Control-Alt-Backspace on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 In
In
 When shortcuts are referred to as ''key bindings,'' it carries the connotation that the shortcuts are customizable to a user's preference and that program functions may be 'bound' to a different set of keystrokes instead of or in addition to the default. This highlights a difference in philosophy regarding shortcuts. Some systems, typically
When shortcuts are referred to as ''key bindings,'' it carries the connotation that the shortcuts are customizable to a user's preference and that program functions may be 'bound' to a different set of keystrokes instead of or in addition to the default. This highlights a difference in philosophy regarding shortcuts. Some systems, typically
 The simplest keyboard shortcuts consist of only one key. For these, one generally just writes out the name of the key, as in the message "Press F1 for Help". The name of the key is sometimes surrounded in brackets or similar characters. For example: 1or <F1>. The key name may also be set off using special formatting (bold, italic,
The simplest keyboard shortcuts consist of only one key. For these, one generally just writes out the name of the key, as in the message "Press F1 for Help". The name of the key is sometimes surrounded in brackets or similar characters. For example: 1or <F1>. The key name may also be set off using special formatting (bold, italic,

 In
In computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, ...
, a keyboard shortcut also known as hotkey is a series of one or several keys
Key or The Key may refer to:
Common meanings
* Key (cryptography), a piece of information that controls the operation of a cryptography algorithm
* Key (lock), device used to control access to places or facilities restricted by a lock
* Key (ma ...
to quickly invoke a software program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. Computer programs are one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components.
A computer program ...
or perform a preprogrammed action. This action may be part of the standard functionality of the operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ef ...
or application program
Application may refer to:
Mathematics and computing
* Application software, computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks
** Application layer, an abstraction layer that specifies protocols and interface methods used in a ...
, or it may have been written by the user in a scripting language
A scripting language or script language is a programming language that is used to manipulate, customize, and automate the facilities of an existing system. Scripting languages are usually interpreted at runtime rather than compiled.
A scripti ...
. Some integrated keyboards also include pointing device
A pointing device is a human interface device that allows a user to input spatial (i.e., continuous and multi-dimensional) data to a computer. CAD systems and graphical user interfaces (GUI) allow the user to control and provide data t ...
s; the definition of exactly what counts as a "key" sometimes differs.
The meaning of term "keyboard shortcut" can vary depending on software manufacturer. In Windows, hotkeys consists of a specific key combination used to trigger an action (these are usually system-wide shortcuts that are available in all contexts so long as receiving program is active); mnemonics represent a designated letter in a menu command or toolbar button that when pressed together with the Alt key, activates such command.
The term is generally associated with computer keyboards, but many electronic musical instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person who pl ...
s now contain keyboards with advanced configuration options.
Description
Keyboard shortcuts are typically a means for invoking one or more commands using the keyboard that would otherwise be accessible only through amenu
In a restaurant, the menu is a list of food and beverages offered to customers and the prices. A menu may be à la carte – which presents a list of options from which customers choose – or table d'hôte, in which case a pre-established seque ...
, a pointing device
A pointing device is a human interface device that allows a user to input spatial (i.e., continuous and multi-dimensional) data to a computer. CAD systems and graphical user interfaces (GUI) allow the user to control and provide data t ...
, different levels of a user interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine f ...
, or via a command-line interface. Keyboard shortcuts are generally used to expedite common operations by reducing input sequences to a few keystroke
In programming and software design, an event is an action or occurrence recognized by software, often originating asynchronously from the external environment, that may be handled by the software. Computer events can be generated or triggered ...
s, hence the term "shortcut".In the English language a "shortcut" may unintentionally suggest an incomplete or sloppy way of completing something. Consequently, some computer applications designed to be controlled mainly by the keyboard, such as Emacs
Emacs , originally named EMACS (an acronym for "Editor MACroS"), is a family of text editors that are characterized by their extensibility. The manual for the most widely used variant, GNU Emacs, describes it as "the extensible, customizable, ...
, use the alternative term "key binding".
To differentiate from general keyboard input, most keyboard shortcuts require the user to press and hold several keys simultaneously or a sequence of keys one after the other. Unmodified key presses are sometimes accepted when the keyboard is not used for general input - such as with graphics packages e.g. Adobe Photoshop
Adobe Photoshop is a raster graphics editor developed and published by Adobe Inc. for Windows and macOS. It was originally created in 1988 by Thomas and John Knoll. Since then, the software has become the industry standard not only in ras ...
or IBM Lotus Freelance Graphics. Other keyboard shortcuts use function keys
A function key is a key on a computer or terminal keyboard that can be programmed so as to cause an operating system command interpreter or application program to perform certain actions, a form of soft key. On some keyboards/computers, funct ...
that are dedicated for use in shortcuts and may only require a single keypress. For simultaneous keyboard shortcuts, one usually first holds down the modifier key
In computing, a modifier key is a special key (or combination) on a computer keyboard that temporarily modifies the normal action of another key when pressed together. By themselves, modifier keys usually do nothing; that is, pressing any of the , ...
(s), then quickly presses and releases the regular (non-modifier) key, and finally releases the modifier key(s). This distinction is important, as trying to press all the keys simultaneously will frequently either miss some of the modifier keys, or cause unwanted auto-repeat. Sequential shortcuts usually involve pressing and releasing a dedicated prefix key, such as the Esc key
On computer keyboards, the Esc key (named ''Escape key'' in the international standard series ISO/IEC 9995) is a key used to generate the escape character (which can be represented as ASCII code 27 in decimal, Unicode U+001B, or ). The esca ...
, followed by one or more keystrokes.
Mnemonics
A mnemonic ( ) device, or memory device, is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval (remembering) in the human memory for better understanding.
Mnemonics make use of elaborative encoding, retrieval cues, and imager ...
are distinguishable from keyboard shortcuts. One difference between them is that the keyboard shortcuts are not localized on multi-language software but the mnemonics are generally localized to reflect the symbols and letters used in the specific locale. In most GUIs, a program's keyboard shortcuts are discoverable by browsing the program's menus – the shortcut is indicated next to the menu choice. There are keyboards that have the shortcuts for a particular application already marked on them. These keyboards are often used for editing video, audio, or graphics, as well as in software training courses. There are also stickers with shortcuts printed on them that can be applied to a regular keyboard. Reference cards
A reference card or reference sheet (or quick reference card) or crib sheet is a concise bundling of condensed notes about a specific topic, such as mathematical formulas to calculate area/volume, or common syntactic rules and idioms of a particula ...
intended to be propped up in the user's workspace also exist for many applications. In the past, when keyboard design was more standardized, it was common for computer books and magazines to print cards that were cut out, intended to be placed over the user's keyboard with the printed shortcuts noted next to the appropriate keys.
Customization
end-user
In product development, an end user (sometimes end-user) is a person who ultimately uses or is intended to ultimately use a product. The end user stands in contrast to users who support or maintain the product, such as sysops, system administrato ...
-oriented systems such as Mac OS
Two major famlies of Mac operating systems were developed by Apple Inc.
In 1984, Apple debuted the operating system that is now known as the "Classic" Mac OS with its release of the original Macintosh System Software. The system, rebranded " ...
or Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for ...
, consider standardized shortcuts essential to the environment's ease of use. These systems often limit a user's ability to change shortcuts, possibly even requiring a separate or third-party utility to perform the task. Other systems, typically Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, a ...
and related, consider shortcuts to be a user's prerogative, and that they should be customizable to suit individual preference. In most real-world environments, both philosophies co-exist; a core set of ''sacred'' shortcuts remain fixed while others, typically involving an otherwise unused modifier key or keys, are under the user's control.
The motivations for customizing key bindings vary. Users new to a program or software environment may customize the new environment's shortcuts to be similar to another environment with which they are more familiar. More advanced users may customize key bindings to better suit their workflow
A workflow consists of an orchestrated and repeatable pattern of activity, enabled by the systematic organization of resources into processes that transform materials, provide services, or process information. It can be depicted as a sequence ...
, adding shortcuts for their commonly used actions and possibly deleting or replacing bindings for less-used functions. Hardcore gamers
A gamer is a proactive hobbyist who Player (game), plays interactive games, especially video games, tabletop role-playing games, and skill-based card games, and who plays for usually long periods of time. Some gamers are competitive, meaning ...
often customize their key bindings in order to increase performance via faster reaction times.
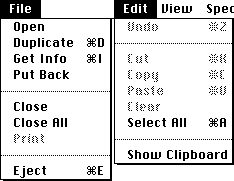
"Sacred" keybindings
The original Macintosh User Interface Guidelines defined a set of keyboard shortcuts that would remain consistent across application programs. This provides a better user experience than the then-prevalent situation of applications using the same keys for different functions. This could result inuser error
A user error is an error made by the human user of a complex system, usually a computer system, in interacting with it. Although the term is sometimes used by human–computer interaction practitioners, the more formal human error term is used in ...
s if one program used to mean ''Delete'' while another used it to ''Duplicate'' an item. The standard bindings were:
* : Quit
* : Close Window
* : Bold text
* : Italicize text
* : Underline text
* : Open
* : Print
* : Select All
* : Save
* : Find
* : Find Again (the G key is next to the F key on a QWERTY
QWERTY () is a keyboard layout for Latin-script alphabets. The name comes from the order of the first six keys on the top left letter row of the keyboard ( ). The QWERTY design is based on a layout created for the Sholes and Glidden ty ...
keyboard)
* : Undo
Undo is an interaction technique which is implemented in many computer programs. It erases the last change done to the document, reverting it to an older state. In some more advanced programs, such as graphic processing, undo will negate the las ...
(resembles the action of striking out a mistake)
* : Cut (resembles scissors – and the X key is next to the C key on a QWERTY keyboard)
* : Copy
* : Paste
Paste is a term for any very thick viscous fluid. It may refer to:
Science and technology
* Adhesive or paste
** Wallpaper paste
** Wheatpaste, A liquid adhesive made from vegetable starch and water
* Paste (rheology), a substance that behaves a ...
(resembles an arrow pointing downward "into" the document, or a brush used for applying paste, as well as the proofreader's mark for "insert" – and the V key is next to the C key on a QWERTY keyboard)
* : New Document
A document is a written, drawn, presented, or memorialized representation of thought, often the manifestation of non-fictional, as well as fictional, content. The word originates from the Latin ''Documentum'', which denotes a "teaching" o ...
* (full stop
The full stop ( Commonwealth English), period ( North American English), or full point , is a punctuation mark. It is used for several purposes, most often to mark the end of a declarative sentence (as distinguished from a question or exclam ...
): User interrupt
* : Help ( ? signifies a question or confusion)
Later environments such as Microsoft Windows retain some of these bindings, while adding their own from alternate standards like Common User Access
Common User Access (CUA) is a standard for user interfaces to operating systems and computer programs. It was developed by IBM and first published in 1987 as part of their Systems Application Architecture. Used originally in the MVS/ESA, VM/CM ...
. The shortcuts on these platforms (or on macOS
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. Within the market of ...
) are not as strictly standardized across applications as on the early Macintosh user interface, where if a program did not include the function normally carried out by one of the standard keystrokes, guidelines stated that it should not redefine the key to do something else as it would potentially confuse users.
Notation
 The simplest keyboard shortcuts consist of only one key. For these, one generally just writes out the name of the key, as in the message "Press F1 for Help". The name of the key is sometimes surrounded in brackets or similar characters. For example: 1or <F1>. The key name may also be set off using special formatting (bold, italic,
The simplest keyboard shortcuts consist of only one key. For these, one generally just writes out the name of the key, as in the message "Press F1 for Help". The name of the key is sometimes surrounded in brackets or similar characters. For example: 1or <F1>. The key name may also be set off using special formatting (bold, italic, all caps
In typography, all caps (short for "all capitals") refers to text or a font in which all letters are capital letters, for example: "THIS TEXT IS IN ALL CAPS". All caps may be used for emphasis (for a word or phrase). They are commonly seen in ...
, etc.)
Many shortcuts require two or more keys to be pressed simultaneously. For these, the usual notation is to list the keys names separated by plus signs or hyphens. For example: "Ctrl+C", "Ctrl-C", or "". The Ctrl key is sometimes indicated by a caret character (^). Thus Ctrl-C is sometimes written as ^C. At times, usually on Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, a ...
platforms, the case of the second character is significant – if the character would normally require pressing the Shift key
The Shift key is a modifier key on a keyboard, used to type capital letters and other alternate "upper" characters. There are typically two shift keys, on the left and right sides of the row below the home row. The Shift key's name originated ...
to type, then the Shift key is part of the shortcut e.g. '^C' vs. '^c' or '^%' vs. '^5'. ^% may also be written "".
Some keyboard shortcuts, including all shortcuts involving the key, require keys (or sets of keys) to be pressed individually, in sequence. These shortcuts are sometimes written with the individual keys (or sets) separated by commas or semicolons. The Emacs
Emacs , originally named EMACS (an acronym for "Editor MACroS"), is a family of text editors that are characterized by their extensibility. The manual for the most widely used variant, GNU Emacs, describes it as "the extensible, customizable, ...
text editor uses many such shortcuts, using a designated set of "prefix keys" such as or . Default Emacs keybindings include to save a file or to view a list of open buffers. Emacs uses the letter C to denote the Ctrl key, the letter S to denote the Shift key
The Shift key is a modifier key on a keyboard, used to type capital letters and other alternate "upper" characters. There are typically two shift keys, on the left and right sides of the row below the home row. The Shift key's name originated ...
, and the letter M to denote the Meta key
The Meta key is a modifier key on certain keyboards. It first appeared on the Stanford Artificial Intelligence Lab (SAIL) keyboard in 1970.
History
The Meta key first appeared on the Stanford Artificial Intelligence Lab (SAIL) keyboard in 19 ...
(commonly mapped to the Alt key
The Alt key (pronounced or ) on a computer keyboard is used to change (alternate) the function of other pressed keys. Thus, the Alt key is a modifier key, used in a similar fashion to the Shift key. For example, simply pressing ''A'' will ...
on modern keyboards.) Thus, in Emacs parlance, the above shortcuts would be written C-x C-s and C-x C-b. A common backronym
A backronym is an acronym formed from an already existing word by expanding its letters into the words of a phrase. Backronyms may be invented with either serious or humorous intent, or they may be a type of false etymology or folk etymology. The ...
for Emacs is "Escape Meta Alt Ctrl Shift", poking fun at its use of many modifiers and extended shortcut sequences.
See also
* Access key *Accelerator table In Windows programming, an accelerator table allows an application to specify a list of ''accelerators'' (keyboard shortcuts) for menu items or other commands. For example, Ctrl+S is often used as a shortcut to the File→Save menu item, Ctrl+O is a ...
* Common User Access
Common User Access (CUA) is a standard for user interfaces to operating systems and computer programs. It was developed by IBM and first published in 1987 as part of their Systems Application Architecture. Used originally in the MVS/ESA, VM/CM ...
(CUA)
* Human interface guidelines
* Table of keyboard shortcuts
Notes and references
{{Authority control User interface techniques