Cue Sports on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cue sports are a wide variety of games of skill played with a cue, which is used to strike billiard balls and thereby cause them to move around a  There are three major subdivisions of games within cue sports:
* Carom billiards, played on tables without , typically 10 feet in length, including straight rail, balkline, one-cushion carom, three-cushion billiards, artistic billiards, and four-ball
* Pool, played on six-pocket tables of 7-, 8-, 9-, or 10-foot length, including among others eight-ball (the world's most widely played cue sport), nine-ball (the dominant professional game), ten-ball, straight pool (the formerly dominant pro game), one-pocket, and bank pool
*
There are three major subdivisions of games within cue sports:
* Carom billiards, played on tables without , typically 10 feet in length, including straight rail, balkline, one-cushion carom, three-cushion billiards, artistic billiards, and four-ball
* Pool, played on six-pocket tables of 7-, 8-, 9-, or 10-foot length, including among others eight-ball (the world's most widely played cue sport), nine-ball (the dominant professional game), ten-ball, straight pool (the formerly dominant pro game), one-pocket, and bank pool
*
, no byline, 1893-12-10, p. 10; The New York Times Company, New York Quite a variety of particular games (i.e., sets of rules and equipment) are the subject of present-day competition, including many of those already mentioned, with competition being especially broad in nine-ball, snooker, three-cushion, and eight-ball. Snooker, though a pocket billiards variant and closely related in its equipment and origin to the game of English billiards, is a professional sport organized at an international level, and its rules bear little resemblance to those of modern pool, pyramid, and other such games. A "Billiards" category encompassing pool, snooker, and carom has been part of the
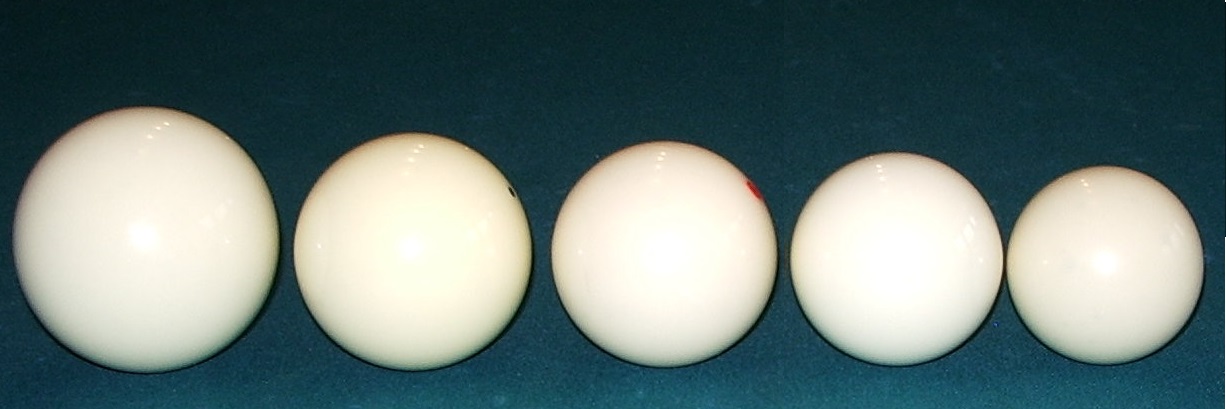 Billiard balls vary from game to game, in size, design and quantity.
Billiard balls vary from game to game, in size, design and quantity.
Explosive Teeth.
. Retrieved January 2, 2007.
, Clark, Neil M.; originally published in ''The American'' magazine, May 1927; republished in ''hotwire: The Newsletter of the Toaster Museum Foundation'', vol. 3, no. 3, online edition. Retrieved February 24, 2007. The piece is largely an interview of Hoskins., 9 March 1897 is made by crushing
, ChemIndustry.com database. Retrieved February 24, 2007."Substance Summary: Aluminum Oxide"
''PubChem Database'',
cloth
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
-covered table bounded by elastic bumpers known as .
 There are three major subdivisions of games within cue sports:
* Carom billiards, played on tables without , typically 10 feet in length, including straight rail, balkline, one-cushion carom, three-cushion billiards, artistic billiards, and four-ball
* Pool, played on six-pocket tables of 7-, 8-, 9-, or 10-foot length, including among others eight-ball (the world's most widely played cue sport), nine-ball (the dominant professional game), ten-ball, straight pool (the formerly dominant pro game), one-pocket, and bank pool
*
There are three major subdivisions of games within cue sports:
* Carom billiards, played on tables without , typically 10 feet in length, including straight rail, balkline, one-cushion carom, three-cushion billiards, artistic billiards, and four-ball
* Pool, played on six-pocket tables of 7-, 8-, 9-, or 10-foot length, including among others eight-ball (the world's most widely played cue sport), nine-ball (the dominant professional game), ten-ball, straight pool (the formerly dominant pro game), one-pocket, and bank pool
*Snooker
Snooker (pronounced , ) is a cue sport played on a rectangular table covered with a green cloth called baize, with six pockets, one at each corner and one in the middle of each long side. First played by British Army officers stationed in Ind ...
, English billiards, and Russian pyramid
Russian pyramid, also known as Russian billiards (russian: ру́сский билья́рд, ), is a form of billiards played on a large billiard table with narrow pockets. It is popular across Eastern Europe as well as countries of the form ...
, played on a large, six-pocket table (dimensions just under 12 ft by 6 ft), all of which are classified separately from pool based on distinct development histories, player culture, rules, and terminology.
Billiards has a long history from its inception in the 15th century, with many mentions in the works of Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's natio ...
, including the line "let's to billiards" in ''Antony and Cleopatra
''Antony and Cleopatra'' ( First Folio title: ''The Tragedie of Anthonie, and Cleopatra'') is a tragedy by William Shakespeare. The play was first performed, by the King's Men, at either the Blackfriars Theatre or the Globe Theatre in arou ...
'' (1606–07), and enthusiasts of the sport include Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 17565 December 1791), baptised as Joannes Chrysostomus Wolfgangus Theophilus Mozart, was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition r ...
, Louis XIV of France
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of V ...
, Marie Antoinette
Marie Antoinette Josèphe Jeanne (; ; née Maria Antonia Josepha Johanna; 2 November 1755 – 16 October 1793) was the last queen of France before the French Revolution. She was born an archduchess of Austria, and was the penultimate child ...
, Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant (, , ; 22 April 1724 – 12 February 1804) was a German philosopher and one of the central Enlightenment thinkers. Born in Königsberg, Kant's comprehensive and systematic works in epistemology, metaphysics, ethics, and aes ...
, Napoleon, Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln ( ; February 12, 1809 – April 15, 1865) was an American lawyer, politician, and statesman who served as the 16th president of the United States from 1861 until his assassination in 1865. Lincoln led the nation thro ...
, Mark Twain
Samuel Langhorne Clemens (November 30, 1835 – April 21, 1910), known by his pen name Mark Twain, was an American writer, humorist, entrepreneur, publisher, and lecturer. He was praised as the "greatest humorist the United States has p ...
, George Washington, French president Jules Grévy, Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian e ...
, George Armstrong Custer
George Armstrong Custer (December 5, 1839 – June 25, 1876) was a United States Army officer and cavalry commander in the American Civil War and the American Indian Wars.
Custer graduated from West Point in 1861 at the bottom of his clas ...
, Theodore Roosevelt
Theodore Roosevelt Jr. ( ; October 27, 1858 – January 6, 1919), often referred to as Teddy or by his initials, T. R., was an American politician, statesman, soldier, conservationist, naturalist, historian, and writer who served as the 26t ...
, Lewis Carroll, W. C. Fields, Babe Ruth
George Herman "Babe" Ruth Jr. (February 6, 1895 – August 16, 1948) was an American professional baseball player whose career in Major League Baseball (MLB) spanned 22 seasons, from 1914 through 1935. Nicknamed "the Bambino" and "the Su ...
, Bob Hope
Leslie Townes "Bob" Hope (May 29, 1903 – July 27, 2003) was a British-American comedian, vaudevillian, actor, singer and dancer. With a career that spanned nearly 80 years, Hope appeared in Bob Hope filmography, more than 70 short and ...
, and Jackie Gleason
John Herbert Gleason (February 26, 1916June 24, 1987) was an American actor, comedian, writer, composer, and conductor known affectionately as "The Great One." Developing a style and characters from growing up in Brooklyn, New York, he was know ...
.
History
All cue sports are generally regarded to have evolved into indoor games from outdoor stick-and-ball lawn games, specifically those retroactively termed ground billiards, and as such to be related to the historical games jeu de mail and palle-malle, and modern trucco,croquet
Croquet ( or ; french: croquet) is a sport that involves hitting wooden or plastic balls with a mallet through hoops (often called "wickets" in the United States) embedded in a grass playing court.
Its international governing body is the W ...
, and golf
Golf is a club-and-ball sport in which players use various clubs to hit balls into a series of holes on a course in as few strokes as possible.
Golf, unlike most ball games, cannot and does not use a standardized playing area, and coping ...
, and more distantly to the stickless bocce and bowls
Bowls, also known as lawn bowls or lawn bowling, is a sport in which the objective is to roll biased balls so that they stop close to a smaller ball called a "jack" or "kitty". It is played on a bowling green, which may be flat (for "flat-g ...
.
The word ''billiard'' may have evolved from the French word or , meaning 'stick', in reference to the , an implement similar to a golf putter, and which was the forerunner to the modern cue; however, the term's origin could have been from French , meaning 'ball'. This is a revised version of ''The Story of Billiards and Snooker'' (1979). The modern term ''cue sports'' can be used to encompass the ancestral mace games, and even the modern cueless variants, such as finger billiards, for historical reasons. ''Cue'' itself came from , the French word for ' tail'. This refers to the early practice of using the tail or butt of the mace, instead of its club foot, to strike the ball when it lay against a .
A recognizable form of billiards was played outdoors in the 1340s, and was reminiscent of croquet. King Louis XI of France (1461–1483) had the first known indoor billiard table. Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Ve ...
further refined and popularized the game, and it swiftly spread among the French nobility. While the game had long been played on the ground, this version appears to have died out (aside from trucco) in the 17th century, in favor of croquet, golf and bowling games, even as table billiards had grown in popularity as an indoor activity. The imprisoned Mary, Queen of Scots
Mary, Queen of Scots (8 December 1542 – 8 February 1587), also known as Mary Stuart or Mary I of Scotland, was Queen of Scotland from 14 December 1542 until her forced abdication in 1567.
The only surviving legitimate child of James V of S ...
, complained when her was taken away (by those who eventually became her executioners, who were to cover her body with the table's cloth). Billiards grew to the extent that by 1727, it was being played in almost every Paris café. In England, the game was developing into a very popular activity for members of the gentry.
By 1670, the thin butt end of the mace began to be used not only for shots under the cushion (which itself was originally only there as a preventative method to stop balls from rolling off), but players increasingly preferred it for other shots as well. The footless, straight cue as it is known today was finally developed by about 1800.
Initially, the mace was used to push the balls, rather than strike them. The newly developed striking cue provided a new challenge. Cushions began to be stuffed with substances to allow the balls to rebound, in order to enhance the appeal of the game. After a transitional period where only the better players would use cues, the cue came to be the first choice of equipment.
The demand for tables and other equipment was initially met in Europe by John Thurston and other furniture makers of the era. The early balls were made from wood and clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay part ...
, but the rich preferred to use ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals ...
.
Early billiard games involved various pieces of additional equipment, including the "arch" (related to the croquet hoop), "port" (a different hoop, often rectangular), and "king" (a pin or skittle near the arch) in the early 17th to late 18th century, but other game variants, relying on the cushions (and pockets cut into them), were being formed that would go on to play fundamental roles in the development of modern billiards.
The early croquet-like games eventually led to the development of the carom billiards category. These games are games played with three or sometimes four balls, on a table without holes in which the goal is generally to strike one with a , then have the cue ball rebound off of one or more of the cushions and strike a second object ball. Variations include straight rail, balkline, one-cushion
One-cushion billiards is a carom billiards discipline generally played on a cloth-covered, , pocketless billiard table with two cue balls and a third red-colored ball.
In a one-cushion shot, the cue ball off both with at least one rail being str ...
, three-cushion, five-pins, and four-ball, among others.
One type of obstacle remained a feature of many tables, originally as a hazard and later as a target, in the form of pockets, or holes partly cut into the table bed and partly into the cushions, leading to the rise of pocket billiards
Pool is a classification of cue sports played on a table with six pockets along the , into which balls are deposited. "Pool billiards" is sometimes hyphenated and/or spelled with a singular "billiard". The WPA itself uses "pool-billiard" in ...
, including "pool" games such as eight-ball, nine-ball, straight pool, and one-pocket; Russian pyramid
Russian pyramid, also known as Russian billiards (russian: ру́сский билья́рд, ), is a form of billiards played on a large billiard table with narrow pockets. It is popular across Eastern Europe as well as countries of the form ...
; snooker
Snooker (pronounced , ) is a cue sport played on a rectangular table covered with a green cloth called baize, with six pockets, one at each corner and one in the middle of each long side. First played by British Army officers stationed in Ind ...
; English billiards; and others.
In the United States, pool and billiards had died out for a bit, but between 1878 and 1956 the games became very popular. Players in annual championships began to receive their own cigarette cards. This was mainly due to the fact that it was a popular pastime for troops to take their minds off from battle. However, by the end of World War II, pool and billiards began to die down once again. It was not until 1961 when the film ''The Hustler'' came out that sparked a new interest in the game. Now the game is generally a well-known game and has many players of all different skill levels.
As a sport
The games with regulated international professional competition, if not others, have been referred to as "sports" or "sporting" events, not simply "games", since 1893 at the latest."Meeting of the Champions; The Big Billiard Tournament to Begin To-morrow – What Ives, Schaefer, and Slosson Have Been Doing in Practice – The Older Players Not Afraid of the Big Runs Made by Ives – Something About the Rise and Progress of the Young 'Napoleon' of the Billiard World", no byline, 1893-12-10, p. 10; The New York Times Company, New York Quite a variety of particular games (i.e., sets of rules and equipment) are the subject of present-day competition, including many of those already mentioned, with competition being especially broad in nine-ball, snooker, three-cushion, and eight-ball. Snooker, though a pocket billiards variant and closely related in its equipment and origin to the game of English billiards, is a professional sport organized at an international level, and its rules bear little resemblance to those of modern pool, pyramid, and other such games. A "Billiards" category encompassing pool, snooker, and carom has been part of the
World Games
The World Games are an international multi-sport event comprising sports and sporting disciplines that are not contested in the Olympic Games. They are usually held every four years, one year after a Summer Olympic Games, over the course of 11 ...
since 2001
The September 11 attacks against the United States by Al-Qaeda, which killed 2,977 people and instigated the global war on terror, were a defining event of 2001. The United States led a multi-national coalition in an invasion of Afghanistan ...
.
Equipment
Billiard balls
 Billiard balls vary from game to game, in size, design and quantity.
Billiard balls vary from game to game, in size, design and quantity.
Russian pyramid
Russian pyramid, also known as Russian billiards (russian: ру́сский билья́рд, ), is a form of billiards played on a large billiard table with narrow pockets. It is popular across Eastern Europe as well as countries of the form ...
and kaisa have a size of 68 mm ( in). In Russian pyramid there are sixteen balls, as in pool, but fifteen are white and numbered, and the is usually red. In kaisa, five balls are used: the yellow (called the ''kaisa'' in Finnish), two red object balls, and the two white cue balls (usually differentiated by one cue ball having a dot or other marking on it and each of which serves as an object ball for the opponent).
Carom billiards balls are larger than pool balls, having a diameter of 61.5 mm ( in), and come as a set of two cue balls (one colored or marked) and an object ball (or two object balls in the case of the game four-ball).
Standard pool balls are 57.15 mm ( in), are used in many pool games found throughout the world, come in sets of two of object balls, seven and seven , an and a ; the balls are racked differently for different games (some of which do not use the entire ball set). Blackball (English-style eight-ball) sets are similar, but have unmarked of and balls instead of solids and stripes, known as "casino" style. They are used principally in Britain, Ireland, and some Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with " republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from th ...
countries, though not exclusively, since they are unsuited for playing nine-ball. The diameter varies but is typically slightly smaller than that of standard solids-and-stripes sets.
Snooker balls are smaller than American-style pool balls with a diameter of 52.5 mm ( in), and come in sets of 22 (15 reds, 6 "", and a cue ball). English billiard balls are the same size as snooker balls and come in sets of three balls (two cue balls and a red object ball). Other games, such as bumper pool
Bumper pool is a cue sport played on an rectangular (or sometimes octagonal) table fitted with two pockets and an array of fixed cushioned obstacles, called bumpers, within the interior of the table surface.
Table
Typically, bumper pool table ...
, have custom ball sets.
Billiard balls have been made from many different materials since the start of the game, including clay, bakelite, celluloid, crystallite, ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals ...
, plastic, steel and wood. The dominant material from 1627 until the early 20th century was ivory. The search for a substitute for ivory use was not for environmental concerns, but based on economic motivation and fear of danger for elephant hunters. It was in part spurred on by a New York billiard table manufacturer who announced a prize of $10,000 for a substitute material. The first viable substitute was celluloid, invented by John Wesley Hyatt in 1868, but the material was volatile, sometimes exploding during manufacture, and was highly flammable.The New York Times Company (September 16, 1875)Explosive Teeth.
. Retrieved January 2, 2007.
Tables
There are many sizes and styles ofbilliard table
A billiard table or billiards table is a bounded table on which cue sports are played. In the modern era, all billiards tables (whether for carom billiards, pool, pyramid or snooker) provide a flat surface usually made of quarried slate, ...
s. Generally, tables are rectangles twice as long as they are wide. Table sizes are typically referred to by the nominal length of their longer dimension. Full-size snooker tables are long. Carom billiards tables are typically . Regulation pool tables are , though pubs and other establishments catering to casual play will typically use tables which are often coin-operated, nicknamed . Formerly, ten-foot pool tables were common, but such tables are now considered antiques.
High-quality tables have a made of thick slate, in three pieces to prevent warping and changes due to temperature and humidity. The slates on modern carom tables are usually heated to stave off moisture and provide a consistent playing surface. Smaller bar tables are most commonly made with a single piece of slate. Pocket billiards tables of all types normally have six pockets, three on each side (four corner pockets, and two side or middle pockets).
Cloth
All types of tables are covered with billiard cloth (often called "felt", but actually a woven wool or wool/nylon blend called baize). Cloth has been used to cover billiards tables since the 15th century. Bar or tavern tables, which get a lot of play, use "slower", more durable cloth. The cloth used in upscale pool (and snooker) halls and home billiard rooms is "faster" (i.e., provides less friction, allowing the balls to roll farther across the table ), and competition-quality pool cloth is made from 100% worsted wool. Snooker cloth traditionally has a nap (consistent fiber directionality) and balls behave differently when rolling against versus along with the nap. The cloth of the billiard table has traditionally been green, reflecting its origin (originally the grass of ancestral lawn games), and has been so colored since at least the 16th century, but it is also produced in other colors such as red and blue. Television broadcasting of pool as well as 3 Cushion billiards prefers a blue colored cloth which was chosen for better visibility and contrast against colored balls.Rack
A rack is the name given to a frame (usually wood, plastic or aluminium) used to organize billiard balls at the beginning of a game. This is traditionally triangular in shape, but varies with the type of billiards played. There are two main types of racks; the more common triangular shape which is used for eight-ball and straight pool and the diamond-shaped rack used for nine-ball. There are several other types of less common rack types that are also used, based on a "template" to hold the billiard balls tightly together. Most commonly it is a thin plastic sheet with diamond-shaped cut-outs that hold the balls that is placed on the table with the balls set on top of the rack. The rack is used to set up the “break” and removed once the break has been completed and no balls are obstructing the template.Cues
Billiards games are mostly played with a stick known as a cue. A cue is usually either a one-piece tapered stick or a two-piece stick divided in the middle by a joint of metal or phenolic resin. High-quality cues are generally two pieces and are made of a hardwood, generally maple for billiards and ash for snooker. The end of the cue is of larger circumference and is intended to be gripped by a player's hand. The of the cue is of smaller circumference, usually tapering to an terminus called a (usually made of fiberglass or brass in better cues), where a rounded leather is affixed, flush with the ferrule, to make final contact with balls. The tip, in conjunction with chalk, can be used to impart spin to the cue ball when it is not hit in its center. Cheap cues are generally made of pine, low-grade maple (and formerly often of ramin, which is now endangered), or other low-quality wood, with inferior plastic ferrules. A quality cue can be expensive and may be made of exotic woods and other expensive materials which are artfully inlaid in decorative patterns. Many modern cues are also made, like golf clubs, with high-tech materials such as woven graphite. Recently,carbon fiber
Carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (American English), carbon-fibre-reinforced polymers (Commonwealth English), carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics, carbon-fiber reinforced-thermoplastic (CFRP, CRP, CFRTP), also known as carbon fiber, carbon compo ...
woven composites have been developed and utilized by top professional players and amateurs. Advantages include less flexibility and no worry of nicks, scratches, or damages to the cue. Skilled players may use more than one cue during a game, including a separate cue with a hard phenolic resin tip for the opening break shot, and another, shorter cue with a special tip for .
Mechanical bridge
The mechanical bridge, sometimes called a "rake", "crutch", "bridge stick" or simply "bridge", and in the UK a "rest", is used to extend a player's reach on a shot where the cue ball is too far away for normal hand bridging. It consists of a stick with a grooved metal or plastic head which the cue slides on. Some players, especially current or former snooker players, use a screw-on cue butt extension instead of or in addition to the mechanical bridge. Bridge head design is varied, and not all designs (especially those with cue shaft-enclosing rings, or wheels on the bottom of the head), are broadly tournament-approved. In Italy, a longer, thicker cue is typically available for this kind of tricky shot. For snooker, bridges are normally available in three forms, their use depending on how the player is hampered; the standard rest is a simple cross, the 'spider' has a raised arch around 12 cm with three grooves to rest the cue in and for the most awkward of shots, the 'giraffe' (or 'swan' in England) which has a raised arch much like the 'spider' but with a slender arm reaching out around 15 cm with the groove.Chalk
Chalk is applied to the tip of the cue stick, ideally before every shot, to increase the tip's friction coefficient so that when it impacts the cue ball on a non-center hit, no (unintentional slippage between the cue tip and the struck ball) occurs. Chalk is an important element to make good shots in pool orsnooker
Snooker (pronounced , ) is a cue sport played on a rectangular table covered with a green cloth called baize, with six pockets, one at each corner and one in the middle of each long side. First played by British Army officers stationed in Ind ...
. Cue tip chalk is not actually the substance typically referred to as "chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. Cha ...
" (generally calcium carbonate), but any of several proprietary compounds, with a silicate base. It was around the time of the Industrial Revolution that newer compounds formed that provided better grip for the ball. This is when the English began to experiment with side spin or applying curl to the ball. This was shortly introduced to the American players and is how the term "putting English on the ball" came to be. "Chalk" may also refer to a cone of fine, white ; like talc (talcum powder) it can be used to reduce friction between the cue and bridge hand during shooting, for a smoother stroke. Some brands of hand chalk are made of compressed talc. (Tip chalk is not used for this purpose because it is abrasive, hand-staining and difficult to apply.) Many players prefer a slick pool glove over hand chalk or talc because of the messiness of these powders; buildup of particles on the cloth will affect ball behavior and necessitate more-frequent cloth cleaning.
Cue tip chalk (invented in its modern form by straight rail billiard pro William A. Spinks
William Alexander Spinks Jr. (July 11, 1865 – January 15, 1933) was an American professional player of carom billiards in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. He was often referred to as W. A. Spinks, and occasionally Billy Spinks. In ad ...
and chemist William Hoskins in 1897)"The World's Most Tragic Man Is the One Who Never Starts", Clark, Neil M.; originally published in ''The American'' magazine, May 1927; republished in ''hotwire: The Newsletter of the Toaster Museum Foundation'', vol. 3, no. 3, online edition. Retrieved February 24, 2007. The piece is largely an interview of Hoskins., 9 March 1897 is made by crushing
silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is o ...
and the abrasive substance corundum
Corundum is a crystalline form of aluminium oxide () typically containing traces of iron, titanium, vanadium and chromium. It is a rock-forming mineral. It is a naturally transparent material, but can have different colors depending on the ...
or aloxite (aluminium oxide),"Aloxite", ChemIndustry.com database. Retrieved February 24, 2007."Substance Summary: Aluminum Oxide"
''PubChem Database'',
National Library of Medicine
The United States National Library of Medicine (NLM), operated by the United States federal government, is the world's largest medical library.
Located in Bethesda, Maryland, the NLM is an institute within the National Institutes of Health. It ...
, US National Institutes of Health. Retrieved February 24, 2007. into a powder. It is combined with dye (originally and most commonly green or blue-green, like traditional billiard cloth, but available today, like the cloth, in many colours) and a binder (glue). Each manufacturer's brand has different qualities, which can significantly affect play. High humidity can also impair the effectiveness of chalk. Harder, drier compounds are generally considered superior by most players.
Major games
There are two main varieties of billiard games: carom and pocket. The main carom billiards games are straight rail, balkline and three cushion billiards. All are played on a pocketless table with three balls; two cue balls and one object ball. In all, players shoot a cue ball so that it makes contact with the opponent's cue ball as well as the object ball. Others of multinational interest are four-ball and five-pins. The most globally popular of the large variety of pocket games are pool andsnooker
Snooker (pronounced , ) is a cue sport played on a rectangular table covered with a green cloth called baize, with six pockets, one at each corner and one in the middle of each long side. First played by British Army officers stationed in Ind ...
. A third, English billiards, has some features of carom billiards. English billiards used to be one of the two most-competitive cue sports along with the carom game balkline, at the turn of the 20th century and is still enjoyed today in Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with " republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from th ...
countries. Another pocket game, Russian pyramid
Russian pyramid, also known as Russian billiards (russian: ру́сский билья́рд, ), is a form of billiards played on a large billiard table with narrow pockets. It is popular across Eastern Europe as well as countries of the form ...
and its variants like kaisa are popular in the former Eastern bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
.
Games played on a carom billiards table
Straight rail
In straight rail, a player scores a point and may continue shooting each time his cue ball makes contact with both other balls. Some of the best players of straight billiards developed the skill to the balls in a corner or along the same rail for the purpose of playing a series of to score a seemingly limitless number of points. The first straight rail professional tournament was held in 1879 where Jacob Schaefer Sr. scored 690 points in a single turn (that is, 690 separate strokes without a miss). With the balls repetitively hit and barely moving in endless "nursing", there was little for the fans to watch.Balkline
In light of these skill developments in straight rail, the game of balkline soon developed to make it impossible for a player to keep the balls gathered in one part of the table for long, greatly limiting the effectiveness of nurse shots. A is a line parallel to one end of a billiards table. In the game of balkline, the players have to drive at least one object ball past a balkline parallel to each rail after a specified number of points have been scored.Cushion billiards
Another solution was to require a player's cue ball to make contact with the rail cushions in the process of contacting the other balls. This in turn saw the three-cushion version emerge, where the cue ball must make three separate cushion contacts during a shot. This is difficult enough that even the best players can only manage to average one to two points per turn. This is sometimes described as "hardest to learn" and "require most skill" of all billiards.Games played on a pool table
There are many variations of games played on a standard pool table. Popular pool games include eight-ball, nine-ball, straight pool and one-pocket. Even within games types (e.g. eight-ball), there may be variations, and people may play recreationally using relaxed or local rules. A few of the more popular examples of pool games are given below. In eight-ball and nine-ball, the object is to sink object balls until one can legally pocket the winningeponym
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Usage of the word
The term ''epon ...
ous "". Well-known but waning in popularity is straight pool, in which players seek to continue sinking balls, rack after rack if they can, to reach a pre-determined winning score (typically 150). Related to nine-ball, another well-known game is rotation, where the lowest-numbered object ball on the table must be struck first, although any object ball may be pocketed (i.e., combination shot). Each pocketed ball is worth its number, and the player with the highest score at the end of the rack is the winner. Since there are only 120 points available (1 + 2 + 3 ⋯ + 15 = 120), scoring 61 points leaves no opportunity for the opponent to catch up. In both one-pocket and bank pool, the players must sink a set number of balls; respectively, all in a particular , or all by . In snooker, players score points by alternately potting and various special "".
Two-player or -team games
* Eight-ball: The goal is to () all of one's designated of balls (either vs. , or vs. , depending upon the equipment), and then pocket the in a pocket. * Nine-ball: The goal is to pocket the 9 ball; the initial contact of the each turn must be with the lowest-numbered remaining on the table; there are numerous variants such asseven-ball
Seven-ball is a pool game with rules similar to nine-ball, though it differs in two key ways: the game uses only seven as implied by its name, and play is restricted to particular pockets of the table. William D. Clayton is credited with the g ...
, six-ball, and the older forms of three-ball and ten-ball, that simply use a different number of balls and have a different .
* Straight pool (a.k.a. 14.1 continuous pool): The goal is to reach a predetermined number of (e.g. 100); a point is earned by pocketing any called ball into a designated pocket; game play is by of 15 balls, and the last object ball of a rack is not pocketed, but left on the table with the opponent re-racking the remaining 14 before game play continues.
* Bank pool: The goal is to reach a predetermined number of points; a point is earned by pocketing any called ball by it into a designated pocket using one or more .
Speed pool
Speed pool is a standard billiards game where the balls must be pocketed in as little time as possible. Rules vary greatly from tournament to tournament. The International Speed Pool Challenge has been held annually since 2006.Games played on a snooker table
English billiards
Dating to approximately 1800, English billiards, called simply billiards in many former British colonies and in the UK where it originated, was originally called the ''winning and losing carambole game'', folding in the names of three predecessor games, ''the winning game'', ''the losing game'' and ''the carambole game'' (an early form of straight rail), that combined to form it. The game features both (caroms) and the pocketing of balls as objects of play. English billiards requires two and a red . The object of the game is to score either a fixed number of points, or score the most points within a set time frame, determined at the start of the game. Points are awarded for: *Two-ball cannons: striking both the object ball and the other (opponent's) cue ball on the same shot (2 points). *: the red ball (3 points); potting the other cue ball (2 points). * (or "in-offs"): potting one's cue ball by cannoning off another ball (3 points if the red ball was hit first; 2 points if the other cue ball was hit first, or if the red and other cue ball were "", i.e., hit simultaneously).Snooker
Snooker is a pocket billiards game originated byBritish officers
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
stationed in India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
during the 19th century, based on earlier pool games such as black pool and life pool. The name of the game became generalized to also describe one of its prime strategies: to "" the opposing player by causing that player to foul or leave an opening to be exploited.
In the United Kingdom, snooker is by far the most popular cue sport at the competitive level, and major national pastime along with association football and cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by st ...
. It is played in many Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with " republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from th ...
countries as well, and in areas of Asia, becoming increasingly popular in China in particular. Snooker is uncommon in North America, where pool games such as eight-ball and nine-ball dominate, and Latin America and Continental Europe, where carom games dominate. The first World Snooker Championship was held in 1927, and it has been held annually since then with few exceptions. The World Professional Billiards and Snooker Association (WPBSA) was established in 1968 to regulate the professional game, while the International Billiards and Snooker Federation (IBSF) regulates the amateur games.
List of cue sports and games
Carom games
* Artistic billiards * Balkline * Four-ball billiards (, ) * One-cushion billiards * Straight rail * Three-cushion billiardsPocket games
Pool games
Non-pool pocket games
* Golf billiards *Russian pyramid
Russian pyramid, also known as Russian billiards (russian: ру́сский билья́рд, ), is a form of billiards played on a large billiard table with narrow pockets. It is popular across Eastern Europe as well as countries of the form ...
Snooker games
*Snooker
Snooker (pronounced , ) is a cue sport played on a rectangular table covered with a green cloth called baize, with six pockets, one at each corner and one in the middle of each long side. First played by British Army officers stationed in Ind ...
**Six-red snooker
Six-red snooker (sometimes spelled six-reds, 6-red, and also known as super 6s), is a variant of snooker, but with only six initially on the table as opposed to the standard fifteen.
Overview
In Six-red snooker, the traditional game of snooker ...
** American snooker
** Brazilian snooker
** Volunteer snooker
** Snooker plus
** Power Snooker
Games with pockets and caroms
*Bottle pool
Bottle pool, also known as bottle-billiards and bottle pocket billiards, is a hybrid billiards game combining aspects of both carom billiards and pocket billiards. Played on a standard pool table, the game uses just two , a cue ball, and a 6¾ inc ...
* Cowboy pool
* English billiards
* Kaisa
Obstacle and target games
* Bagatelle * Bar billiards *Bumper pool
Bumper pool is a cue sport played on an rectangular (or sometimes octagonal) table fitted with two pockets and an array of fixed cushioned obstacles, called bumpers, within the interior of the table surface.
Table
Typically, bumper pool table ...
* Danish pin billiards
* Five-pin billiards
*' (or nine-pin billiards)
Disk games
* Novuss (uses full-length cues)Cueless games
* Boccette * CrudSee also
* Glossary of cue sports terms * BCA Hall of Fame * Hustling * Cue sports techniquesReferences
Citations
Sources
* *External links
* {{Authority control Sports entertainment French inventions