Custody transfer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Custody Transfer in the 

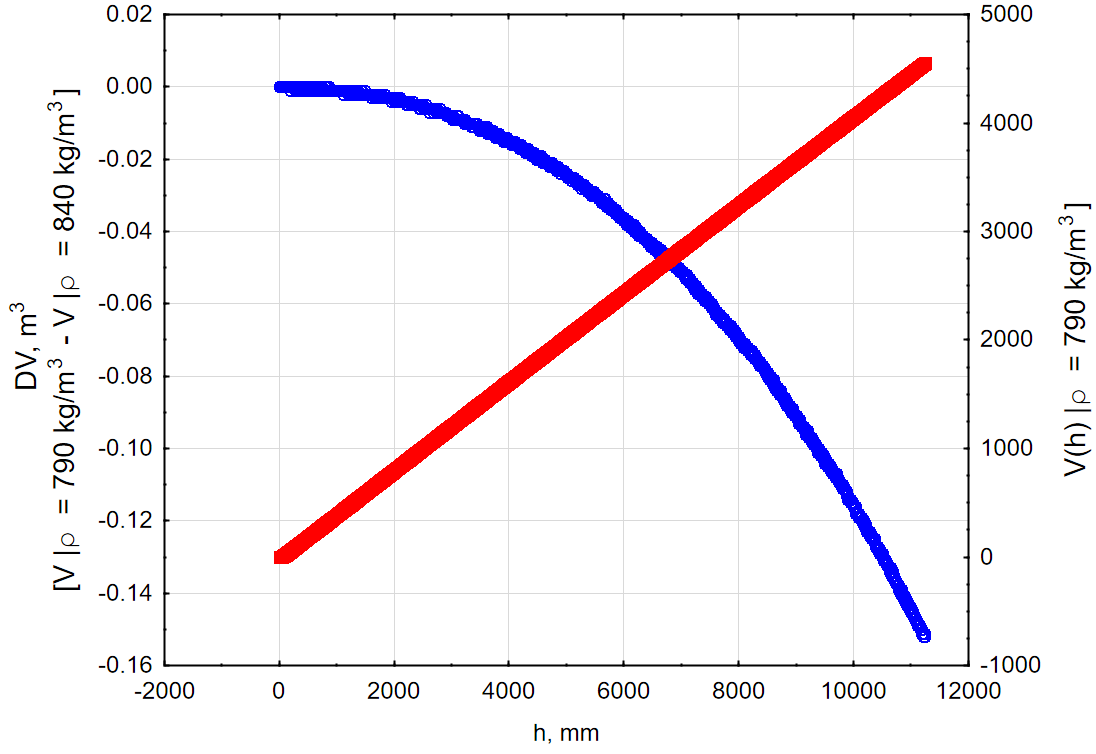 Current volume of a product stored in a tank can be calculated using a tank capacity table (sometimes called "tank calibration table") and current levels and temperatures of a product in a tank. Tank capacity table stores data about level and appropriate volume in a tank and have a very high impact on overall accuracy of volume calculation. Typical accuracy of a capacity tables for custody transfer operations is 0.05..0.1%. Initial installation of a tank, its accuracy and lifecycle changes (like inclination or sediments) affect on the accuracy of the capacity table so they must be revised periodically. Some capacity tables are multidimensional and store additional data - like heel and trim for ships tanks density of stored products and/or are used in systems for automated volume/mass calculations.
Current volume of a product stored in a tank can be calculated using a tank capacity table (sometimes called "tank calibration table") and current levels and temperatures of a product in a tank. Tank capacity table stores data about level and appropriate volume in a tank and have a very high impact on overall accuracy of volume calculation. Typical accuracy of a capacity tables for custody transfer operations is 0.05..0.1%. Initial installation of a tank, its accuracy and lifecycle changes (like inclination or sediments) affect on the accuracy of the capacity table so they must be revised periodically. Some capacity tables are multidimensional and store additional data - like heel and trim for ships tanks density of stored products and/or are used in systems for automated volume/mass calculations.
Measurement Canada
CMC
Tokyo KEIKI
API
Flow Research
GUIDANCE NOTES FOR PETROLEUM MEASUREMENT (Highly recommended)
Fluid mechanics
oil and gas industry
The petroleum industry, also known as the oil industry or the oil patch, includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transportation (often by oil tankers and pipelines), and marketing of petroleum products. The largest ...
refers to the transactions involving transporting physical substance from one operator to another. This includes the transferring of raw and refined petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
between tanks and railway tank car
A tank car ( International Union of Railways (UIC): tank wagon) is a type of railroad car (UIC: railway car) or rolling stock designed to transport liquid and gaseous commodities.
History
Timeline
The following major events occurred in t ...
s; onto ships, and other transactions. Custody transfer in fluid measurement is defined as a metering point (location) where the fluid is being measured for sale from one party to another. During custody transfer, accuracy
Accuracy and precision are two measures of ''observational error''.
''Accuracy'' is how close a given set of measurements (observations or readings) are to their ''true value'', while ''precision'' is how close the measurements are to each other ...
is of great importance to both the company delivering the material and the eventual recipient, when transferring a material.
The term "fiscal metering" is often interchanged with custody transfer, and refers to metering that is a point of a commercial transaction such as when a change in ownership takes place. Custody transfer takes place any time fluids are passed from the possession of one party to another. The use of the phrase "fiscal metering" does not necessary imply any single expectation of the quality of the instrumentation to be installed. "Fiscal" refers to the meter's service, not its quality. "Fiscal" usually means ‘concerned with government finance’.
Custody transfer generally involves:
* Industry standards;
* National metrology standards;
* Contractual agreements between custody transfer parties; and
* Government regulation and taxation.
Due to the high level of accuracy required during custody transfer applications, the flowmeters
Flow measurement is the quantification of bulk fluid movement. Flow can be measured in a variety of ways. The common types of flowmeters with industrial applications are listed below:
* a) Obstruction type (differential pressure or variable area) ...
which are used to perform this are subject to approval by an organization such as the American Petroleum Institute
The American Petroleum Institute (API) is the largest U.S. trade association for the oil and natural gas industry. It claims to represent nearly 600 corporations involved in production, refinement, distribution, and many other aspects of the pet ...
(API).
Custody transfer operations can occur at a number of points along the way; these may include operations, transactions or transferring of oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
from an oil production
Petroleum is a fossil fuel that can be drawn from beneath the earth's surface. Reservoirs of petroleum was formed through the mixture of plants, algae, and sediments in shallow seas under high pressure. Petroleum is mostly recovered from oil dri ...
platform to a ship, barge, railcar, truck and also to the final destination point, such as a refinery
A refinery is a production facility composed of a group of chemical engineering unit processes and unit operations refining certain materials or converting raw material into products of value.
Types of refineries
Different types of refineries ...
.
To complete standards and/or agreements and achieve maximum accuracy all parties included in fuel distribution processes (sellers and buyers, transport & storage services, fiscal depts) must follow the custody transfer procedures, appropriate measurements and related documenting operations must be fully implemented. Custody transfer measurements involve measurements in pipelines, storage tanks, transportation tanks (tankers, trailers or railway tanks) - whole fuel distribution process must be traceable. In order measurements can be made in a volume or mass units (or both), so various metering methods are commonly used.


 Current volume of a product stored in a tank can be calculated using a tank capacity table (sometimes called "tank calibration table") and current levels and temperatures of a product in a tank. Tank capacity table stores data about level and appropriate volume in a tank and have a very high impact on overall accuracy of volume calculation. Typical accuracy of a capacity tables for custody transfer operations is 0.05..0.1%. Initial installation of a tank, its accuracy and lifecycle changes (like inclination or sediments) affect on the accuracy of the capacity table so they must be revised periodically. Some capacity tables are multidimensional and store additional data - like heel and trim for ships tanks density of stored products and/or are used in systems for automated volume/mass calculations.
Current volume of a product stored in a tank can be calculated using a tank capacity table (sometimes called "tank calibration table") and current levels and temperatures of a product in a tank. Tank capacity table stores data about level and appropriate volume in a tank and have a very high impact on overall accuracy of volume calculation. Typical accuracy of a capacity tables for custody transfer operations is 0.05..0.1%. Initial installation of a tank, its accuracy and lifecycle changes (like inclination or sediments) affect on the accuracy of the capacity table so they must be revised periodically. Some capacity tables are multidimensional and store additional data - like heel and trim for ships tanks density of stored products and/or are used in systems for automated volume/mass calculations.
Metering methods
Custody transfer is one of the most important applications forflow measurement
Flow measurement is the quantification of bulk fluid movement. Flow can be measured in a variety of ways. The common types of flowmeters with industrial applications are listed below:
* a) Obstruction type (differential pressure or variable area ...
. Many flow measurement technologies are used for custody transfer applications; these include differential pressure (DP) flowmeters, turbine flowmeters, positive displacement flowmeters, Coriolis flowmeters and ultrasonic flowmeters.
Differential pressure flowmeters
Differential pressure (DP) flowmeters are used for the ''custody transfer'' of liquid and gas to measure the flow of liquid, gas, and steam. The DP flowmeter consist of a differentialpressure transmitter
A pressure sensor is a device for pressure measurement of gases or liquids. Pressure is an expression of the force required to stop a fluid from expanding, and is usually stated in terms of force per unit area. A pressure sensor usually act ...
and a primary element. The primary element places a constriction in a flow stream, while the DP transmitter measures the difference in pressure upstream
Upstream may refer to:
* Upstream (bioprocess)
* ''Upstream'' (film), a 1927 film by John Ford
* Upstream (networking)
* ''Upstream'' (newspaper), a newspaper covering the oil and gas industry
* Upstream (petroleum industry)
* Upstream (software ...
and downstream
Downstream may refer to:
* Downstream (bioprocess)
* Downstream (manufacturing)
* Downstream (networking)
* Downstream (software development)
* Downstream (petroleum industry)
* Upstream and downstream (DNA), determining relative positions on DNA ...
of the constriction.
In many cases, pressure transmitters and primary elements are bought by the end-users from different suppliers. However, several vendors have integrated the pressure transmitter with the primary element to form a complete flowmeter. The advantage of this is that they can be calibrated with the primary element and DP transmitter already in place.
Standards and criteria for the use of DP flowmeters for custody transfer applications are specified by the American Gas Association
The American Gas Association (AGA) is an American trade organization founded in 1918 representing and advocating on behalf of local energy companies that deliver natural gas throughout the United States.
History
The American Gas Association forme ...
(AGA) and the American Petroleum Institute
The American Petroleum Institute (API) is the largest U.S. trade association for the oil and natural gas industry. It claims to represent nearly 600 corporations involved in production, refinement, distribution, and many other aspects of the pet ...
(API).
An advantage of using a DP flowmeters is that they are the most studied and best understood type of flowmeter. A disadvantage of using a DP flowmeters is that they introduce a pressure drop into the flowmeter line. This is a necessary result of the constriction in the line that is required to make the DP flow measurement.
One important development in the use of DP flowmeters for custody transfer applications has been the development of single and dual chamber orifice
An orifice is any opening, mouth, hole or vent, as in a pipe, a plate, or a body
* Body orifice, any opening in the body of a human or animal
*Orifice plate, a restriction used to measure flow or to control pressure or flow, sometimes given specia ...
fittings.
Turbine flowmeters
The first turbine flowmeter was invented by Reinhard Woltman, a German engineer in 1790. Turbine flowmeters consist of a rotor with propeller-like blades that spins as water or some other fluid passes over it. The rotor spins in proportion to flow rate (see turbine meters) . There are many types of turbine meters, but many of those used for gas flow are called axial meters. The turbine flowmeter is most useful when measuring clean, steady, high-speed flow of low-viscosity fluids. In comparison to other flowmeters, the turbine flowmeter has a significant cost advantage over ultrasonic flowmeters, especially in the larger line sizes, and it also has a favourable price compared to the prices of DP flowmeters, especially in cases where one turbine meter can replace several DP meters. The disadvantage of turbine flowmeters is that they have moving parts that are subject to wear. To prevent wear and inaccuracy, durable materials are used, including ceramicball bearing
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.
The purpose of a ball bearing is to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads. It achieves this ...
s.
Positive displacement flowmeters
Positive displacement (PD) flowmeters are highly accurate meters that are widely used for custody transfer ofcommercial
Commercial may refer to:
* a dose of advertising conveyed through media (such as - for example - radio or television)
** Radio advertisement
** Television advertisement
* (adjective for:) commerce, a system of voluntary exchange of products and s ...
and industrial water, as well as for custody transfer of many other liquids. PD flowmeters have the advantage that they have been approved by a number of regulatory bodies for this purpose, and they have not yet been displaced by other applications.
PD meters excel at measuring low flows, and also at measuring highly viscous flows, because PD meters captures the flow in a container of known volume. Speed
In everyday use and in kinematics, the speed (commonly referred to as ''v'') of an object is the magnitude of the change of its position over time or the magnitude of the change of its position per unit of time; it is thus a scalar quanti ...
of flow doesn't matter when using a PD meter.
Coriolis flowmeters
Coriolis flowmeters have been around for more than 30 years and are preferred in process industries such aschemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wi ...
and food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is inge ...
and beverage
A drink or beverage is a liquid intended for human consumption. In addition to their basic function of satisfying thirst, drinks play important roles in human culture. Common types of drinks include plain drinking water, milk, juice, smoothies a ...
. Coriolis technology offers accuracy and reliability in measuring material flow, and is often hailed as among the best flow measurement technologies due to direct mass flow, fluid density, temperature, and precise calculated volume flow rates. Coriolis meters do not have any moving parts and provide long term stability, repeatability, and reliability. Because they are direct mass flow measurement devices, Coriolis meters can handle the widest range of fluids from gases to heavy liquids and are not impacted by viscosity or density changes that often effect velocity based technologies (PD, Turbine, Ultrasonic). With the widest flow range capability of any flow technology, Coriolis can be sized for low pressure drop. This combined with the fact that they are not flow profile dependent helps eliminate the need for straight runs and flow conditioning which enables custody transfer systems to be designed with minimal pressure drop.
It has to be mentioned that any measurement instrument that relies on one measurement principle only will show a higher measurement uncertainty
In metrology, measurement uncertainty is the expression of the statistical dispersion of the values attributed to a measured quantity. All measurements are subject to uncertainty and a measurement result is complete only when it is accompanied by ...
under two-phase flow conditions. Conventional measurement principles, like positive displacement, turbine meters, orifice plates will seemingly continue to measure, but will not be able to inform the user about the occurrence of two-phase flow. Yet modern principles based on the Coriolis effect
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
or ultrasonic flow measurement will inform the user by means of diagnostic functions.
Flow is measured using Coriolis meters by analyzing the changes in the Coriolis force of a flowing substance. The force is generated in a mass moving within a rotating frame of reference. An angular, outward acceleration
In mechanics, acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Accelerations are vector quantities (in that they have magnitude and direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by the ...
, which is factored with linear velocity
Velocity is the directional speed of an object in motion as an indication of its rate of change in position as observed from a particular frame of reference and as measured by a particular standard of time (e.g. northbound). Velocity is a ...
is produced due to the rotation. With a fluid mass, the Coriolis force is proportional to the mass flow rate of that fluid.
A Coriolis meter has two main components: an oscillating flow tube equipped with sensors
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends ...
and drivers, and an electronic transmitter
In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna (radio), antenna. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which i ...
that controls the oscillations, analyzes the results, and transmits the information. The Coriolis principle for flow measurement
Flow measurement is the quantification of bulk fluid movement. Flow can be measured in a variety of ways. The common types of flowmeters with industrial applications are listed below:
* a) Obstruction type (differential pressure or variable area ...
requires the oscillating
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
section of a rotating pipe to be exploited. Oscillation produces the Coriolis force, which traditionally is sensed and analyzed to determine the rate of flow. Modern coriolis meters utilize the phase difference measured at each end of the oscillating pipe.
Ultrasonic flowmeters
Ultrasonic flowmeters were first introduced into industrial markets in 1963 by ''Tokyo Keiki'' (now Tokimec) in Japan. Custody transfer measurements have been around for a long time, and over the past ten years, Coriolis and ultrasonic meters have become the flowmeters of choice for custody transfer in theoil and gas industry
The petroleum industry, also known as the oil industry or the oil patch, includes the global processes of exploration, extraction, refining, transportation (often by oil tankers and pipelines), and marketing of petroleum products. The largest ...
.
Ultrasonic meters provide volumetric flow rate. They typically use the transit-time method, where sounds waves transmitted in the direction of fluid flow travel faster than those travelling upstream. The transit time difference is proportional to fluid velocity. Ultrasonic flow meters have negligible pressure drop if recommended installation is followed, have high turndown capability, and can handle a wide range of applications. Crude oil production, transportation, and processing are typical applications for this technology.
The use of ultrasonic flowmeters is continuing to grow for custody transfer. Unlike PD and turbine meters, ultrasonic flowmeters do not have moving parts. Pressure drop is much reduced with an ultrasonic meter when compared to PD, turbine, and DP meters. Installation of ultrasonic meters is relatively straightforward, and maintenance requirements are low.
In June 1998, The American Gas Association
The American Gas Association (AGA) is an American trade organization founded in 1918 representing and advocating on behalf of local energy companies that deliver natural gas throughout the United States.
History
The American Gas Association forme ...
published a standard called AGA-9. This standard lays out the criteria for the use of ultrasonic flowmeters for Custody Transfer of Natural Gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
.
Components
Custody transfer requires an entire metering system that is designed and engineered for the application, not just flowmeters. Components of a custody transfer system typically include: * Multiple meters/meter runs; *Flow computer
A flow computer is an electronic computer which implements algorithms using the analog and digital signals received from flow meters, temperature, pressure and density transmitters to which it is connected into volumes at base conditions. They ar ...
s;
* Quality system
A quality management system (QMS) is a collection of business processes focused on consistently meeting customer requirements and enhancing their satisfaction. It is aligned with an organization's purpose and strategic direction (ISO 9001:2015). I ...
s (gas chromatographs to measure energy content of natural gas and sampling systems for liquid);
* Calibration
In measurement technology and metrology, calibration is the comparison of measurement values delivered by a device under test with those of a calibration standard of known accuracy. Such a standard could be another measurement device of know ...
using in-place or mobile provers for liquid, or master-meter for liquid or gas; and
* Supporting automation.
A typical liquid custody transfer skid includes multiple flowmeters
Flow measurement is the quantification of bulk fluid movement. Flow can be measured in a variety of ways. The common types of flowmeters with industrial applications are listed below:
* a) Obstruction type (differential pressure or variable area) ...
and meter provers. Provers are used to calibrate meters in-situ and are performed frequently; typically before, during, and after a batch transfer for metering assurance. A good example of this is a Lease Automatic Custody Transfer (LACT) unit in a crude oil production facility.
Accuracy
In theISO
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization.
ISO or Iso may also refer to: Business and finance
* Iso (supermarket), a chain of Danish supermarkets incorporated into the SuperBest chain in 2007
* Iso ...
5725-1 standard accuracy for measuring instruments is defined as “the closeness of agreement between a test result and the accepted reference value”. This term “accuracy” includes both the systematic error
An error (from the Latin ''error'', meaning "wandering") is an action which is inaccurate or incorrect. In some usages, an error is synonymous with a mistake. The etymology derives from the Latin term 'errare', meaning 'to stray'.
In statistics ...
and the bias component. Each device has its manufacturer stated accuracy specification
A specification often refers to a set of documented requirements to be satisfied by a material, design, product, or service. A specification is often a type of technical standard.
There are different types of technical or engineering specificati ...
and its tested accuracy. Uncertainty
Uncertainty refers to epistemic situations involving imperfect or unknown information. It applies to predictions of future events, to physical measurements that are already made, or to the unknown. Uncertainty arises in partially observable or ...
takes all the metering system factors that impact measurement accuracy into account. The accuracy of flowmeters could be used in two different metering systems that ultimately have different calculated uncertainties due to other factors in the system that affect flow calculations. Uncertainty even includes such factors as the flow computer's A/D converter accuracy. The quest for accuracy in a custody transfer system requires meticulous attention to detail.
Custody transfer requirements
Custody transfer metering systems must meet requirements set by industry bodies such asAGA
Aga or AGA may refer to:
Business
* Architectural Glass and Aluminum (AGA), a glazing contractor, established in 1970
* AGA (automobile), ''Autogen Gasaccumulator AG'', 1920s German car company
*AGA AB, ''Aktiebolaget Svenska Gasaccumulator'', a ...
, API
An application programming interface (API) is a way for two or more computer programs to communicate with each other. It is a type of software Interface (computing), interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standa ...
, or ISO
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization.
ISO or Iso may also refer to: Business and finance
* Iso (supermarket), a chain of Danish supermarkets incorporated into the SuperBest chain in 2007
* Iso ...
, and national metrology standards such as OIML
The International Organization of Legal Metrology (french: Organisation Internationale de Métrologie Légale - OIML), is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental organisation that was created in 1955 to promote the global harmonisation ...
(International), NIST
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is an agency of the United States Department of Commerce whose mission is to promote American innovation and industrial competitiveness. NIST's activities are organized into physical sci ...
(U.S.), PTB (Germany), CMC (China), and GOST
GOST (russian: ГОСТ) refers to a set of international technical standards maintained by the ''Euro-Asian Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (EASC)'', a regional standards organization operating under the auspices of th ...
(Russia), DSTU (Ukraine) among others. These requirements can be of two types: Legal
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vario ...
and Contract
A contract is a legally enforceable agreement between two or more parties that creates, defines, and governs mutual rights and obligations between them. A contract typically involves the transfer of goods, services, money, or a promise to tran ...
.
Legal
The national Weights & Measures codes and regulations control the wholesale and retail trade requirements to facilitate fair trade. The regulations and accuracy requirements vary widely between countries and commodities, but they all have one common characteristic - “traceability Traceability is the capability to trace something. In some cases, it is interpreted as the ability to verify the history, location, or application of an item by means of documented recorded identification.
Other common definitions include the capab ...
”. There is always a procedure that defines the validation process where the duty meter is compared to a standard that is traceable to the legal metrology agency of the respective region.
Contract
Acontract
A contract is a legally enforceable agreement between two or more parties that creates, defines, and governs mutual rights and obligations between them. A contract typically involves the transfer of goods, services, money, or a promise to tran ...
is a written agreement between buyers and sellers that defines the measurement requirements. These are large-volume sales between operating companies where refined products and crude oils are transported by marine
Marine is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the sea or ocean.
Marine or marines may refer to:
Ocean
* Maritime (disambiguation)
* Marine art
* Marine biology
* Marine debris
* Marine habitats
* Marine life
* Marine pollution
Military
* ...
, pipeline
Pipeline may refer to:
Electronics, computers and computing
* Pipeline (computing), a chain of data-processing stages or a CPU optimization found on
** Instruction pipelining, a technique for implementing instruction-level parallelism within a s ...
or rail
Rail or rails may refer to:
Rail transport
*Rail transport and related matters
*Rail (rail transport) or railway lines, the running surface of a railway
Arts and media Film
* ''Rails'' (film), a 1929 Italian film by Mario Camerini
* ''Rail'' ( ...
. Custody transfer measurement must be at the highest level of accuracy possible because a small error in measurement can amount to a large financial difference. Due to these critical natures of measurements, petroleum companies around the world have developed and adopted standards to meet the industry's needs.
In Canada, for instance, all measurement of a custody transfer nature falls under the purview of Measurement Canada
Measurement Canada (french: Mesures Canada) is a special operating agency of the Government of Canada's Innovation, Science and Economic Development portfolio, in the Small Business, Tourism and Marketplace Services sector. The agency's mandate i ...
. In the US, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) is the United States federal agency that regulates the transmission and wholesale sale of electricity and natural gas in interstate commerce and regulates the transportation of oil by pipeline in ...
(FERC) controls the standards which must be met for interstate trade.
Liquid custody transfer
Custody transfer of liquid flow measurement follow guidelines set by theISO
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization.
ISO or Iso may also refer to: Business and finance
* Iso (supermarket), a chain of Danish supermarkets incorporated into the SuperBest chain in 2007
* Iso ...
. By industrial consensus, liquid flow measurement is defined as having an overall uncertainty
Uncertainty refers to epistemic situations involving imperfect or unknown information. It applies to predictions of future events, to physical measurements that are already made, or to the unknown. Uncertainty arises in partially observable or ...
of ±0.25% or better. The overall uncertainty is derived from an appropriate statistical combination of the component uncertainties in the measurement system.
Mode of measurement
Volume or mass measurement
Liquid flow measurements are usually in volumetric or mass unit. Volume is normally used for stand-alone field tanker loading operations, while mass is used for multi-field pipeline or offshore pipeline with an allocation requirement. Mass measurement and reporting are achieved by * Measurement of volume flow rate (for example, by turbine or ultrasonic meter) and fluid density * Direct mass measurement by Coriolis meterSampling system
An automatic flow-proportional sampling system is used in flow measurement to determine the average water content, average density and for analysis purposes. Sampling systems should be broadly in accordance withISO
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization.
ISO or Iso may also refer to: Business and finance
* Iso (supermarket), a chain of Danish supermarkets incorporated into the SuperBest chain in 2007
* Iso ...
3171.
The sampling system is a critical section during flow measurement. Any errors introduced through sampling error will generally have a direct, linear effect on the overall measurement.
Temperature and pressure measurement
Temperature and pressure measurement are important factors to consider when taking flow measurements of liquids. Temperature and pressure measurement points should be situated as close to the meter as possible, in reference to their conditions at the meter inlet. Temperature measurements that affect the accuracy of the metering system should have an overall loop accuracy of 0.5 °C or better, and the corresponding readout should have a resolution of 0.2 °C or better. Temperature checks are performed by certifiedthermometers
A thermometer is a device that measures temperature or a temperature gradient (the degree of hotness or coldness of an object). A thermometer has two important elements: (1) a temperature sensor (e.g. the bulb of a mercury-in-glass thermomete ...
with the aid of Thermowell
Thermowells are cylindrical fittings used to protect temperature sensors installed in industrial processes. A thermowell consists of a tube closed at one end and mounted in the process stream. A temperature sensor such as a thermometer, thermocoup ...
s
Pressure measurements that affect the accuracy of the metering system should have an overall loop accuracy of 0.5 bar or better and the corresponding readout should have a resolution of 0.1 bar or better.
Gaseous custody transfer
Custody transfer of gaseous flow measurement follow guidelines set by theinternational bodies
International is an adjective (also used as a noun) meaning "between nations".
International may also refer to:
Music Albums
* ''International'' (Kevin Michael album), 2011
* ''International'' (New Order album), 2002
* ''International'' (The T ...
. By industrial consensus, gaseous flow measurement is defined as mass flow measurement with an overall uncertainty of ±1.0% or better. The overall uncertainty is derived from an appropriate statistical combination of the component uncertainties in the measurement system.
Mode of measurement
Volume or mass unit
All gaseous flow measurement must be made on single-phase gas streams, having measurements in either volumetric or mass units.Sampling
Sampling is an important aspect, as they help to ascertain accuracy. Apt facilities should be provided for the purpose of obtaining representative samples. The type of instrumentation and the measuring system may influence this requirement.Gas density
Gasdensity
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematical ...
at the meter may be determined either by:
* Continuous direct measurement, by on-line densitometer
A densitometer is a device that measures the degree of darkness (the optical density) of a photographic or semitransparent material or of a reflecting surface. The densitometer is basically a light source aimed at a photoelectric cell. It determ ...
* Calculation, using a recognised equation of state together with measurements of the gas temperature, pressure and composition.
Most industries prefer to use the continuous measurement of gas density. However, both methods may be used simultaneously, and the comparison of their respective results may provide additional confidence in the accuracy of each method.
Best practices
In any custody transfer application, a true randomuncertainty
Uncertainty refers to epistemic situations involving imperfect or unknown information. It applies to predictions of future events, to physical measurements that are already made, or to the unknown. Uncertainty arises in partially observable or ...
has an equal chance of favouring either party, the net impact should be zero to both parties, and measurement accuracy and repeatability should not be valued. Measurement accuracy and repeatability are of high value to most seller because many users install check meters.
The first step in designing any custody transfer system is to determine the mutual measurement performance expectations of the supplier and the user over the range of flow rates. This determination of mutual performance expectations should be made by individuals who have a clear understanding of all of the costs of measurement disputes caused by poor repeatability.
The second step is to quantify the operating conditions which are not controllable. For a flow measurement, these can include:
* Expected ambient temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
variation;
* Maximum static line pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country and e ...
;
* Static line pressure and temperature variation;
* Maximum allowable permanent pressure loss;
* Flow turndown; and
* Expected frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
of flow variation and/or pulsation.
The third and final step is to select hardware, installation and maintenance procedures which will ensure that the measurement provides the required installed performance under the expected (uncontrollable) operating conditions. For example, the user can:
* Select a static and/or differential pressure transmitter which has better or worse performance under the given real-world operating conditions.
* Calibrate the transmitter(s) frequently or infrequently.
* In the case of a DP flowmeter, size the primary element for a higher or lower differential pressure (higher DP's provide higher accuracy, at the expense of higher pressure loss).
* Select a flowmeter and pressure transmitter with faster or slower response.
* Use long or short interconnection (impulse) lines, or direct connect for fastest response.
While the first and second steps involve gathering data, the third step may require calculations and/or testing.
General formula for calculating energy transferred (LNG)
The formula for calculating theLNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volu ...
transferred depends on the contractual sales conditions. These can relate to three types of sale contract as defined by Incoterms
The Incoterms or International Commercial Terms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law. Incoterms define the responsiblities of exporters and ...
2000: an FOB sale, a CIF
Cif is a French brand of household cleaning products owned by the Anglo-Dutch company Unilever, known as Jif in Australia, New Zealand, Japan, Middle East and the Nordic countries.
Cif was launched in France in 1965 and was marketed in competit ...
sale or a DES
Des is a masculine given name, mostly a short form (hypocorism) of Desmond. People named Des include:
People
* Des Buckingham, English football manager
* Des Corcoran, (1928–2004), Australian politician
* Des Dillon (disambiguation), sever ...
sale.
In the case of an FOB (Free On Board) sale, the determination of the energy transferred and invoiced for will be made in the loading port.
In the case of a CIF
Cif is a French brand of household cleaning products owned by the Anglo-Dutch company Unilever, known as Jif in Australia, New Zealand, Japan, Middle East and the Nordic countries.
Cif was launched in France in 1965 and was marketed in competit ...
(Cost Insurance & Freight) or a DES
Des is a masculine given name, mostly a short form (hypocorism) of Desmond. People named Des include:
People
* Des Buckingham, English football manager
* Des Corcoran, (1928–2004), Australian politician
* Des Dillon (disambiguation), sever ...
(Delivered Ex Ship) sale, the energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat a ...
transferred and invoiced for will be determined in the unloading port.
In FOB contracts, the buyer is responsible to provide and maintain the custody transfer measurement systems on board the vessel for volume, temperature and pressure determination and the seller is responsible to provide and maintain the custody transfer measurement systems at the loading terminal such as the sampling and gas analysis. For CIF
Cif is a French brand of household cleaning products owned by the Anglo-Dutch company Unilever, known as Jif in Australia, New Zealand, Japan, Middle East and the Nordic countries.
Cif was launched in France in 1965 and was marketed in competit ...
and DES
Des is a masculine given name, mostly a short form (hypocorism) of Desmond. People named Des include:
People
* Des Buckingham, English football manager
* Des Corcoran, (1928–2004), Australian politician
* Des Dillon (disambiguation), sever ...
contracts the responsibility is reversed.
Both buyer and seller have the right to verify the accuracy of each system that is provided, maintained and operated by the other party.
The determination of the transferred energy usually happens in the presence of one or more surveyors, the ship's cargo officer and a representative of the LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volu ...
terminal operator. A representative of the buyer can also be present.
In all cases, the transferred energy can be calculated with the following formula:
''E =(VLNG × DLNG × GVCLNG) - Egas displaced ± Egas to ER (if applicable)''
Where:
''E'' = the total net energy transferred from the loading facilities to the LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volu ...
carrier, or from the LNG carrier to the unloading facilities.
''VLNG''= the volume of LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volu ...
loaded or unloaded in m3.
''DLNG'' = the density of LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volu ...
loaded or unloaded in kg/m3.
''GCVLNG'' = the gross calorific value of the LNG loaded or unloaded in million BTU
The British thermal unit (BTU or Btu) is a unit of heat; it is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. It is also part of the United States customary units. The modern SI u ...
/kg
''E gas displaced'' = The net energy of the displaced gas, also in million BTU
The British thermal unit (BTU or Btu) is a unit of heat; it is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. It is also part of the United States customary units. The modern SI u ...
, which is either:
sent back onshore by the LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volu ...
carrier when loading (volume of gas in cargo tanks displaced by same volume of loaded LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volu ...
),
Or, gas
Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).
A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. oxygen), or ...
received by the LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volu ...
carrier in its cargo tanks when unloading in replacement of the volume of discharged LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volu ...
.
''E(gas to ER)'' = If applicable, the energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat a ...
of the gas consumed in the LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volu ...
carrier's engine room during the time between opening and closing custody transfer surveys, i.e. used by the vessel at the port, which is:
''+ For an LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volu ...
loading transfer'' or
''- For an LNG
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volu ...
unloading transfer''
References
{{ReflistExternal links
Measurement Canada
CMC
Tokyo KEIKI
API
Flow Research
GUIDANCE NOTES FOR PETROLEUM MEASUREMENT (Highly recommended)
Fluid mechanics