Claus Van Amsberg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Prince Claus of the Netherlands, Jonkheer van Amsberg (born Klaus-Georg Wilhelm Otto Friedrich Gerd von Amsberg; 6 September 1926 – 6 October 2002) was
 Claus suffered various health problems, such as depression,
Claus suffered various health problems, such as depression,
 Knight Grand Cross of the
Knight Grand Cross of the  Recipient of the Cross Medal of Nijmegen Marching Proficiency
**
Recipient of the Cross Medal of Nijmegen Marching Proficiency
** Recipient of the Queen Beatrix Inauguration Medal
**
Recipient of the Queen Beatrix Inauguration Medal
** Recipient of the Wedding Medal of Prince Willem-Alexander, Prince of Orange and Maxima Zorreguieta
Recipient of the Wedding Medal of Prince Willem-Alexander, Prince of Orange and Maxima Zorreguieta
 Grand Star of the
Grand Star of the  Knight of the Order of the Elephant (29 October 1975)
* Ethiopian Imperial Family:
**
Knight of the Order of the Elephant (29 October 1975)
* Ethiopian Imperial Family:
** Grand Cordon of the
Grand Cordon of the  Grand Cross of the Order of the Legion of Honour (1984)
*:
**
Grand Cross of the Order of the Legion of Honour (1984)
*:
** Grand Cross Special Class of the
Grand Cross Special Class of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Knight Grand Cross with Collar of the
Knight Grand Cross with Collar of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Cordon of the
Grand Cordon of the  Grand Cross with Collar of the
Grand Cross with Collar of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Knight Grand Cross of the
Knight Grand Cross of the  Knight Grand Cross of the
Knight Grand Cross of the Prince Claus wearing the Order of Isabella the Catholic
/ref> *: ** Commander Grand Cross of the
Commander Grand Cross of the  Grand Corodn of the of the
Grand Corodn of the of the  Honorary Knight Grand Cross of the
Honorary Knight Grand Cross of the
In pictures: Prince Claus remembered
Video: Condolences pour in, 7 October 2002
Dutch Royal Family website: Biography
Profile at The International Institute of Social Studies
(ISS) , - {{DEFAULTSORT:Claus Of The Netherlands, Prince 1926 births 2002 deaths 20th-century Dutch diplomats German diplomats Former Lutherans German Calvinist and Reformed Christians German humanitarians German emigrants to the Netherlands German expatriates in the Dominican Republic German expatriates in Ivory Coast Development specialists Honorary consuls Princes of the Netherlands Dutch royal consorts Dutch people of German descent Dutch nonprofit executives Converts to Calvinism from Lutheranism German Army personnel of World War II Amsberg Members of the Council of State (Netherlands) People in international development Jonkheers of Amsberg Dutch members of the Dutch Reformed Church Dutch nonprofit directors Dutch corporate directors People from Hitzacker People from the Province of Hanover Deaths from Parkinson's disease Deaths from pneumonia in the Netherlands Hitler Youth members German prisoners of war in World War II held by the United States Neurological disease deaths in the Netherlands House of Orange-Nassau 20th-century German civil servants Burials in the Royal Crypt at Nieuwe Kerk, Delft Recipients of the Grand Decoration with Sash for Services to the Republic of Austria Grand Crosses Special Class of the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany Knights Grand Cross of the Order of the Falcon Grand Crosses of the Order of Christ (Portugal) Honorary Knights Grand Cross of the Royal Victorian Order
Prince consort of the Netherlands
A consort of the Netherlands is a person married to a Dutch monarch during his or her reign. All female spouses of the monarchs of the Netherlands have been titled "Queen of the Netherlands" with the style ''Majesty''. The male spouses of the three ...
from 30 April 1980 until his death in 2002 as the husband of Queen Beatrix
Beatrix (Beatrix Wilhelmina Armgard, ; born 31 January 1938) is a member of the Dutch royal house who reigned as Queen of the Netherlands from 1980 until her abdication in 2013.
Beatrix is the eldest daughter of Queen Juliana and her husban ...
.
Biography
Klaus-Georg Wilhelm Otto Friedrich Gerd von Amsberg was born on his family's estate, Castle Dötzingen,Hitzacker
Hitzacker is a town in the Lüchow-Dannenberg district of Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated on the river Elbe, approx. 8 km north of Dannenberg, and 45 km east of Lüneburg. The 2007 population of Hitzacker was 4,982, and its posta ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, on 6 September 1926. His parents were Claus Felix von Amsberg and Baroness Gösta von dem Bussche-Haddenhausen. His father, by birth member of House of Amsberg
Amsberg (german: von Amsberg, nl, van Amsberg) is the name of a German noble family from Mecklenburg. A great-grandson of a blacksmith, parish pastor August Amsberg (1747–1820) started calling himself "von Amsberg" in 1795 and the family's r ...
which belonged to the untitled German nobility
The German nobility (german: deutscher Adel) and royalty were status groups of the medieval society in Central Europe, which enjoyed certain privileges relative to other people under the laws and customs in the German-speaking area, until the b ...
, operated a large farm in Tanganyika
Tanganyika may refer to:
Places
* Tanganyika Territory (1916–1961), a former British territory which preceded the sovereign state
* Tanganyika (1961–1964), a sovereign state, comprising the mainland part of present-day Tanzania
* Tanzania Main ...
(formerly German East Africa) from 1928 until World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. From 1938, Claus and his six sisters grew up on their maternal grandparents' estate in Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
; he attended the Friderico-Francisceum-Gymnasium
The Friderico-Francisceum (FFG) is a gymnasium in Bad Doberan, Germany.
History
In 1879, Frederick Francis II, Grand Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin decided to establish a gymnasium in Doberan, a city of 4000 inhabitants which had been granted to ...
in Bad Doberan
Bad Doberan () is a town in the district of Rostock, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It was the capital of the former district of Bad Doberan. In 2012, its population was 11,427.
Geography
Bad Doberan is situated just west of Rostock's city c ...
from 1933 to 1936 and a boarding school in Tanganyika from 1936 to 1938.
Claus was a member of such Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
youth organisation
The following is a list of youth organizations. A youth organization is a type of organization with a focus upon providing activities and socialization for minors. In this list, most organizations are international unless noted otherwise.
...
s as Deutsches Jungvolk
The ''Deutsches Jungvolk in der Hitlerjugend'' (; DJ, also DJV; German for "German Youngsters in the Hitler Youth") was the separate section for boys aged 10 to 13 of the Hitler Youth organisation in Nazi Germany. Through a programme of outdoor a ...
and the Hitler Youth
The Hitler Youth (german: Hitlerjugend , often abbreviated as HJ, ) was the youth organisation of the Nazi Party in Germany. Its origins date back to 1922 and it received the name ("Hitler Youth, League of German Worker Youth") in July 1926. ...
. From 1938 until 1942, he attended the Baltenschule Misdroy.
In 1944, Claus was conscripted into the German Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
, becoming a soldier in the German 90th Panzergrenadier Division in Italy in March 1945. He was taken prisoner of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold prisoners of w ...
by the American forces at Meran
Merano (, , ) or Meran () is a city and ''comune'' in South Tyrol, northern Italy. Generally best known for its spa resorts, it is located within a basin, surrounded by mountains standing up to above sea level, at the entrance to the Passeier ...
before taking part in any fighting. After his repatriation
Repatriation is the process of returning a thing or a person to its country of origin or citizenship. The term may refer to non-human entities, such as converting a foreign currency into the currency of one's own country, as well as to the pro ...
, he finished school in Lüneburg
Lüneburg (officially the ''Hanseatic City of Lüneburg'', German: ''Hansestadt Lüneburg'', , Low German ''Lümborg'', Latin ''Luneburgum'' or ''Lunaburgum'', Old High German ''Luneburc'', Old Saxon ''Hliuni'', Polabian ''Glain''), also calle ...
and studied law
Law is a set of rules that are created and are enforceable by social or governmental institutions to regulate behavior,Robertson, ''Crimes against humanity'', 90. with its precise definition a matter of longstanding debate. It has been vario ...
in Hamburg
(male), (female) en, Hamburger(s),
Hamburgian(s)
, timezone1 = Central (CET)
, utc_offset1 = +1
, timezone1_DST = Central (CEST)
, utc_offset1_DST = +2
, postal ...
. He then joined the German diplomatic corps
The diplomatic corps (french: corps diplomatique) is the collective body of foreign diplomats accredited to a particular country or body.
The diplomatic corps may, in certain contexts, refer to the collection of accredited heads of mission ( ...
and worked in Santo Domingo
, total_type = Total
, population_density_km2 = auto
, timezone = AST (UTC −4)
, area_code_type = Area codes
, area_code = 809, 829, 849
, postal_code_type = Postal codes
, postal_code = 10100–10699 ( Distrito Nacional)
, webs ...
and Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
. In the 1960s, he was transferred to Bonn
The federal city of Bonn ( lat, Bonna) is a city on the banks of the Rhine in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia, with a population of over 300,000. About south-southeast of Cologne, Bonn is in the southernmost part of the Rhine-Ruhr r ...
.
Claus met Princess Beatrix for the first time on New Year's Eve 1962 in Bad Driburg at a dinner hosted by the Count von Oeynhausen-Sierstorpff, who was a distant relative of both of them. Claus and Beatrix were also distantly related (5th cousins twice removed), as both being descendants from von dem Bussche family. They met again at the wedding-eve party of Princess Tatjana of Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg
Sayn-Wittgenstein-Berleburg was one of several imperial counties and later principalities ruled by the House of Sayn-Wittgenstein.
Most of the former county is located in the present district of Siegen-Wittgenstein (in the modern state of Nort ...
and Moritz, Landgrave of Hesse
Moritz, Landgrave of Hesse (legally ''Moritz Friedrich Karl Emanuel Humbert Prinz und Landgraf von Hessen'' 6 August 1926 – 23 May 2013) was the son of Prince Philip, Landgrave of Hesse, and the head of the House of Brabant and the German H ...
, in the summer of 1964. With memories of German oppression still very strong 20 years after the war, sections of the Dutch population were unhappy that Beatrix's fiancé was a German and former member of the Hitler Youth
The Hitler Youth (german: Hitlerjugend , often abbreviated as HJ, ) was the youth organisation of the Nazi Party in Germany. Its origins date back to 1922 and it received the name ("Hitler Youth, League of German Worker Youth") in July 1926. ...
. Nonetheless, Queen Juliana
Juliana (; Juliana Louise Emma Marie Wilhelmina; 30 April 1909 – 20 March 2004) was Queen of the Netherlands from 1948 until her abdication in 1980.
Juliana was the only child of Queen Wilhelmina and Prince Henry of Mecklenburg-Schwerin. S ...
gave the engagement her blessing after giving serious thought to canceling it. The engagement was approved by the States-General—a necessary step for Beatrix to remain in the line of succession to the throne—in 1965. He was granted Dutch citizenship later that year and changed the spellings of his names to Dutch.
The couple were married on 10 March 1966. Their wedding day saw violent protests, most notably by the anarchist-artist group Provo. They included such memorable slogans as "Claus, 'raus!" (Claus, get out!) and "Mijn fiets terug" (Give me back my bike), a reference to the memory of occupying German soldiers confiscating Dutch bicycles. A smoke bomb was thrown at the wedding carriage by a group of Provos. For a time, it was thought that Beatrix would be the last monarch of the Netherlands.
However, over time, Claus became accepted by the public, so much so that during the last part of his life he was considered by some to be the most popular member of the Royal Family
A royal family is the immediate family of kings/queens, emirs/emiras, sultans/ sultanas, or raja/ rani and sometimes their extended family. The term imperial family appropriately describes the family of an emperor or empress, and the term ...
. This change in Dutch opinion was brought about by Claus's strong motivation to contribute to public causes (especially Third World
The term "Third World" arose during the Cold War to define countries that remained non-aligned with either NATO or the Warsaw Pact. The United States, Canada, Japan, South Korea, Western European nations and their allies represented the " First ...
development, on which he was considered an expert), his sincere modesty and his candor (within but sometimes on the edge of royal protocol).
The public also sympathised with Claus for his efforts to give meaning to his life beyond the restrictions that Dutch law imposed on the Royal Family's freedom of speech and action. However, these restrictions were gradually loosened; Claus was even appointed as senior staff member at the Department of Developing Aid, albeit in an advisory role.
One example of his attitude toward protocol was the "Declaration of the Tie". In 1998, after presenting the annual Prince Claus Awards
The Prince Claus Fund was established in 1996, named in honor of Prince Claus of the Netherlands. It receives an annual subsidy from the Dutch Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
The Fund has presented the international Prince Claus Awards annually si ...
to three Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
n fashion design
Fashion design is the art of applying design, aesthetics, clothing construction and natural beauty to clothing and its accessories. It is influenced by culture and different trends, and has varied over time and place. "A fashion designer creates ...
ers, Claus told "workers of all nations to unite and cast away the new shackles they have voluntarily cast upon themselves", meaning the necktie, that "snake around my neck," and encouraged the audience to "venture into open-collar
Collar may refer to:
Human neckwear
*Clerical collar (informally ''dog collar''), a distinctive collar used by the clergy of some Christian religious denominations
*Collar (clothing), the part of a garment that fastens around or frames the neck
...
paradise
In religion, paradise is a place of exceptional happiness and delight. Paradisiacal notions are often laden with pastoral imagery, and may be cosmogonical or eschatological or both, often compared to the miseries of human civilization: in parad ...
". He then removed his tie and threw it on the floor.
Claus battled depression for a number of years, and underwent surgery in 1998 to remove his prostate. In 2001, he underwent another surgery to remove one of his kidneys. He eventually died on 6 October 2002 from Parkinson's disease and heart failure.
Activities
As a husband of the heir, Claus was a member of the National Advisory Council for Development Cooperation and its Bureau, and was a chair of the National Committee for Development Strategy 1970‑1980 and the Netherlands Development Organization. He also worked as special advisor to the Minister for Development Cooperation. He held these positions until 1980. On 30 April 1980, Claus' mother-in-law, Queen Juliana, abdicated in favour of Princess Beatrix, who became Queen of the Netherlands. After the investiture, the couple visited the Netherlands Antilles andAruba
Aruba ( , , ), officially the Country of Aruba ( nl, Land Aruba; pap, Pais Aruba) is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands physically located in the mid-south of the Caribbean Sea, about north of the Venezuela peninsula of ...
. As a prince consort, Prince Claus frequently visited public organisations, commercial and industrial enterprises, and companies in the agriculture and fisheries sector.
In 1984, Claus became the Inspector General for Development Cooperation, member of the Board of Directors of De Nederlandsche Bank N.V. (until 1998), member of the Board of Directors of Royal PTT Nederland, and Chair of the Transport and Public Works Platform.
Claus was an honorary chair of the National Coordinating Committee for the Protection of Monuments and Historic Buildings and the King William I Foundation. He was also a patron of the Concertgebouw Orchestra and Scouting Netherlands.
On Claus' seventieth birthday, the Prince Claus Fund for Culture and Development was established on the initiative of the Dutch government. The fund focused on enhancing understanding of cultures and promoting interaction between culture and development.
Declining health and death
 Claus suffered various health problems, such as depression,
Claus suffered various health problems, such as depression, cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
and Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms becom ...
. He died of complications of pneumonia
Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and difficulty breathing. The severity ...
and Parkinson's at the Academic Medical Center
An academic medical centre (AMC), variously also known as academic health science centre, academic health science system, or academic health science partnership, is an educational and healthcare institute formed by the grouping of a health profes ...
in Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the Capital of the Netherlands, capital and Municipalities of the Netherlands, most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population ...
on 6 October 2002 after a long illness, aged 76. He died less than four months after the birth of his first grandchild.
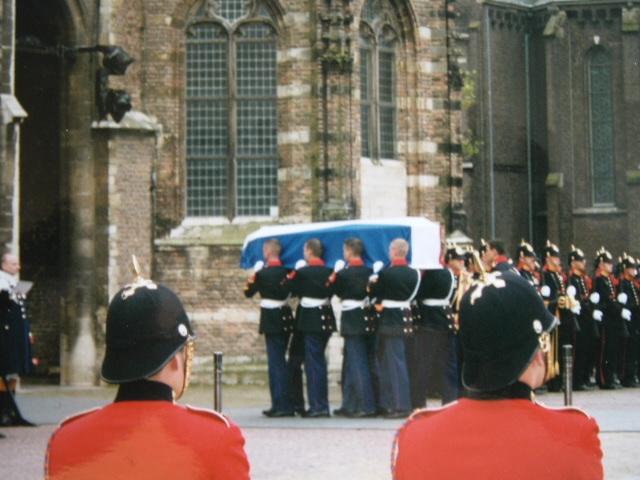
Claus was interred in the Royal Family's tomb in Delft on 15 October. It was the first full state funeral
A state funeral is a public funeral ceremony, observing the strict rules of Etiquette, protocol, held to honour people of national significance. State funerals usually include much pomp and ceremony as well as religious overtones and distinctive ...
since Queen Wilhelmina
Wilhelmina (; Wilhelmina Helena Pauline Maria; 31 August 1880 – 28 November 1962) was Queen of the Netherlands from 1890 until her abdication in 1948. She reigned for nearly 58 years, longer than any other Dutch monarch. Her reign saw World Wa ...
's in 1962.
Titles, styles, honours, and arms
Titles
*6 September 1926 – 16 February 1966: Klaus von Amsberg *16 February 1966 – 10 March 1966: Claus van Amsberg *10 March 1966 – 6 October 2002: ''His Royal Highness'' Prince Claus of the Netherlands, Jonkheer van AmsbergHonours
National
*: **Order of the Netherlands Lion
The Order of the Netherlands Lion, also known as the Order of the Lion of the Netherlands ( nl, De Orde van de Nederlandse Leeuw, french: L'Ordre du Lion Néerlandais) is a Dutch order of chivalry founded by King William I of the Netherlands on ...
(1966)
** Recipient of the Cross Medal of Nijmegen Marching Proficiency
**
Recipient of the Cross Medal of Nijmegen Marching Proficiency
** Recipient of the Queen Beatrix Inauguration Medal
**
Recipient of the Queen Beatrix Inauguration Medal
** Recipient of the Wedding Medal of Prince Willem-Alexander, Prince of Orange and Maxima Zorreguieta
Recipient of the Wedding Medal of Prince Willem-Alexander, Prince of Orange and Maxima Zorreguieta
Foreign
*: ** Grand Star of the
Grand Star of the Decoration of Honour for Services to the Republic of Austria
The Decoration of Honour for Services to the Republic of Austria (german: Ehrenzeichen für Verdienste um die Republik Österreich) is a state decoration of the Republic of Austria. It is divided into 15 classes and is the highest award in the A ...
(1994)
*:
** Grand Cordon of the
Grand Cordon of the Order of the Queen of Sheba
The Order of the Queen of Sheba was originally instituted as a ladies' order in 1922 in the Ethiopian Empire by Empress Zawditu and would later become the diplomatic symbol of a holy pact.
Classes
The Order of the Queen of Sheba is presented in ...
(1969)
*:
**Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany
The Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany (german: Verdienstorden der Bundesrepublik Deutschland, or , BVO) is the only federal decoration of Germany. It is awarded for special achievements in political, economic, cultural, intellect ...
(1 March 1983)
*:
** Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the Order of the Falcon
The Order of the Falcon ( is, Hin íslenska fálkaorða) is the only order of chivalry in Iceland, founded by King Christian X of Denmark and Iceland on 3 July 1921. The award is awarded for merit for Iceland and humanity and has five degrees. N ...
(1994)
*:
**Order of Merit of the Italian Republic
The Order of Merit of the Italian Republic ( it, Ordine al Merito della Repubblica Italiana) is the senior Italian order of merit. It was established in 1951 by the second President of the Italian Republic, Luigi Einaudi.
The highest-ranking ...
(27 March 1985)
*:
**National Order of the Ivory Coast
The National Order of the Ivory Coast (sometimes simply mentioned as National Order) is the highest state order of knighthood of the Ivory Coast.
History
The Order was founded on 10 April 1961 to celebrate the independence of the Ivory Coast wh ...
(1973)
*:
**Order of the Chrysanthemum
is Japan's highest order. The Grand Cordon of the Order was established in 1876 by Emperor Meiji of Japan; the Collar of the Order was added on 4 January 1888. Unlike its European counterparts, the order may be conferred posthumously.
Apart fr ...
(2000)
*:
**Order of Saint Olav
The Royal Norwegian Order of Saint Olav ( no, Den Kongelige Norske Sankt Olavs Orden; or ''Sanct Olafs Orden'', the old Norwegian name) is a Norwegian order of chivalry instituted by King Oscar I on 21 August 1847. It is named after King Olav I ...
(1968)
*:
**Military Order of Christ
The Military Order of Christ is the former order of Knights Templar as it was reconstituted in Portugal. Before 1910 it was known as the Royal Military Order of Our Lord Jesus Christ and the Order of the Knights of Our Lord Jesus Christ. It was ...
(14 May 1991)
*:
** Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the Order of Good Hope
The Order of Good Hope or Order of the Cape of Good Hope is a dormant order of merit of the Republic of South Africa.
History
The Order of Good Hope was founded in 1973, by the republican government of South Africa, to grant those who had disti ...
(1999)
*:
**Order of Charles III
The Royal and Distinguished Spanish Order of Charles III, originally Royal and Much Distinguished Order of Charles III ( es, Real y Distinguida Orden Española de Carlos III, originally es, Real y Muy Distinguida Orden de Carlos III) was establ ...
(7 October 1985)
**Order of Isabella the Catholic
The Order of Isabella the Catholic ( es, Orden de Isabel la Católica) is a Spanish civil order and honor granted to persons and institutions in recognition of extraordinary services to the homeland or the promotion of international relations a ...
/ref> *: **
Royal Order of the Polar Star
The Royal Order of the Polar Star ( Swedish: ''Kungliga Nordstjärneorden'') is a Swedish order of chivalry created by King Frederick I on 23 February 1748, together with the Order of the Sword and the Order of the Seraphim.
The Order of ...
(1976)
*:
** Grand Corodn of the of the
Grand Corodn of the of the National Order of Merit of Tunisia
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, c ...
(1973)
*:
**Royal Victorian Order
The Royal Victorian Order (french: Ordre royal de Victoria) is a dynastic order of knighthood established in 1896 by Queen Victoria. It recognises distinguished personal service to the British monarch, Canadian monarch, Australian monarch, o ...
(18 November 1982)
Academic awards
*Honorary Doctor of theInternational Institute of Social Studies
The International Institute of Social Studies (ISS) of Erasmus University Rotterdam is an independent and international graduate school of policy-oriented critical social science. ISS was established in 1952 by Dutch universities and the Neth ...
(1988)
Prince Claus was also appointed Honorary Fellow of the International Institute of Social Studies (ISS) in 1988. Prince Claus was held in very high esteem in the international development cooperation community, partly because of his considerable insight and understanding of the problems involved, and partly because of his exceptional gift for expressing the hopes and anxieties felt by all.
Ancestry
Issue
References
External links
In pictures: Prince Claus remembered
Video: Condolences pour in, 7 October 2002
Dutch Royal Family website: Biography
Profile at The International Institute of Social Studies
(ISS) , - {{DEFAULTSORT:Claus Of The Netherlands, Prince 1926 births 2002 deaths 20th-century Dutch diplomats German diplomats Former Lutherans German Calvinist and Reformed Christians German humanitarians German emigrants to the Netherlands German expatriates in the Dominican Republic German expatriates in Ivory Coast Development specialists Honorary consuls Princes of the Netherlands Dutch royal consorts Dutch people of German descent Dutch nonprofit executives Converts to Calvinism from Lutheranism German Army personnel of World War II Amsberg Members of the Council of State (Netherlands) People in international development Jonkheers of Amsberg Dutch members of the Dutch Reformed Church Dutch nonprofit directors Dutch corporate directors People from Hitzacker People from the Province of Hanover Deaths from Parkinson's disease Deaths from pneumonia in the Netherlands Hitler Youth members German prisoners of war in World War II held by the United States Neurological disease deaths in the Netherlands House of Orange-Nassau 20th-century German civil servants Burials in the Royal Crypt at Nieuwe Kerk, Delft Recipients of the Grand Decoration with Sash for Services to the Republic of Austria Grand Crosses Special Class of the Order of Merit of the Federal Republic of Germany Knights Grand Cross of the Order of the Falcon Grand Crosses of the Order of Christ (Portugal) Honorary Knights Grand Cross of the Royal Victorian Order