Culture of Cornwall on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 The culture of Cornwall ( kw, Gonisogeth Kernow) forms part of the
The culture of Cornwall ( kw, Gonisogeth Kernow) forms part of the

 Cornwall produced a substantial number of passion plays such as the
Cornwall produced a substantial number of passion plays such as the


 The culture of Cornwall ( kw, Gonisogeth Kernow) forms part of the
The culture of Cornwall ( kw, Gonisogeth Kernow) forms part of the culture of the United Kingdom
British culture is influenced by History of the United Kingdom, the combined nations' history; its historically Christianity, Christian Religion in the United Kingdom, religious life, its interaction with the cultures of Europe, the traditions o ...
, but has distinct customs, traditions and peculiarities. Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
has many strong local traditions. After many years of decline, Cornish culture has undergone a strong revival, and many groups exist to promote Cornwall's culture and language today.
Language
The Cornish language is aCeltic language
The Celtic languages ( usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward ...
closely related to Breton
Breton most often refers to:
*anything associated with Brittany, and generally
** Breton people
** Breton language, a Southwestern Brittonic Celtic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken in Brittany
** Breton (horse), a breed
**Ga ...
and slightly less so to Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
and Cumbric
Cumbric was a variety of the Common Brittonic language spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North" in what is now the counties of Westmorland, Cumberland and northern Lancashire in Northern England and the souther ...
. All of these are directly descended from the British language formerly spoken throughout most of Britain. The language went into decline following the introduction of the English ''Book of Common Prayer
The ''Book of Common Prayer'' (BCP) is the name given to a number of related prayer books used in the Anglican Communion and by other Christian churches historically related to Anglicanism. The original book, published in 1549 in the reign ...
'' (in 1549) and by the turn of the 19th century had ceased to be used as a community language (see main article for further discussion).
During the 19th century researchers began to study the language from any remaining isolated speakers and in 1904 Henry Jenner
Henry Jenner (8 August 1848 – 8 May 1934) was a British scholar of the Celtic languages, a Cornish cultural activist, and the chief originator of the Cornish language revival.
Jenner was born at St Columb Major on 8 August 1848. He was the ...
published ''A Handbook in the Cornish Language'' which started the revival proper. Although less than 1% of Cornwall's population speak the language and 'mother tongue' speakers are in their hundreds rather than thousands, the language continues to play a significant part in the culture of Cornwall.
Some events will use Cornish, in short phrases, openings, greetings or names. There is a healthy tradition of music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect ...
in the language, which can also be enjoyed by non-speakers. The vast majority of place names in Cornwall are derived from the language, and many people who live in Cornwall know a few words or phrases, e.g. 'Kernow bys vyken!' ('Cornwall forever!). Many Cornish houses, businesses, children, pets and boats are named in the language, thus it has use as an "official community language" and any Cornish speaker will often be asked to provide translations. The language is also used in official business, with the home of Cornwall Council
Cornwall Council ( kw, Konsel Kernow) is the unitary authority for Cornwall in the United Kingdom, not including the Isles of Scilly, which has its own unitary council. The council, and its predecessor Cornwall County Council, has a tradition o ...
being renamed from New County Hall to Lys Kernow and several of the region's MPs using the language in the Houses of Parliament
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parliament, the Palace lies on the north bank ...
. These include Andrew George, Dan Rogerson
Daniel John Rogerson (born 23 July 1975, St Austell) is a British Liberal Democrat politician. He was the Member of Parliament (MP) for North Cornwall from the 2005 general election until his defeat at the 2015 general election. In October 20 ...
, Sarah Newton
Sarah Louise Newton, ( Hick; 19 July 1961) is a British Conservative Party politician who served as Member of Parliament (MP) for Truro and Falmouth from 2010 to 2019.
Early life
Born in Gloucestershire, Newton moved to Cornwall at an early ...
and Scott Mann, who have all used the language, at various times, to swear their oaths of allegiance
An oath of allegiance is an oath whereby a subject or citizen acknowledges a duty of allegiance and swears loyalty to a monarch or a country. In modern republics, oaths are sworn to the country in general, or to the country's constitution. For ...
to the Queen.
Cornish literature and folklore
The ancientBrythonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
country shares much of its cultural history with neighbouring Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devon is ...
and Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lord_ ...
in England and Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
and Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo language, Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, Historical region, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known ...
further afield. Historic records of authentic Cornish mythology or history are hard to verify but the earliest Cornish language
Cornish (Standard Written Form: or ) , is a Southwestern Brittonic language, Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language family. It is a List of revived languages, revived language, having become Extinct language, extinct as a livin ...
(such as the Bodmin manumissions
The Bodmin manumissions are records included in a manuscript Gospel book, the Bodmin Gospels or St Petroc Gospels, British Library, Add MS 9381. The manuscript is mostly in Latin, but with elements in Old English and the earliest written example ...
) marks the separation of Primitive Cornish
Primitive may refer to:
Mathematics
* Primitive element (field theory)
* Primitive element (finite field)
* Primitive cell (crystallography)
* Primitive notion, axiomatic systems
* Primitive polynomial (disambiguation), one of two concepts
* Prim ...
from Old Welsh
Old Welsh ( cy, Hen Gymraeg) is the stage of the Welsh language from about 800 AD until the early 12th century when it developed into Middle Welsh.Koch, p. 1757. The preceding period, from the time Welsh became distinct from Common Brittonic ...
often dated to the Battle of Deorham
The Battle of Deorham (or Dyrham) is claimed as a decisive military encounter between the West Saxons and the Britons of the West Country in 577. The battle, which was a major victory for Wessex's forces led by Ceawlin and his son, Cuthwine, r ...
in 577.
Due to language erosion and possible suppression caused by the dominant English language and culture in the later medieval period, many works of Cornish language are thought to have been lost, particularly at the time of the dissolution of the religious houses of Glasney College
Glasney College ( kw, Kolji Glasneth) was founded in 1265 at Penryn, Cornwall, by Bishop Bronescombe and was a centre of ecclesiastical power in medieval Cornwall and probably the best known and most important of Cornwall's religious institut ...
and Crantock College, which were regarded as repertories of 'Welsh' (i.e., foreign) conservatism by the English. Cornish grievances against the policies of the English government led to the unsuccessful uprisings of the Cornish Rebellion of 1497 and the Prayer Book Rebellion
The Prayer Book Rebellion or Western Rising was a popular revolt in Cornwall and Devon in 1549. In that year, the ''Book of Common Prayer'', presenting the theology of the English Reformation, was introduced. The change was widely unpopular, ...
of 1549.
However, significant portions of the 'Matter of Britain
The Matter of Britain is the body of medieval literature and legendary material associated with Great Britain and Brittany and the list of legendary kings of Britain, legendary kings and heroes associated with it, particularly King Arthur. It ...
' relate to the people of Cornwall and Brittany as they do to the modern 'Welsh'--this extends from Geoffrey of Monmouth
Geoffrey of Monmouth ( la, Galfridus Monemutensis, Galfridus Arturus, cy, Gruffudd ap Arthur, Sieffre o Fynwy; 1095 – 1155) was a British cleric from Monmouth, Wales and one of the major figures in the development of British historiograph ...
to the Mabinogion
The ''Mabinogion'' () are the earliest Welsh prose stories, and belong to the Matter of Britain. The stories were compiled in Middle Welsh in the 12th–13th centuries from earlier oral traditions. There are two main source manuscripts, create ...
and the Breton
Breton most often refers to:
*anything associated with Brittany, and generally
** Breton people
** Breton language, a Southwestern Brittonic Celtic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken in Brittany
** Breton (horse), a breed
**Ga ...
-derived tales of King Arthur
King Arthur ( cy, Brenin Arthur, kw, Arthur Gernow, br, Roue Arzhur) is a legendary king of Britain, and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain.
In the earliest traditions, Arthur appears as a ...
which make frequent and explicit reference to the geography of the early Brythonic nation, such as his capital at ' Kelliwic in Cerniw' and the legendary sea fortress of King Mergh at Tintagel
Tintagel () or Trevena ( kw, Tre war Venydh, meaning ''Village on a Mountain'') is a civil parish and village situated on the Atlantic coast of Cornwall, England. The village and nearby Tintagel Castle are associated with the legends surroundin ...
.
By the Shakespearean period, these ancient texts still maintained a currency demonstrated by ''King Lear
''King Lear'' is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare.
It is based on the mythological Leir of Britain. King Lear, in preparation for his old age, divides his power and land between two of his daughters. He becomes destitute and insane an ...
'' based on the ancient tale of Leir of Britain
Leir was a legendary king of the Britons whose story was recounted by Geoffrey of Monmouth in his pseudohistorical 12th-century ''History of the Kings of Britain''. According to Geoffrey's genealogy of the British dynasty, Leir's reign would ha ...
which names Corineus
Corineus, in medieval British legend, was a prodigious warrior, a fighter of giants, and the eponymous founder of Cornwall.
''History of the Kings of Britain''
In Geoffrey of Monmouth's pseudo-history ''History of the Kings of Britain'' (113 ...
the eponymous founder of the Cornish nation; he traditionally wrestled the giant Goemagot
Gogmagog (also ''Goemagot, Goemagog, Goëmagot'' and ''Gogmagoc'') was a legendary giant in Welsh and later English mythology. According to Geoffrey of Monmouth's ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' ("The History of The Kings of Britain", 12th century) ...
into the sea at Plymouth Hoe
Plymouth Hoe, referred to locally as the Hoe, is a large south-facing open public space in the English coastal city of Plymouth. The Hoe is adjacent to and above the low limestone cliffs that form the seafront and it commands views of Plymouth ...
and claimed the land beyond for his people; the probable origin of the tale of Jack the Giant Killer
"Jack the Giant Killer" is a Cornish fairy tale and legend about a young adult who slays a number of bad giants during King Arthur's reign. The tale is characterised by violence, gore and blood-letting. Giants are prominent in Cornish folklor ...
.
The earliest Cornish literature is in the Cornish language and Cornwall produced a substantial number of passion plays during the Middle Ages. Many are still extant, and provide valuable information about the language: they were performed in round ' plen a gwary' (place for playing) open-air theatres.
There is much traditional folklore in Cornwall, often tales of giants, mermaids, piskies or the 'pobel vean' (little people). These are still surprisingly popular today, with many events hosting a 'droll teller' to tell the stories: such myths and stories have found much publishing success, particularly in children's books.
The fairy tale Jack the Giant Killer
"Jack the Giant Killer" is a Cornish fairy tale and legend about a young adult who slays a number of bad giants during King Arthur's reign. The tale is characterised by violence, gore and blood-letting. Giants are prominent in Cornish folklor ...
takes place in Cornwall.
Cornish dialect writing
Writing in theCornish dialect
The Cornish dialect (also known as Cornish English, Cornu-English, kw, Sowsnek Kernowek) is a dialect of English spoken in Cornwall by Cornish people. Dialectal English spoken in Cornwall is to some extent influenced by Cornish grammar, and o ...
existed from the 19th century; in the 20th century the revival of interest in the Cornish language led eventually to a few of those who had mastered the latter turning to writing in it. Poems, essays and short stories have also been published in newspapers and magazines e.g. '' The Cornish & Devon Post''. Then there are literary works in standard English including conversations between dialect speakers, often with a typically Cornish humour.
''Cornish World'', a colour magazine produced in Cornwall and covering all aspects of Cornish life, has proved popular with the descendants of Cornish emigrants as well as Cornish residents. It includes a column in the Cornish language.
Cornish writers and poets
Charles Causley
Charles Stanley Causley CBE FRSL (24 August 1917 – 4 November 2003) was a British poet, school teacher and writer. His work is often noted for its simplicity and directness as well as its associations with folklore, legends and magic, especi ...
was born in Launceston and is perhaps the best known of Cornish poets.
The Nobel-prizewinning novelist William Golding
Sir William Gerald Golding (19 September 1911 – 19 June 1993) was a British novelist, playwright, and poet. Best known for his debut novel ''Lord of the Flies'' (1954), he published another twelve volumes of fiction in his lifetime. In 1980 ...
was born in St Columb Minor
St Columb Minor ( kw, Sen Kolumm Vyghan) (Latin: ''Columba Minor Sancta'') is a village on the north coast of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom.
''St. Columb'' alone by default refers to the nearby St. Columb Major.The village of St Columb Mino ...
in 1911, and returned to live near Truro
Truro (; kw, Truru) is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city and civil parishes in England, civil parish in Cornwall, England. It is Cornwall's county town, sole city and centre for administration, leisure and retail trading. Its ...
from 1985 until his death in 1993.
Other notable Cornish writers include Arthur Quiller-Couch
Sir Arthur Thomas Quiller-Couch (; 21 November 186312 May 1944) was a British writer who published using the pseudonym Q. Although a prolific novelist, he is remembered mainly for the monumental publication '' The Oxford Book of English Verse 1 ...
, alias "Q", novelist and literary critic; Jack Clemo
Reginald John Clemo (11 March 1916 – 25 July 1994) was a British poet and writer who was strongly associated both with his native Cornwall and his strong Christian belief. His work was considered to be visionary and inspired by the rugged Corn ...
, deaf-blind poet; Ronald Bottrall
(Francis James) Ronald Bottrall (2 September 1906, Camborne, Cornwall – 25 June 1989) was a Cornish poet. He was praised highly by F.R. Leavis, Anthony Burgess and Martin Seymour-Smith, and deprecated by Ian Hamilton and Martin Amis.
Bottral ...
, modernist poet; Robert Stephen Hawker
Robert Stephen Hawker (1803–1875) was a British Anglican priest, poet, antiquarian and reputed eccentric, known to his parishioners as Parson Hawker. He is best known as the writer of "The Song of the Western Men" with its chorus line of "An ...
, eccentric Victorian poet and priest; Geoffrey Grigson
Geoffrey Edward Harvey Grigson (2 March 1905 – 25 November 1985) was a British poet, writer, editor, critic, exhibition curator, anthologist and naturalist. In the 1930s he was editor of the influential magazine ''New Verse'', and went on to p ...
, poet and critic; Silas Hocking
Silas Kitto Hocking (24 March 1850 – 15 September 1935) was a British novelist and Methodist preacher. He is known for his novel for youth called '' Her Benny'' (1879), which was a best-seller.
Biography
Hocking was born at St Stephen-in-Br ...
, prolific novelist; and D. M. Thomas
Donald Michael Thomas (born 27 January 1935), is a British poet, translator, novelist, editor, biographer and playwright. His work has been translated into 30 languages.
Working primarily as a poet throughout the 1960s and 1970s, Thomas's 1981 ...
, novelist and poet.
Poetry written about Cornwall
The latePoet Laureate
A poet laureate (plural: poets laureate) is a poet officially appointed by a government or conferring institution, typically expected to compose poems for special events and occasions. Albertino Mussato of Padua and Francesco Petrarca (Petrarch) ...
Sir John Betjeman
Sir John Betjeman (; 28 August 190619 May 1984) was an English poet, writer, and broadcaster. He was Poet Laureate from 1972 until his death. He was a founding member of The Victorian Society and a passionate defender of Victorian architecture, ...
was famously fond of Cornwall and it featured prominently in his poetry. He is buried in the churchyard at St Enodoc's Church, Trebetherick
St. Enodoc Church, Trebetherick (Old kw, Gwenedek, ''St. Guenedoc'') is a chapel in the parish of St Minver. It is located to the south of the village of Trebetherick, Cornwall, England, United Kingdom (). It is a Grade I listed building.
Backgr ...
.
The poet Laurence Binyon
Robert Laurence Binyon, CH (10 August 1869 – 10 March 1943) was an English poet, dramatist and art scholar. Born in Lancaster, England, his parents were Frederick Binyon, a clergyman, and Mary Dockray. He studied at St Paul's School, London ...
wrote "For the Fallen" (first published in 1914) while sitting on the cliffs between Pentire Point and The Rumps and a stone plaque was erected in 2001 to commemorate the fact. The plaque bears the inscription 'For The Fallen Composed on these cliffs 1914'. The plaque also bears the fourth stanza (sometimes referred to as 'The Ode') of the poem.
The English-born poet Sylvia Kantaris
Sylvia Kantaris (9 January 1936 – 19 November 2021, also known as Sylvia Kantarizis) was a British (and Australian) poet, based for much of her life in Cornwall, who published eight collections of poetry, of which two were in collaboration. H ...
returned to the UK in 1971 and settled in Helston
Helston ( kw, Hellys) is a town and civil parish in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is situated at the northern end of the Lizard Peninsula approximately east of Penzance and south-west of Falmouth.Ordnance Survey: Landranger map shee ...
in 1974. She was appointed as Cornwall's first Writer in the Community in 1986.
Novels set in Cornwall
Novels or parts of novels set in Cornwall include:Daphne du Maurier
Dame Daphne du Maurier, Lady Browning, (; 13 May 1907 – 19 April 1989) was an English novelist, biographer and playwright. Her parents were actor-manager Sir Gerald du Maurier and his wife, actress Muriel Beaumont. Her grandfather was Geor ...
lived in Bodinnick-by-Fowey, Cornwall and many of her novels had Cornish settings, including ''Rebecca
Rebecca, ; Syriac: , ) from the Hebrew (lit., 'connection'), from Semitic root , 'to tie, couple or join', 'to secure', or 'to snare') () appears in the Hebrew Bible as the wife of Isaac and the mother of Jacob and Esau. According to biblical ...
'', ''Jamaica Inn
The Jamaica Inn is a traditional inn on Bodmin Moor in Cornwall in the UK, which was built as a coaching inn in 1750, and has a historical association with smuggling. Located just off the A30, near the middle of the moor close to the hamle ...
'', '' Frenchman's Creek'', ''My Cousin Rachel
''My Cousin Rachel'' is a Gothic novel written by English author Daphne du Maurier, published in 1951. Bearing thematic similarities to her earlier and more famous novel '' Rebecca'', it is a mystery-romance, set primarily on a large estate in ...
'', and ''The House on the Strand
''The House on the Strand'' is a novel by Daphne du Maurier, first published in the UK in 1969 by Victor Gollancz, with a jacket illustration by her daughter, Flavia Tower. The US edition was published by Doubleday.
Like many of du Maurier's no ...
''. She is also noted for writing ''Vanishing Cornwall''. Cornwall provided the inspiration for " The Birds", one of her terrifying series of short stories, made famous as a film by Alfred Hitchcock
Sir Alfred Joseph Hitchcock (13 August 1899 – 29 April 1980) was an English filmmaker. He is widely regarded as one of the most influential figures in the history of cinema. In a career spanning six decades, he directed over 50 featur ...
.
Conan Doyle
Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle (22 May 1859 – 7 July 1930) was a British writer and physician. He created the character Sherlock Holmes in 1887 for ''A Study in Scarlet'', the first of four novels and fifty-six short stories about Hol ...
's ''The Adventure of the Devil's Foot
"The Adventure of the Devil's Foot" from 1910 is one of the 56 Sherlock Holmes short stories written by Arthur Conan Doyle. It is one of eight stories in the cycle collected as ''His Last Bow''.
Doyle ranked "The Adventure of the Devil's Foot ...
'' featuring Sherlock Holmes
Sherlock Holmes () is a fictional detective created by British author Arthur Conan Doyle. Referring to himself as a " consulting detective" in the stories, Holmes is known for his proficiency with observation, deduction, forensic science and ...
is set in Cornwall.

Howard Spring
Howard Spring (10 February 1889 – 3 May 1965) was a Welsh author and journalist who wrote in English. He began his writing career as a journalist but from 1934 produced a series of best-selling novels for adults and children. The most su ...
lived in Cornwall from 1939 and set part or all of various novels in the county.
Medieval Cornwall is also the setting of the trilogy by Monica Furlong
Monica Furlong (17 January 1930 – 14 January 2003) was a British author, journalist, and activist. She was born at Kenton near Harrow, north-west of London and died at Umberleigh in Devon. An obituary called her the Church of England's ...
''Wise Child'', ''Juniper'', and ''Colman'', as well as part of Charles Kingsley's ''Hereward the Wake
Hereward the Wake (Traditional pronunciation /ˈhɛ.rɛ.ward/, modern pronunciation /ˈhɛ.rɪ.wəd/) (1035 – 1072) (also known as Hereward the Outlaw or Hereward the Exile) was an Anglo-Saxon nobleman and a leader of local resista ...
''.
Winston Graham
Winston Mawdsley Graham OBE, born Winston Grime (30 June 1908 – 10 July 2003), was an English novelist best known for the Poldark series of historical novels set in Cornwall, though he also wrote numerous other works, including contemporary ...
's series ''Poldark
''Poldark'' is a series of historical novels by Winston Graham, published from 1945 to 1953 and continued from 1973 to 2002. The first novel, '' Ross Poldark'', was named for the protagonist of the series. The novel series was adapted twice fo ...
'' (and the television series derived from it), Kate Tremayne
Kate Tremayne is a British novelist from East Tilbury in Essex.Kate Tremayne , Facebook
Retrieved ...
's Retrieved ...
Adam Loveday
''Adam Loveday'' is a novel by Kate Tremayne, and is the first in the ''Loveday'' series of books.
Plot summary
The plot centres on the rivalry between Adam and his brother St John. As the younger of the two, Adam knows that when their father ...
series, and ''Greenwitch'', and Mary Wesley
Mary Wesley was the pen name of Mary Aline Siepmann CBE (24 June 191230 December 2002), an English novelist. During her career, she was one of Britain's most successful novelists, selling three million copies of her books, including ten bestsell ...
's ''The Camomile Lawn
''The Camomile Lawn'' is a 1984 novel by Mary Wesley beginning with a family holiday in Cornwall in the last summer of peace before the Second World War. When the family is reunited for a funeral nearly fifty years later, it brings home to them ...
'' are all set in Cornwall. Writing under the pseudonym of Alexander Kent, Douglas Reeman
Douglas Edward Reeman (15 October 1924 – 23 January 2017), who also used the pseudonym Alexander Kent, was a British author who wrote many historical novels about the Royal Navy, mainly set during either World War II or the Napoleonic Wars. He ...
sets parts of his Richard Bolitho
The ''Bolitho'' novels are a series of nautical war novels written by British author Douglas Reeman (using the pseudonym Alexander Kent). They focus on the military careers of the fictional Richard Bolitho and Adam Bolitho in the Royal Navy, from ...
and Adam Bolitho series in the Cornwall of the late 18th and the early 19th centuries, particularly in Falmouth.
Hammond Innes
Ralph Hammond Innes (15 July 1913 – 10 June 1998) was a British novelist who wrote over 30 novels, as well as works for children and travel books.
Biography
Innes was born in Horsham, Sussex, and educated at Feltonfleet School, Cobham, Surrey ...
's novel ''The Killer Mine'' also has a Cornish setting.
Charles de Lint
Charles de Lint (born December 22, 1951) is a Canadian writer of Dutch, Spanish, and Japanese ancestry. He is married to, and plays music with, MaryAnn Harris.
Primarily a writer of fantasy fiction, he has composed works of urban fantasy, cont ...
, writer of many modern and urban fairy tales
A fairy tale (alternative names include fairytale, fairy story, magic tale, or wonder tale) is a short story that belongs to the folklore genre. Such stories typically feature magic, enchantments, and mythical or fanciful beings. In most cult ...
, set his novel ''The Little Country
''The'' () is a grammatical Article (grammar), article in English language, English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite ...
'' in the village of Mousehole
Mousehole (; kw, Porthenys) is a village and fishing port in Cornwall, England, UK. It is approximately south of Penzance on the shore of Mount's Bay. The village is in the civil parish of Penzance. An islet called St Clement's Isle lies ab ...
in Cornwall.
Chapters 24 and 25 of J. K. Rowling
Joanne Rowling ( "rolling"; born 31 July 1965), also known by her pen name J. K. Rowling, is a British author and Philanthropy, philanthropist. She wrote ''Harry Potter'', a seven-volume children's fantasy series published from 1997 to ...
's ''Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows
''Harry Potter and the Deathly Hallows'' is a fantasy novel written by British author J. K. Rowling and the seventh and final novel of the main ''Harry Potter'' series. It was released on 21 July 2007 in the United Kingdom by Bloomsbury Publi ...
'' take place in Cornwall (the Harry Potter story at Shell Cottage, which is on the beach outside the fictional village of Tinworth in Cornwall).
''Over Sea, Under Stone
''Over Sea, Under Stone'' is a contemporary fantasy novel written for children by the English author Susan Cooper, first published in London by Jonathan Cape in 1965. Cooper wrote four sequels about ten years later, making it the first volume ...
'' and ''Greenwitch
Greenwitch is a contemporary fantasy novel by Susan Cooper, published by Atheneum Press in 1974. It is the third entry in the five book ''Dark Is Rising Sequence''.
Synopsis
The Drew children – Simon, Jane, and Barney – return to Cornwa ...
'' from the series of fantasy novels '' The Dark Is Rising'', by Susan Cooper
Susan Mary Cooper (born 23 May 1935) is an English author of children's books. She is best known for '' The Dark Is Rising'', a contemporary fantasy series set in England and Wales, which incorporates British mythology such as the Arthurian le ...
, are set in Cornwall. Ciji Ware* set her 1997 novel ''A Cottage by the Sea'' on the Cornish coast. Sue Limb
Sue Limb (born 1946, Hitchin, Hertfordshire) is a British writer and broadcaster.
Biography
Limb was born in Hitchin, Hertfordshire. She studied Elizabethan lyric poetry at Newnham College, Cambridge and then trained in education.
While he ...
's ''Girl, (Nearly) 16: Absolute Torture'' is partly set in St Ives on the Cornish coast.
Cornwall is featured heavily in the beginning of ''The Mists of Avalon
''The Mists of Avalon'' is a 1983 historical fantasy novel by American writer Marion Zimmer Bradley, in which the author relates the Arthurian legends from the perspective of the female characters. The book follows the trajectory of Morgaine (Mo ...
'' by Marion Zimmer Bradley
Marion Eleanor Zimmer Bradley (June 3, 1930 – September 25, 1999) was an American author of fantasy, historical fantasy, science fiction, and science fantasy novels, and is best known for the Arthurian fiction novel ''The Mists of Avalon'' an ...
as the home of Igraine, wife of Gorlois, Duke of Cornwall. The castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified r ...
at Tintagel has been said to be where King Arthur was conceived (when Uther Pendragon entered the castle in the form of Gorlois).
Agatha Christie
Dame Agatha Mary Clarissa Christie, Lady Mallowan, (; 15 September 1890 – 12 January 1976) was an English writer known for her 66 detective novels and 14 short story collections, particularly those revolving around fictiona ...
's "Poirot
Hercule Poirot (, ) is a fictional Belgian detective created by British writer Agatha Christie. Poirot is one of Christie's most famous and long-running characters, appearing in 33 novels, two plays ('' Black Coffee'' and ''Alibi''), and more ...
" short story "The Cornish Adventure" take place in Polgarwith, an (imaginary) small market town in Cornwall.
In the ''Paddington Bear
Paddington Bear is a fictional character in children's literature. He first appeared on 13 October 1958 in the children's book ''A Bear Called Paddington'' and has been featured in more than twenty books written by British author Michael Bond, a ...
'' novels by Michael Bond
Thomas Michael Bond (13 January 1926 – 27 June 2017) was a British author. He is best known for a series of fictional stories for children, featuring the character of Paddington Bear. More than 35 million Paddington books have been sold ...
the title character is said to have landed at an unspecified port in Cornwall having travelled in a lifeboat
Lifeboat may refer to:
Rescue vessels
* Lifeboat (shipboard), a small craft aboard a ship to allow for emergency escape
* Lifeboat (rescue), a boat designed for sea rescues
* Airborne lifeboat, an air-dropped boat used to save downed airmen
...
aboard a cargo ship
A cargo ship or freighter is a merchant ship that carries cargo, goods, and materials from one port to another. Thousands of cargo carriers ply the world's seas and oceans each year, handling the bulk of international trade. Cargo ships are usu ...
from darkest Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal
, national_motto = "Fi ...
. From here he travels to London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
on a train and eventually arrives at Paddington Station
Paddington, also known as London Paddington, is a Central London railway terminus and London Underground station complex, located on Praed Street in the Paddington area. The site has been the London terminus of services provided by the Great We ...
.
Drama and other literary works
 Cornwall produced a substantial number of passion plays such as the
Cornwall produced a substantial number of passion plays such as the Ordinalia
The are three medieval mystery plays dating to the late fourteenth century, written primarily in Middle Cornish, with stage directions in Latin. The three plays are (The Origin of the World, also known as , 2,846 lines), (The Passion of Christ ...
during the Middle Ages. Many are still extant, and provide valuable information about the Cornish language. Other notable plays include ''Beunans Meriasek
(English: ''The Life of Saint Meriasek'') is a Cornish play completed in 1504. Its subject is the legends of the life of Saint Meriasek or Meriadoc, patron saint of Camborne, whose veneration was popular in Cornwall, Brittany, and elsewhere ...
'' and ''Beunans Ke
''Bewnans Ke'' (''The Life of Saint Ke'') is a Middle Cornish play on the life of Saint Kea or Ke, who was venerated in Cornwall, Brittany and elsewhere. It was written around 1500 but survives only in an incomplete manuscript from the second ha ...
'', the only two surviving plays written in any of Britain's vernacular tongues that take a saint's life as their subject.
Sir Arthur Quiller-Couch
Sir Arthur Thomas Quiller-Couch (; 21 November 186312 May 1944) was a British writer who published using the pseudonym Q. Although a prolific novelist, he is remembered mainly for the monumental publication '' The Oxford Book of English Verse 1 ...
author of many novels and works of literary criticism lived in Fowey: his novels are mainly set in Cornwall. Prolific writer Colin Wilson
Colin Henry Wilson (26 June 1931 – 5 December 2013) was an English writer, philosopher and novelist. He also wrote widely on true crime, mysticism and the paranormal, eventually writing more than a hundred books. Wilson called his phil ...
, best known for his debut work '' The Outsider'' (1956) and for ''The Mind Parasites
''The Mind Parasites'' is a science fiction horror novel by English author Colin Wilson. It was published by Arkham House in 1967 in an edition of 3,045 copies. It was Wilson's first and only book published by Arkham House.
The book is based ...
'' (1967), lived in Gorran Haven
Gorran Haven () is a fishing village, in the civil parish of St Goran, on the south coast of Cornwall, England, UK. It is about south of Mevagissey and lies within the Cornwall Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB).
Overview
The village ...
, a village on the southern Cornish coast, not far from Mevagissey
Mevagissey (; kw, Lannvorek) is a village, fishing port and civil parishes in England, civil parish in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom.A. L. Rowse, the historian and poet, was born near St Austell.




 So-called 'Celtic art' is found in Cornwall reflecting its ancient Britons (historical), Brythonic heritage, often in the form of Celtic crosses erected from the 6th century onwards. The Trewhiddle style is an Insular art, insular style of black and white niello metalwork named after an important Cornish find from the 9th century. Many place-names are formed with the element ''Llan (placename element), Lan'' of sacred enclosures of early Cornish saints from Wales, Ireland and Brittany. The activities of these saints resulted in a shared cultural inheritance which particularly includes the post-Roman corpus of literature relating to
So-called 'Celtic art' is found in Cornwall reflecting its ancient Britons (historical), Brythonic heritage, often in the form of Celtic crosses erected from the 6th century onwards. The Trewhiddle style is an Insular art, insular style of black and white niello metalwork named after an important Cornish find from the 9th century. Many place-names are formed with the element ''Llan (placename element), Lan'' of sacred enclosures of early Cornish saints from Wales, Ireland and Brittany. The activities of these saints resulted in a shared cultural inheritance which particularly includes the post-Roman corpus of literature relating to
File:Celtic Cross in St Just in Roseland Churchyard - geograph.org.uk - 308170.jpg, The cross on the grave of Charles Bowen Cooke, St Just in Roseland
File:War Memorial Churchyard of Constantine Kerrier.jpg, The War Memorial, in the churchyard, Constantine, Kerrier, carved from local stone by Elkana Symons
File:Celtic Cross at the end of Higher Bore Street - geograph.org.uk - 754614.jpg, The cross at the end of Higher Bore Street, Bodmin
File:Millennium Cross, Landrake - geograph.org.uk - 99003.jpg, Millennium Cross, Landrake
 Cornish vernacular architecture is characterised by its use of abundant natural stone, especially Cornubian batholith, Cornubian granite, Delabole, slate, and local white whitewash, lime-washing and its plain unadorned simplicity, sharing cultural and stylistic similarities, with the architecture of Atlantic
Cornish vernacular architecture is characterised by its use of abundant natural stone, especially Cornubian batholith, Cornubian granite, Delabole, slate, and local white whitewash, lime-washing and its plain unadorned simplicity, sharing cultural and stylistic similarities, with the architecture of Atlantic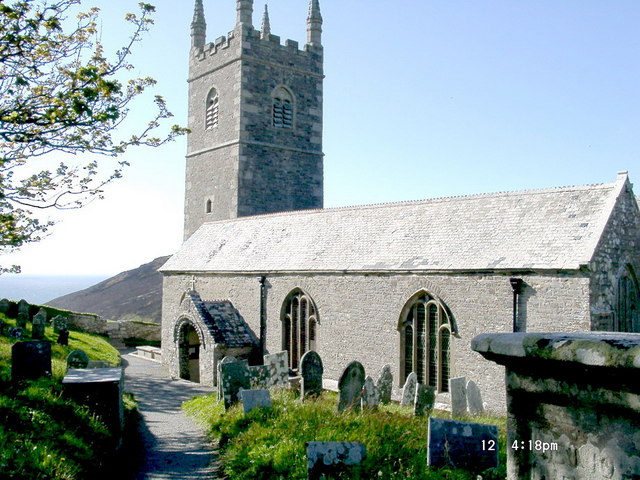  The medieval Dartmoor longhouse, longhouse was the typical form of housing in early Cornish 'Tre' dispersed settlements of small hamlets of farmsteads and associated field systems apparently originating from before the time of the Norman conquest. The Dartmoor longhouse, longhouse form is notable for its combined accommodation of humans and precious livestock under a single roof in a form found distributed across northwestern Atlantic Europe; France (''Longère'') Brittany (administrative region), Brittany (''Ty Hir''), Normandy, Devon and South
The medieval Dartmoor longhouse, longhouse was the typical form of housing in early Cornish 'Tre' dispersed settlements of small hamlets of farmsteads and associated field systems apparently originating from before the time of the Norman conquest. The Dartmoor longhouse, longhouse form is notable for its combined accommodation of humans and precious livestock under a single roof in a form found distributed across northwestern Atlantic Europe; France (''Longère'') Brittany (administrative region), Brittany (''Ty Hir''), Normandy, Devon and South  Ecclesiastical architecture of Cornwall and Devon typically differs from that of the rest of southern England: most medieval churches in the larger parishes were rebuilt in the later medieval period with one or two aisles and a western tower, the aisles being the same width as the nave and the piers of the arcades being of one of a few standard types; the former monastery church at St German's Priory, St Germans demonstrates these features over several periods as the former seat of the bishop of Cornwall. Wagon roofs often survive in these churches. The typical tower is of three stages, often with buttresses set back from the angles.
Churches of the Decorated period are relatively rare, as are those with spires. There are very few churches from the 17th and 18th centuries. There is a distinctive type of Norman font in many Cornish churches which is sometimes called the Altarnun type. The style of carving in benchends is also recognisably Cornish.
Ecclesiastical architecture of Cornwall and Devon typically differs from that of the rest of southern England: most medieval churches in the larger parishes were rebuilt in the later medieval period with one or two aisles and a western tower, the aisles being the same width as the nave and the piers of the arcades being of one of a few standard types; the former monastery church at St German's Priory, St Germans demonstrates these features over several periods as the former seat of the bishop of Cornwall. Wagon roofs often survive in these churches. The typical tower is of three stages, often with buttresses set back from the angles.
Churches of the Decorated period are relatively rare, as are those with spires. There are very few churches from the 17th and 18th centuries. There is a distinctive type of Norman font in many Cornish churches which is sometimes called the Altarnun type. The style of carving in benchends is also recognisably Cornish.
 Cornwall has a rich and vibrant folk music tradition which has survived into the present.
Cornish players are regular participants in inter-Celtic festivals, and Cornwall itself has several lively inter-Celtic festivals such as Perranporth's folk festival, Lowender Peran.
Cornish Celtic music is a relatively large phenomenon given the size of the region. A recent tally found over 100 bands playing mostly or entirely Cornish folk music. Traditional dancing (Cornish dance) is associated with the music. These dance events are either ''Troyls'' (a dance night more similar to a céilí, ceilidh) or ''Noze looan, Nozow looan'' (a dance night more similar to a Brittany, Breton ''Fest Noz'').
Aphex Twin is a Cornish-based electronic music artist, though he was born of Wales, Welsh parents in Ireland. Many other pop musicians are based in Cornwall but many of them originate elsewhere.
Lanner and District Silver Band is a Cornish Brass band (British style), Brass band based in Lanner, Cornwall, United Kingdom, and well known for its concerts. There are many other brass and silver bands in Cornwall, particularly in the former mining areas: Camborne Town Band is a notable example.
Recently some bands, such as Hanterhir, have fused classical Cornish folk music with other genres like rock music.
Cornwall has a rich and vibrant folk music tradition which has survived into the present.
Cornish players are regular participants in inter-Celtic festivals, and Cornwall itself has several lively inter-Celtic festivals such as Perranporth's folk festival, Lowender Peran.
Cornish Celtic music is a relatively large phenomenon given the size of the region. A recent tally found over 100 bands playing mostly or entirely Cornish folk music. Traditional dancing (Cornish dance) is associated with the music. These dance events are either ''Troyls'' (a dance night more similar to a céilí, ceilidh) or ''Noze looan, Nozow looan'' (a dance night more similar to a Brittany, Breton ''Fest Noz'').
Aphex Twin is a Cornish-based electronic music artist, though he was born of Wales, Welsh parents in Ireland. Many other pop musicians are based in Cornwall but many of them originate elsewhere.
Lanner and District Silver Band is a Cornish Brass band (British style), Brass band based in Lanner, Cornwall, United Kingdom, and well known for its concerts. There are many other brass and silver bands in Cornwall, particularly in the former mining areas: Camborne Town Band is a notable example.
Recently some bands, such as Hanterhir, have fused classical Cornish folk music with other genres like rock music.
 There is a long tradition of processional dance and music in Cornwall. The best known tradition is the Furry Dance, Helston Furry. The term 'furry' is used generally to describe such a dance or associated tune. These bands have been referred to as 'crowders and horners' and generally have a motley mix of instruments with folk instruments such as the fiddle, bagpipe or Crowdy-crawn, crowdy crawn mixed up with brass, reed and anything that can be carried.
Padstow 'Obby 'Oss festival takes place on 1 May, the feast of Beltane to Celtic people.
Golowan festival in Penzance, which was revived in 1991, was part of a much wider tradition of midsummer festivals where bonfires were lit on hilltops on Midsummer's Eve. The tradition of midsummer bonfires continues, albeit to a lesser extent than when fires could be seen on every hilltop, throughout Cornwall.
Lowender Perran is held at the end of October in Perranporth. This is a gathering of musicians and dancers from the six Celtic nations.
There is a long tradition of processional dance and music in Cornwall. The best known tradition is the Furry Dance, Helston Furry. The term 'furry' is used generally to describe such a dance or associated tune. These bands have been referred to as 'crowders and horners' and generally have a motley mix of instruments with folk instruments such as the fiddle, bagpipe or Crowdy-crawn, crowdy crawn mixed up with brass, reed and anything that can be carried.
Padstow 'Obby 'Oss festival takes place on 1 May, the feast of Beltane to Celtic people.
Golowan festival in Penzance, which was revived in 1991, was part of a much wider tradition of midsummer festivals where bonfires were lit on hilltops on Midsummer's Eve. The tradition of midsummer bonfires continues, albeit to a lesser extent than when fires could be seen on every hilltop, throughout Cornwall.
Lowender Perran is held at the end of October in Perranporth. This is a gathering of musicians and dancers from the six Celtic nations.
 Historically Cornwall has had close links with
Historically Cornwall has had close links with  The Gorseth Kernow (or gorsedh), which was set up in 1928, is similar to the Welsh Gorsedd, and indeed was formed by the
The Gorseth Kernow (or gorsedh), which was set up in 1928, is similar to the Welsh Gorsedd, and indeed was formed by the
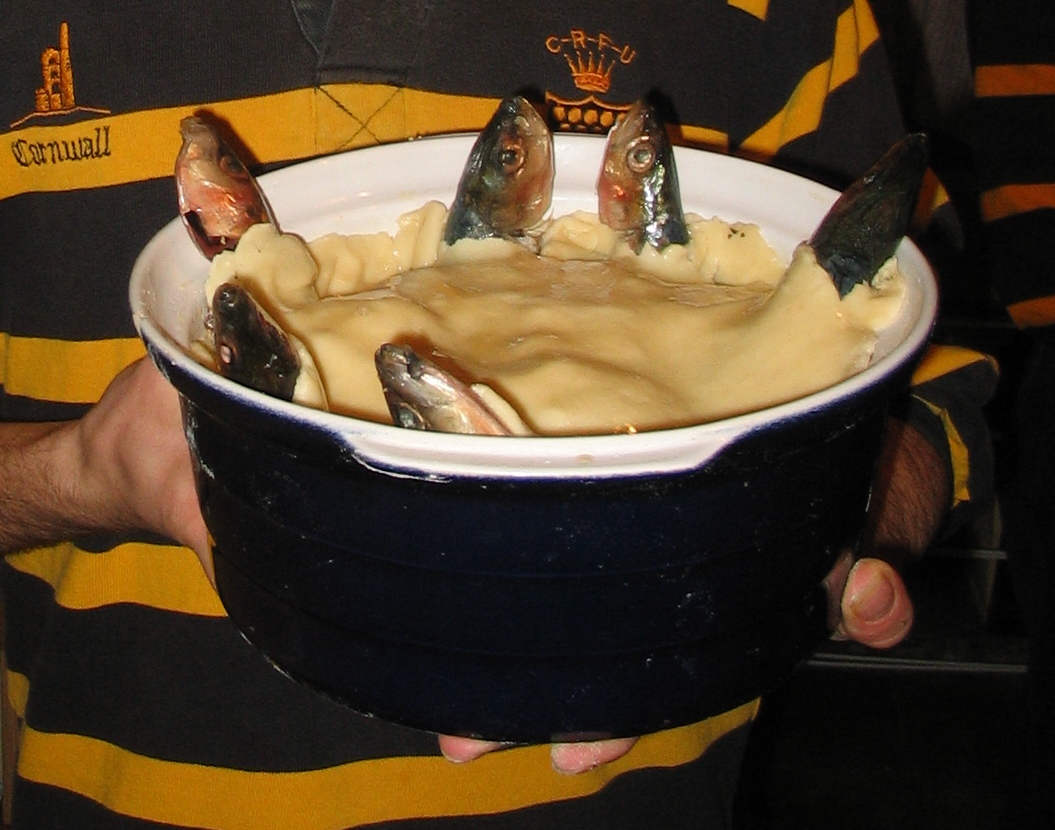 Cornwall is famous for its Pasty, pasties (a type of pie often containing meat), but saffron buns, Heavy cake, Cornish Heavy (Hevva) Cake, Cornish fairings (biscuit), Cornish fudge and Cornish ice cream are also common.
Cornish clotted cream is a popular topping on splits and on scones. Opinion varies as to whether or not the cream should be spread on before or after the jam. Clotted cream is often served as ''thunder and lightning'' (with syrup on bread.)
There are also many types of beers brewed in Cornwall including a stout, and there is some small scale production of cider and wine.
Cornwall is famous for its Pasty, pasties (a type of pie often containing meat), but saffron buns, Heavy cake, Cornish Heavy (Hevva) Cake, Cornish fairings (biscuit), Cornish fudge and Cornish ice cream are also common.
Cornish clotted cream is a popular topping on splits and on scones. Opinion varies as to whether or not the cream should be spread on before or after the jam. Clotted cream is often served as ''thunder and lightning'' (with syrup on bread.)
There are also many types of beers brewed in Cornwall including a stout, and there is some small scale production of cider and wine.
 The "traditional dress" of Cornwall for women is a bal maiden's or fishwife's costume. This includes the wearing of a bonnet known as a "Gook (headgear), gook" (which were peculiar to a district or community,) aprons and woollen shawls.
For men fishermen's smocks, Guernsey sweaters (known as worsted-frocks in Cornwall) and long cut shirts are worn.
The adoption of the Cornish kilt has recently become popular, and these kilts are available in various Cornish tartans or plain black. The first reference to a "Cornish" kilt is from 1903 when the Cornish delegate to the Celtic Congress, convening at Caernarfon, Caernarvon, L. C. R. Duncombe-Jewell, appeared in a woad blue kilt, to impress upon the delegates the Celtic character of Cornwall. Black kilts are proposed by some as the traditional version of the garment, some claiming that the Duke of Cornwall's Light Infantry wore black kilts on occasions in the 19th centuryKoch, John T. (2005) ''Celtic Culture: a historical encyclopedia'' (this may have been similar to the Irish saffron kilt). The most common kilt used in Cornwall is pleated Scottish-style with a leather,
The "traditional dress" of Cornwall for women is a bal maiden's or fishwife's costume. This includes the wearing of a bonnet known as a "Gook (headgear), gook" (which were peculiar to a district or community,) aprons and woollen shawls.
For men fishermen's smocks, Guernsey sweaters (known as worsted-frocks in Cornwall) and long cut shirts are worn.
The adoption of the Cornish kilt has recently become popular, and these kilts are available in various Cornish tartans or plain black. The first reference to a "Cornish" kilt is from 1903 when the Cornish delegate to the Celtic Congress, convening at Caernarfon, Caernarvon, L. C. R. Duncombe-Jewell, appeared in a woad blue kilt, to impress upon the delegates the Celtic character of Cornwall. Black kilts are proposed by some as the traditional version of the garment, some claiming that the Duke of Cornwall's Light Infantry wore black kilts on occasions in the 19th centuryKoch, John T. (2005) ''Celtic Culture: a historical encyclopedia'' (this may have been similar to the Irish saffron kilt). The most common kilt used in Cornwall is pleated Scottish-style with a leather,
The Institute of Cornish StudiesReal Cornwall
- explores the themes of food & drink, people & places, sports & games and arts & media
BBC Nations – Cornish history by Dr Mark Stoyle
- ''The Cornish: A Neglected Nation?'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Culture of Cornwall Cornish culture,
Thomas Hardy
Thomas Hardy (2 June 1840 – 11 January 1928) was an English novelist and poet. A Victorian realist in the tradition of George Eliot, he was influenced both in his novels and in his poetry by Romanticism, including the poetry of William Word ...
's drama ''The Queen of Cornwall'' (1923) is a version of the Tristan story; the second act of Richard Wagner
Wilhelm Richard Wagner ( ; ; 22 May 181313 February 1883) was a German composer, theatre director, polemicist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas (or, as some of his mature works were later known, "music dramas"). Unlike most op ...
's opera ''Tristan und Isolde
''Tristan und Isolde'' (''Tristan and Isolde''), WWV 90, is an opera in three acts by Richard Wagner to a German libretto by the composer, based largely on the 12th-century romance Tristan and Iseult by Gottfried von Strassburg. It was compose ...
'' takes place in Cornwall, as do Gilbert and Sullivan
Gilbert and Sullivan was a Victorian era, Victorian-era theatrical partnership of the dramatist W. S. Gilbert (1836–1911) and the composer Arthur Sullivan (1842–1900), who jointly created fourteen comic operas between 1871 and 1896, of which ...
's operettas ''The Pirates of Penzance
''The Pirates of Penzance; or, The Slave of Duty'' is a comic opera in two acts, with music by Arthur Sullivan and libretto by W. S. Gilbert, W. S. Gilbert. Its official premiere was at the Fifth Avenue Theatre in New York City on 31 ...
'' and ''Ruddigore
''Ruddigore; or, The Witch's Curse'', originally called ''Ruddygore'', is a comic opera in two acts, with music by Arthur Sullivan and libretto by W. S. Gilbert. It is one of the Savoy Operas and the tenth of fourteen comic operas written tog ...
''. A level of '' Tomb Raider: Legend'', a videogame dealing with Arthurian legend, takes place in Cornwall at a tacky museum above King Arthur's tomb.
The theatre company Kneehigh Theatre
Kneehigh Theatre was an international touring theatre company founded in 1980 by Mike Shepherd and based in Cornwall, England. The company was based in barns on the southern Cornish coast, at Gorran Haven, but the administration was in Truro. O ...
is active in Cornwall. Amateur theatre groups exist in many villages, and the open air Minack Theatre
The Minack Theatre ( kw, Gwaryjy Minack) is an open-air theatre, constructed above a gully with a rocky granite outcrop jutting into the sea. The theatre is at Porthcurno, from Land's End in Cornwall, England. The season runs each year from May ...
is well known.
The fairy tale "Jack the Giant Killer
"Jack the Giant Killer" is a Cornish fairy tale and legend about a young adult who slays a number of bad giants during King Arthur's reign. The tale is characterised by violence, gore and blood-letting. Giants are prominent in Cornish folklor ...
" takes place in Cornwall.
Religion
See alsoList of Cornish saints
This is a list of Cornish saints, including saints more loosely associated with Cornwall: many of them will have links to sites elsewhere in regions with significant ancient British history, such as Wales, Brittany or Devon.
List of some o ...


Celtic Christianity
Celtic Christianity ( kw, Kristoneth; cy, Cristnogaeth; gd, Crìosdaidheachd; gv, Credjue Creestee/Creestiaght; ga, Críostaíocht/Críostúlacht; br, Kristeniezh; gl, Cristianismo celta) is a form of Christianity that was common, or held ...
was a feature of Cornwall and many Cornish Saints
This is a list of Cornish saints, including saints more loosely associated with Cornwall: many of them will have links to sites elsewhere in regions with significant ancient British history, such as Wales, Brittany or Devon.
List of some o ...
are commemorated in legends, churches and placenames.
Traditionally, the Cornish have been non-conformists in religion. In 1549, the Prayer Book Rebellion
The Prayer Book Rebellion or Western Rising was a popular revolt in Cornwall and Devon in 1549. In that year, the ''Book of Common Prayer'', presenting the theology of the English Reformation, was introduced. The change was widely unpopular, ...
caused the deaths of thousands of people from Devon and Cornwall. The Methodism
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's br ...
of John Wesley
John Wesley (; 2 March 1791) was an English people, English cleric, Christian theology, theologian, and Evangelism, evangelist who was a leader of a Christian revival, revival movement within the Church of England known as Methodism. The soci ...
also proved to be very popular with the working classes in Cornwall in the 18th century. Methodist chapels became important social centres, with male voice choirs and other church-affiliated groups playing a central role in the social lives of working-class Cornishmen. Methodism still plays a large part in the religious life of Cornwall today, although Cornwall has shared in the post-World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
decline in British religious feeling.
In contrast to the situation in Wales, the churches failed to produce a translation of the Bible into the local language, and this has been seen by some as a crucial factor in the demise of the language.
The Bible was translated into Cornish in 2002.
Recent developments
Renewed interest in Celtic Christianity In the late 20th century and early 21st century there has been a renewed interest in the older forms of Christianity in Cornwall. Cowethas Peran Sans, the Fellowship of St Piran, is one such group promotingCeltic Christianity
Celtic Christianity ( kw, Kristoneth; cy, Cristnogaeth; gd, Crìosdaidheachd; gv, Credjue Creestee/Creestiaght; ga, Críostaíocht/Críostúlacht; br, Kristeniezh; gl, Cristianismo celta) is a form of Christianity that was common, or held ...
. The group was founded by Andrew Phillips and membership is open to baptised Christians in good standing in their local community who support the aims of the group.
The aims of the group are these:
:To understand and embody the spirituality of the Celtic Saints
:To share this spirituality with others
:To use Cornwall’s ancient Christian holy places again in worship
:To promote Cornwall as a place of Christian spiritual pilgrimage
:To promote the use of the Cornish language in prayer and worship
Fry an Spyrys
In 2003, a campaign group was formed called '' Fry an Spyrys'' ('free the spirit' in Cornish). It is dedicated to disestablishing the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britain ...
in Cornwall and to forming an autonomous province of the Anglican Communion – a Church of Cornwall. Its chairman is Dr Garry Tregidga
Garry Harcourt Tregidga is a Cornish academic, director of the Institute of Cornish Studies at the University of Exeter's Penryn Campus in Cornwall, UK, and editor of the journal '' Cornish Studies''.
He lives in Bugle, near St Austell, an ...
of the Institute of Cornish Studies
The Institute of Cornish Studies (, ICS) is a research institute in west Cornwall, England, United Kingdom, affiliated with the University of Exeter. Formerly at Pool, near Redruth, then in Truro, it is now on the Penryn Campus near Penryn, Co ...
. The Anglican Church was disestablished in Wales to form the Church in Wales
The Church in Wales ( cy, Yr Eglwys yng Nghymru) is an Anglicanism, Anglican church in Wales, composed of six dioceses.
The Archbishop of Wales does not have a fixed archiepiscopal see, but serves concurrently as one of the six diocesan bishop ...
in 1920 and in Ireland to form the Church of Ireland
The Church of Ireland ( ga, Eaglais na hÉireann, ; sco, label= Ulster-Scots, Kirk o Airlann, ) is a Christian church in Ireland and an autonomous province of the Anglican Communion. It is organised on an all-Ireland basis and is the second ...
in 1869.
Cornish symbols
Saint Piran's Flag
Saint Piran's Flag ( kw, Baner Peran) is the flag of Cornwall. The earliest known description of the flag as the Standard of Cornwall was written in 1838. It is used by some Cornish people as a symbol of their identity.
The flag is attribut ...
, a white cross on a black background is often seen in Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
. The Duchy of Cornwall
The Duchy of Cornwall ( kw, Duketh Kernow) is one of two royal duchies in England, the other being the Duchy of Lancaster. The eldest son of the reigning British monarch obtains possession of the duchy and the title of 'Duke of Cornwall' at ...
shield of 15 gold bezants
In the Middle Ages, the term bezant (Old French ''besant'', from Middle Latin, Latin ''bizantius aureus'') was used in Western Europe to describe several gold coins of the east, all derived ultimately from the Solidus (coin), Roman ''solidus''. ...
on a black field is also used. Because of these two symbols black, white and gold are considered colours symbolic of Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
.
The chough
There are two species of passerine birds commonly called chough ( ) that constitute the genus ''Pyrrhocorax'' of the Corvidae (crow) family of birds. These are the red-billed chough (''Pyrrhocorax pyrrhocorax''), and the Alpine chough (or yellow- ...
(in Cornish = ''palores'') is also used as a symbol of Cornwall. In Cornish poetry the chough is used to symbolise the spirit of Cornwall. Also there is a Cornish belief that King Arthur
King Arthur ( cy, Brenin Arthur, kw, Arthur Gernow, br, Roue Arzhur) is a legendary king of Britain, and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain.
In the earliest traditions, Arthur appears as a ...
lives in the form of a chough. "Chough" was also used as a nickname for Cornish people.
Another animal with a deep association with Cornwall is the "White Horse of Lyonesse". Arthurian legends tell of a rider escaping on a white horse as the land sunk beneath the waves, surviving and settling in Cornwall.
An anvil is sometimes used to symbolise Cornish nationalism
Cornish nationalism is a cultural, political and social movement that seeks the recognition of Cornwall – the south-westernmost part of the island of Great Britain – as a nation distinct from England. It is usually based on three general ...
, particularly in its more extreme forms. This is a reference to 'Michael An Gof
Michael Joseph (died 27 June 1497), better known as Michael An Gof, was one of the leaders of the Cornish rebellion of 1497, along with Thomas Flamank.
Background
The rebels marched on London to protest against King Henry VII's levy of a t ...
', 'the smith', one of two leaders of the Cornish Rebellion of 1497.
Fish, tin and copper together are used symbolically as they show the 'traditional' three main industries of Cornwall. Tin has a special place in the Cornish culture, the 'Cornish Stannary Parliament, Stannary Parliament' and 'Cornish pennies' are a testament to the former power of the Mining in Cornwall, Cornish tin industry. Cornish tin is highly prized for jewellery, often of mine engines or Celtic art, Celtic designs.
Although Cornwall has no official flower many people favour the Cornish heath (Erica vagans). In recent years daffodils have been popular on the annual Saint Piran's day march on Perran Sands although they are donated by a local daffodil grower and it is already considered to be the national flower of Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
.
Cornish studies
TheInstitute of Cornish Studies
The Institute of Cornish Studies (, ICS) is a research institute in west Cornwall, England, United Kingdom, affiliated with the University of Exeter. Formerly at Pool, near Redruth, then in Truro, it is now on the Penryn Campus near Penryn, Co ...
, established in 1970, moved to the new Combined Universities in Cornwall Campus at Tremough, Penryn, Cornwall, Penryn in October 2004: the institute is a branch of the University of Exeter. A detailed overview of literature is provided by Alan M. Kent's ''The Literature of Cornwall'': it covers everything from medieval mystery plays to more recent literary works that draw on the Cornish landscape.
The historian Philip Payton, professor at Exeter University's department of Cornish studies, has written ''Cornwall: a History'' as well as editing the Cornish studies series. Mark Stoyle, Senior Lecturer in Early Modern History at the University of Southampton, asks 'Are the Cornish English?’ in his book ''West Britons'', a work on Cornish history exploring the nature of Cornishness in the early modern period. John Angarrack of the human rights organisation Cornwall 2000 has self-published two books to date, ''Breaking the Chains'' and ''Our Future is History'': both are polemical re-examinations of Cornish history and identity, not historical works.
The Federation of Old Cornwall Societies is a group of societies of those interested in Cornwall's past which has published a number of books.
Cornish art

 So-called 'Celtic art' is found in Cornwall reflecting its ancient Britons (historical), Brythonic heritage, often in the form of Celtic crosses erected from the 6th century onwards. The Trewhiddle style is an Insular art, insular style of black and white niello metalwork named after an important Cornish find from the 9th century. Many place-names are formed with the element ''Llan (placename element), Lan'' of sacred enclosures of early Cornish saints from Wales, Ireland and Brittany. The activities of these saints resulted in a shared cultural inheritance which particularly includes the post-Roman corpus of literature relating to
So-called 'Celtic art' is found in Cornwall reflecting its ancient Britons (historical), Brythonic heritage, often in the form of Celtic crosses erected from the 6th century onwards. The Trewhiddle style is an Insular art, insular style of black and white niello metalwork named after an important Cornish find from the 9th century. Many place-names are formed with the element ''Llan (placename element), Lan'' of sacred enclosures of early Cornish saints from Wales, Ireland and Brittany. The activities of these saints resulted in a shared cultural inheritance which particularly includes the post-Roman corpus of literature relating to King Arthur
King Arthur ( cy, Brenin Arthur, kw, Arthur Gernow, br, Roue Arzhur) is a legendary king of Britain, and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain.
In the earliest traditions, Arthur appears as a ...
and Tristan and Iseult, presumed nobility of ancient Dumnonia. Cornwall boasts the highest density of traditional 'stone crosses in Cornwall, Celtic crosses' of any nation, and medieval holy wells are numerous. The destruction of monastic institutions such as Glasney College
Glasney College ( kw, Kolji Glasneth) was founded in 1265 at Penryn, Cornwall, by Bishop Bronescombe and was a centre of ecclesiastical power in medieval Cornwall and probably the best known and most important of Cornwall's religious institut ...
and Crantock during the dissolution of the monasteries (1536–45) is often regarded as the death knell of independence in Cornish language and culture; the very few remaining Cornish language manuscripts, including the miracle plays Beunans Ke
''Bewnans Ke'' (''The Life of Saint Ke'') is a Middle Cornish play on the life of Saint Kea or Ke, who was venerated in Cornwall, Brittany and elsewhere. It was written around 1500 but survives only in an incomplete manuscript from the second ha ...
and Beunans Meriasek
(English: ''The Life of Saint Meriasek'') is a Cornish play completed in 1504. Its subject is the legends of the life of Saint Meriasek or Meriadoc, patron saint of Camborne, whose veneration was popular in Cornwall, Brittany, and elsewhere ...
are thought to have originated at these ancient centres of academic excellence, some areas however retain their outdoor performance spaces, known as Plen-an-gwary, plen an gwary. After the First World War, many new crosses were erected as war memorials and to celebrate events, e.g. the beginning of the third millennium.
Cornwall and its dramatic landscape and distinctive remoteness have produced and inspired many later artists. John Opie was the first Cornish-born artist of note and J. M. W. Turner visited in 1811. A number of London artists settled in the Newlyn area in the 1880s, following the building of the Great Western Railway, who went on to form the Newlyn School.
Sickert and Whistler both visited St Ives at the end of the 19th century, and the internationally famous studio potter, Bernard Leach set up his pottery in the town in 1920 St Ives, Cornwall, St. Ives. In 1928 Ben Nicholson and Christopher Wood (English painter), Christopher Wood visited the town and met Alfred Wallis the naive painter, native to St Ives, who was to become an important influence on a generation of British artists: particularly those who were members of the Seven and Five Society.
At the outbreak of World War II Nicholson came to live in St Ives with his wife Barbara Hepworth, staying initially with the philosopher and writer Adrian Stokes (critic), Adrian Stokes and his wife Margaret Mellis. Naum Gabo also joined them there as well as artists who at the time were at an earlier stage in their careers: John Wells (artist), John Wells, Wilhelmina Barns-Graham, Terry Frost and Bryan Wynter. Other artists of international repute joined the colony later: notably Patrick Heron, Roger Hilton and Sandra Blow.
There are still a lot of artists in Cornwall, many associated with the Newlyn Society of Artists. Artist led projects like PALP and artsurgery have also been important in the 21st century.
;Some modern crosses
Architecture
 Cornish vernacular architecture is characterised by its use of abundant natural stone, especially Cornubian batholith, Cornubian granite, Delabole, slate, and local white whitewash, lime-washing and its plain unadorned simplicity, sharing cultural and stylistic similarities, with the architecture of Atlantic
Cornish vernacular architecture is characterised by its use of abundant natural stone, especially Cornubian batholith, Cornubian granite, Delabole, slate, and local white whitewash, lime-washing and its plain unadorned simplicity, sharing cultural and stylistic similarities, with the architecture of Atlantic Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo language, Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, Historical region, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known ...
, Ireland and Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
, as well as neighbouring Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devon is ...
. The architecture of west Cornish towns such as St Ives, Cornwall, St Ives is particularly distinctive for its use of solid granite and featuring also the type of early promontory hermitage (religious retreat), hermitage particularly associated with Celtic Christianity
Celtic Christianity ( kw, Kristoneth; cy, Cristnogaeth; gd, Crìosdaidheachd; gv, Credjue Creestee/Creestiaght; ga, Críostaíocht/Críostúlacht; br, Kristeniezh; gl, Cristianismo celta) is a form of Christianity that was common, or held ...
.
Early and continuous use of stone architecture over more than two thousand years, begins with the Romano-British enclosed courtyard houses at Carn Euny and Chysauster is regionally distinct from the largely rectangular timber-derived architecture of Saxon England and often features characteristically rounded or circular forms – such as the ringforts, roundhouse (dwelling), roundhouses and enclosed settlements known locally as "rounds" – the influence of which can be detected up to the building of Launceston Castle and Restormel Castle in the later medieval.
 The medieval Dartmoor longhouse, longhouse was the typical form of housing in early Cornish 'Tre' dispersed settlements of small hamlets of farmsteads and associated field systems apparently originating from before the time of the Norman conquest. The Dartmoor longhouse, longhouse form is notable for its combined accommodation of humans and precious livestock under a single roof in a form found distributed across northwestern Atlantic Europe; France (''Longère'') Brittany (administrative region), Brittany (''Ty Hir''), Normandy, Devon and South
The medieval Dartmoor longhouse, longhouse was the typical form of housing in early Cornish 'Tre' dispersed settlements of small hamlets of farmsteads and associated field systems apparently originating from before the time of the Norman conquest. The Dartmoor longhouse, longhouse form is notable for its combined accommodation of humans and precious livestock under a single roof in a form found distributed across northwestern Atlantic Europe; France (''Longère'') Brittany (administrative region), Brittany (''Ty Hir''), Normandy, Devon and South Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
(''Ty Hir'') .
 Ecclesiastical architecture of Cornwall and Devon typically differs from that of the rest of southern England: most medieval churches in the larger parishes were rebuilt in the later medieval period with one or two aisles and a western tower, the aisles being the same width as the nave and the piers of the arcades being of one of a few standard types; the former monastery church at St German's Priory, St Germans demonstrates these features over several periods as the former seat of the bishop of Cornwall. Wagon roofs often survive in these churches. The typical tower is of three stages, often with buttresses set back from the angles.
Churches of the Decorated period are relatively rare, as are those with spires. There are very few churches from the 17th and 18th centuries. There is a distinctive type of Norman font in many Cornish churches which is sometimes called the Altarnun type. The style of carving in benchends is also recognisably Cornish.
Ecclesiastical architecture of Cornwall and Devon typically differs from that of the rest of southern England: most medieval churches in the larger parishes were rebuilt in the later medieval period with one or two aisles and a western tower, the aisles being the same width as the nave and the piers of the arcades being of one of a few standard types; the former monastery church at St German's Priory, St Germans demonstrates these features over several periods as the former seat of the bishop of Cornwall. Wagon roofs often survive in these churches. The typical tower is of three stages, often with buttresses set back from the angles.
Churches of the Decorated period are relatively rare, as are those with spires. There are very few churches from the 17th and 18th centuries. There is a distinctive type of Norman font in many Cornish churches which is sometimes called the Altarnun type. The style of carving in benchends is also recognisably Cornish.
Music
 Cornwall has a rich and vibrant folk music tradition which has survived into the present.
Cornish players are regular participants in inter-Celtic festivals, and Cornwall itself has several lively inter-Celtic festivals such as Perranporth's folk festival, Lowender Peran.
Cornish Celtic music is a relatively large phenomenon given the size of the region. A recent tally found over 100 bands playing mostly or entirely Cornish folk music. Traditional dancing (Cornish dance) is associated with the music. These dance events are either ''Troyls'' (a dance night more similar to a céilí, ceilidh) or ''Noze looan, Nozow looan'' (a dance night more similar to a Brittany, Breton ''Fest Noz'').
Aphex Twin is a Cornish-based electronic music artist, though he was born of Wales, Welsh parents in Ireland. Many other pop musicians are based in Cornwall but many of them originate elsewhere.
Lanner and District Silver Band is a Cornish Brass band (British style), Brass band based in Lanner, Cornwall, United Kingdom, and well known for its concerts. There are many other brass and silver bands in Cornwall, particularly in the former mining areas: Camborne Town Band is a notable example.
Recently some bands, such as Hanterhir, have fused classical Cornish folk music with other genres like rock music.
Cornwall has a rich and vibrant folk music tradition which has survived into the present.
Cornish players are regular participants in inter-Celtic festivals, and Cornwall itself has several lively inter-Celtic festivals such as Perranporth's folk festival, Lowender Peran.
Cornish Celtic music is a relatively large phenomenon given the size of the region. A recent tally found over 100 bands playing mostly or entirely Cornish folk music. Traditional dancing (Cornish dance) is associated with the music. These dance events are either ''Troyls'' (a dance night more similar to a céilí, ceilidh) or ''Noze looan, Nozow looan'' (a dance night more similar to a Brittany, Breton ''Fest Noz'').
Aphex Twin is a Cornish-based electronic music artist, though he was born of Wales, Welsh parents in Ireland. Many other pop musicians are based in Cornwall but many of them originate elsewhere.
Lanner and District Silver Band is a Cornish Brass band (British style), Brass band based in Lanner, Cornwall, United Kingdom, and well known for its concerts. There are many other brass and silver bands in Cornwall, particularly in the former mining areas: Camborne Town Band is a notable example.
Recently some bands, such as Hanterhir, have fused classical Cornish folk music with other genres like rock music.
Festivals
 Historically Cornwall has had close links with
Historically Cornwall has had close links with Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo language, Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, Historical region, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known ...
and this is reflected in the music. The Cornish and Breton languages were mutually intelligible until Tudor times and there were many Bretons living in Cornwall before the Prayer Book Rebellion
The Prayer Book Rebellion or Western Rising was a popular revolt in Cornwall and Devon in 1549. In that year, the ''Book of Common Prayer'', presenting the theology of the English Reformation, was introduced. The change was widely unpopular, ...
. Myths, saints, dances and tunes are often shared with Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo language, Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, Historical region, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known ...
. It has been noted that The Kroaz Du (Black Cross) flag used in medieval Brittany is the exact inverse of the Saint Piran's Flag, Cornish flag, whether there is a reason for this is unknown. Breton flags are popular in Cornwall and are often seen alongside the Cornish flag on car bumpers and at musical events. This link continues today with Cornish-Breton festivals such as 'AberFest' in Falmouth (Aberfal) and the twinning of Cornish and Breton towns.
 The Gorseth Kernow (or gorsedh), which was set up in 1928, is similar to the Welsh Gorsedd, and indeed was formed by the
The Gorseth Kernow (or gorsedh), which was set up in 1928, is similar to the Welsh Gorsedd, and indeed was formed by the Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
Gorsedd at the request of Henry Jenner
Henry Jenner (8 August 1848 – 8 May 1934) was a British scholar of the Celtic languages, a Cornish cultural activist, and the chief originator of the Cornish language revival.
Jenner was born at St Columb Major on 8 August 1848. He was the ...
. The Cornish Gorseth promotes the arts and the Cornish language
Cornish (Standard Written Form: or ) , is a Southwestern Brittonic language, Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language family. It is a List of revived languages, revived language, having become Extinct language, extinct as a livin ...
through competitions at the open gorseth.Cornish GorsethCornish film
Cornwall has a small but growing film industry, mostly focusing on the Cornish language and culture. Numerous films, short and long, have been made in Cornwall. The Cornish film industry is supported by organisations such as War-rag (War-rag meaning "ahead" in Cornish). The Celtic Media Festival, Celtic Film and Television Festival includes entries from Cornish film makers, and was held in Falmouth in 2006. The Goel Fylm Kernow/Cornwall Film Festival is held once a year, and supports Cornish film making, including films made in the Cornish or English language. Goel Fylm Kernow also hosts workshops, screenings and the "Govynn Kernewek" competition. In this competition applicants can present their ideas for films to be made in the Cornish language. The prizes in the competition consist of financial, material and technical support for making the film. Films made following this award include ''Kernow's Kick Ass Kung-Fu Kweens'' (2004), a kung fu film in Cornish. The only known feature-length film in the Cornish language is ''Hwerow Hweg'' (''Bitter Sweet''), which was filmed alongside an English version. It was premiered at the 2002 Cornwall Film Festival and entered for the 2003 Celtic Film Festival. There are a number of short films which have been made in the language.Food
 Cornwall is famous for its Pasty, pasties (a type of pie often containing meat), but saffron buns, Heavy cake, Cornish Heavy (Hevva) Cake, Cornish fairings (biscuit), Cornish fudge and Cornish ice cream are also common.
Cornish clotted cream is a popular topping on splits and on scones. Opinion varies as to whether or not the cream should be spread on before or after the jam. Clotted cream is often served as ''thunder and lightning'' (with syrup on bread.)
There are also many types of beers brewed in Cornwall including a stout, and there is some small scale production of cider and wine.
Cornwall is famous for its Pasty, pasties (a type of pie often containing meat), but saffron buns, Heavy cake, Cornish Heavy (Hevva) Cake, Cornish fairings (biscuit), Cornish fudge and Cornish ice cream are also common.
Cornish clotted cream is a popular topping on splits and on scones. Opinion varies as to whether or not the cream should be spread on before or after the jam. Clotted cream is often served as ''thunder and lightning'' (with syrup on bread.)
There are also many types of beers brewed in Cornwall including a stout, and there is some small scale production of cider and wine.
Sports and games
Outdoor sports and games
See Sport in Cornwall.Indoor games
Euchre is a popular card game in Cornwall, it is normally a game for four players consisting of two teams. Its origins are unclear but some claim it is a Cornish game, and was popularised in part by Cornish immigrants to the United States. There are several leagues in Cornwall at present. Whist and pub quizzes are also popular in many villages.Traditional dress
 The "traditional dress" of Cornwall for women is a bal maiden's or fishwife's costume. This includes the wearing of a bonnet known as a "Gook (headgear), gook" (which were peculiar to a district or community,) aprons and woollen shawls.
For men fishermen's smocks, Guernsey sweaters (known as worsted-frocks in Cornwall) and long cut shirts are worn.
The adoption of the Cornish kilt has recently become popular, and these kilts are available in various Cornish tartans or plain black. The first reference to a "Cornish" kilt is from 1903 when the Cornish delegate to the Celtic Congress, convening at Caernarfon, Caernarvon, L. C. R. Duncombe-Jewell, appeared in a woad blue kilt, to impress upon the delegates the Celtic character of Cornwall. Black kilts are proposed by some as the traditional version of the garment, some claiming that the Duke of Cornwall's Light Infantry wore black kilts on occasions in the 19th centuryKoch, John T. (2005) ''Celtic Culture: a historical encyclopedia'' (this may have been similar to the Irish saffron kilt). The most common kilt used in Cornwall is pleated Scottish-style with a leather,
The "traditional dress" of Cornwall for women is a bal maiden's or fishwife's costume. This includes the wearing of a bonnet known as a "Gook (headgear), gook" (which were peculiar to a district or community,) aprons and woollen shawls.
For men fishermen's smocks, Guernsey sweaters (known as worsted-frocks in Cornwall) and long cut shirts are worn.
The adoption of the Cornish kilt has recently become popular, and these kilts are available in various Cornish tartans or plain black. The first reference to a "Cornish" kilt is from 1903 when the Cornish delegate to the Celtic Congress, convening at Caernarfon, Caernarvon, L. C. R. Duncombe-Jewell, appeared in a woad blue kilt, to impress upon the delegates the Celtic character of Cornwall. Black kilts are proposed by some as the traditional version of the garment, some claiming that the Duke of Cornwall's Light Infantry wore black kilts on occasions in the 19th centuryKoch, John T. (2005) ''Celtic Culture: a historical encyclopedia'' (this may have been similar to the Irish saffron kilt). The most common kilt used in Cornwall is pleated Scottish-style with a leather, Duchy of Cornwall
The Duchy of Cornwall ( kw, Duketh Kernow) is one of two royal duchies in England, the other being the Duchy of Lancaster. The eldest son of the reigning British monarch obtains possession of the duchy and the title of 'Duke of Cornwall' at ...
shield-style, sporran.
The Cornish national tartan was designed by E. E Morton Nance in 1963 using colours traditionally associated with Cornwall. Fragments of tartan have been found in Penwith.
See also
*Cornish National Library *List of topics related to Cornwall *List of Cornish people *:Festivals in Cornwall *:Cornish novelsReferences
* Baker, Denys Val (1973) ''The Timeless Land: the creative spirit in Cornwall''. Bath: Adams & Dart * Paynter, William H. & Semmens, J. (2008) ''The Cornish Witch-finder: The Witchery, Ghosts, Charms and Folklore of Cornwall''. Federation of Old Cornwall Societies. * Edmund Harold Sedding, Sedding, Edmund H. (1909) ''Norman Architecture in Cornwall: a handbook to old ecclesiastical architecture''; with over 160 plates. London: Ward & Co.Further reading
*Pill, Colin (2011) ''Cornish Art Metalwork''. Bristol: Sansom & Co. *Hardie, Melissa, ed. ''Artists in Newlyn and West Cornwall''. Bristol: Sansom & C.External links
The Institute of Cornish Studies
- explores the themes of food & drink, people & places, sports & games and arts & media
BBC Nations – Cornish history by Dr Mark Stoyle
- ''The Cornish: A Neglected Nation?'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Culture of Cornwall Cornish culture,