Constant Spectrum Melody on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
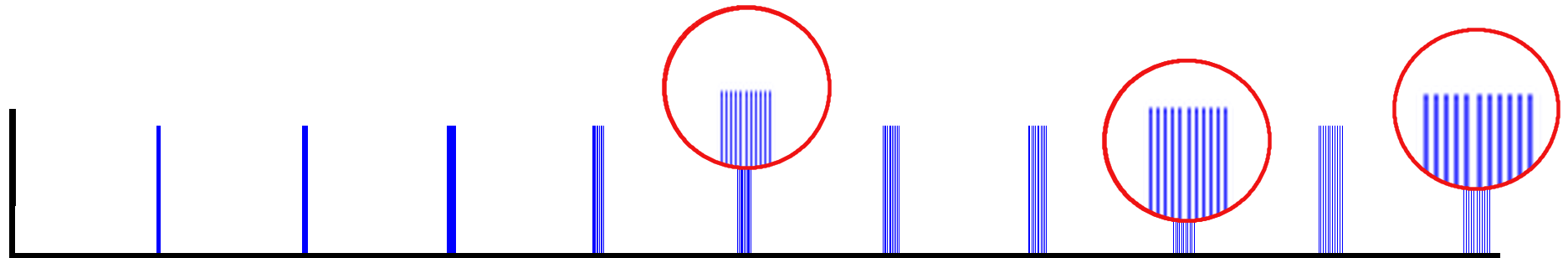 A constant
A constant
 A constant
A constant timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instrument ...
at a constant pitch is characterized by a spectrum
A spectrum (: spectra or spectrums) is a set of related ideas, objects, or properties whose features overlap such that they blend to form a continuum. The word ''spectrum'' was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of co ...
.
Along a piece of music, the spectrum measured within a narrow time window varies with the melody and the possible effects of instruments.
Therefore, it may seem paradoxical that a constant spectrum can be perceived as a melody rather than a stamp.
The paradoxA. Chaigne (1988), “Psychoacoustique”, ENST, 114 pages. is that the ear is not an abstract spectrograph
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify mate ...
: it "calculates" the Fourier transform
In mathematics, the Fourier transform (FT) is an integral transform that takes a function as input then outputs another function that describes the extent to which various frequencies are present in the original function. The output of the tr ...
of the audio signal
An audio signal is a representation of sound, typically using either a changing level of electrical voltage for analog signals or a series of binary numbers for Digital signal (signal processing), digital signals. Audio signals have frequencies i ...
in a narrow time window, but the slower variations are seen as temporal evolution and not as pitch.
However, the example of paradoxical melody above contains no infrasound (i.e. pure tone of period slower than the time window).
The second paradox is that when two pitches are very close, they create a beat
Beat, beats, or beating may refer to:
Common uses
* Assault, inflicting physical harm or unwanted physical contact
* Battery (crime), a criminal offense involving unlawful physical contact
* Battery (tort), a civil wrong in common law of inte ...
. If the period of this beat is longer than the integration window, it is seen as a sinusoidal variation in the average rating: sin(2π(f+ε)t) + sin(2π(f-ε)t) = sin(2πft)cos(2πεt), where 1/ε is the slow period.
The present spectrum is made of multiple frequencies beating together, resulting in a superimposition of various pitches fading in and out at different moments and pace, thus forming the melody.
MATLAB/Scilab/Octave code
Here is the program used to generate the paradoxical melody: n=10; length=20; harmon=10; df=0.1; t=(1:length*44100)/44100; y=0; for i = 0:n, for j = 1:harmon, y=y+sin(2*3.1415927*(55+i*df)*j*t); end; end; sound(y/(n*harmon),44100);References
See also
* Shepard-Risset tone, forever increasing pitch * : forever accelerating beat *Spectral music
Spectral music uses the acoustic properties of sound – or sound spectra – as a basis for composition.
Definition
Defined in technical language, spectral music is an acoustic musical practice where compositional decisions are often inform ...
* Auditory illusion
Auditory illusions are Illusion, illusions of real sound or outside stimulus. These false perceptions are the equivalent of an optical illusion: the listener hears either sounds which are not present in the Stimulus (physiology), stimulus, or sound ...
* Musical acoustics
Musical acoustics or music acoustics is a multidisciplinary field that combines knowledge from physics, psychophysics, organology (classification of the instruments), physiology, music theory, ethnomusicology, signal processing and instrument buil ...
{{Auditory illusions
Perception
Sound
Melody