Cross-strait Relations on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Cross-Strait relations (sometimes called Mainland–Taiwan relations, or Taiwan-China relations) are the relations between
Cross-Strait relations (sometimes called Mainland–Taiwan relations, or Taiwan-China relations) are the relations between
ImageSize = width:900 height:auto barincrement:70
PlotArea = left:150 right:100 bottom:80 top:0
DateFormat = dd/mm/yyyy
Define $now = 31/12/2019
Period = from:01/01/1950 till:$now
TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal
ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:5 start:01/01/1950
ScaleMinor = unit:year increment:1 start:01/01/1950
Legend = orientation:horizontal position:bottom
Colors =
id:ccp value:coral legend:Communist_Party_of_China
id:kmt value:powderblue legend:Kuomintang
id:dpp value:drabgreen legend:Democratic_Progressive_Party
BarData =
bar:cn text:People's Republic of China
bar:tw text:Republic of China
PlotData=
align:center mark:(line,black)
bar:cn
from: 15/11/2012 till: $now text:" Xi Jinping" color:ccp
from: 15/11/2002 till: 15/11/2012 text:"
South China morning post
" ''Details of Chiang Kai-shek's attempts to recapture mainland to be made public.'' Retrieved on 2009-04-26.
 Following the break of official relations between the United States and the ROC in 1979, the ROC government under Chiang Ching-kuo maintained a " Three Noes" policy in regards to communicating with the Chinese government. However, he was forced to break from this policy during the May 1986 hijacking of a China Airlines cargo plane, in which the Taiwanese pilot subdued other members of the crew and flew the plane to Guangzhou. In response, Chiang sent delegates to Hong Kong to discuss with PRC officials for the return of the plane and crew, which is seen as a turning point between cross-strait relations.
In 1987, the ROC government began to allow visits to China. This benefited many, especially old KMT soldiers, who had been separated from their family in China for decades. This also proved a catalyst for the thawing of relations between the two sides. Problems engendered by increased contact necessitated a mechanism for regular negotiations. In 1988, a guideline was approved by PRC to encourage ROC investments in the PRC. It guaranteed ROC establishments would not be nationalized, and that exports were free from tariffs, ROC businessmen would be granted multiple visas for easy movement.
In order to negotiate with China on operational issues without compromising the government's position on denying the other side's legitimacy, the ROC government under
Following the break of official relations between the United States and the ROC in 1979, the ROC government under Chiang Ching-kuo maintained a " Three Noes" policy in regards to communicating with the Chinese government. However, he was forced to break from this policy during the May 1986 hijacking of a China Airlines cargo plane, in which the Taiwanese pilot subdued other members of the crew and flew the plane to Guangzhou. In response, Chiang sent delegates to Hong Kong to discuss with PRC officials for the return of the plane and crew, which is seen as a turning point between cross-strait relations.
In 1987, the ROC government began to allow visits to China. This benefited many, especially old KMT soldiers, who had been separated from their family in China for decades. This also proved a catalyst for the thawing of relations between the two sides. Problems engendered by increased contact necessitated a mechanism for regular negotiations. In 1988, a guideline was approved by PRC to encourage ROC investments in the PRC. It guaranteed ROC establishments would not be nationalized, and that exports were free from tariffs, ROC businessmen would be granted multiple visas for easy movement.
In order to negotiate with China on operational issues without compromising the government's position on denying the other side's legitimacy, the ROC government under
 Chen Shui-bian of the pro-independence
Chen Shui-bian of the pro-independence
 On 22 March 2008, Ma Ying-jeou of the KMT won the presidential election in Taiwan. It also won a large majority in the Legislature.
A series of meetings between the two sides have followed. On 12 April 2008, Hu Jintao held a meeting with ROC's then vice-president elect Vincent Siew as chairman of the Cross-Straits Common Market Foundation during the
On 22 March 2008, Ma Ying-jeou of the KMT won the presidential election in Taiwan. It also won a large majority in the Legislature.
A series of meetings between the two sides have followed. On 12 April 2008, Hu Jintao held a meeting with ROC's then vice-president elect Vincent Siew as chairman of the Cross-Straits Common Market Foundation during the  On 11 February 2014, Wang met with Zhang in Nanjing, in the first official, high-level, government-to-government contact between the two sides since 1949. The meeting took place at
On 11 February 2014, Wang met with Zhang in Nanjing, in the first official, high-level, government-to-government contact between the two sides since 1949. The meeting took place at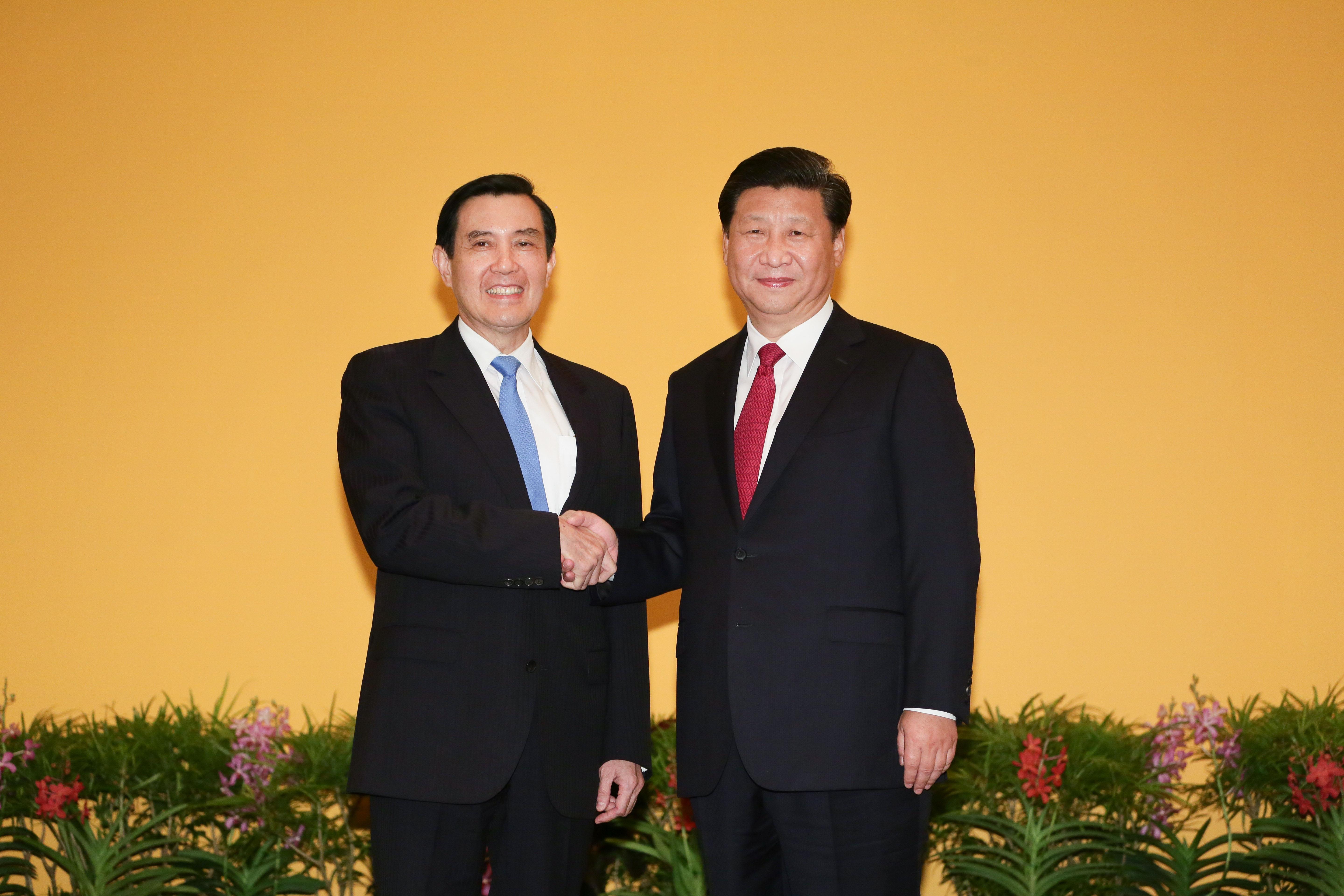  On 7 November 2015, Xi and Ma met and shook hands in Singapore, marking the first ever meeting between leaders of both sides since the end of Chinese Civil War in 1949. They met within their capacity as ''Leader of Mainland China'' and ''Leader of Taiwan'' respectively.
On 30 December 2015, a
On 7 November 2015, Xi and Ma met and shook hands in Singapore, marking the first ever meeting between leaders of both sides since the end of Chinese Civil War in 1949. They met within their capacity as ''Leader of Mainland China'' and ''Leader of Taiwan'' respectively.
On 30 December 2015, a
 On 10 June 2022, China's Defence Minister Wei Fenghe warned the United States that "if anyone dares to split Taiwan from China, the Chinese army will definitely not hesitate to start a war no matter the cost." Wei further said that the People’s Liberation Army "would have no choice but to fight … and crush any attempt of
On 10 June 2022, China's Defence Minister Wei Fenghe warned the United States that "if anyone dares to split Taiwan from China, the Chinese army will definitely not hesitate to start a war no matter the cost." Wei further said that the People’s Liberation Army "would have no choice but to fight … and crush any attempt of
 Semi-governmental contact is maintained through the Straits Exchange Foundation (SEF) and the Association for Relations Across the Taiwan Straits (ARATS). Negotiations between the SEF and the ARATS resumed on 11 June 2008.
Although formally privately constituted bodies, the SEF and the ARATS are both directly led by the Executive Government of each side: the SEF by the Mainland Affairs Council of the
Semi-governmental contact is maintained through the Straits Exchange Foundation (SEF) and the Association for Relations Across the Taiwan Straits (ARATS). Negotiations between the SEF and the ARATS resumed on 11 June 2008.
Although formally privately constituted bodies, the SEF and the ARATS are both directly led by the Executive Government of each side: the SEF by the Mainland Affairs Council of the
 * Initiate direct passenger airline services every weekend from 4 July 2008. Both parties agreed to negotiate the routes of cross-strait direct flights and establish direct communication procedures concerning air traffic management systems as soon as possible. But before the routes of direct flights are finalized, charter flights may temporarily fly across Hong Kong Flight Information Region. There is no need to stop in Hong Kong, but planes still have to fly through its airspace. Weekend charter flights shall fly from each Friday to the following Monday for a total of four full days.
::PRC agreed to open the following five cities as destinations: Beijing, Shanghai ( Pudong), Guangzhou, Xiamen and Nanjing. Mainland China shall open
* Initiate direct passenger airline services every weekend from 4 July 2008. Both parties agreed to negotiate the routes of cross-strait direct flights and establish direct communication procedures concerning air traffic management systems as soon as possible. But before the routes of direct flights are finalized, charter flights may temporarily fly across Hong Kong Flight Information Region. There is no need to stop in Hong Kong, but planes still have to fly through its airspace. Weekend charter flights shall fly from each Friday to the following Monday for a total of four full days.
::PRC agreed to open the following five cities as destinations: Beijing, Shanghai ( Pudong), Guangzhou, Xiamen and Nanjing. Mainland China shall open
 In 2016, a poll by the Taiwan Public Opinion Foundation showed that 51% approved and 40% disapproved of President Tsai Ing-wen's cross-strait policy. In 2017, a similar poll showed that 36% approved and 52% disapproved. In 2018, 31% were satisfied while 59% were dissatisfied.
Taiwanese polls have consistently shown rejection of the notion of "one China" and support for the fate of Taiwan to be decided solely by the Taiwanese. A June 2017 poll found that 70% of Taiwanese reject the idea of "one China". In November 2017, a poll by the Mainland Affairs Council showed that 85% of respondents believed that the Taiwan's future should be decided only by the people of Taiwan, while 74% wanted China to respect the sovereignty of the Republic of China (Taiwan). In January 2019, a poll by the Mainland Affairs Council showed that 75% of Taiwanese rejected Beijing's view that the
In 2016, a poll by the Taiwan Public Opinion Foundation showed that 51% approved and 40% disapproved of President Tsai Ing-wen's cross-strait policy. In 2017, a similar poll showed that 36% approved and 52% disapproved. In 2018, 31% were satisfied while 59% were dissatisfied.
Taiwanese polls have consistently shown rejection of the notion of "one China" and support for the fate of Taiwan to be decided solely by the Taiwanese. A June 2017 poll found that 70% of Taiwanese reject the idea of "one China". In November 2017, a poll by the Mainland Affairs Council showed that 85% of respondents believed that the Taiwan's future should be decided only by the people of Taiwan, while 74% wanted China to respect the sovereignty of the Republic of China (Taiwan). In January 2019, a poll by the Mainland Affairs Council showed that 75% of Taiwanese rejected Beijing's view that the
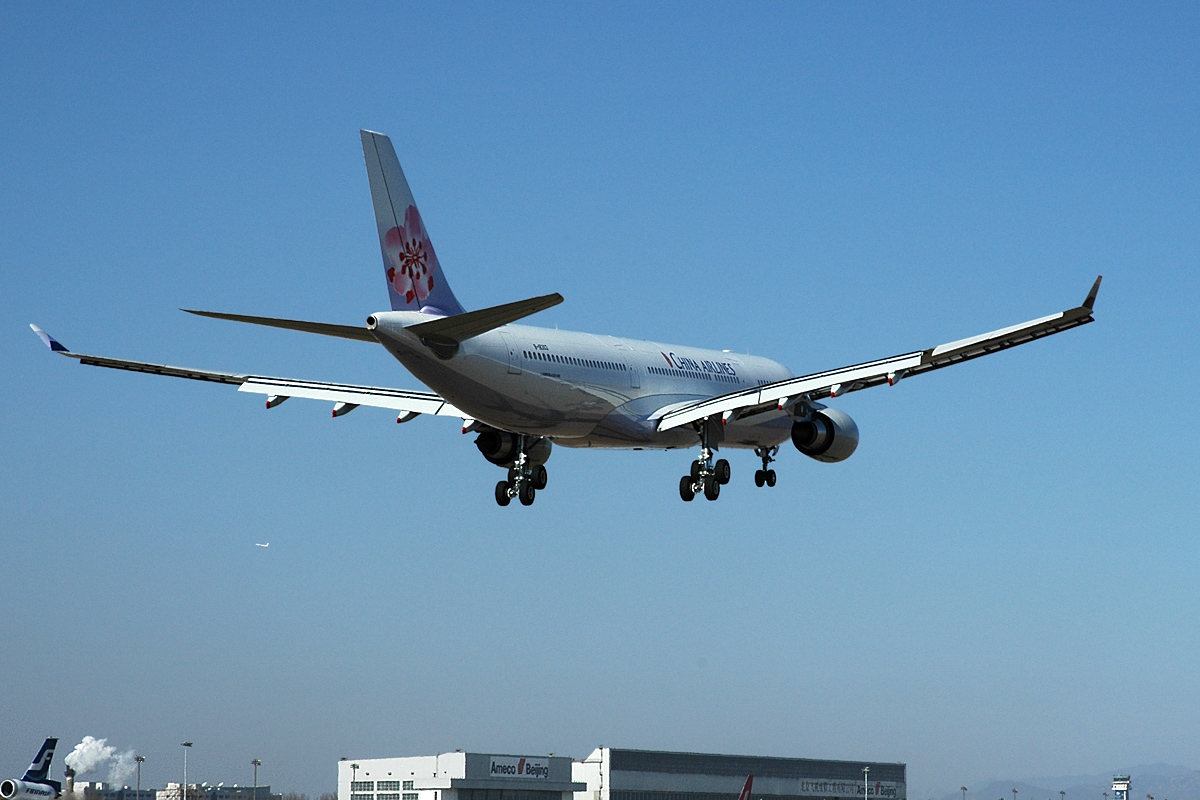 Regular weekend direct, cross-strait charter flights between mainland China and Taiwan resumed on 4 July 2008 for the first time since 1950. Liu Shaoyong, China Southern Airlines chair, piloted the first flight from Guangzhou to Taipei. Simultaneously, a Taiwan-based China Airlines flight flew to Shanghai. As of 2015, 61 mainland Chinese cities are connected with eight airports in Taiwan. The flights operate every day, totaling 890 round-trip flights across the Taiwan Strait per week. Previously, regular passengers (other than festive or emergency charters) had to make a time-consuming stopover at a third destination, usually Hong Kong.
Taiwan residents cannot use the Republic of China passport to travel to mainland China and Mainland China residents cannot use the
Regular weekend direct, cross-strait charter flights between mainland China and Taiwan resumed on 4 July 2008 for the first time since 1950. Liu Shaoyong, China Southern Airlines chair, piloted the first flight from Guangzhou to Taipei. Simultaneously, a Taiwan-based China Airlines flight flew to Shanghai. As of 2015, 61 mainland Chinese cities are connected with eight airports in Taiwan. The flights operate every day, totaling 890 round-trip flights across the Taiwan Strait per week. Previously, regular passengers (other than festive or emergency charters) had to make a time-consuming stopover at a third destination, usually Hong Kong.
Taiwan residents cannot use the Republic of China passport to travel to mainland China and Mainland China residents cannot use the
 Since the resumption of trade between the two sides of the Taiwan Strait in 1979, cross-strait economic exchanges have become increasingly close. Predominantly, this involves Taiwan-based firms moving to, or collaborating in joint ventures, in Mainland China. The collective body of Taiwanese investors in Mainland China is now a significant economic force for both Mainland China and Taiwan. In 2014, trade values between the two sides reached US$198.31 billion, with imports from Taiwan to the mainland counted up to US$152 billion.
In 2015, 58% of Taiwanese working outside Taiwan worked in Mainland China, with a total number of 420,000 people.
Between 2001 and 2011, the percentage of Taiwanese exports to mainland China and Hong Kong grew from 27% to 40%. In 2020, mainland China accounted for 24.3% of Taiwan's total trade and 20.1% of its imports, while Hong Kong accounted for 6.7% of its total trade volume. Mainland Chinese exports to Taiwan account for 2% of total exports, and imports from Taiwan account for 7% of total imports.
Since the governments on both sides of the strait do not recognize the other side's legitimacy, there is a lack of legal protection for cross-strait economic exchanges. The Economic Cooperation Framework Agreement (ECFA) was viewed as providing legal protection for investments. In 2014 the Sunflower Student Movement effectively halted the Cross-Strait Service Trade Agreement (CSSTA).
Since the resumption of trade between the two sides of the Taiwan Strait in 1979, cross-strait economic exchanges have become increasingly close. Predominantly, this involves Taiwan-based firms moving to, or collaborating in joint ventures, in Mainland China. The collective body of Taiwanese investors in Mainland China is now a significant economic force for both Mainland China and Taiwan. In 2014, trade values between the two sides reached US$198.31 billion, with imports from Taiwan to the mainland counted up to US$152 billion.
In 2015, 58% of Taiwanese working outside Taiwan worked in Mainland China, with a total number of 420,000 people.
Between 2001 and 2011, the percentage of Taiwanese exports to mainland China and Hong Kong grew from 27% to 40%. In 2020, mainland China accounted for 24.3% of Taiwan's total trade and 20.1% of its imports, while Hong Kong accounted for 6.7% of its total trade volume. Mainland Chinese exports to Taiwan account for 2% of total exports, and imports from Taiwan account for 7% of total imports.
Since the governments on both sides of the strait do not recognize the other side's legitimacy, there is a lack of legal protection for cross-strait economic exchanges. The Economic Cooperation Framework Agreement (ECFA) was viewed as providing legal protection for investments. In 2014 the Sunflower Student Movement effectively halted the Cross-Strait Service Trade Agreement (CSSTA).
ChinaPower Project
at the Center for Strategic and International Studies polled 64 leading experts on the People’s Republic of China (PRC), Taiwan, and cross-Strait relations, including 28 former high-level U.S. government (USG) officials from both Democrat and Republican administrations, as well as 23 former USG policy and intelligence analysts and 13 top experts from academia and think tanks.Responses were collected from August 10–September 8, 2022. The CSIS summarized the responses of the experts as follows: 1) China is determined to unify with Taiwan, but Beijing does not have a coherent strategy. 2) China is willing to wait to unify with Taiwan, and the August 2022 exercises are not an indicator of accelerated PRC timelines. 3) Xi Jinping feels there are still avenues to peaceful unification. 4) The potential for a military crisis or conflict in the Taiwan Strait is very real. 5) China would immediately invade if Taiwan declared independence. 6) China assumes that the United States would intervene in a Taiwan conflict.
Chinese Nuclear Forces and U.S. Nuclear War Planning
* Sutter, Robert
Taiwan's Future: Narrowing Straits
(NBR Special Report, May 2011)
China, Taiwan, and the Battle for Latin America
21p. * Review o
Convergence or Conflict in the Taiwan Strait
The Illusion of Peace? by J. Michael Cole, in ''Pacific Affairs'' (2017): 90, 573–575.
Taiwan Affairs Office website (PRC government department in charge of relations with Taiwan)
Mainland Affairs Council website (Taiwan government department in charge of Relations with PRC)
– March 2010 radio interview with Professor T.Y. Wang (Illinois State University) {{DEFAULTSORT:Cross-Strait Relations Taiwan
 Cross-Strait relations (sometimes called Mainland–Taiwan relations, or Taiwan-China relations) are the relations between
Cross-Strait relations (sometimes called Mainland–Taiwan relations, or Taiwan-China relations) are the relations between China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
(officially the People's Republic of China) and Taiwan (officially the Republic of China).
The relationship has been complex and controversial due to the dispute on the political status of Taiwan
The controversy surrounding the political status of Taiwan or the Taiwan issue is a result of World War II, the second phase of the Chinese Civil War (1945–1949), and the Cold War.
The basic issue hinges on who the islands of Taiwan, Peng ...
after the administration of Taiwan was transferred from Japan to the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
at the end of World War II in 1945, and the subsequent split between the PRC and ROC as a result of the Chinese Civil War. The essential question is whether the two governments are still in a civil war over One China, each holding within one of two "regions" or parts of the same country (e.g. "1992 Consensus
The 1992 Consensus is a political term referring to the alleged outcome of a meeting in 1992 between the semiofficial representatives of the People's Republic of China (PRC) of mainland China and the Republic of China (ROC) of Taiwan. They are of ...
"), whether they can be reunified as One country, two systems
"One country, two systems" is a constitutional principle of the People's Republic of China (PRC) describing the governance of the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau.
The constitutional principle was formulated in the early ...
, or whether they are now separate countries (either as "Taiwan" and "China" or Two Chinas). The English expression "cross-strait relations" is considered to be a neutral term which avoids reference to the political status of either side.
At the end of World War II in 1945, the administration of Taiwan was transferred to the Republic of China (ROC) from the Empire of Japan, though legal questions remain regarding the language in the Treaty of San Francisco. In 1949, with the Chinese Civil War turning decisively in favour of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), the Republic of China government, led by the Kuomintang (KMT), retreated to Taiwan and established the provisional capital in Taipei, while the CCP proclaimed the People's Republic of China (PRC) government in Beijing. No armistice or peace treaty has ever been signed and debate continues as to whether the civil war has legally ended.
Since then, the relations between the governments in Beijing and Taipei have been characterized by limited contact, tensions, and instability. In the early years, military conflicts continued, while diplomatically both governments competed to be the " legitimate government of China". Since the democratization of Taiwan, the question regarding the political and legal status of Taiwan has shifted focus to the choice between political unification with mainland China or ''de jure'' Taiwanese independence. The PRC remains hostile to any formal declaration of independence and maintains its claim over Taiwan.
At the same time, non-governmental and semi-governmental exchanges between the two sides have increased. In 2008, negotiations began to restore the Three Links (postal, transportation, trade) between the two sides, cut off since 1949. Diplomatic contact between the two sides has generally been limited to Kuomintang administrations on Taiwan. However, during Democratic Progressive Party
The Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) is a Taiwanese nationalist and centre-left political party in the Republic of China (Taiwan). Controlling both the Republic of China presidency and the unicameral Legislative Yuan, it is the majori ...
administrations, negotiations continue to occur on practical matters through informal channels.
History
Timeline
Leaders of the two governmentsHu Jintao
Hu Jintao (born 21 December 1942) is a Chinese politician who served as the 16–17th general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) from 2002 to 2012, the 6th president of the People's Republic of China (PRC) from 2003 to 2013, an ...
" color:ccp
from: 09/11/1989 till: 15/11/2002 text:" Jiang Zemin" color:ccp
from: 22/12/1978 till: 09/11/1989 text:" Deng Xiaoping" color:ccp
from: 09/09/1976 till: 22/12/1978 text:" Hua G." color:ccp
from: 01/01/1950 till: 09/09/1976 text:" Mao Zedong" color:ccp
bar:tw
from: 20/05/2016 till: $now text:" Tsai Ing-wen" color:dpp shift:(30,0)
from: 20/05/2008 till: 20/05/2016 text:" Ma Ying-jeou" color:kmt
from: 20/05/2000 till: 20/05/2008 text:" Chen Shui-bian" color:dpp
from: 13/01/1988 till: 20/05/2000 text:"Lee Teng-hui
Lee Teng-hui (; 15 January 192330 July 2020) was a Taiwanese statesman and economist who served as President of the Republic of China (Taiwan) under the 1947 Constitution and chairman of the Kuomintang (KMT) from 1988 to 2000. He was the fir ...
" color:kmt
from: 20/05/1978 till: 13/01/1988 text:" Chiang Ching-kuo" color:kmt
from: 05/04/1975 till: 20/05/1978 text:" Yen C.-K." color:kmt
from: 01/01/1950 till: 05/04/1975 text:"Chiang Kai-shek
Chiang Kai-shek (31 October 1887 – 5 April 1975), also known as Chiang Chung-cheng and Jiang Jieshi, was a Chinese Nationalist politician, revolutionary, and military leader who served as the leader of the Republic of China (ROC) from 1928 ...
" color:kmt
Before 1949
The early history of cross-strait relations involved the exchange of cultures, people, and technology. However, no Chinese dynasty formally incorporated Taiwan in ancient times. In the 16th and 17th centuries, Taiwan caught the attention of first Portuguese, then Dutch and Spanish explorers. In 1624, the Dutch established their first settlement in Taiwan. In 1662,Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
(Zheng Chenggong), a Ming dynasty loyalist, defeated the Dutch rulers of Taiwan, and took the island, establishing the first formally Han Chinese regime in Taiwan. Koxinga's heirs used Taiwan as a base for launching raids into mainland China against the Manchu
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
Qing dynasty. However, they were defeated in 1683 by Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speaki ...
forces. The following year, Taiwan was incorporated into Fujian province. Over the next two centuries, the Imperial government paid little attention to Taiwan.
The situation changed in the 19th century, with other powers increasingly eyeing Taiwan for its strategic location and resources. In response, the administration began to implement a modernization drive. In 1887, Fujian-Taiwan Province
Taiwan Province (; PFS: ''Thòi-vàn-sén'' or ''Thòi-vân-sén'') is a nominal administrative division of the Republic of China (ROC). Its definition has remained part of the Constitution of the Republic of China, but the province is no long ...
was declared by Imperial decree. Within 10 years, Taiwan had become one of the most modern provinces in the Empire. However, the fall of the Qing outpaced the development of Taiwan, and in 1895, following its defeat in the First Sino-Japanese War, the Imperial government ceded Taiwan to Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
in perpetuity. Qing loyalists briefly resisted the Japanese rule under the banner of the " Republic of Taiwan", but were quickly put down by Japanese authorities.
Japan ruled Taiwan until 1945. During this time, Taiwan, as part of the Japanese Empire, was a foreign jurisdiction in relation to first the Qing dynasty, and, after 1912, the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
. In 1945, Japan was defeated in World War II and surrendered its forces in Taiwan to the Allies, with the ROC, then ruled by the Kuomintang (KMT), taking custody of the island. The period of post-war Kuomintang rule over China (1945–1949) was marked in Taiwan by conflict between local residents and the new KMT authority. The Taiwanese rebelled against on 28 February 1947 in the February 28 incident, which was put down violently by the KMT. The seeds for the Taiwan independence movement were sown in this time.
China was soon engulfed in full-scale civil war. In 1949, the war turned decisively against the KMT and in favor of the CCP. On 1 October 1949, CCP Chairman Mao Zedong proclaimed the founding of the People's Republic of China in Beijing. The capitalist ROC government retreated to Taiwan, eventually declaring Taipei its temporary capital in December 1949.
Military stalemate to diplomatic war (1949–1979)
The two governments continued in a state of war until 1979. In October 1949, the PRC's attempt to take the ROC-controlled island of Kinmen was thwarted in the Battle of Kuningtou, halting the PLA advance towards Taiwan.Qi, Bangyuan. Wang, Dewei. Wang, David Der-wei. 003(2003). The Last of the Whampoa Breed: Stories of the Chinese Diaspora. Columbia University Press. . pg 2 In the Battle of Dengbu Island on 3 November 1949, the ROC forces beat the PRC forces, but were later forced to retreat after the PRC gained air superiority. The Communists' other amphibious operations of 1950 were more successful: they led to the Communist conquest of Hainan Island in April 1950, capture of Wanshan Islands off the Guangdong coast (May–August 1950) and of Zhoushan Island off Zhejiang (May 1950).MacFarquhar, Roderick. Fairbank, John K. Twitchett, Denis C.991
Year 991 (Roman numerals, CMXCI) was a common year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
* March 1: In Rouen, Pope John XV ratifies the first Peace and Truce of God, Truce of God, between ...
(1991). The Cambridge History of China. Cambridge University Press. . pg 820. The same result happened in the Battle of Dongshan Island on 11 May 1950, as well as the Battle of Nanpeng Island in September and October of the same year. However, supported by the US, the ROC won the Battle of Nanri Island in 1952. later in the year, the communists won the Battle of Nanpeng Archipelago, as well as the Battle of Dalushan Islands
The Battle of Dalushan (Greater Deer Mountain) Islands (大鹿山等岛战斗) was a battle fought between the nationalists and the communists for several islands and islets just off the coast of Zhejiang, China during aftermath of the Chinese Ci ...
and the Dongshan Island Campaign, both in 1953.
In June 1949, the ROC declared a "closure" of all Chinese ports and its navy attempted to intercept all foreign ships. The closure covered from a point north of the mouth of Min river in Fujian province to the mouth of the Liao River
The Liao River () is the principal river in southern Northeast China, and one of the seven main river systems in China. Its name derived from the Liao region, a historical name for southern Manchuria, from which the Liaoning province, Liaodong P ...
in Manchuria.Tsang, Steve Yui-Sang Tsang. The Cold War's Odd Couple: The Unintended Partnership Between the Republic of China and the UK, 1950–1958. 006
Alec Trevelyan (006) is a fictional character and the main antagonist in the 1995 James Bond film ''GoldenEye'', the first film to feature actor Pierce Brosnan as Bond. Trevelyan is portrayed by actor Sean Bean. The likeness of Bean as Alec T ...
(2006). I.B. Tauris. . p 155, p 115-120, p 139-145 Since China's railroad network was underdeveloped, north–south trade depended heavily on sea lanes. ROC naval activity also caused severe hardship for Chinese fishermen.
After losing China, a group of approximately 12,000 KMT soldiers escaped to Burma and continued launching guerrilla attacks into southern China. Their leader, General Li Mi, was paid a salary by the ROC government and given the nominal title of Governor of Yunnan. Initially, the United States supported these remnants and the Central Intelligence Agency provided them with aid. After the Burmese government appealed to the United Nations in 1953, the U.S. began pressuring the ROC to withdraw its loyalists. By the end of 1954, nearly 6,000 soldiers had left Burma and Li Mi declared his army disbanded. However, thousands remained, and the ROC continued to supply and command them, even secretly supplying reinforcements at times.
The Kuomintang Islamic Insurgency in China (1950–1958) was fought by Muslim Kuomintang army officers who refused to surrender to the communists throughout the 1950s and 1960s.
During the Korean War, some captured Communist Chinese soldiers, many of whom were originally KMT soldiers, were repatriated to Taiwan rather than China. A KMT guerrilla force continued to operate cross-border raids into south-western China in the early 1950s. The ROC government launched a number of air bombing raids into key coastal cities of China such as Shanghai.
Though viewed as a military liability by the United States, the ROC viewed its remaining islands in Fujian as vital for any future campaign to defeat the PRC and retake China. On 3 September 1954, the First Taiwan Strait crisis began when the PLA started shelling Quemoy and threatened to take the Dachen Islands. On 20 January 1955, the PLA took nearby Yijiangshan Island
The Yijiangshan Islands () are two small islands eight miles from the Dachen Islands, located off the coast of Taizhou, Zhejiang in the East China Sea.
During the First Taiwan Strait crisis the islands were captured in January 1955 by the People ...
, with the entire ROC garrison of 720 troops killed or wounded defending the island. On January 24 of the same year, the United States Congress passed the Formosa Resolution
The Formosa Resolution of 1955 was a joint resolution passed by the U.S. Senate and signed by U.S. President Dwight D. Eisenhower on January 29, 1955, to counteract the threat of an invasion of Taiwan (Republic of China) by the People’s Republic ...
authorizing the President to defend the ROC's offshore islands. The First Taiwan Straits crisis ended in March 1955 when the PLA ceased its bombardment. The crisis was brought to a close during the Bandung conference
The first large-scale Asian–African or Afro–Asian Conference ( id, Konferensi Asia–Afrika)—also known as the Bandung Conference—was a meeting of Asian and African states, most of which were newly independent, which took place on 18–2 ...
. At the conference, China articulated its Five Principles of Peaceful Coexistence and Premier Zhou Enlai publicly stated, " e Chinese people do not want to have a war with the United States. The Chinese government is willing to sit down to discuss the question of relaxing tension in the Far East, and especially the question of relaxing tension in the Taiwan area." Two years of negotiations with the United States followed, although no agreement was reached on the Taiwan issue.
The Second Taiwan Strait Crisis began on 23 August 1958 with air and naval engagements between the PRC and the ROC military forces, leading to intense artillery bombardment of Quemoy (by the PRC) and Amoy (by the ROC), and ended on November of the same year. PLA patrol boats blockaded the islands from ROC supply ships. Though the United States rejected Chiang Kai-shek's proposal to bomb Chinese artillery batteries, it quickly moved to supply fighter jets and anti-aircraft missiles to the ROC. It also provided amphibious assault ships to land supply, as a sunken ROC naval vessel was blocking the harbor. On September 7, the United States escorted a convoy of ROC supply ships and the PRC refrained from firing. On October 25, the PRC announced an "even-day ceasefire" — the PLA would only shell Quemoy on odd-numbered days.
Despite the end of the hostilities, the two sides have never signed any agreement or treaty to officially end the war.
After the 1950s, the "war" became more symbolic than real, represented by on again, off again artillery bombardment towards and from Kinmen. In later years, live shells were replaced with propaganda sheets. The bombardment finally ceased after the establishment of diplomatic relations between the People's Republic of China and the United States.
During this period, movement of people and goods virtually ceased between PRC- and ROC-controlled territories. There were occasional defectors. One high-profile defector was Justin Yifu Lin, who swam across the Kinmen strait to China and was Chief Economist and Senior Vice President of the World Bank from 2008 to 2012.
Most observers expected Chiang's government to eventually fall in response to a Communist invasion of Taiwan, and the United States initially showed no interest in supporting Chiang's government in its final stand. Things changed radically with the onset of the Korean War in June 1950. At this point, allowing a total Communist victory over Chiang became politically impossible in the United States, and President Harry S. Truman ordered the United States Seventh Fleet into the Taiwan straits to prevent the ROC and PRC from attacking each other.Bush, Richard C. 005
''005'' is a 1981 arcade game by Sega. They advertised it as the first of their RasterScan Convert-a-Game series, designed so that it could be changed into another game in minutes "at a substantial savings". It is one of the first examples of a ...
(2005). Untying the Knot: Making Peace in the Taiwan Strait. Brookings Institution Press. .
After the ROC complained to the United Nations against the Soviet Union supporting the PRC, the UN General Assembly Resolution 505
The United Nations General Assembly Resolution 505 is titled ''Threats to the political independence and territorial integrity of China and to the peace of the Far East, resulting from Soviet violations of the Sino-Soviet Treaty of Friendship an ...
was adopted on 1 February 1952 to condemn the Soviet Union.
Between 1961 and 1972, Chiang Kai-shek initiated Project National Glory, a plan to retake mainland China. On 6 August 1965, the naval warship ''Zhangjiang'' was sunk by a People's Liberation Army Navy
The People's Liberation Army Navy (PLAN; ), also known as the People's Navy, Chinese Navy, or PLA Navy, is the maritime service branch of the People's Liberation Army.
The PLAN traces its lineage to naval units fighting during the Chinese ...
torpedo boat on an assignment to transport special forces to Dongshan Island
() is a county of far southern Fujian Province, People's Republic of China, located along the Taiwan Strait. It comprises 44 islands for a total area of and is under the administration of Zhangzhou City. The total population was 200,000. Dongs ...
for an intelligence gathering operation, killing 200 soldiers. In November 1965, the CNS ''Lin Huai'' was sunk near the island of Magong on a mission to pick up wounded soldiers from Taiwan's offshore islands of Penghu
The Penghu (, Hokkien POJ: ''Phîⁿ-ô͘'' or ''Phêⁿ-ô͘'' ) or Pescadores Islands are an archipelago of 90 islands and islets in the Taiwan Strait, located approximately west from the main island of Taiwan, covering an area ...
and Wuqiu.SCMP.South China morning post
" ''Details of Chiang Kai-shek's attempts to recapture mainland to be made public.'' Retrieved on 2009-04-26.
Chiang Kai-shek
Chiang Kai-shek (31 October 1887 – 5 April 1975), also known as Chiang Chung-cheng and Jiang Jieshi, was a Chinese Nationalist politician, revolutionary, and military leader who served as the leader of the Republic of China (ROC) from 1928 ...
subsequently abandoned the operation.Wang Guangci. Project National Glory. Makung Naval Battle Defeat. Waking up from the dream of retaking the mainland. United Daily News. 20 April 2009. http://udn.com/NEWS/NATIONAL/NAT1/4857575.shtml
Diplomatically during this period, until around 1971, the ROC government continued to be recognized as the legitimate government of China and Taiwan by most NATO governments. The PRC government was recognized by Soviet Bloc countries, members of the non-aligned movement, and some Western nations such as the United Kingdom and the Netherlands. Both governments claimed to be the legitimate government of China, and labeled the other as illegitimate. Civil war propaganda permeated the education curriculum. Each side portrayed the people of the other as living in hell-like misery. In official media, each side called the other "bandits". The ROC also suppressed expressions of support for Taiwanese identity or Taiwan independence.
Both ROC and PRC engaged in proxy warfare in other countries to gain influence and allies. They would either have proxy forces or provide military aid or support during the conflict, to support their interests. Some notable conflicts include: Internal conflict in Myanmar, Korean War, Laotian Civil War
The Laotian Civil War (1959–1975) was a civil war in Laos which was waged between the Communist Pathet Lao and the Royal Lao Government from 23 May 1959 to 2 December 1975. It is associated with the Cambodian Civil War and the Vietnam War ...
, Hong Kong 1956 riots, Communist insurgency in Thailand, 12-3 incident
The 12-3 incident ( zh, c=一二·三事件; pt, Motim 1-2-3) refers to political demonstrations and rioting against Portuguese rule in Macau that occurred on 3 December 1966. The incident, inspired by the Cultural Revolution in the People's R ...
, Hong Kong 1967 leftist riots and the NDF Rebellion.
Thawing of relations (1979–1998)
 Following the break of official relations between the United States and the ROC in 1979, the ROC government under Chiang Ching-kuo maintained a " Three Noes" policy in regards to communicating with the Chinese government. However, he was forced to break from this policy during the May 1986 hijacking of a China Airlines cargo plane, in which the Taiwanese pilot subdued other members of the crew and flew the plane to Guangzhou. In response, Chiang sent delegates to Hong Kong to discuss with PRC officials for the return of the plane and crew, which is seen as a turning point between cross-strait relations.
In 1987, the ROC government began to allow visits to China. This benefited many, especially old KMT soldiers, who had been separated from their family in China for decades. This also proved a catalyst for the thawing of relations between the two sides. Problems engendered by increased contact necessitated a mechanism for regular negotiations. In 1988, a guideline was approved by PRC to encourage ROC investments in the PRC. It guaranteed ROC establishments would not be nationalized, and that exports were free from tariffs, ROC businessmen would be granted multiple visas for easy movement.
In order to negotiate with China on operational issues without compromising the government's position on denying the other side's legitimacy, the ROC government under
Following the break of official relations between the United States and the ROC in 1979, the ROC government under Chiang Ching-kuo maintained a " Three Noes" policy in regards to communicating with the Chinese government. However, he was forced to break from this policy during the May 1986 hijacking of a China Airlines cargo plane, in which the Taiwanese pilot subdued other members of the crew and flew the plane to Guangzhou. In response, Chiang sent delegates to Hong Kong to discuss with PRC officials for the return of the plane and crew, which is seen as a turning point between cross-strait relations.
In 1987, the ROC government began to allow visits to China. This benefited many, especially old KMT soldiers, who had been separated from their family in China for decades. This also proved a catalyst for the thawing of relations between the two sides. Problems engendered by increased contact necessitated a mechanism for regular negotiations. In 1988, a guideline was approved by PRC to encourage ROC investments in the PRC. It guaranteed ROC establishments would not be nationalized, and that exports were free from tariffs, ROC businessmen would be granted multiple visas for easy movement.
In order to negotiate with China on operational issues without compromising the government's position on denying the other side's legitimacy, the ROC government under Lee Teng-hui
Lee Teng-hui (; 15 January 192330 July 2020) was a Taiwanese statesman and economist who served as President of the Republic of China (Taiwan) under the 1947 Constitution and chairman of the Kuomintang (KMT) from 1988 to 2000. He was the fir ...
created the " Straits Exchange Foundation" (SEF), a nominally non-governmental institution directly led by the Mainland Affairs Council, an instrument of the Executive Yuan
The Executive Yuan () is the executive branch of the government of the Republic of China (Taiwan). Its leader is the Premier, who is appointed by the President of the Republic of China, and requires confirmation by the Legislative Yuan.
...
in 1991. The PRC responded to this initiative by setting up the Association for Relations Across the Taiwan Straits (ARATS), directly led by the Taiwan Affairs Office of the State Council State Council may refer to:
Government
* State Council of the Republic of Korea, the national cabinet of South Korea, headed by the President
* State Council of the People's Republic of China, the national cabinet and chief administrative autho ...
. This system, described as "white gloves", allowed the two governments to engage with each other on a semi-official basis without compromising their respective sovereignty policies. Led by Koo Chen-fu and Wang Daohan, the two organizations began a series of talks that culminated in the 1992 meetings, which, together with subsequent correspondence, may have established the 1992 Consensus
The 1992 Consensus is a political term referring to the alleged outcome of a meeting in 1992 between the semiofficial representatives of the People's Republic of China (PRC) of mainland China and the Republic of China (ROC) of Taiwan. They are of ...
, under which both sides agreed to deliberate ambiguity on questions of sovereignty, in order to engage on operational questions affecting both sides.
Also during this time, however, the rhetoric of ROC President Lee Tung-hui began to turn further towards Taiwan independence. Prior to the 1990s, the ROC had been a one-party authoritarian state committed to eventual unification with China. However, with democratic reforms the attitudes of the general public began to influence policy in Taiwan. As a result, the ROC government shifted away from its commitment to the one China principle and towards a separate political identity for Taiwan. The People's Liberation Army
The People's Liberation Army (PLA) is the principal military force of the People's Republic of China and the armed wing of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). The PLA consists of five service branches: the Ground Force, Navy, Air Force, ...
attempted to influence the 1996 ROC election in Taiwan by conducting a missile exercise designed to warn the pro-independence Pan-Green Coalition, leading to the Third Taiwan Strait Crisis. By 1998, semi-official talks had broken down.
Hostile non-contact (1998–2008)
 Chen Shui-bian of the pro-independence
Chen Shui-bian of the pro-independence Democratic Progressive Party
The Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) is a Taiwanese nationalist and centre-left political party in the Republic of China (Taiwan). Controlling both the Republic of China presidency and the unicameral Legislative Yuan, it is the majori ...
was elected President of the ROC
The president of the Republic of China, now often referred to as the president of Taiwan, is the head of state of the Republic of China (ROC), as well as the commander-in-chief of the Republic of China Armed Forces. The position once had au ...
in 2000. In his inaugural speech, Chen Shui-bian pledged to the Four Noes and One Without, in particular, promising to seek neither independence nor unification as well as rejecting the concept of special state-to-state relations expressed by his predecessor, Lee Teng-hui
Lee Teng-hui (; 15 January 192330 July 2020) was a Taiwanese statesman and economist who served as President of the Republic of China (Taiwan) under the 1947 Constitution and chairman of the Kuomintang (KMT) from 1988 to 2000. He was the fir ...
, as well as establishing the Three Mini-Links. Furthermore, he pursued a policy of normalizing economic relations with the PRC. He expressed some willingness to accept the 1992 Consensus, a precondition set by the PRC for dialogue, but backed down after backlash within his own party. The PRC did not engage Chen's administration, but meanwhile in 2001 Chen lifted the 50-year ban on direct trade and investment with the PRC, which made the later ECFA possible. In November 2001, Chen repudiated "one China" and called for talks without preconditions.
Hu Jintao
Hu Jintao (born 21 December 1942) is a Chinese politician who served as the 16–17th general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) from 2002 to 2012, the 6th president of the People's Republic of China (PRC) from 2003 to 2013, an ...
became General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party in late 2002, succeeding Jiang Zemin as ''de facto'' top leader of China. Hu continued to insist that talks can only proceed under an agreement of the "one China" principle. At the same time, Hu and the PRC continued a military missile buildup across the strait from Taiwan while making threats of military action against Taiwan should it declare independence or if the PRC considers that all possibilities for a peaceful unification are completely exhausted. The PRC also continued applying diplomatic pressure to other nations to isolate the ROC diplomatically. However, during the 2003 Iraq war, the PRC allowed Taiwanese airlines use of China's airspace.
After the re-election of Chen Shui-bian in 2004, Hu's government changed the previous blanket no-contact policy, a holdover from the Jiang Zemin administration. Under the new policy, on the one hand, the PRC government continued a no-contact policy towards Chen Shui-bian. It maintained its military build-up against Taiwan, and pursued a vigorous policy of isolating Taiwan diplomatically. In March 2005, the Anti-Secession Law was passed by the National People's Congress, formalizing "non-peaceful means" as an option of response to a formal declaration of independence in Taiwan.
On the other hand, the PRC administration pursued contact with apolitical, or politically non-independence leaning, groups in Taiwan. In his May 17 Statement The May 17 Statement, also called the May 17 Declaration, was a statement jointly issued by the Office for Taiwan Affairs under the Central Committee of the Chinese Communist Party and the Taiwan Affairs Office of the State Council of the People's ...
in 2004, Hu Jintao made friendly overtures to Taiwan on resuming negotiations for the " three links", reducing misunderstandings, and increasing consultation. However, the Anti-Secession Law was passed in 2005, which was not well received in Taiwan. The CCP increased contacts on a party-to-party basis with the KMT, then the opposition party in Taiwan, due to their support for the one China principle. The increased contacts culminated in the 2005 Pan-Blue visits to China
5 (five) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number. It has attained significance throughout history in part because typical humans have five digits on eac ...
, including a meeting between Hu and then-KMT chairman Lien Chan in April 2005.
Resumption of high level contact (2008–2016)
 On 22 March 2008, Ma Ying-jeou of the KMT won the presidential election in Taiwan. It also won a large majority in the Legislature.
A series of meetings between the two sides have followed. On 12 April 2008, Hu Jintao held a meeting with ROC's then vice-president elect Vincent Siew as chairman of the Cross-Straits Common Market Foundation during the
On 22 March 2008, Ma Ying-jeou of the KMT won the presidential election in Taiwan. It also won a large majority in the Legislature.
A series of meetings between the two sides have followed. On 12 April 2008, Hu Jintao held a meeting with ROC's then vice-president elect Vincent Siew as chairman of the Cross-Straits Common Market Foundation during the Boao Forum for Asia
The Boao Forum for Asia (BFA; ), initiated by 25 Asian countries and Australia (increased to 28 in 2006), is a non-profit organisation that hosts high-level forums for leaders from government, business and academia in Asia and other continents to ...
. On 28 May 2008, Hu met with former KMT chairman Wu Po-hsiung
Wu Po-hsiung (; born 19 June 1939) is a Taiwanese politician who is a former chairman of the Kuomintang (KMT). He has been the Interior Minister (1984-1988), Mayor of Taipei (1988–1990), Secretary-General to the President (1991–1996), and ...
, the first meeting between the heads of the CCP and the KMT as ruling parties. During this meeting, Hu and Wu agreed that both sides should recommence semi-official dialogue under the 1992 consensus
The 1992 Consensus is a political term referring to the alleged outcome of a meeting in 1992 between the semiofficial representatives of the People's Republic of China (PRC) of mainland China and the Republic of China (ROC) of Taiwan. They are of ...
. Wu committed the KMT against Taiwanese independence, but also stressed that a "Taiwan identity" did not equate to "Taiwanese independence". Hu committed his government to addressing the concerns of the Taiwanese people in regard to security, dignity, and "international living space", with a priority given to discussing Taiwan's wish to participate in the World Health Organization.
Both Hu and his new counterpart Ma Ying-jeou agree that the 1992 Consensus is the basis for negotiations between the two sides of the Taiwan strait. On 26 March 2008, Hu Jintao held a telephone talk with the US President George W. Bush, in which he explained that the "1992 Consensus" sees "both sides recognize there is only one China, but agree to differ on its definition". The first priority for the SEF–ARATS meeting will be opening of the three links, especially direct flights between China and Taiwan.
These events suggest a policy by the two sides to rely on the deliberate ambiguity of the 1992 Consensus to avoid difficulties arising from asserting sovereignty. As Wu Po-hsiung put it during a press conference in his 2008 China visit, "we do not refer to the 'Republic of China' so long as the other side does not refer to the 'People's Republic of China'". Since the March elections in Taiwan, the PRC government has not mentioned the " one China policy" in any official announcements. The only exception has been one brief aberration in a press release by the Ministry of Commerce, which described Vincent Siew as agreeing to the "1992 consensus
The 1992 Consensus is a political term referring to the alleged outcome of a meeting in 1992 between the semiofficial representatives of the People's Republic of China (PRC) of mainland China and the Republic of China (ROC) of Taiwan. They are of ...
and the " one China policy". Upon an immediate protest from Siew, the PRC side retracted the press release and issued apologetic statements emphasizing that only press releases published by the Xinhua News Agency represented the official PRC position. The official press release on this event did not mention the One China Policy.
Former ROC President Ma Ying-jeou has advocated that cross-strait relations should shift from "mutual non-recognition" to "mutual non-denial".
Dialogue through semi-official organisations (the SEF and the ARATS) reopened on 12 June 2008 on the basis of the 1992 Consensus, with the first meeting held in Beijing. Neither the PRC nor the ROC recognizes the other side as a legitimate entity, so the dialogue was in the name of contacts between the SEF and the ARATS instead of the two governments, though most participants were actually officials in PRC or ROC governments. Chen Yunlin
Chen Yunlin (; born December 1941) was the chairman of the Association for Relations Across the Taiwan Straits (ARATS), the body responsible for negotiations with Taiwan in the People's Republic of China in 2008–2013.
Early life
Chen was born ...
, President of the ARATS, and Chiang Pin-kung, President of the SEF, signed files on June 13, agreeing that direct flights between the two sides would begin on July 4 and that Taiwan would allow entrance of up to 3000 visitors from China every day.
The financial relationship between the two areas improved on 1 May 2009 in a move described as "a major milestone" by '' The Times''. The ROC's financial regulator, the Financial Supervisory Commission, announced that Chinese investors would be permitted to invest in Taiwan's money markets for the first time since 1949. Investors can now apply to purchase Taiwan shares that do not exceed one tenth of the value of the firm's total shares. The move came as part of a “step by step” movement which is supposed to relax restrictions on Chinese investment. Taipei economist Liang Chi-yuan, commented: “Taiwan's risk factor as a flash point has dropped significantly with its improved ties with Chinese. The Chinese would be hesitant about launching a war as their investment increases here.” China's biggest telecoms carrier, China Mobile, was the first company to avail of the new movement by spending $529 million on buying 12 percent of Far EasTone, the third largest telecoms operator in Taiwan.
President Ma has called repeatedly for the PRC to dismantle the missile batteries targeted on Taiwan's cities, without result.
On 30 January 2010, the Obama administration announced it intended to sell $6.4 billion worth of antimissile systems, helicopters and other military hardware to Taiwan, an expected move which was met with reaction from Beijing: in retaliation, China cut off all military-to-military ties with Washington and warned that US-China cooperation on international issues could suffer as a result of the sales.
A report from Taiwan's Ministry of National Defense said that China's current charm offensive
Charm offensive may refer to:
* ''Charm. Offensive.'', a 2017 album by Die!_Die!_Die!
* '' Charm Offensive'', a 2018 album by Damien Done
* ''Armando Iannucci's Charm Offensive
''Armando Iannucci's Charm Offensive'' is a British radio comedy p ...
is only accommodating on issues that do not undermine China's claim to Taiwan and that the PRC would invade if Taiwan declared independence, developed weapons of mass destruction, or suffered from civil chaos.
On the 100th anniversary of the Republic of China ( Xinhai Revolution), President Ma called on the PRC to embrace Sun Yat-sen's call for freedom and democracy.
In June 2013, China offered 31 new measures to better integrate Taiwan economically.
In October 2013, in a hotel lobby on the sidelines of the APEC Indonesia 2013 meetings in the Indonesian island of Bali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and Nu ...
, Wang Yu-chi
Wang Yu-chi () is a Taiwanese politician. He was the Minister of the Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) of the Executive Yuan since 28 September 2012 until 16 February 2015, when he resigned over the dropping of espionage charges brought against Chan ...
, Minister of the Mainland Affairs Council, spoke briefly with Zhang Zhijun, Minister of the Taiwan Affairs Office, each addressing the other by his official title. Both called for the establishment of a regular dialogue mechanism between their two agencies to facilitate cross-strait engagement. Zhang also invited Wang to visit China.
 On 11 February 2014, Wang met with Zhang in Nanjing, in the first official, high-level, government-to-government contact between the two sides since 1949. The meeting took place at
On 11 February 2014, Wang met with Zhang in Nanjing, in the first official, high-level, government-to-government contact between the two sides since 1949. The meeting took place at Purple Palace Nanjing
Purple is any of a variety of colors with hue between red and blue. In the RGB color model used in computer and television screens, purples are produced by mixing red and blue light. In the RYB color model historically used by painters, pur ...
. Nanjing was the capital of the Republic of China during the period in which it actually ruled China. During the meeting, Wang and Zhang agreed on establishing a direct and regular communication channel between the two sides for future engagement under the 1992 Consensus. They also agreed on finding a solution for health insurance coverage for Taiwanese students studying in Mainland China, on pragmatically establishing SEF and ARATS offices in their respective territories and on studying the feasibility of allowing visits to detained persons once these offices have been established. Before shaking hands, Wang addressed Zhang as "TAO Director Zhang Zhijun" and Zhang addressed Wang as "Minister Wang Yu-chi" without mentioning the name ''Mainland Affairs Council''. However, China's Xinhua News Agency referred to Wang as the "Responsible Official of Taiwan's Mainland Affairs Council" () in its Chinese-language news and as "Taiwan's Mainland Affairs Chief" in its English-language news. On 25–28 June 2014, Zhang paid a retrospective visit to Taiwan, making him the highest CCP official to ever visit Taiwan.
In September 2014, Xi Jinping, General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party to adopt a more uncompromising stance than his predecessors as he called for the "one country, two systems
"One country, two systems" is a constitutional principle of the People's Republic of China (PRC) describing the governance of the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau.
The constitutional principle was formulated in the early ...
" model to be applied to Taiwan. In Taiwan it was noted that Beijing was no longer referring to the 1992 Consensus.
 On 7 November 2015, Xi and Ma met and shook hands in Singapore, marking the first ever meeting between leaders of both sides since the end of Chinese Civil War in 1949. They met within their capacity as ''Leader of Mainland China'' and ''Leader of Taiwan'' respectively.
On 30 December 2015, a
On 7 November 2015, Xi and Ma met and shook hands in Singapore, marking the first ever meeting between leaders of both sides since the end of Chinese Civil War in 1949. They met within their capacity as ''Leader of Mainland China'' and ''Leader of Taiwan'' respectively.
On 30 December 2015, a hotline
A hotline is a point-to-point communications link in which a call is automatically directed to the preselected destination without any additional action by the user when the end instrument goes off-hook. An example would be a phone that automat ...
connecting the head of the Mainland Affairs Council and the head of the Taiwan Affairs Office was established. First conversation via the hotline between the two heads was made on 5 February 2016.
In March 2016, former ROC Justice Minister Luo Ying-shay
Luo Ying-shay (; 8 November 1951 – 3 April 2021) was a Taiwanese politician who served as the Minister of Justice from 30 September 2013 until 20 May 2016.
Education
Luo graduated with a bachelor's degree from the Department of Law of the N ...
embarked on a 5-day historic visit to Mainland China, making her the first Minister of the Government of the Republic of China to visit Mainland China after the end of Chinese Civil War in 1949.
During this period, the PRC also began openly citing territorial disputes in the South China Sea, constructing a Great Wall of Sand
"Great Wall of Sand" is a name first used in March 2015 by US Admiral Harry Harris, who was commander of the Pacific Fleet, to describe a series of uniquely large-scale land reclamation projects by the People's Republic of China (PRC) in th ...
in the Spratly islands region. This is part of the ' Nine-dash line' policy wherein the PRC has made large expansionist claims on ocean territory in the South China Sea.
Deteriorating relations (2016–present)
In the2016 Taiwan general election
General elections were held in Taiwan, officially the Republic of China, on Saturday, 16 January 2016 to elect the 14th President and Vice President of the Republic of China, and all 113 members of the ninth Legislative Yuan:
Presidential election ...
s, Tsai Ing-wen and the DPP captured landslide victories. Beijing has expressed its dissatisfaction with Tsai's refusal to accept the "1992 Consensus".
On 1 June 2016, it was confirmed that former President Ma Ying-jeou would visit Hong Kong on 15 June to attend and deliver speech on Cross-Strait relations and East Asia at the 2016 Award for Editorial Excellence dinner at Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Centre. The Tsai Ing-wen administration blocked Ma from traveling to Hong Kong, and he gave prepared remarks via teleconference instead.
In September 2016, eight magistrates and mayors from Taiwan visited Beijing, which were Hsu Yao-chang (Magistrate of Miaoli County
Miaoli County (Mandarin Pinyin: ''miáo lì xiàn''; Hakka PFS: ''Mèu-li̍t-yen''; Hokkien POJ: ''Biâu-le̍k-koān'' or ''Miâu-le̍k-koān'') is a county in western Taiwan. Miaoli is adjacent with Hsinchu County and Hsinchu City to the nort ...
), Chiu Ching-chun (Magistrate of Hsinchu County
Hsinchu County (Wade–Giles: ''Hsin¹-chu²'') is a county in north-western Taiwan. The population of the county is mainly Hakka; with a Taiwanese aboriginal minority in the southeastern part of the county. Zhubei is the county capital, where ...
), Liu Cheng-ying (Magistrate of Lienchiang County), Yeh Hui-ching (Deputy Mayor of New Taipei City), Chen Chin-hu (Deputy Magistrate of Taitung County
Taitung County (; Mandarin pinyin: ''Táidōng Xiàn''; Hokkien POJ: ''Tâi-tang-koān''; Hakka PFS: ''Thòi-tûng-yen''; Paiwan: ''Valangaw'';lit:Eastern part of Taiwan) is the third largest county in Taiwan, located primarily on the island' ...
), Lin Ming-chen (Magistrate of Nantou County
Nantou County (; Hokkien POJ: ''Lâm-tâu-koān''; Hakka PFS: ''Nàm-thèu-yen'') is the second largest county of Taiwan by area, located in the central part of the country. It is also the only non-coastal county in Taiwan. Its name derives fro ...
), Fu Kun-chi
Fu Kun-chi (; born 8 May 1962) is a Taiwanese politician. He was a member of the Legislative Yuan from 2002 to 2009, when he assumed the Hualien County magistracy. In September 2018, Fu was removed from the latter office, as the Supreme Court is ...
(Magistrate of Hualien County) and Wu Cheng-tien (Deputy Magistrate of Kinmen County
Kinmen, alternatively known as Quemoy, is a group of islands governed as a county by the Republic of China (Taiwan), off the southeastern coast of mainland China. It lies roughly east of the city of Xiamen in Fujian, from which it is separate ...
). Their visit was aimed to reset and restart cross-strait relations after President Tsai Ing-wen took office on 20 May 2016. The eight local leaders reiterated their support of One-China policy under the 1992 consensus
The 1992 Consensus is a political term referring to the alleged outcome of a meeting in 1992 between the semiofficial representatives of the People's Republic of China (PRC) of mainland China and the Republic of China (ROC) of Taiwan. They are of ...
. They met with Taiwan Affairs Office Head Zhang Zhijun and Chairperson of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference
The Chairman of the National Committee of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference () is the leader of the National Committee of the Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference (CPPCC), which is a political advisory body i ...
Yu Zhengsheng.
In November 2016, First Lady Peng Liyuan's brother Peng Lei () visited Chiayi City from Mainland China to attend the funeral of their uncle Lee Hsin-kai (), a veteran KMT member. The funeral was kept low key and was attended by KMT Chairperson Hung Hsiu-chu, KMT Vice Chairperson Huang Min-hui and other government and party officials.
In October 2017, Tsai Ing-wen expressed hopes that both sides would restart their cross-strait relations after the 19th National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party
The 19th National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party (commonly referred to as ''Shíjiǔ Dà''; ) was held at the Great Hall of the People, Beijing, between 18 and 24 October 2017. 2,280 delegates represented the party's estimated 89 mill ...
, and argued that new practices and guidelines governing mutual interaction should be examined. Regarding the old practices, Tsai stated that "If we keep sticking to these past practices and ways of thinking, it will probably be very hard for us to deal with the volatile regional situations in Asia". Relations with the Mainland had stalled since Tsai took office in 2016.
In his opening speech at the 19th National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party
The 19th National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party (commonly referred to as ''Shíjiǔ Dà''; ) was held at the Great Hall of the People, Beijing, between 18 and 24 October 2017. 2,280 delegates represented the party's estimated 89 mill ...
, CCP General Secretary Xi Jinping emphasized the PRC's sovereignty over Taiwan, stating that "We have sufficient abilities to thwart any form of Taiwan independence attempts." At the same time, he offered the chance for open talks and "unobstructed exchanges" with Taiwan as long as the government moved to accept the 1992 consensus. His speech received a tepid response from Taiwanese observers, who argued that it did not signal any significant changes in Beijing's Taiwan policy, and showed "no significant goodwill, nor major malice."
Beginning in the mid-to-late 2010s, Beijing has significantly restricted the number of Chinese tour groups allowed to visit Taiwan in order to place pressure upon President Tsai Ing-wen. Apart from Taiwan, the Holy See and Palau have also been pressured to recognize the PRC over the ROC.
In April 2018, political parties and organizations demanding a referendum on Taiwan's independence formed an alliance to further their initiative. The Formosa Alliance was established, prompted by a sense of crisis in the face of growing pressure from China for unification. The alliance wanted to hold a referendum on Taiwan independence in April 2019, change the polity's official name from the Republic of China to Taiwan, and apply for membership in the United Nations. In May 2018, the PRC engaged in military exercises around Taiwan in an attempt to pressure the Taiwan Area against Taiwan independence.
In 2018, The Diplomat reported that the PRC conducts hybrid warfare against the ROC. ROC political leaders, including President Tsai and Premier William Lai, as well as international media outlets, have repeatedly accused the PRC of spreading fake news via social media to create divisions in Taiwanese society, influence voters and support candidates more sympathetic to Beijing ahead of the 2018 Taiwanese local elections
Local elections were held on 24 November 2018 in Taiwan, to elect county magistrates (city mayors), county (city) councilors, township mayors, township councilors and chiefs of village (borough) in 6 municipalities and 16 counties (cities). Elec ...
. Researchers have argued that the PRC government is allowing misinformation about the COVID-19 pandemic to flow into Taiwan.
In January 2020, Tsai Ing-wen argued that Taiwan already was an independent country called the "Republic of China (Taiwan)", further arguing that the mainland Chinese authorities had to recognize that situation. Reuters reports that somewhere in 2020, the Taiwanese public turned further against mainland China, due to fallout from the Hong Kong protests and also due to the PRC's continued determination to keep the ROC out of the World Health Organization despite the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
The opposition KMT also appeared to distance itself from the Chinese mainland in 2020, stating it would review its unpopular advocacy of closer ties with the PRC.
On 9 January 2021, the US State Department announced that it was Lifting Self-Imposed Restrictions on the U.S.-Taiwan Relationship, to protests from the PRC.
In March 2021, KMT chairman Johnny Chiang rejected "one country, two systems
"One country, two systems" is a constitutional principle of the People's Republic of China (PRC) describing the governance of the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau.
The constitutional principle was formulated in the early ...
" as a feasible model for Taiwan, citing Beijing's response to protests in Hong Kong as well as the value that Taiwanese place in political freedoms.
In 2021, multiple PRC military planes entered the ROC's ADIZ.
The Hong Kong Economic, Trade and Cultural Office in Taiwan suspended its operation indefinitely on 18 May 2021, followed by the Macau Economic and Cultural Office starting 19 June 2021.
In July 2021, the ROC's presidential office extended its condolences and sympathy to those affected by historic flooding in Zhengzhou
Zhengzhou (; ), also spelt Zheng Zhou and alternatively romanized as Chengchow, is the capital and largest city of Henan Province in the central part of the People's Republic of China. Located in north-central Henan, it is one of the National ...
in mainland China. In addition, Taiwanese companies and individuals made donations of money and supplies to help those affected. The PRC indirectly thanked President Tsai for expressing concern, as well as offering thanks to companies and individuals who made contributions to relief efforts.
In October 2021, the PRC denounced a speech by Tsai during commemorations for the National Day of the Republic of China. The PRC said that Tsai's speech "incited confrontation and distorted facts", and added that seeking Taiwanese independence was closing doors to dialogue. Tsai responded by saying that the ROC would not be forced to "bow" down to mainland Chinese pressure, and said that the ROC would keep bolstering its defenses.
In October 2021, Victor Gao
Gao Zhikai (; born 1962) is a Chinese lawyer, academic and media spokesman for the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). He is the Vice President of the Beijing based Center for China and Globalization (CCG), and Chair Professor of Soochow University. ...
, who served as an interpreter for former PRC paramount leader
Paramount leader () is an informal term for the most important political figure in the People's Republic of China (PRC). The paramount leader typically controls the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) and the People's Liberation Army (PLA), often hol ...
Deng Xiaoping, called for ethnic cleansing of any Taiwanese with Japanese heritage if the PRC were to take over the Taiwan Area in an interview. Later in October a tweet from the Global Times called for a "final solution to the Taiwan question" which was condemned by German politician Frank Müller-Rosentritt for its similarity to the Nazis' " Final Solution to the Jewish question" which culminated in the Holocaust.
In a biennial report released in November 2021, Taiwan's Ministry of Defense warned that the PRC had obtained the capacity to surround and blockade the island's harbours, airports, and outbound flight routes.
On 7 May 2022, Taiwanese Foreign Minister Joseph Wu stated that if Beijing invaded the island, the world would censure China as it does Russia for its conflict in Ukraine.
 On 10 June 2022, China's Defence Minister Wei Fenghe warned the United States that "if anyone dares to split Taiwan from China, the Chinese army will definitely not hesitate to start a war no matter the cost." Wei further said that the People’s Liberation Army "would have no choice but to fight … and crush any attempt of
On 10 June 2022, China's Defence Minister Wei Fenghe warned the United States that "if anyone dares to split Taiwan from China, the Chinese army will definitely not hesitate to start a war no matter the cost." Wei further said that the People’s Liberation Army "would have no choice but to fight … and crush any attempt of Taiwan independence
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
, safeguarding national sovereignty and territorial integrity."
Following a ban on the importation of pineapples from Taiwan and wax apples in 2021, the Chinese government banned the import of grouper fish in June 2022, claiming they had found banned chemicals and excessive levels of other substances.
In 10 August 2022, the PRC's Taiwan Affairs Office and the State Council Information Office jointly published the first white paper about Taiwan's status since 2000 called "The Taiwan Question and China’s Reunification in the New Era The Taiwan Question and China's Reunification in the New Era () is a white paper published by the Taiwan Affairs Office and State Council Information Office of the People's Republic of China (PRC). It is the first white paper concerning Taiwan ...
". In it, the PRC urged again for Taiwan to unify under the "one country, two systems" formula. Notably, the white paper didn't contain a previous line that said that no troops would be sent to Taiwan after unification. In response, Taiwan's Mainland Affairs Council said the white paper was "wishful thinking and disregarding facts”.
2022 military exercises
On 2 August 2022, in response to the visit by US House Speaker Nancy Pelosi to Taiwan, the PLA announced it would conduct live-fire exercises in six zones surrounding Taiwan. The live-fire drills were unprecedented in recent history and took place in six zones that surrounded the island's busiest international waterways and aviation routes. China announced an end to the exercises on 10 August, but also stated that regular "patrols" would be launched in the Taiwan Strait. The exercises drew criticism from the G7, the EU's foreign policy representative and the European Parliament. The military exercises took place between August 3rd and 8th. and involved the usage of live-fire ammunition, air assets, naval deployments, and ballistic missile launches by the People's Liberation Army. China deployed several military naval and aerial assets, including destroyers, frigates, corvettes, submarines, and amphibious assault ships. In addition, the PRC deployed a carrier group with a naval fleet made up of an aircraft carrier ship and its large number of escorts as well as at least one nuclear submarine to the Taiwan Strait. Furthermore, China fired at least 11 cross ballistic missiles in Taiwan's exclusive economic zone (EEZ). Towards the end of these demonstrations the PLA deployed 27 warships from the naval division and 105 combat planes from the air force in just two days as stated by the Taiwanese Ministry of National Defense. In response, Taiwan deployed ships and aircraft. No military conflict came of this, although it greatly increased tensions between the two countries. China’s response to Nancy Pelosi’s visit may have been so strong relative to other demonstrations due to her status as the U.S. Speaker of the House. Pelosi has become the highest ranking U.S. government official to visit Taiwan in 25 years. China perceived her visit as a violation of its sovereign rights on Taiwan. As Xi Jinping stated, “We are keeping our eyes open. We continue to look at the world with eyes wide open to not miss a single provocation from US reactionaries.” Moreover, China intended to show its military force to deter a possible US involvement in mainland China’s “internal Chinese affairs” and to demonstrate Chinese military power in order to prove to the international and domestic audience that the status of Taiwan is China’s red line. As a result of the crisis, mainland China imposed an air and sea blockade of Taiwan and announced further PLA patrols around the island. This also led to the further deterioration of China-US relations, indicating that the two superpowers grew their suspicion for each other, are less willing to compromise as they have canceled 8 official military dialogues and cooperation channels between them.Semi-official relations
Interpretation of the relations by sitting leaders
PresidentsChiang Kai-shek
Chiang Kai-shek (31 October 1887 – 5 April 1975), also known as Chiang Chung-cheng and Jiang Jieshi, was a Chinese Nationalist politician, revolutionary, and military leader who served as the leader of the Republic of China (ROC) from 1928 ...
and Chiang Ching-kuo have steadily maintained that there is only one China, the sole representative of which was the ROC, and that the PRC government was illegitimate, while PRC leaders have maintained the converse that the PRC was the sole representative of China. In 1979, Deng Xiaoping proposed a model for the incorporation of Taiwan into the People's Republic of China which involved a high degree of autonomy within the Chinese state, similar to the model proposed to Hong Kong which would eventually become one country, two systems
"One country, two systems" is a constitutional principle of the People's Republic of China (PRC) describing the governance of the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau.
The constitutional principle was formulated in the early ...
. On 26 June 1983, Deng proposed a meeting between the Kuomintang and the Chinese Communist Party as equal political parties and on 22 February, he officially proposed the one country, two systems
"One country, two systems" is a constitutional principle of the People's Republic of China (PRC) describing the governance of the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau.
The constitutional principle was formulated in the early ...
model. In September 1990, under the presidency of Lee Teng-hui
Lee Teng-hui (; 15 January 192330 July 2020) was a Taiwanese statesman and economist who served as President of the Republic of China (Taiwan) under the 1947 Constitution and chairman of the Kuomintang (KMT) from 1988 to 2000. He was the fir ...
, the National Unification Council was established in Taiwan and in January 1991, the Mainland Affairs Council was established; in March 1991, the "Guidelines for National Unification" were adopted and on 30 April 1991, the period of mobilization for the suppression of Communist rebellion was terminated. Thereafter, the two sides conducted several rounds of negotiations through the informal Straits Exchange Foundation and Association for Relations Across the Taiwan Straits.
On 22 May 1995, the United States granted Lee Teng-hui
Lee Teng-hui (; 15 January 192330 July 2020) was a Taiwanese statesman and economist who served as President of the Republic of China (Taiwan) under the 1947 Constitution and chairman of the Kuomintang (KMT) from 1988 to 2000. He was the fir ...
a visit to his alma mater, Cornell University, which resulted in the suspension of cross-strait exchanges by China, as well as the subsequent Third Taiwan Strait Crisis. Lee was labelled as a "traitor" attempting to "split China" by the PRC. In an interview on 9 July 1999, President Lee Teng-hui
Lee Teng-hui (; 15 January 192330 July 2020) was a Taiwanese statesman and economist who served as President of the Republic of China (Taiwan) under the 1947 Constitution and chairman of the Kuomintang (KMT) from 1988 to 2000. He was the fir ...
defined the relations between Taiwan and mainland China as "between two countries (國家), at least special relations between two countries," and that there was no need for the Republic of China to declare independence since it had been independent since 1912 (the founding date of the Republic of China), thereby identifying the Taiwanese state with the Republic of China. Later, the MAC published an English translation of Lee's remarks referring instead to "two states of one nation," later changed on 22 July to "special state-to-state relations." In response, China denounced the theory and demanded retractions. Lee began to backpedal from his earlier marks, emphasizing the 1992 consensus
The 1992 Consensus is a political term referring to the alleged outcome of a meeting in 1992 between the semiofficial representatives of the People's Republic of China (PRC) of mainland China and the Republic of China (ROC) of Taiwan. They are of ...
, whereby representatives from the two sides agreed that there was only one China, of which Taiwan was a part. However, the ROC maintained that the two sides agreed to disagree about which government represented China, whereas the PRC maintains that the two sides agreed that the PRC was the sole representative of China.
On August 3, 2002, president Chen Shui-bian defined the relationship as One Country on Each Side
One Country on Each Side is a concept originating in the Democratic Progressive Party government led by Chen Shui-bian, the former president of the Republic of China (2000–2008), regarding the political status of Taiwan. It emphasizes that th ...
. The PRC subsequently cut off official contact with the ROC government.
The ROC position under President Ma Ying-jeou backpedalled to a weaker version of Lee Teng-hui's position. On 2 September 2008, former ROC President Ma Ying-jeou was interviewed by the Mexico-based newspaper El Sol de México and he was asked about his views on the subject of ' two Chinas' and if there is a solution for the sovereignty issues between the two. Ma replied that the relations are neither between two Chinas nor two states. It is a special relationship
The Special Relationship is a term that is often used to describe the politics, political, social, diplomacy, diplomatic, culture, cultural, economics, economic, law, legal, Biophysical environment, environmental, religion, religious, military ...
. Further, he stated that the sovereignty issues between the two cannot be resolved at present, but he quoted the '1992 Consensus' as a temporary measure until a solution becomes available. Former spokesman for the ROC Presidential Office Wang Yu-chi
Wang Yu-chi () is a Taiwanese politician. He was the Minister of the Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) of the Executive Yuan since 28 September 2012 until 16 February 2015, when he resigned over the dropping of espionage charges brought against Chan ...
later elaborated the President's statement and said that the relations are between two regions of one country, based on the ROC Constitutional position, the Statute Governing the Relations Between the Peoples of the Taiwan Area and Mainland Area and the '1992 Consensus'. On 7 October 2008 Ma Ying-jeou was interviewed by a Japan-based magazine "World". He said that laws relating to international relations cannot be applied regarding the relations between Taiwan and the mainland, as they are parts of a state.
President Tsai Ing-wen, in her first inauguration speech in 2016, acknowledged that the talks surrounding the 1992 Consensus took place without agreeing that a consensus was reached. She credited the talks with spurring 20 years of dialogue and exchange between the two sides. She hoped that exchanges would continue on the basis of these historical facts, as well as the existence of the Republic of China constitutional system and democratic will of the Taiwanese people. In response, Beijing called Tsai's answer an "incomplete test paper" because Tsai did not agree to the content of the 1992 Consensus. On June 25, 2016, Beijing suspended official cross-strait communications, with any remaining cross-strait exchanges thereafter taking place through unofficial channels.
In January 2019, Xi Jinping, General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party wrote an open letter to Taiwan proposing a one country, two systems
"One country, two systems" is a constitutional principle of the People's Republic of China (PRC) describing the governance of the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau.
The constitutional principle was formulated in the early ...
formula for eventual unification. Tsai responded to Xi in a January 2019 speech by stating that Taiwan rejects "one country, two systems
"One country, two systems" is a constitutional principle of the People's Republic of China (PRC) describing the governance of the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau.
The constitutional principle was formulated in the early ...
" and that because Beijing equates the 1992 Consensus with "one country, two systems", Taiwan rejects the 1992 Consensus as well. Tsai rejected one country, two systems
"One country, two systems" is a constitutional principle of the People's Republic of China (PRC) describing the governance of the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau.
The constitutional principle was formulated in the early ...
explicitly again in her second inauguration speech, and reaffirmed her previous stance that cross-strait exchanges be held on the basis of parity between the two sides. She affirmed the DPP position that Taiwan, also known as the Republic of China, was already an independent country, and that Beijing must accept this reality. She further remarked that cross-strait relations had reached a "historical turning point."
In 2021, the Chinese Government stated that they would not allow pro-Taiwan independence people into China and also Hong Kong and Macau.
On 5 March 2022, Chinese Premier Li Keqiang
Li Keqiang (born 1 July 1955) is a Chinese politician who is the outgoing premier of China. An economist by profession, Li is head of China's executive branch as well as one of the leading figures behind China's Financial and Economic Affai ...
committed to promote peaceful growth and "reunification" in relations with Taiwan, and stated his government resolutely rejects any separatist actions or foreign intervention, bringing a sharp rebuke from Taipei.
Inter-government
Executive Yuan
The Executive Yuan () is the executive branch of the government of the Republic of China (Taiwan). Its leader is the Premier, who is appointed by the President of the Republic of China, and requires confirmation by the Legislative Yuan.
...
of the ROC, and the ARATS by the Taiwan Affairs Office of the State Council State Council may refer to:
Government
* State Council of the Republic of Korea, the national cabinet of South Korea, headed by the President
* State Council of the People's Republic of China, the national cabinet and chief administrative autho ...
of the PRC. The heads of the two bodies, Lin Join-sane and Chen Deming, are both full-time appointees and do not hold other government positions. However, both are senior members of their respective political parties ( Kuomintang and Chinese Communist Party respectively), and both have previously served as senior members of their respective governments. Their deputies, who in practice are responsible for the substantive negotiations, are concurrently senior members of their respective governments. For the June 2008 negotiations, the main negotiators, who are deputy heads of the SEF and the ARATS respectively, are concurrently deputy heads of the Mainland Affairs Council and the Taiwan Affairs Office respectively.
To date, the 'most official' representative offices between the two sides are the PRC's Cross-Strait Tourism Exchange Association (CSTEA) in Taiwan, established on 7 May 2010, and ROC's Taiwan Strait Tourism Association (TSTA) in China, established on 4 May 2010. However, the duties of these offices are limited only to tourism-related affairs so far.
2008 meetings
First 2008 meeting
A series of meetings were held between the SEF and the ARATS at Diaoyutai State Guesthouse in Beijing from 11 June 2008 to 14 June 2008. By convention, SEF–ARATS negotiations proceed in three rounds: a technical round led by negotiators seconded from the relevant government departments, a draft round led by deputy heads of the two organisations, and a formal round led by the heads of the two organisations. In this case, however, both sides have already reached broad consensus on these issues on both the technical and political levels through previous negotiations via the non-governmental and inter-party channels. As a result, the initial technical round was dispensed with, and the negotiations began with the second, draft round. The two sides agreed to the following: * Initiate direct passenger airline services every weekend from 4 July 2008. Both parties agreed to negotiate the routes of cross-strait direct flights and establish direct communication procedures concerning air traffic management systems as soon as possible. But before the routes of direct flights are finalized, charter flights may temporarily fly across Hong Kong Flight Information Region. There is no need to stop in Hong Kong, but planes still have to fly through its airspace. Weekend charter flights shall fly from each Friday to the following Monday for a total of four full days.
::PRC agreed to open the following five cities as destinations: Beijing, Shanghai ( Pudong), Guangzhou, Xiamen and Nanjing. Mainland China shall open
* Initiate direct passenger airline services every weekend from 4 July 2008. Both parties agreed to negotiate the routes of cross-strait direct flights and establish direct communication procedures concerning air traffic management systems as soon as possible. But before the routes of direct flights are finalized, charter flights may temporarily fly across Hong Kong Flight Information Region. There is no need to stop in Hong Kong, but planes still have to fly through its airspace. Weekend charter flights shall fly from each Friday to the following Monday for a total of four full days.
::PRC agreed to open the following five cities as destinations: Beijing, Shanghai ( Pudong), Guangzhou, Xiamen and Nanjing. Mainland China shall open Chengdu
Chengdu (, ; Simplified Chinese characters, simplified Chinese: 成都; pinyin: ''Chéngdū''; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively Romanization of Chi ...
, Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), Postal Romanization, alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a Direct-administered municipalities of China, municipality in Southwes ...
, Hangzhou, Dalian
Dalian () is a major sub-provincial port city in Liaoning province, People's Republic of China, and is Liaoning's second largest city (after the provincial capital Shenyang) and the third-most populous city of Northeast China. Located on the ...
, Guilin, Shenzhen and other destinations later on and other cities if so demanded by the market.
::ROC agreed to open the following eight cities as destinations: Taoyuan, Kaohsiung
Kaohsiung City (Mandarin Chinese: ; Wade–Giles: ''Kao¹-hsiung²;'' Pinyin: ''Gāoxióng'') is a special municipality located in southern Taiwan. It ranges from the coastal urban center to the rural Yushan Range with an area of . Kaohsi ...
(Siaogang
Siaogang District, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency () is a district of Kaohsiung City in southern Taiwan. Before the merging of Kaohsiung City and Kaohsiung County in 2010, Siaogang was the southernmost district in Kaohsiu ...
), Taichung (Chingchunkang), Taipei ( Sungshan), Penghu
The Penghu (, Hokkien POJ: ''Phîⁿ-ô͘'' or ''Phêⁿ-ô͘'' ) or Pescadores Islands are an archipelago of 90 islands and islets in the Taiwan Strait, located approximately west from the main island of Taiwan, covering an area ...
(Makung), Hualien, Kinmen and Taitung.
* Opening Taiwan to Chinese tourists. Both parties agreed that Mainland Chinese tourists must travel to Taiwan in groups. Tourists must enter into, visit, and exit from Taiwan in groups. The maximum quota of tourists received by the party responsible for tourist reception shall not exceed the average of 3,000 persons per day, and each group shall consist of a minimum of ten persons and forty persons at the maximum, being in Taiwan for a maximum of ten days.
* However, in 2012, it was agreed by both parties that individual tourists from the PRC cities of Beijing, Shanghai, and Xiamen were allowed to visit Taiwan. Later, tourists from Chengdu, Chongqing, Nanjing, Hangzhou, Guangzhou, and Tianjin were allowed to visit Taiwan individually. Finally, Fuzhou, Jinan, and Xi'an were to join the list by the end of 2012. In 2019, the Chinese government stopped issuing permits for individual tourists to visit Taiwan, amid worsening cross-strait relations.
To facilitate the above, both sides also agreed to further discuss on the possibilities of exchanging representative offices, with an SEF office to be opened in Beijing and an ARATS office in Taipei to issue travel permits to cross-strait visitors, among other duties.
Second 2008 meeting
Following an invitation issued by the SEF at the first meeting, the head of ARATS,Chen Yunlin
Chen Yunlin (; born December 1941) was the chairman of the Association for Relations Across the Taiwan Straits (ARATS), the body responsible for negotiations with Taiwan in the People's Republic of China in 2008–2013.
Early life
Chen was born ...
, began a visit to Taiwan on 3 November 2008. Items on the agenda raised by SEF Chairman Chiang Pin-kung included direct maritime shipping, chartered cargo flights, direct postal service, and co-operation in ensuring food safety, in response to the 2008 Chinese milk scandal
The 2008 Chinese milk scandal was a significant Food safety incidents in China, food safety incident in China. The scandal involved Sanlu Group, Sanlu Group's milk and infant formula along with other food materials and components being adultera ...
, while ARATS chairman Chen Yunlin
Chen Yunlin (; born December 1941) was the chairman of the Association for Relations Across the Taiwan Straits (ARATS), the body responsible for negotiations with Taiwan in the People's Republic of China in 2008–2013.
Early life
Chen was born ...
raised the matters of direct freight service, and opening up air routes that directly cross the Taiwan Strait. Previous routes avoided crossing the Strait for security reasons, with planes detouring through Hong Kong or Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
air control areas.
On 4 November 2008, ARATS and SEF signed a number of agreements in Taipei. The agreement relating to direct passenger flights increased the number of charter flights from 36 to 108 per week, operating daily instead of the four days a week previously. Flights would now operate to and from 21 Chinese cities. Flights would also take a more direct route. Private business jet flights would also be allowed. The agreement relating to cargo shipping allowed direct shipping between 11 seaports in Taiwan and 63 in China. The shipping would be tax-free. The agreement relating to cargo flights provided for up to 60 direct cargo flights per month. Finally, an agreement was made to set up food safety
Food safety (or food hygiene) is used as a scientific method/discipline describing handling, preparation, and storage of food in ways that prevent food-borne illness. The occurrence of two or more cases of a similar illness resulting from t ...
alerts between the two sides.
During Chen's visit to Taipei, he was met with a series of strong protests directed at himself and Ma Ying-jeou, some of which were violent with Molotov cocktails
A Molotov cocktail (among several other names – ''see other names'') is a hand thrown incendiary weapon constructed from a frangible container filled with flammable substances equipped with a fuse (typically a glass bottle filled with flammab ...
being thrown by the protesters at riot police. A series of arrests were made after the protests. Local police reported that 149 of its officers were injured during the opposition protests. Consistent with the 1992 Consensus
The 1992 Consensus is a political term referring to the alleged outcome of a meeting in 1992 between the semiofficial representatives of the People's Republic of China (PRC) of mainland China and the Republic of China (ROC) of Taiwan. They are of ...
, Chen did not call Ma as "President". Similarly, the representatives from Taiwan did not call the PRC leader Hu Jintao
Hu Jintao (born 21 December 1942) is a Chinese politician who served as the 16–17th general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) from 2002 to 2012, the 6th president of the People's Republic of China (PRC) from 2003 to 2013, an ...
as "President of China", but called him "CCP General Secretary
The general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party () is the Party leader, head of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP), the One-party state, sole ruling party of the China, People's Republic of China (PRC). Since 1989, the CCP general secr ...
" in the previous meeting in Beijing.
''China Post'' reported that some polls have indicated that the public may be pleased with Chen's visit, with about 50% of the Taiwanese public considering Chen's visit to have a positive effect on Taiwan's development, while 18 to 26% of the respondents thought the effect would be negative. In another poll, it suggested that 26% of the respondents were satisfied with the DPP Chairwoman Tsai Ing-wen's handling of the crowds in the series of protests, while 53% of the respondents were unsatisfied. The same poll also showed that 33% of the respondents were satisfied with President Ma's performance at his meeting with Chen Yunlin, while 32% of the respondents were not satisfied.
Inter-party
The Kuomintang (former ruling party of Taiwan) and the Chinese Communist Party, maintain regular dialogue via the KMT–CCP Forum. This has been called a "second rail" in Taiwan, and helps to maintain political understanding and aims for political consensus between the two parties.Inter-city
TheShanghai-Taipei City Forum
The Shanghai-Taipei City Forum () or Taipei-Shanghai City Forum () is an annual forum between the government and civilians of Shanghai and Taipei
Taipei (), officially Taipei City, is the capital and a special municipality of the Republic ...
is an annual forum between the city of Shanghai and Taipei. Launched in 2010 by then-Taipei Mayor
The Mayor of Taipei is the head of the Taipei City Government and is elected to a four-year term. Until the election of Tsai Ing-wen, the office was seen as a stepping stone to the presidency: presidents Lee Teng-hui, Chen Shui-bian and Ma Ying-jeo ...
Hau Lung-pin to promote city-to-city exchanges, it led to Shanghai's participation in the Taipei International Flora Exposition
The 2010 Taipei International Flora Exposition (2010 Flora Expo) opened on 6 November 2010 and ran until 25 April 2011 in Taipei, Taiwan. It was a garden festival recognized by the International Association of Horticultural Producers (AIPH / IAHP ...
end of that year. Both Taipei and Shanghai are the first two cities across the Taiwan Strait that carries out exchanges. In 2015, the newly elected Taipei Mayor Ko Wen-je attended the forum. He was addressed as ''Mayor Ko of Taipei'' by Shanghai Mayor Yang Xiong.
Non-governmental
The third mode of contact is through private bodies accredited by the respective governments to negotiate technical and operational aspects of issues between the two sides. Called the " Macau mode", this avenue of contact was maintained even through the years of the Chen Shui-bian administration. For example, on the issue of opening Taiwan to Chinese tourists, the accredited bodies were tourism industry representative bodies from both sides.Public opinion
According to an opinion poll released by the Mainland Affairs Council taken after the second 2008 meeting, 71.79% of the Taiwanese public supported continuing negotiations and solving issues between the two sides through the semi-official organizations, SEF and ARATS, 18.74% of the Taiwanese public did not support this, while 9.47% of the Taiwanese public did not have an opinion. In 2015, a poll conducted by the Taiwan Braintrust showed that about 90 percent of the population would identify themselves as Taiwanese rather than Chinese if they were to choose between the two. Also, 31.2 percent of respondents said they support independence for Taiwan, while 56.2 percent would prefer to maintain the status quo and 7.9 percent support unification with China.1992 Consensus
The 1992 Consensus is a political term referring to the alleged outcome of a meeting in 1992 between the semiofficial representatives of the People's Republic of China (PRC) of mainland China and the Republic of China (ROC) of Taiwan. They are of ...
meant the "one China principle" under the framework of "one country, two systems
"One country, two systems" is a constitutional principle of the People's Republic of China (PRC) describing the governance of the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau.
The constitutional principle was formulated in the early ...
". Further, 89% felt that the future of Taiwan should be decided by only the people of Taiwan.
In 2020, an annual poll conducted by Academia Sinica
Academia Sinica (AS, la, 1=Academia Sinica, 3=Chinese Academy; ), headquartered in Nangang, Taipei, is the national academy of Taiwan. Founded in Nanking, the academy supports research activities in a wide variety of disciplines, ranging from ...
showed that 73% of Taiwanese felt that China was "not a friend" of Taiwan, an increase of 15% from the previous year. An annual poll run by National Chengchi University found that a record 67% of respondents identified as Taiwanese only, versus 27.5% who identified as both Chinese and Taiwanese and 2.4% who identified as Chinese only. The same poll showed that 52.3% of respondents favored postponing a decision or maintaining the status quo indefinitely, 35.1% of respondents favored eventual or immediate independence, and 5.8% favored eventual or immediate unification.
On November 12, 2020, the Mainland Affairs Council (MAC) poll was released and showed Taiwanese thinking on a set of topics. 90% of Taiwanese oppose China's military aggression against Taiwan. 80% believe maintaining cross-strait peace is the responsibility of both sides and not just Taiwan. 76% reject the "one country, two systems" approach proposed by Beijing. 86% believe only Taiwanese have right to choose the path of self determination for Taiwan.
Sunflower Movement
In 2014, the Sunflower Student Movement broke out. Citizens occupied the Taiwanese legislature for 23 days, protesting against the government's forcing through Cross-Strait Service Trade Agreement. The protesters felt that the trade pact with China would leave Taiwan vulnerable to political pressure from Beijing.2016 meme campaign
In January 2016, the leader of the pro-independenceDemocratic Progressive Party
The Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) is a Taiwanese nationalist and centre-left political party in the Republic of China (Taiwan). Controlling both the Republic of China presidency and the unicameral Legislative Yuan, it is the majori ...
, Tsai Ing-wen, was elected to the presidency of the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
. On 20 January thousands of mainland Chinese internet users, primarily from the forum "Li Yi Tieba" (), bypassed the Great Firewall of China to flood with messages and stickers the Facebook pages of the president-elect, Taiwanese news agencies Apple Daily and SET News, and other individuals to protest the idea of Taiwanese independence.
Informal relations
The Three Links
People's Republic of China passport
The People's Republic of China Passport (), commonly referred to as the Chinese passport, is a passport issued to citizens of the People's Republic of China (PRC) for the purpose of international travel, and entitles its bearer to the protecti ...
to travel to Taiwan, as neither the ROC nor the PRC considers this international travel. The PRC government requires Taiwan residents to hold a Mainland Travel Permit for Taiwan Residents when entering mainland China, whereas the ROC government requires mainland Chinese residents to hold the Exit and Entry Permit for the Taiwan Area of the Republic of China to enter the Taiwan Area.
Economy
 Since the resumption of trade between the two sides of the Taiwan Strait in 1979, cross-strait economic exchanges have become increasingly close. Predominantly, this involves Taiwan-based firms moving to, or collaborating in joint ventures, in Mainland China. The collective body of Taiwanese investors in Mainland China is now a significant economic force for both Mainland China and Taiwan. In 2014, trade values between the two sides reached US$198.31 billion, with imports from Taiwan to the mainland counted up to US$152 billion.
In 2015, 58% of Taiwanese working outside Taiwan worked in Mainland China, with a total number of 420,000 people.
Between 2001 and 2011, the percentage of Taiwanese exports to mainland China and Hong Kong grew from 27% to 40%. In 2020, mainland China accounted for 24.3% of Taiwan's total trade and 20.1% of its imports, while Hong Kong accounted for 6.7% of its total trade volume. Mainland Chinese exports to Taiwan account for 2% of total exports, and imports from Taiwan account for 7% of total imports.
Since the governments on both sides of the strait do not recognize the other side's legitimacy, there is a lack of legal protection for cross-strait economic exchanges. The Economic Cooperation Framework Agreement (ECFA) was viewed as providing legal protection for investments. In 2014 the Sunflower Student Movement effectively halted the Cross-Strait Service Trade Agreement (CSSTA).
Since the resumption of trade between the two sides of the Taiwan Strait in 1979, cross-strait economic exchanges have become increasingly close. Predominantly, this involves Taiwan-based firms moving to, or collaborating in joint ventures, in Mainland China. The collective body of Taiwanese investors in Mainland China is now a significant economic force for both Mainland China and Taiwan. In 2014, trade values between the two sides reached US$198.31 billion, with imports from Taiwan to the mainland counted up to US$152 billion.
In 2015, 58% of Taiwanese working outside Taiwan worked in Mainland China, with a total number of 420,000 people.
Between 2001 and 2011, the percentage of Taiwanese exports to mainland China and Hong Kong grew from 27% to 40%. In 2020, mainland China accounted for 24.3% of Taiwan's total trade and 20.1% of its imports, while Hong Kong accounted for 6.7% of its total trade volume. Mainland Chinese exports to Taiwan account for 2% of total exports, and imports from Taiwan account for 7% of total imports.
Since the governments on both sides of the strait do not recognize the other side's legitimacy, there is a lack of legal protection for cross-strait economic exchanges. The Economic Cooperation Framework Agreement (ECFA) was viewed as providing legal protection for investments. In 2014 the Sunflower Student Movement effectively halted the Cross-Strait Service Trade Agreement (CSSTA).
Cultural, educational, religious and sporting exchanges
TheNational Palace Museum
The National Palace Museum (; Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: Kwet-li̍p kù-kiung pok-vu̍t-yèn), is a museum in Taipei, Republic of China (Taiwan). It has a permanent collection of nearly 700,000 pieces of Chinese artifacts and artworks, many of which wer ...
in Taipei and the Palace Museum
The Palace Museum () is a huge national museum complex housed in the Forbidden City at the core of Beijing, China. With , the museum inherited the imperial royal palaces from the Ming and Qing dynasties of China and opened to the public in 192 ...
in Beijing have collaborated on exhibitions. Scholars and academics frequently visit institutions on the other side. Books published on each side are regularly re-published in the other side, though restrictions on direct imports and the different writing systems between the two sides somewhat impede the exchange of books and ideas.
Students of Taiwan origin receive special concessions in the National Higher Education Entrance Examination in mainland China. There are regular programs for school students from each side to visit the other. In 2019, there were 30,000 mainland Chinese and Hong Kong students studying in Taiwan. There were also more than 7,000 Taiwanese students studying in Hong Kong that same year.
Religious exchange has become frequent. Frequent interactions occur between worshipers of Matsu, and also between Buddhists
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
.
The Chinese football team Changchun Yatai F.C.
Changchun Yatai Football Club () is a professional Chinese football club that currently participates in the Chinese Super League under licence from the Chinese Football Association (CFA). The team is based in Changchun, Jilin and their home stadi ...
chose Taiwan as the first stop of their 2015 winter training session, which is the first Chinese professional football team's arrival in Taiwan, and they were supposed to have an exhibition against Tatung F.C.
Leopard Cat Football Club (), formerly known as Tatung Football Club, is a Taiwanese professional football club based in Taipei, that competes in the Taiwan Football Premier League. The club, affiliated with the electronics-producing Tatung Compa ...
, which, however, wasn't successfully held, under unknown circumstances.
Humanitarian actions
Both sides have provided humanitarian aid to each other on several occasions. Following the 2008 Sichuan earthquake, an expert search and rescue team was sent from Taiwan to help rescue survivors in Sichuan. Shipments of aid material were also provided under the coordination of the Red Cross Society of The Republic of China and charities such as Tzu Chi.Military build-up
Taiwan has more than 170,000air raid shelter
Air raid shelters are structures for the protection of non-combatants as well as combatants against enemy attacks from the air. They are similar to bunkers in many regards, although they are not designed to defend against ground attack (but many ...
s which would shelter much of the civilian population in the event of Chinese air or missile attack.
US Secretary of Defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
Robert Gates said in 2011 that the United States would reduce arms sales to Taiwan if tensions are eased, but that this was not a change in American policy.
In 2012, United States Pacific Command commander Willard said that there was a reduced possibility of a cross-strait conflict accompanying greater interaction, though there were no reductions in military spending on either side.
Beginning in 2016, China embarked on a massive military build-up.
In 2017, under the Trump administration, the United States began increasing military exchanges with Taiwan as well as passing two bills to allow high level visits between government officials, and US military vessels passed through the strait at a far greater rate than during President Barack Obama's two terms.
In 2020, German Defense Minister Annegret Kramp-Karrenbauer warned China not to pursue military action against Taiwan saying that such a decision would be a "major failure of statecraft" which would produce only losers. Japan is increasingly concerned with China's aggression as Taiwan was mentioned in Japanese Prime Minister Suga's and President Joe Biden's joint statement in April 2021.
The Deputy Director-General of Taiwan's National Security Bureau Chen Wen-fan stated in 2020 that Xi Jinping intends to solve the "Taiwan Problem" by 2049.
In 2022 INDOPACOM described the situation of Cross-straits relations as being dire, as China amassed the biggest build up f military personnel and assets
F, or f, is the sixth Letter (alphabet), letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabet#Let ...
seen since WWII.
In October, 2022, Admiral Mike Gilday, Chief of Naval Operations of the U.S. Navy, said that the American military must be prepared for the possibility of a Chinese invasion of Taiwan before 2024.
Following the visit to Taiwan of Nancy Pelosi
Nancy Patricia Pelosi (; ; born March 26, 1940) is an American politician who has served as Speaker of the United States House of Representatives since 2019 and previously from 2007 to 2011. She has represented in the United States House of ...
, Speaker of the U.S. House of Representatives, in August of 2022, thChinaPower Project
at the Center for Strategic and International Studies polled 64 leading experts on the People’s Republic of China (PRC), Taiwan, and cross-Strait relations, including 28 former high-level U.S. government (USG) officials from both Democrat and Republican administrations, as well as 23 former USG policy and intelligence analysts and 13 top experts from academia and think tanks.Responses were collected from August 10–September 8, 2022. The CSIS summarized the responses of the experts as follows: 1) China is determined to unify with Taiwan, but Beijing does not have a coherent strategy. 2) China is willing to wait to unify with Taiwan, and the August 2022 exercises are not an indicator of accelerated PRC timelines. 3) Xi Jinping feels there are still avenues to peaceful unification. 4) The potential for a military crisis or conflict in the Taiwan Strait is very real. 5) China would immediately invade if Taiwan declared independence. 6) China assumes that the United States would intervene in a Taiwan conflict.
See also
*China–United States relations
The relationship between the People's Republic of China (PRC) and the United States of America (USA) has been complex since 1949 with mutual distrust leading to complications. The relationship is one of close economic ties (economic ties grew ...
* Cross-Strait Economic, Trade and Culture Forum
* Cross-Strait high-level talks
*Cross-Strait Peace Forum
The Cross-Strait Peace Forum () is a forum between Mainland China and Taiwan to discuss the peaceful development of the cross-strait relations. The forum was firstly held in October 2013 and it acts as an important platform for non-political dialo ...
* Foreign relations of China
* Foreign relations of Taiwan
* North Korea–South Korea relations
*Political status of Taiwan
The controversy surrounding the political status of Taiwan or the Taiwan issue is a result of World War II, the second phase of the Chinese Civil War (1945–1949), and the Cold War.
The basic issue hinges on who the islands of Taiwan, Peng ...
* Taiwan–United States relations
* Taiwan–Japan relations
* Wang–Koo summit
* Zhu Rongji
Explanatory notes
References
Further reading
; Books * Bush, R. & O'Hanlon, M. (2007). ''A War Like No Other: The Truth About China's Challenge to America''. Wiley. * Bush, R. (2006). ''Untying the Knot: Making Peace in the Taiwan Strait''. Brookings Institution Press. * * Carpenter, T. (2006). ''America's Coming War with China: A Collision Course over Taiwan''. Palgrave Macmillan. * Cole, B. (2006). ''Taiwan's Security: History and Prospects''. Routledge. * Copper, J. (2006). ''Playing with Fire: The Looming War with China over Taiwan''. Praeger Security International General Interest. * Gill, B. (2007). ''Rising Star: China's New Security Diplomacy''. Brookings Institution Press. * Shirk, S. (2007). ''China: Fragile Superpower: How China's Internal Politics Could Derail Its Peaceful Rise''. Oxford University Press. * Tsang, S. (2006). ''If China Attacks Taiwan: Military Strategy, Politics and Economics''. Routledge. * Tucker, N.B. (2005). ''Dangerous Strait: the U.S.-Taiwan-China Crisis''. Columbia University Press. * Wachman, Alan M. (2007 ) ''Why Taiwan? Geostrategic Rationales for China's Territorial Integrity''. Stanford University Press. ; Articles * Federation of American Scientists et al. (2006)Chinese Nuclear Forces and U.S. Nuclear War Planning
* Sutter, Robert
Taiwan's Future: Narrowing Straits
(NBR Special Report, May 2011)
China, Taiwan, and the Battle for Latin America
21p. * Review o
Convergence or Conflict in the Taiwan Strait
The Illusion of Peace? by J. Michael Cole, in ''Pacific Affairs'' (2017): 90, 573–575.
External links
Taiwan Affairs Office website (PRC government department in charge of relations with Taiwan)
Mainland Affairs Council website (Taiwan government department in charge of Relations with PRC)
– March 2010 radio interview with Professor T.Y. Wang (Illinois State University) {{DEFAULTSORT:Cross-Strait Relations Taiwan
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
Politics of China
Politics of Taiwan
Taiwan Strait