Computer-assisted Detection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Computer-aided detection (CADe), also called computer-aided diagnosis (CADx), are systems that assist doctors in the interpretation of
 CAD is used in the diagnosis of
CAD is used in the diagnosis of
 ''Histogram equalization'' is useful in enhancing contrast within an image. This technique is used to increase ''local contrast.'' At the end of the processing, areas that were dark in the input image would be brightened, greatly enhancing the contrast among the features present in the area. On the other hand, brighter areas in the input image would remain bright or be reduced in brightness to equalize with the other areas in the image. Besides vessel segmentation, other features related to diabetic retinopathy can be further separated by using this pre-processing technique. Microaneurysm and hemorrhages are red lesions, whereas exudates are yellow spots. Increasing contrast between these two groups allow better visualization of lesions on images. With this technique, 2014 review found that 10 out of the 14 recently (since 2011) published primary research.
''Green channel filtering'' is another technique that is useful in differentiating lesions rather than vessels. This method is important because it provides the maximal contrast between diabetic retinopathy-related lesions. Microaneurysms and hemorrhages are red lesions that appear dark after application of green channel filtering. In contrast, exudates, which appear yellow in normal image, are transformed into bright white spots after green filtering. This technique is mostly used according to the 2014 review, with appearance in 27 out of 40 published articles in the past three years. In addition, green channel filtering can be used to detect center of optic disc in conjunction with double-windowing system.
''Non-uniform illumination correction'' is a technique that adjusts for non-uniform illumination in fundoscopic image. Non-uniform illumination can be a potential error in automated detection of diabetic retinopathy because of changes in statistical characteristics of image. These changes can affect latter processing such as feature extraction and are not observable by humans. Correction of non-uniform illumination (f') can be achieved by modifying the pixel intensity using known original pixel intensity (f), and average intensities of local (λ) and desired pixels (μ) (see formula below). Walter-Klein transformation is then applied to achieve the uniform illumination. This technique is the least used pre-processing method in the review from 2014.
''Morphological operations'' is the second least used pre-processing method in 2014 review. The main objective of this method is to provide contrast enhancement, especially darker regions compared to background.
''Histogram equalization'' is useful in enhancing contrast within an image. This technique is used to increase ''local contrast.'' At the end of the processing, areas that were dark in the input image would be brightened, greatly enhancing the contrast among the features present in the area. On the other hand, brighter areas in the input image would remain bright or be reduced in brightness to equalize with the other areas in the image. Besides vessel segmentation, other features related to diabetic retinopathy can be further separated by using this pre-processing technique. Microaneurysm and hemorrhages are red lesions, whereas exudates are yellow spots. Increasing contrast between these two groups allow better visualization of lesions on images. With this technique, 2014 review found that 10 out of the 14 recently (since 2011) published primary research.
''Green channel filtering'' is another technique that is useful in differentiating lesions rather than vessels. This method is important because it provides the maximal contrast between diabetic retinopathy-related lesions. Microaneurysms and hemorrhages are red lesions that appear dark after application of green channel filtering. In contrast, exudates, which appear yellow in normal image, are transformed into bright white spots after green filtering. This technique is mostly used according to the 2014 review, with appearance in 27 out of 40 published articles in the past three years. In addition, green channel filtering can be used to detect center of optic disc in conjunction with double-windowing system.
''Non-uniform illumination correction'' is a technique that adjusts for non-uniform illumination in fundoscopic image. Non-uniform illumination can be a potential error in automated detection of diabetic retinopathy because of changes in statistical characteristics of image. These changes can affect latter processing such as feature extraction and are not observable by humans. Correction of non-uniform illumination (f') can be achieved by modifying the pixel intensity using known original pixel intensity (f), and average intensities of local (λ) and desired pixels (μ) (see formula below). Walter-Klein transformation is then applied to achieve the uniform illumination. This technique is the least used pre-processing method in the review from 2014.
''Morphological operations'' is the second least used pre-processing method in 2014 review. The main objective of this method is to provide contrast enhancement, especially darker regions compared to background.
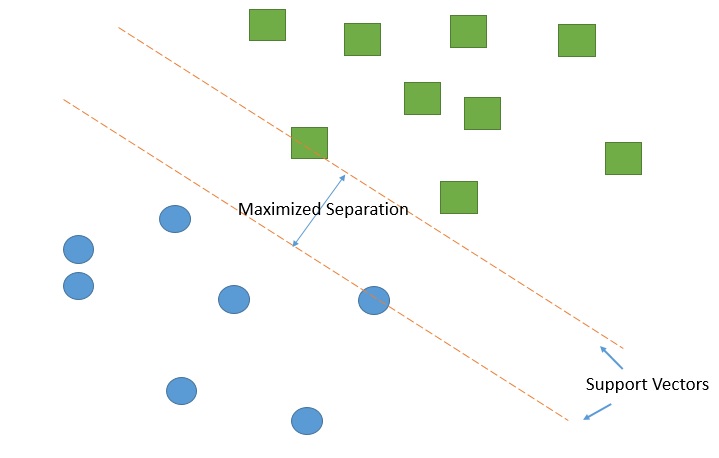 ''Support vector machine'' is by far the most frequently used classifier in vessel segmentation, up to 90% of cases. SVM is a supervised learning model that belongs to the broader category of pattern recognition technique. The algorithm works by creating a largest gap between distinct samples in the data. The goal is to create the largest gap between these components that minimize the potential error in classification. In order to successfully segregate blood vessel information from the rest of the eye image, SVM algorithm creates support vectors that separate the blood vessel pixel from the rest of the image through a supervised environment. Detecting blood vessel from new images can be done through similar manner using support vectors. Combination with other pre-processing technique, such as green channel filtering, greatly improves the accuracy of detection of blood vessel abnormalities. Some beneficial properties of SVM include
* Flexibility – Highly flexible in terms of function
* Simplicity – Simple, especially with large datasets (only support vectors are needed to create separation between data)
''Multi-scale'' approach is a multiple resolution approach in vessel segmentation. At low resolution, large-diameter vessels can first be extracted. By increasing resolution, smaller branches from the large vessels can be easily recognized. Therefore, one advantage of using this technique is the increased analytical speed. Additionally, this approach can be used with 3D images. The surface representation is a surface normal to the curvature of the vessels, allowing the detection of abnormalities on vessel surface.
''Vessel tracking'' is the ability of the algorithm to detect "centerline" of vessels. These centerlines are maximal peak of vessel curvature. Centers of vessels can be found using directional information that is provided by Gaussian filter. Similar approaches that utilize the concept of centerline are the skeleton-based and differential geometry-based.
''Region growing'' approach is a method of detecting neighboring pixels with similarities. A seed point is required for such method to start. Two elements are needed for this technique to work: similarity and spatial proximity. A neighboring pixel to the seed pixel with similar intensity is likely to be the same type and will be added to the growing region. One disadvantage of this technique is that it requires manual selection of seed point, which introduces bias and inconsistency in the algorithm. This technique is also being used in optic disc identification.
''Model-based'' approaches employ representation to extract vessels from images. Three broad categories of model-based are known: deformable, parametric, and template matching. Deformable methods uses objects that will be deformed to fit the contours of the objects on the image. Parametric uses geometric parameters such as tubular, cylinder, or ellipsoid representation of blood vessels. Classical snake contour in combination with blood vessel topological information can also be used as a model-based approach. Lastly, template matching is the usage of a template, fitted by stochastic deformation process using Hidden Markov Mode 1.
''Support vector machine'' is by far the most frequently used classifier in vessel segmentation, up to 90% of cases. SVM is a supervised learning model that belongs to the broader category of pattern recognition technique. The algorithm works by creating a largest gap between distinct samples in the data. The goal is to create the largest gap between these components that minimize the potential error in classification. In order to successfully segregate blood vessel information from the rest of the eye image, SVM algorithm creates support vectors that separate the blood vessel pixel from the rest of the image through a supervised environment. Detecting blood vessel from new images can be done through similar manner using support vectors. Combination with other pre-processing technique, such as green channel filtering, greatly improves the accuracy of detection of blood vessel abnormalities. Some beneficial properties of SVM include
* Flexibility – Highly flexible in terms of function
* Simplicity – Simple, especially with large datasets (only support vectors are needed to create separation between data)
''Multi-scale'' approach is a multiple resolution approach in vessel segmentation. At low resolution, large-diameter vessels can first be extracted. By increasing resolution, smaller branches from the large vessels can be easily recognized. Therefore, one advantage of using this technique is the increased analytical speed. Additionally, this approach can be used with 3D images. The surface representation is a surface normal to the curvature of the vessels, allowing the detection of abnormalities on vessel surface.
''Vessel tracking'' is the ability of the algorithm to detect "centerline" of vessels. These centerlines are maximal peak of vessel curvature. Centers of vessels can be found using directional information that is provided by Gaussian filter. Similar approaches that utilize the concept of centerline are the skeleton-based and differential geometry-based.
''Region growing'' approach is a method of detecting neighboring pixels with similarities. A seed point is required for such method to start. Two elements are needed for this technique to work: similarity and spatial proximity. A neighboring pixel to the seed pixel with similar intensity is likely to be the same type and will be added to the growing region. One disadvantage of this technique is that it requires manual selection of seed point, which introduces bias and inconsistency in the algorithm. This technique is also being used in optic disc identification.
''Model-based'' approaches employ representation to extract vessels from images. Three broad categories of model-based are known: deformable, parametric, and template matching. Deformable methods uses objects that will be deformed to fit the contours of the objects on the image. Parametric uses geometric parameters such as tubular, cylinder, or ellipsoid representation of blood vessels. Classical snake contour in combination with blood vessel topological information can also be used as a model-based approach. Lastly, template matching is the usage of a template, fitted by stochastic deformation process using Hidden Markov Mode 1.
Digital Retinal Images for Vessel Extraction (DRIVE)
STructured Analysis of the REtina (STARE)
High-Resolution Fundus (HRF) Image Database
{{Computer vision footer Medical expert systems Radiology Health informatics Applications of computer vision
medical images
Medicine is the science and practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care prac ...
. Imaging techniques in X-ray
X-rays (or rarely, ''X-radiation'') are a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. In many languages, it is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it in 1895 and named it ' ...
, MRI, Endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are inse ...
, and ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies fr ...
diagnostics yield a great deal of information that the radiologist or other medical professional has to analyze and evaluate comprehensively in a short time. CAD systems process digital images or videos for typical appearances and to highlight conspicuous sections, such as possible diseases, in order to offer input to support a decision taken by the professional.
CAD also has potential future applications in digital pathology
Digital pathology is a sub-field of pathology that focuses on data management based on information generated from digitized specimen slides. Through the use of computer-based technology, digital pathology utilizes virtual microscopy. Glass slides ...
with the advent of whole-slide imaging and machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence.
Machine ...
algorithms. So far its application has been limited to quantifying immunostaining
In biochemistry, immunostaining is any use of an antibody-based method to detect a specific protein in a sample. The term "immunostaining" was originally used to refer to the immunohistochemical staining of tissue sections, as first described by ...
but is also being investigated for the standard H&E stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin-eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnos ...
.
CAD is an interdisciplinary
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several other fields like sociology, anthropology, psychology, ec ...
technology combining elements of artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech r ...
and computer vision
Computer vision is an Interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary scientific field that deals with how computers can gain high-level understanding from digital images or videos. From the perspective of engineering, it seeks to understand and automate t ...
with radiological
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'', such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visib ...
and pathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in ...
image processing. A typical application is the detection of a tumor. For instance, some hospitals use CAD to support preventive medical check-ups in mammography
Mammography (also called mastography) is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 kVp) to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through d ...
(diagnosis of breast cancer), the detection of polyps in Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy () or coloscopy () is the endoscopic examination of the large bowel and the distal part of the small bowel with a CCD camera or a fiber optic camera on a flexible tube passed through the anus. It can provide a visual diagnosis ( ...
, and lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign ...
.
Computer-aided detection (CADe) systems are usually confined to marking conspicuous structures and sections. Computer-aided diagnosis (CADx) systems evaluate the conspicuous structures. For example, in mammography CAD highlights microcalcification clusters and hyperdense structures in the soft tissue. This allows the radiologist to draw conclusions about the condition of the pathology. Another application is CADq, which quantifies, ''e.g.'', the size of a tumor or the tumor's behavior in contrast medium uptake. Computer-aided simple triage (CAST) is another type of CAD, which performs a fully automatic initial interpretation and triage
In medicine, triage () is a practice invoked when acute care cannot be provided for lack of resources. The process rations care towards those who are most in need of immediate care, and who benefit most from it. More generally it refers to pri ...
of studies into some meaningful categories (''e.g.'' negative and positive). CAST is particularly applicable in emergency diagnostic imaging, where a prompt diagnosis of critical, life-threatening condition is required.
Although CAD has been used in clinical environments for over 40 years, CAD usually does not substitute the doctor or other professional, but rather plays a supporting role. The professional (generally a radiologist) is generally responsible for the final interpretation of a medical image. However, the goal of some CAD systems is to detect earliest signs of abnormality in patients that human professionals cannot, as in diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy (also known as diabetic eye disease), is a medical condition in which damage occurs to the retina due to diabetes mellitus. It is a leading cause of blindness in developed countries.
Diabetic retinopathy affects up to 80 perc ...
, architectural distortion in mammograms, ground-glass nodules in thoracic CT, and non-polypoid (“flat”) lesions in CT colonography.
Topics
A Brief History
In the late 1950s, with the dawn of modern computers researchers in various fields started exploring the possibility of building computer-aided medical diagnostic (CAD) systems. These first CAD systems used flow-charts, statistical pattern-matching, probability theory or knowledge bases to drive their decision-making process. Since the early 1970s, some of the very early CAD systems in medicine, which were often referred as “expert systems
In artificial intelligence, an expert system is a computer system emulating the decision-making ability of a human expert.
Expert systems are designed to solve complex problems by reasoning through bodies of knowledge, represented mainly as if� ...
” in medicine, were developed and used mainly for educational purposes. The MYCIN expert system, the Internist-I expert system and the CADUCEUS (expert system) are some of such examples.
During the beginning of the early developments, the researchers were aiming at building entirely automated CAD / expert systems. The expectation of what computers can do was unrealistically optimistic among these scientists. However, after the breakthrough paper, “Reducibility among Combinatorial Problems” by Richard M. Karp, it became clear that there were limitations but also potential opportunities when one develops algorithms to solve groups of important computational problems.
As result of the new understanding of the various algorithmic limitations that Karp discovered in the early 1970s, researchers started realizing the serious limitations that CAD and expert systems in medicine have. The recognition of these limitations brought the investigators to develop new kinds of CAD systems by using advanced approaches. Thus, by the late 1980s and early 1990s the focus sifted in the use of data mining approaches for the purpose of using more advanced and flexible CAD systems.
In 1998, the first commercial CAD system for mammography, the ImageChecker system, was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). In the following years several commercial CAD systems for analyzing mammography, breast MRI, medical imagining of lung, colon, and heart also received FDA approvals. Currently, CAD systems are used as a diagnostic aid to provide physicians for better medical decision-making.
Methodology
CAD is fundamentally based on highly complexpattern recognition
Pattern recognition is the automated recognition of patterns and regularities in data. It has applications in statistical data analysis, signal processing, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphic ...
. X-ray or other types of images are scanned for suspicious structures. Normally a few thousand images are required to optimize the algorithm. Digital image data are copied to a CAD server in a DICOM
Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) is the standard for the communication and management of medical imaging information and related data. DICOM is most commonly used for storing and transmitting medical images enabling the integ ...
-format and are prepared and analyzed in several steps.
''1. Preprocessing'' for
* Reduction of artifacts (bugs in images)
* Image noise reduction
* Leveling (harmonization) of image quality (increased contrast) for clearing the image's different basic conditions e.g. different exposure parameter.
* Filtering
''2. Segmentation'' for
* Differentiation of different structures in the image, e.g. heart, lung, ribcage, blood vessels, possible round lesions
* Matching with anatomic databank
* Sample gray-values in volume of interest
''3. Structure/ROI (Region of Interest) Analyze''
Every detected region is analyzed individually for special characteristics:
* Compactness
* Form, size and location
* Reference to close by structures / ROIs
* Average greylevel value analyze within a ROI
* Proportion of greylevels to border of the structure inside the ROI
''4. Evaluation / classification''
After the structure is analyzed, every ROI is evaluated individually (scoring) for the probability of a TP. The following procedures are examples of classification algorithms.
* Nearest-Neighbor Rule (e.g. ''k''-nearest neighbors)
* Minimum distance classifier
* Cascade classifier
Cascading is a particular case of ensemble learning based on the concatenation of several classifiers, using all information collected from the output from a given classifier as additional information for the next classifier in the cascade. Unli ...
* Naive Bayesian Classifier
* Artificial Neural Network
Artificial neural networks (ANNs), usually simply called neural networks (NNs) or neural nets, are computing systems inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains.
An ANN is based on a collection of connected units ...
* Radial basis function network (RBF)
* Support Vector Machine (SVM)
* Principle Component Analysis (PCA)
If the detected structures have reached a certain threshold level, they are highlighted in the image for the radiologist. Depending on the CAD system these markings can be permanently or temporary saved. The latter's advantage is that only the markings which are approved by the radiologist are saved. False hits should not be saved, because an examination at a later date becomes more difficult then.
Sensitivity and specificity
CAD systems seek to highlight suspicious structures. Today's CAD systems cannot detect 100% of pathological changes. The hit rate (sensitivity
Sensitivity may refer to:
Science and technology Natural sciences
* Sensitivity (physiology), the ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli
** Sensory processing sensitivity in humans
* Sensitivity and specificity, statisti ...
) can be up to 90% depending on system and application.
A correct hit is termed a True Positive (TP), while the incorrect marking of healthy sections constitutes a False Positive (FP). The less FPs indicated, the higher the specificity is. A low specificity reduces the acceptance of the CAD system because the user has to identify all of these wrong hits. The FP-rate in lung overview examinations (CAD Chest) could be reduced to 2 per examination. In other segments (''e.g.'' CT lung examinations) the FP-rate could be 25 or more. In CAST
Cast may refer to:
Music
* Cast (band), an English alternative rock band
* Cast (Mexican band), a progressive Mexican rock band
* The Cast, a Scottish musical duo: Mairi Campbell and Dave Francis
* ''Cast'', a 2012 album by Trespassers William
...
systems the FP rate must be extremely low (less than 1 per examination) to allow a meaningful study triage
In medicine, triage () is a practice invoked when acute care cannot be provided for lack of resources. The process rations care towards those who are most in need of immediate care, and who benefit most from it. More generally it refers to pri ...
.
Absolute detection rate
The absolute detection rate of the radiologist is an alternative metric to sensitivity and specificity. Overall, results of clinical trials about sensitivity, specificity, and the absolute detection rate can vary markedly. Each study result depends on its basic conditions and has to be evaluated on those terms. The following facts have a strong influence: * Retrospective or prospective design * Quality of the used images * Condition of the x-ray examination * Radiologist's experience and education * Type of lesion * Size of the considered lesionChallenges that CAD in Medicine Faces Today
Despite the many developments that CAD has achieved since the dawn of computers, there are still certain challenges that CAD systems face today. Some challenges are related to various algorithmic limitations in the procedures of a CAD system including input data collection, preprocessing, processing and system assessments. Algorithms are generally designed to select a single likely diagnosis, thus providing suboptimal results for patients with multiple, concurrent disorders. Today input data for CAD mostly come fromelectronic health records
An electronic health record (EHR) is the systematized collection of patient and population electronically stored health information in a digital format. These records can be shared across different health care settings. Records are shared throu ...
(EHR). Effective designing, implementing and analyzing for EHR is a major necessity on any CAD systems.
Due to the massive availability of data and the need to analyze such data, big data is also one of the biggest challenges that CAD systems face today. The increasingly vast amount of patient data is a serious problem. Often the patient data are complex and can be semi-structured or unstructured data
Unstructured data (or unstructured information) is information that either does not have a pre-defined data model or is not organized in a pre-defined manner. Unstructured information is typically text-heavy, but may contain data such as dates, n ...
. It requires highly developed approaches to store, retrieve and analyze them in reasonable time.
During the preprocessing stage, input data requires to be normalized. The normalization of input data includes noise reduction, and filtering. Processing may contain a few sub-steps depending on applications. Basic three sub-steps on medical imaging are segmentation, feature extraction
In machine learning, pattern recognition, and image processing, feature extraction starts from an initial set of measured data and builds derived values ( features) intended to be informative and non-redundant, facilitating the subsequent learning ...
/ selection and classification. These sub-steps require advanced techniques to analyze input data with less computational time. Although much effort has been devoted on creating innovative techniques for these procedures of CAD systems, there is still not the single best algorithm for each step. Ongoing studies in building innovative algorithms for all the aspects of CAD systems is essential.
There is also a lack of standardized assessment measures for CAD Systems. This fact may cause the difficulty for obtaining FDA approval for commercial use. Moreover, while many positive developments of CAD systems have been proven, studies for validating their algorithms for clinical practice has hardly been confirmed.
Other challenges are related to the problem for healthcare providers to adopt new CAD systems in clinical practice. Some negative studies may discourage the use of CAD. In addition, the lack of training of health professionals on the use of CAD sometimes brings the incorrect interpretation of the system outcomes. These challenges are described in more detail in.
Applications
 CAD is used in the diagnosis of
CAD is used in the diagnosis of breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or ...
, lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign ...
, colon cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel ...
, prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that su ...
, bone metastases, coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the myocardium, heart muscle due to build-up o ...
, congenital heart defect
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascula ...
, pathological brain detection, fracture detection, Alzheimer's disease, and diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy (also known as diabetic eye disease), is a medical condition in which damage occurs to the retina due to diabetes mellitus. It is a leading cause of blindness in developed countries.
Diabetic retinopathy affects up to 80 perc ...
.
Breast cancer
CAD is used in screeningmammography
Mammography (also called mastography) is the process of using low-energy X-rays (usually around 30 kVp) to examine the human breast for diagnosis and screening. The goal of mammography is the early detection of breast cancer, typically through d ...
(X-ray examination of the female breast). Screening mammography is used for the early detection of breast cancer. CAD systems are often utilized to help classify a tumor as malignant or benign. CAD is especially established in US and the Netherlands and is used in addition to human evaluation, usually by a radiologist
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiati ...
. The first CAD system for mammography was developed in a research project at the University of Chicago. Today it is commercially offered by iCAD and Hologic. However, while achieving high sensitivities, CAD systems tend to have very low specificity and the benefits of using CAD remain uncertain. A 2008 systematic review on computer-aided detection in screening mammography concluded that CAD does not have a significant effect on cancer detection rate, but does undesirably increase recall rate (''i.e.'' the rate of false positives). However, it noted considerable heterogeneity in the impact on recall rate across studies.
Recent advances in machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence.
Machine ...
, deep-learning and artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is intelligence—perceiving, synthesizing, and inferring information—demonstrated by machines, as opposed to intelligence displayed by animals and humans. Example tasks in which this is done include speech r ...
technology have enabled the development of CAD systems that are clinically proven to assist radiologists
Radiology ( ) is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose diseases and guide their treatment, within the bodies of humans and other animals. It began with radiography (which is why its name has a root referring to radiati ...
in addressing the challenges of reading mammographic images by improving cancer detection rates and reducing false positives and unnecessary patient recalls, while significantly decreasing reading times.
Procedures to evaluate mammography based on magnetic resonance imaging exist too.
Lung cancer (bronchial carcinoma)
In the diagnosis of lung cancer,computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
with special three-dimensional CAD systems are established and considered as appropriate second opinions. At this a volumetric dataset with up to 3,000 single images is prepared and analyzed. Round lesions (lung cancer
Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma (since about 98–99% of all lung cancers are carcinomas), is a malignant lung tumor characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. Lung carcinomas derive from transformed, malign ...
, metastases and benign changes) from 1 mm are detectable. Today all well-known vendors of medical systems offer corresponding solutions.
Early detection of lung cancer is valuable. However, the random detection of lung cancer in the early stage (stage 1) in the X-ray image is difficult. Round lesions that vary from 5–10 mm are easily overlooked.
The routine application of CAD Chest Systems may help to detect small changes without initial suspicion. A number of researchers developed CAD systems for detection of lung nodules (round lesions less than 30 mm) in chest radiography and CT, and CAD systems for diagnosis (''e.g.'', distinction between malignant and benign) of lung nodules in CT. Virtual dual-energy imaging improved the performance of CAD systems in chest radiography.
Colon cancer
CAD is available for detection of colorectal polyps in the colon in CT colonography. Polyps are small growths that arise from the inner lining of the colon. CAD detects the polyps by identifying their characteristic "bump-like" shape. To avoid excessive false positives, CAD ignores the normal colon wall, including the haustral folds.Cardiovascular disease
State-of-the-art methods in cardiovascular computing, cardiovascular informatics, and mathematical andcomputational model
A computational model uses computer programs to simulate and study complex systems using an algorithmic or mechanistic approach and is widely used in a diverse range of fields spanning from physics, chemistry and biology to economics, psychology, ...
ing can provide valuable tools in clinical decision-making. CAD systems with novel image-analysis-based markers as input can aid vascular physicians to decide with higher confidence on best suitable treatment for cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, ...
patients.
Reliable early-detection and risk-stratification of carotid atherosclerosis is of outmost importance for predicting strokes in asymptomatic patients.
To this end, various noninvasive and low-cost markers have been proposed, using ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies fr ...
-image-based features. These combine echogenicity, texture, and motion
In physics, motion is the phenomenon in which an object changes its position with respect to time. Motion is mathematically described in terms of displacement, distance, velocity, acceleration, speed and frame of reference to an observer and mea ...
characteristics to assist clinical decision towards improved prediction, assessment and management of cardiovascular risk.
CAD is available for the automatic detection of significant (causing more than 50% stenosis
A stenosis (from Ancient Greek στενός, "narrow") is an abnormal narrowing in a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture).
''Stricture' ...
) coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the myocardium, heart muscle due to build-up o ...
in coronary CT angiography (CCTA) studies.
Congenital heart defect
Early detection of pathology can be the difference between life and death. CADe can be done by auscultation with a digital stethoscope and specialized software, also known as Computer-aided auscultation. Murmurs, irregular heart sounds, caused by blood flowing through a defective heart, can be detected with high sensitivity and specificity. Computer-aided auscultation is sensitive to external noise and bodily sounds and requires an almost silent environment to function accurately.Pathological brain detection (PBD)
Chaplot et al. was the first to useDiscrete Wavelet Transform
In numerical analysis and functional analysis, a discrete wavelet transform (DWT) is any wavelet transform for which the wavelets are discretely sampled. As with other wavelet transforms, a key advantage it has over Fourier transforms is temporal ...
(DWT) coefficients to detect pathological brains. Maitra and Chatterjee employed the Slantlet transform, which is an improved version of DWT. Their feature vector of each image is created by considering the magnitudes of Slantlet transform outputs corresponding to six spatial positions chosen according to a specific logic.
In 2010, Wang and Wu presented a forward neural network (FNN) based method to classify a given MR brain image as normal or abnormal. The parameters of FNN were optimized via adaptive chaotic particle swarm optimization (ACPSO). Results over 160 images showed that the classification accuracy was 98.75%.
In 2011, Wu and Wang proposed using DWT for feature extraction, PCA for feature reduction, and FNN with scaled chaotic artificial bee colony (SCABC) as classifier.
In 2013, Saritha et al. were the first to apply wavelet entropy (WE) to detect pathological brains. Saritha also suggested to use spider-web plots. Later, Zhang et al. proved removing spider-web plots did not influence the performance. Genetic pattern search method was applied to identify abnormal brain from normal controls. Its classification accuracy was reported as 95.188%. Das et al. proposed to use Ripplet transform. Zhang et al. proposed to use particle swarm optimization (PSO). Kalbkhani et al. suggested to use GARCH model.
In 2014, El-Dahshan et al. suggested to use pulse coupled neural network.
In 2015, Zhou et al. suggested to apply naive Bayes classifier to detect pathological brains.
Alzheimer's disease
CADs can be used to identify subjects with Alzheimer's and mild cognitive impairment from normal elder controls. In 2014, Padma ''et al''. used combined wavelet statistical texture features to segment and classify AD benign and malignant tumor slices. Zhang et al. found kernel support vector machine decision tree had 80% classification accuracy, with an average computation time of 0.022s for each image classification. In 2019, Signaevsky ''et al''. have first reported a trained Fully Convolutional Network (FCN) for detection and quantification ofneurofibrillary tangle
Neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) are aggregates of hyperphosphorylated tau protein that are most commonly known as a primary biomarker of Alzheimer's disease. Their presence is also found in numerous other diseases known as tauopathies. Little is ...
s (NFT) in Alzheimer's disease and an array of other tauopathies. The trained FCN achieved high precision and recall in naive digital whole slide image (WSI) semantic segmentation, correctly identifying NFT objects using a SegNet model trained for 200 epochs. The FCN reached near-practical efficiency with average processing time of 45 min per WSI per Graphic Processing Unit (GPU), enabling reliable and reproducible large-scale detection of NFTs. The measured performance on test data of eight naive WSI across various tauopathies resulted in the recall
Recall may refer to:
* Recall (bugle call), a signal to stop
* Recall (information retrieval), a statistical measure
* ''ReCALL'' (journal), an academic journal about computer-assisted language learning
* Recall (memory)
* ''Recall'' (Overwat ...
, precision, and an F1 score
In statistical analysis of binary classification, the F-score or F-measure is a measure of a test's accuracy. It is calculated from the precision and recall of the test, where the precision is the number of true positive results divided by the ...
of 0.92, 0.72, and 0.81, respectively.
Eigenbrain is a novel brain feature that can help to detect AD, based on Principal Component Analysis
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a popular technique for analyzing large datasets containing a high number of dimensions/features per observation, increasing the interpretability of data while preserving the maximum amount of information, and ...
or Independent Component Analysis
In signal processing, independent component analysis (ICA) is a computational method for separating a multivariate signal into additive subcomponents. This is done by assuming that at most one subcomponent is Gaussian and that the subcomponents a ...
decomposition. Polynomial kernel SVM has been shown to achieve good accuracy. The polynomial KSVM performs better than linear SVM and RBF kernel SVM. Other approaches with decent results involve the use of texture analysis, morphological features, or high-order statistical features
Nuclear medicine
CADx is available for nuclear medicine images. Commercial CADx systems for the diagnosis of bone metastases in whole-body bone scans and coronary artery disease in myocardial perfusion images exist. With a high sensitivity and an acceptable false lesions detection rate, computer-aided automatic lesion detection system is demonstrated as useful and will probably in the future be able to help nuclear medicine physicians to identify possible bone lesions.Diabetic retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is a disease of the retina that is diagnosed predominantly by fundoscopic images. Diabetic patients in industrialised countries generally undergo regular screening for the condition. Imaging is used to recognize early signs of abnormal retinal blood vessels. Manual analysis of these images can be time-consuming and unreliable. CAD has been employed to enhance the accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of automated detection method. The use of some CAD systems to replace human graders can be safe and cost effective. Image pre-processing, and feature extraction and classification are two main stages of these CAD algorithms.Pre-processing methods
''Image normalization'' is minimizing the variation across the entire image. Intensity variations in areas between periphery and central macular region of the eye have been reported to cause inaccuracy of vessel segmentation. Based on the 2014 review, this technique was the most frequently used and appeared in 11 out of 40 recently (since 2011) published primary research. ''Histogram equalization'' is useful in enhancing contrast within an image. This technique is used to increase ''local contrast.'' At the end of the processing, areas that were dark in the input image would be brightened, greatly enhancing the contrast among the features present in the area. On the other hand, brighter areas in the input image would remain bright or be reduced in brightness to equalize with the other areas in the image. Besides vessel segmentation, other features related to diabetic retinopathy can be further separated by using this pre-processing technique. Microaneurysm and hemorrhages are red lesions, whereas exudates are yellow spots. Increasing contrast between these two groups allow better visualization of lesions on images. With this technique, 2014 review found that 10 out of the 14 recently (since 2011) published primary research.
''Green channel filtering'' is another technique that is useful in differentiating lesions rather than vessels. This method is important because it provides the maximal contrast between diabetic retinopathy-related lesions. Microaneurysms and hemorrhages are red lesions that appear dark after application of green channel filtering. In contrast, exudates, which appear yellow in normal image, are transformed into bright white spots after green filtering. This technique is mostly used according to the 2014 review, with appearance in 27 out of 40 published articles in the past three years. In addition, green channel filtering can be used to detect center of optic disc in conjunction with double-windowing system.
''Non-uniform illumination correction'' is a technique that adjusts for non-uniform illumination in fundoscopic image. Non-uniform illumination can be a potential error in automated detection of diabetic retinopathy because of changes in statistical characteristics of image. These changes can affect latter processing such as feature extraction and are not observable by humans. Correction of non-uniform illumination (f') can be achieved by modifying the pixel intensity using known original pixel intensity (f), and average intensities of local (λ) and desired pixels (μ) (see formula below). Walter-Klein transformation is then applied to achieve the uniform illumination. This technique is the least used pre-processing method in the review from 2014.
''Morphological operations'' is the second least used pre-processing method in 2014 review. The main objective of this method is to provide contrast enhancement, especially darker regions compared to background.
''Histogram equalization'' is useful in enhancing contrast within an image. This technique is used to increase ''local contrast.'' At the end of the processing, areas that were dark in the input image would be brightened, greatly enhancing the contrast among the features present in the area. On the other hand, brighter areas in the input image would remain bright or be reduced in brightness to equalize with the other areas in the image. Besides vessel segmentation, other features related to diabetic retinopathy can be further separated by using this pre-processing technique. Microaneurysm and hemorrhages are red lesions, whereas exudates are yellow spots. Increasing contrast between these two groups allow better visualization of lesions on images. With this technique, 2014 review found that 10 out of the 14 recently (since 2011) published primary research.
''Green channel filtering'' is another technique that is useful in differentiating lesions rather than vessels. This method is important because it provides the maximal contrast between diabetic retinopathy-related lesions. Microaneurysms and hemorrhages are red lesions that appear dark after application of green channel filtering. In contrast, exudates, which appear yellow in normal image, are transformed into bright white spots after green filtering. This technique is mostly used according to the 2014 review, with appearance in 27 out of 40 published articles in the past three years. In addition, green channel filtering can be used to detect center of optic disc in conjunction with double-windowing system.
''Non-uniform illumination correction'' is a technique that adjusts for non-uniform illumination in fundoscopic image. Non-uniform illumination can be a potential error in automated detection of diabetic retinopathy because of changes in statistical characteristics of image. These changes can affect latter processing such as feature extraction and are not observable by humans. Correction of non-uniform illumination (f') can be achieved by modifying the pixel intensity using known original pixel intensity (f), and average intensities of local (λ) and desired pixels (μ) (see formula below). Walter-Klein transformation is then applied to achieve the uniform illumination. This technique is the least used pre-processing method in the review from 2014.
''Morphological operations'' is the second least used pre-processing method in 2014 review. The main objective of this method is to provide contrast enhancement, especially darker regions compared to background.
Feature extractions and classifications
After pre-processing of funduscopic image, the image will be further analyzed using different computational methods. However, the current literature agreed that some methods are used more often than others during vessel segmentation analyses. These methods are SVM, multi-scale, vessel-tracking, region growing approach, and model-based approaches. ''Support vector machine'' is by far the most frequently used classifier in vessel segmentation, up to 90% of cases. SVM is a supervised learning model that belongs to the broader category of pattern recognition technique. The algorithm works by creating a largest gap between distinct samples in the data. The goal is to create the largest gap between these components that minimize the potential error in classification. In order to successfully segregate blood vessel information from the rest of the eye image, SVM algorithm creates support vectors that separate the blood vessel pixel from the rest of the image through a supervised environment. Detecting blood vessel from new images can be done through similar manner using support vectors. Combination with other pre-processing technique, such as green channel filtering, greatly improves the accuracy of detection of blood vessel abnormalities. Some beneficial properties of SVM include
* Flexibility – Highly flexible in terms of function
* Simplicity – Simple, especially with large datasets (only support vectors are needed to create separation between data)
''Multi-scale'' approach is a multiple resolution approach in vessel segmentation. At low resolution, large-diameter vessels can first be extracted. By increasing resolution, smaller branches from the large vessels can be easily recognized. Therefore, one advantage of using this technique is the increased analytical speed. Additionally, this approach can be used with 3D images. The surface representation is a surface normal to the curvature of the vessels, allowing the detection of abnormalities on vessel surface.
''Vessel tracking'' is the ability of the algorithm to detect "centerline" of vessels. These centerlines are maximal peak of vessel curvature. Centers of vessels can be found using directional information that is provided by Gaussian filter. Similar approaches that utilize the concept of centerline are the skeleton-based and differential geometry-based.
''Region growing'' approach is a method of detecting neighboring pixels with similarities. A seed point is required for such method to start. Two elements are needed for this technique to work: similarity and spatial proximity. A neighboring pixel to the seed pixel with similar intensity is likely to be the same type and will be added to the growing region. One disadvantage of this technique is that it requires manual selection of seed point, which introduces bias and inconsistency in the algorithm. This technique is also being used in optic disc identification.
''Model-based'' approaches employ representation to extract vessels from images. Three broad categories of model-based are known: deformable, parametric, and template matching. Deformable methods uses objects that will be deformed to fit the contours of the objects on the image. Parametric uses geometric parameters such as tubular, cylinder, or ellipsoid representation of blood vessels. Classical snake contour in combination with blood vessel topological information can also be used as a model-based approach. Lastly, template matching is the usage of a template, fitted by stochastic deformation process using Hidden Markov Mode 1.
''Support vector machine'' is by far the most frequently used classifier in vessel segmentation, up to 90% of cases. SVM is a supervised learning model that belongs to the broader category of pattern recognition technique. The algorithm works by creating a largest gap between distinct samples in the data. The goal is to create the largest gap between these components that minimize the potential error in classification. In order to successfully segregate blood vessel information from the rest of the eye image, SVM algorithm creates support vectors that separate the blood vessel pixel from the rest of the image through a supervised environment. Detecting blood vessel from new images can be done through similar manner using support vectors. Combination with other pre-processing technique, such as green channel filtering, greatly improves the accuracy of detection of blood vessel abnormalities. Some beneficial properties of SVM include
* Flexibility – Highly flexible in terms of function
* Simplicity – Simple, especially with large datasets (only support vectors are needed to create separation between data)
''Multi-scale'' approach is a multiple resolution approach in vessel segmentation. At low resolution, large-diameter vessels can first be extracted. By increasing resolution, smaller branches from the large vessels can be easily recognized. Therefore, one advantage of using this technique is the increased analytical speed. Additionally, this approach can be used with 3D images. The surface representation is a surface normal to the curvature of the vessels, allowing the detection of abnormalities on vessel surface.
''Vessel tracking'' is the ability of the algorithm to detect "centerline" of vessels. These centerlines are maximal peak of vessel curvature. Centers of vessels can be found using directional information that is provided by Gaussian filter. Similar approaches that utilize the concept of centerline are the skeleton-based and differential geometry-based.
''Region growing'' approach is a method of detecting neighboring pixels with similarities. A seed point is required for such method to start. Two elements are needed for this technique to work: similarity and spatial proximity. A neighboring pixel to the seed pixel with similar intensity is likely to be the same type and will be added to the growing region. One disadvantage of this technique is that it requires manual selection of seed point, which introduces bias and inconsistency in the algorithm. This technique is also being used in optic disc identification.
''Model-based'' approaches employ representation to extract vessels from images. Three broad categories of model-based are known: deformable, parametric, and template matching. Deformable methods uses objects that will be deformed to fit the contours of the objects on the image. Parametric uses geometric parameters such as tubular, cylinder, or ellipsoid representation of blood vessels. Classical snake contour in combination with blood vessel topological information can also be used as a model-based approach. Lastly, template matching is the usage of a template, fitted by stochastic deformation process using Hidden Markov Mode 1.
Effects on employment
Automation of medical diagnosis labor (for example, quantifying red blood cells) has some historical precedent. The deep learning revolution of the 2010s has already produced AIs that are more accurate in many areas of visual diagnosis than radiologists and dermatologists, and this gap is expected to grow. Some experts, including many doctors, are dismissive of the effects that AI will have on medical specialties. In contrast, many economists and artificial intelligence experts believe that fields such as radiology will be massively disrupted, with unemployment or downward pressure on the wages of radiologists; hospitals will need fewer radiologists overall, and many of the radiologists who still exist will require substantial retraining.Geoffrey Hinton
Geoffrey Everest Hinton One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from the royalsociety.org website where: (born 6 December 1947) is a British-Canadian cognitive psychologist and computer scientist, most noted for his work on ...
, the "Godfather of deep learning", argues that (in view of the likely advances expected in the next five or ten years) hospitals should immediately stop training radiologists, as their time-consuming and expensive training on visual diagnosis will soon be mostly obsolete, leading to a glut of traditional radiologists. An op-ed in ''JAMA
''The Journal of the American Medical Association'' (''JAMA'') is a peer-reviewed medical journal published 48 times a year by the American Medical Association. It publishes original research, reviews, and editorials covering all aspects of bi ...
'' argues that pathologists and radiologists should merge into a single "information specialist" role, and state that "To avoid being replaced by computers, radiologists must allow themselves to be displaced by computers." Information specialists would be trained in "Bayesian logic, statistics, data science", and some genomics and biometrics; manual visual pattern recognition would be greatly de-emphasized compared with current onerous radiology training.
See also
* Computerized Systems Used In Clinical Trials *Diagnostic robot In medicine and robotics, diagnostic robots are diagnosis tools in the form of a physical robot or a software expert system. Developed in the 1970s near the height of the AI boom, automatic diagnosis systems are capable of gathering data for medical ...
References
External links
Digital Retinal Images for Vessel Extraction (DRIVE)
STructured Analysis of the REtina (STARE)
High-Resolution Fundus (HRF) Image Database
{{Computer vision footer Medical expert systems Radiology Health informatics Applications of computer vision