neuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy is the study of the structure and organization of the nervous system. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defin ...
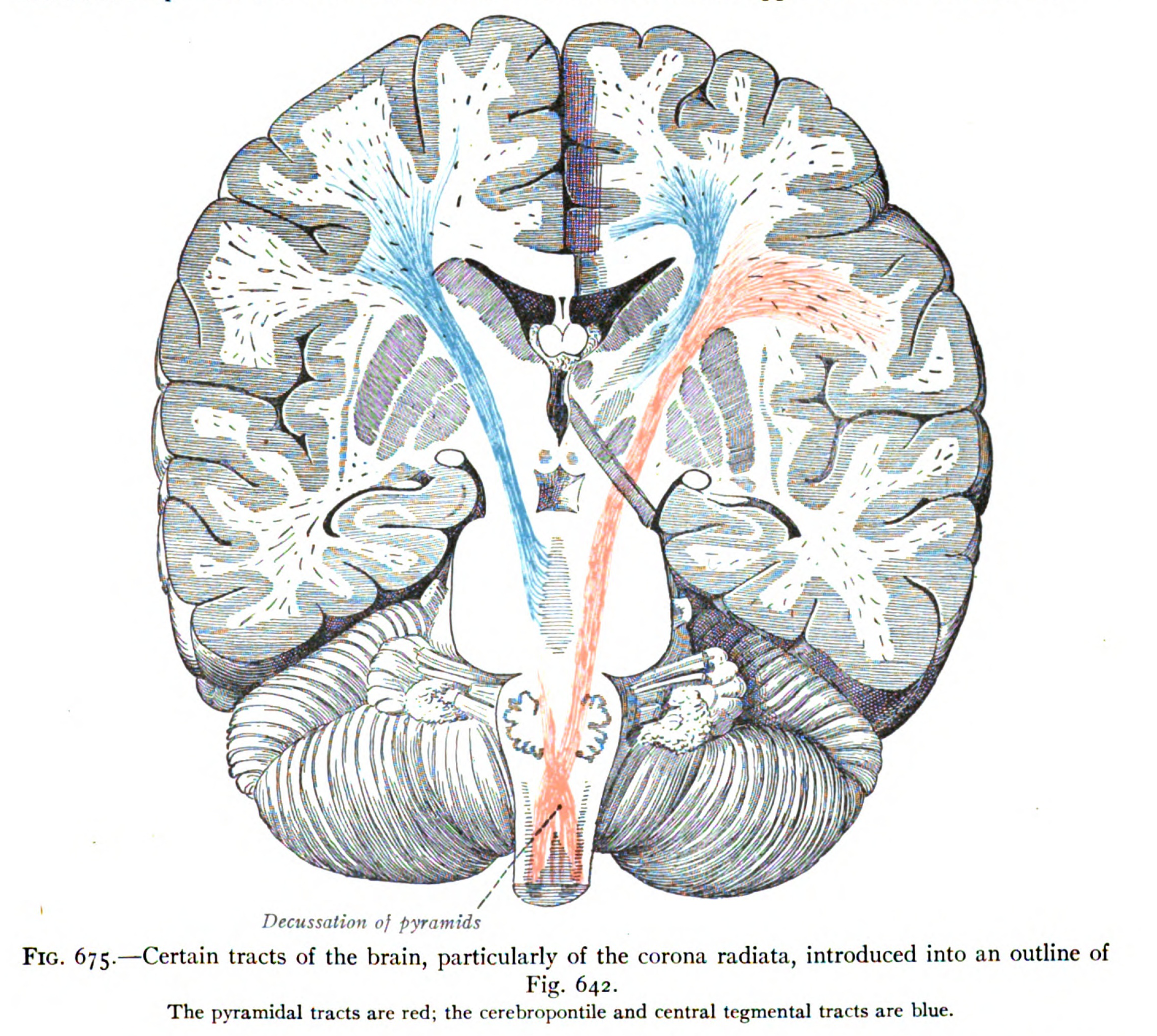
, the corona radiata is a white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distributi ...
sheet that continues inferiorly as the internal capsule
The internal capsule is a white matter structure situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the basal ganglia, separating the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the g ...
and superiorly as the centrum semiovale
In neuroanatomy, the centrum semiovale, semioval center or centrum ovale is the central area of white matter found underneath the cerebral cortex.
The white matter, located in each hemisphere between the cerebral cortex and nuclei, as a whole ha ...
. This sheet of both ascending and descending axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action ...
s carries most of the neural traffic from and to the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting o ...
. The corona radiata is associated with the corticopontine tract, the corticobulbar tract, and the corticospinal tract
The corticospinal tract is a white matter motor pathway starting at the cerebral cortex that terminates on lower motor neurons and interneurons in the spinal cord, controlling movements of the limbs and trunk. There are more than one million neuro ...
.
Structure
Projection fibers
The projection fibers consist of efferent and afferent fibers uniting the cortex with the lower parts of the brain and with the spinal cord. In human neuroanatomy, bundles of axons (nerve fibers) called tracts, within the brain, can be catego ...
are afferents carrying information to the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting o ...
, and efferents carrying information away from it. The most prominent projection fibers are the corona radiata, which radiate out from the cortex and then come together in the brain stem
The brainstem (or brain stem) is the posterior stalk-like part of the brain that connects the cerebrum with the spinal cord. In the human brain the brainstem is composed of the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. The midbrain is cont ...
. The projection fibers that make up the corona radiata also radiate out of the brain stem via the internal capsule
The internal capsule is a white matter structure situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the basal ganglia, separating the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the g ...
. Cerebral white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distributi ...
is commonly regarded today as an intricately organized system of fasciculi that facilitate the highest expression of cerebral activity.

Function
Motor pathway
Evidence from subcortical small infarcts suggests that motor fibers aresomatotopically
Somatotopy is the point-for-point correspondence of an area of the body to a specific point on the central nervous system. Typically, the area of the body corresponds to a point on the primary somatosensory cortex ( postcentral gyrus). This cortex ...
arranged in the human corona radiata. Following subtotal brain damage, localization of the corticofugal projection in the corona radiata and internal capsule
The internal capsule is a white matter structure situated in the inferomedial part of each cerebral hemisphere of the brain. It carries information past the basal ganglia, separating the caudate nucleus and the thalamus from the putamen and the g ...
can assist in evaluating a patient's residual motor capacity and predicting their potential for functional restitution. Data suggests that the corona radiata and superior capsular lesions may correlate with more favorable levels of functional recovery. Lesions seated inferiorly are likely to correlate with poorer levels of recovery regarding upper limb movement. Findings also suggest that motor deficit severity is likely to increase as a lesion occupies progressively more posterior regions of the internal capsule.
Clinical significance
Thcorona radiata
may be affected by diseases affecting the cerebral
white matter
White matter refers to areas of the central nervous system (CNS) that are mainly made up of myelinated axons, also called tracts. Long thought to be passive tissue, white matter affects learning and brain functions, modulating the distributi ...
, including ischemic leukoencephalopathy Leukoencephalopathy (leukodystrophy-like diseases) is a term that describes all of the brain white matter diseases, whether their molecular cause is known or unknown. It can refer specifically to any of these diseases:
*Progressive multifocal leuko ...
, multiple sclerosis, and progressive leukoencephalopathy Leukoencephalopathy (leukodystrophy-like diseases) is a term that describes all of the brain white matter diseases, whether their molecular cause is known or unknown. It can refer specifically to any of these diseases:
*Progressive multifocal leuko ...
. These may have major effects on intellectual, social, and emotional functioning.
In normal pressure hydrocephalus
Normal-pressure hydrocephalus (NPH), also called malresorptive hydrocephalus, is a form of communicating hydrocephalus in which excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) occurs in the ventricles, and with normal or slightly elevated cerebrospinal fluid p ...
, expansion of the lateral ventricles causes distortion of the fibers of the corona radiata. This contributes to the urinary incontinence seen with NPH.
Additional images
External links
*Somatotopic Organization of Motor Fibers in the Corona Radiata in Monoparetic Patients With Small Subcortical Infarct
Localization of arm representation in the corona radiata and internal capsule in the non‐human primate
Somatotopically located motor fibers in corona radiata: Evidence from subcortical small infarcts
Fiber Tract–based Atlas of Human White Matter Anatomy
Color Atlas of Neuroscience: Neuroanatomy and Neurophysiology:Meninges and Tracts
at
Google Books
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google Inc. that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical ...
{{Authority control
Cerebral white matter