Crickets on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Crickets are
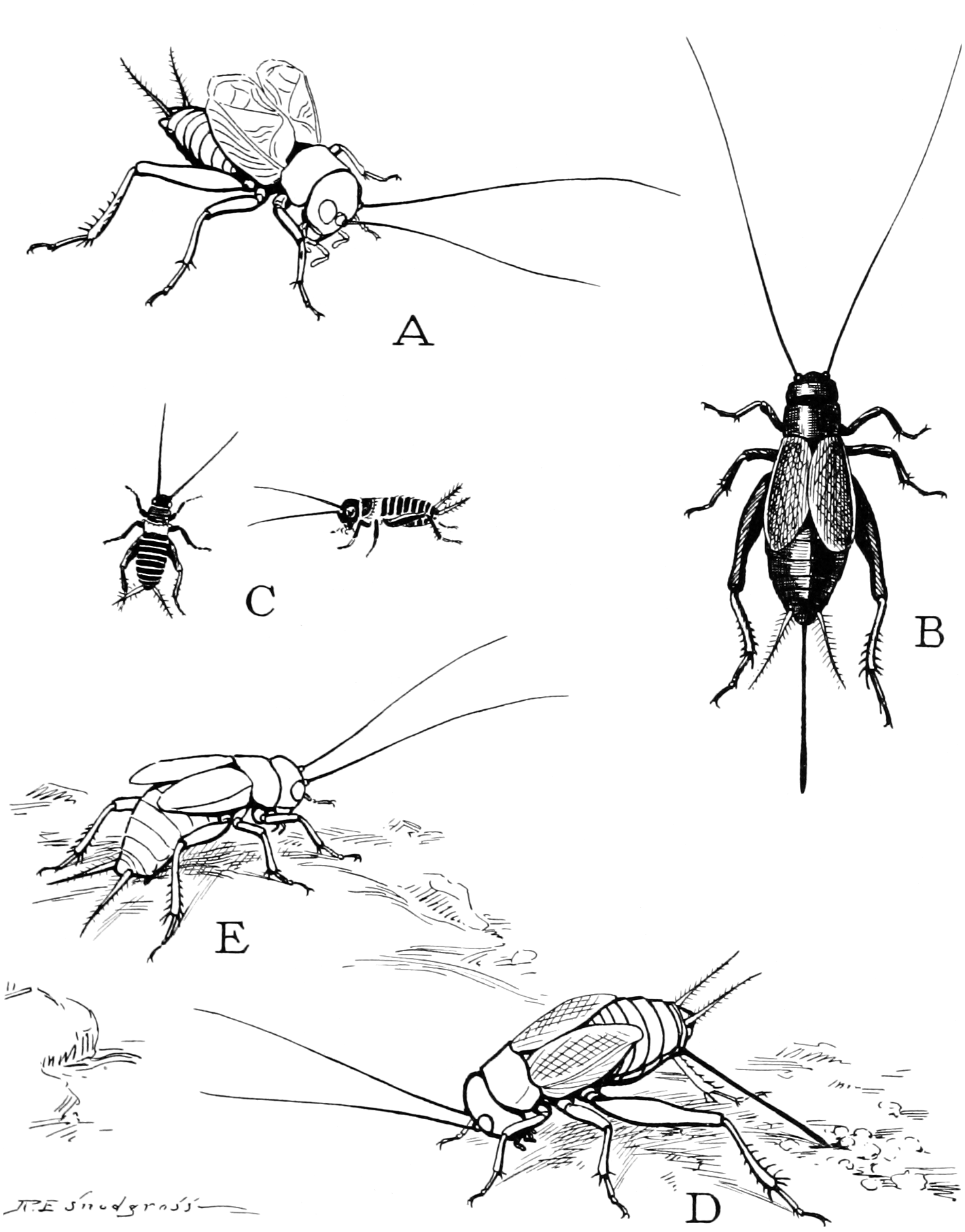
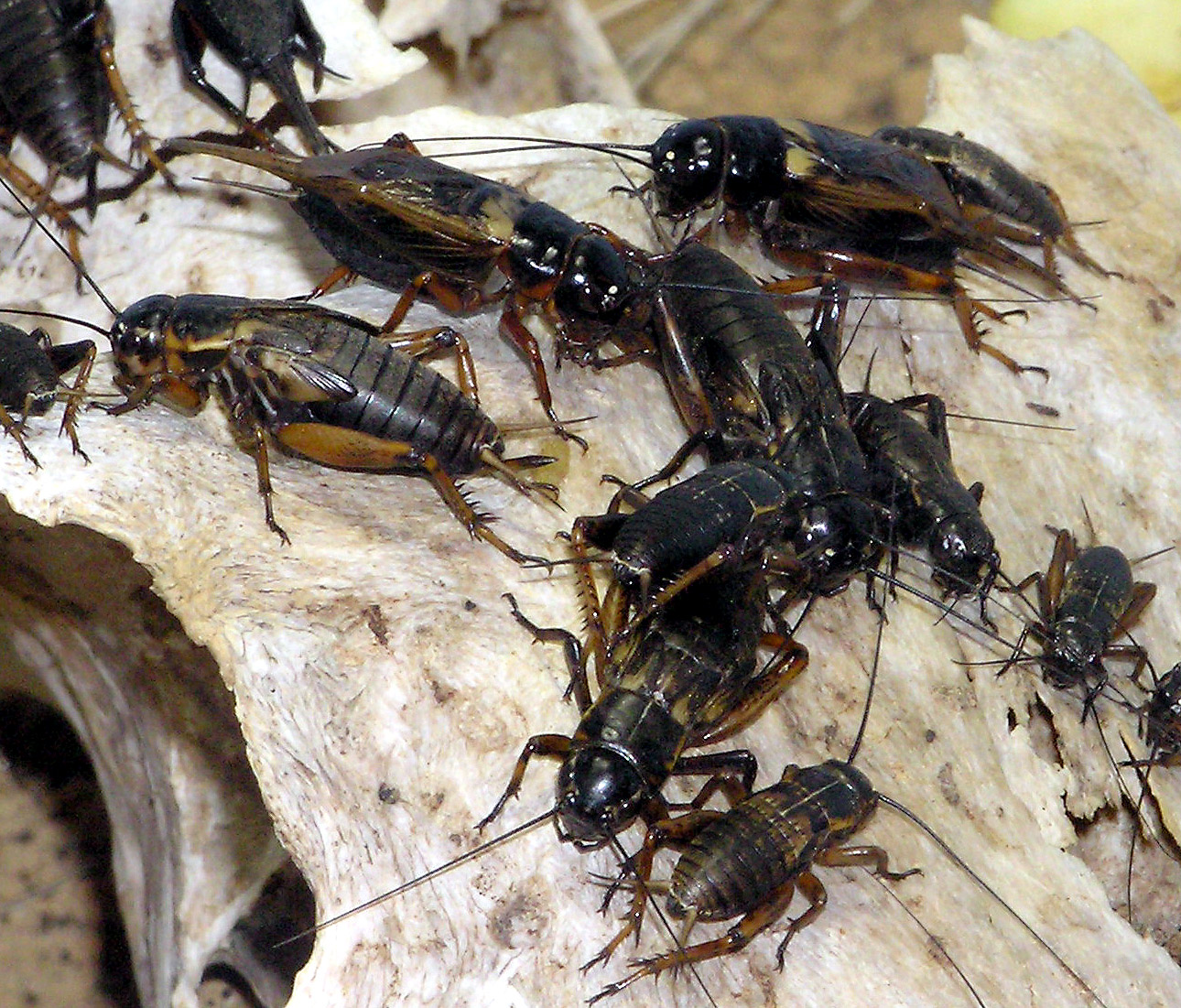 Crickets are small to medium-sized insects with mostly cylindrical, somewhat vertically flattened bodies. The head is spherical with long slender antennae arising from cone-shaped scapes (first segments) and just behind these are two large compound eyes. On the forehead are three ocelli (simple eyes). The
Crickets are small to medium-sized insects with mostly cylindrical, somewhat vertically flattened bodies. The head is spherical with long slender antennae arising from cone-shaped scapes (first segments) and just behind these are two large compound eyes. On the forehead are three ocelli (simple eyes). The
 Most male crickets make a loud chirping sound by
Most male crickets make a loud chirping sound by
 Captive crickets are
Captive crickets are
 Most crickets lay their eggs in the soil or inside the stems of plants, and to do this, female crickets have a long, needle-like or sabre-like egg-laying organ called an
Most crickets lay their eggs in the soil or inside the stems of plants, and to do this, female crickets have a long, needle-like or sabre-like egg-laying organ called an
 The entomopathogenic fungus '' Metarhizium anisopliae'' attacks and kills crickets and has been used as the basis of control in pest populations. The insects are also affected by the cricket paralysis virus, which has caused high levels of fatalities in cricket-rearing facilities. Other fatal diseases that have been identified in mass-rearing establishments include ''
The entomopathogenic fungus '' Metarhizium anisopliae'' attacks and kills crickets and has been used as the basis of control in pest populations. The insects are also affected by the cricket paralysis virus, which has caused high levels of fatalities in cricket-rearing facilities. Other fatal diseases that have been identified in mass-rearing establishments include ''
 The phylogenetic relationships of the Gryllidae, summarized by Darryl Gwynne in 1995 from his own work (using mainly anatomical characteristics) and that of earlier authors, are shown in the following
The phylogenetic relationships of the Gryllidae, summarized by Darryl Gwynne in 1995 from his own work (using mainly anatomical characteristics) and that of earlier authors, are shown in the following

 Crickets feature as major characters in novels and children's books.
Crickets feature as major characters in novels and children's books.
 Crickets are kept as pets and are considered good luck in some countries; in China, they are sometimes kept in cages or in hollowed-out
Crickets are kept as pets and are considered good luck in some countries; in China, they are sometimes kept in cages or in hollowed-out
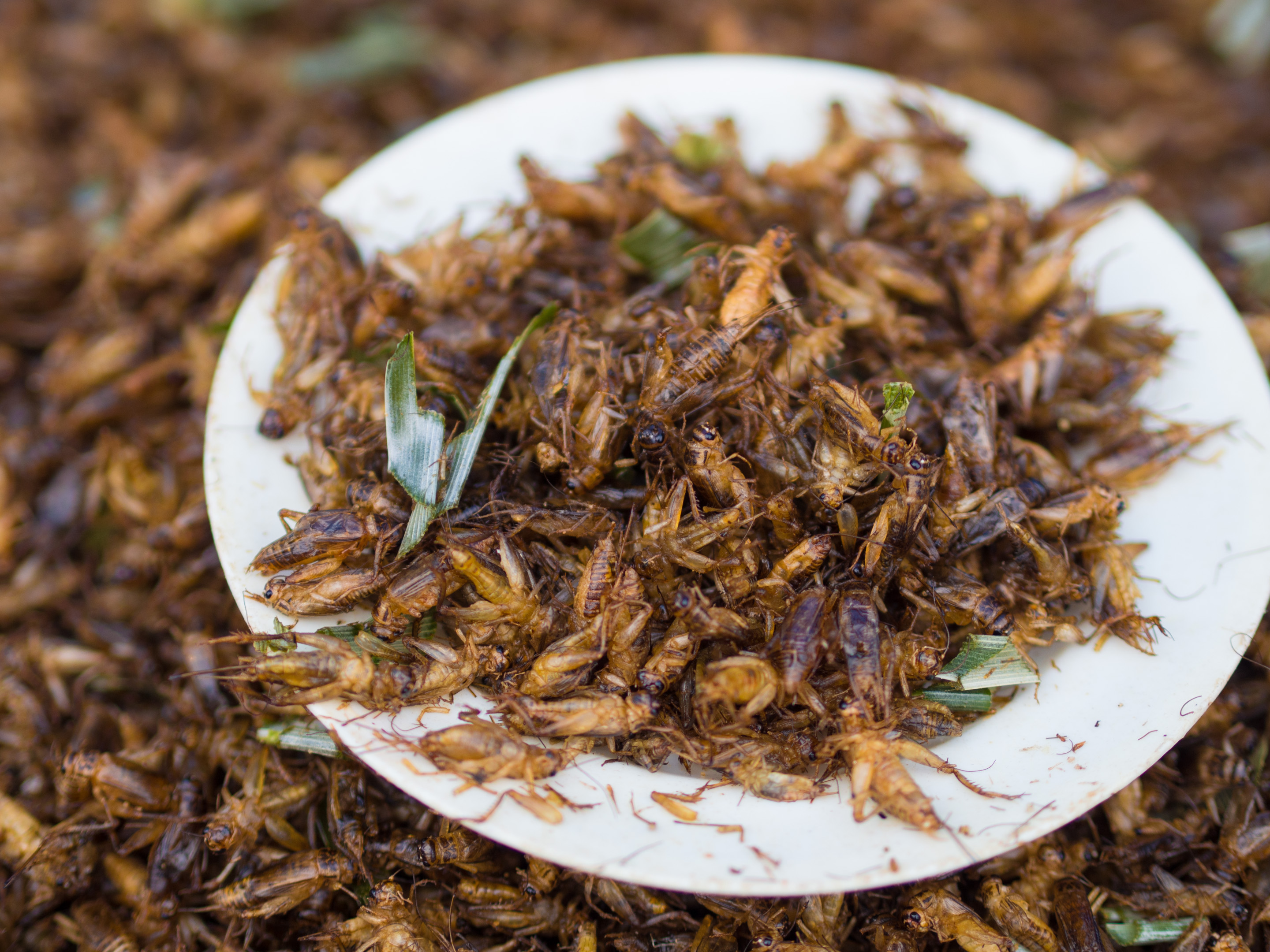 In the southern part of Asia including
In the southern part of Asia including
 Cricket characters feature in the
Cricket characters feature in the
Insect musicians & cricket champions: a cultural history of singing insects in China and Japan
'. China Books. . * Franz Huber, Thomas Edwin Moore, Werner Loher (1989).
Cricket behavior and neurobiology
'. Cornell University Press. .
{{Authority control * Extant Triassic first appearances Insect rearing Insects in culture
orthoptera
Orthoptera () is an order of insects that comprises the grasshoppers, locusts, and crickets, including closely related insects, such as the bush crickets or katydids and wētā. The order is subdivided into two suborders: Caelifera – grass ...
n insect
Insects (from Latin ') are pancrustacean hexapod invertebrates of the class Insecta. They are the largest group within the arthropod phylum. Insects have a chitinous exoskeleton, a three-part body (head, thorax and abdomen), three pairs ...
s which are related to bush cricket
Insects in the family Tettigoniidae are commonly called katydids (especially in North America), or bush crickets. They have previously been known as "long-horned grasshoppers". More than 8,000 species are known. Part of the suborder Ensifer ...
s, and, more distantly, to grasshoppers. In older literature, such as Imms
The Institute for Marine Mammal Studies ("IMMS") is a research organization located in Gulfport, Mississippi and dedicated to education, conservation, and research on marine mammals in the wild and in captivity. It was founded in 1984 as a researc ...
,Imms AD, rev. Richards OW & Davies RG (1970) ''A General Textbook of Entomology'' 9th Ed. Methuen 886 pp. "crickets" were placed at the family level (''i.e.'' Gryllidae
The family ''Gryllidae'' contains the subfamilies and genera which entomologists now term true crickets. Having long, whip-like antennae, they belong to the Orthopteran suborder Ensifera, which has been greatly reduced in the last 100 years ( ...
), but contemporary authorities including Otte now place them in the superfamily Grylloidea
Grylloidea is the superfamily of insects, in the order Orthoptera, known as crickets. It includes the " true crickets", scaly crickets, wood crickets and other families, some only known from fossils.
Grylloidea dates from the Triassic period ...
. The word has been used in combination to describe more distantly related taxa in the suborder Ensifera, such as king crickets and mole crickets.
Crickets have mainly cylindrically-shaped bodies, round heads, and long antennae. Behind the head is a smooth, robust pronotum
The prothorax is the foremost of the three segments in the thorax of an insect, and bears the first pair of legs. Its principal sclerites (exoskeletal plates) are the pronotum ( dorsal), the prosternum ( ventral), and the propleuron ( lateral) o ...
. The abdomen ends in a pair of long cerci; females have a long, cylindrical ovipositor
The ovipositor is a tube-like organ used by some animals, especially insects, for the laying of eggs. In insects, an ovipositor consists of a maximum of three pairs of appendages. The details and morphology of the ovipositor vary, but typica ...
. Diagnostic features include legs with 3-segmented tarsi; as with many Orthoptera, the hind legs have enlarged femora, providing power for jumping. The front wings are adapted as tough, leathery elytra, and some crickets chirp by rubbing parts of these together. The hind wings are membranous and folded when not in use for flight; many species, however, are flightless. The largest members of the family are the bull crickets, '' Brachytrupes'', which are up to long.
Crickets are distributed all around the world except at latitudes 55° or higher, with the greatest diversity being in the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred ...
. They occur in varied habitats from grassland, bushes, and forests to marshes, beaches, and caves. Crickets are mainly nocturnal
Nocturnality is an ethology, animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnality, diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatures generally have ...
, and are best known for the loud, persistent, chirping song of males trying to attract females, although some species are mute. The singing species have good hearing, via the tympana on the tibiae of the front legs.
Crickets often appear as characters in literature. The Talking Cricket features in Carlo Collodi's 1883 children's book, ''The Adventures of Pinocchio
''The Adventures of Pinocchio'' ( ; it, Le avventure di Pinocchio ; commonly shortened to ''Pinocchio'') is a children's fantasy novel by Italian author Carlo Collodi. It is about the mischievous adventures of an animated marionette named Pin ...
'', and in films based on the book. The insect is central to Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian e ...
's 1845 '' The Cricket on the Hearth'' and George Selden's 1960 '' The Cricket in Times Square''. Crickets are celebrated in poems by William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth (7 April 177023 April 1850) was an English Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romantic Age in English literature with their joint publication ''Lyrical Ballads'' (1798).
Wordsworth's '' ...
, John Keats
John Keats (31 October 1795 – 23 February 1821) was an English poet of the second generation of Romantic poets, with Lord Byron and Percy Bysshe Shelley. His poems had been in publication for less than four years when he died of tuberculo ...
, and Du Fu. They are kept as pets in countries from China to Europe, sometimes for cricket fighting. Crickets are efficient at converting their food into body mass, making them a candidate for food production. They are used as human food in Southeast Asia, where they are sold deep-fried in markets as snacks. They are also used to feed carnivorous pets and zoo animals. In Brazilian folklore, crickets feature as omens of various events.
Description
 Crickets are small to medium-sized insects with mostly cylindrical, somewhat vertically flattened bodies. The head is spherical with long slender antennae arising from cone-shaped scapes (first segments) and just behind these are two large compound eyes. On the forehead are three ocelli (simple eyes). The
Crickets are small to medium-sized insects with mostly cylindrical, somewhat vertically flattened bodies. The head is spherical with long slender antennae arising from cone-shaped scapes (first segments) and just behind these are two large compound eyes. On the forehead are three ocelli (simple eyes). The pronotum
The prothorax is the foremost of the three segments in the thorax of an insect, and bears the first pair of legs. Its principal sclerites (exoskeletal plates) are the pronotum ( dorsal), the prosternum ( ventral), and the propleuron ( lateral) o ...
(first thoracic segment) is trapezoidal in shape, robust, and well- sclerotized. It is smooth and has neither dorsal nor lateral keels (ridges).
At the tip of the abdomen is a pair of long cerci (paired appendages on rearmost segment), and in females, the ovipositor
The ovipositor is a tube-like organ used by some animals, especially insects, for the laying of eggs. In insects, an ovipositor consists of a maximum of three pairs of appendages. The details and morphology of the ovipositor vary, but typica ...
is cylindrical, long and narrow, smooth and shiny. The femora (third segments) of the back pair of legs are greatly enlarged for jumping. The tibiae (fourth segments) of the hind legs are armed with a number of moveable spurs, the arrangement of which is characteristic of each species. The tibiae of the front legs bear one or more tympani which are used for the reception of sound.
The wings lie flat on the body and are very variable in size between species, being reduced in size in some crickets and missing in others. The fore wings are elytra made of tough chitin
Chitin ( C8 H13 O5 N)n ( ) is a long-chain polymer of ''N''-acetylglucosamine, an amide derivative of glucose. Chitin is probably the second most abundant polysaccharide in nature (behind only cellulose); an estimated 1 billion tons of chit ...
, acting as a protective shield for the soft parts of the body and in males, bear the stridulatory
Stridulation is the act of producing sound by rubbing together certain body parts. This behavior is mostly associated with insects, but other animals are known to do this as well, such as a number of species of fish, snakes and spiders. The mech ...
organs for the production of sound. The hind pair is membranous, folding fan-wise under the fore wings. In many species, the wings are not adapted for flight.
The largest members of the family are the -long bull crickets ('' Brachytrupes'') which excavate burrows a metre or more deep. The tree crickets ( Oecanthinae) are delicate white or pale green insects with transparent fore wings, while the field crickets (Gryllinae
Gryllinae, or field crickets, are a subfamily of insects in the order Orthoptera and the family Gryllidae.
They hatch in spring, and the young crickets (called nymphs) eat and grow rapidly. They shed their skin ( molt) eight or more times bef ...
) are robust brown or black insects.
Distribution and habitat
Crickets have a cosmopolitan distribution, being found in all parts of the world with the exception of cold regions atlatitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north po ...
s higher than about 55° North and South. They have colonised many large and small islands, sometimes flying over the sea to reach these locations, or perhaps conveyed on floating timber or by human activity. The greatest diversity occurs in tropical locations, such as in Malaysia, where 88 species were heard chirping from a single location near Kuala Lumpur
, anthem = ''Maju dan Sejahtera''
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, pushpin_map = Malaysia#Southeast Asia#Asia
, pushpin_map_caption =
, coordinates =
, sub ...
. A greater number than this could have been present because some species are mute.
Crickets are found in many habitats. Members of several subfamilies are found in the upper tree canopy, in bushes, and among grasses and herbs. They also occur on the ground and in caves, and some are subterranean, excavating shallow or deep burrows. Some make home in rotting wood, and certain beach-dwelling species can run and jump over the surface of water.
Crickets can grow more legs
Biology
Defence
Crickets are relatively defenceless, soft-bodied insects. Most species arenocturnal
Nocturnality is an ethology, animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnality, diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatures generally have ...
and spend the day hidden in cracks, under bark, inside curling leaves, under stones or fallen logs, in leaf litter, or in the cracks in the ground that develop in dry weather. Some excavate their own shallow holes in rotting wood or underground and fold in their antennae to conceal their presence. Some of these burrows are temporary shelters, used for a single day, but others serve as more permanent residences and places for mating and laying eggs. Crickets burrow by loosening the soil with the mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bon ...
s and then carrying it with the limbs, flicking it backwards with the hind legs or pushing it with the head.
Other defensive strategies are the use of camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the b ...
, fleeing, and aggression
Aggression is overt or covert, often harmful, social interaction with the intention of inflicting damage or other harm upon another individual; although it can be channeled into creative and practical outlets for some. It may occur either reacti ...
. Some species have adopted colourings, shapes, and patterns that make it difficult for predators that hunt by sight to detect them. They tend to be dull shades of brown, grey, and green that blend into their background, and desert species tend to be pale. Some species can fly, but the mode of flight tends to be clumsy, so the most usual response to danger is to scuttle away to find a hiding place. While some crickets have a weak bite, a member of the Gryllacrididae or raspy crickets from Australia were found to have the strongest bite of any insect.
Chirping
 Most male crickets make a loud chirping sound by
Most male crickets make a loud chirping sound by stridulation
Stridulation is the act of producing sound by rubbing together certain body parts. This behavior is mostly associated with insects, but other animals are known to do this as well, such as a number of species of fish, snakes and spiders. The mech ...
(scraping two specially textured body parts together). The stridulatory organ is located on the tegmen
A tegmen (plural: ''tegmina'') designates the modified leathery front wing on an insect particularly in the orders Dermaptera (earwigs), Orthoptera (grasshoppers, crickets and similar families), Mantodea (praying mantis), Phasmatodea (stick and ...
, or fore wing, which is leathery in texture. A large vein runs along the centre of each tegmen, with comb-like serrations on its edge forming a file-like structure, and at the rear edge of the tegmen is a scraper. The tegmina are held at an angle to the body and rhythmically raised and lowered which causes the scraper on one wing to rasp on the file on the other. The central part of the tegmen contains the "harp", an area of thick, sclerotized membrane which resonates and amplifies the volume of sound, as does the pocket of air between the tegmina and the body wall. Most female crickets lack the necessary adaptations to stridulate, so make no sound.
Several types of cricket songs are in the repertoire of some species. The calling song attracts females and repels other males, and is fairly loud. The courting song is used when a female cricket is near and encourages her to mate with the caller. A triumphal song is produced for a brief period after a successful mating and may reinforce the mating bond to encourage the female to lay some eggs rather than find another male. An aggressive song is triggered by contact chemoreceptor
A chemoreceptor, also known as chemosensor, is a specialized sensory receptor which transduces a chemical substance (endogenous or induced) to generate a biological signal. This signal may be in the form of an action potential, if the chemorecep ...
s on the antennae that detect the presence of another male cricket.
Crickets chirp at different rates depending on their species and the temperature of their environment
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, all living and non-living things occurring naturally
* Biophysical environment, the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism or ...
. Most species chirp at higher rates the higher the temperature is (about 62 chirps a minute at in one common species; each species has its own rate). The relationship between temperature and the rate of chirping is known as Dolbear's law. According to this law, counting the number of chirps produced in 14 seconds by the snowy tree cricket, common in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
, and adding 40 will approximate the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit.
In 1975, Dr. William H. Cade
Dr. William H. "Bill" Cade is a biologist and a former president of the University of Lethbridge. He researches the role of acoustic signals in field cricket mating behaviour.
Education
Cade completed his BA (1968), MA (1972) and PhD (1976) in ...
discovered that the parasitic
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
tachinid fly '' Ormia ochracea'' is attracted to the song of the cricket, and uses it to locate the male to deposit her larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle.
Th ...
e on him. It was the first known example of a natural enemy that locates its host or prey using the mating signal. Since then, many species of crickets have been found to be carrying the same parasitic fly, or related species. In response to this selective pressure, a mutation leaving males unable to chirp was observed amongst a population of '' Teleogryllus oceanicus'' on the Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only ...
an island of Kauai, enabling these crickets to elude their parasitoid predators. A different mutation with the same effect was also discovered on the neighboring island of Oahu (ca. away). Recently, new "purring" males of the same species in Hawaii are able to produce a novel auditory sexual signal that can be used to attract females while greatly reducing the likelihood of parasitoid attack from the fly.
Flight
Some species, such as the ground crickets ( Nemobiinae), are wingless; others have small fore wings and no hind wings (''Copholandrevus
''Copholandrevus'' is an Australian genus of crickets in the tribe
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English language, English is ...
''), others lack hind wings and have shortened fore wings in females only, while others are macropterous, with the hind wings longer than the fore wings. In '' Teleogryllus'', the proportion of macropterous individuals varies from very low to 100%. Probably, most species with hind wings longer than fore wings engage in flight.
Some species, such as ''Gryllus assimilis
''Gryllus assimilis'', commonly known as the Jamaican field cricket and sometimes referred to as the silent cricket (a misnomer) among other names, is one of many cricket species known as a field cricket. Its natural habitats are the West Indies ...
'', take off, fly, and land efficiently and well, while other species are clumsy fliers. In some species, the hind wings are shed, leaving wing stumps, usually after dispersal of the insect by flight. In other species, they may be pulled off and consumed by the cricket itself or by another individual, probably providing a nutritional boost.
'' Gryllus firmus'' exhibits wing polymorphism
Polymorphism, polymorphic, polymorph, polymorphous, or polymorphy may refer to:
Computing
* Polymorphism (computer science), the ability in programming to present the same programming interface for differing underlying forms
* Ad hoc polymorphis ...
; some individuals have fully functional, long hind wings and others have short wings and cannot fly. The short-winged females have smaller flight muscles, greater ovarian development, and produce more eggs, so the polymorphism adapts the cricket for either dispersal or reproduction. In some long-winged individuals, the flight muscles deteriorate during adulthood and the insect's reproductive capabilities improve.
Diet
 Captive crickets are
Captive crickets are omnivorous
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nut ...
; when deprived of their natural diet, they accept a wide range of organic foodstuffs. Some species are completely herbivorous
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
, feeding on flowers, fruit, and leaves, with ground-based species consuming seedlings, grasses, pieces of leaf, and the shoots of young plants. Others are more predatory
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill t ...
and include in their diet invertebrate eggs, larvae, pupae, moulting insects, scale insect
Scale insects are small insects of the order Hemiptera, suborder Sternorrhyncha. Of dramatically variable appearance and extreme sexual dimorphism, they comprise the infraorder Coccomorpha which is considered a more convenient grouping than th ...
s, and aphid
Aphids are small sap-sucking insects and members of the superfamily Aphidoidea. Common names include greenfly and blackfly, although individuals within a species can vary widely in color. The group includes the fluffy white woolly aphids. A ...
s. Many are scavengers and consume various organic remains, decaying plants, seedlings, and fungi. In captivity, many species have been successfully raised on a diet of ground, commercial dry dog food, supplemented with lettuce
Lettuce (''Lactuca sativa'') is an annual plant of the family Asteraceae. It is most often grown as a leaf vegetable, but sometimes for its stem and seeds. Lettuce is most often used for salads, although it is also seen in other kinds of foo ...
and aphids.
Crickets have relatively powerful jaws, and several species have been known to bite humans.
Reproduction and lifecycle
Male crickets establish their dominance over each other by aggression. They start by lashing each other with their antennae and flaring their mandibles. Unless one retreats at this stage, they resort to grappling, at the same time each emitting calls that are quite unlike those uttered in other circumstances. When one achieves dominance, it sings loudly, while the loser remains silent. Females are generally attracted to males by their calls, though in nonstridulatory species, some other mechanism must be involved. After the pair has made antennal contact, a courtship period may occur during which the character of the call changes. The female mounts the male and a single spermatophore is transferred to the external genitalia of the female. Sperm flows from this into the female'soviduct
The oviduct in mammals, is the passageway from an ovary. In human females this is more usually known as the Fallopian tube or uterine tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, ...
over a period of a few minutes or up to an hour, depending on species. After copulation, the female may remove or eat the spermatophore; males may attempt to prevent this with various ritualised behaviours. The female may mate on several occasions with different males.
 Most crickets lay their eggs in the soil or inside the stems of plants, and to do this, female crickets have a long, needle-like or sabre-like egg-laying organ called an
Most crickets lay their eggs in the soil or inside the stems of plants, and to do this, female crickets have a long, needle-like or sabre-like egg-laying organ called an ovipositor
The ovipositor is a tube-like organ used by some animals, especially insects, for the laying of eggs. In insects, an ovipositor consists of a maximum of three pairs of appendages. The details and morphology of the ovipositor vary, but typica ...
. Some ground-dwelling species have dispensed with this, either depositing their eggs in an underground chamber or pushing them into the wall of a burrow. The short-tailed cricket (''Anurogryllus
''Anurogryllus'', commonly known as short-tailed crickets, is a genus of crickets in the tribe Gryllini; species are recorded from the Americas. The common and scientific names derive from the vestigial, poorly developed ovipositors of females. ...
'') excavates a burrow with chambers and a defecating area, lays its eggs in a pile on a chamber floor, and after the eggs have hatched, feeds the juveniles for about a month.
Crickets are hemimetabolic insects, whose lifecycle consists of an egg stage, a larval or nymph
A nymph ( grc, νύμφη, nýmphē, el, script=Latn, nímfi, label=Modern Greek; , ) in ancient Greek folklore is a minor female nature deity. Different from Greek goddesses, nymphs are generally regarded as personifications of nature, are ty ...
stage that increasingly resembles the adult form as the nymph grows, and an adult stage. The egg hatches into a nymph about the size of a fruit fly. This passes through about 10 larval stages, and with each successive moult
In biology, moulting (British English), or molting (American English), also known as sloughing, shedding, or in many invertebrates, ecdysis, is the manner in which an animal routinely casts off a part of its body (often, but not always, an outer ...
, it becomes more like an adult. After the final moult, the genitalia and wings are fully developed, but a period of maturation is needed before the cricket is ready to breed.
Inbreeding avoidance
Some species of cricket are polyandrous. In '' Gryllus bimaculatus'', the females select and mate with multiple viable sperm donors, preferring novel mates. Female '' Teleogryllus oceanicus'' crickets from natural populations similarly mate and store sperm from multiple males. Female crickets exert a postcopulatoryfertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Pro ...
bias in favour of unrelated males to avoid the genetic consequences of inbreeding
Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely related genetically. By analogy, the term is used in human reproduction, but more commonly refers to the genetic disorders an ...
. Fertilization bias depends on the control of sperm transport to the sperm storage organs. The inhibition of sperm storage by female crickets can act as a form of cryptic female choice to avoid the severe negative effects of inbreeding. Controlled-breeding experiments with the cricket ''Gryllus firmus'' demonstrated inbreeding depression, as nymphal weight and early fecundity
Fecundity is defined in two ways; in human demography, it is the potential for reproduction of a recorded population as opposed to a sole organism, while in population biology, it is considered similar to fertility, the natural capability to pr ...
declined substantially over the generations' this was caused as expected by an increased frequency of homozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mo ...
combinations of deleterious recessive alleles.
Predators, parasites, and pathogens
Crickets have many natural enemies and are subject to variouspathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a ger ...
s and parasites. They are eaten by large numbers of vertebrate and invertebrate predators and their hard parts are often found during the examination of animal intestines. Mediterranean house geckos (''Hemidactylus turcicus'') have learned that although a calling decorated cricket (''Gryllodes supplicans'') may be safely positioned in an out-of-reach burrow, female crickets attracted to the call can be intercepted and eaten.
 The entomopathogenic fungus '' Metarhizium anisopliae'' attacks and kills crickets and has been used as the basis of control in pest populations. The insects are also affected by the cricket paralysis virus, which has caused high levels of fatalities in cricket-rearing facilities. Other fatal diseases that have been identified in mass-rearing establishments include ''
The entomopathogenic fungus '' Metarhizium anisopliae'' attacks and kills crickets and has been used as the basis of control in pest populations. The insects are also affected by the cricket paralysis virus, which has caused high levels of fatalities in cricket-rearing facilities. Other fatal diseases that have been identified in mass-rearing establishments include ''Rickettsia
''Rickettsia'' is a genus of nonmotile, gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci (0.1 μm in diameter), bacilli (1–4 μm long), or threads (up to about 10 μm long). The term "ricke ...
'' and three further viruses. The diseases may spread more rapidly if the crickets become cannibalistic and eat the corpses.
Red parasitic mites sometimes attach themselves to the dorsal region of crickets and may greatly affect them. The horsehair worm ''Paragordius varius
''Paragordius varius'' is a parasite species in the horsehair worm group (Nematomorpha). They cycle between terrestrial and aquatic habitats and are most commonly known for their ability to manipulate their definitive host to jump into a pool of ...
'' is an internal parasite and can control the behaviour of its cricket host and cause it to enter water, where the parasite continues its lifecycle and the cricket likely drowns. The larvae of the sarcophagid fly ''Sarcophaga kellyi
''Sarcophaga'' is a genus of true flies and the type genus of the flesh-fly family (Sarcophagidae). The members of this cosmopolitan genus are frequently known as common flesh flies.
This genus occurs essentially worldwide. These flies are gene ...
'' develop inside the body cavity of field crickets. Female parasitic wasps of '' Rhopalosoma'' lay their eggs on crickets, and their developing larvae gradually devour their hosts. Other wasps in the family Scelionidae are egg parasitoids, seeking out batches of eggs laid by crickets in plant tissues in which to insert their eggs.
The fly ''Ormia ochracea'' has very acute hearing and targets calling male crickets. It locates its prey by ear and then lays its eggs nearby. The developing larvae burrow inside any crickets with which they come in contact and in the course of a week or so, devour what remains of the host before pupating. In Florida, the parasitic flies were only present in the autumn, and at that time of year, the males sang less but for longer periods. A trade-off exists for the male between attracting females and being parasitized.
Phylogeny and taxonomy
 The phylogenetic relationships of the Gryllidae, summarized by Darryl Gwynne in 1995 from his own work (using mainly anatomical characteristics) and that of earlier authors, are shown in the following
The phylogenetic relationships of the Gryllidae, summarized by Darryl Gwynne in 1995 from his own work (using mainly anatomical characteristics) and that of earlier authors, are shown in the following cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to ...
, with the Orthoptera divided into two main groups, Ensifera (crickets '' sensu lato'') and Caelifera (grasshoppers). Fossil Ensifera are found from the late Carboniferous period (300 Mya) onwards, and the true crickets, Gryllidae, from the Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period ...
period (250 to 200 Mya).
Cladogram after Gwynne, 1995:
A phylogenetic study by Jost & Shaw in 2006 using sequences from 18S, 28S, and 16S rRNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from riboso ...
supported the monophyly of Ensifera. Most ensiferan families were also found to be monophyletic, and the superfamily Gryllacridoidea was found to include Stenopelmatidae, Anostostomatidae, Gryllacrididae and Lezina. Schizodactylidae and Grylloidea were shown to be sister taxa, and Rhaphidophoridae and Tettigoniidae were found to be more closely related to Grylloidea than had previously been thought. The authors stated that "a high degree of conflict exists between the molecular and morphological data, possibly indicating that much homoplasy is present in Ensifera, particularly in acoustic structures." They considered that tegmen stridulation and tibial tympanae are ancestral to Ensifera and have been lost on multiple occasions, especially within the Gryllidae.
"Cricket" families
Several families and other taxa in the Ensifera may be called "crickets", including: ;Within the Grylloidea: *Gryllidae
The family ''Gryllidae'' contains the subfamilies and genera which entomologists now term true crickets. Having long, whip-like antennae, they belong to the Orthopteran suborder Ensifera, which has been greatly reduced in the last 100 years ( ...
– "true crickets"
* Mogoplistidae – scaly crickets;
* Phalangopsidae
The Phalangopsidae are a recently reconstituted family of crickets (Orthoptera: Ensifera), based on the type genus ''Phalangopsis'' Serville, 1831 from South America. Priority for family-group names based on this genus dates from Blanchard's " ...
– "spider-crickets" and their allies;
* Trigonidiidae - sword-tail crickets and wood or ground-crickets.
* other families in the infraorder Gryllidea
GryllideaKevan DKM (1982) In Parker d. ''Synopsis and Classification of Living Organisms'' 2: 361. is an infraorder that includes crickets and similar insects in the order Orthoptera. There are two superfamilies, and more than 6,000 described s ...
may be included:
** Gryllotalpidae – mole crickets;
** Myrmecophilidae – ant crickets.
;Strictly, taxa in Infraorder Tettigoniidea
Tettigoniidea is an infraorder of the order Orthoptera, with six extant families.
Families
The ''Orthoptera Species File'' lists:
*superfamily Hagloidea Handlirsch, 1906
** † Eospilopteronidae Cockerell, 1916
** †Haglidae Handlirsch, 1906
** ...
and other superfamilies are excluded:
* Tettigoniidae
Insects in the family Tettigoniidae are commonly called katydids (especially in North America), or bush crickets. They have previously been known as "long-horned grasshoppers". More than 8,000 species are known. Part of the suborder Ensifera, ...
– the bush crickets or katydids – which are quite distinct and unrelated, with 4-segmented tarsi (at least in the middle and hind legs) and females with flattened ovipositor
The ovipositor is a tube-like organ used by some animals, especially insects, for the laying of eggs. In insects, an ovipositor consists of a maximum of three pairs of appendages. The details and morphology of the ovipositor vary, but typica ...
s. Also note:
** within this family is the genus Anabrus
''Anabrus'' is a genus of insects in the family Tettigoniidae that includes the Mormon cricket
The Mormon cricket (''Anabrus simplex'') is a large insect that can grow to almost in length. It lives throughout western North America in rangelan ...
– the "mormon crickets";
** "bush crickets" (American usage) include members of the subfamily Trigonidiinae – which are " true crickets".
* Superfamily Stenopelmatoidea – includes: king crickets (wētā), leaf-rolling, Jerusalem or sand crickets;
* Superfamily Rhaphidophoroidea – cave or camel crickets;
* Superfamily Schizodactyloidea - dune or splay-footed crickets.
In human culture

Folklore and myth
The folklore and mythology surrounding crickets is extensive. The singing of crickets in the folklore of Brazil and elsewhere is sometimes taken to be a sign of impending rain, or of a financial windfall. InÁlvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca
Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca (; 1488/90/92"Cabeza de Vaca, Alvar Núñez (1492?-1559?)." American Eras. Vol. 1: Early American Civilizations and Exploration to 1600. Detroit: Gale, 1997. 50-51. Gale Virtual Reference Library. Web. 10 Decembe ...
's chronicles of the Spanish conquest of the Americas, the sudden chirping of a cricket heralded the sighting of land for his crew, just as their water supply had run out. In Caraguatatuba, Brazil, a black cricket in a room is said to portend illness; a grey one, money; and a green one, hope
Hope is an optimistic state of mind that is based on an expectation of positive outcomes with respect to events and circumstances in one's life or the world at large.
As a verb, its definitions include: "expect with confidence" and "to cherish ...
. In Alagoas
Alagoas (, ) is one of the 27 federative units of Brazil and is situated in the eastern part of the Northeast Region. It borders: Pernambuco (N and NW); Sergipe (S); Bahia (SW); and the Atlantic Ocean (E). Its capital is the city of Maceió. ...
state, northeast Brazil, a cricket announces death, thus it is killed if it chirps in a house. In Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate ...
, a loud cricket means money is coming in; hence, a cricket must not be killed or evicted if it chirps inside a house. However, another type of cricket that is less noisy forebodes illness or death.
In literature
 Crickets feature as major characters in novels and children's books.
Crickets feature as major characters in novels and children's books. Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian e ...
's 1845 novella '' The Cricket on the Hearth'', divided into sections called "Chirps", tells the story of a cricket which chirps on the hearth and acts as a guardian angel
A guardian angel is a type of angel that is assigned to protect and guide a particular person, group or nation. Belief in tutelary deity, tutelary beings can be traced throughout all antiquity. The idea of angels that guard over people played a ...
to a family. Carlo Collodi's 1883 children's book "Le avventure di Pinocchio" (''The Adventures of Pinocchio
''The Adventures of Pinocchio'' ( ; it, Le avventure di Pinocchio ; commonly shortened to ''Pinocchio'') is a children's fantasy novel by Italian author Carlo Collodi. It is about the mischievous adventures of an animated marionette named Pin ...
'') featured "Il Grillo Parlante" (The Talking Cricket) as one of its characters. George Selden's 1960 children's book '' The Cricket in Times Square'' tells the story of Chester the cricket from Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. Its cap ...
who joins a family and their other animals, and is taken to see Times Square
Times Square is a major commercial intersection, tourist destination, entertainment hub, and neighborhood in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. It is formed by the junction of Broadway, Seventh Avenue, and 42nd Street. Together with adjacent ...
in New York. The story, which won the Newbery Honor, came to Selden on hearing a real cricket chirp in Times Square.
''Souvenirs entomologiques'', a book written by the French entomologist Jean-Henri Fabre
Jean-Henri Casimir Fabre (21 December 1823 – 11 October 1915) was a French naturalist, entomologist, and author known for the lively style of his popular books on the lives of insects.
Biography
Fabre was born on 21 December 1823 in Saint-L ...
, devotes a whole chapter to the cricket, discussing its construction of a burrow and its song-making. The account is mainly of the field cricket, but also mentions the Italian cricket.
Crickets have from time to time appeared in poetry. William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth (7 April 177023 April 1850) was an English Romantic poet who, with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, helped to launch the Romantic Age in English literature with their joint publication ''Lyrical Ballads'' (1798).
Wordsworth's '' ...
's 1805 poem ''The Cottager to Her Infant'' includes the couplet "The kitten sleeps upon the hearth, The crickets long have ceased their mirth". John Keats
John Keats (31 October 1795 – 23 February 1821) was an English poet of the second generation of Romantic poets, with Lord Byron and Percy Bysshe Shelley. His poems had been in publication for less than four years when he died of tuberculo ...
's 1819 poem ''Ode to Autumn
"To Autumn" is a poem by English Romantic poet John Keats (31 October 1795 – 23 February 1821). The work was composed on 19 September 1819 and published in 1820 in a volume of Keats's poetry that included ''Lamia'' and ''The Eve of St. Agne ...
'' includes the lines "Hedge-crickets sing; and now with treble soft / The redbreast whistles from a garden-croft". The Chinese Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdo ...
poet Du Fu (712–770) wrote a poem that in the translation by J. P. Seaton begins "House cricket ... Trifling thing. And yet how his mournful song moves us. Out in the grass his cry was a tremble, But now, he trills beneath our bed, to share his sorrow."
As pets and fighting animals
 Crickets are kept as pets and are considered good luck in some countries; in China, they are sometimes kept in cages or in hollowed-out
Crickets are kept as pets and are considered good luck in some countries; in China, they are sometimes kept in cages or in hollowed-out gourd
Gourds include the fruits of some flowering plant species in the family Cucurbitaceae, particularly '' Cucurbita'' and '' Lagenaria''. The term refers to a number of species and subspecies, many with hard shells, and some without. One of the e ...
s specially created in novel shapes. The practice was common in Japan for thousands of years; it peaked in the 19th century, though crickets are still sold at pet shops.Huber et al., p. 40. It is also common to have them as caged pets in some Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located enti ...
an countries, particularly in the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
. Cricket fighting
Cricket fighting is a hobby and gambling activity involving the fighting of male crickets.
is a traditional Chinese pastime that dates back to the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdo ...
(618–907). Originally an indulgence of emperors, cricket fighting later became popular among commoners. The dominance and fighting ability of males does not depend on strength alone; it has been found that they become more aggressive after certain pre-fight experiences such as isolation, or when defending a refuge. Crickets forced to fly for a short while will afterwards fight for two to three times longer than they otherwise would.
As food
 In the southern part of Asia including
In the southern part of Asia including Cambodia
Cambodia (; also Kampuchea ; km, កម្ពុជា, UNGEGN: ), officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country located in the southern portion of the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia, spanning an area of , bordered by Thailan ...
, Laos, Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
, and Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making it ...
, crickets commonly are eaten as a snack, prepared by deep frying soaked and cleaned insects. In Thailand, there are 20,000 farmers rearing crickets, with an estimated production of 7,500 tons per year and United Nation's FAO has implemented a project in Laos to improve cricket farming and, consequently, food security. The food conversion efficiency of house crickets (''Acheta domesticus'') is 1.7, some five times higher than that for beef cattle
Beef cattle are cattle raised for meat production (as distinguished from dairy cattle, used for milk production). The meat of mature or almost mature cattle is mostly known as beef.
In beef production there are three main stages: cow-calf oper ...
, and if their fecundity is taken into account, 15 to 20 times higher.
Cricket flour
Cricket flour (or cricket powder) is a protein-rich powder made from crickets, using various processes. Cricket flour differs from true flours made from grains by being composed mainly of protein rather than starches and dietary fiber.
Nutritiona ...
may be used as an additive to consumer foods such as pasta, bread, crackers, and cookies. The cricket flour is being used in protein bars
Protein bars are nutrition bars that contain a high proportion of protein to carbohydrates/ fats.
Dietary purpose
Protein bars are targeted to people who primarily want a convenient source of protein that does not require preparation (unless h ...
, pet foods
Pet food is animal feed intended for consumption by pets. Typically sold in pet stores and supermarkets, it is usually specific to the type of animal, such as dog food or cat food. Most meat used for animals is a byproduct of the human food in ...
, livestock feed, nutraceuticals
A nutraceutical or bioceutical is a pharmaceutical alternative which claims physiological benefits. In the US, "nutraceuticals" are largely unregulated, as they exist in the same category as dietary supplements and food additives by the FDA, un ...
, and other industrial uses. The United Nations says the use of insect protein, such as cricket flour, could be critical in feeding the growing population of the planet while being less damaging to the environment.
Crickets are also raised as food for carnivorous zoo animals, laboratory animals, and pets. They may be "gut loaded" with additional minerals, such as calcium, to provide a balanced diet for predators such as tree frogs (Hylidae
Hylidae is a wide-ranging family of frogs commonly referred to as " tree frogs and their allies". However, the hylids include a diversity of frog species, many of which do not live in trees, but are terrestrial or semiaquatic.
Taxonomy and ...
).
Common expressions
By the 19th century "cricket" and "crickets" were in use aseuphemism
A euphemism () is an innocuous word or expression used in place of one that is deemed offensive or suggests something unpleasant. Some euphemisms are intended to amuse, while others use bland, inoffensive terms for concepts that the user wishes ...
s for using Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religi ...
as an interjection
An interjection is a word or expression that occurs as an utterance on its own and expresses a spontaneous feeling or reaction. It is a diverse category, encompassing many different parts of speech, such as exclamations ''(ouch!'', ''wow!''), curse ...
. The addition of "Jiminy" (a variation of " Gemini"), sometimes shortened to "Jimmy" created the expressions "Jiminy Cricket!" or "Jimmy Crickets!" as less blasphemous alternatives to exclaiming "Jesus Christ!"
By the end of the 20th century the sound of chirping crickets came to represent quietude in literature, theatre and film. From this sentiment arose expressions equating "crickets" with silence altogether, particularly when a group of assembled people makes no noise. These expressions have grown from the more descriptive, "so quiet that you can hear crickets," to simply saying, "crickets" as shorthand for "complete silence."
In popular culture
 Cricket characters feature in the
Cricket characters feature in the Walt Disney
Walter Elias Disney (; December 5, 1901December 15, 1966) was an American animator, film producer and entrepreneur. A pioneer of the American animation industry, he introduced several developments in the production of cartoons. As a film p ...
animated movies ''Pinocchio
Pinocchio ( , ) is a fictional character and the protagonist of the children's novel ''The Adventures of Pinocchio'' (1883) by Italian writer Carlo Collodi of Florence, Tuscany. Pinocchio was carved by a woodcarver named Geppetto in a Tuscan vil ...
'' (1940), where Jiminy Cricket
Jiminy Cricket is the The Walt Disney Company, Disney version of the "Talking Cricket" (Italian language, Italian: ''Il Grillo Parlante''), a fictional character created by Italian writer Carlo Collodi for his 1883 children's book ''The Adventu ...
becomes the title character's conscience
Conscience is a cognitive process that elicits emotion and rational associations based on an individual's moral philosophy or value system. Conscience stands in contrast to elicited emotion or thought due to associations based on immediate sen ...
, and in ''Mulan
Hua Mulan () is a legendary folk heroine from the Northern and Southern dynasties era (4th to 6th century CE) of Chinese history.
According to legend, Mulan took her aged father's place in the conscription for the army by disguising herself as ...
'' (1998), where Cri-Kee is carried in a cage as a symbol of luck, in the Asian manner. The Crickets was the name of Buddy Holly
Charles Hardin Holley (September 7, 1936 – February 3, 1959), known as Buddy Holly, was an American singer and songwriter who was a central and pioneering figure of mid-1950s rock and roll. He was born to a musical family in Lubbock, Texas ...
's rock and roll band; Holly's home town baseball team in the 1990s was called the Lubbock Crickets. ''Cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by st ...
'' is the name of a US children's literary magazine founded in 1973; it uses a cast of insect characters. The sound of crickets is often used in media to emphasize silence, often for comic effect after an awkward joke, in a similar manner to tumbleweed
A tumbleweed is a structural part of the above-ground anatomy of a number of species of plants. It is a diaspore that, once mature and dry, detaches from its root or stem and rolls due to the force of the wind. In most such species, the tumb ...
.
Notes
References
Further reading
* Lisa Gail Ryan, Berthold Laufer, Lafcadio Hearn (1996).Insect musicians & cricket champions: a cultural history of singing insects in China and Japan
'. China Books. . * Franz Huber, Thomas Edwin Moore, Werner Loher (1989).
Cricket behavior and neurobiology
'. Cornell University Press. .
External links
{{Authority control * Extant Triassic first appearances Insect rearing Insects in culture