Classical Pharmacology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
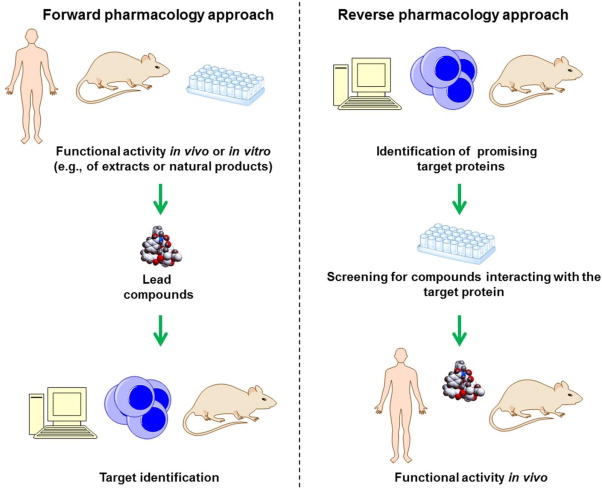 In the field of
In the field of
 In the field of
In the field of drug discovery
In the fields of medicine, biotechnology and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which new candidate medications are discovered.
Historically, drugs were discovered by identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or by ...
, classical pharmacology, also known as forward pharmacology, or phenotypic drug discovery (PDD), relies on phenotypic screening
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological proper ...
(screening in intact cells or whole organisms) of chemical libraries
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wi ...
of synthetic small molecule
Within the fields of molecular biology and pharmacology, a small molecule or micromolecule is a low molecular weight (≤ 1000 daltons) organic compound that may regulate a biological process, with a size on the order of 1 nm. Many drugs ar ...
s, natural product
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical syn ...
s or extract
An extract is a substance made by extracting a part of a raw material, often by using a solvent such as ethanol, oil or water. Extracts may be sold as tinctures, absolutes or in powder form.
The aromatic principles of many spices, nuts, h ...
s to identify substances that have a desirable therapeutic
A therapy or medical treatment (often abbreviated tx, Tx, or Tx) is the attempted remediation of a health problem, usually following a medical diagnosis.
As a rule, each therapy has indications and contraindications. There are many different ...
effect. Using the techniques of medicinal chemistry
Medicinal or pharmaceutical chemistry is a scientific discipline at the intersection of chemistry and pharmacy involved with designing and developing pharmaceutical drugs. Medicinal chemistry involves the identification, synthesis and developm ...
, the potency, selectivity, and other properties of these screening hits are optimized to produce candidate drugs.
Historical background
Classical pharmacology traditionally has been the basis for the discovery of new drugs. Compounds are screened in cellular or animal models of disease to identify compounds that cause a desirable change in phenotype. Only after the compounds have been discovered, an effort is made to determine thebiological target
A biological target is anything within a living organism to which some other entity (like an endogenous ligand or a drug) is directed and/or binds, resulting in a change in its behavior or function. Examples of common classes of biological targets ...
of the compounds through target validation experiments often involving chemoproteomics Chemoproteomics entails a broad array of techniques used to identify and interrogate protein- small molecule interactions. Chemoproteomics complements phenotypic drug discovery, a paradigm that aims to discover lead compounds on the basis of allev ...
. More recently it has become popular to develop a hypothesis that a certain biological target is disease modifying and screen
Screen or Screens may refer to:
Arts
* Screen printing (also called ''silkscreening''), a method of printing
* Big screen, a nickname associated with the motion picture industry
* Split screen (filmmaking), a film composition paradigm in which mul ...
for compounds that modulate the activity of this purified target. Afterwards, these compounds are tested in animals to see if they have the desired effect. This approach is known as "reverse pharmacology
In the field of drug discovery, reverse pharmacology also known as target-based drug discovery (TDD), a hypothesis is first made that modulation of the activity of a specific protein target thought to be disease modifying will have beneficial t ...
" or "target based drug discovery" (TDD). However, recent statistical analysis reveals that a disproportionate number of first-in-class drugs with novel mechanisms of action come from phenotypic screening, which has led to a resurgence of interest in this method.
Similarity with pharmacognosy
Pharmacognosy
Pharmacognosy is the study of medicinal plants and other natural substances as sources of drugs. The American Society of Pharmacognosy defines pharmacognosy as "the study of the physical, chemical, biochemical, and biological properties of drug ...
, the investigation of botanics used in indigenous medical traditions is essentially classical pharmacology. Pharmacognosy and classical pharmacology are both often contrasted with reverse pharmacology
In the field of drug discovery, reverse pharmacology also known as target-based drug discovery (TDD), a hypothesis is first made that modulation of the activity of a specific protein target thought to be disease modifying will have beneficial t ...
, that is, working from the target backward to identify new drugs starting with screening libraries of compounds for affinity for particular target. In pharmacognosy, folk medicine
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) comprises medical aspects of traditional knowledge that developed over generations within the folk beliefs of various societies, including indigenous peoples, before the ...
s are first tested in clinical trials for efficacy. Only after efficacy has been established, is an effort made to determine the biologic target of the drug.
See also
*Reverse pharmacology
In the field of drug discovery, reverse pharmacology also known as target-based drug discovery (TDD), a hypothesis is first made that modulation of the activity of a specific protein target thought to be disease modifying will have beneficial t ...
* Phenotypic screening
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological proper ...
* Pharmacognosy
Pharmacognosy is the study of medicinal plants and other natural substances as sources of drugs. The American Society of Pharmacognosy defines pharmacognosy as "the study of the physical, chemical, biochemical, and biological properties of drug ...
*Chemoproteomics Chemoproteomics entails a broad array of techniques used to identify and interrogate protein- small molecule interactions. Chemoproteomics complements phenotypic drug discovery, a paradigm that aims to discover lead compounds on the basis of allev ...
References
{{Pharmacology, state=collapsed Ayurvedic medicaments Drug discovery Pharmacology