co-fired ceramic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
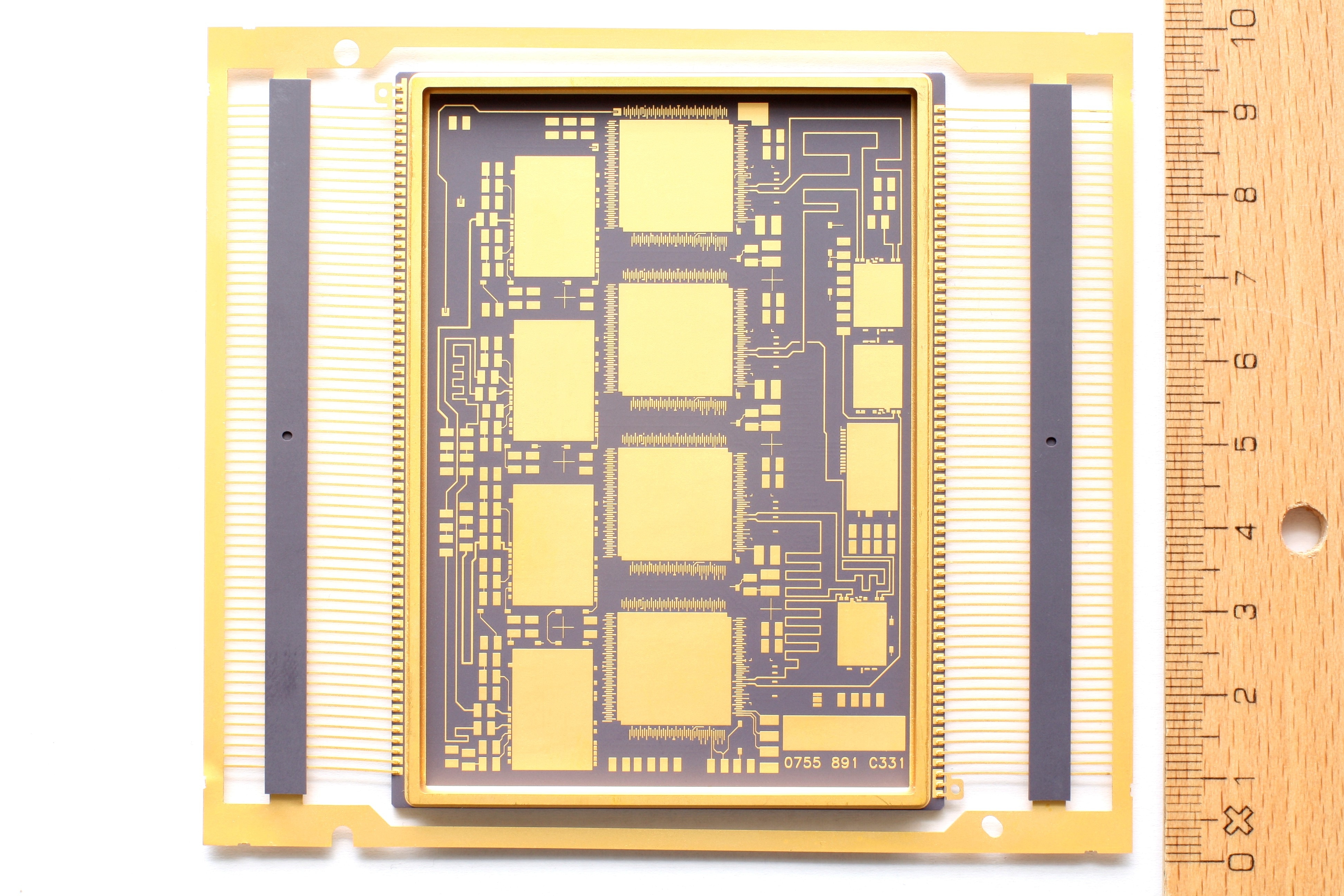 Co-fired ceramic devices are
Co-fired ceramic devices are
Millimeter-wave Performance of Alumina High Temperature Cofired Ceramics IC Packages
, Rick Sturdivant, 2006 IMAPS Conference, San Diego, CA. Compared to LTCC, HTCC has higher- resistance conductive layers.
Animation of LTCC production process
Packaging (microfabrication) Electronics manufacturing
 Co-fired ceramic devices are
Co-fired ceramic devices are monolithic
A monolith is a monument or natural feature consisting of a single massive stone or rock.
Monolith or monolithic may also refer to:
Architecture
* Monolithic architecture, a style of construction in which a building is carved, cast or excavated ...
, ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain ...
microelectronic devices where the entire ceramic support structure and any conductive, resistive, and dielectric materials are fired in a kiln at the same time. Typical devices include capacitors, inductors
An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a c ...
, resistors, transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...
s, and hybrid circuits. The technology is also used for robust assembly and packaging of electronic components multi-layer packaging in the electronics industry, such as military electronics, MEMS
Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), also written as micro-electro-mechanical systems (or microelectronic and microelectromechanical systems) and the related micromechatronics and microsystems constitute the technology of microscopic devices, ...
, microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circ ...
and RF applications.
Co-fired ceramic devices are fabricated using a multilayer approach. The starting material is composite green tapes, consisting of ceramic particles mixed with polymer binders. The tapes are flexible and can be machined, for example, using cutting, milling, punching and embossing. Metal structures can be added to the layers, commonly using filling and screen printing. Individual tapes are then bonded together in a lamination procedure before the devices are fired in a kiln, where the polymer part of the tape is combusted and the ceramic particles sinter together, forming a hard and dense ceramic component.
Co-firing can be divided into low-temperature (LTCC) and high-temperature (HTCC) applications: low temperature means that the sintering
Clinker nodules produced by sintering
Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by pressure or heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction.
Sintering happens as part of a manufacturing ...
temperature is below , while high temperature is around . The lower sintering temperature for LTCC materials is made possible through the addition of a glassy phase to the ceramic, which lowers its melting temperature.
Due to a multilayer approach based on glass-ceramics sheets, this technology offers the possibility to integrate into the LTCC body passive electrical components and conductor lines typically manufactured in thick-film technology. This differs from semiconductor device fabrication
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuit (IC) chips such as modern computer processors, microcontrollers, and memory chips such as NAND flash and DRAM that are p ...
, where layers are processed serially, and each new layer is fabricated on top of previous layers.
History
Co-fired ceramics were first developed in the late 1950s and early 1960s to make more robust capacitors. The technology was later expanded in the 1960s to include multilayer structures similar to printed circuit boards.Components
Hybrid circuits
LTCC technology is especially beneficial for RF and high-frequency applications. In RF andwireless
Wireless communication (or just wireless, when the context allows) is the transfer of information between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most ...
applications, LTCC technology is also used to produce multilayer hybrid integrated circuits, which can include resistors, inductors, capacitors, and active components in the same package. In detail, these applications comprise mobile telecommunication devices (0.8–2 GHz), wireless
Wireless communication (or just wireless, when the context allows) is the transfer of information between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most ...
local networks such as Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard that is used for exchanging data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances and building personal area networks (PANs). In the most widely used mode, transmission power is limi ...
(2.4 GHz) to in-car radars
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance (''ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, ...
(50–140 GHz, and 76 GHz). LTCC hybrids have a smaller initial ("non recurring") cost as compared with ICs, making them an attractive alternative to ASICs for small scale integration devices.
Inductors
Inductors are formed by printing conductor windings on ferrite ceramic tape. Depending on the desired inductance and current carrying capabilities a partial winding to several windings may be printed on each layer. Under certain circumstances, a non-ferrite ceramic may be used. This is most common for hybrid circuits where capacitors, inductors, and resistors will all be present and for high operating frequency applications where the hysteresis loop of the ferrite becomes an issue.Resistors
Resistors may be embedded components or added to the top layer post-firing. Using screen printing, a resistor paste is printed onto the LTCC surface, from which resistances needed in the circuit are generated. When fired, these resistors deviate from their design value (±25%) and therefore require adjustment to meet the final tolerance. WithLaser trimming
{{Unreferenced, date=June 2015
Laser trimming is the manufacturing process of using a laser to adjust the operating parameters of an electronic circuit.
One of the most common applications uses a laser to burn away small portions of resistors, ...
one can achieve these resistances with different cut forms to the exact resistance value (±1%) desired. With this procedure, the need for additional discrete resistors can be reduced, thereby allowing a further miniaturization of the printed circuit boards.
Transformers
LTCC transformers are similar to LTCC inductors except transformers contain two or more windings. To improve coupling between windings transformers includes a low-permeability dielectric material printed over the windings on each layer. The monolithic nature of LTCC transformers leads to a lower height than traditional wire wound transformers. Also, the integrated core and windings mean these transformers are not prone to wire break failures in high mechanical stress environments.Sensors
Integration of thick-film passive components and 3D mechanical structures inside one module permitted the fabrication of sophisticated 3D LTCC sensors e.g. accelerometers.Microsystems
The possibility of the fabrication of many various passive thick-film components, sensors and 3D mechanical structures enabled the fabrication of multilayer LTCC microsystems. Using HTCC technology, microsystems for harsh environments, such as working temperatures of 1000 °C, have been realized.Applications
LTCC substrates can be most beneficially used for the realization of miniaturized devices and robust substrates. LTCC technology allows the combination of individual layers with different functionalities such as high permittivity and low dielectric loss into a single multilayer laminated package and thereby to achieve multi-functionality in combination with a high integration and interconnection level. It also provides the possibility to fabricate three-dimensional, robust structures enabling in combination with thick film technology the integration of passive, electronic components, such as capacitors, resistors, and inductors into a single device.Comparison
Low-temperature co-firing technology presents advantages compared to other packaging technologies including high-temperature co-firing: the ceramic is generally fired below 1,000 °C due to a special composition of the material. This permits the co-firing with highly conductive materials (silver, copper, and gold). LTCC also features the ability to embed passive elements, such as resistors, capacitors and inductors into the ceramic package, minimising the size of the completed module. HTCC components generally consist of multilayers of alumina orzirconia
Zirconium dioxide (), sometimes known as zirconia (not to be confused with zircon), is a white crystalline oxide of zirconium. Its most naturally occurring form, with a monoclinic crystalline structure, is the mineral baddeleyite. A dopant sta ...
with platinum, tungsten and molymanganese metalization. The advantages of HTCC in packaging technology includes mechanical rigidity and hermeticity, both of which are important in high-reliability and environmentally stressful applications. Another advantage is HTCC's thermal dissipation capability, which makes this a microprocessor packaging choice, especially for higher-performance processors., Rick Sturdivant, 2006 IMAPS Conference, San Diego, CA. Compared to LTCC, HTCC has higher- resistance conductive layers.
See also
*Tape casting Tape casting (also called doctor blading, knife coating, and shank shifting) is a casting process used in the manufacture of thin ceramic tapes and sheets from ceramic slurry. The ceramic slurry is cast in a thin layer onto a flat surface and then d ...
* Laser trimming
{{Unreferenced, date=June 2015
Laser trimming is the manufacturing process of using a laser to adjust the operating parameters of an electronic circuit.
One of the most common applications uses a laser to burn away small portions of resistors, ...
* Hybrid integrated circuit
A hybrid integrated circuit (HIC), hybrid microcircuit, hybrid circuit or simply hybrid is a miniaturized electronic circuit constructed of individual devices, such as semiconductor devices (e.g. transistors, diodes or monolithic ICs) and pa ...
References
{{ReflistExternal links
Animation of LTCC production process
Packaging (microfabrication) Electronics manufacturing