Consumer spending on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Consumer spending is the total money spent on final goods and services by individuals and households.
There are two components of consumer spending:
Consumer spending is the total money spent on final goods and services by individuals and households.
There are two components of consumer spending:
 In 1929, consumer spending was 75% of the nation's economy. This grew to 83% in 1932, when business spending dropped. Consumer spending dropped to about 50% during
In 1929, consumer spending was 75% of the nation's economy. This grew to 83% in 1932, when business spending dropped. Consumer spending dropped to about 50% during  For U.S. domestic consumer spending by population and income demographics collected by the U.S Census Bureau at the household level and analyzed and published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, see the link at BLS.gov/CEX
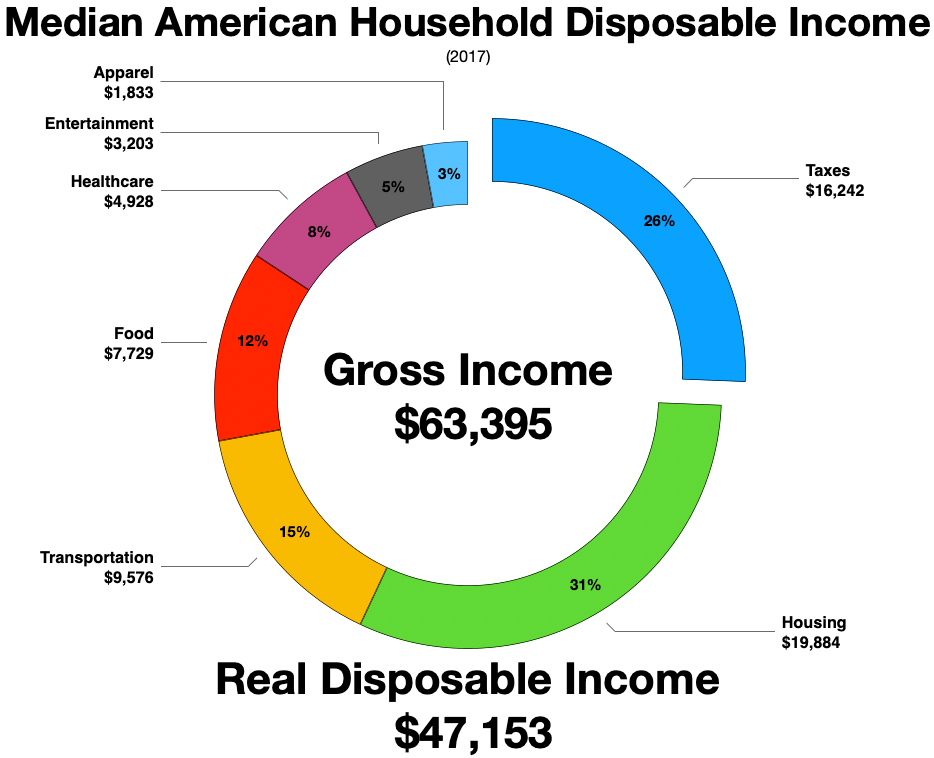
For U.S. domestic consumer spending by population and income demographics collected by the U.S Census Bureau at the household level and analyzed and published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, see the link at BLS.gov/CEX
 Consumer spending is the total money spent on final goods and services by individuals and households.
There are two components of consumer spending:
Consumer spending is the total money spent on final goods and services by individuals and households.
There are two components of consumer spending: induced consumption
Induced consumption is the portion of consumption that varies with disposable income. When a change in disposable income “induces” a change in consumption on goods and services, then that changed consumption is called “induced consumption” ...
(which is affected by the level of income
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. For ...
) and autonomous consumption
Autonomous consumption (also exogenous consumption) is the consumption expenditure that occurs when income levels are zero. Such consumption is considered autonomous of income only when expenditure on these consumables does not vary with changes ...
(which is not).
Macroeconomic factors
Taxes
Taxes
A tax is a compulsory financial charge or some other type of levy imposed on a taxpayer (an individual or legal entity) by a governmental organization in order to fund government spending and various public expenditures (regional, local, or ...
are a tool in the adjustment of the economy
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
. Tax policies designed by governments affect consumer groups, net consumer spending and consumer confidence. Economists expect tax manipulation to increase or decrease consumer spending, though the precise impact of specific manipulations are often the subject of controversy.
Underlying tax manipulation as a stimulant or suppression of consumer spending is an equation for gross domestic product (GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
). The equation is GDP = C + I + G + NX, where C is private consumption, I is private investment, G is government and NX is the net of exports minus imports. Increases in government spending create demand and economic expansion. However, government spending increases translates to tax increases or deficit spending
Within the budgetary process, deficit spending is the amount by which spending exceeds revenue over a particular period of time, also called simply deficit, or budget deficit; the opposite of budget surplus. The term may be applied to the budget ...
. This creates a potential negative impact on private consumption, investment, and/or the balance of trade.
Consumer sentiment
Consumer sentiment is the general attitude of toward the economy and the health of the fiscal markets, and they are a strong constituent of consumer spending. Sentiments have a powerful ability to cause fluctuations in the economy, because if the attitude of the consumer regarding the state of the economy is bad, then they will be reluctant to spend. Therefore, sentiments prove to be a powerful predictor of the economy, because when people have faith in the economy or in what they believe will soon occur, they will spend and invest with confidence. However sentiments do not always affect the spending habits of some people as much as they do for others. For example, some households set their spending strictly off of their income, so that their income closely equals, or nearly equals their consumption (including savings). Others rely on their sentiments to dictate how they spend their income and such.Government economic stimulus
In times of economic trouble or uncertainty, thegovernment
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a ...
often tries to rectify the issue by distributing economic stimuli, often in the form of rebates or checks. However such techniques have failed in the past for several reasons. As was discussed earlier, temporary financial reprieve rarely succeeds because people do not often like rapidly shifting their spending habits. Also, people are many times intelligent enough to realize that economic stimulus packages are due to economic downturns, and therefore they are even more reluctant to spend them. Instead they put them into savings, which can potentially also help spur the economy. By putting money into savings, banks profit and are able to decrease the interest rates
An interest rate is the amount of interest due per period, as a proportion of the amount lent, deposited, or borrowed (called the principal sum). The total interest on an amount lent or borrowed depends on the principal sum, the interest rate, th ...
, which then encourage others to save less and promote future spending.
Fuel
When fuel supplies are disrupted, the demand for goods that are dependent on fuel, like motor vehicles and machinery, may decrease. Disruption in energy supplies creates uncertainty regarding availability and upcoming prices of these supplies. Often, consumers will not purchase energy-dependent products until they can be sure that fuel will be available to use the product. Increases in the price of fuel do not lead to decreases in demand because it isinelastic
In economics, elasticity measures the percentage change of one economic variable in response to a percentage change in another. If the price elasticity of the demand of something is -2, a 10% increase in price causes the demand quantity to fall ...
. Rather, a greater portion of income is spent on fuel, and less is available to purchase other goods. This leads to an overall decrease in consumer spending.
Data
United States
 In 1929, consumer spending was 75% of the nation's economy. This grew to 83% in 1932, when business spending dropped. Consumer spending dropped to about 50% during
In 1929, consumer spending was 75% of the nation's economy. This grew to 83% in 1932, when business spending dropped. Consumer spending dropped to about 50% during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
due to large expenditures by the government and lack of consumer products. Consumer spending in the US rose from about 62% of GDP in 1960, where it stayed until about 1981, and has since risen to 71% in 2013.
In the United States, the Consumer Spending figure published by the Bureau of Economic Analysis includes three broad categories of personal spending.
* Durable goods: motor vehicles and parts, furnishings and durable household equipment, recreational goods and vehicles, and other durable goods.
* Nondurable goods: food and beverages purchased for off-premises consumption, clothing and footwear, gasoline and other energy goods, and other nondurable goods.
* Services: housing and utilities, healthcare, transportation services, recreation services, food services and accommodations, financial services and insurance, and other services.
 For U.S. domestic consumer spending by population and income demographics collected by the U.S Census Bureau at the household level and analyzed and published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, see the link at BLS.gov/CEX
For U.S. domestic consumer spending by population and income demographics collected by the U.S Census Bureau at the household level and analyzed and published by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, see the link at BLS.gov/CEX
See also
*Consumer Expenditure Survey The Consumer Expenditure Survey (CE or CEX) is a Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) household survey that collects information on the buying habits of U.S. consumers. The program consists of two components — the Interview Survey and the Dia ...
* List of largest consumer markets
Below is a list of the largest consumer markets of the world, according to data from the World Bank. The countries are sorted by their Household final consumption expenditure (HFCE) which represents consumer spending in nominal terms. If measured ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Consumer Spending Consumption (macroeconomics)