Cuboidal Epithelia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of
 In general, epithelial tissues are classified by the number of their layers and by the
In general, epithelial tissues are classified by the number of their layers and by the
punakoidal
, are tightly packed and form a continuous sheet. It has almost no intercellular spaces. All epithelia is usually separated from underlying tissues by an extracellular fibrous basement membrane. The lining of the mouth, lung alveoli and kidney tubules are all made of epithelial tissue. The lining of the blood and lymphatic vessels are of a specialised form of epithelium called

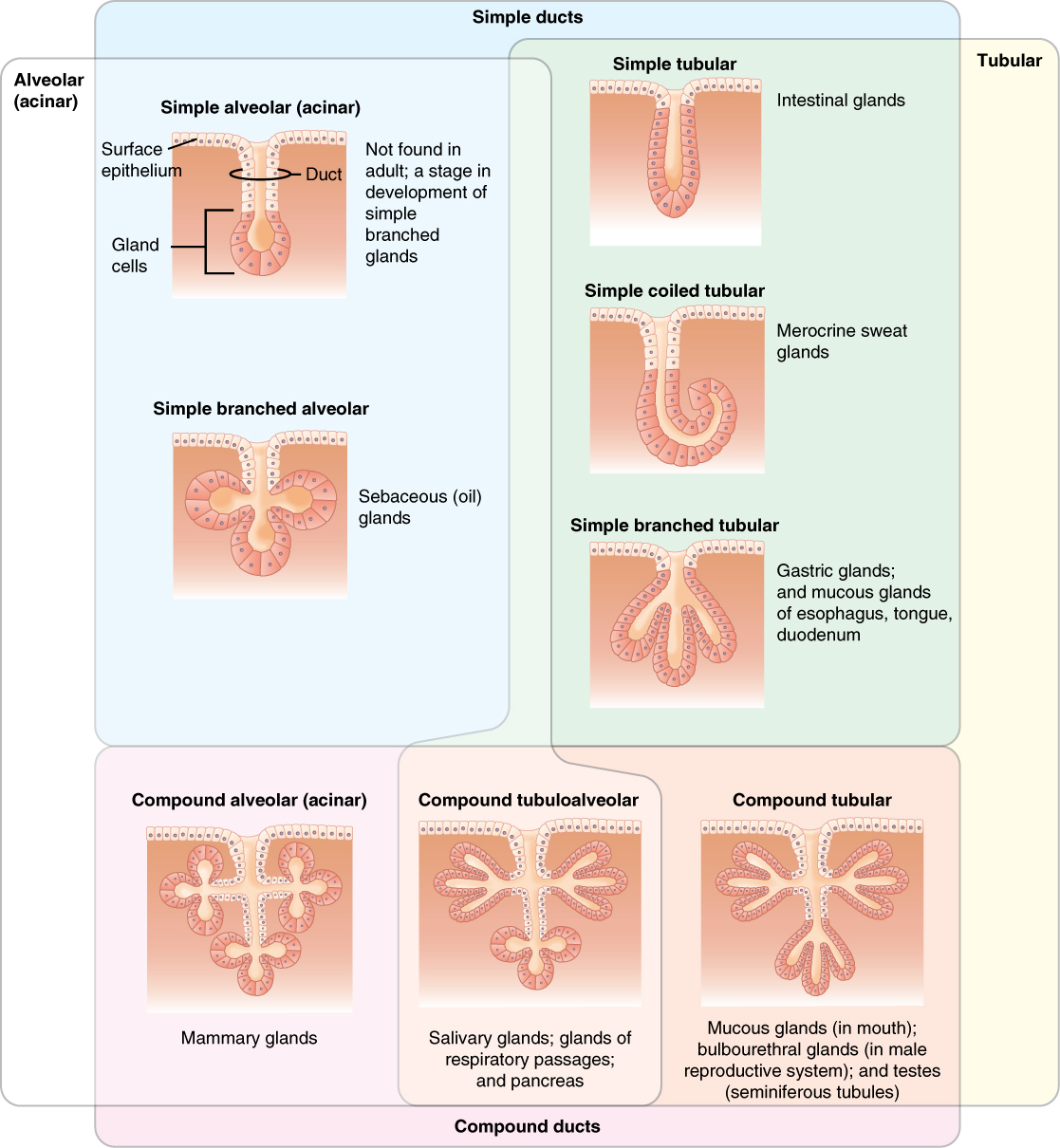 Epithelial tissues have as their primary functions:
# to protect the tissues that lie beneath from
Epithelial tissues have as their primary functions:
# to protect the tissues that lie beneath from
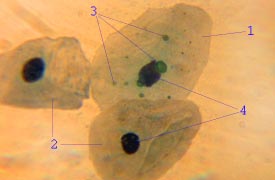 The slide shows at (1) an epithelial cell infected by ''Chlamydia pneumoniae''; their
The slide shows at (1) an epithelial cell infected by ''Chlamydia pneumoniae''; their
File:Dogsquamos100x.jpg, Squamous epithelium 100×
File:Cheekcells stained.jpg, Human cheek cells (Nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium) 500×
File:Female urethra histology.jpg, Histology of female urethra showing transitional epithelium
File:Sweat gland histology 2014.jpg, Histology of sweat gland showing stratified cuboidal epithelium
Epithelium Photomicrographs
* Simple squamous epithelium of the
Diagrams of simple squamous epithelium
* Stratified squamous epithelium of the vagina * Stratified squamous epithelium of the skin (thin skin) * Stratified squamous epithelium of the skin (thick skin)
{{Authority control Tissues (biology)
animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motilit ...
tissue, along with connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue ...
, muscle tissue
Muscle tissue (or muscular tissue) is soft tissue that makes up the different types of muscles in most animals, and give the ability of muscles to contract. Muscle tissue is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. ...
and nervous tissue
Nervous tissue, also called neural tissue, is the main tissue component of the nervous system. The nervous system regulates and controls body functions and activity. It consists of two parts: the central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain ...
. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery w ...
with a little intercellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide struct ...
. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessel
Blood vessels are the structures of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from ...
s throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the ...
, the outermost layer of the skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have diffe ...
.
There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All gland
In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream ( endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface ( exocrine gland).
Structure
...
s are made up of epithelial cells. Functions of epithelial cells include diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
, filtration, secretion 440px
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classica ...
, selective absorption, germination
Germination is the process by which an organism grows from a seed or spore. The term is applied to the sprouting of a seedling from a seed of an angiosperm or gymnosperm, the growth of a sporeling from a spore, such as the spores of fungi, ...
, and transcellular transport
Transcellular transport involves the transportation of solutes by a cell ''through'' a cell. Transcellular transport can occur in three different ways active transport, passive transport, and transcytosis.
Active Transport
Main article: Activ ...
. Compound epithelium has protective functions.
Epithelial layers contain no blood vessels (avascular
Blood vessels are the structures of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from ...
), so they must receive nourishment via diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
of substances from the underlying connective tissue, through the basement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and ...
. Cell junction
Cell junctions (or intercellular bridges) are a class of cellular structures consisting of multiprotein complexes that provide contact or adhesion between neighboring cells or between a cell and the extracellular matrix in animals. They also main ...
s are especially abundant in epithelial tissues.
Classification
Simple epithelium
Simple epithelium is a single layer of cells with every cell in direct contact with thebasement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and ...
that separates it from the underlying connective tissue. In general, it is found where absorption and filtration occur. The thinness of the epithelial barrier facilitates these processes.
 In general, epithelial tissues are classified by the number of their layers and by the
In general, epithelial tissues are classified by the number of their layers and by the shape
A shape or figure is a graphical representation of an object or its external boundary, outline, or external surface, as opposed to other properties such as color, texture, or material type.
A plane shape or plane figure is constrained to lie on ...
and function of the cells. The basic cell types are squamous, cuboidal, and columnar, classed by their shape.
By layer, epithelium is classed as either simple epithelium, only one cell thick (unilayered), or stratified epithelium having two or more cells in thickness, or multi-layered – as stratified squamous epithelium
A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural i ...
, stratified cuboidal epithelium, and stratified columnar epithelium, and both types of layering can be made up of any of the cell shapes. However, when taller simple columnar epithelial cells are viewed in cross section showing several nuclei appearing at different heights, they can be confused with stratified epithelia. This kind of epithelium is therefore described as pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
Transitional epithelium
Transitional epithelium also known as urothelium is a type of stratified epithelium. Transitional epithelium is a type of tissue that changes shape in response to stretching (stretchable epithelium). The transitional epithelium usually appears ...
has cells that can change from squamous to cuboidal, depending on the amount of tension on the epithelium.
Stratified epithelium
Stratified or compound epithelium differs from simple epithelium in that it is multilayered. It is therefore found where body linings have to withstand mechanical or chemical insult such that layers can be abraded and lost without exposing subepithelial layers. Cells flatten as the layers become more apical, though in their most basal layers, the cells can be squamous, cuboidal, or columnar. Stratified epithelia (of columnar, cuboidal, or squamous type) can have the following specializations:Structure
Epithelial tissue cells can adopt shapes of varying complexity (from polyhedral to scutoidal tpunakoidal
, are tightly packed and form a continuous sheet. It has almost no intercellular spaces. All epithelia is usually separated from underlying tissues by an extracellular fibrous basement membrane. The lining of the mouth, lung alveoli and kidney tubules are all made of epithelial tissue. The lining of the blood and lymphatic vessels are of a specialised form of epithelium called
endothelium
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the ve ...
.
Location
Epithelium lines both the outside (skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have diffe ...
) and the inside cavities and lumina of bodies. The outermost layer of human skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to m ...
is composed of dead stratified squamous
A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural i ...
, keratinized epithelial cells.
Tissues that line the inside of the mouth, the esophagus
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the ...
, the vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hy ...
, and part of the rectum
The rectum is the final straight portion of the large intestine in humans and some other mammals, and the gut in others. The adult human rectum is about long, and begins at the rectosigmoid junction (the end of the sigmoid colon) at the l ...
are composed of nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium. Other surfaces that separate body cavities from the outside environment are lined by simple squamous, columnar, or pseudostratified epithelial cells. Other epithelial cells line the insides of the lungs, the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans a ...
, the reproductive and urinary tracts, and make up the exocrine
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances on to an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of ...
and endocrine gland
Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid ...
s. The outer surface of the cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical ...
is covered with fast-growing, easily regenerated epithelial cells. A specialised form of epithelium, endothelium
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the ve ...
, forms the inner lining of blood vessel
Blood vessels are the structures of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away from ...
s and the heart
The heart is a muscular organ found in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon diox ...
, and is known as vascular endothelium, and lining lymphatic vessels as lymphatic endothelium. Another type, mesothelium
The mesothelium is a membrane composed of simple squamous epithelium, simple squamous epithelial cells of mesodermal origin, which forms the lining of several body cavities: the pleura (pleural cavity around the lungs), peritoneum (abdominopelvic c ...
, forms the walls of the pericardium
The pericardium, also called pericardial sac, is a double-walled sac containing the heart and the roots of the great vessels. It has two layers, an outer layer made of strong connective tissue (fibrous pericardium), and an inner layer made of ...
, pleurae, and peritoneum
The peritoneum is the serous membrane forming the lining of the abdominal cavity or coelom in amniotes and some invertebrates, such as annelids. It covers most of the intra-abdominal (or coelomic) organs, and is composed of a layer of mesot ...
.
In arthropods, the integument
In biology, an integument is the tissue surrounding an organism's body or an organ within, such as skin, a husk, shell, germ or rind.
Etymology
The term is derived from ''integumentum'', which is Latin for "a covering". In a transferred, or ...
, or external "skin", consists of a single layer of epithelial ectoderm from which arises the cuticle, an outer covering of chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
, the rigidity of which varies as per its chemical composition.
Basement membrane
The basal surface of epithelial tissue rests on abasement membrane
The basement membrane is a thin, pliable sheet-like type of extracellular matrix that provides cell and tissue support and acts as a platform for complex signalling. The basement membrane sits between epithelial tissues including mesothelium and ...
and the free/apical surface faces body fluid or outside. The basement membrane acts as a scaffolding on which epithelium can grow and regenerate after injuries. Epithelial tissue has a nerve supply, but no blood supply and must be nourished by substances diffusing from the blood vessels in the underlying tissue. The basement membrane acts as a selectively permeable membrane that determines which substances will be able to enter the epithelium.
The Basal lamina
The basal lamina is a layer of extracellular matrix secreted by the epithelial cells, on which the epithelium sits. It is often incorrectly referred to as the basement membrane, though it does constitute a portion of the basement membrane. The ba ...
is made up of laminin (glycoproteins) secreted by epithelial cells. The Reticular lamina beneath the basal lamina is made up of collagen proteins secreted by connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue ...
.
Cell junctions
Cell junctions are especially abundant in epithelial tissues. They consist of protein complexes and provide contact between neighbouring cells, between a cell and theextracellular matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide struc ...
, or they build up the paracellular barrier of epithelia and control the paracellular transport
Paracellular transport refers to the transfer of substances across an epithelium by passing through the intercellular space ''between'' the cells. It is in contrast to transcellular transport, where the substances travel ''through'' the cell, pa ...
.
Cell junctions are the contact points between plasma membrane and tissue cells. There are mainly 5 different types of cell junctions: tight junction
Tight junctions, also known as occluding junctions or ''zonulae occludentes'' (singular, ''zonula occludens''), are multiprotein junctional complexes whose canonical function is to prevent leakage of solutes and water and seals between the epith ...
s, adherens junction
Adherens junctions (or zonula adherens, intermediate junction, or "belt desmosome") are protein complexes that occur at cell–cell junctions, cell–matrix junctions in epithelial and endothelial tissues, usually more basal than tight junctions. ...
s, desmosome
A desmosome (; "binding body"), also known as a macula adherens (plural: maculae adherentes) (Latin for ''adhering spot''), is a cell structure specialized for cell-to-cell adhesion. A type of junctional complex, they are localized spot-like adh ...
s, hemidesmosomes, and gap junction
Gap junctions are specialized intercellular connections between a multitude of animal cell-types. They directly connect the cytoplasm of two cells, which allows various molecules, ions and electrical impulses to directly pass through a regula ...
s.
Tight junctions are a pair of trans-membrane protein fused on outer plasma membrane.
Adherens junctions are a plaque (protein layer on the inside plasma membrane) which attaches both cells' microfilaments.
Desmosomes attach to the microfilaments of cytoskeleton made up of keratin protein.
Hemidesmosomes resemble desmosomes on a section. They are made up of the integrin (a transmembrane protein) instead of cadherin. They attach the epithelial cell to the basement membrane.
Gap junctions connect the cytoplasm of two cells and are made up of proteins called connexins (six of which come together to make a connexion).
Development
Epithelial tissues are derived from all of the embryologicalgerm layers
A germ layer is a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development. The three germ layers in vertebrates are particularly pronounced; however, all eumetazoans (animals that are sister taxa to the sponges) produce two or three pr ...
:
* from ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from the o ...
(e.g., the epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the ...
);
* from endoderm
Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and mesoderm (middle layer). Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gast ...
(e.g., the lining of the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans a ...
);
* from mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical Emb ...
(e.g., the inner linings of body cavities).
However, it is important to note that pathologists do not consider endothelium
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the ve ...
and mesothelium
The mesothelium is a membrane composed of simple squamous epithelium, simple squamous epithelial cells of mesodermal origin, which forms the lining of several body cavities: the pleura (pleural cavity around the lungs), peritoneum (abdominopelvic c ...
(both derived from mesoderm) to be true epithelium. This is because such tissues present very different pathology. For that reason, pathologists label cancers in endothelium and mesothelium sarcoma
A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from transformed cells of mesenchymal (connective tissue) origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, fat, vascular, or hematopoietic tissues, and sa ...
s, whereas true epithelial cancers are called carcinoma
Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesoderma ...
s. Additionally, the filaments that support these mesoderm-derived tissues are very distinct. Outside of the field of pathology, it is generally accepted that the epithelium arises from all three germ layers.
Cell turnover
Epithelia turn over at some of the fastest rates in the body. For epithelial layers to maintain constant cell numbers essential to their functions, the number of cells that divide must match those that die. They do this mechanically. If there are too few the cells the stretch that they experience rapidly activates cell division. Alternatively, when too many cells accumulate, crowding triggers their death by activation epithelial cell extrusion. Here, cells fated for elimination are seamlessly squeezed out by contracting a band of actin and myosin around and below the cell, preventing any gaps from forming that could disrupt their barriers. Failure to do so can result in aggressive tumors and their invasion by aberrant basal cell extrusion.Functions
 Epithelial tissues have as their primary functions:
# to protect the tissues that lie beneath from
Epithelial tissues have as their primary functions:
# to protect the tissues that lie beneath from radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'', such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, vi ...
, desiccation, toxins
A toxin is a naturally occurring organic poison produced by metabolic activities of living cells or organisms. Toxins occur especially as a protein or conjugated protein. The term toxin was first used by organic chemist Ludwig Brieger (1849 ...
, invasion by pathogens, and physical trauma
# the regulation and exchange of chemicals between the underlying tissues and a body cavity
A body cavity is any space or compartment, or potential space, in an animal body. Cavities accommodate organs and other structures; cavities as potential spaces contain fluid.
The two largest human body cavities are the ventral body cavity, and ...
# the secretion of hormones into the circulatory system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
, as well as the secretion of sweat, mucus, enzymes, and other products that are delivered by ducts
# to provide sensation
#Absorb water and digested food in the lining of digestive canal.
Glandular tissue
Glandular tissue is the type of epithelium that forms theglands
In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream (endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface (exocrine gland).
Structure
De ...
from the infolding of epithelium and subsequent growth in the underlying connective tissue. They may be specialized columnar or cuboidal tissues consisting of goblet cell
Goblet cells are simple columnar epithelial cells that secrete gel-forming mucins, like mucin 5AC. The goblet cells mainly use the merocrine method of secretion, secreting vesicles into a duct, but may use apocrine methods, budding off their se ...
s, which secrete mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
. There are two major classifications of glands: endocrine gland
Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones, directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid ...
s and exocrine gland
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances on to an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of ...
s:
* Endocrine glands secrete their product into the extracellular space where it is rapidly taken up by the circulatory system.
* Exocrine glands secrete their products into a duct that then delivers the product to the lumen of an organ or onto the free surface of the epithelium. Their secretions include tears
Tears are a clear liquid secreted by the lacrimal glands (tear gland) found in the eyes of all land mammals. Tears are made up of water, electrolytes, proteins, lipids, and mucins that form layers on the surface of eyes. The different types of ...
, saliva, oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturate ...
(sebum), enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
, digestive juices
Gastric acid, gastric juice, or stomach acid is a digestive fluid formed within the stomach lining. With a pH between 1 and 3, gastric acid plays a key role in digestion of proteins by activating digestive enzymes, which together break down the ...
, sweat
Perspiration, also known as sweating, is the production of fluids secreted by the sweat glands in the skin of mammals.
Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are dist ...
, etc.
Sensing the extracellular environment
Some epithelial cells areciliated The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projec ..., especially inrespiratory epithelium Respiratory epithelium, or airway epithelium, is a type of ciliated columnar epithelium found lining most of the respiratory tract as respiratory mucosa, where it serves to moisten and protect the airways. It is not present in the vocal cords o ..., and they commonly exist as a sheet of polarised cells forming a tube or tubule with cilia projecting into the lumen."Primary cilia The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projecti ...on epithelial cells provide chemosensation,thermoception Thermoception or thermoreception is the sensation and perception of temperature, or more accurately, temperature differences inferred from heat flux. It deals with a series of events and processes required for an organism to receive a temperature s ..., andmechanosensation Mechanosensation is the transduction of mechanical stimuli into neural signals. Mechanosensation provides the basis for the senses of light touch, hearing, proprioception, and pain. Mechanoreceptors found in the skin, called cutaneous mechanorecept ...of the extracellular environment by playing "a sensory role mediating specific signalling cues, including soluble factors in the external cell environment, a secretory role in which a soluble protein is released to have an effect downstream of the fluid flow, and mediation of fluid flow if the cilia aremotile Motility is the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy. Definitions Motility, the ability of an organism to move independently, using metabolic energy, can be contrasted with sessility, the state of organisms th ....
Host immune response
Epithelial cells express many genes that encode immune mediators and proteins involved in cell-cell communication with hematopoietic immune cells. The resulting immune functions of these non-hematopoietic, structural cells contribute to the mammalian immune system ("structural immunity"). Relevant aspects of the epithelial cell response to infections are encoded in theepigenome
An epigenome consists of a record of the chemical changes to the DNA and histone proteins of an organism; these changes can be passed down to an organism's offspring via transgenerational stranded epigenetic inheritance. Changes to the epigenome ...
of these cells, which enables a rapid response to immunological challenges.
Clinical significance
 The slide shows at (1) an epithelial cell infected by ''Chlamydia pneumoniae''; their
The slide shows at (1) an epithelial cell infected by ''Chlamydia pneumoniae''; their inclusion bodies
Inclusion bodies are aggregates of specific types of protein found in neurons, a number of tissue cells including red blood cells, bacteria, viruses, and plants. Inclusion bodies of aggregations of multiple proteins are also found in muscle cells ...
shown at (3); an uninfected cell shown at (2) and (4) showing the difference between an infected cell nucleus and an uninfected cell nucleus.
Epithelium grown in culture can be identified by examining its morphological characteristics. Epithelial cells tend to cluster together, and have a "characteristic tight pavement-like appearance". But this is not always the case, such as when the cells are derived from a tumor. In these cases, it is often necessary to use certain biochemical markers to make a positive identification. The intermediate filament proteins in the cytokeratin
Cytokeratins are keratin proteins found in the intracytoplasmic cytoskeleton of epithelial tissue. They are an important component of intermediate filaments, which help cells resist mechanical stress. Expression of these cytokeratins within epi ...
group are almost exclusively found in epithelial cells, so they are often used for this purpose.
Cancers originating from the epithelium are classified as carcinoma
Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesoderma ...
s. In contrast, sarcoma
A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from transformed cells of mesenchymal (connective tissue) origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, fat, vascular, or hematopoietic tissues, and sa ...
s develop in connective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue ...
.
When epithelial cells or tissues are damaged from cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. Long-term issues include difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent lung infections. ...
, sweat glands are also damaged, causing a frosty coating of the skin.
Etymology and pronunciation
The word ''epithelium'' uses the Greek roots ἐπί (''epi''), "on" or "upon", and θηλή (''thēlē''), "nipple". Epithelium is so called because the name was originally used to describe the translucent covering of small "nipples" of tissue on the lip. The word has bothmass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different element ...
and count
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New Yor ...
senses; the plural form is epithelia.
Additional images
See also
* Dark cell * Epithelial-mesenchymal transition *Epithelial polarity Epithelial polarity is one example of the cell polarity that is a fundamental feature of many types of cells. Epithelial cells feature distinct 'apical', 'lateral' and 'basal' plasma membrane domains. Epithelial cells connect to one another via th ...
* Glycocalyx
The glycocalyx, also known as the pericellular matrix, is a glycoprotein and glycolipid covering that surrounds the cell membranes of bacteria, epithelial cells, and other cells. In 1970, Martinez-Palomo discovered the cell coating in animal cel ...
* Inner and Outer enamel epithelium
The outer enamel epithelium, also known as the external enamel epithelium, is a layer of cuboidal cells located on the periphery of the enamel organ in a developing tooth. This layer is first seen during the bell stage.
The rim of the enamel org ...
* Iris pigment epithelium
The iris pigment epithelium (IPE) is a one cell thick layer of cuboidal cells lying behind the iris. The epithelial cells are highly pigmented due to the numerous large melanosomes which pack the cytoplasm of each cell. Towards the central axi ...
* Neuroepithelial cell
* Retinal pigment epithelium
The pigmented layer of retina or retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is the pigmented cell layer just outside the neurosensory retina that nourishes retinal visual cells, and is firmly attached to the underlying choroid and overlying retinal visual ...
* Skin cancer
Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. There are three main types of skin cancers: basal-cell skin cancer (BC ...
* Sulcular epithelium
References
Further reading
* * * *External links
Epithelium Photomicrographs
* Simple squamous epithelium of the
glomerulus
''Glomerulus'' () is a common term used in anatomy to describe globular structures of entwined vessels, fibers, or neurons. ''Glomerulus'' is the diminutive of the Latin ''glomus'', meaning "ball of yarn".
''Glomerulus'' may refer to:
* the filter ...
(kidney)
Diagrams of simple squamous epithelium
* Stratified squamous epithelium of the vagina * Stratified squamous epithelium of the skin (thin skin) * Stratified squamous epithelium of the skin (thick skin)
{{Authority control Tissues (biology)