Crohn's disease is a type of
inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine, with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine and large intestine ...
(IBD) that may affect any segment of the
gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
.
Symptoms often include
abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Since the abdomen contains most of the body's vital organs, it can be an indicator of a wide variety of diseases. Given th ...
,
diarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
,
fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
,
abdominal distension
Abdominal distension occurs when substances, such as air (gas) or fluid, accumulate in the abdomen causing its expansion. It is typically a symptom of an underlying disease or dysfunction in the body, rather than an illness in its own right. Peo ...
, and
weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other conn ...
.
Complications outside of the
gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
may include
anemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availabl ...
,
skin rashes
A rash is a change of the skin that affects its color, appearance, or texture.
A rash may be localized in one part of the body, or affect all the skin. Rashes may cause the skin to change color, itch, become warm, bumpy, chapped, dry, cracke ...
,
arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of ...
,
inflammation of the eye, and
fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself.
Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated wit ...
.
The skin rashes may be due to infections, as well as
pyoderma gangrenosum
Pyoderma gangrenosum is a rare, Inflammation, inflammatory skin disease where painful pustules or skin condition, nodules become ulcer (dermatology), ulcers that progressively grow. Pyoderma gangrenosum is not infectious.
Treatments may include ...
or
erythema nodosum.
Bowel obstruction
Bowel obstruction, also known as intestinal obstruction, is a mechanical or Ileus, functional obstruction of the Gastrointestinal tract#Lower gastrointestinal tract, intestines which prevents the normal movement of the products of digestion. Ei ...
may occur as a complication of chronic inflammation, and those with the disease are at greater risk of
colon cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel ...
and
small bowel cancer.
Although the precise causes of Crohn's disease (CD) are unknown, it is believed to be caused by a combination of environmental,
immune, and bacterial factors in genetically susceptible individuals.
It results in a
chronic inflammatory disorder, in which the body's
immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
defends the gastrointestinal tract, possibly targeting
microbial
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic size, which may exist in its single-celled form or as a colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen microbial life was suspected from antiquity, with an early attestation in ...
antigens
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule, moiety, foreign particulate matter, or an allergen, such as pollen, that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response.
An ...
.
Although Crohn's is an immune-related disease, it does not seem to be an
autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated tha ...
(the immune system is not triggered by the body itself). The exact underlying immune problem is not clear; however, it may be an
immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromise, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that aff ...
state.
About half of the overall risk is related to genetics, with more than 70
gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s involved.
Tobacco smokers are three times as likely to develop Crohn's disease as non-smokers.
Crohn's disease is often triggered after a
gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea, is an inflammation of the Human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of ...
episode.
Other conditions with similar symptoms include
irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain, abdominal bloating, and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may ...
and
Behçet's disease.
There is no known cure for Crohn's disease.
are intended to help with symptoms, maintain
remission, and prevent
relapse
In internal medicine, relapse or recidivism is a recurrence of a past (typically medical) condition. For example, multiple sclerosis and malaria often exhibit peaks of activity and sometimes very long periods of dormancy, followed by relapse or r ...
.
In those newly diagnosed, a
corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
may be used for a brief period of time to improve symptoms rapidly, alongside another medication such as either
methotrexate
Methotrexate, formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immunosuppressive drug, immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancy, ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is u ...
or a
thiopurine to prevent recurrence.
Cessation of smoking is recommended for people with Crohn's disease.
One in five people with the disease is admitted to the hospital each year, and half of those with the disease will require surgery at some time during a ten-year period.
Surgery is kept to a minimum whenever possible, but it is sometimes essential for treating
abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body, usually caused by bacterial infection. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pre ...
es, certain bowel obstructions, and cancers.
Checking for bowel cancer via
colonoscopy
Colonoscopy () or coloscopy () is a medical procedure involving the Endoscopy, endoscopic examination of the large bowel (colon) and the distal portion of the small bowel. This examination is performed using either a Charge-coupled device, CCD ...
is recommended every 1-3 years, starting eight years after the disease has begun.
Crohn's disease affects about 3.2 per 1,000 people in Europe and North America;
it is less common in Asia and Africa.
It has historically been more common in the
developed world
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for eval ...
.
Rates have, however, been increasing, particularly in the developing world, since the 1970s.
Inflammatory bowel disease resulted in 47,400 deaths in 2015, and those with Crohn's disease have a slightly reduced
life expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where '' ...
.
Onset of Crohn's disease tends to start in adolescence and young adulthood, though it can occur at any age.
Males and females are affected roughly equally.
Name controversy
The disease was named after
gastroenterologist Burrill Bernard Crohn, who in 1932, together with
Leon Ginzburg (1898–1988) and
Gordon D. Oppenheimer (1900–1974) at
Mount Sinai Hospital in New York, described a series of people with inflammation of the
terminal ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine ma ...
of the
small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ (anatomy), organ in the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract where most of the #Absorption, absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intes ...
, the area most commonly affected by the illness.
The decision to name the disease after Crohn remains controversial. While Crohn, in his memoir, describes his original investigation of the disease, Ginzburg provided strong evidence of how he and Oppenheimer were the first to study the disease.
Signs and symptoms
Gastrointestinal
Many people with Crohn's disease have symptoms for years before the diagnosis.
The usual onset is in the teens and twenties, but can occur at any age.
People with Crohn's disease experience chronic recurring periods of flare-ups and
remission.
Perianal
Perianal discomfort may also be prominent in Crohn's disease. Itchiness or pain around the
anus
In mammals, invertebrates and most fish, the anus (: anuses or ani; from Latin, 'ring' or 'circle') is the external body orifice at the ''exit'' end of the digestive tract (bowel), i.e. the opposite end from the mouth. Its function is to facil ...
may be suggestive of
inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
of the anus, or perianal complications such as
anal fissures,
fistula
In anatomy, a fistula (: fistulas or fistulae ; from Latin ''fistula'', "tube, pipe") is an abnormal connection (i.e. tube) joining two hollow spaces (technically, two epithelialized surfaces), such as blood vessels, intestines, or other h ...
e, or
abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body, usually caused by bacterial infection. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pre ...
es around the
anal area.
Perianal
skin tags are also common in Crohn's disease, and may appear with or without the presence of
colorectal polyp
A colorectal polyp is a polyp (fleshy growth) occurring on the lining of the colon or rectum. Untreated colorectal polyps can develop into colorectal cancer.
Colorectal polyps are often classified by their behaviour (i.e. benign vs. malignant) ...
s.
Intestines
The intestines, especially the colon and terminal ileum, are the areas of the body affected most commonly.
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain, also known as a stomach ache, is a symptom associated with both non-serious and serious medical issues. Since the abdomen contains most of the body's vital organs, it can be an indicator of a wide variety of diseases. Given th ...
is a common initial symptom of Crohn's disease,
especially in the lower right abdomen.
Flatulence, bloating, and abdominal distension are additional symptoms and may also add to the intestinal discomfort. Pain is often accompanied by non-bloody
diarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
, however in some cases the diarrhea can be bloody. Inflammation in different areas of the
intestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. ...
can affect the quality of the
feces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the ...
.
Ileitis typically results in large-volume, watery feces, while
colitis may result in a smaller volume of feces of greater frequency. Fecal consistency may range from solid to watery. In severe cases, an individual may have more than 20
bowel movements
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular syste ...
per day, and may need to awaken at night to defecate.
Visible bleeding in the feces is less common in Crohn's disease than in ulcerative colitis, but is not unusual.
Bloody bowel movements are usually intermittent, and may be bright red, dark maroon, or even
black in color. The color of bloody stool depends on the location of the bleed. In severe Crohn's colitis, bleeding may be copious.
Stomach and esophagus
The stomach is rarely the sole or predominant site of Crohn's disease. To date, there are only a few documented case reports of adults with isolated gastric Crohn's disease and no reports in the pediatric population. Isolated stomach involvement is very unusual presentation accounting for less than 0.07% of all gastrointestinal Crohn's disease. However, the
esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
and
stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
are increasingly understood to be affected in people with intestinal Crohn's disease. Recent studies suggest upper GI involvement occurs in 13-16% of cases, typically presenting after distal symptoms. Upper gastrointestinal symptoms may include difficulty swallowing (
dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or l ...
), painful swallowing (
odynophagia), upper abdominal pain, and vomiting.
Oropharynx (mouth)
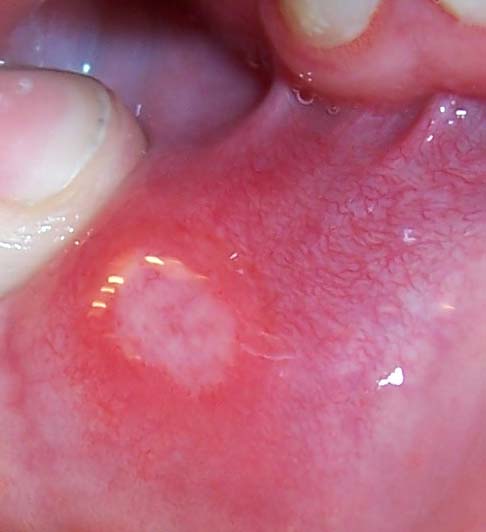
The mouth may be affected by recurrent canker sores (
aphthous ulcer
Aphthous stomatitis, or recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS), commonly referred to as a canker sore or salt blister, is a common condition characterized by the repeated formation of benignity, benign and non-contagious disease, contagious mouth ...
s). Recurrent aphthous ulcers are common; however, it is not clear whether this is due to Crohn's disease or simply that they are common in the general population. Other findings may include diffuse or nodular swelling of the mouth, a cobblestone appearance inside the mouth, granulomatous ulcers, or
pyostomatitis vegetans. Medications that are commonly prescribed to treat Crohn's disease, such as anti-inflammatory and sulfa-containing drugs, may cause lichenoid drug reactions in the mouth. Fungal infection such as candidiasis is also common due to the immunosuppression required in the treatment of the disease. Signs of anemia such as pallor and angular cheilitis or glossitis are also common due to nutritional malabsorption.
People with Crohn's disease are also susceptible to
angular stomatitis, an inflammation of the corners of the mouth, and
pyostomatitis vegetans.
Systemic
Like many other chronic, inflammatory diseases, Crohn's disease can cause a variety of
systemic symptoms.
Among children,
growth failure is common. Many children are first diagnosed with Crohn's disease based on
inability to maintain growth.
As it may manifest at the time of the growth spurt in
puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes through which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of sexual reproduction. It is initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads: the ovaries in a female, the testicles i ...
, as many as 30% of children with Crohn's disease may have retardation of growth. Fever may also be present, though fevers greater than 38.5 °C (101.3 °F) are uncommon unless there is a complication such as an abscess.
Among older individuals, Crohn's disease may manifest as weight loss, usually related to decreased food intake, since individuals with intestinal symptoms from Crohn's disease often feel better when they do not eat and might
lose their appetite.
People with extensive
small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ (anatomy), organ in the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract where most of the #Absorption, absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intes ...
disease may also have
malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a varie ...
of
carbohydrate
A carbohydrate () is a biomolecule composed of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms. The typical hydrogen-to-oxygen atomic ratio is 2:1, analogous to that of water, and is represented by the empirical formula (where ''m'' and ''n'' ...
s or
lipid
Lipids are a broad group of organic compounds which include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing ...
s, which can further exacerbate weight loss.
Extraintestinal
Crohn's disease can affect many
organ system
An organ system is a biological system consisting of a group of organ (biology), organs that work together to perform one or more bodily functions. Each organ has a specialized role in an organism body, and is made up of distinct Tissue (biolog ...
s beyond the
gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the Digestion, digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascula ...
.
Visual
Inflammation of the interior portion of the eye, known as
uveitis
Uveitis () is inflammation of the uvea, the pigmented layer of the eye between the inner retina and the outer fibrous layer composed of the sclera and cornea. The uvea consists of the middle layer of pigmented vascular structures of the eye and ...
, can cause blurred vision and eye pain, especially when exposed to light (
photophobia
Photophobia is a medical symptom of abnormal intolerance to visual perception of light. As a medical symptom, photophobia is not a morbid fear or phobia, but an experience of discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure or by presence o ...
).
Uveitis can lead to loss of vision if untreated.
Inflammation may also involve the white part of the eye (
sclera
The sclera, also known as the white of the eye or, in older literature, as the tunica albuginea oculi, is the opaque, fibrous, protective outer layer of the eye containing mainly collagen and some crucial elastic fiber.
In the development of t ...
) or the overlying connective tissue (
episclera), which causes conditions called
scleritis and
episcleritis, respectively.
Other very rare ophthalmological manifestations include:
conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis, also known as pink eye or Madras eye, is inflammation of the conjunctiva, the thin, clear layer that covers the white surface of the eye and the inner eyelid. It makes the eye appear pink or reddish. Pain, burning, scratchiness ...
,
glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to damage of the optic nerve. The optic nerve transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. Glaucoma may cause vision loss if left untreated. It has been called the "silent thief of ...
, and retinal vascular disease.
The pathophysiology of ocular inflammation in people with Crohn's disease is complex and remains uncertain. The association between inflammatory conditions of the eye and Crohn's disease is due to many people with Crohn's disease having genetic markers such as HLA-B07, HLA-B27 and HLA-DRB1*0103. Additionally, cytokines IL-6, IL-10, and IL-17 which are produced in the bowel enter the circulatory system and travel to the eyes to trigger inflammation.
Gallbladder and liver
Crohn's disease that affects the
ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine may ...
may result in an increased risk of
gallstone
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of ...
s. This is due to a decrease in
bile acid resorption in the ileum, resulting in
bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), also known as gall, is a yellow-green/misty green fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is primarily composed of water, is pro ...
excretion in the stool. As a result, the
cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
/bile ratio increases in the
gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow Organ (anatomy), organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath t ...
, resulting in an increased risk for gallstones.
Although the association is greater in the context of
ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is one of the two types of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), with the other type being Crohn's disease. It is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary sympto ...
, Crohn's disease may also be associated with
primary sclerosing cholangitis
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is a long-term progressive disease of the liver and gallbladder characterized by inflammation and scarring of the bile ducts, which normally allow bile to drain from the gallbladder. Affected individuals may ...
, a type of inflammation of the
bile duct
A bile duct is any of a number of long tube-like structures that carry bile, and is present in most vertebrates. The bile duct is separated into three main parts: the fundus (superior), the body (middle), and the neck (inferior).
Bile is requ ...
s. Specifically, 0.96% of people with Crohn's disease also have primary sclerosing cholangitis.
Liver involvement of Crohn's disease can include
cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, chronic liver failure or chronic hepatic failure and end-stage liver disease, is a chronic condition of the liver in which the normal functioning tissue, or parenchyma, is replaced ...
and
steatosis.
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, NAFLD) are relatively common and can slowly progress to end-stage liver disease. NAFLD sensitizes the liver to injury and increases the risk of developing acute or chronic liver failure following another liver injury.
Other rare hepatobiliary manifestations of Crohn's disease include:
cholangiocarcinoma, granulomatous hepatitis, cholelithiasis,
autoimmune hepatitis,
hepatic abscess, and pericholangitis.
Renal and urological
Nephrolithiasis,
obstructive uropathy, and
fistulization of the urinary tract directly result from the underlying disease process. Nephrolithiasis is due to calcium oxalate or uric acid stones. Calcium oxalate stones due to hyperoxaluria are typically associated with either distal ileal Crohn's disease or ileal resection. Oxalate absorption increases in the presence of unabsorbed fatty acids in the colon. The fatty acids compete with oxalate to bind calcium, displacing the oxalate, which can then be absorbed as unbound sodium oxalate across colonocytes and excreted into the urine. Because sodium oxalate is only absorbed in the colon, calcium oxalate stones form only in people with an intact colon. People with an
ileostomy are prone to formation of uric acid stones because of frequent dehydration. The sudden onset of severe abdominal, back, or flank pain in patients with IBD, particularly if different from the usual discomfort, should lead to inclusion of a renal stone in the differential diagnosis.
manifestations in people with IBD may include ureteral calculi, enterovesical
fistula
In anatomy, a fistula (: fistulas or fistulae ; from Latin ''fistula'', "tube, pipe") is an abnormal connection (i.e. tube) joining two hollow spaces (technically, two epithelialized surfaces), such as blood vessels, intestines, or other h ...
, perivesical infection, perinephric abscess, and obstructive uropathy with
hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis is the hydrostatic dilation of the renal pelvis and Renal calyx, calyces as a result of obstruction to urine flow downstream. Alternatively, hydroureter describes the dilation of the ureter, and hydronephroureter describes the dila ...
. Ureteral compression is associated with retroperitoneal extension of the phlegmonous inflammatory process involving the
terminal ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine ma ...
and
cecum
The cecum ( caecum, ; plural ceca or caeca, ) is a pouch within the peritoneum that is considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. It is typically located on the right side of the body (the same side of the body as the appendix (a ...
, and may result in
hydronephrosis
Hydronephrosis is the hydrostatic dilation of the renal pelvis and Renal calyx, calyces as a result of obstruction to urine flow downstream. Alternatively, hydroureter describes the dilation of the ureter, and hydronephroureter describes the dila ...
severe enough to cause
hypertension
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a Chronic condition, long-term Disease, medical condition in which the blood pressure in the artery, arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms i ...
.
Immune complex
glomerulonephritis presenting with
proteinuria
Proteinuria is the presence of excess proteins in the urine. In healthy persons, urine contains very little protein, less than 150 mg/day; an excess is suggestive of illness. Excess protein in the urine often causes the urine to become fo ...
and
hematuria
Hematuria or haematuria is defined as the presence of blood or red blood cells in the urine. "Gross hematuria" occurs when urine appears red, brown, or tea-colored due to the presence of blood. Hematuria may also be subtle and only detectable with ...
has been described in children and adults with Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis. Diagnosis is by renal biopsy, and treatment parallels the underlying IBD.
Amyloidosis
Amyloidosis is a group of diseases in which abnormal proteins, known as amyloid fibrils, build up in tissue. There are several non-specific and vague signs and symptoms associated with amyloidosis. These include fatigue, peripheral edema, weigh ...
(see endocrinological involvement) secondary to Crohn's disease has been described and is known to affect the kidneys.
Pancreatic
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a large organ behind the stomach that produces digestive enzymes and a number of hormone
A hormone (from the Ancient Greek, Greek participle , "se ...
may be associated with both ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. The most common cause is
iatrogenic
Iatrogenesis is the causation of a disease, a harmful complication, or other ill effect by any medical activity, including diagnosis, intervention, error, or negligence." Iatrogenic", ''Merriam-Webster.com'', Merriam-Webster, Inc., accessed 27 ...
and involves sensitivity to medications used to treat IBD, including
sulfasalazine,
mesalamine,
6-mercaptopurine, and
azathioprine. Pancreatitis may present as symptomatic or more commonly asymptomatic disease in adults with IBD.
Cardiovascular and circulatory
Children and adults with IBD have been rarely (<1%) reported developing
pleuropericarditis either at initial presentation or during active or quiescent disease. The pathogenesis of pleuropericarditis is unknown, although certain medications (e.g.,
sulfasalazine and
mesalamine derivatives) have been implicated in some cases. The clinical presentation may include chest pain,
dyspnea
Shortness of breath (SOB), known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing discomfort that ...
, or in severe cases
pericardial tamponade
Cardiac tamponade, also known as pericardial tamponade (), is a compression of the heart due to pericardial effusion (the build-up of pericardial fluid in the sac around the heart). Onset may be rapid or gradual. Symptoms typically include those ...
requiring rapid drainage.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a Indication (medicine), therapeutic drug class which Analgesic, reduces pain, Anti-inflammatory, decreases inflammation, Antipyretic, decreases fever, and Antithrombotic, prevents bl ...
s have been used as therapy, although this should be weighed against the hypothetical risk of exacerbating the underlying IBD.
In rare cases,
cardiomyopathy
Cardiomyopathy is a group of primary diseases of the heart muscle. Early on there may be few or no symptoms. As the disease worsens, shortness of breath, feeling tired, and swelling of the legs may occur, due to the onset of heart failure. A ...
,
endocarditis
Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner layer of the heart, the endocardium. It usually involves the heart valves. Other structures that may be involved include the interventricular septum, the chordae tendineae, the mural endocardium, o ...
, and
myocarditis
Myocarditis is inflammation of the cardiac muscle. Myocarditis can progress to inflammatory cardiomyopathy when there is associated ventricular remodeling and cardiac dysfunction due to chronic inflammation. Symptoms can include shortness of bre ...
have been described.
Crohn's disease also increases the risk of
blood clot
A thrombus ( thrombi) is a solid or semisolid aggregate from constituents of the blood (platelets, fibrin, red blood cells, white blood cells) within the circulatory system during life. A blood clot is the final product of the blood coagulatio ...
s;
painful swelling of the lower legs can be a sign of
deep venous thrombosis, while difficulty breathing may be a result of
pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain ...
.
Respiratory
Laryngeal involvement in inflammatory bowel disease is extremely rare. Only 12 cases of laryngeal involvement in Crohn's disease have been reported . Moreover, only one case of laryngeal manifestations in ulcerative colitis has been reported as of the same date. Nine people complained of difficulty in breathing due to
edema
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, swelling, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue (biology), tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. S ...
and
ulcer
An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes normal function of the affected organ. According to Robbins's pathology, "ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caused by sloughin ...
ation from the
larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ (anatomy), organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal ...
to the
hypopharynx
The pharynx (: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the esophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs respectively). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its ...
. Hoarseness, sore throat, and
odynophagia are other symptoms of laryngeal involvement of Crohn's disease.
Considering extraintestinal manifestations of Crohn's disease, those involving the
lung
The lungs are the primary Organ (biology), organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the Vertebral column, backbone on either side of the heart. Their ...
are relatively rare. However, there is a wide array of lung manifestations, ranging from subclinical alterations, airway diseases and lung
parenchyma
upright=1.6, Lung parenchyma showing damage due to large subpleural bullae.
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ such as the brain or lungs, or a structure such as a tumour. In zoology, it is the tissue that ...
l diseases to
pleural
The pleural cavity, or pleural space (or sometimes intrapleural space), is the potential space between the pulmonary pleurae, pleurae of the pleural sac that surrounds each lung. A small amount of serous fluid, serous pleural fluid is maintained ...
diseases and drug-related diseases. The most frequent manifestation is bronchial inflammation and
suppuration with or without bronchiectasis. There are a number of mechanisms by which the lungs may become involved in Crohn's disease. These include the same embryological origin of the lung and gastrointestinal tract by ancestral intestine, similar immune systems in the pulmonary and intestinal mucosa, the presence of circulating immune complexes and auto-antibodies, and the adverse pulmonary effects of some drugs. A complete list of known pulmonary manifestations include: fibrosing alveolitis, pulmonary
vasculitis
Vasculitis is a group of disorders that destroy blood vessels by inflammation. Both artery, arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis (inflammation of lymphatic vessels) is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis. Vasculitis is primarily c ...
, apical
fibrosis,
bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is a disease in which there is permanent enlargement of parts of the bronchi, airways of the lung. Symptoms typically include a chronic cough with sputum, mucus production. Other symptoms include shortness of breath, hemoptysis, co ...
,
bronchitis
Bronchitis is inflammation of the bronchi (large and medium-sized airways) in the lungs that causes coughing. Bronchitis usually begins as an infection in the nose, ears, throat, or sinuses. The infection then makes its way down to the bronchi. ...
,
bronchiolitis,
tracheal stenosis,
granuloma
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages (along with other cells) that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such sub ...
tous lung disease, and abnormal pulmonary function.
Musculoskeletal
Crohn's disease is associated with a type of
rheumatologic disease known as
seronegative spondyloarthropathy.
This group of diseases is characterized by inflammation of one or more
joint
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
s (
arthritis
Arthritis is a general medical term used to describe a disorder that affects joints. Symptoms generally include joint pain and stiffness. Other symptoms may include redness, warmth, Joint effusion, swelling, and decreased range of motion of ...
) or muscle insertions (
enthesitis).
The arthritis in Crohn's disease can be divided into two types. The first type affects larger weight-bearing joints such as the knee (most common), hips, shoulders, wrists, or elbows.
The second type symmetrically involves five or more of the small joints of the hands and feet.
The arthritis may also involve the
spine, leading to
ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis from the disease spectrum of axial spondyloarthritis. It is characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine, typically where the spine joins the pelvis. With AS, eye and bow ...
if the entire spine is involved, or simply
sacroiliitis if only the
sacroiliac joint
The sacroiliac joint or SI joint (SIJ) is the joint between the sacrum and the ilium bones of the pelvis, which are connected by strong ligaments. In humans, the sacrum supports the spine and is supported in turn by an ilium on each side. The ...
is involved.
Crohn's disease increases the risk of
osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a systemic skeletal disorder characterized by low bone mass, micro-architectural deterioration of bone tissue leading to more porous bone, and consequent increase in Bone fracture, fracture risk.
It is the most common reason f ...
or thinning of the bones.
Individuals with osteoporosis are at increased risk of
bone fracture
A bone fracture (abbreviated FRX or Fx, Fx, or #) is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a ''c ...
s.
Dermatological
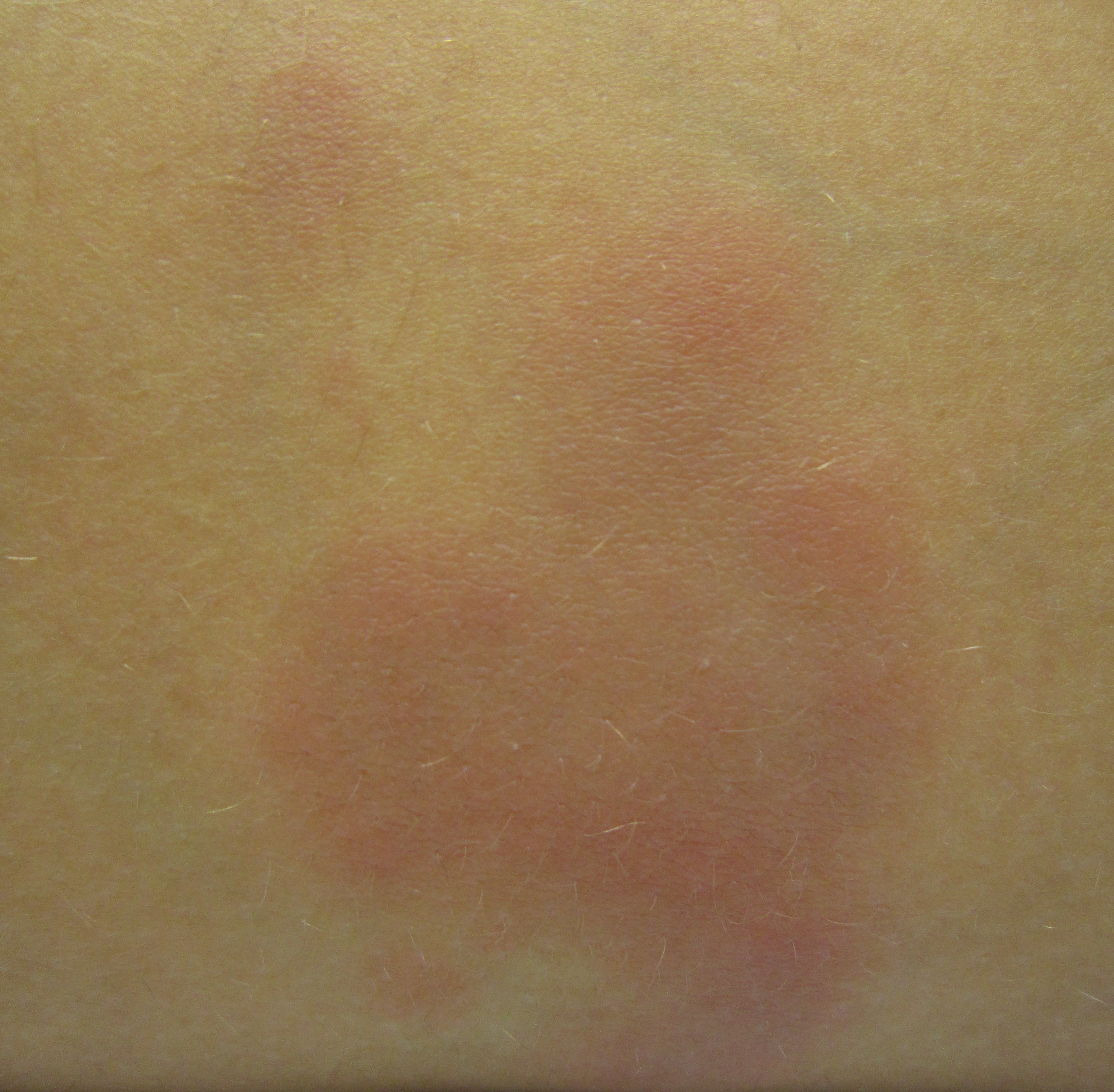
Crohn's disease may also involve the skin, blood, and
endocrine system
The endocrine system is a messenger system in an organism comprising feedback loops of hormones that are released by internal glands directly into the circulatory system and that target and regulate distant Organ (biology), organs. In vertebrat ...
.
Erythema nodosum is the most common type of skin problem, occurring in around 8% of people with Crohn's disease, producing raised, tender red
nodule
Nodule may refer to:
* Nodule (geology), a small rock or mineral cluster
* Manganese nodule, a metallic concretion found on the seafloor
*Nodule (medicine), a small aggregation of cells
*Root nodule
Root nodules are found on the roots of plants, ...
s usually appearing on the
shins.
Erythema nodosum is due to inflammation of the underlying
subcutaneous tissue
The subcutaneous tissue (), also called the hypodermis, hypoderm (), subcutis, or superficial fascia, is the lowermost layer of the integumentary system in vertebrates. The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and ma ...
, and is characterized by
septal panniculitis.
Pyoderma gangrenosum
Pyoderma gangrenosum is a rare, Inflammation, inflammatory skin disease where painful pustules or skin condition, nodules become ulcer (dermatology), ulcers that progressively grow. Pyoderma gangrenosum is not infectious.
Treatments may include ...
is a less common skin problem, occurring in under 2%,
and is typically a painful ulcerating nodule.
, a deformity of the ends of the fingers, may also be a result of Crohn's disease.
Other very rare dermatological manifestations include:
pyostomatitis vegetans,
erythema multiforme,
epidermolysis bullosa acquista (described in a case report), and metastatic Crohn's disease (the spread of Crohn's inflammation to the skin
).
It is unknown if
Sweet's syndrome is connected to Crohn's disease.
Neurological
Crohn's disease can also cause
neurological
Neurology (from , "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the brain, the s ...
complications (reportedly in up to 15% of cases).
[Crohn's disease](_blank)
. professionals.epilepsy.com. Retrieved July 13, 2007. The most common of these are
seizures
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
,
stroke
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemor ...
,
myopathy
In medicine, myopathy is a disease of the muscle in which the muscle fibers do not function properly. ''Myopathy'' means muscle disease ( Greek : myo- ''muscle'' + patheia '' -pathy'' : ''suffering''). This meaning implies that the primary defec ...
,
peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
,
headache
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of Depression (mood), depression in those with severe ...
, and
depression.
Central and peripheral neurological disorders are described in people with IBD and include peripheral
neuropathies
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropa ...
,
myopathies
In medicine, myopathy is a disease of the muscle in which the muscle fibers do not function properly. ''Myopathy'' means muscle disease (Greek language, Greek : myo- ''muscle'' + patheia ''pathos, -pathy'' : ''suffering''). This meaning implies t ...
, focal
central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain, spinal cord and retina. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity o ...
defects,
convulsion
A convulsion is a medical condition where the body muscles contract and relax rapidly and repeatedly, resulting in uncontrolled shaking. Because epileptic seizures typically include convulsions, the term ''convulsion'' is often used as a synony ...
s, confusional episodes,
meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, intense headache, vomiting and neck stiffness and occasion ...
,
syncope,
optic neuritis
Optic neuritis (ON) is a debilitating condition that is defined as inflammation of cranial nerve II which results in disruption of the neurologic pathways that allow visual sensory information received by the retina to be able to be transmitted to ...
, and
sensorineural loss.
Autoimmune
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an " autoimmune disease" ...
mechanisms are proposed for involvement with IBD. Nutritional deficiencies associated with neurological manifestations, such as
vitamin B12 deficiency, should be investigated. Spinal
abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body, usually caused by bacterial infection. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pre ...
has been reported in both a child and an adult with initial complaints of severe back pain due to extension of a psoas abscess from the epidural space to the subarachnoid space.
Psychiatric and psychological
Crohn's disease is linked to many psychological disorders, including
depression and
anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion characterised by an unpleasant state of inner wikt:turmoil, turmoil and includes feelings of dread over Anticipation, anticipated events. Anxiety is different from fear in that fear is defined as the emotional response ...
, denial of one's disease, the need for dependence or dependent behaviors, feeling overwhelmed, and having a poor self-image.
Many studies have found that people with IBD report a higher frequency of depressive and anxiety disorders than the general population; most studies confirm that women with IBD are more likely than men to develop affective disorders and show that up to 65% of them may have
depression and
anxiety disorder
Anxiety disorders are a group of mental disorders characterized by significant and uncontrollable feelings of anxiety and fear such that a person's social, occupational, and personal functions are significantly impaired. Anxiety may cause phys ...
.
Endocrinological or hematological
Leukocytosis and thrombocytopenia are usually due to immunosuppressant treatments or
sulfasalazine. Plasma erythropoietin levels often are lower in patients with IBD than expected, in conjunction with severe
anemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availabl ...
.
Thrombocythemia, Thrombocytosis and thromboembolic events resulting from a Thrombophilia, hypercoagulable state in people with IBD can lead to
pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an pulmonary artery, artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include dyspnea, shortness of breath, chest pain ...
or thrombosis elsewhere in the body. Thrombosis has been reported in 1.8% of people with ulcerative colitis and 3.1% of people with Crohn's disease. Thromboembolism and thrombosis are less frequently reported among children, with three people with ulcerative colitis and one with Crohn's disease described in case reports.
In rare cases, hypercoagulation disorders and portal vein thrombosis have been described.
Malnutrition symptoms
People with Crohn's disease may develop anemia due to vitamin B12, vitamin B
12, folate, iron deficiency, or due to anemia of chronic disease.
The most common is iron deficiency anemia from chronic blood loss,
reduced dietary intake, and persistent inflammation leading to increased hepcidin levels, restricting iron absorption in the duodenum.
As Crohn's disease most commonly affects the
terminal ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine ma ...
where the vitamin B
12/intrinsic factor complex is absorbed, B
12 deficiency may be seen.
This is particularly common after one has had a surgical procedure to Bowel resection, remove the ileum.
Involvement of the duodenum and jejunum can impair the absorption of many other nutrients including folate. People with Crohn's often also have issues with small bowel bacterial overgrowth syndrome, which can produce micronutrient deficiencies.
[ ] Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Text was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 2.0 Generic (CC BY 2.0)
license.
Complications
Intestinal damage

Crohn's disease can lead to several mechanical complications within the intestines, including Bowel obstruction, obstruction,
fistula
In anatomy, a fistula (: fistulas or fistulae ; from Latin ''fistula'', "tube, pipe") is an abnormal connection (i.e. tube) joining two hollow spaces (technically, two epithelialized surfaces), such as blood vessels, intestines, or other h ...
e, and
abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body, usually caused by bacterial infection. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pre ...
es. Obstruction typically occurs from strictures or adhesions that narrow the Lumen (anatomy), lumen, blocking the passage of the intestinal contents. A fistula can develop between two loops of bowel, between the bowel and bladder, between the bowel and vagina, and between the bowel and skin. Abscesses are walled-off concentrations of infection, which can occur in the abdomen or in the perianal area. Crohn's is responsible for 10% of vesicoenteric fistulae, and is the most common cause of Ileum, ileovesical
fistula
In anatomy, a fistula (: fistulas or fistulae ; from Latin ''fistula'', "tube, pipe") is an abnormal connection (i.e. tube) joining two hollow spaces (technically, two epithelialized surfaces), such as blood vessels, intestines, or other h ...
e.
Symptoms caused by bowel obstruction, intestinal stenosis, or the tightening and narrowing of the bowel, are also common in Crohn's disease. Abdominal pain is often most severe in areas of the bowel with stenosis. Persistent vomiting and nausea may indicate stenosis from small bowel obstruction or disease involving the
stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
, pylorus, or duodenum.
Intestinal
granuloma
A granuloma is an aggregation of macrophages (along with other cells) that forms in response to chronic inflammation. This occurs when the immune system attempts to isolate foreign substances that it is otherwise unable to eliminate. Such sub ...
s are a walled-off portions of the intestine by macrophages in order to isolate infections. Granuloma formation is more often seen in younger people, and mainly in the severe, active penetrating disease.
Granuloma is considered the hallmark of microscopic diagnosis in Crohn's disease, but granulomas can be detected in only 21–60% of people with Crohn's disease.
Cancer
Crohn's disease also increases the risk of cancer in the area of inflammation. For example, individuals with Crohn's disease involving the small bowel are at higher risk for small intestinal cancer. Similarly, people with Crohn's colitis have a relative risk of 5.6 for developing
colon cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel ...
. Screening for colon cancer with
colonoscopy
Colonoscopy () or coloscopy () is a medical procedure involving the Endoscopy, endoscopic examination of the large bowel (colon) and the distal portion of the small bowel. This examination is performed using either a Charge-coupled device, CCD ...
is recommended for anyone who has had Crohn's colitis for at least eight years.
Some studies suggest there is a role for chemoprotection in the prevention of colorectal cancer in Crohn's involving the colon; two agents have been suggested, folate and mesalamine preparations. Also, immunotherapy, immunomodulators and biological therapy for inflammatory bowel disease, biologic agents used to treat this disease may promote the development of extra-intestinal cancers.
Some cancers, such as Acute myeloid leukemia, acute myelocytic leukaemia have been described in cases of Crohn's disease.
Hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL) is a rare, lethal disease generally seen in young males with inflammatory bowel disease. TNF-α Inhibitor treatments (infliximab, adalimumab, Certolizumab pegol, certolizumab, natalizumab, and etanercept) are thought to be the cause of this rare disease.

Major complications
Major complications of Crohn's disease include bowel obstruction, abscesses, free Bowel perforation, perforation, and hemorrhage, which in rare cases may be fatal.
Other complications
Individuals with Crohn's disease are at risk of malnutrition for many reasons, including decreased food intake and
malabsorption
Malabsorption is a state arising from abnormality in absorption of food nutrients across the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Impairment can be of single or multiple nutrients depending on the abnormality. This may lead to malnutrition and a varie ...
. The risk increases following resection of the small bowel. Such individuals may require oral supplements to increase their caloric intake, or in severe cases, total parenteral nutrition (TPN). Most people with moderate or severe Crohn's disease are referred to a dietitian for assistance with nutrition.
Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) is characterized by excessive proliferation of colonic bacterial species in the small bowel. Potential causes of SIBO include fistulae, strictures, or motility disturbances. Hence, people with Crohn's disease are especially predisposed to develop SIBO. As a result, people with Crohn's disease may experience malabsorption and report symptoms such as weight loss, watery diarrhea, meteorism, flatulence, and abdominal pain, mimicking acute flare.
Pregnancy
Crohn's disease can be problematic during pregnancy, and some medications can cause adverse outcomes for the fetus or mother. Consultation with an obstetrician and gastroenterologist about Crohn's disease and all medications facilitates preventive measures. In some cases, remission occurs during pregnancy. Certain medications can also lower sperm count or otherwise adversely affect a man's fertility.
Ostomy-related complications
Common complications of an ostomy (a common surgery in Crohn's disease) are: mucosal edema, peristomal dermatitis, retraction, ostomy prolapse, mucosal/skin detachment, hematoma, necrosis, parastomal hernia, and stenosis.
Etiology
The etiology, or cause, of Crohn's disease is unknown. Many theories have been disputed, with four main theories hypothesized to be the primary mechanism of Crohn's disease. In autoimmune diseases, Antibody, antibodies and T cell, T lymphocytes are the primary mode of inflammation. These cells and bodies are part of the adaptive immune system, or the part of the immune system that learns to fight foreign bodies when first identified. Autoinflammatory diseases are diseases where the innate immune system, or the immune system we are genetically coded with, is designed to attack our own cells.
Crohn's disease likely has involvement of both the adaptive and innate immune systems.
Autoinflammatory theory
Crohn's disease can be described as a multifactorial autoinflammatory disease. The etiopathogenesis of Crohn's disease is still unknown. In any event, a loss of the regulatory capacity of the immune apparatus would be implicated in the onset of the disease. In this respect interestingly enough, as for Blau syndrome, Blau's disease (a Monogenic (genetics), monogenic autoinflammatory disease), the NOD2 gene mutations have been linked to Crohn's disease. However, in Crohn's disease, NOD2 mutations act as a risk factor, being more common among people with Crohn's disease than the background population, while in Blau's disease NOD2 mutations are linked directly to this syndrome, as it is an Autosomal dominant, autosomal-dominant disease. All this new knowledge in the pathogenesis of Crohn's disease allows us to put this multifactorial disease in the group of Autoinflammatory diseases, autoinflammatory syndromes.
Some examples of how the innate immune system affects bowel inflammation have been described.
A meta-analysis of Crohn's disease genome-wide association studies revealed 71 distinct Crohn's disease-susceptibility Locus (genetics), loci. Interestingly, three very important Crohn's disease-susceptibility genes (the intracellular pathogen-recognition receptor, NOD2; the autophagy-related 16-like 1, ATG16L1 and the immunity-related GTPase M, IRGM) are involved in innate immune responses against gut microbiota, while one (the X-box binding protein 1) is involved in regulation of the [adaptive] immune pathway via MHC class II, resulting in autoinflammatory inflammation. Studies have also found that increased Type 3 innate lymphoid cells, ILC3 can overexpress Major histocompatibility complex, major histocompatibility complex (MHC) II. MHC class II can induce CD4+ T cell apoptosis, thus avoiding the T cell response to normal bowel micro bacteria. Further studies of people with IBD compared with people without IBD found that the expression of MHC II by ILC3 was significantly reduced in people with IBD, thus causing an immune reaction against intestinal cells or normal bowel bacteria and damaging the intestines. This can also make the intestines more susceptible to environmental factors, such as food or bacteria.
The thinking is that because Crohn's disease has strong innate immune system involvement and has NOD2 mutations as a predisposition, Crohn's disease is more likely an autoinflammatory disease than an autoimmune disease.
Immunodeficiency theory
A substantial body of data has emerged in recent years to suggest that the primary defect in Crohn's disease is actually one of relative
immunodeficiency
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromise, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that aff ...
.
This view has been bolstered recently by novel immunological and clinical studies that have confirmed gross aberrations in this early response, consistent with subsequent genetic studies that have highlighted molecules important for Innate immune system, innate immune function. The suggestion therefore is that Crohn's pathogenesis actually results from partial immunodeficiency, a theory that coincides with the frequent recognition of a virtually identical, non-infectious inflammatory bowel disease arising in people with congenital Monogenic (genetics), monogenic disorders impairing phagocyte function.
Risk factors
While the exact cause or causes are unknown, Crohn's disease seems to be due to a combination of environmental factors and genetic predisposition. Crohn's is the first genetically complex disease in which the relationship between genetic Risk factor (epidemiology), risk factors and the immune system is understood in considerable detail. Each individual risk mutation makes a small contribution to the overall risk of Crohn's (approximately 1:200). The genetic data, and direct assessment of immunity, indicates a malfunction in the innate immune system.
[
] In this view, the chronic inflammation of Crohn's is caused when the adaptive immune system tries to compensate for a deficient innate immune system.
Genetics

Crohn's has a genetic component. Because of this, siblings of known people with Crohn's are 30 times more likely to develop Crohn's than the general population.
The first mutation found to be associated with Crohn's was a frameshift mutation, frameshift in the NOD2 gene (also known as the CARD15 gene), followed by the discovery of point mutations. Over 30 genes have been associated with Crohn's; a biological function is known for most of them. For example, one association is with mutations in the XBP1 gene, which is involved in the unfolded protein response pathway of the endoplasmic reticulum. The gene variants of NOD2/CARD15 seem to be related with small-bowel involvement. Other well documented genes which increase the risk of developing Crohn's disease are ATG16L1,
IL23R, IRGM, and SLC11A1.
There is considerable overlap between susceptibility loci for IBD and mycobacterial infections.
Genome-wide association studies have shown that Crohn's disease is genetically linked to coeliac disease.
Crohn's has been linked to the gene LRRK2 with one variant potentially increasing the risk of developing the disease by 70%, while another lowers it by 25%. The gene is responsible for making a protein, which collects and eliminates waste product in cells, and is also associated with Parkinson's disease.
Immune system
There was a prevailing view that Crohn's disease is a primary T cell autoimmune disorder; however, a newer theory hypothesizes that Crohn's results from an impaired innate immunity. The later hypothesis describes impaired cytokine secretion by macrophages, which contributes to impaired innate immunity and leads to a sustained microbial-induced inflammatory response in the colon, where the bacterial load is high.
Another theory is that the inflammation of Crohn's was caused by an overactive Th2 cells, T
h1 and Th17, T
h17 cytokine response.
In 2007, the ATG16L1 gene was implicated in Crohn's disease, which may induce Autophagy (cellular), autophagy and hinder the body's ability to attack invasive bacteria.
Another study theorized that the human immune system traditionally evolved with the presence of parasites inside the body and that the lack thereof due to modern hygiene standards has weakened the immune system. Test subjects were reintroduced to harmless parasites, with positive responses.
Microbes
It is hypothesized that maintenance of commensal microorganism growth in the GI tract is dysregulated, either as a result or cause of immune dysregulation.
There is an apparent connection between Crohn's disease, ''Mycobacterium'', other pathogenic bacteria, and genetic markers. A number of studies have suggested a causal role for Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis, ''Mycobacterium avium'' subspecies ''paratuberculosis'' (MAP), which causes a similar disease, Johne's disease, in cattle.
In many individuals, genetic factors predispose individuals to ''Mycobacterium avium'' subsp.'' paratuberculosis'' infection. This bacterium may produce certain compounds containing mannose, which may protect both itself and various other bacteria from phagocytosis, thereby possibly causing a variety of secondary infections.
NOD2 is a gene involved in Crohn's genetic susceptibility. It is associated with macrophages' diminished ability to phagocytize MAP. This same gene may reduce innate and adaptive immunity in gastrointestinal tissue and impair the ability to resist infection by the MAP bacterium. Macrophages that ingest the MAP bacterium are associated with high production of TNF-α.
Other studies have linked specific strains of enteroadherent ''Escherichia coli, E. coli'' to the disease.
Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli (AIEC), more common in people with Crohn's disease,
have the ability to make strong biofilms compared to non-AIEC strains correlating with high adhesion and invasion indices of neutrophils and the ability to block autophagy at the autolysosomal step, which allows for intracellular survival of the bacteria and induction of inflammation.
Inflammation drives the proliferation of AIEC and dysbiosis in the ileum, irrespective of genotype.
AIEC strains replicate extensively inside macrophages inducing the secretion of very large amounts of TNF-α.
Mouse studies have suggested some symptoms of Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, and
irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain, abdominal bloating, and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may ...
have the same underlying cause. Biopsy samples taken from the colons of all three patient groups were found to produce elevated levels of a serine protease. Experimental introduction of the serine protease into mice has been found to produce widespread pain associated with irritable bowel syndrome, as well as colitis, which is associated with all three diseases. Regional and temporal variations in those illnesses follow those associated with infection with the protozoan ''Blastocystis''.
The "cold-chain" hypothesis is that psychrotrophic bacteria such as ''Yersinia'' and ''Listeria'' species contribute to the disease. A statistical correlation was found between the advent of the use of refrigeration in the United States and various parts of Europe and the rise of the disease.
There is also a tentative association between ''Candida (fungus), Candida'' colonization and Crohn's disease.
Still, these relationships between specific pathogens and Crohn's disease remain unclear.
Environmental factors
The increased incidence of Crohn's disease in the industrialized world indicates an environmental component. Crohn's is associated with an increased intake of animal protein, milk protein, and an increased ratio of Omega-6 fatty acid, omega-6 to Omega-3 fatty acid, omega-3 Polyunsaturated fat, polyunsaturated fatty acids.
[
]
Those who consume vegetable proteins appear to have a lower incidence of Crohn's disease. Consumption of fish protein has no association.
Tobacco smoking, Smoking increases the risk of the return of active disease (flares).
The introduction of hormonal contraception in the United States in the 1960s is associated with a dramatic increase in incidence, and one hypothesis is that these drugs work on the digestive system in ways similar to smoking. Isotretinoin is associated with Crohn's.
Although stress (physiology), stress is sometimes claimed to exacerbate Crohn's disease, there is no concrete evidence to support such claim.
Still, it is well known that immune function is related to stress. Dietary microparticles, such as those found in toothpaste, have been studied as they produce effects on immunity, but they were not consumed in greater amounts in people with Crohn's. The use of doxycycline has also been associated with increased risk of developing inflammatory bowel diseases.
In one large retrospective study, participants who were prescribed doxycycline for their acne had a 2.25-fold greater risk of developing Crohn's disease.
Pathophysiology
During a
colonoscopy
Colonoscopy () or coloscopy () is a medical procedure involving the Endoscopy, endoscopic examination of the large bowel (colon) and the distal portion of the small bowel. This examination is performed using either a Charge-coupled device, CCD ...
, Biopsy, biopsies of the colon are often taken to confirm the diagnosis. Certain characteristic features of the pathology seen point toward Crohn's disease. Common features include a transmural pattern of
inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
, meaning the inflammation may span the entire depth of the Gastrointestinal wall, intestinal wall.
Granulomas, aggregates of macrophage derivatives known as giant cells, are found in 50% of cases and are most specific for Crohn's disease. The granulomas of Crohn's disease do not show "caseation", a cheese-like appearance on microscopic examination characteristic of granulomas associated with infections, such as tuberculosis. Biopsies may also show chronic mucosal damage, as evidenced by blunting of the intestinal Intestinal villus, villi, atypical branching of the crypts, and a change in the tissue type (metaplasia). One example of such metaplasia, ''Paneth cell metaplasia'', involves the development of Paneth cells (typically found in the small intestine and a key regulator of intestinal microbiota) in other parts of the gastrointestinal system.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of Crohn's disease can sometimes be challenging,
and many tests are often required to assist the physician in making the diagnosis.
Even with a full battery of tests, it may not be possible to diagnose Crohn's with complete certainty; a colonoscopy is approximately 70% effective in diagnosing the disease, with further tests being less effective. Disease in the small bowel is particularly difficult to diagnose, as a traditional colonoscopy allows access to only the colon and lower portions of the small intestines; introduction of the capsule endoscopy aids in endoscopic diagnosis. Intestinal ultrasound should be considered an early step in the diagnosis and follow-up of people with Crohn's disease even in people with a proximal small bowel localization of the disease.
Giant cells, Giant (multinucleate) cells, a common finding in the lesions of Crohn's disease, are less common in the lesions of lichen nitidus.
CD colitis.jpg, Endoscopic image of Crohn's colitis showing deep ulceration
CT scan gastric CD.jpg, CT scan showing Crohn's disease in the fundus of the stomach
Crohn's transmural path.jpg, Section of colectomy showing transmural inflammation
ResectedIleum.jpg, Resected ileum from a person with Crohn's disease
Classification

Crohn's disease is one type of
inflammatory bowel disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine, with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine and large intestine ...
(IBD). It typically manifests in the gastrointestinal tract and can be categorized by the specific tract region affected.
Gastroduodenal Crohn's disease causes inflammation in the stomach and the first part of the small intestine called the duodenum. Jejunoileitis causes spotty patches of inflammation in the top half of the small intestine, called the jejunum. The disease can attack any part of the digestive tract, from the mouth to the anus. However, individuals affected by the disease rarely fall outside these three classifications, with presentations in other areas.
Crohn's disease may also be categorized by the behavior of the disease as it progresses. These categorizations formalized in the Vienna classification of the disease.
There are three categories of disease presentation in Crohn's disease: stricturing, penetrating, and inflammatory. Stricturing disease causes narrowing of the bowel that may lead to bowel obstruction or changes in the caliber of the
feces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the ...
. Penetrating disease creates abnormal passageways (fistulae) between the bowel and other structures, such as the skin. Inflammatory disease (or nonstricturing, nonpenetrating disease) causes inflammation without causing strictures or fistulae.
Endoscopy
A
colonoscopy
Colonoscopy () or coloscopy () is a medical procedure involving the Endoscopy, endoscopic examination of the large bowel (colon) and the distal portion of the small bowel. This examination is performed using either a Charge-coupled device, CCD ...
is the best test for making the diagnosis of Crohn's disease, as it allows direct visualization of the colon and the
terminal ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine ma ...
, identifying the pattern of disease involvement. On occasion, the colonoscope can travel past the terminal ileum, but it varies from person to person. During the procedure, the gastroenterologist can also perform a biopsy, taking small samples of tissue for laboratory analysis, which may help confirm a diagnosis. As 30% of Crohn's disease involves only the ileum,
cannulation of the terminal ileum is required in making the diagnosis. Finding a patchy distribution of disease, with involvement of the colon or ileum, but not the rectum, is suggestive of Crohn's disease, as are other endoscopic stigmata.
The utility of capsule endoscopy for this, however, is still uncertain. A 2025 clinical guideline indicated that video capsule endoscopy is a useful adjunct in the diagnosis of people with small bowel Crohn's disease.
Radiologic tests
A barium follow-through, small bowel follow-through may suggest the diagnosis of Crohn's disease and is useful when the disease involves only the small intestine. Because colonoscopy and Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, gastroscopy allow direct visualization of only the terminal ileum and beginning of the duodenum, they cannot be used to evaluate the remainder of the small intestine. As a result, a barium follow-through X-ray, wherein barium sulfate suspension is ingested and fluoroscopy, fluoroscopic images of the bowel are taken over time, is useful for looking for inflammation and narrowing of the small bowel.
Barium enemas, in which barium is inserted into the rectum and fluoroscopy is used to image the bowel, are rarely used in the work-up of Crohn's disease due to the advent of colonoscopy. They remain useful for identifying anatomical abnormalities when strictures of the colon are too small for a colonoscope to pass through, or in the detection of colonic fistulae (in this case contrast should be performed with iodate substances).
CT scan, CT and MRI scans are useful for evaluating the small bowel with enteroclysis protocols. They are also useful for looking for intra-abdominal complications of Crohn's disease, such as abscesses, small bowel obstructions, or fistulae. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is another option for imaging the small bowel as well as looking for complications, though it is more expensive and less readily available. MRI techniques such as diffusion-weighted imaging and high-resolution imaging are more sensitive in detecting ulceration and inflammation compared to CT.
Pediatrics considerations
Imaging in pediatric Crohn's disease requires careful consideration to minimize radiation exposure while ensuring accurate diagnosis and monitoring. Magnetic Resonance Enterography (MRE) is favored over Computed Tomography Enterography (CTE) due to its lack of ionizing radiation and superior soft tissue contrast. MRE effectively assesses bowel wall thickening, inflammation, and complications such as strictures or fistulas. However, it demands longer scan times and patient cooperation, which can be challenging for younger children.
Ultrasound (US), particularly contrast-enhanced ultrasound, serves as a valuable, radiation-free alternative for evaluating bowel wall thickness, vascularity, and inflammatory changes. It is especially useful for initial assessments and ongoing disease monitoring, though its effectiveness can be operator-dependent.
In urgent situations where rapid imaging is necessary to evaluate severe disease complications, such as bowel perforation or abscess formation, CTE may be utilized despite its associated radiation exposure.
Regular imaging follow-ups should be guided by clinical symptoms and biomarkers to minimize unnecessary scans. Emerging imaging techniques continue to improve the safety and efficacy of pediatric Crohn's disease evaluation.
Blood tests
A complete blood count may reveal anemia, which commonly is caused by blood loss leading to iron deficiency or by Cyanocobalamin, vitamin B deficiency, usually caused by ileal disease impairing vitamin B absorption. Rarely autoimmune hemolysis may occur. Ferritin levels help assess if iron deficiency is contributing to the anemia. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein help assess the degree of inflammation, which is important as ferritin can also be raised in inflammation.
Other causes of anemia include medication used in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease, like azathioprine, which can lead to cytopenia, and sulfasalazine, which can also result in folate deficiency. Testing for ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' antibodies (ASCA) and anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody, antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA) has been evaluated to identify inflammatory diseases of the intestine and to differentiate Crohn's disease from ulcerative colitis. Furthermore, increasing amounts and levels of serological antibodies such as ASCA, antilaminaribioside [Glc(β1,3)Glb(β); ALCA], antichitobioside [GlcNAc(β1,4)GlcNAc(β); ACCA], antimannobioside [Man(α1,3)Man(α)AMCA], antiLaminarin [(Glc(β1,3))3n(Glc(β1,6))n; anti-L] and antichitin [GlcNAc(β1,4)n; anti-C] associate with disease behavior and surgery, and may aid in the prognosis of Crohn's disease.
Low serum levels of vitamin D are associated with Crohn's disease.
Further studies are required to determine the significance of this association.
Comparison with ulcerative colitis
The most common disease that mimics the symptoms of Crohn's disease is ulcerative colitis, as both are inflammatory bowel diseases that can affect the colon with similar symptoms. It is important to differentiate these diseases, since the course of the diseases and treatments may be different. In some cases, however, it may not be possible to tell the difference, in which case the disease is classified as indeterminate colitis.
Differential diagnosis
Other conditions with similar symptoms as Crohn's disease includes intestinal tuberculosis,
Behçet's disease,
ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is one of the two types of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), with the other type being Crohn's disease. It is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary sympto ...
, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug enteropathy,
irritable bowel syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a functional gastrointestinal disorder characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain, abdominal bloating, and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may ...
and celiac disease.
Irritable bowel syndrome is excluded when there are inflammatory changes.
Celiac disease cannot be excluded if specific antibodies (Anti-transglutaminase antibodies#Anti-tissue transglutaminase, anti-transglutaminase antibodies) are negative, nor in the absence of intestinal villi atrophy.
Management
There is no cure for Crohn's disease and
remission may not be possible or prolonged if achieved. In cases where remission is possible,
relapse
In internal medicine, relapse or recidivism is a recurrence of a past (typically medical) condition. For example, multiple sclerosis and malaria often exhibit peaks of activity and sometimes very long periods of dormancy, followed by relapse or r ...
can be prevented and symptoms controlled with medication, lifestyle and dietary changes, changes to eating habits (eating smaller amounts more often), reduction of stress, moderate activity, and exercise. Surgery is generally contraindicated and has not been shown to prevent relapse. Adequately controlled, Crohn's disease may not significantly restrict daily living.
Treatment for Crohn's disease involves first treating the acute (medical), acute problem and its symptoms, then maintaining remission of the disease.
Lifestyle changes
Certain lifestyle changes can reduce symptoms, including Diet (nutrition), dietary adjustments, elemental diet, proper Drinking water, hydration, and smoking cessation. Some reviews underlined the importance to adopt diets that are best supported by evidence, even if little is known about the impact of diets on these people.
Diets that include higher levels of fiber and fruit are associated with reduced risk, while diets rich in total fats, polyunsaturated fatty acids, meat, and omega-6 fatty acids may increase the risk of Crohn's. Maintaining a balanced diet with proper portion control can help manage symptoms of the disease. Eating small meals frequently instead of big meals may also help with a low appetite. A food diary may help with identifying foods that trigger symptoms. Despite the recognized importance of dietary fiber for intestinal health, some people should follow a Low-fiber/low-residue diet, low residue diet to control acute symptoms especially if foods high in insoluble fiber cause symptoms, e.g., due to obstruction or irritation of the bowel.
Some find relief in eliminating casein (a protein found in cow's milk) and gluten (a protein found in wheat, rye and barley) from their diets. They may have specific dietary intolerances (not allergies), for example, lactose. Fatigue (medical), Fatigue can be helped with regular exercise, a healthy diet, and enough sleep, and for those with malabsorption of vitamin B12, vitamin B
12 due to disease or surgical resection of the
terminal ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine ma ...
, cobalamin injections. Smoking may worsen symptoms and the course of the disease, and stopping is recommended. Alcohol consumption can also worsen symptoms, and moderation or cessation is advised.
Medication
Acute treatment uses medications to treat any infection (normally antibiotics) and to reduce inflammation (normally
corticosteroid
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are invo ...
s). When symptoms are in remission, treatment enters maintenance, intending to avoid the recurrence of symptoms. Prolonged use of corticosteroids has significant Adverse effect (medicine), side-effects; as a result, they are, in general, not used for long-term treatment. Alternatives include aminosalicylates alone, though only a minority can maintain the treatment, and many require immunosuppressive drugs.
It has also been suggested that antibiotics change the enteric flora, and their continuous use may pose the risk of overgrowth with pathogens such as ''Clostridioides difficile (bacteria), Clostridioides difficile''.
Medications used to treat the symptoms of Crohn's disease include mesalazine, 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) formulations, prednisone, immunomodulators such as
azathioprine (given as the prodrug for 6-mercaptopurine),
methotrexate
Methotrexate, formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immunosuppressive drug, immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancy, ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is u ...
,
and anti-TNF therapies and monoclonal antibodies, such as infliximab, adalimumab,
certolizumab, vedolizumab, ustekinumab, natalizumab,Risankizumab, risankizumab-rzaa, and upadacitinib Hydrocortisone should be used in severe attacks of Crohn's disease.
Biological therapy for inflammatory bowel disease, Biological therapies are medications used to avoid long-term steroid use, decrease inflammation, and treat people who have fistulas with abscesses.
The monoclonal antibody ustekinumab appears to be a safe treatment option, and may help people with moderate to severe active Crohn's disease.
The long term safety and effectiveness of monoclonal antibody treatment is not known.
The monoclonal antibody briakinumab is not effective for people with active Crohn's disease and it is no longer being manufactured.
The gradual loss of blood from the gastrointestinal tract, as well as chronic inflammation, often leads to anemia, and professional guidelines suggest routine monitoring for this.
Immunosuppressant therapies, infection risks and vaccinations
Many people affected by Crohn's disease need immunosuppressant therapies, which are known to be associated with a higher risk of contracting opportunistic infectious diseases and of pre-neoplastic or neoplastic lesions such as cervical high-grade dysplasia and cancer.
Many of these potentially harmful diseases, such as Hepatitis B, Influenza, Varicella zoster virus, herpes zoster virus, pneumococcal pneumonia, or Human papillomavirus infection, human papilloma virus, can be prevented by vaccines.
Compared to the rest of the population, people affected by IBD are known to be at higher risk of contracting some vaccine-preventable diseases such as the flu and pneumonia.
Nevertheless, despite the increased risk of infections, vaccination rates in people with IBD are known to be suboptimal and may also be lower than vaccination rates in the general population.
Surgery
Crohn's cannot be cured by surgery, as the disease eventually recurs, though it is used in the case of partial or full blockage of the intestine. Surgery may also be required for complications such as obstructions, fistulas, or abscesses, or if the disease does not respond to drugs. After the first surgery, Crohn's usually comes back at the site where the diseased intestine was removed and the healthy ends were rejoined; it can also come back in other locations. After a resection, scar tissue builds up, which can cause stenosis, strictures, which form when the intestines become too small to allow excrement to pass through easily, which can lead to a blockage. After the first resection, another resection may be necessary within five years. For people with an obstruction due to a stricture, two options for treatment are strictureplasty and resection of that portion of the bowel. There is no statistical significance between strictureplasty alone versus strictureplasty and resection in cases of duodenal involvement. In these cases, re-operation rates were 31% and 27%, respectively, indicating that strictureplasty is a safe and effective treatment for selected people with duodenal involvement.
Postsurgical recurrence of Crohn's disease is relatively common. Crohn's lesions are nearly always found at the site of the resected bowel. The join (or Surgical anastomosis, anastomosis) after surgery may be inspected, usually during a colonoscopy, and disease activity graded. The "Rutgeerts score" is an endoscopic scoring system for postoperative disease recurrence in Crohn's disease. Postsurgical remission per the Rutgeerts score is graded as i0; while mild postsurgical recurrences are graded i1 and i2, and moderate to severe recurrences are graded i3 and i4.
Fewer lesions result in a lower grade. Based on the score, treatment plans can be designed to give the patient the best chance of managing the recurrence of the disease.
Short bowel syndrome (SBS, also short gut syndrome or simply short gut) is caused by the surgical removal of part of the small intestine. It usually develops in those people who have had half or more of their small intestines removed. Diarrhea is the main symptom, but others may include weight loss, cramping, bloating, and heartburn. Short bowel syndrome is treated with changes in diet, intravenous feeding, vitamin and mineral supplements, and treatment with medications. In some cases of SBS, intestinal transplant surgery may be considered; though the number of transplant centres offering this procedure is quite small and it comes with a high risk due to the chance of infection and rejection of the transplanted intestine.
Bile acid diarrhea is another complication following surgery for Crohn's disease in which the
terminal ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine ma ...
has been removed. This leads to the development of excessive watery diarrhea. It is usually thought to be due to an inability of the ileum to reabsorb bile acids after resection of the terminal ileum and was the first type of bile acid malabsorption recognized.
Microbiome modification
The use of oral probiotic supplements to modify the composition and behaviour of the gastrointestinal microbiome has been researched to understand whether it may help to improve remission rates in people with Crohn's disease. However, only two controlled trials were available in 2020, with no clear overall evidence of higher remission nor lower adverse effects, in people with Crohn's disease receiving probiotic supplementation.
Mental health
Crohn's may result in anxiety disorders, anxiety or mood disorders, especially in young people who may have stunted growth or embarrassment from fecal incontinence.
Counselling as well as antidepressant or anxiolytic medication may help some people manage.
there is a small amount of research looking at Mindfulness#Therapy programs, mindfulness-based therapies, hypnotherapy, and cognitive behavioural therapy. A meta analysis of interventions to improve mood (including talking therapy, Antidepressant, antidepressants, and exercise) in people with inflammatory bowel disease found that they reduced inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein and faecal calprotectin. Psychological therapies reduced inflammation more than antidepressants or exercise.
Alternative medicine
It is common for people with Crohn's disease to try complementary or alternative medicine, complementary or alternative therapy.
These include diets, probiotics, fish oil, and other Herbalism, herbal and nutritional supplements. A 2006 survey in Germany found that about half of people with IBD used some form of alternative medicine, with the most common being homeopathy, and a study in France found that about 30% used alternative medicine.
* There is insufficient evidence to recommend the use of acupuncture.
* Homeopathic preparations are of no benefit with this or any other condition.
* There is no good evidence that cannabis or cannabis oil are an effective or safe treatment.
Prognosis
Crohn's disease is a Chronic (medicine), chronic condition for which there is no known cure. It is characterised by periods of improvement followed by episodes when symptoms flare up. With treatment, most people achieve a healthy weight, and the mortality rate for the disease is relatively low. It can vary from being benign to very severe, and people with CD could experience just one episode or have continuous symptoms. It usually reoccurs, although some people can remain disease-free for years or decades. Up to 80% of people with Crohn's disease are hospitalized at some point during the course of their disease, with the highest rate occurring in the first year after diagnosis.
Most people diagnosed with Crohn's require surgery for complications or symptoms of the disease within their lifetime, although the rate associated with this is decreasing with better access to modern treatments. Most people with Crohn's live a normal lifespan. However, Crohn's disease is associated with a small increase in risk of small bowel and colorectal carcinoma (bowel cancer).
Epidemiology
The percentage of people with Crohn's disease has been determined in Norway and the United States and is similar at 6 to 7.1:100,000. The Crohn's & Colitis Foundation of America cites this number as approx 149:100,000; NIH cites 28 to 199 per 100,000.
Crohn's disease is more common in northern countries, and with higher rates still in the northern areas of these countries. The incidence of Crohn's disease is thought to be similar in Europe but lower in Asia and Africa.
It also has a higher incidence in Ashkenazi Jews
and smokers.
Crohn's disease begins most commonly in people in their teens and 20s, and people in their 50s through to their 70s.
It is rarely diagnosed in early childhood. It usually affects female children more severely than males. However, only slightly more women than men have Crohn's disease. Parents, siblings or children of people with Crohn's disease are 3 to 20 times more likely to develop the disease. Twin studies find that if one has the disease there is a 55% chance the other will too.
The incidence of Crohn's disease is increasing in Europe
and in newly industrialised countries.
For example, in Brazil, there has been an annual increase of 11% in the incidence of Crohn's disease since 1990.
History
Inflammatory bowel diseases were described by Giovanni Battista Morgagni (1682–1771) and by Scottish physician Thomas Kennedy Dalziel in 1913.
''Ileitis terminalis'' was first described by Polish surgeon Antoni Leśniowski in 1904, although it was not conclusively distinguished from intestinal tuberculosis.
In Poland, it is still called Leśniowski-Crohn's disease ().
Burrill Bernard Crohn, an American gastroenterologist at New York City's Mount Sinai Hospital, New York, Mount Sinai Hospital, described fourteen cases in 1932, and submitted them to the American Medical Association under the rubric of "Terminal ileitis: A new clinical entity". Later that year, he, along with colleagues
Leon Ginzburg and Gordon Oppenheimer, published the case series "Regional ileitis: a pathologic and clinical entity". However, due to the precedence of Crohn's name in the alphabet, it later became known in the worldwide literature as Crohn's disease.
References
Further reading
*
External links
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Crohn's Disease
Abdominal pain
Articles containing video clips
Autoimmune diseases
Crohn's disease
Inflammations
Membrane transport protein disorders
Noninfective enteritis and colitis
Steroid-responsive inflammatory conditions
Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate
Diseases named after discoverers
 Many people with Crohn's disease have symptoms for years before the diagnosis. The usual onset is in the teens and twenties, but can occur at any age. People with Crohn's disease experience chronic recurring periods of flare-ups and remission.
Many people with Crohn's disease have symptoms for years before the diagnosis. The usual onset is in the teens and twenties, but can occur at any age. People with Crohn's disease experience chronic recurring periods of flare-ups and remission.
 Crohn's disease can lead to several mechanical complications within the intestines, including Bowel obstruction, obstruction,
Crohn's disease can lead to several mechanical complications within the intestines, including Bowel obstruction, obstruction, 
 Crohn's has a genetic component. Because of this, siblings of known people with Crohn's are 30 times more likely to develop Crohn's than the general population.
The first mutation found to be associated with Crohn's was a frameshift mutation, frameshift in the NOD2 gene (also known as the CARD15 gene), followed by the discovery of point mutations. Over 30 genes have been associated with Crohn's; a biological function is known for most of them. For example, one association is with mutations in the XBP1 gene, which is involved in the unfolded protein response pathway of the endoplasmic reticulum. The gene variants of NOD2/CARD15 seem to be related with small-bowel involvement. Other well documented genes which increase the risk of developing Crohn's disease are ATG16L1, IL23R, IRGM, and SLC11A1.
There is considerable overlap between susceptibility loci for IBD and mycobacterial infections. Genome-wide association studies have shown that Crohn's disease is genetically linked to coeliac disease.
Crohn's has been linked to the gene LRRK2 with one variant potentially increasing the risk of developing the disease by 70%, while another lowers it by 25%. The gene is responsible for making a protein, which collects and eliminates waste product in cells, and is also associated with Parkinson's disease.
Crohn's has a genetic component. Because of this, siblings of known people with Crohn's are 30 times more likely to develop Crohn's than the general population.
The first mutation found to be associated with Crohn's was a frameshift mutation, frameshift in the NOD2 gene (also known as the CARD15 gene), followed by the discovery of point mutations. Over 30 genes have been associated with Crohn's; a biological function is known for most of them. For example, one association is with mutations in the XBP1 gene, which is involved in the unfolded protein response pathway of the endoplasmic reticulum. The gene variants of NOD2/CARD15 seem to be related with small-bowel involvement. Other well documented genes which increase the risk of developing Crohn's disease are ATG16L1, IL23R, IRGM, and SLC11A1.
There is considerable overlap between susceptibility loci for IBD and mycobacterial infections. Genome-wide association studies have shown that Crohn's disease is genetically linked to coeliac disease.
Crohn's has been linked to the gene LRRK2 with one variant potentially increasing the risk of developing the disease by 70%, while another lowers it by 25%. The gene is responsible for making a protein, which collects and eliminates waste product in cells, and is also associated with Parkinson's disease.