coast, Turkish troop ships landed 6,000 men as well as tanks, trucks and armoured vehicles.
Three days later, when a ceasefire had been agreed, Turkey had landed 30,000 troops on the island and captured Kyrenia, the corridor linking Kyrenia to Nicosia, and the Turkish Cypriot quarter of Nicosia itself. The junta in Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
, and then the Sampson regime in Cyprus fell from power. In Nicosia, Glafkos Clerides
Glafcos Ioannou Clerides ( el, Γλαύκος Ιωάννου Κληρίδης; 24 April 1919 – 15 November 2013) was a Cypriot politician and barrister who served as the fourth president of Cyprus from 1993 to 2003. At the time of his death, ...
temporarily assumed the presidency. But after the peace negotiations in Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the List of cities in Switzerland, second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaki ...
, the Turkish government reinforced their Kyrenia bridgehead and started a second invasion on 14 August. The invasion resulted in Morphou
Morphou ( el, Μόρφου; tr, Omorfo or ) is a town in the northwestern part of Cyprus, under the ''de facto'' control of Northern Cyprus. It is the administrative center of the Güzelyurt District of Northern Cyprus. Having been a predominantl ...
, Karpass, Famagusta and the Mesaoria
The Mesaoria ( el, Μεσαορία, tr, Mesarya) is a broad, sweeping plain which makes up the north centre of the island of Cyprus.
Geography
The Mesaoria is the name given to the broad tract of plain which extends across the island from the ...
coming under Turkish control.
International pressure led to a ceasefire, and by then 36% of the island had been taken over by the Turks and 180,000 Greek Cypriots had been evicted from their homes in the north. At the same time, around 50,000 Turkish Cypriots were displaced to the north and settled in the properties of the displaced Greek Cypriots. Among a variety of sanctions against Turkey, in mid-1975 the US Congress imposed an arms embargo on Turkey for using US-supplied equipment during the Turkish invasion of Cyprus
The Turkish invasion of Cyprus began on 20 July 1974 and progressed in two phases over the following month. Taking place upon a background of Cypriot intercommunal violence, intercommunal violence between Greek Cypriots, Greek and Turkish ...
in 1974. There were 1,534 Greek Cypriots and 502 Turkish Cypriots missing as a result of the fighting from 1963 to 1974.
The Republic of Cyprus has ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally ...
'' sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
over the entire island, including its territorial waters
The term territorial waters is sometimes used informally to refer to any area of water over which a sovereign state has jurisdiction, including internal waters, the territorial sea, the contiguous zone, the exclusive economic zone, and potenti ...
and exclusive economic zone, with the exception of the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia
Akrotiri and Dhekelia, officially the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia (SBA),, ''Periochés Kyríarchon Váseon Akrotiríou ke Dekélias''; tr, Ağrotur ve Dikelya İngiliz Egemen Üs Bölgeleri is a British Overseas Territory o ...
, which remain under the UK's control according to the London and Zürich Agreements
The London and Zürich Agreements ( el, Συμφωνίες Ζυρίχης–Λονδίνου; tr, Zürih ve Londra Antlaşmaları) for the constitution of Cyprus started with an agreement on 19 February 1959 in Lancaster House, London, between T ...
. However, the Republic of Cyprus is de facto partitioned into two main parts: the area under the effective control of the Republic, located in the south and west and comprising about 59% of the island's area, and the north, administered by the self-declared Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus ( tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs), officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC; tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti, ''KKTC''), is a ''de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the island of Cyprus. Recog ...
, covering about 36% of the island's area. Another nearly 4% of the island's area is covered by the UN buffer zone. The international community considers the northern part of the island to be territory of the Republic of Cyprus occupied by Turkish forces. The occupation is viewed as illegal under international law and amounting to illegal occupation of EU territory since Cyprus became a member of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
.
Post-division
 After the restoration of constitutional order and the return of Archbishop Makarios III to Cyprus in December 1974, Turkish troops remained, occupying the northeastern portion of the island. In 1983, the Turkish Cypriot parliament, led by the Turkish Cypriot leader
After the restoration of constitutional order and the return of Archbishop Makarios III to Cyprus in December 1974, Turkish troops remained, occupying the northeastern portion of the island. In 1983, the Turkish Cypriot parliament, led by the Turkish Cypriot leader Rauf Denktaş
Rauf Raif Denktaş (27 January 1924 – 13 January 2012) was a Turkish Cypriot politician, barrister and jurist who served as the founding president of Northern Cyprus. He occupied this position as the president of the Turkish Republic of North ...
, proclaimed the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC), which is recognised only by Turkey.
The events of the summer of 1974 dominate the politics
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies ...
on the island, as well as Greco-Turkish relations. Turkish settlers have been settled in the north with the encouragement of the Turkish and Turkish Cypriot states. The Republic of Cyprus considers their presence a violation of the Geneva Convention
upright=1.15, Original document in single pages, 1864
The Geneva Conventions are four treaties, and three additional protocols, that establish international legal standards for humanitarian treatment in war. The singular term ''Geneva Conven ...
, whilst many Turkish settlers have since severed their ties to Turkey and their second generation considers Cyprus to be their homeland.
The Turkish invasion, the ensuing occupation and the declaration of independence by the TRNC have been condemned by United Nations resolutions, which are reaffirmed by the Security Council every year. Attempts to resolve the Cyprus dispute have continued. In 2004, the Annan Plan, drafted by the UN Secretary General Kofi Annan
Kofi Atta Annan (; 8 April 193818 August 2018) was a Ghanaian diplomat who served as the seventh secretary-general of the United Nations from 1997 to 2006. Annan and the UN were the co-recipients of the 2001 Nobel Peace Prize. He was the founder ...
, was put to a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
in both Northern Cyprus and the Cypriot Republic. 65% of Turkish Cypriots voted in support of the plan and 74% Greek Cypriots voted against the plan, claiming that it disproportionately favoured the Turkish side. In total, 66.7% of the voters rejected the Annan Plan.
On 1 May 2004 Cyprus joined the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
, together with nine other countries. Cyprus was accepted into the EU as a whole, although the EU legislation is suspended in Northern Cyprus until a final settlement of the Cyprus problem.
Efforts have been made to enhance freedom of movement between the two sides. In April 2003, Northern Cyprus unilaterally eased border restrictions, permitting Cypriots to cross between the two sides for the first time in 30 years. In March 2008, a wall that had stood for decades at the boundary between the Republic of Cyprus and the UN buffer zone was demolished. The wall had cut across Ledra Street
Ledra Street ( el, Οδός Λήδρας ''Odos Lidras''; tr, Ledra Caddesi) is a major shopping thoroughfare in central Nicosia, Cyprus, which links North Nicosia, the part of the city under the control of the ''de facto'' Northern Cyprus, and ...
in the heart of Nicosia and was seen as a strong symbol of the island's 32-year division. On 3 April 2008, Ledra Street was reopened in the presence of Greek and Turkish Cypriot officials. North and South relaunched reunification talks in 2015, but these collapsed in 2017.
The European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
issued a warning in February 2019 that Cyprus, an EU member, was selling EU passports to Russian oligarchs, saying it would allow organised crime
Organized crime (or organised crime) is a category of transnational, national, or local groupings of highly centralized enterprises run by criminals to engage in illegal activity, most commonly for profit. While organized crime is generally th ...
syndicates to infiltrate the EU. In 2020 leaked documents revealed a wider range of former and current officials from Afghanistan, China, Dubai, Lebanon, the Russian Federation, Saudi Arabia, Ukraine and Vietnam who bought a Cypriot citizenship prior to a change of the law in July 2019. Cyprus and Turkey have been engaged in a dispute over the extent of their exclusive economic zones, ostensibly sparked by oil and gas exploration in the area.
Geography

 Cyprus is the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after the Italian islands of
Cyprus is the third largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after the Italian islands of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
and Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label=Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after ...
(both in terms of area and population). It is also the world's 80th largest by area and world's 51st largest by population. It measures long from end to end and wide at its widest point, with Turkey to the north. It lies between latitudes 34° and 36° N, and longitudes 32° and 35° E.
Other neighbouring territories include Syria and Lebanon to the east and southeast (, respectively), Israel to the southeast, The Gaza Strip 427 kilometres (265 mi) to the southeast, Egypt to the south, and Greece to the northwest: to the small Dodecanesian island of Kastellorizo
Kastellorizo or Castellorizo (; el, Καστελλόριζο, Kastellórizo), officially Megisti ( ''Megísti''), is a Greece, Greek island and Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality of the Dodecanese in the Eastern Mediterranean ...
(Megisti), to Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the So ...
and to the Greek mainland. Sources alternatively place Cyprus in Europe, or Western Asia and the Middle East.
The physical relief of the island is dominated by two mountain ranges, the Troodos Mountains
Troodos (sometimes spelled Troödos; el, Τρόοδος ; tr, Trodos Dağları) is the largest mountain range in Cyprus, located in roughly the center of the island. Its highest peak is Mount Olympus ( el, Όλυμπος), also known as Chion ...
and the smaller Kyrenia Range
The Kyrenia Mountains ( el, Κερύνειο Όρος; tr, Girne Dağları) is a long, narrow mountain range that runs for approximately along the northern coast of the island of Cyprus. It is primarily made of hard crystalline limestone, w ...
, and the central plain they encompass, the Mesaoria
The Mesaoria ( el, Μεσαορία, tr, Mesarya) is a broad, sweeping plain which makes up the north centre of the island of Cyprus.
Geography
The Mesaoria is the name given to the broad tract of plain which extends across the island from the ...
. The Mesaoria plain is drained by the Pedieos River
The Pedieos (also Pediaios or Pediaeus or Pithkias; Greek: Πεδιαίος/Πηθκιάς, Turkish: ''Kanlı Dere'') is the longest river in Cyprus. The river originates in the Troodos Mountains close to Machairas Monastery
Machairas Monaste ...
, the longest on the island. The Troodos Mountains cover most of the southern and western portions of the island and account for roughly half its area. The highest point on Cyprus is Mount Olympus
Mount Olympus (; el, Όλυμπος, Ólympos, also , ) is the highest mountain in Greece. It is part of the Olympus massif near the Thermaic Gulf of the Aegean Sea, located in the Olympus Range on the border between Thessaly and Macedonia, be ...
at , located in the centre of the Troodos range. The narrow Kyrenia Range, extending along the northern coastline, occupies substantially less area, and elevations are lower, reaching a maximum of . The island lies within the Anatolian Plate.
Cyprus contains the Cyprus Mediterranean forests ecoregion. It had a 2018 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 7.06/10, ranking it 59th globally out of 172 countries.
Geopolitics, Geopolitically, the island is subdivided into four main segments. The Republic of Cyprus occupies the southern two-thirds of the island (59.74%). The Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus occupies the northern third (34.85%), and the United Nations-controlled Green Line provides a buffer zone that separates the two and covers 2.67% of the island. Lastly, Sovereign Base Areas, two bases under British sovereignty are located on the island: Akrotiri and Dhekelia
Akrotiri and Dhekelia, officially the Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia (SBA),, ''Periochés Kyríarchon Váseon Akrotiríou ke Dekélias''; tr, Ağrotur ve Dikelya İngiliz Egemen Üs Bölgeleri is a British Overseas Territory o ...
, covering the remaining 2.74%.
Climate
Water supply
 Cyprus suffers from a chronic shortage of water. The country relies heavily on rain to provide household water, but in the past 30 years average yearly precipitation has decreased. Between 2001 and 2004, exceptionally heavy annual rainfall pushed water reserves up, with supply exceeding demand, allowing total storage in the island's reservoirs to rise to an all-time high by the start of 2005.
However, since then demand has increased annually – a result of local population growth, foreigners moving to Cyprus and the number of visiting tourists – while supply has fallen as a result of more frequent droughts.
Dams remain the principal source of water both for domestic and agricultural use; Cyprus has a total of 107 dams (plus one currently under construction) and reservoirs, with a total water storage capacity of about . Water desalination plants are gradually being constructed to deal with recent years of prolonged drought.
The Government has invested heavily in the creation of water desalination plants which have supplied almost 50 per cent of domestic water since 2001. Efforts have also been made to raise public awareness of the situation and to encourage domestic water users to take more responsibility for the conservation of this increasingly scarce commodity.
Turkey has built a water pipeline under the Mediterranean Sea from Anamur on its southern coast to the northern coast of Cyprus, to supply Northern Cyprus with potable and irrigation water ''(see Northern Cyprus Water Supply Project)''.
Cyprus suffers from a chronic shortage of water. The country relies heavily on rain to provide household water, but in the past 30 years average yearly precipitation has decreased. Between 2001 and 2004, exceptionally heavy annual rainfall pushed water reserves up, with supply exceeding demand, allowing total storage in the island's reservoirs to rise to an all-time high by the start of 2005.
However, since then demand has increased annually – a result of local population growth, foreigners moving to Cyprus and the number of visiting tourists – while supply has fallen as a result of more frequent droughts.
Dams remain the principal source of water both for domestic and agricultural use; Cyprus has a total of 107 dams (plus one currently under construction) and reservoirs, with a total water storage capacity of about . Water desalination plants are gradually being constructed to deal with recent years of prolonged drought.
The Government has invested heavily in the creation of water desalination plants which have supplied almost 50 per cent of domestic water since 2001. Efforts have also been made to raise public awareness of the situation and to encourage domestic water users to take more responsibility for the conservation of this increasingly scarce commodity.
Turkey has built a water pipeline under the Mediterranean Sea from Anamur on its southern coast to the northern coast of Cyprus, to supply Northern Cyprus with potable and irrigation water ''(see Northern Cyprus Water Supply Project)''.
Flora and fauna
Cyprus is home to a number of Endemism, endemites, including the Cypriot mouse, the Quercus alnifolia, golden oak and the Cedrus brevifolia, Cyprus cedar.Politics
 Cyprus is a presidential republic. The head of state and of the government is elected by a process of universal suffrage for a five-year term. Executive power is exercised by the government with legislative power vested in the House of Representatives whilst the Judiciary is independent of both the executive and the legislature.
The 1960 Constitution provided for a presidential system of government with independent executive, legislative and judicial branches as well as a complex system of checks and balances including a weighted power-sharing ratio designed to protect the interests of the Turkish Cypriots. The executive was led by a Greek Cypriot president and a Turkish Cypriot vice-president elected by their respective communities for five-year terms and each possessing a right of veto over certain types of legislation and executive decisions. Legislative power rested on the House of Representatives who were also elected on the basis of separate voters' rolls.
Cyprus is a presidential republic. The head of state and of the government is elected by a process of universal suffrage for a five-year term. Executive power is exercised by the government with legislative power vested in the House of Representatives whilst the Judiciary is independent of both the executive and the legislature.
The 1960 Constitution provided for a presidential system of government with independent executive, legislative and judicial branches as well as a complex system of checks and balances including a weighted power-sharing ratio designed to protect the interests of the Turkish Cypriots. The executive was led by a Greek Cypriot president and a Turkish Cypriot vice-president elected by their respective communities for five-year terms and each possessing a right of veto over certain types of legislation and executive decisions. Legislative power rested on the House of Representatives who were also elected on the basis of separate voters' rolls.
 Since 1965, following clashes between the two communities, the Turkish Cypriot seats in the House remain vacant. In 1974 Cyprus was divided de facto when the Turkish army occupied the northern third of the island. The Turkish Cypriots subsequently declared independence in 1983 as the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus but were recognised only by Turkey. In 1985 the TRNC adopted a constitution and held its first elections. The United Nations recognises the sovereignty of the Republic of Cyprus over the entire island of Cyprus.
The House of Representatives currently has 59 members elected for a five-year term, 56 members by proportional representation and three observer members representing the Armenians in Cyprus, Armenian, Roman Catholicism in Cyprus, Latin and Maronites in Cyprus, Maronite minorities. 24 seats are allocated to the Turkish people, Turkish community but remain vacant since 1964. The political environment is dominated by the communist Progressive Party of Working People, AKEL, the liberal conservative Democratic Rally, the centrism, centrist Democratic Party (Cyprus), Democratic Party, the social democracy, social-democratic Movement for Social Democracy, EDEK and the centrist European Party (Cyprus), EURO.KO.
In 2008, Dimitris Christofias became the country's first Communist head of state. Due to his involvement in the 2012–13 Cypriot financial crisis, Christofias did not run for re-election in 2013. The Presidential election in 2013 resulted in Democratic Rally candidate Nicos Anastasiades winning 57.48% of the vote. As a result, Anastasiades was sworn in on and has been president since 28 February 2013. Anastasiades was re-elected with 56% of the vote in the Cypriot presidential election, 2018, 2018 presidential election.
Since 1965, following clashes between the two communities, the Turkish Cypriot seats in the House remain vacant. In 1974 Cyprus was divided de facto when the Turkish army occupied the northern third of the island. The Turkish Cypriots subsequently declared independence in 1983 as the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus but were recognised only by Turkey. In 1985 the TRNC adopted a constitution and held its first elections. The United Nations recognises the sovereignty of the Republic of Cyprus over the entire island of Cyprus.
The House of Representatives currently has 59 members elected for a five-year term, 56 members by proportional representation and three observer members representing the Armenians in Cyprus, Armenian, Roman Catholicism in Cyprus, Latin and Maronites in Cyprus, Maronite minorities. 24 seats are allocated to the Turkish people, Turkish community but remain vacant since 1964. The political environment is dominated by the communist Progressive Party of Working People, AKEL, the liberal conservative Democratic Rally, the centrism, centrist Democratic Party (Cyprus), Democratic Party, the social democracy, social-democratic Movement for Social Democracy, EDEK and the centrist European Party (Cyprus), EURO.KO.
In 2008, Dimitris Christofias became the country's first Communist head of state. Due to his involvement in the 2012–13 Cypriot financial crisis, Christofias did not run for re-election in 2013. The Presidential election in 2013 resulted in Democratic Rally candidate Nicos Anastasiades winning 57.48% of the vote. As a result, Anastasiades was sworn in on and has been president since 28 February 2013. Anastasiades was re-elected with 56% of the vote in the Cypriot presidential election, 2018, 2018 presidential election.
Administrative divisions
The Republic of Cyprus is divided into six districts: Nicosia District, Nicosia, Famagusta District, Famagusta, Kyrenia District, Kyrenia, Larnaca District, Larnaca, Limassol District, Limassol and Paphos District, Paphos.Exclaves and enclaves
 Cyprus has four exclaves, all in territory that belongs to the Akrotiri and Dhekelia, British Sovereign Base Area of Dhekelia. The first two are the villages of Ormidhia and Xylotymvou. The third is the Dhekelia Power Station, which is divided by a British road into two parts. The northern part is the Electricity Authority of Cyprus, EAC refugee settlement. The southern part, even though located by the sea, is also an exclave because it has no
Cyprus has four exclaves, all in territory that belongs to the Akrotiri and Dhekelia, British Sovereign Base Area of Dhekelia. The first two are the villages of Ormidhia and Xylotymvou. The third is the Dhekelia Power Station, which is divided by a British road into two parts. The northern part is the Electricity Authority of Cyprus, EAC refugee settlement. The southern part, even though located by the sea, is also an exclave because it has no territorial waters
The term territorial waters is sometimes used informally to refer to any area of water over which a sovereign state has jurisdiction, including internal waters, the territorial sea, the contiguous zone, the exclusive economic zone, and potenti ...
of its own, those being UK waters.
The UN buffer zone runs up against Dhekelia and picks up again from its east side off Ayios Nikolaos, SBA, Ayios Nikolaos and is connected to the rest of Dhekelia by a thin land corridor. In that sense the buffer zone turns the Paralimni area on the southeast corner of the island into a de facto, though not ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally ...
'', exclave.
Foreign relations
The Republic of Cyprus is a member of the following international groups: Australia Group, Commonwealth of Nations, CN, Council of Europe, CE, CFSP, EBRD, European Investment Bank, EIB, EU, FAO, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, International Chamber of Commerce, ICC, International Criminal Court, ICCt, International Trade Union Confederation, ITUC, International Development Association, IDA, IFAD, International Finance Corporation, IFC, IHO, International Labour Organization, ILO, International Monetary Fund, IMF, International Meteorological Organization, IMO, Interpol, IOC, International Organization for Migration, IOM, Inter-Parliamentary Union, IPU, ITU, MIGA, Non-Aligned Movement, NAM, Nuclear Suppliers Group, NSG, OPCW, Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, OSCE, Permanent Court of Arbitration, PCA, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, United Nations Industrial Development Organization, UNIDO, UPU, World Confederation of Labour, WCL, World Customs Organization, WCO, World Federation of Trade Unions, WFTU, WHO, WIPO, WMO, WToO, World Trade Organization, WTO.Armed forces
 The Cypriot National Guard is the main military institution of the Republic of Cyprus. It is a combined arms force, with land, air and naval elements. Historically all men were required to spend 24 months serving in the National Guard after their 17th birthday, but in 2016 this period of compulsory service was reduced to 14 months.
Annually, approximately 10,000 persons are trained in recruit centres. Depending on their awarded speciality the conscript recruits are then transferred to speciality training camps or to operational units.
While until 2016 the armed forces were mainly conscript based, since then a large Professional Enlisted institution has been adopted (ΣΥΟΠ), which combined with the reduction of conscript service produces an approximate 3:1 ratio between conscript and professional enlisted.
The Cypriot National Guard is the main military institution of the Republic of Cyprus. It is a combined arms force, with land, air and naval elements. Historically all men were required to spend 24 months serving in the National Guard after their 17th birthday, but in 2016 this period of compulsory service was reduced to 14 months.
Annually, approximately 10,000 persons are trained in recruit centres. Depending on their awarded speciality the conscript recruits are then transferred to speciality training camps or to operational units.
While until 2016 the armed forces were mainly conscript based, since then a large Professional Enlisted institution has been adopted (ΣΥΟΠ), which combined with the reduction of conscript service produces an approximate 3:1 ratio between conscript and professional enlisted.
Law, justice and human rights
 The Cyprus Police (Greek: , tr, Kıbrıs Polisi) is the only National Police Service of the Republic of Cyprus and is under the Ministry of Justice and Public Order since 1993.Cyprus Government Web Portal
In "Freedom in the World 2011", Freedom House rated Cyprus as "free". In January 2011, the Report of the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights on the question of Human Rights in Cyprus noted that the ongoing division of Cyprus continues to affect human rights throughout the island "including freedom of movement, human rights pertaining to the question of missing persons, discrimination, the right to life, freedom of religion, and economic, social and cultural rights". The constant focus on the division of the island can sometimes mask other human rights issues.
In 2014, Turkey was ordered by the European Court of Human Rights to pay well over $100m in compensation to Cyprus for the invasion; Ankara announced that it would ignore the judgment. In 2014, a group of Cypriot refugees and a European parliamentarian, later joined by the Cypriot government, filed a complaint to the International Court of Justice, accusing Turkey of violating the Geneva Conventions by directly or indirectly transferring Turkish settlers in Northern Cyprus, its civilian population into occupied territory. Other violations of the Geneva and the Hague Conventions—both ratified by Turkey—amount to what archaeologist Sophocles Hadjisavvas called "the organized destruction of Greek and Christian heritage in the north". These violations include looting of cultural treasures, deliberate destruction of churches, neglect of works of art, and altering the names of important historical sites, which was condemned by the International Council on Monuments and Sites. Hadjisavvas has asserted that these actions are motivated by a Turkish policy of erasing the Greek presence in Northern Cyprus within a framework of ethnic cleansing. But some perpetrators are just motivated by greed and are seeking profit. Quote on p. 129: "the deliberate destruction of [Greek] heritage as an instrument toward the obliteration of an identity of a people in the framework of ethnic cleansing." Art law expert Alessandro Chechi has classified the connection of cultural heritage destruction to ethnic cleansing as the "Greek Cypriot viewpoint", which he reports as having been dismissed by two Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe, PACE reports. Chechi asserts joint Greek and Turkish Cypriot responsibility for the destruction of cultural heritage in Cyprus, noting the destruction of Turkish Cypriot heritage in the hands of Greek Cypriot extremists.
The Cyprus Police (Greek: , tr, Kıbrıs Polisi) is the only National Police Service of the Republic of Cyprus and is under the Ministry of Justice and Public Order since 1993.Cyprus Government Web Portal
In "Freedom in the World 2011", Freedom House rated Cyprus as "free". In January 2011, the Report of the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights on the question of Human Rights in Cyprus noted that the ongoing division of Cyprus continues to affect human rights throughout the island "including freedom of movement, human rights pertaining to the question of missing persons, discrimination, the right to life, freedom of religion, and economic, social and cultural rights". The constant focus on the division of the island can sometimes mask other human rights issues.
In 2014, Turkey was ordered by the European Court of Human Rights to pay well over $100m in compensation to Cyprus for the invasion; Ankara announced that it would ignore the judgment. In 2014, a group of Cypriot refugees and a European parliamentarian, later joined by the Cypriot government, filed a complaint to the International Court of Justice, accusing Turkey of violating the Geneva Conventions by directly or indirectly transferring Turkish settlers in Northern Cyprus, its civilian population into occupied territory. Other violations of the Geneva and the Hague Conventions—both ratified by Turkey—amount to what archaeologist Sophocles Hadjisavvas called "the organized destruction of Greek and Christian heritage in the north". These violations include looting of cultural treasures, deliberate destruction of churches, neglect of works of art, and altering the names of important historical sites, which was condemned by the International Council on Monuments and Sites. Hadjisavvas has asserted that these actions are motivated by a Turkish policy of erasing the Greek presence in Northern Cyprus within a framework of ethnic cleansing. But some perpetrators are just motivated by greed and are seeking profit. Quote on p. 129: "the deliberate destruction of [Greek] heritage as an instrument toward the obliteration of an identity of a people in the framework of ethnic cleansing." Art law expert Alessandro Chechi has classified the connection of cultural heritage destruction to ethnic cleansing as the "Greek Cypriot viewpoint", which he reports as having been dismissed by two Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe, PACE reports. Chechi asserts joint Greek and Turkish Cypriot responsibility for the destruction of cultural heritage in Cyprus, noting the destruction of Turkish Cypriot heritage in the hands of Greek Cypriot extremists.
Economy
 In the early 21st century the Cypriot economy has diversified and become prosperous. However, in 2012 it became affected by the European sovereign-debt crisis, Eurozone financial and banking crisis. In June 2012, the Cypriot government announced it would need € in foreign aid to support the Cyprus Popular Bank, and this was followed by Fitch Group, Fitch downgrading Cyprus's credit rating to junk status. Fitch said Cyprus would need an additional € to support its banks and the downgrade was mainly due to the exposure of Bank of Cyprus, Cyprus Popular Bank and Hellenic Bank, Cyprus's three largest banks, to the Greek government-debt crisis, Greek financial crisis.
In the early 21st century the Cypriot economy has diversified and become prosperous. However, in 2012 it became affected by the European sovereign-debt crisis, Eurozone financial and banking crisis. In June 2012, the Cypriot government announced it would need € in foreign aid to support the Cyprus Popular Bank, and this was followed by Fitch Group, Fitch downgrading Cyprus's credit rating to junk status. Fitch said Cyprus would need an additional € to support its banks and the downgrade was mainly due to the exposure of Bank of Cyprus, Cyprus Popular Bank and Hellenic Bank, Cyprus's three largest banks, to the Greek government-debt crisis, Greek financial crisis.
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
and also priority Electricity Highway Interconnector Project.
In recent years significant quantities of offshore natural gas have been discovered in the area known as Block 12, Aphrodite (at the exploratory drilling block 12) in Cyprus's exclusive economic zone (EEZ), about south of Limassol at 33°5'40″N and 32°59'0″E. However, Turkey's offshore drilling companies have accessed both natural gas and oil resources since 2013. Cyprus demarcated its maritime border with Egypt in 2003, with Lebanon in 2007, and with Israel in 2010. In August 2011, the US-based firm Noble Energy entered into a production-sharing agreement with the Cypriot government regarding the block's commercial development.
Turkey, which does not recognise the border agreements of Cyprus with its neighbours, threatened to mobilise its naval forces if Cyprus proceeded with plans to begin drilling at Block 12. Cyprus's drilling efforts have the support of the US, EU, and UN, and on 19 September 2011 drilling in Block 12 began without any incidents being reported.
Because of the heavy influx of tourists and foreign investors, the property rental market in Cyprus has grown in recent years. In late 2013, the Cyprus Town Planning Department announced a series of incentives to stimulate the property market and increase the number of property developments in the country's town centres. This followed earlier measures to quickly give immigration permits to third country nationals investing in Cyprus property.
Transport
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
Development Bank. In 2010 the new bus network was implemented.
Cyprus has several heliports and two international airports: Larnaca International Airport and Paphos International Airport. A third airport, Ercan International Airport, operates in the Turkish Cypriot administered area with direct flights only to Turkey (Turkish Cypriot ports are closed to international traffic apart from Turkey). Nicosia International Airport has been closed since 1974.
The main harbours of the island are Limassol Port, Limassol and Larnaca, which service cargo, passenger and cruise ships.
Communications
CYTA, Cyta, the Public ownership, state-owned telecommunications company, manages most telecommunications and Internet connections on the island. However, following deregulation of the sector, a few private telecommunications companies emerged, including Monaco Telecom, epic, Cablenet, OTEnet Telecom, Omega Telecom and PrimeTel. In the Turkish-controlled area of Cyprus, two different companies administer the mobile phone network: Turkcell and KKTC Telsim.Demographics

Greek Cypriots
Greek Cypriots or Cypriot Greeks ( el, Ελληνοκύπριοι, Ellinokýprioi, tr, Kıbrıs Rumları) are the ethnic Greek population of Cyprus, forming the island's largest ethnolinguistic community. According to the 2011 census, 659,115 r ...
comprised 77%, Turkish Cypriots
Turkish Cypriots or Cypriot Turks ( tr, Kıbrıs Türkleri or ''Kıbrıslı Türkler''; el, Τουρκοκύπριοι, Tourkokýprioi) are ethnic Turks originating from Cyprus. Following the Ottoman conquest of the island in 1571, about 30,00 ...
18%, and others 5% of the Cypriot population. At the time of the 2011 government census, there were 10,520 people of Russians in Cyprus, Russian origin living in Cyprus.
According to the first population census after the declaration of independence, carried out in December 1960 and covering the entire island, Cyprus had a total population of 573,566, of whom 442,138 (77.1%) were Greeks, 104,320 (18.2%) Turkish, and 27,108 (4.7%) others.Hatay, Mete "Is the Turkish Cypriot Population Shrinking?", International Peace Research Institute, 2007. Pages 22–23.
Due to the inter-communal ethnic tensions between 1963 and 1974, an island-wide census was regarded as impossible. Nevertheless, the Cypriot government conducted one in 1973, without the Turkish Cypriot populace. According to this census, the Greek Cypriot population was 482,000. One year later, in 1974, the Cypriot government's Department of Statistics and Research estimated the total population of Cyprus at 641,000; of whom 506,000 (78.9%) were Greeks, and 118,000 (18.4%) Turkish. After the partition of the island in 1974, the government of Cyprus conducted six more censuses: in 1976, 1982, 1992, 2001, 2011 and 2021; these excluded the Turkish population which was resident in the northern part of the island.
According to the Republic of Cyprus's estimate in 2005, the number of Cypriot citizens currently living in the Republic of Cyprus is around 871,036. In addition to this, the Republic of Cyprus is home to 110,200 foreign permanent residents and an estimated 10,000–30,000 undocumented illegal immigrants currently living in the south of the island. According to the Republic of Cyprus's website, the population was 856,857 at the Census in 2011 and 918,100 at the 2021 Census
According to the 2006 census carried out by Northern Cyprus, there were 256,644 (de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally ...
) people living in Northern Cyprus. 178,031 were citizens of Northern Cyprus, of whom 147,405 were born in Cyprus (112,534 from the north; 32,538 from the south; 371 did not indicate what part of Cyprus they were from); 27,333 born in Turkey; 2,482 born in the UK and 913 born in Bulgaria. Of the 147,405 citizens born in Cyprus, 120,031 say both parents were born in Cyprus; 16,824 say both parents born in Turkey; 10,361 have one parent born in Turkey and one parent born in Cyprus.
In 2010, the International Crisis Group estimated that the total population of Cyprus was 1.1 million, of which there was an estimated 300,000 residents in the north, perhaps half of whom were Turkish settlers in Northern Cyprus, either born in Turkey or are children of such settlers.
The villages of Rizokarpaso (in Northern Cyprus), Potamia (in Nicosia district) and Pyla (in Larnaca District) are the only settlements remaining with a mixed Greek and Turkish Cypriot population.
Human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup, Y-Dna haplogroups are found at the following frequencies in Cyprus: Haplogroup J (Y-DNA), J (43.07% including 6.20% J1), Haplogroup E1b1b (Y-DNA), E1b1b (20.00%), Haplogroup R1 (Y-DNA), R1 (12.30% including 9.2% R1b), Haplogroup F (Y-DNA), F (9.20%), Haplogroup I (Y-DNA), I (7.70%), Haplogroup K (Y-DNA), K (4.60%), Haplogroup A (Y-DNA), A (3.10%). J, K, F and E1b1b haplogroups consist of lineages with differential distribution within Middle East, North Africa and Europe.
Outside Cyprus there are significant and thriving diasporas - both a Greek Cypriot diaspora and a Turkish Cypriot diaspora - in the United Kingdom, Australia, Canada, the United States, Greece and Turkey.
Largest cities
Functional urban areas
Religion
The majority of Greek Cypriots identify as Christians, specifically Church of Cyprus, Greek Orthodox, whereas most Turkish Cypriots are adherents of Sunni Islam. According to Eurobarometer 2005, Cyprus was the second most religious state in the European Union at that time, after Malta (although in 2005 Romania wasn't in the European Union; currently Romania is the most religious state in the EU) ''(see Religion in the European Union)''. The first President of Cyprus, Makarios III, was an archbishop, and the Vice-President of Cyprus was Fazıl Küçük. The current leader of the Greek Orthodox Church of Cyprus is Archbishop Chrysostomos II of Cyprus, Chrysostomos II. Hala Sultan Tekke, situated near the Larnaca Salt Lake is an object of pilgrimage for Muslims. According to the 2001 census carried out in the Government-controlled area,Statistical Service of Cyprus: Population and Social StatisticsMain Results of the 2001 Census. Retrieved 29 February 2009. 94.8% of the population were Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox, 0.9% Armenian religion in Cyprus, Armenians and Maronite Church, Maronites, 1.5% Roman Catholics, 1.0% Church of England, and 0.6% Muslims. There is also a History of the Jews in Cyprus, Jewish community on Cyprus. The remaining 1.3% adhered to other religious denominations or did not state their religion.
Languages
 Cyprus has two official languages, Greek and Turkish language, Turkish. Armenian language, Armenian and Cypriot Maronite Arabic are recognised as minority languages. Although without official status, English is widely spoken and it features widely on road signs, public notices, and in advertisements, etc. English was the sole official language during British colonial rule and the lingua franca until 1960, and continued to be used (de facto) in courts of law until 1989 and in legislation until 1996. 80.4% of Cypriots are proficient in the English language as a second language. Russian is widely spoken among the country's minorities, residents and citizens of post-Soviet countries, and Pontic Greeks. Russian, after English and Greek, is the third language used on many signs of shops and restaurants, particularly in Limassol and Paphos. In addition to these languages, 12% speak French and 5% speak German.Europeans and their Languages
Cyprus has two official languages, Greek and Turkish language, Turkish. Armenian language, Armenian and Cypriot Maronite Arabic are recognised as minority languages. Although without official status, English is widely spoken and it features widely on road signs, public notices, and in advertisements, etc. English was the sole official language during British colonial rule and the lingua franca until 1960, and continued to be used (de facto) in courts of law until 1989 and in legislation until 1996. 80.4% of Cypriots are proficient in the English language as a second language. Russian is widely spoken among the country's minorities, residents and citizens of post-Soviet countries, and Pontic Greeks. Russian, after English and Greek, is the third language used on many signs of shops and restaurants, particularly in Limassol and Paphos. In addition to these languages, 12% speak French and 5% speak German.Europeans and their Languages, Eurobarometer, European Commission, 2006. The everyday spoken language of Greek Cypriots is Cypriot Greek and that of Turkish Cypriots is Cypriot Turkish. These vernaculars both differ from their standard language, standard registers significantly.
Education
Cyprus has a highly developed system of primary and secondary education offering both public and private education. The high quality of instruction can be attributed in part to the fact that nearly 7% of the GDP is spent on education which makes Cyprus one of the top three spenders of education in the EU along with Denmark and Sweden. State schools are generally seen as equivalent in quality of education to private-sector institutions. However, the value of a state high-school diploma is limited by the fact that the grades obtained account for only around 25% of the final grade for each topic, with the remaining 75% assigned by the teacher during the semester, in a minimally transparent way. Cypriot universities (like universities in Greece) ignore high school grades almost entirely for admissions purposes. While a high-school diploma is mandatory for university attendance, admissions are decided almost exclusively on the basis of scores at centrally administered university entrance examinations that all university candidates are required to take. The majority of Cypriots receive their higher education at Greek, British, Turkish, other European and North American universities. Cyprus currently has the highest percentage of citizens of Legal working age, working age who have higher-level education in the EU at 30% which is ahead of Finland's 29.5%. In addition, 47% of its population aged 25–34 have tertiary education, which is the highest in the EU. The body of Cypriot students is highly mobile, with 78.7% studying in a university outside Cyprus.Culture
 Greek Cypriots and Turkish Cypriots share a lot in common in their culture due to cultural exchanges but also have differences. Several traditional food (such as souvla and halloumi) and beverages are similar, as well as expressions and ways of life. Hospitality and buying or offering food and drinks for guests or others are common among both. In both communities, music, dance and art are integral parts of social life and many artistic, verbal and nonverbal expressions, traditional dances such as tsifteteli, similarities in dance costumes and importance placed on social activities are shared between the communities. However, the two communities have distinct religions and religious cultures, with the Greek Cypriots traditionally being Church of Cyprus, Greek Orthodox and Turkish Cypriots traditionally being Sunni Muslims, which has partly hindered cultural exchange. Greek Cypriots have influences from Greece and Christianity, while Turkish Cypriots have influences from Turkey and Islam.
The Limassol Carnival Festival is an annual carnival which is held at
Greek Cypriots and Turkish Cypriots share a lot in common in their culture due to cultural exchanges but also have differences. Several traditional food (such as souvla and halloumi) and beverages are similar, as well as expressions and ways of life. Hospitality and buying or offering food and drinks for guests or others are common among both. In both communities, music, dance and art are integral parts of social life and many artistic, verbal and nonverbal expressions, traditional dances such as tsifteteli, similarities in dance costumes and importance placed on social activities are shared between the communities. However, the two communities have distinct religions and religious cultures, with the Greek Cypriots traditionally being Church of Cyprus, Greek Orthodox and Turkish Cypriots traditionally being Sunni Muslims, which has partly hindered cultural exchange. Greek Cypriots have influences from Greece and Christianity, while Turkish Cypriots have influences from Turkey and Islam.
The Limassol Carnival Festival is an annual carnival which is held at Limassol
Limassol (; el, Λεμεσός, Lemesós ; tr, Limasol or ) is a city on the southern coast of Cyprus and capital of the district with the same name. Limassol is the second largest urban area in Cyprus after Nicosia, with an urban population ...
, in Cyprus. The event which is very popular in Cyprus was introduced in the 20th century.
Arts
 The art history of Cyprus can be said to stretch back up to 10,000 years, following the discovery of a series of Chalcolithic period carved figures in the villages of Khoirokoitia and Lempa (Lemba), Lempa. The island is the home to numerous examples of high quality religious icon painting from the Cyprus in the Middle Ages, Middle Ages as well as List of painted churches in Cyprus, many painted churches. Cypriot architecture was heavily influenced by French Gothic architecture, French Gothic and Italian renaissance architecture, renaissance introduced in the island during the era of Latin domination (1191–1571).
A well known traditional art that dates at least from the 14th century is the Lefkara lace (also known as "Lefkaratika", which originates from the village Pano Lefkara, Lefkara. Lefkara lace is recognised as an intangible cultural heritage (ICH) by Unesco, and it is characterised by distinct design patterns, and its intricate, time-consuming production process. A genuine Lefkara lace with full embroidery can take typically hundreds of hours to be made, and that is why it is usually priced quite high. Another local form of art that originated from Lefkara is the production of Cypriot Filigree (locally known as ''Trifourenio''), a type of jewellery that is made with twisted threads of silver. In Lefkara village there is government funded centre named Lefkara Handicraft Centre the mission of which is to educate and teach the art of making the embroidery and silver jewellery. There's also the Museum of Traditional Embroidery and Silversmithing located in the village which has large collection of local handmade art.
In modern times Cypriot art history begins with the painter Vassilis Vryonides (1883–1958) who studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Venice. Arguably the two founding fathers of modern Cypriot art were Adamantios Diamantis (1900–1994) who studied at London's Royal College of Art and
Christopheros Savva (1924–1968) who also studied in London, at Saint Martin's School of Art. In 1960, Savva founded, together with Welsh artist Glyn Hughes, Apophasis [Decision], the first independent cultural centre of the newly established Republic of Cyprus. In 1968, Savva was among the artists representing Cyprus in its inaugural Pavilion at the 34th Venice Biennale. English Cypriot Artis
The art history of Cyprus can be said to stretch back up to 10,000 years, following the discovery of a series of Chalcolithic period carved figures in the villages of Khoirokoitia and Lempa (Lemba), Lempa. The island is the home to numerous examples of high quality religious icon painting from the Cyprus in the Middle Ages, Middle Ages as well as List of painted churches in Cyprus, many painted churches. Cypriot architecture was heavily influenced by French Gothic architecture, French Gothic and Italian renaissance architecture, renaissance introduced in the island during the era of Latin domination (1191–1571).
A well known traditional art that dates at least from the 14th century is the Lefkara lace (also known as "Lefkaratika", which originates from the village Pano Lefkara, Lefkara. Lefkara lace is recognised as an intangible cultural heritage (ICH) by Unesco, and it is characterised by distinct design patterns, and its intricate, time-consuming production process. A genuine Lefkara lace with full embroidery can take typically hundreds of hours to be made, and that is why it is usually priced quite high. Another local form of art that originated from Lefkara is the production of Cypriot Filigree (locally known as ''Trifourenio''), a type of jewellery that is made with twisted threads of silver. In Lefkara village there is government funded centre named Lefkara Handicraft Centre the mission of which is to educate and teach the art of making the embroidery and silver jewellery. There's also the Museum of Traditional Embroidery and Silversmithing located in the village which has large collection of local handmade art.
In modern times Cypriot art history begins with the painter Vassilis Vryonides (1883–1958) who studied at the Academy of Fine Arts in Venice. Arguably the two founding fathers of modern Cypriot art were Adamantios Diamantis (1900–1994) who studied at London's Royal College of Art and
Christopheros Savva (1924–1968) who also studied in London, at Saint Martin's School of Art. In 1960, Savva founded, together with Welsh artist Glyn Hughes, Apophasis [Decision], the first independent cultural centre of the newly established Republic of Cyprus. In 1968, Savva was among the artists representing Cyprus in its inaugural Pavilion at the 34th Venice Biennale. English Cypriot ArtisGlyn HUGHES
1931–2014. In many ways these two artists set the template for subsequent Cypriot art and both their artistic styles and the patterns of their education remain influential to this day. In particular the majority of Cypriot artists still train in England while others train at art schools in Greece and local art institutions such as the Cyprus College of Art, University of Nicosia and the Frederick Institute of Technology. One of the features of Cypriot art is a tendency towards figurative painting although conceptual art is being rigorously promoted by a number of art "institutions" and most notably the Nicosia Municipal Art Centre. Municipal art galleries exist in all the main towns and there is a large and lively commercial art scene. Cyprus was due to host the international art festival Manifesta in 2006 but this was cancelled at the last minute following a dispute between the Dutch organisers of Manifesta and the Cyprus Ministry of Education and Culture over the location of some of the Manifesta events in the Turkish sector of the capital
Nicosia
Nicosia ( ; el, Λευκωσία, Lefkosía ; tr, Lefkoşa ; hy, Նիկոսիա, romanized: ''Nikosia''; Cypriot Arabic: Nikusiya) is the largest city, capital, and seat of government of Cyprus. It is located near the centre of the Mesaor ...
. There were also complaints from some Cypriot artists that the Manifesta organisation was importing international artists to take part in the event while treating members of the local art community in Cyprus as 'ignorant' and 'uncivilised natives' who need to be taught 'how to make proper art'.
Other notable Greek Cypriot artists include Helene Black, Kalopedis family, Panayiotis Kalorkoti, Nicos Nicolaides, Stass Paraskos, Arestís Stasí, Telemachos Kanthos, Konstantia Sofokleous and Chris Achilleos, and Turkish Cypriot artists include İsmet Güney, Ruzen Atakan and Mutlu Çerkez.
Music
 The traditional folk music of Cyprus has several common elements with Music of Greece, Greek, Music of Turkey, Turkish, and Arabic Music, all of which have descended from Byzantine music, including Greek Cypriot and Turkish Cypriot dances such as the ''sousta'', ''syrtos'', ''zeibekikos'', ''tatsia'', and ''karsilamas'' as well as the Middle Eastern-inspired ''tsifteteli'' and ''arapies''. There is also a form of musical poetry known as ''chattista'' which is often performed at traditional feasts and celebrations. The instruments commonly associated with Cyprus folk music are the violin ("fkiolin"), lute ("laouto"), Cyprus flute (fipple flute, ''pithkiavlin''), oud ("outi"), kanonaki and percussions (including the "drum, tamboutsia"). Composers associated with traditional Cypriot music include Solon Michaelides, Marios Tokas, Evagoras Karageorgis and Savvas Salides. Among musicians is also the acclaimed pianist Cyprien Katsaris, composer Andreas G. Orphanides, and composer and artistic director of the European Capital of Culture initiative Marios Joannou Elia.
Popular music in Cyprus is generally influenced by the Greek ''Laïka'' scene; artists who play in this genre include international Music recording sales certification, platinum star Anna Vissi, Evridiki, and Sarbel. Hip hop music, Hip hop and R&B have been supported by the emergence of Cypriot rap and the urban music scene at Ayia Napa, while in the last years the reggae scene is growing, especially through the participation of many Cypriot artists at the annual Reggae Sunjam festival. Is also noted Cypriot rock music and ''Éntekhno'' rock is often associated with artists such as Michalis Hatzigiannis and Alkinoos Ioannidis. Heavy metal music, Metal also has a small following in Cyprus represented by bands such as Armageddon (rev.16:16), Blynd, Winter's Verge, Methysos and Quadraphonic.
The traditional folk music of Cyprus has several common elements with Music of Greece, Greek, Music of Turkey, Turkish, and Arabic Music, all of which have descended from Byzantine music, including Greek Cypriot and Turkish Cypriot dances such as the ''sousta'', ''syrtos'', ''zeibekikos'', ''tatsia'', and ''karsilamas'' as well as the Middle Eastern-inspired ''tsifteteli'' and ''arapies''. There is also a form of musical poetry known as ''chattista'' which is often performed at traditional feasts and celebrations. The instruments commonly associated with Cyprus folk music are the violin ("fkiolin"), lute ("laouto"), Cyprus flute (fipple flute, ''pithkiavlin''), oud ("outi"), kanonaki and percussions (including the "drum, tamboutsia"). Composers associated with traditional Cypriot music include Solon Michaelides, Marios Tokas, Evagoras Karageorgis and Savvas Salides. Among musicians is also the acclaimed pianist Cyprien Katsaris, composer Andreas G. Orphanides, and composer and artistic director of the European Capital of Culture initiative Marios Joannou Elia.
Popular music in Cyprus is generally influenced by the Greek ''Laïka'' scene; artists who play in this genre include international Music recording sales certification, platinum star Anna Vissi, Evridiki, and Sarbel. Hip hop music, Hip hop and R&B have been supported by the emergence of Cypriot rap and the urban music scene at Ayia Napa, while in the last years the reggae scene is growing, especially through the participation of many Cypriot artists at the annual Reggae Sunjam festival. Is also noted Cypriot rock music and ''Éntekhno'' rock is often associated with artists such as Michalis Hatzigiannis and Alkinoos Ioannidis. Heavy metal music, Metal also has a small following in Cyprus represented by bands such as Armageddon (rev.16:16), Blynd, Winter's Verge, Methysos and Quadraphonic.
Literature
 Literary production of the antiquity includes the ''Cypria'', an epic poetry, epic poem, probably composed in the late 7th century BC and attributed to Stasinus. The ''Cypria'' is one of the first specimens of Greek and European poetry. The Cypriot Zeno of Citium was the founder of the Stoic school of philosophy.
Epic poetry, notably the "acritic songs", flourished during Middle Ages. Two chronicles, one written by Leontios Machairas and the other by Georgios Boustronios, cover the entire Middle Ages until the end of Frankish rule (4th century–1489). Poèmes d'amour written in medieval Greek Cypriot date back from the 16th century. Some of them are actual translations of poems written by Petrarch, Bembo, Ariosto and G. Sannazzaro. Many Cypriot scholars fled Cyprus at troubled times such as Ioannis Kigalas (c. 1622–1687) who migrated from Cyprus to Italy in the 17th century, several of his works have survived in books of other scholars.
Literary production of the antiquity includes the ''Cypria'', an epic poetry, epic poem, probably composed in the late 7th century BC and attributed to Stasinus. The ''Cypria'' is one of the first specimens of Greek and European poetry. The Cypriot Zeno of Citium was the founder of the Stoic school of philosophy.
Epic poetry, notably the "acritic songs", flourished during Middle Ages. Two chronicles, one written by Leontios Machairas and the other by Georgios Boustronios, cover the entire Middle Ages until the end of Frankish rule (4th century–1489). Poèmes d'amour written in medieval Greek Cypriot date back from the 16th century. Some of them are actual translations of poems written by Petrarch, Bembo, Ariosto and G. Sannazzaro. Many Cypriot scholars fled Cyprus at troubled times such as Ioannis Kigalas (c. 1622–1687) who migrated from Cyprus to Italy in the 17th century, several of his works have survived in books of other scholars.
 Hasan Hilmi Efendi, a Turkish Cypriot poet, was rewarded by the Ottoman sultan Mahmud II and said to be the "sultan of the poems".
Modern Greek Cypriot literary figures include the poet and writer Kostas Montis, poet Kyriakos Charalambides, poet Michalis Pasiardis, writer Nicos Nicolaides, Stylianos Atteshlis, Altheides, Loukis Akritas and Demetris Th. Gotsis. Dimitris Lipertis, Vasilis Michaelides and Pavlos Liasides are folk poets who wrote poems mainly in the Cypriot Greek, Cypriot-Greek dialect. Among leading Turkish Cypriot writers are Osman Türkay, twice nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature, Özker Yaşın, Neriman Cahit, Urkiye Mine Balman, Mehmet Yaşın and Neşe Yaşın.
There is an increasingly strong presence of both temporary and permanent emigre Cypriot writers in world literature, as well as writings by second and third -generation Cypriot writers born or raised abroad, often writing in English. This includes writers such as Michael Paraskos and Stephanos Stephanides.
Examples of Cyprus in foreign literature include the works of Shakespeare, with most of the play ''Othello'' by William Shakespeare set on the island of Cyprus. British writer Lawrence Durrell lived in Cyprus from 1952 until 1956, during his time working for the British colonial government on the island, and wrote the book ''Bitter Lemons'' about his time in Cyprus which won the second Duff Cooper Prize in 1957.
Hasan Hilmi Efendi, a Turkish Cypriot poet, was rewarded by the Ottoman sultan Mahmud II and said to be the "sultan of the poems".
Modern Greek Cypriot literary figures include the poet and writer Kostas Montis, poet Kyriakos Charalambides, poet Michalis Pasiardis, writer Nicos Nicolaides, Stylianos Atteshlis, Altheides, Loukis Akritas and Demetris Th. Gotsis. Dimitris Lipertis, Vasilis Michaelides and Pavlos Liasides are folk poets who wrote poems mainly in the Cypriot Greek, Cypriot-Greek dialect. Among leading Turkish Cypriot writers are Osman Türkay, twice nominated for the Nobel Prize in Literature, Özker Yaşın, Neriman Cahit, Urkiye Mine Balman, Mehmet Yaşın and Neşe Yaşın.
There is an increasingly strong presence of both temporary and permanent emigre Cypriot writers in world literature, as well as writings by second and third -generation Cypriot writers born or raised abroad, often writing in English. This includes writers such as Michael Paraskos and Stephanos Stephanides.
Examples of Cyprus in foreign literature include the works of Shakespeare, with most of the play ''Othello'' by William Shakespeare set on the island of Cyprus. British writer Lawrence Durrell lived in Cyprus from 1952 until 1956, during his time working for the British colonial government on the island, and wrote the book ''Bitter Lemons'' about his time in Cyprus which won the second Duff Cooper Prize in 1957.
Mass media
In the 2015 Freedom of the Press report of Freedom House, the Republic of Cyprus andNorthern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus ( tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs), officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC; tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti, ''KKTC''), is a ''de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the Geography of Cyprus, isl ...
were ranked "free". The Republic of Cyprus scored 25/100 in press freedom, 5/30 in Legal Environment, 11/40 in Political Environment, and 9/30 in Economic Environment (the lower scores the better). Reporters Without Borders rank the Republic of Cyprus 24th out of 180 countries in the 2015 World Press Freedom Index, with a score of 15.62
The law provides for freedom of speech and Freedom of the press, press, and the government generally respects these rights in practice. An independent press, an effective judiciary, and a functioning democratic political system combine to ensure freedom of speech and of the press. The law prohibits arbitrary interference with privacy, family, home, or correspondence, and the government generally respects these prohibitions in practice."Cyprus"''Country Reports on Human Rights Practices for 2012'', Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor, U.S. Department of State, 22 March 2013. Retrieved 7 January 2014. Local television companies in Cyprus include the state owned Cyprus Broadcasting Corporation which runs two television channels. In addition on the Greek side of the island there are the private channels ANT1 Cyprus, Plus TV, Mega Channel, Sigma TV, Nimonia TV (NTV) and New Extra. In Northern Cyprus, the local channels are Bayrak, BRT, the Turkish Cypriot equivalent to the Cyprus Broadcasting Corporation, and a number of private channels. The majority of local arts and cultural programming is produced by the Cyprus Broadcasting Corporation and BRT, with local arts documentaries, review programmes and filmed drama series.
Cinema
The most worldwide known Cypriot director, to have worked abroad, is Michael Cacoyannis. In the late 1960s and early 1970s, George Filis produced and directed ''Gregoris Afxentiou'', ''Etsi Prodothike i Kypros'', and ''The Mega Document''. In 1994, Cypriot film production received a boost with the establishment of the Cinema Advisory Committee. In 2000, the annual amount set aside for filmmaking in the national budget was Cypriot pound, CYP£500,000 (about €850,000). In addition to government grants, Cypriot co-productions are eligible for funding from the Council of Europe's Eurimages Fund, which finances European film co-productions. To date, four feature films on which a Cypriot was an executive producer have received funding from Eurimages. The first was ''I Sphagi tou Kokora'' (1996), followed by ''Hellados'' (unreleased), ''To Tama'' (1999), and ''O Dromos gia tin Ithaki'' (2000). Only a small number of foreign films have been made in Cyprus. This includes ''Incense for the Damned'' (1970), The Beloved (1970 film), ''The Beloved'' (1970), and ''Ghost in the Noonday Sun'' (1973). Parts of the John Wayne film ''The Longest Day (film), The Longest Day'' (1962) were also filmed in Cyprus.Cuisine
 During the medieval period, under the French Lusignan monarchs of Cyprus an elaborate form of courtly cuisine developed, fusing French, Byzantine and Middle Eastern forms. The Lusignan kings were known for importing Syrian cooks to Cyprus, and it has been suggested that one of the key routes for the importation of Middle Eastern recipes into France and other Western European countries, such as blancmange, was via the Lusignan Kingdom of Cyprus. These recipes became known in the West as ''vyands de Chypre'', or foods of Cyprus, and the food historian William Woys Weaver has identified over one hundred of them in English, French, Italian and German recipe books of the Middle Ages. One that became particularly popular across Europe in the medieval and early modern periods was a stew made with chicken or fish called ''malmonia'', which in English became mawmeny.
Another example of a Cypriot food ingredient entering the Western European canon is the cauliflower, still popular and used in a variety of ways on the island today, which was associated with Cyprus from the early Middle Ages. Writing in the 12th and 13th centuries the Arab botanists Ibn al-'Awwam and Ibn al-Baitar claimed the vegetable had its origins in Cyprus, and this association with the island was echoed in Western Europe, where cauliflowers were originally known as Cyprus cabbage or ''Cyprus colewart''. There was also a long and extensive trade in cauliflower seeds from Cyprus, until well into the sixteenth century.
Although much of the Lusignan food culture was lost after the fall of Cyprus to the Ottomans in 1571, a number of dishes that would have been familiar to the Lusignans survive today, including various forms of tahini and houmous, zalatina, skordalia and pickled wild song birds called ambelopoulia. Ambelopoulia, which is today highly controversial, and illegal, was exported in vast quantities from Cyprus during the Lusignan and Venetian periods, particularly to Italy and France. In 1533 the English traveller to Cyprus, John Locke, claimed to have seen the pickled wild birds packed into large jars, or which 1200 jars were exported from Cyprus annually.
Also familiar to the Lusignans would have been Halloumi cheese, which some food writers today claim originated in Cyprus during the Byzantine period although the name of the cheese itself is thought by academics to be of Arabic origin.P. Papademas, "Halloumi Cheese" in A.Y. Tamime (ed.), ''Brined Cheeses'' (Oxford: Blackwell Publishing, 2006) p.117 There is no surviving written documentary evidence of the cheese being associated with Cyprus before the year 1554, when the Italian historian Florio Bustron wrote of a sheep-milk cheese from Cyprus he called ''calumi''. Halloumi (Hellim) is commonly served sliced, grilled, fried and sometimes fresh, as an appetiser or meze dish.
During the medieval period, under the French Lusignan monarchs of Cyprus an elaborate form of courtly cuisine developed, fusing French, Byzantine and Middle Eastern forms. The Lusignan kings were known for importing Syrian cooks to Cyprus, and it has been suggested that one of the key routes for the importation of Middle Eastern recipes into France and other Western European countries, such as blancmange, was via the Lusignan Kingdom of Cyprus. These recipes became known in the West as ''vyands de Chypre'', or foods of Cyprus, and the food historian William Woys Weaver has identified over one hundred of them in English, French, Italian and German recipe books of the Middle Ages. One that became particularly popular across Europe in the medieval and early modern periods was a stew made with chicken or fish called ''malmonia'', which in English became mawmeny.
Another example of a Cypriot food ingredient entering the Western European canon is the cauliflower, still popular and used in a variety of ways on the island today, which was associated with Cyprus from the early Middle Ages. Writing in the 12th and 13th centuries the Arab botanists Ibn al-'Awwam and Ibn al-Baitar claimed the vegetable had its origins in Cyprus, and this association with the island was echoed in Western Europe, where cauliflowers were originally known as Cyprus cabbage or ''Cyprus colewart''. There was also a long and extensive trade in cauliflower seeds from Cyprus, until well into the sixteenth century.
Although much of the Lusignan food culture was lost after the fall of Cyprus to the Ottomans in 1571, a number of dishes that would have been familiar to the Lusignans survive today, including various forms of tahini and houmous, zalatina, skordalia and pickled wild song birds called ambelopoulia. Ambelopoulia, which is today highly controversial, and illegal, was exported in vast quantities from Cyprus during the Lusignan and Venetian periods, particularly to Italy and France. In 1533 the English traveller to Cyprus, John Locke, claimed to have seen the pickled wild birds packed into large jars, or which 1200 jars were exported from Cyprus annually.
Also familiar to the Lusignans would have been Halloumi cheese, which some food writers today claim originated in Cyprus during the Byzantine period although the name of the cheese itself is thought by academics to be of Arabic origin.P. Papademas, "Halloumi Cheese" in A.Y. Tamime (ed.), ''Brined Cheeses'' (Oxford: Blackwell Publishing, 2006) p.117 There is no surviving written documentary evidence of the cheese being associated with Cyprus before the year 1554, when the Italian historian Florio Bustron wrote of a sheep-milk cheese from Cyprus he called ''calumi''. Halloumi (Hellim) is commonly served sliced, grilled, fried and sometimes fresh, as an appetiser or meze dish.

, ''BBC News'', 18 October 2004 This island has Protected geographical indications in the European Union#General regime, protected geographical indication (PGI) for its ''lokum'' produced in the village of Geroskipou.
Sports
See also
*Ancient regions of Anatolia *Index of Cyprus-related articles *Outline of CyprusNotes
References
Further reading
* * * Clark, Tommy. ''A Brief History of Cyprus'' (2020excerpt
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Sacopoulo, Marina (1966). ''Chypre d'aujourd'hui''. Paris: G.-P. Maisonneuve et Larose. 406 p., ill. with b&w photos. and fold. maps. * *
External links
Cyprus
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
Timeline of Cyprus by BBC
from ''UCB Libraries GovPubs''
Cyprus
information from the United States Department of State includes Background Notes, Country Study and major reports *
Cyprus profile
from the BBC News
The UN in Cyprus
Cypriot Pottery, Bryn Mawr College Art and Artifact Collections
''The Cesnola collection of Cypriot art : stone sculpture''
a fully digitised text from The Metropolitan Museum of Art libraries * http://cypernochkreta.dinstudio.se Government
Cyprus High Commission Trade Centre – London
Republic of Cyprus – English Language
Press and Information Office – Ministry of Interior
Annan Plan
Tourism
Read about Cyprus on visitcyprus.com
– the official travel portal for Cyprus
Cyprus informational portal and open platform for contribution of Cyprus-related content
– www.Cyprus.com * Official publications
* [http://www.moi.gov.cy/moi/pio/pio.nsf/All/BD477C55623013C5C2256D740027CF98?OpenDocument Legal Issues arising from certain population transfers and displacements on the territory of the Republic of Cyprus in the period since 20 July 1974]
Address to Cypriots by President Papadopoulos (FULL TEXT)
Official Cyprus Government Web Site
Embassy of Greece, USA – Cyprus: Geographical and Historical Background
{{coord, 35, N, 33, E, type:country_region:CY_scale:2500000_source:GNS , display=title Cyprus, Republics in the Commonwealth of Nations Eastern Mediterranean International islands Island countries Islands of Asia Islands of Europe Mediterranean islands Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations Member states of the European Union Member states of the Union for the Mediterranean Member states of the United Nations Middle Eastern countries Near Eastern countries Southeastern European countries Southern European countries Western Asian countries States and territories established in 1960 Countries in Asia Countries in Europe Greek-speaking countries and territories Turkish-speaking countries and territories Countries of Europe with multiple official languages