Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the
largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metropo ...
in the
Commonwealth of
Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
,
the
sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the
Northeast megalopolis
The Northeast megalopolis, also known as the Northeast Corridor, Acela Corridor, Boston–Washington corridor, or BosWash, is the world's largest megalopolis in terms of economic output and the second most populous megalopolis in the United St ...
and
Mid-Atlantic regions after
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
.
Since 1854, the city has been coextensive with
Philadelphia County
Philadelphia County is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. It is the most populous county in Pennsylvania. As of the 2020 census, Philadelphia County had a population of 1,603,797. The county is the second smallest county in Pennsyl ...
, the
most populous county in Pennsylvania and the urban core of the
Delaware Valley
The Delaware Valley is a metropolitan region on the East Coast of the United States that comprises and surrounds Philadelphia, the sixth most populous city in the nation and 68th largest city in the world as of 2020. The toponym Delaware Val ...
, the
nation's seventh-largest and one of
world's largest metropolitan regions, with 6.245 million residents . The city's population at the
2020 census was 1,603,797, and over 56 million people live within of Philadelphia.
Philadelphia was founded in 1682 by
William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer and religious thinker belonging to the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers), and founder of the Province of Pennsylvania, a North American colony of England. He was an early advocate of democracy a ...
, an
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belie ...
. The city served as capital of the
Pennsylvania Colony
The Province of Pennsylvania, also known as the Pennsylvania Colony, was a British North American colony founded by William Penn after receiving a land grant from Charles II of England in 1681. The name Pennsylvania ("Penn's Woods") refers to Wi ...
during the
British colonial era[ and went on to play a historic and vital role as the central meeting place for the nation's founding fathers whose plans and actions in Philadelphia ultimately inspired the ]American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
and the nation's independence. Philadelphia hosted the First Continental Congress
The First Continental Congress was a meeting of delegates from 12 of the 13 British colonies that became the United States. It met from September 5 to October 26, 1774, at Carpenters' Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, after the British Navy ...
in 1774 following the Boston Tea Party
The Boston Tea Party was an American political and mercantile protest by the Sons of Liberty in Boston, Massachusetts, on December 16, 1773. The target was the Tea Act of May 10, 1773, which allowed the British East India Company to sell t ...
, preserved the Liberty Bell
The Liberty Bell, previously called the State House Bell or Old State House Bell, is an iconic symbol of American independence, located in Philadelphia. Originally placed in the steeple of the Pennsylvania State House (now renamed Independence ...
, and hosted the Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a late-18th-century meeting of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolutionary War. The Congress was creating a new country it first named "United Colonies" and in 1 ...
during which the founders signed the Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence or declaration of statehood or proclamation of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the ...
, which historian Joseph Ellis
Joseph John-Michael Ellis III (born July 18, 1943) is an American historian whose work focuses on the lives and times of the founders of the United States of America. '' American Sphinx: The Character of Thomas Jefferson'' won a National Boo ...
has described as "the most potent and consequential words in American history".Battle of Germantown
The Battle of Germantown was a major engagement in the Philadelphia campaign of the American Revolutionary War. It was fought on October 4, 1777, at Germantown, Pennsylvania, between the British Army led by Sir William Howe, and the American Con ...
and the Siege of Fort Mifflin
The siege of Fort Mifflin or siege of Mud Island Fort from September 26 to November 16, 1777 saw British land batteries commanded by Captain John Montresor and a British naval squadron under Vice Admiral Lord Richard Howe attempt to capture an ...
were fought within Philadelphia's city limits. The U.S. Constitution
The Constitution of the United States is the supreme law of the United States of America. It superseded the Articles of Confederation, the nation's first constitution, in 1789. Originally comprising seven articles, it delineates the natio ...
was later ratified in Philadelphia at the Philadelphia Convention
The Constitutional Convention took place in Philadelphia from May 25 to September 17, 1787. Although the convention was intended to revise the league of states and first system of government under the Articles of Confederation, the intention fr ...
of 1787. Philadelphia remained the nation's largest city until 1790, when it was surpassed by New York City, and served as the nation's first capital from May 10, 1775, until December 12, 1776, and on four subsequent occasions during and following the American Revolution, including from 1790 to 1800 while the new national capital of Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, was under construction.
With 18 four-year universities and colleges, Philadelphia is one of the nation's leading centers for higher education and academic research
Research is " creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness ...
.gross metropolitan product
Gross metropolitan product (GMP) is a monetary measure of the value of all final goods and services produced within a metropolitan statistical area during a specified period (''e.g.'', a quarter, a year). GMP estimates are commonly used to compare ...
(GMP
GMP may refer to:
Finance and economics
* Gross metropolitan product
* Guaranteed maximum price
* Guaranteed Minimum Pension
Science and technology
* GNU Multiple Precision Arithmetic Library, a software library
* Granulocyte-macrophage progenito ...
) of US$479 billion.Fortune 500
The ''Fortune'' 500 is an annual list compiled and published by ''Fortune'' magazine that ranks 500 of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for their respective fiscal years. The list includes publicly held companies, along ...
corporate headquarters as of 2022. The Philadelphia skyline, which includes several globally renowned commercial skyscrapers
A skyscraper is a tall continuously habitable building having multiple floors. Modern sources currently define skyscrapers as being at least or in height, though there is no universally accepted definition. Skyscrapers are very tall high-ris ...
, is expanding, primarily with new residential high-rise condominium
A condominium (or condo for short) is an ownership structure whereby a building is divided into several units that are each separately owned, surrounded by common areas that are jointly owned. The term can be applied to the building or complex ...
s.biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
venture capital
Venture capital (often abbreviated as VC) is a form of private equity financing that is provided by venture capital firms or funds to startups, early-stage, and emerging companies that have been deemed to have high growth potential or which ha ...
hub; and the Philadelphia Stock Exchange
Philadelphia Stock Exchange (PHLX), now known as Nasdaq PHLX, is the first stock exchange established in the United States and the oldest stock exchange in the nation. The exchange is owned by Nasdaq, which acquired it in 2007 for $652 million, a ...
, owned by NASDAQ
The Nasdaq Stock Market () (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations Stock Market) is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the US by volume, and ranked second ...
, is the nation's oldest stock exchange and a global leader in options trading.30th Street Station
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societie ...
, the city's primary rail station, is the third-busiest Amtrak hub in the nation, and the city's multimodal transport
Multimodal transport (also known as combined transport) is the transportation of goods under a single contract, but performed with at least two different modes of transport; the carrier is liable (in a legal sense) for the entire carriage, even th ...
and logistics
Logistics is generally the detailed organization and implementation of a complex operation. In a general business sense, logistics manages the flow of goods between the point of origin and the point of consumption to meet the requirements of ...
infrastructure, including Philadelphia International Airport
Philadelphia International Airport is the primary airport serving Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The airport served 19.6 million passengers annually in 2021, making it the 21st busiest airport in the United States. The airport is located from t ...
, the PhilaPort seaport, freight rail
Rail freight transport is the use of railroads and trains to transport cargo as opposed to human passengers.
A freight train, cargo train, or goods train is a group of freight cars (US) or goods wagons (International Union of Railways) hauled ...
infrastructure, roadway traffic capacity, and warehouse
A warehouse is a building for storing goods. Warehouses are used by manufacturers, importers, exporters, wholesalers, transport businesses, customs, etc. They are usually large plain buildings in industrial parks on the outskirts of cities ...
storage space, are all expanding.
Philadelphia is a national cultural hub, hosting more outdoor sculptures and murals than any other American city. Fairmount Park
Fairmount Park is the largest municipal park in Philadelphia and the historic name for a group of parks located throughout the city. Fairmount Park consists of two park sections named East Park and West Park, divided by the Schuylkill River, with ...
, when combined with adjacent Wissahickon Valley Park
Wissahickon Valley Park is a large urban park in Northwest Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It protects of woodland surrounding the Wissahickon Creek between the Montgomery County border and the Schuylkill River. For several miles, the creek winds th ...
in the same watershed, is , representing one of the nation's largest contiguous urban park
An urban park or metropolitan park, also known as a municipal park (North America) or a public park, public open space, or municipal gardens ( UK), is a park in cities and other incorporated places that offer recreation and green space to resi ...
s and the 45th largest urban park in the world.culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tyl ...
, cuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, techniques and dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, customs, and ingredients combine to ...
, and colonial
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to:
* Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology)
Architecture
* American colonial architecture
* French Colonial
* Spanish Colonial architecture
Automobiles
* Colonial (1920 au ...
and Revolution-era history; in 2016, it attracted 42 million domestic tourists who spent $6.8 billion, representing $11 billion in total economic impact to the city and surrounding Pennsylvania counties.soul
In many religious and philosophical traditions, there is a belief that a soul is "the immaterial aspect or essence of a human being".
Etymology
The Modern English noun ''soul'' is derived from Old English ''sāwol, sāwel''. The earliest attes ...
, and rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
.
Philadelphia is a city of many firsts, including the nation's first library
A library is a collection of materials, books or media that are accessible for use and not just for display purposes. A library provides physical (hard copies) or digital access (soft copies) materials, and may be a physical location or a vir ...
(1731),hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emerge ...
(1751),medical school
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution, or part of such an institution, that teaches medicine, and awards a professional degree for physicians. Such medical degrees include the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS, M ...
(1765), national capital
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city that physically encompasses the g ...
(1774),stock exchange
A stock exchange, securities exchange, or bourse is an exchange where stockbrokers and traders can buy and sell securities, such as shares of stock, bonds and other financial instruments. Stock exchanges may also provide facilities for th ...
(1790),zoo
A zoo (short for zoological garden; also called an animal park or menagerie) is a facility in which animals are kept within enclosures for public exhibition and often bred for conservation purposes.
The term ''zoological garden'' refers to zoo ...
(1874), and business school
A business school is a university-level institution that confers degrees in business administration or management. A business school may also be referred to as school of management, management school, school of business administration, o ...
(1881). Philadelphia contains 67 National Historic Landmarks
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places listed ...
, including Independence Hall
Independence Hall is a historic civic building in Philadelphia, where both the United States Declaration of Independence and the United States Constitution were debated and adopted by America's Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Fa ...
.[ From the city's 17th century founding through the present, Philadelphia has been the birthplace or home to an extensive number of prominent and influential Americans. In 2021, '']Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, to ...
'' magazine named Philadelphia one of the world's greatest 100 places.
History
Native peoples
Prior to the arrival of Europeans in the early 17th century, the Philadelphia area was home to the Lenape (Delaware) Indians in the village of Shackamaxon
The Treaty of Shackamaxon, also called the Great Treaty and Penn's Treaty, was a legendary treaty between William Penn and Tamanend of the Lenape signed in 1682. Penn and Tamanend agreed that their people would live in a state of perpetual peace ...
. They were also called the Delaware Indians,[Josephy 188–189] and their historical territory was along the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock (village), New York, Hancock, New York, the river flows for along the borders of N ...
watershed, western Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United Sta ...
, and the Lower Hudson Valley
The Hudson Valley (also known as the Hudson River Valley) comprises the valley of the Hudson River and its adjacent communities in the U.S. state of New York. The region stretches from the Capital District including Albany and Troy south to Yo ...
. Most Lenape were pushed out of their Delaware homeland during the 18th century by expanding European colonies, exacerbated by losses from intertribal conflicts.[ Lenape communities were weakened by newly introduced diseases, mainly ]smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) c ...
, and conflict with Europeans. The Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
occasionally fought the Lenape. Surviving Lenape moved west into the upper Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
basin. The American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
and the United States' independence pushed them further west. In the 1860s, the United States government sent most Lenape remaining in the eastern United States
The Eastern United States, commonly referred to as the American East, Eastern America, or simply the East, is the region of the United States to the east of the Mississippi River. In some cases the term may refer to a smaller area or the East C ...
to the Indian Territory
The Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the Federal government of the United States, United States Government for the relocation of Native Americans in the United St ...
(present-day Oklahoma and surrounding territory) under the Indian removal
Indian removal was the United States government policy of forced displacement of self-governing tribes of Native Americans from their ancestral homelands in the eastern United States to lands west of the Mississippi Riverspecifically, to a de ...
policy.
Colonial

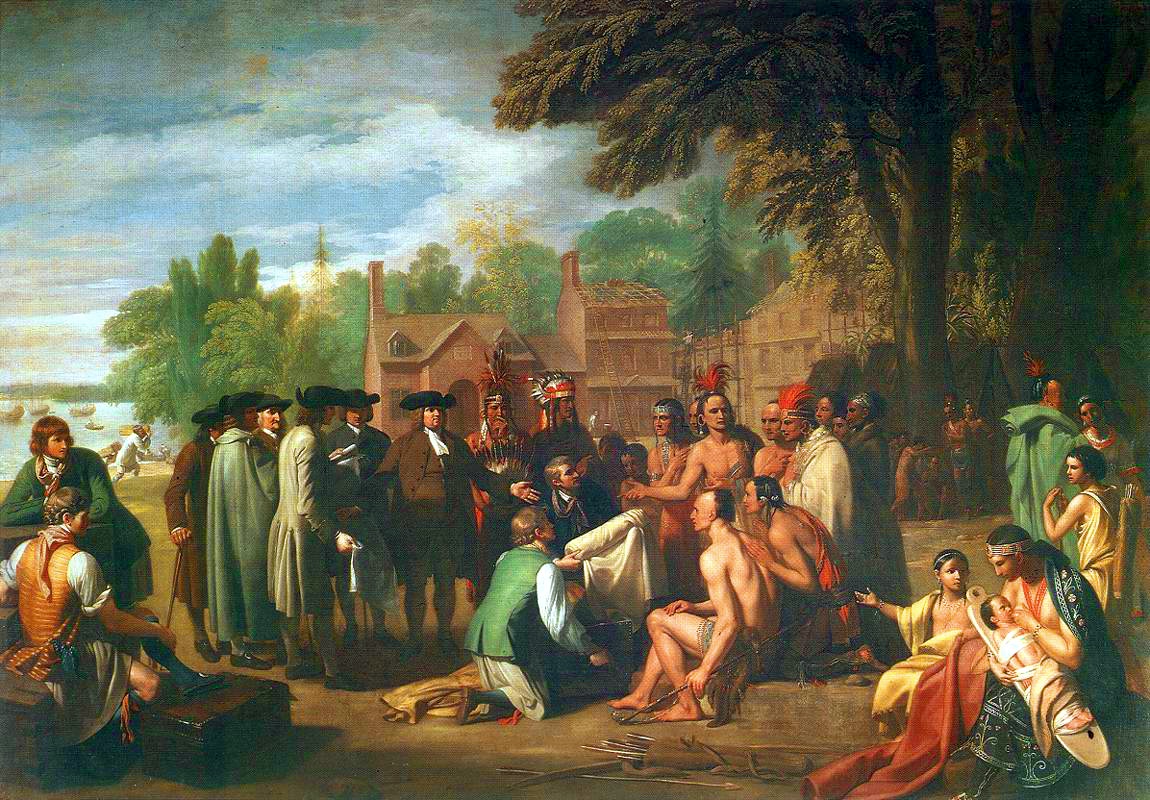 Europeans came to the
Europeans came to the Delaware Valley
The Delaware Valley is a metropolitan region on the East Coast of the United States that comprises and surrounds Philadelphia, the sixth most populous city in the nation and 68th largest city in the world as of 2020. The toponym Delaware Val ...
in the early 17th century, with the first settlements founded by Dutch colonists, who in 1623 built Fort Nassau on the Delaware River in what is now Brooklawn, New Jersey
Brooklawn is a borough in Camden County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. As of the 2010 United States census, the borough's population was 1,815, a drop of 140 from the 2010 census enumeration of 1,955,[New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the East Coast of the United States, east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territor ...]
colony. In 1638, Swedish settlers led by renegade Dutch established the colony of New Sweden
New Sweden ( sv, Nya Sverige) was a Swedish colony along the lower reaches of the Delaware River in what is now the United States from 1638 to 1655, established during the Thirty Years' War when Sweden was a great military power. New Sweden form ...
at Fort Christina (present-day Wilmington, Delaware
Wilmington ( Lenape: ''Paxahakink /'' ''Pakehakink)'' is the largest city in the U.S. state of Delaware. The city was built on the site of Fort Christina, the first Swedish settlement in North America. It lies at the confluence of the Christina ...
) and quickly spread out in the valley. In 1644, New Sweden supported the Susquehannock
The Susquehannock people, also called the Conestoga by some English settlers or Andastes were Iroquoian Native Americans who lived in areas adjacent to the Susquehanna River and its tributaries, ranging from its upper reaches in the southern p ...
s in their war against Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
colonists. In 1648, the Dutch built Fort Beversreede
Fort Beversreede (after 1633–1651) was a Dutch-built palisaded factorij located near the confluence of the Schuylkill River and the Delaware River. It was an outpost of the colony of New Netherland, which was centered on its capital, New Amste ...
on the west bank of the Delaware, south of the Schuylkill River
The Schuylkill River ( , ) is a river running northwest to southeast in eastern Pennsylvania. The river was improved by navigations into the Schuylkill Canal, and several of its tributaries drain major parts of Pennsylvania's Coal Region. It fl ...
near the present-day Eastwick neighborhood, to reassert their dominion over the area. The Swedes
Swedes ( sv, svenskar) are a North Germanic ethnic group native to the Nordic region, primarily their nation state of Sweden, who share a common ancestry, culture, history and language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countr ...
responded by building Fort Nya Korsholm, or New Korsholm
Korsholm (; fi, Mustasaari) is a municipality of Finland. The town of Vaasa was founded in Korsholm parish in 1606 and today the municipality completely surrounds the city. It is a coastal, mostly rural municipality, consisting of a rural landscap ...
, named after a town in Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
with a Swedish majority. In 1655, a Dutch military campaign led by New Netherland Director-General Peter Stuyvesant
Peter Stuyvesant (; in Dutch also ''Pieter'' and ''Petrus'' Stuyvesant, ; 1610 – August 1672)Mooney, James E. "Stuyvesant, Peter" in p.1256 was a Dutch colonial officer who served as the last Dutch director-general of the colony of New Net ...
took control of the Swedish colony, ending its claim to independence. The Swedish and Finnish settlers continued to have their own militia, religion, and court, and to enjoy substantial autonomy under the Dutch. An English fleet captured the New Netherland colony in 1664, though the situation did not change substantially until 1682, when the area was included in William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer and religious thinker belonging to the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers), and founder of the Province of Pennsylvania, a North American colony of England. He was an early advocate of democracy a ...
's charter for Pennsylvania.
In 1681, in partial repayment of a debt, Charles II of England
Charles II (29 May 1630 – 6 February 1685) was King of Scotland from 1649 until 1651, and King of England, Scotland and Ireland from the 1660 Restoration of the monarchy until his death in 1685.
Charles II was the eldest surviving child of ...
granted Penn a charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the rec ...
for what would become the Pennsylvania colony
The Province of Pennsylvania, also known as the Pennsylvania Colony, was a British North American colony founded by William Penn after receiving a land grant from Charles II of England in 1681. The name Pennsylvania ("Penn's Woods") refers to Wi ...
. Despite the royal charter, Penn bought the land from the local Lenape to be on good terms with the Native Americans and ensure peace for his colony. Penn made a treaty of friendship with Lenape chief Tammany
Tamanend (historically also known as Taminent, Tammany, Saint Tammany or King Tammany, "the Affable," ) (–) was the Chief of Chiefs and Chief of the Turtle Clan of the Lenni-Lenape nation in the Delaware Valley signing the Peace Treaty with ...
under an elm tree at Shackamaxon
The Treaty of Shackamaxon, also called the Great Treaty and Penn's Treaty, was a legendary treaty between William Penn and Tamanend of the Lenape signed in 1682. Penn and Tamanend agreed that their people would live in a state of perpetual peace ...
, in what is now the city's Fishtown neighborhood.Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
for "brotherly love," derived from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
terms φίλος ''phílos'' (beloved, dear) and ἀδελφός ''adelphós'' (brother, brotherly). There were a number of cities named ''Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
'' in the Eastern Mediterranean during the Greek and Roman periods, including one (modern Alaşehir
Alaşehir (), in Antiquity and the Middle Ages known as Philadelphia ( el, Φιλαδέλφεια, i.e., "the city of him who loves his brother"), is a town and district of Manisa Province in the Aegean region of Turkey. It is situated in the va ...
) mentioned as the site of an early Christian congregation in the Book of Revelation
The Book of Revelation is the final book of the New Testament (and consequently the final book of the Christian Bible). Its title is derived from the first word of the Koine Greek text: , meaning "unveiling" or "revelation". The Book of R ...
. As a Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belie ...
, Penn had experienced religious persecution and wanted his colony to be a place where anyone could worship freely. This tolerance, far more than afforded by most other colonies, led to better relations with the local native tribes and fostered Philadelphia's rapid growth into America's most important city.
Penn planned a city on the Delaware River to serve as a port and place for government. Hoping that Philadelphia would become more like an English rural town instead of a city, Penn laid out roads on a grid plan
In urban planning, the grid plan, grid street plan, or gridiron plan is a type of city plan in which streets run at right angles to each other, forming a grid.
Two inherent characteristics of the grid plan, frequent intersections and orthogona ...
to keep houses and businesses spread far apart, with areas for gardens and orchard
An orchard is an intentional plantation of trees or shrubs that is maintained for food production. Orchards comprise fruit- or nut-producing trees which are generally grown for commercial production. Orchards are also sometimes a feature of larg ...
s.
The city's inhabitants did not follow Penn's plans, however, as they crowded by the present-day Port of Philadelphia The Port of Philadelphia is located on the Delaware River in Philadelphia in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania.
Generally the term applies to the publicly owned marine terminals located within Philadelphia city limits along west bank of the river. Th ...
on the Delaware River, and subdivided and resold their lots. Before Penn left Philadelphia for the last time, he issued the Charter of 1701 establishing it as a city. Though poor at first, the city became an important trading center with tolerable living conditions by the 1750s. Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading inte ...
, a leading citizen, helped improve city services and founded new ones, such as fire protection, a library, and one of the American colonies' first hospitals.
A number of philosophical societies were formed, which were centers of the city's intellectual life: the Philadelphia Society for Promoting Agriculture (1785), the Pennsylvania Society for the Encouragement of Manufactures and the Useful Arts (1787), the Academy of Natural Sciences
The Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University, formerly the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, is the oldest natural science research institution and museum in the Americas. It was founded in 1812, by many of the leading natura ...
(1812), and the Franklin Institute
The Franklin Institute is a science museum and the center of science education and research in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It is named after the American scientist and statesman Benjamin Franklin. It houses the Benjamin Franklin National Memori ...
(1824). These societies developed and financed new industries, attracting skilled and knowledgeable immigrants from Europe.
Revolution
 Philadelphia's importance and central location in the colonies made it a natural center for America's revolutionaries. By the 1750s, Philadelphia had surpassed
Philadelphia's importance and central location in the colonies made it a natural center for America's revolutionaries. By the 1750s, Philadelphia had surpassed Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- mo ...
as the largest city and busiest port in British America
British America comprised the colonial territories of the English Empire, which became the British Empire after the 1707 union of the Kingdom of England with the Kingdom of Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain, in the Americas from 16 ...
, and the second-largest city in the entire British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
, after London. Before the Revolutionary War, in 1774, as resentment of British colonial practices and support for independence was burgeoning in the colonies, Philadelphia hosted the First Continental Congress
The First Continental Congress was a meeting of delegates from 12 of the 13 British colonies that became the United States. It met from September 5 to October 26, 1774, at Carpenters' Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, after the British Navy ...
. From 1775 to 1781, Philadelphia hosted the Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a late-18th-century meeting of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolutionary War. The Congress was creating a new country it first named "United Colonies" and in 1 ...
,Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence or declaration of statehood or proclamation of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the ...
in what was then called the Independence Hall, Pennsylvania State House and now is called Independence Hall, on July 4, 1776.
Historian Joseph Ellis
Joseph John-Michael Ellis III (born July 18, 1943) is an American historian whose work focuses on the lives and times of the founders of the United States of America. '' American Sphinx: The Character of Thomas Jefferson'' won a National Boo ...
, in 2007, described the Declaration of Independence as "the most potent and consequential words in American history,"Siege of Fort Mifflin
The siege of Fort Mifflin or siege of Mud Island Fort from September 26 to November 16, 1777 saw British land batteries commanded by Captain John Montresor and a British naval squadron under Vice Admiral Lord Richard Howe attempt to capture an ...
(September 26 to November 16, 1777) and the Battle of Germantown
The Battle of Germantown was a major engagement in the Philadelphia campaign of the American Revolutionary War. It was fought on October 4, 1777, at Germantown, Pennsylvania, between the British Army led by Sir William Howe, and the American Con ...
(October 4, 1777), were both fought within Philadelphia's city limits.
In Philadelphia, the Second Continental Congress adopted the Articles of Confederation on November 15, 1777, and the city later served as the meeting place for the Constitutional Convention (United States), Constitutional Convention, which ratified the United States Constitution, Constitution in Independence Hall in Philadelphia on September 17, 1787.
Philadelphia served as capital of the United States for much of the colonial and early post-colonial periods, including for a decade, from 1790 to 1800, while the Washington, D.C., District of Columbia was being constructed and prepared to serve as the new nation's national capital. In 1793, the largest 1793 Philadelphia yellow fever epidemic, yellow fever epidemic in U.S. history killed approximately 4,000 to 5,000 people in Philadelphia, or about 10% of the city's population.
The state capital was moved to Lancaster, Pennsylvania, Lancaster in 1799, then Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, Harrisburg in 1812, while the federal government was moved to Washington, D.C., in 1800 upon completion of the White House and United States Capitol, U.S. Capitol building. Philadelphia remained the young nation's largest city until the late 18th century, serving as the nation's financial and cultural center, until ultimately being eclipsed in total population by New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
in 1790. In 1816, the city's free Black community founded the African Methodist Episcopal Church (AME), the first independent Black denomination in the country, and the first Black Episcopal Church (United States), Episcopal Church. The free black community also established many schools for its children, with the help of Quakers. Large-scale construction projects for new roads, canals, and railroads made Philadelphia the first major Industrial Revolution, industrial city in the United States.
19th century
 Throughout the 19th century, Philadelphia hosted a variety of industries and businesses, the largest being textile industry, textiles. Major corporations in the 19th and early 20th centuries included the Baldwin Locomotive Works, William Cramp & Sons, William Cramp & Sons Shipbuilding Company, and the Pennsylvania Railroad. Established in 1870, the Philadelphia Conveyancers' Association was chartered by the state in 1871. Industry, along with the U.S. Centennial, was celebrated in 1876 with the Centennial Exposition, the first official World's fair in the United States.
Immigrants, mostly from Ireland and Germany, settled in Philadelphia and the surrounding districts. These immigrants were largely responsible for the 1835 Philadelphia general strike, first general strike in North America in 1835, in which workers in the city won the ten-hour workday. The city was a destination for thousands of Irish immigrants fleeing the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine in the 1840s; housing for them was developed south of South Street (Philadelphia), South Street and later occupied by succeeding immigrants. They established a network of Catholic church, Catholic churches and schools and dominated the Catholic clergy for decades. Anti-Irish, anti-Catholic Nativism (politics), nativist Philadelphia nativist riots, riots erupted in Philadelphia in 1844. The rise in population of the surrounding districts helped lead to the Act of Consolidation, 1854, Act of Consolidation of 1854, which extended the city limits from the of Center City, Philadelphia, Center City to the roughly of
Throughout the 19th century, Philadelphia hosted a variety of industries and businesses, the largest being textile industry, textiles. Major corporations in the 19th and early 20th centuries included the Baldwin Locomotive Works, William Cramp & Sons, William Cramp & Sons Shipbuilding Company, and the Pennsylvania Railroad. Established in 1870, the Philadelphia Conveyancers' Association was chartered by the state in 1871. Industry, along with the U.S. Centennial, was celebrated in 1876 with the Centennial Exposition, the first official World's fair in the United States.
Immigrants, mostly from Ireland and Germany, settled in Philadelphia and the surrounding districts. These immigrants were largely responsible for the 1835 Philadelphia general strike, first general strike in North America in 1835, in which workers in the city won the ten-hour workday. The city was a destination for thousands of Irish immigrants fleeing the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine in the 1840s; housing for them was developed south of South Street (Philadelphia), South Street and later occupied by succeeding immigrants. They established a network of Catholic church, Catholic churches and schools and dominated the Catholic clergy for decades. Anti-Irish, anti-Catholic Nativism (politics), nativist Philadelphia nativist riots, riots erupted in Philadelphia in 1844. The rise in population of the surrounding districts helped lead to the Act of Consolidation, 1854, Act of Consolidation of 1854, which extended the city limits from the of Center City, Philadelphia, Center City to the roughly of Philadelphia County
Philadelphia County is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. It is the most populous county in Pennsylvania. As of the 2020 census, Philadelphia County had a population of 1,603,797. The county is the second smallest county in Pennsyl ...
.
20th century
 By the 20th century, Philadelphia had an entrenched Republican Party (United States), Republican political machine and a complacent population. The first major reform came in 1917 when outrage over the election-year murder of a police officer led to the shrinking of the Philadelphia City Council, City Council from two houses to just one. In July 1919, Philadelphia was one of more than 36 industrial cities nationally to suffer a Race riots in Philadelphia during the 1919 Red Summer, race riot of ethnic whites against blacks during Red Summer, in post-World War I unrest, as recent immigrants competed with blacks for jobs. In the 1920s, the public flouting of Prohibition in the United States, Prohibition laws, organized crime, mob violence, and police involvement in illegal activities led to the appointment of Brigadier general, Brig. Gen. Smedley Butler of the United States Marine Corps, U.S. Marine Corps as director of public safety, but political pressure prevented any long-term success in fighting crime and corruption.
In 1940, non-Hispanic whites constituted 86.8% of the city's population. The population peaked at more than two million residents in 1950, then began to decline with the restructuring of industry, which led to the loss of many middle-class union jobs. In addition, suburbanization had enticed many of the more affluent residents to outlying railroad commuting towns and newer housing. The resulting reduction in Philadelphia's tax base and the resources of local government caused the city to struggle through a long period of adjustment, with it approaching bankruptcy by the late 1980s.
Revitalization and gentrification of neighborhoods began in the late 1970s and continues into the 21st century, with much of the development occurring in the Center City, Philadelphia, Center City and University City, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, University City neighborhoods, while simultaneously exacerbating a shortage of affordable housing in Philadelphia. After many of the old manufacturers and businesses left Philadelphia or shut down, the city started attracting service businesses and began to market itself more aggressively as a tourist destination. Contemporary glass-and-granite
By the 20th century, Philadelphia had an entrenched Republican Party (United States), Republican political machine and a complacent population. The first major reform came in 1917 when outrage over the election-year murder of a police officer led to the shrinking of the Philadelphia City Council, City Council from two houses to just one. In July 1919, Philadelphia was one of more than 36 industrial cities nationally to suffer a Race riots in Philadelphia during the 1919 Red Summer, race riot of ethnic whites against blacks during Red Summer, in post-World War I unrest, as recent immigrants competed with blacks for jobs. In the 1920s, the public flouting of Prohibition in the United States, Prohibition laws, organized crime, mob violence, and police involvement in illegal activities led to the appointment of Brigadier general, Brig. Gen. Smedley Butler of the United States Marine Corps, U.S. Marine Corps as director of public safety, but political pressure prevented any long-term success in fighting crime and corruption.
In 1940, non-Hispanic whites constituted 86.8% of the city's population. The population peaked at more than two million residents in 1950, then began to decline with the restructuring of industry, which led to the loss of many middle-class union jobs. In addition, suburbanization had enticed many of the more affluent residents to outlying railroad commuting towns and newer housing. The resulting reduction in Philadelphia's tax base and the resources of local government caused the city to struggle through a long period of adjustment, with it approaching bankruptcy by the late 1980s.
Revitalization and gentrification of neighborhoods began in the late 1970s and continues into the 21st century, with much of the development occurring in the Center City, Philadelphia, Center City and University City, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, University City neighborhoods, while simultaneously exacerbating a shortage of affordable housing in Philadelphia. After many of the old manufacturers and businesses left Philadelphia or shut down, the city started attracting service businesses and began to market itself more aggressively as a tourist destination. Contemporary glass-and-granite skyscrapers
A skyscraper is a tall continuously habitable building having multiple floors. Modern sources currently define skyscrapers as being at least or in height, though there is no universally accepted definition. Skyscrapers are very tall high-ris ...
were built in Center City beginning in the 1980s. Historic areas such as Old City, Philadelphia, Old City and Society Hill were renovated during the reformist mayoral era of the 1950s through the 1980s, making those areas among the most desirable neighborhoods in Center City. Many immigrants from around the world began to enter the U.S. through Philadelphia as their gateway. These developments led to a reversal of the city's population decline between 1950 and 2000, during which it lost about 25 percent of its residents.
21st century
Philadelphia eventually began experiencing a growth in its population in 2007, which continued with gradual yearly increases through the present.
Geography
Topography
The geographic center of Philadelphia is about 40° 0′ 34″ north latitude and 75° 8′ 0″ west longitude. The 40th parallel north passes through neighborhoods in Northeast Philadelphia, North Philadelphia, and West Philadelphia including Fairmount Park
Fairmount Park is the largest municipal park in Philadelphia and the historic name for a group of parks located throughout the city. Fairmount Park consists of two park sections named East Park and West Park, divided by the Schuylkill River, with ...
. The city encompasses , of which is land and , or 6%, is water.
Cityscape
City planning
Philadelphia's central city was created in the 17th century following the plan by William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer and religious thinker belonging to the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers), and founder of the Province of Pennsylvania, a North American colony of England. He was an early advocate of democracy a ...
's surveyor Thomas Holme. Center City, Philadelphia, Center City is structured with long, straight streets running nearly due east–west and north–south, forming a grid pattern between the Delaware River, Delaware and Schuylkill River, Schuylkill rivers that is aligned with their courses. The original city plan was designed to allow for easy travel and to keep residences separated by open space that would help prevent the spread of fire.
Architecture

 Philadelphia's architectural history dates back to
Philadelphia's architectural history dates back to colonial
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to:
* Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology)
Architecture
* American colonial architecture
* French Colonial
* Spanish Colonial architecture
Automobiles
* Colonial (1920 au ...
times and includes a wide range of styles. The earliest structures were constructed with Log house, logs, but brick structures were common by 1700. During the 18th century, the cityscape was dominated by Georgian architecture, including Independence Hall
Independence Hall is a historic civic building in Philadelphia, where both the United States Declaration of Independence and the United States Constitution were debated and adopted by America's Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Fa ...
and Christ Church, Philadelphia, Christ Church.
In the first decades of the 19th century, Federal architecture, Federal and Greek Revival architecture were the dominant styles produced by Philadelphia architects such as Benjamin Henry Latrobe, Benjamin Latrobe, William Strickland (architect), William Strickland, John Haviland, John Notman, Thomas Ustick Walter, Thomas Walter, and Samuel Sloan (architect), Samuel Sloan.[
For much of Philadelphia's history, the typical home has been the Terraced house, row house. The row house was introduced to the United States via Philadelphia in the early 19th century and, for a time, row houses built elsewhere in the United States were known as "Philadelphia rows".][ A variety of row houses are found throughout the city, from Federal-style continuous blocks in Old City, Philadelphia, Old City and Society Hill to Victorian-style homes in North Philadelphia to twin row houses in West Philadelphia. While newer homes have been built recently, much of the housing dates to the 18th, 19th and early 20th centuries, which has created problems such as urban decay and vacant lots. Some neighborhoods, including Northern Liberties, Philadelphia, Northern Liberties and Society Hill, have been rehabilitated through gentrification.
File:Elfreth's Alley, Philadelphia, 2008.jpg, Elfreth's Alley, "Our nation's oldest residential street", 1702–1836][Historical marker on Elfreth's Alley]
File:Carpenters' Hall, Philadelphia, USA, May 2015.jpg, Carpenters' Hall exhibiting Georgian architecture, 1770–1774
File:Second Bank of the United States with Robert Morris, Jr. statue, Philadelphia.jpg, Second Bank of the United States exhibiting Greek Revival architecture, 1818–1824
File:City hall Philadelphia.jpg, Second Empire architecture in the United States and Canada, Second Empire-style Philadelphia City Hall, 1871–1901, from South Broad Street (Philadelphia), Broad Street
File:Thirty St Station.jpg, The Art Deco-style concourse, grand concourse at 30th Street Station
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societie ...
, 1927–1933
Parks
 , the total city parkland, including municipal, state and federal parks within the city limits, amounts to .
, the total city parkland, including municipal, state and federal parks within the city limits, amounts to .[ Philadelphia's largest park is ]Fairmount Park
Fairmount Park is the largest municipal park in Philadelphia and the historic name for a group of parks located throughout the city. Fairmount Park consists of two park sections named East Park and West Park, divided by the Schuylkill River, with ...
which includes the Philadelphia Zoo and encompasses of the total parkland, while the adjacent Wissahickon Valley Park
Wissahickon Valley Park is a large urban park in Northwest Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It protects of woodland surrounding the Wissahickon Creek between the Montgomery County border and the Schuylkill River. For several miles, the creek winds th ...
contains .urban park
An urban park or metropolitan park, also known as a municipal park (North America) or a public park, public open space, or municipal gardens ( UK), is a park in cities and other incorporated places that offer recreation and green space to resi ...
areas in the United States.[ The two parks, along with the Colonial Revival architecture, Colonial Revival, Georgian architecture, Georgian and Federal architecture, Federal-style List of houses in Fairmount Park, mansions contained in them, have been listed as one entity on the National Register of Historic Places since 1972.]
Climate
According to the Köppen climate classification, Philadelphia falls under the northern periphery of the humid subtropical climate zone (Köppen ''Cfa''), whereas according to the Trewartha climate classification, the city has a temperate maritime climate (''Do'') limited to the north by the continental climate (''Dc''). Summers are typically hot and muggy, fall and spring are generally mild, and winter is moderately cold. The plant life hardiness zone#Selected U.S. cities, hardiness zones are 7a and 7b, representing an average annual extreme minimum temperature between .
Snowfall is highly variable, with some winters experiencing only light snow, while others include major snowstorms. The normal seasonal snowfall averages , with rare snowfalls in November or April, and rarely any sustained snow cover.Philadelphia International Airport
Philadelphia International Airport is the primary airport serving Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The airport served 19.6 million passengers annually in 2021, making it the 21st busiest airport in the United States. The airport is located from t ...
.[
The January daily average temperature is , though the temperature frequently rises to during thaws and dips to for 2 or 3 nights in a normal winter. July averages , although heat waves accompanied by high humidity and heat index, heat indices are frequent, with highs reaching or exceeding on 30 days of the year. The average window for freezing temperatures is November 6 thru April 2,]
Air quality
Philadelphia County received an ozone grade of F and a 24-hour Particulates, particle pollution rating of D in the American Lung Association's 2017 State of the Air report, which analyzed data from 2013 to 2015.[ Five of the ten largest Combined statistical area#List of combined statistical areas, combined statistical areas (CSAs) were ranked higher for ozone: Los Angeles (1st), New York City (9th), Houston (12th), Dallas (13th), and San Jose, California, San Jose (18th). Many smaller CSAs were also ranked higher for ozone including Sacramento, California, Sacramento (8th), Las Vegas (10th), Denver (11th), El Paso, Texas, El Paso (16th), and Salt Lake City (20th); however, only two of those same ten CSAs—San Jose and Los Angeles—were ranked higher than Philadelphia for both year-round and short-term particle pollution.][
]
Demographics
According to the 2020 United States Census Bureau, U.S. Census Bureau's tabulation, there were 1,603,797 people residing in Philadelphia, representing a 1.2% increase from the 2019 census estimate.
Immigration and cultural diversity
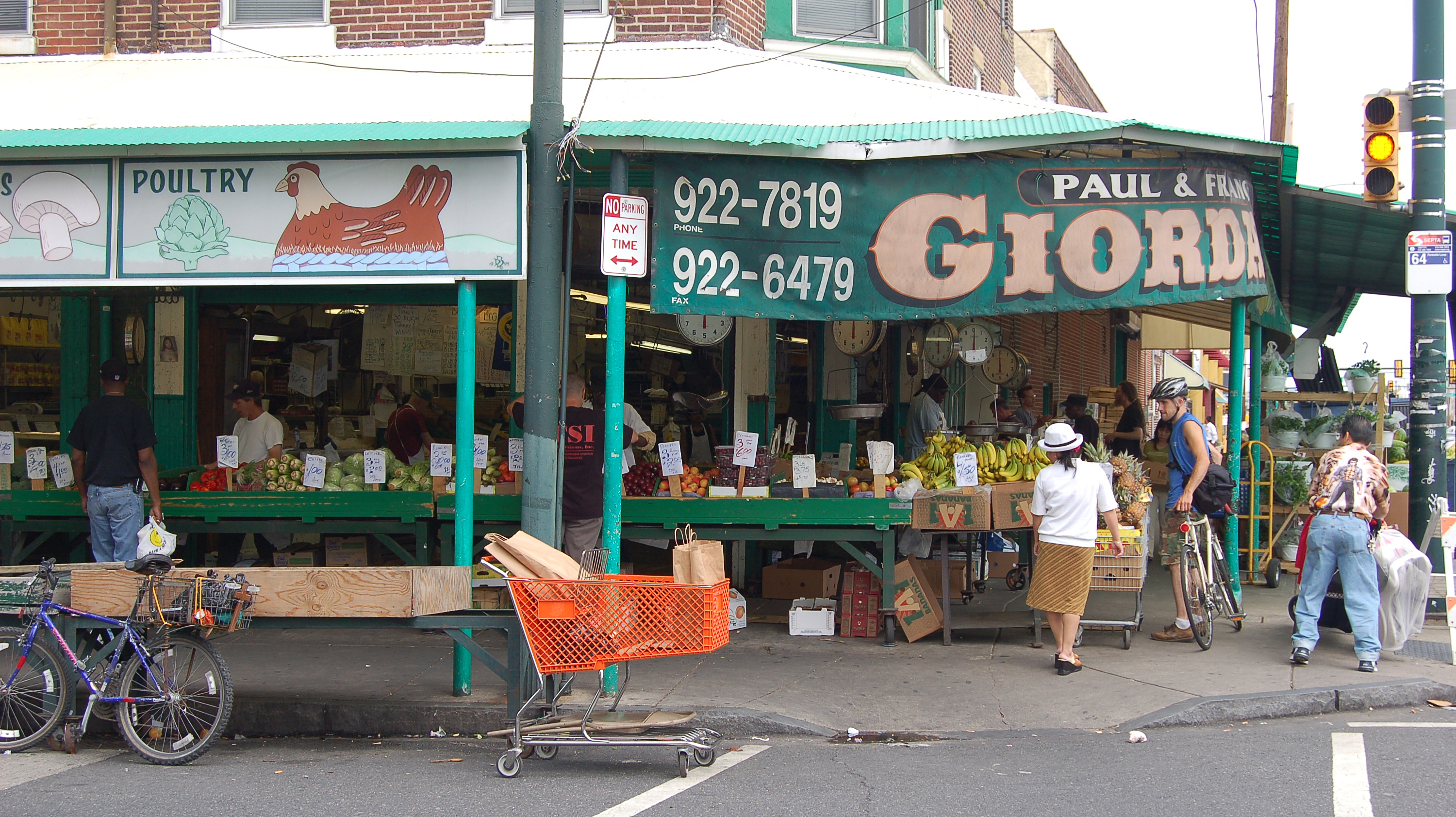

 Apart from economic growth, another factor contributing to the population increase is Philadelphia's rising immigration rate. Like the millennial population, Philadelphia's immigrant population is also growing rapidly. According to research by The Pew Charitable Trusts, the city's foreign born, foreign-born population had increased by 69% between 2000 and 2016 to constitute nearly 20% of Philadelphia's work force,
Apart from economic growth, another factor contributing to the population increase is Philadelphia's rising immigration rate. Like the millennial population, Philadelphia's immigrant population is also growing rapidly. According to research by The Pew Charitable Trusts, the city's foreign born, foreign-born population had increased by 69% between 2000 and 2016 to constitute nearly 20% of Philadelphia's work force,
Religion
 According to a 2014 study by the Pew Research Center, 68% of the population of the city identified themselves as Christianity, Christian. Approximately 41% of Christians in the city and area professed attendance at a variety of churches that could be considered Protestantism, Protestant, while 26% professed Catholic Church, Catholic beliefs.
The Protestant Christian community in Philadelphia is dominated by Mainline Protestant, mainline Protestant denominations including the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America, United Church of Christ, the Episcopal Church (United States), Episcopal Church in the United States, Presbyterian Church (USA) and American Baptist Churches USA. One of the most prominent mainline Protestant jurisdictions is the Episcopal Diocese of Pennsylvania. The African Methodist Episcopal Church was established in Philadelphia. Historically, the city has strong connections to the Quakers, Unitarian Universalism, and the Ethical movement, Ethical Culture movement, all of which continue to be represented in the city. The Quaker Friends General Conference is based in Philadelphia. Evangelical Protestants making up less than 15% of the population were also prevalent. Evangelical Protestant bodies included the Anglican Church in North America, Lutheran Church–Missouri Synod, Lutheran Church—Missouri Synod, Presbyterian Church in America, and National Baptist Convention of America International, Inc., National Baptist Convention of America.
The Catholic community is primarily served by the Latin Church, Latin Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Philadelphia, Catholic Archdiocese of Philadelphia, the Ukrainian Catholic Archeparchy of Philadelphia, and the Syro-Malankara Catholic Eparchy of the United States of America and Canada, though some Independent Catholicism, independent Catholic churches exist throughout Philadelphia and its suburbs. The Latin Church-based jurisdiction is headquartered in the city, and its see is the Cathedral Basilica of Saints Peter and Paul (Philadelphia), Cathedral Basilica of Saints Peter and Paul. The Ukrainian Catholic jurisdiction is also headquartered in Philadelphia, and is seated at the Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception (Philadelphia), Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception.
Less than 1% of Philadelphia's Christians were Mormons. The remainder of the Christian demographic is spread among smaller Protestant denominations and the Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern and Oriental Orthodox Churches, Oriental Orthodox among others. The Orthodox Church in America Diocese of Eastern Pennsylvania, Diocese of Eastern Pennsylvania (Orthodox Church in America) and Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of America (Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, Ecumenical Patriarchate) divide the Eastern Orthodox in Philadelphia. The Russian Orthodox Church, Russian Orthodox St. Andrew's Cathedral, Philadelphia, St. Andrew's Cathedral is in the city.
The same study says that other religions collectively compose about 8% of the population, including Judaism, Hinduism, Islam, Buddhism, and Sikhism. Philadelphia has the fifth largest Muslim population among American cities. The remaining 24% claimed Irreligion, no religious affiliation.
The Philadelphia List of Metropolitan Statistical Areas, metropolitan area's History of the Jews in Philadelphia, Jewish population was estimated at 206,000 in 2001, which was the sixth largest in the United States at that time. Jewish traders were operating in southeastern Pennsylvania long before
According to a 2014 study by the Pew Research Center, 68% of the population of the city identified themselves as Christianity, Christian. Approximately 41% of Christians in the city and area professed attendance at a variety of churches that could be considered Protestantism, Protestant, while 26% professed Catholic Church, Catholic beliefs.
The Protestant Christian community in Philadelphia is dominated by Mainline Protestant, mainline Protestant denominations including the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America, United Church of Christ, the Episcopal Church (United States), Episcopal Church in the United States, Presbyterian Church (USA) and American Baptist Churches USA. One of the most prominent mainline Protestant jurisdictions is the Episcopal Diocese of Pennsylvania. The African Methodist Episcopal Church was established in Philadelphia. Historically, the city has strong connections to the Quakers, Unitarian Universalism, and the Ethical movement, Ethical Culture movement, all of which continue to be represented in the city. The Quaker Friends General Conference is based in Philadelphia. Evangelical Protestants making up less than 15% of the population were also prevalent. Evangelical Protestant bodies included the Anglican Church in North America, Lutheran Church–Missouri Synod, Lutheran Church—Missouri Synod, Presbyterian Church in America, and National Baptist Convention of America International, Inc., National Baptist Convention of America.
The Catholic community is primarily served by the Latin Church, Latin Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Philadelphia, Catholic Archdiocese of Philadelphia, the Ukrainian Catholic Archeparchy of Philadelphia, and the Syro-Malankara Catholic Eparchy of the United States of America and Canada, though some Independent Catholicism, independent Catholic churches exist throughout Philadelphia and its suburbs. The Latin Church-based jurisdiction is headquartered in the city, and its see is the Cathedral Basilica of Saints Peter and Paul (Philadelphia), Cathedral Basilica of Saints Peter and Paul. The Ukrainian Catholic jurisdiction is also headquartered in Philadelphia, and is seated at the Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception (Philadelphia), Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception.
Less than 1% of Philadelphia's Christians were Mormons. The remainder of the Christian demographic is spread among smaller Protestant denominations and the Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern and Oriental Orthodox Churches, Oriental Orthodox among others. The Orthodox Church in America Diocese of Eastern Pennsylvania, Diocese of Eastern Pennsylvania (Orthodox Church in America) and Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of America (Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople, Ecumenical Patriarchate) divide the Eastern Orthodox in Philadelphia. The Russian Orthodox Church, Russian Orthodox St. Andrew's Cathedral, Philadelphia, St. Andrew's Cathedral is in the city.
The same study says that other religions collectively compose about 8% of the population, including Judaism, Hinduism, Islam, Buddhism, and Sikhism. Philadelphia has the fifth largest Muslim population among American cities. The remaining 24% claimed Irreligion, no religious affiliation.
The Philadelphia List of Metropolitan Statistical Areas, metropolitan area's History of the Jews in Philadelphia, Jewish population was estimated at 206,000 in 2001, which was the sixth largest in the United States at that time. Jewish traders were operating in southeastern Pennsylvania long before William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer and religious thinker belonging to the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers), and founder of the Province of Pennsylvania, a North American colony of England. He was an early advocate of democracy a ...
. Furthermore, Jews in Philadelphia took a prominent part in the American Revolutionary War, War of Independence. Although the majority of the early Jewish residents were of Portuguese or Spanish descent, some among them had emigrated from Germany and Poland. About the beginning of the 19th century, a number of Jews from the latter countries, finding the services of the Congregation Mikveh Israel, Congregation Mickvé Israel unfamiliar to them, resolved to form a new congregation which would use the ritual to which they had been accustomed.
Afro-American religion, African diasporic religions are practiced in some Latino and Hispanic and Caribbean communities in North and West Philadelphia.
Languages
, 79.12% (1,112,441) of Philadelphia residents age 5 and older spoke English at home as a primary language, while 9.72% (136,688) spoke Spanish, 1.64% (23,075) Chinese, 0.89% (12,499) Vietnamese language, Vietnamese, 0.77% (10,885) Russian, 0.66% (9,240) French, 0.61% (8,639) Languages of Asia, other Asian languages, 0.58% (8,217) Languages of Africa, African languages, 0.56% (7,933) Cambodian language, Cambodian (Austroasiatic languages, Mon-Khmer), and Italian was spoken as a main language by 0.55% (7,773) of the population over the age of five. In total, 20.88% (293,544) of Philadelphia's population age 5 and older spoke a mother language other than English.
Economy
Philadelphia’s close geographical and transportation connections to other large metropolitan economies along the East Coast of the United States, Eastern Seaboard of the United States have been cited as offering a significant competitive advantage for business creation and entrepreneurship.Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
and the four-state Delaware Valley
The Delaware Valley is a metropolitan region on the East Coast of the United States that comprises and surrounds Philadelphia, the sixth most populous city in the nation and 68th largest city in the world as of 2020. The toponym Delaware Val ...
metropolitan region. Five Fortune 500
The ''Fortune'' 500 is an annual list compiled and published by ''Fortune'' magazine that ranks 500 of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for their respective fiscal years. The list includes publicly held companies, along ...
companies are headquartered in the city. , the Philadelphia metropolitan area is estimated to produce a gross metropolitan product (GMP) of US$479 billion,biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
, information technology, trade and transportation, manufacturing, Oil refinery, oil refining, food processing, and tourism. Financial activities account for the largest economic sector of the metropolitan area, which is also one of the largest health education and research centers in the United States. The city's two largest employers are the federal and city governments. Philadelphia's largest private employer is the University of Pennsylvania, followed by the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
Corporations

 The
The Philadelphia Stock Exchange
Philadelphia Stock Exchange (PHLX), now known as Nasdaq PHLX, is the first stock exchange established in the United States and the oldest stock exchange in the nation. The exchange is owned by Nasdaq, which acquired it in 2007 for $652 million, a ...
, acquired by NASDAQ
The Nasdaq Stock Market () (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations Stock Market) is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the US by volume, and ranked second ...
in 2007, tracks the Philadelphia Semiconductor Index, known in financial circles as the SOX.[ The city is also home to the headquarters of cable television and internet service provider Comcast, insurance companies Cigna, Colonial Penn, and Independence Blue Cross, food services company Aramark, chemical makers FMC Corporation and Rohm and Haas, pharmaceutical companies GlaxoSmithKline, Amicus Therapeutics, Spark Therapeutics, apparel retailers Five Below and Urban Outfitters and its subsidiary Anthropologie, automotive parts retailer Pep Boys, and stainless steel producer Carpenter Technology Corporation. Other corporation headquarters in the city include RiteAid, Crown Holdings, and Brandywine Realty Trust. The headquarters of Boeing Rotorcraft Systems and its main rotorcraft factory are in the Philadelphia suburb of Ridley Park, Pennsylvania, Ridley Park; The Vanguard Group and the U.S. headquarters of Siemens Healthineers are headquartered in Malvern, Pennsylvania, a Philadelphia suburb; healthcare conglomerate AmerisourceBergen is headquartered in suburban Conshohocken, Pennsylvania; and the Campbell Soup Company and automobile manufacturer Subaru, Subaru USA are headquartered across the ]Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock (village), New York, Hancock, New York, the river flows for along the borders of N ...
in adjacent Camden, New Jersey, Camden, New Jersey.
Tech and biotech
Philadelphia is a hub for information technology and biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
.
Accessed April 18, 2019.venture capital
Venture capital (often abbreviated as VC) is a form of private equity financing that is provided by venture capital firms or funds to startups, early-stage, and emerging companies that have been deemed to have high growth potential or which ha ...
funding.[
]
Tourism
 Philadelphia's history attracts many tourists, with the Independence National Historical Park (which includes the Liberty Bell,
Philadelphia's history attracts many tourists, with the Independence National Historical Park (which includes the Liberty Bell, Independence Hall
Independence Hall is a historic civic building in Philadelphia, where both the United States Declaration of Independence and the United States Constitution were debated and adopted by America's Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Fa ...
, and other historic sites) receiving over 5 million visitors in 2016. The city welcomed 42 million domestic tourists in 2016 who spent $6.8 billion, generating an estimated $11 billion in total economic impact in the city and surrounding four counties of Pennsylvania.
Trade and transportation
Philadelphia International Airport
Philadelphia International Airport is the primary airport serving Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The airport served 19.6 million passengers annually in 2021, making it the 21st busiest airport in the United States. The airport is located from t ...
is undergoing a $900 million infrastructure, infrastructural expansion to increase passenger capacity and augment passenger experience;Port of Philadelphia The Port of Philadelphia is located on the Delaware River in Philadelphia in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania.
Generally the term applies to the publicly owned marine terminals located within Philadelphia city limits along west bank of the river. Th ...
, having experienced the highest percentage growth by Twenty-foot equivalent unit, tonnage loaded in 2017 among major U.S. seaports, was in the process of doubling its shipping tonnage, capacity to accommodate super-sized post-Panamax shipping vessels in 2018.30th Street Station
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societie ...
is the third-busiest Amtrak rail hub, following Pennsylvania Station (New York), Penn Station in Manhattan and Washington Union Station, Union Station in Washington, D.C., transporting over 4 million inter-city rail passengers annually.
Education
Primary and secondary education
Education in Philadelphia is provided by many private and public institutions. The School District of Philadelphia is the local school district, operating Public school (government funded), public schools, in all of the city. The Philadelphia School District is the eighth largest school district in the United States with 142,266 students in 218 traditional public schools and 86 charter schools .
The city's K-12 enrollment in district–run schools dropped from 156,211 students in 2010 to 130,104 students in 2015. During the same time period, the enrollment in charter schools increased from 33,995 students in 2010 to 62,358 students in 2015.
Higher education
 Medical and research facilities of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine and the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
Philadelphia has the third-largest student concentration on the East Coast of the United States, East Coast, with more than 120,000 college and university students enrolled within the city and nearly 300,000 in the metropolitan area. More than 80 colleges, universities, trade, and specialty schools are in the Philadelphia region. One of the founding members of the Association of American Universities is in the city, the University of Pennsylvania, an Ivy League institution with claims to be the First university in the United States.
Medical and research facilities of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine and the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
Philadelphia has the third-largest student concentration on the East Coast of the United States, East Coast, with more than 120,000 college and university students enrolled within the city and nearly 300,000 in the metropolitan area. More than 80 colleges, universities, trade, and specialty schools are in the Philadelphia region. One of the founding members of the Association of American Universities is in the city, the University of Pennsylvania, an Ivy League institution with claims to be the First university in the United States.
Culture
Philadelphia is home to many National Historic Site (United States), national historical sites that relate to the founding of the United States. Independence National Historical Park is the center of these historical landmarks being one of the country's 22 UNESCO World Heritage Sites. Independence Hall
Independence Hall is a historic civic building in Philadelphia, where both the United States Declaration of Independence and the United States Constitution were debated and adopted by America's Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Fa ...
, where the Declaration of Independence
A declaration of independence or declaration of statehood or proclamation of independence is an assertion by a polity in a defined territory that it is independent and constitutes a state. Such places are usually declared from part or all of the ...
was signed, and the Liberty Bell are the city's most famous attractions. Other national historic sites include the homes of Edgar Allan Poe National Historic Site, Edgar Allan Poe and Thaddeus Kosciuszko National Memorial, Thaddeus Kosciuszko, early government buildings like the First Bank of the United States, First and the Second Bank of the United States, Fort Mifflin, and the Gloria Dei (Old Swedes') Church.[
Philadelphia's major science museums include the ]Franklin Institute
The Franklin Institute is a science museum and the center of science education and research in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It is named after the American scientist and statesman Benjamin Franklin. It houses the Benjamin Franklin National Memori ...
, which contains the Benjamin Franklin National Memorial; the Academy of Natural Sciences
The Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University, formerly the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, is the oldest natural science research institution and museum in the Americas. It was founded in 1812, by many of the leading natura ...
; the Mütter Museum; and the University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology. History museums include the National Constitution Center, the Museum of the American Revolution, the Philadelphia History Museum, the National Museum of American Jewish History, the African American Museum in Philadelphia, the Historical Society of Pennsylvania, the Masonic Library and Museum of Pennsylvania in the Masonic Temple (Philadelphia, Pennsylvania), Masonic Temple, and the Eastern State Penitentiary. Philadelphia is home to the United States's first zoo
A zoo (short for zoological garden; also called an animal park or menagerie) is a facility in which animals are kept within enclosures for public exhibition and often bred for conservation purposes.
The term ''zoological garden'' refers to zoo ...
and hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emerge ...
, as well as Fairmount Park
Fairmount Park is the largest municipal park in Philadelphia and the historic name for a group of parks located throughout the city. Fairmount Park consists of two park sections named East Park and West Park, divided by the Schuylkill River, with ...
, one of America's oldest and largest urban parks,[ founded in 1855.
The city is home to important archival repositories, including the Library Company of Philadelphia, established in 1731 by ]Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading inte ...
, and the Athenaeum of Philadelphia, founded in 1814. The Presbyterian Historical Society is the country's oldest denominational historical society, organized in 1852.
Arts

 The city contains many art museums, such as the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts and the Rodin Museum, which holds the largest collection of work by Auguste Rodin outside France. The city's major art museum, the Philadelphia Museum of Art, is one of the List of largest art museums, largest art museums in the world. The long flight of Rocky Steps, steps to the Art Museum's main entrance became famous after the film ''Rocky'' (1976).
The city contains many art museums, such as the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts and the Rodin Museum, which holds the largest collection of work by Auguste Rodin outside France. The city's major art museum, the Philadelphia Museum of Art, is one of the List of largest art museums, largest art museums in the world. The long flight of Rocky Steps, steps to the Art Museum's main entrance became famous after the film ''Rocky'' (1976).["Walnut Street Theatre Historical Marker"]
''ExplorePAhistory.com''. Retrieved May 4, 2019. In May 2019, the Walnut Street Theatre announced a major expansion to begin in 2020.
Music
 The Philadelphia Orchestra is generally considered one of the Big Five (orchestras), top five orchestras in the United States. The orchestra performs at the Kimmel Center for the Performing Arts, Kimmel Center and has a summer concert series at the Mann Center for the Performing Arts. Opera Philadelphia performs at the nation's oldest continually operating opera house—the Academy of Music (Philadelphia), Academy of Music.
The Philadelphia Orchestra is generally considered one of the Big Five (orchestras), top five orchestras in the United States. The orchestra performs at the Kimmel Center for the Performing Arts, Kimmel Center and has a summer concert series at the Mann Center for the Performing Arts. Opera Philadelphia performs at the nation's oldest continually operating opera house—the Academy of Music (Philadelphia), Academy of Music.["Live Aid 1985: A day of magic"](_blank)
CNN. Retrieved March 2, 2018. The city also hosted the Live 8 concert, which attracted about 700,000 people to the Benjamin Franklin Parkway on July 2, 2005. Notable rock and pop musicians from Philadelphia and its suburbs include Bill Haley & His Comets, Nazz, Todd Rundgren, Hall & Oates, The Hooters, Cinderella (band), Cinderella, DJ Jazzy Jeff & the Fresh Prince, Ween, Schoolly D, Pink (singer), Pink, The Roots, Beanie Sigel, State Property (band), State Property, Lisa Lopes, Lisa "Left Eye" Lopes, Meek Mill, Lil Uzi Vert, and others.
Cuisine
 The city is known for its Submarine sandwich, hoagies, Stromboli (food), stromboli, roast pork sandwich, scrapple, pretzel#Pennsylvania, soft pretzels, Italian ice, water ice, Irish potato candy, tastykakes, and the cheesesteak sandwich which was developed by Italian immigrants. The Philadelphia area has many establishments that serve cheesesteaks, including restaurants, taverns, delicatessens and pizza parlors. The originator of the thinly-sliced steak sandwich in the 1930s, initially without cheese, is Pat's King of Steaks, which faces its rival Geno's Steaks, founded in 1966, across the intersection of 9th Street and Passyunk Avenue in the Italian Market, Philadelphia, Italian Market of South Philadelphia.
McGillin's Olde Ale House, opened in 1860 on Drury Street in Center City, Philadelphia, Center City, is the oldest continuously operated tavern in the city. The City Tavern is a replica of a historic 18th-century building first opened in 1773, demolished in 1854 after a fire, and rebuilt in 1975 on the same site as part of Independence National Historical Park. The tavern offers authentic 18th-century recipes, served in seven period dining rooms, three wine cellar rooms and an outdoor garden.
The Reading Terminal Market is a historic Marketplace, food market founded in 1893 in the Reading Terminal building, a designated National Historic Landmark. The enclosed market is one of the oldest and largest markets in the country, hosting over a hundred merchants offering Pennsylvania Dutch specialties, artisan cheese and meat, locally grown groceries, and specialty and ethnic foods.
The city is known for its Submarine sandwich, hoagies, Stromboli (food), stromboli, roast pork sandwich, scrapple, pretzel#Pennsylvania, soft pretzels, Italian ice, water ice, Irish potato candy, tastykakes, and the cheesesteak sandwich which was developed by Italian immigrants. The Philadelphia area has many establishments that serve cheesesteaks, including restaurants, taverns, delicatessens and pizza parlors. The originator of the thinly-sliced steak sandwich in the 1930s, initially without cheese, is Pat's King of Steaks, which faces its rival Geno's Steaks, founded in 1966, across the intersection of 9th Street and Passyunk Avenue in the Italian Market, Philadelphia, Italian Market of South Philadelphia.
McGillin's Olde Ale House, opened in 1860 on Drury Street in Center City, Philadelphia, Center City, is the oldest continuously operated tavern in the city. The City Tavern is a replica of a historic 18th-century building first opened in 1773, demolished in 1854 after a fire, and rebuilt in 1975 on the same site as part of Independence National Historical Park. The tavern offers authentic 18th-century recipes, served in seven period dining rooms, three wine cellar rooms and an outdoor garden.
The Reading Terminal Market is a historic Marketplace, food market founded in 1893 in the Reading Terminal building, a designated National Historic Landmark. The enclosed market is one of the oldest and largest markets in the country, hosting over a hundred merchants offering Pennsylvania Dutch specialties, artisan cheese and meat, locally grown groceries, and specialty and ethnic foods.
Dialect
The traditional Philadelphia accent is considered by some linguists to be the most distinctive accent in North America.[New York Times Sunday Review, Loose Ends](_blank)
"The Sound of Philadelphia Fades Out" Daniel Nester March 1, 2014 The Philadelphia dialect, which is spread throughout the Delaware Valley
The Delaware Valley is a metropolitan region on the East Coast of the United States that comprises and surrounds Philadelphia, the sixth most populous city in the nation and 68th largest city in the world as of 2020. The toponym Delaware Val ...
and South Jersey, is part of a larger Mid-Atlantic American English family, a designation that also includes the Baltimore dialect. Additionally, it shares many similarities with the New York accent. Owing to over a century of linguistic data collected by researchers at the University of Pennsylvania under sociolinguist William Labov, the Philadelphia dialect has been one of the best-studied forms of American English.
Sports

 Philadelphia's first professional sports team was baseball's Philadelphia Athletics (1860–1876), Athletics, organized in 1860. The Athletics were initially an National Association of Base Ball Players, amateur league team that National Association of Professional Base Ball Players, turned professional in 1871, and then became a founding team of the current National League in 1876. The city is one of 13 U.S. cities to have teams in U.S. cities with teams from four major league sports, all four major league sports: the Philadelphia Phillies of Major League Baseball (MLB), the Philadelphia Eagles of the National Football League (NFL), the Philadelphia Flyers of the National Hockey League (NHL), and the Philadelphia 76ers of the National Basketball Association (NBA). The Phillies, formed in 1883 as the Quakers and renamed in 1884, are the oldest team continuously playing under the same name in the same city in the history of American professional sports.
The Philadelphia metro area is also home to the Philadelphia Union of Major League Soccer (MLS). The Union began playing their home games in 2010 at PPL Corporation, PPL Park, a soccer-specific stadium in Chester, Pennsylvania. The stadium's name was changed to Talen Energy Stadium in 2016 and to Subaru Park in 2020.
Philadelphia was the second of eight American cities to have won titles in all four major leagues (MLB, NFL, NHL and NBA), and also has a title in soccer (from the now-defunct North American Soccer League (1968–1984), North American Soccer League in the 1970s). The city's professional teams and their fans endured 25 years without a championship, from the 76ers 1983 NBA Finals win until the Phillies 2008 World Series win. The lack of championships was sometimes attributed in jest to the Curse of Billy Penn after Liberty Place#One Liberty Place, One Liberty Place became the first building to surpass the height of the
Philadelphia's first professional sports team was baseball's Philadelphia Athletics (1860–1876), Athletics, organized in 1860. The Athletics were initially an National Association of Base Ball Players, amateur league team that National Association of Professional Base Ball Players, turned professional in 1871, and then became a founding team of the current National League in 1876. The city is one of 13 U.S. cities to have teams in U.S. cities with teams from four major league sports, all four major league sports: the Philadelphia Phillies of Major League Baseball (MLB), the Philadelphia Eagles of the National Football League (NFL), the Philadelphia Flyers of the National Hockey League (NHL), and the Philadelphia 76ers of the National Basketball Association (NBA). The Phillies, formed in 1883 as the Quakers and renamed in 1884, are the oldest team continuously playing under the same name in the same city in the history of American professional sports.
The Philadelphia metro area is also home to the Philadelphia Union of Major League Soccer (MLS). The Union began playing their home games in 2010 at PPL Corporation, PPL Park, a soccer-specific stadium in Chester, Pennsylvania. The stadium's name was changed to Talen Energy Stadium in 2016 and to Subaru Park in 2020.
Philadelphia was the second of eight American cities to have won titles in all four major leagues (MLB, NFL, NHL and NBA), and also has a title in soccer (from the now-defunct North American Soccer League (1968–1984), North American Soccer League in the 1970s). The city's professional teams and their fans endured 25 years without a championship, from the 76ers 1983 NBA Finals win until the Phillies 2008 World Series win. The lack of championships was sometimes attributed in jest to the Curse of Billy Penn after Liberty Place#One Liberty Place, One Liberty Place became the first building to surpass the height of the William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer and religious thinker belonging to the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers), and founder of the Province of Pennsylvania, a North American colony of England. He was an early advocate of democracy a ...
statue on top of Philadelphia City Hall, City Hall's tower in 1987. After nine years passed without another championship, the Eagles won their first Super Bowl LII, Super Bowl following the 2017 NFL season, 2017 season. In 2004, ESPN placed Philadelphia second on its list of The Fifteen Most Tortured Sports Cities. Fans of the Eagles and Phillies were singled out as the worst fans in the country by ''GQ'' magazine in 2011, which used the subtitle of "Meanest Fans in America" to summarize incidents of drunken behavior and a history of booing.
Major professional sports teams that originated in Philadelphia but which later moved to other cities include the Golden State Warriors basketball team—in Philadelphia from 1946 to 1962—and the Oakland Athletics baseball team—originally the History of the Philadelphia Athletics, Philadelphia Athletics from 1901 to 1954 (a different Athletics team than the one mentioned above).
Philadelphia is home to professional, semi-professional, and elite amateur teams in cricket, rugby league (Philadelphia Fight), and rugby union. Major running events in the city include the Penn Relays (track and field), the Philadelphia Marathon, and the Broad Street Run. The Collegiate Rugby Championship is played every June at Talen Energy Stadium in Chester, Pennsylvania, Chester.
Rowing has been popular in Philadelphia since the 18th century.Schuylkill River
The Schuylkill River ( , ) is a river running northwest to southeast in eastern Pennsylvania. The river was improved by navigations into the Schuylkill Canal, and several of its tributaries drain major parts of Pennsylvania's Coal Region. It fl ...
and organized by the Schuylkill Navy, an association of area rowing clubs that has produced numerous Rowing at the Summer Olympics, Olympic rowers.
The Philadelphia Spinners were a professional Ultimate (sport), ultimate team in Major League Ultimate (MLU) until 2016. The Spinners were one of the original eight teams of the American Ultimate Disc League (AUDL) that began in 2012. They played at Franklin Field and won the inaugural AUDL championship and the final MLU championship in 2016. The MLU was suspended indefinitely by its investors in December 2016. , the Philadelphia Phoenix (AUDL), Philadelphia Phoenix continue to play in the AUDL.
Philadelphia is home to the Philadelphia Big 5, a group of five NCAA Division I college basketball programs. The Big 5 are La Salle University, La Salle, University of Pennsylvania, Penn, Saint Joseph's University, Saint Joseph's, Temple University, Temple, and Villanova University, Villanova universities. The sixth NCAA Division I school in Philadelphia is Drexel University. Villanova won the 1985 NCAA Division I men's basketball tournament, 1985, 2016 NCAA Division I men's basketball tournament, 2016, and 2018 NCAA Division I men's basketball tournament, 2018 championship of the NCAA Division I men's basketball tournament. Philadelphia will be one of the eleven US host cities for the 2026 FIFA World Cup.
Law and government
 Philadelphia County is a legal nullity. All county functions were assumed by the city in 1952.
Philadelphia County is a legal nullity. All county functions were assumed by the city in 1952.[
Philadelphia's 1952 Home Rule Municipal charter, Charter was written by the City Charter Commission, which was created by the Pennsylvania General Assembly in an act of April 21, 1949, and a city ordinance of June 15, 1949. The existing city council received a proposed draft on February 14, 1951, and the electors approved it in an election held April 17, 1951.][
]
The city uses the Mayor–council government#Strong-mayor form, strong-mayor version of the mayor–council form of government, which is led by one mayor in whom executive (government), executive authority is vested. The mayor has the authority to appoint and dismiss members of all boards and commissions without the approval of the city council. Elected at-large, the mayor is limited to two consecutive four-year terms, but can run for the position again after an intervening term.[
]
Courts
Philadelphia County
Philadelphia County is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. It is the most populous county in Pennsylvania. As of the 2020 census, Philadelphia County had a population of 1,603,797. The county is the second smallest county in Pennsyl ...
is coterminous with the First Judicial District of Pennsylvania. The Philadelphia County Pennsylvania courts of common pleas, Court of Common Pleas is the trial court of general jurisdiction for the city, hearing felony-level criminal cases and civil suits above the minimum jurisdictional limit of $10,000. The court also has appellate jurisdiction over rulings from the Philadelphia Municipal Court, Municipal and Traffic Courts, and some administrative agencies and boards. The trial division has 70 commissioned judges elected by the voters, along with about one thousand other employees. The court also has a family division with 25 judges and an orphans' court with three judges.
, the city's District Attorney of Philadelphia, District Attorney is Larry Krasner, a Democrat. The last Republican to hold the office is Ronald D. Castille, who left in 1991 and later served as the Chief Justice of the Pennsylvania Supreme Court from 2008 to 2014.
The Philadelphia Municipal Court handles traffic cases, misdemeanor and felony criminal cases with maximum incarceration of five years, and civil cases involving $12,000 or less ($15,000 in real estate and school tax cases), and all landlord-tenant disputes. The municipal court has 27 judges elected by the voters.
Politics
 The current mayor is Jim Kenney who won the election in November 2015.
The current mayor is Jim Kenney who won the election in November 2015.[
As a result of the previously declining population in the city and state, Philadelphia has only three congressional districts of the 18 districts in Pennsylvania, based on the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census apportionment: Pennsylvania's 2nd congressional district, the 2nd district, represented by Brendan Boyle; Pennsylvania's 3rd congressional district, the 3rd, represented by Dwight Evans (politician), Dwight Evans; and Pennsylvania's 5th congressional district, the 5th, represented by Mary Gay Scanlon. All three representatives are Democrats though Republicans still have some support in the city, primarily in the Northeast Philadelphia, Northeast. Sam Katz (Philadelphia), Sam Katz ran competitive mayoral races as the Republican nominee in Philadelphia mayoral election, 1999, 1999 and Philadelphia mayoral election, 2003, 2003, losing to Democrat John F. Street, John Street both times.
Pennsylvania's longest-serving List of United States Senators from Pennsylvania, Senator, Arlen Specter, was an alumnus of the University of Pennsylvania who opened his first law practice in Philadelphia.]["Specter, Arlen, (1930–2012)"]
''bioguide.congress.gov''. Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. Retrieved March 1, 2018. Specter served as a Republican from 1981 and as a Democrat from 2009, losing that party's primary in United States Senate Democratic primary election in Pennsylvania, 2010, 2010 and leaving office in January 2011. He had also been assistant counsel on the Warren Commission in 1964 and the city's district attorney from 1966 to 1974.[
Philadelphia has hosted various United States presidential nominating convention, national conventions, including in 1848 Whig National Convention, 1848 (Whig), 1856 Republican National Convention, 1856 (Republican), 1872 Republican National Convention, 1872 (Republican), 1900 Republican National Convention, 1900 (Republican), 1936 Democratic National Convention, 1936 (Democratic), 1940 Republican National Convention, 1940 (Republican), 1948 Republican National Convention, 1948 (Republican), 1948 Progressive National Convention, 1948 (Progressive), 2000 Republican National Convention, 2000 (Republican), and 2016 Democratic National Convention, 2016 (Democratic).]
Environmental policy
"Green Cities, Clean Water" is an environmental policy initiative based in Philadelphia that has shown promising results in mitigating the effects of climate change.
Public safety
Police and law enforcement
 According to a 2015 report by the Pew Charitable Trusts, the Philadelphia Police Department#Districts, police districts with the highest rates of violent crime were Frankford, Philadelphia, Frankford (15th district) and Kensington, Philadelphia, Kensington (24th district) in the Near Northeast Philadelphia, Near Northeast, and districts to the North Philadelphia, North (22nd, 25th, and 35th districts), West Philadelphia, West (19th district) and Southwest Philadelphia, Southwest (12th district) of Center City, Philadelphia, Center City. Each of those seven districts recorded more than a thousand violent crimes in 2014. The lowest rates of violent crime occurred in Center City, South Philadelphia, the Far Northeast Philadelphia, Far Northeast, and Roxborough, Philadelphia, Roxborough districts, the latter of which includes Manayunk, Philadelphia, Manayunk.
According to a 2015 report by the Pew Charitable Trusts, the Philadelphia Police Department#Districts, police districts with the highest rates of violent crime were Frankford, Philadelphia, Frankford (15th district) and Kensington, Philadelphia, Kensington (24th district) in the Near Northeast Philadelphia, Near Northeast, and districts to the North Philadelphia, North (22nd, 25th, and 35th districts), West Philadelphia, West (19th district) and Southwest Philadelphia, Southwest (12th district) of Center City, Philadelphia, Center City. Each of those seven districts recorded more than a thousand violent crimes in 2014. The lowest rates of violent crime occurred in Center City, South Philadelphia, the Far Northeast Philadelphia, Far Northeast, and Roxborough, Philadelphia, Roxborough districts, the latter of which includes Manayunk, Philadelphia, Manayunk.
Firefighting
The Philadelphia Fire Department provides fire protection and emergency medical services (EMS). The department's official mission is to protect public safety by quick and professional response to emergencies and the promotion of sound emergency prevention measures. This mandate encompasses all traditional Firefighting in the United States, firefighting functions, including fire suppression, with 60 engine companies and 30 ladder companies as well as specialty and support units deployed throughout the city; specialized firefighting units for Philadelphia International Airport
Philadelphia International Airport is the primary airport serving Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The airport served 19.6 million passengers annually in 2021, making it the 21st busiest airport in the United States. The airport is located from t ...
and the Port of Philadelphia The Port of Philadelphia is located on the Delaware River in Philadelphia in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania.
Generally the term applies to the publicly owned marine terminals located within Philadelphia city limits along west bank of the river. Th ...
; investigations conducted by the fire marshal's office to determine the origins of fires and develop preventive strategies; Fire prevention, prevention programs to educate the public; and support services including research and planning, management of the fire communications center within the city's 9-1-1, 911 system, and operation of the Philadelphia Fire Academy.
Media
Newspapers
 Philadelphia's two major Newspaper, daily newspapers are ''The Philadelphia Inquirer'', first published in 1829—the third-oldest surviving daily newspaper in the country—and the ''Philadelphia Daily News'', first published in 1925.
Philadelphia's two major Newspaper, daily newspapers are ''The Philadelphia Inquirer'', first published in 1829—the third-oldest surviving daily newspaper in the country—and the ''Philadelphia Daily News'', first published in 1925.
Radio
The first experimental radio license was issued in Philadelphia in August 1912 to Saint Joseph's University, St. Joseph's College. The first commercial broadcasting, commercial AM broadcasting, AM radio stations began broadcasting in 1922: first WTEL (AM), WIP, then owned by Gimbels department store, followed by WFIL, then owned by Strawbridge's, Strawbridge & Clothier department store, and WOO (Philadelphia), WOO, a defunct station owned by Wanamaker's department store, as well as WPHT, WCAU and WDAS (AM), WDAS.
Television
 In the 1930s, the experimental station KYW-TV, W3XE, owned by Philco, became the first television station in Philadelphia. The station became NBC's first affiliate in 1939, and later became KYW-TV (currently a CBS affiliate). WCAU, WCAU-TV, WFIL-TV, and WHYY-TV were all founded by the 1960s.
In the 1930s, the experimental station KYW-TV, W3XE, owned by Philco, became the first television station in Philadelphia. The station became NBC's first affiliate in 1939, and later became KYW-TV (currently a CBS affiliate). WCAU, WCAU-TV, WFIL-TV, and WHYY-TV were all founded by the 1960s.[
, the city is the nation's fourth-largest consumer in media market, as ranked by the Nielsen Media Research firm, with nearly 2.9 million TV households.
]
Books
Since at least the 1700s, hundreds of Bibliography of Philadelphia, books and articles have been written about Philadelphia's history, culture, sports teams, crime, politics, and other themes related to the city's past, present, and future.
Infrastructure
Transportation

 Philadelphia is served by the Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) which operates buses, trains, rapid transit (as both subways and Elevated railway, elevated trains), Tram, trolleys, and Trolleybus, trackless trolleys (electric buses) throughout Philadelphia, the four Pennsylvania suburban counties of Bucks County, Pennsylvania, Bucks, Chester County, Pennsylvania, Chester, Delaware County, Pennsylvania, Delaware, and Montgomery County, Pennsylvania, Montgomery, in addition to service to Mercer County, New Jersey (Trenton, New Jersey, Trenton) and New Castle County, Delaware (Wilmington, Delaware, Wilmington and Newark, Delaware). The city's subway system consists of two routes: the subway section of the Market–Frankford Line running east–west under Market Street (Philadelphia), Market Street which opened in 1905 to the west and 1908 to the east of City Hall, and the Broad Street Line running north–south beneath Broad Street (Philadelphia), Broad Street which opened in stages from 1928 to 1938.
Beginning in the 1980s, large sections of the SEPTA Regional Rail service to the far suburbs of Philadelphia were discontinued due to a lack of funding for equipment and infrastructure maintenance.
Philadelphia is served by the Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) which operates buses, trains, rapid transit (as both subways and Elevated railway, elevated trains), Tram, trolleys, and Trolleybus, trackless trolleys (electric buses) throughout Philadelphia, the four Pennsylvania suburban counties of Bucks County, Pennsylvania, Bucks, Chester County, Pennsylvania, Chester, Delaware County, Pennsylvania, Delaware, and Montgomery County, Pennsylvania, Montgomery, in addition to service to Mercer County, New Jersey (Trenton, New Jersey, Trenton) and New Castle County, Delaware (Wilmington, Delaware, Wilmington and Newark, Delaware). The city's subway system consists of two routes: the subway section of the Market–Frankford Line running east–west under Market Street (Philadelphia), Market Street which opened in 1905 to the west and 1908 to the east of City Hall, and the Broad Street Line running north–south beneath Broad Street (Philadelphia), Broad Street which opened in stages from 1928 to 1938.
Beginning in the 1980s, large sections of the SEPTA Regional Rail service to the far suburbs of Philadelphia were discontinued due to a lack of funding for equipment and infrastructure maintenance.30th Street Station
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societie ...
is a major railroad station on Amtrak's Northeast Corridor with 4.4 million passengers in 2017 making it the List of busiest Amtrak stations, third-busiest station in the country after Pennsylvania Station (New York City), New York City's Pennsylvania Station and Washington Union Station, Washington's Union Station.
Airports
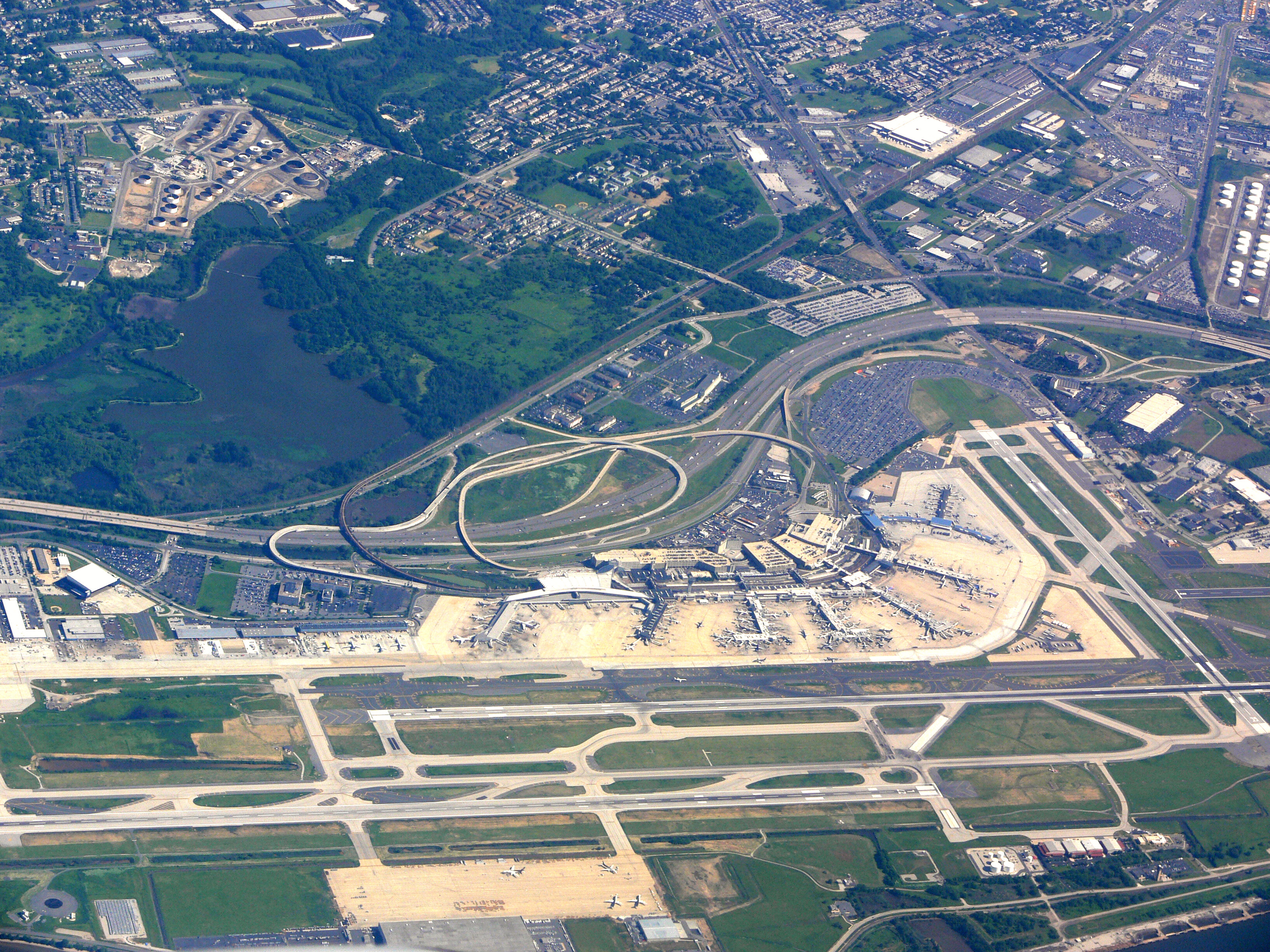 Two airports serve Philadelphia: the
Two airports serve Philadelphia: the Philadelphia International Airport
Philadelphia International Airport is the primary airport serving Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The airport served 19.6 million passengers annually in 2021, making it the 21st busiest airport in the United States. The airport is located from t ...
(PHL) is south-southwest of Center City, Philadelphia, Center City on the boundary with Delaware County, Pennsylvania, Delaware County, providing scheduled domestic and international air service,["Philadelphia International Airport: About Us"]
. ''phl.org''. Philadelphia International Airport. Retrieved January 29, 2018. while Northeast Philadelphia Airport (PNE) is a general aviation relief airport in Northeast Philadelphia serving general and corporate aviation. Philadelphia International Airport is among the busiest airports in the world World's busiest airports by traffic movements, measured by traffic movements (i.e., takeoffs and landings).[ SEPTA's Airport Line (SEPTA), Airport Regional Rail Line provides direct service between Center City railroad stations and Philadelphia International Airport.
]
Roads


William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer and religious thinker belonging to the Religious Society of Friends (Quakers), and founder of the Province of Pennsylvania, a North American colony of England. He was an early advocate of democracy a ...
planned Philadelphia with Numbered street#Philadelphia, numbered streets traversing north and south, and streets named for trees, such as Chestnut Street (Philadelphia), Chestnut, Walnut Street (Philadelphia), Walnut, and Arch Street (Philadelphia), Mulberry, traversing east and west. The two main streets were named Broad Street (Philadelphia), Broad Street (the north–south Arterial road, artery, since designated Pennsylvania Route 611) and High Street (the east–west artery, since renamed Market Street (Philadelphia), Market Street) converging at Centre Square which later became the site of Philadelphia City Hall, City Hall.
Interstate 95 in Pennsylvania, Interstate 95 (the Delaware Expressway) traverses the southern and eastern edges of the city along the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock (village), New York, Hancock, New York, the river flows for along the borders of N ...
as the main north–south controlled-access highway, connecting Philadelphia with Newark, New Jersey and New York City to the north and with Baltimore and Washington, D.C. southward. The city is also served by Interstate 76 (Ohio–New Jersey), Interstate 76 (the Schuylkill Expressway), which runs along the Schuylkill River
The Schuylkill River ( , ) is a river running northwest to southeast in eastern Pennsylvania. The river was improved by navigations into the Schuylkill Canal, and several of its tributaries drain major parts of Pennsylvania's Coal Region. It fl ...
, intersecting the Pennsylvania Turnpike at King of Prussia, Pennsylvania, King of Prussia and providing access to Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, Harrisburg and points west. Interstate 676 (the Vine Street Expressway) links I-95 and I-76 through Center City by running below street level between the eastbound and westbound lanes of Vine Street (Philadelphia), Vine Street. Entrance and exit ramps for the Benjamin Franklin Bridge are near the eastern end of the expressway, just west of the I-95 interchange.["OpenStreetMap"]
''openstreetmap.org''. Retrieved January 29, 2018.
The Roosevelt Boulevard (Philadelphia), Roosevelt Boulevard and Expressway (U.S. Route 1 in Pennsylvania, U.S. 1) connect Northeast Philadelphia with Center City via I-76 through Fairmount Park
Fairmount Park is the largest municipal park in Philadelphia and the historic name for a group of parks located throughout the city. Fairmount Park consists of two park sections named East Park and West Park, divided by the Schuylkill River, with ...
. Woodhaven Road (Pennsylvania Route 63, Route 63) and Cottman Avenue (Pennsylvania Route 73, Route 73) serve the neighborhoods of Northeast Philadelphia, running between I-95 and the Roosevelt Boulevard. The Fort Washington Expressway (Pennsylvania Route 309, Route 309) extends north from the city's northern border, serving Montgomery County, Pennsylvania, Montgomery County and Bucks County, Pennsylvania, Bucks County. U.S. Route 30 in Pennsylvania, U.S. Route 30 (Philadelphia and Lancaster Turnpike, Lancaster Avenue) extends westward from West Philadelphia to Lancaster, Pennsylvania, Lancaster.[
Interstate 476 (locally referred to as the Blue Route) traverses Delaware County, Pennsylvania, Delaware County, bypassing the city to the west and serving the city's western suburbs, as well as providing a direct route to Allentown, Pennsylvania, Allentown and points north, including the Pocono Mountains, Poconos. Interstate 276 (the Pennsylvania Turnpike's Pennsylvania Turnpike#Delaware River extension, Delaware River extension) acts as a bypass and commuter route to the north of the city as well as a link to the New Jersey Turnpike and New York City.][
The Delaware River Port Authority operates four bridges in the Philadelphia area across the Delaware River to New Jersey: the Walt Whitman Bridge (I-76), the Benjamin Franklin Bridge (I-676 and U.S. 30), the Betsy Ross Bridge (New Jersey Route 90), and the Commodore Barry Bridge (U.S. Route 322, U.S. 322 in Delaware County, south of the city). The Burlington County Bridge Commission maintains two bridges across the Delaware River: the Tacony–Palmyra Bridge which connects Pennsylvania Route 73, PA Route 73 in the Tacony, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, Tacony section of Northeast Philadelphia with New Jersey Route 73 in Palmyra, New Jersey, Palmyra, Burlington County, New Jersey, Burlington County, and the Burlington–Bristol Bridge which connects New Jersey Route 413, NJ Route 413/U.S. Route 130 in Burlington, New Jersey with Pennsylvania Route 413, PA Route 413/U.S. Route 13 in Pennsylvania, U.S. 13 in Bristol Township, Bucks County, Pennsylvania, Bristol Township, north of Philadelphia.
]
Bus service
The Philadelphia Greyhound Terminal, Greyhound terminal is at 1001 Filbert Street (at 10th Street) in Center City, southeast of the Pennsylvania Convention Center and south of Chinatown, Philadelphia, Chinatown. Several other bus operators provide service at the Greyhound terminal including Trailways Transportation System, Fullington Trailways, Martz Group, Martz Trailways, Peter Pan Bus Lines, and NJ Transit Bus Operations, NJ Transit buses.
Other intercity bus services include Megabus (North America), Megabus with stops at 30th Street Station
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societie ...
and the visitor center for Independence Hall
Independence Hall is a historic civic building in Philadelphia, where both the United States Declaration of Independence and the United States Constitution were debated and adopted by America's Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Fa ...
, BoltBus (operated by Greyhound) at 30th Street Station, OurBus at various stops in the city.
Rail
 Since the early days of rail transportation in the United States, Philadelphia has served as a hub for several major rail companies, particularly the Pennsylvania Railroad and the Reading Company, Reading Railroad. The Pennsylvania Railroad first operated Broad Street Station (Philadelphia), Broad Street Station, then
Since the early days of rail transportation in the United States, Philadelphia has served as a hub for several major rail companies, particularly the Pennsylvania Railroad and the Reading Company, Reading Railroad. The Pennsylvania Railroad first operated Broad Street Station (Philadelphia), Broad Street Station, then 30th Street Station
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societie ...
and Suburban Station, and the Reading Railroad operated Reading Terminal, now part of the Pennsylvania Convention Center. The two companies also operated competing commuter rail systems in the area. The two systems now operate as a single system under the control of SEPTA, the regional transit authority. Additionally, the PATCO Speedline subway system and NJ Transit's Atlantic City Line operate successor services to southern New Jersey.
In 1911, Philadelphia had nearly 4,000 electric tram, trolleys running on 86 lines. In 2005, SEPTA reintroduced trolley service to the SEPTA Route 15, Girard Avenue Line, Route 15. SEPTA operates six subway-surface trolleys that run on street-level tracks in West Philadelphia and subway tunnels in Center City, Philadelphia, Center City, along with two surface trolleys in adjacent suburbs.
Philadelphia is a regional hub of the State-owned enterprise, federally-owned Amtrak system, with 30th Street Station being a primary stop on the Washington-Boston Northeast Corridor and the Keystone Corridor to Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, Harrisburg and Pittsburgh. 30th Street also serves as a major station for services via the Pennsylvania Railroad's former Main Line (Pennsylvania Railroad), Pennsylvania Main Line to Chicago. , 30th Street is Amtrak's third-busiest station in the country, after New York City and Washington.[
]
Walk Score ranks
A 2017 study by Walk Score ranked Philadelphia the fifth-most walkable major city in the United States with a score of 79 out of 100, in the middle of the "very walkable" range. The city was just edged out by fourth place Miami (79.2), with the top three cities being New York, San Francisco, and Boston. Philadelphia placed fifth in the public transit friendly category, behind Washington, D.C., with the same three cities for walkability topping this category. The city ranked tenth in the bike friendly cities category, with the top three cities being Minneapolis, San Francisco and Portland.
''USA Today'' readers voted the Schuylkill River Trail the best urban trail in the nation in 2015.
Utilities
Water purity and availability
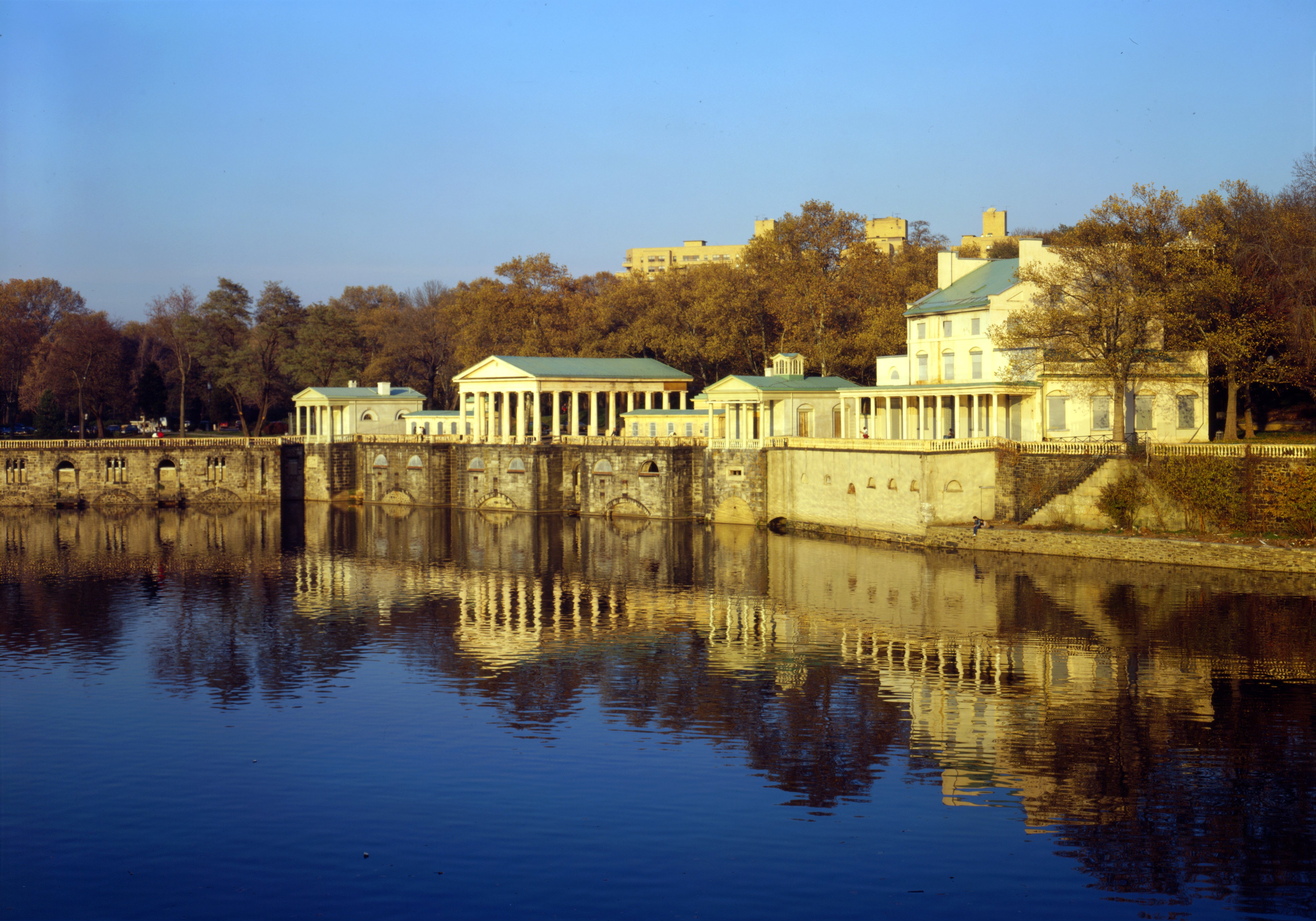 In 1815, Philadelphia began sourcing its water via the Fairmount Water Works on the
In 1815, Philadelphia began sourcing its water via the Fairmount Water Works on the Schuylkill River
The Schuylkill River ( , ) is a river running northwest to southeast in eastern Pennsylvania. The river was improved by navigations into the Schuylkill Canal, and several of its tributaries drain major parts of Pennsylvania's Coal Region. It fl ...
, the nation's first major urban water supply system. In 1909, the Water Works was decommissioned as the city transitioned to modern Sand filter, sand filtration methods. Today, the Philadelphia Water Department (PWD) provides drinking water, wastewater collection, and stormwater services for Philadelphia, as well as surrounding counties. PWD draws about 57 percent of its drinking water from the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock (village), New York, Hancock, New York, the river flows for along the borders of N ...
and the balance from the Schuylkill River.
Electricity
Exelon subsidiary PECO Energy Company, founded as the Brush Electric Light Company of Philadelphia in 1881 and renamed Philadelphia Electric Company (PECO) in 1902, provides electricity to about 1.6 million customers and more than 500,000 natural gas customers in the southeastern Pennsylvania area including the city of Philadelphia and most of its suburbs. PECO is the largest electric and natural gas utility in the state with 472 power substations and nearly of electric transmission and distribution lines, along with of natural gas transmission, distribution & service lines.
Natural gas
Philadelphia Gas Works (PGW), overseen by the Pennsylvania Public Utility Commission, is the nation's largest municipally-owned natural gas utility. PGW serves over 500,000 homes and businesses in the Philadelphia area. Founded in 1836, the company came under city ownership in 1987 and has been providing the majority of gas distributed within city limits. In 2014, the Philadelphia City Council, City Council refused to conduct hearings on a $1.86 billion sale of PGW, part of a two-year effort that was proposed by the mayor. The refusal led to the prospective buyer terminating its offer.
Telecommunications
Southeastern Pennsylvania was assigned the area code 215, 215 area code in 1947 when the North American Numbering Plan of the Bell System went into effect. The geographic area covered by the code was split nearly in half in 1994 when Area codes 610, 484, and 835, area code 610 was created, with the city and its northern suburbs retaining 215. area code overlay, Overlay area code 267 was added to the 215 service area in 1997, and 484 was added to the 610 area in 1999. A plan in 2001 to introduce a third overlay code to both service areas, area code 445 to 215 and Area codes 610, 484, and 835, area code 835 to 610, was delayed and later rescinded. Area code 445 was implemented as an overlay for area codes 215 and 267 starting on February 3, 2018.
Notable people
Sister cities
 Philadelphia also has three partnership cities or regions:
Philadelphia also has three partnership cities or regions:[IVC of Philadelphia Partners with Mosul, Iraq in Groundbreaking Program](_blank)
Retrieved January 26, 2011. as well as accepting visiting delegations from dozens of other countries.[Inbound delegations visiting Philadelphia](_blank)
Retrieved January 26, 2011.
See also
* List of Pennsylvania state historical markers in Philadelphia County
* List of metropolitan areas in the Americas, Metropolitan areas in the Americas
* National Register of Historic Places listings in Philadelphia
Notes
References
Further reading
*
External links
City of Philadelphia government
Encyclopedia of Greater Philadelphia
– historical encyclopedia
Historic Philadelphia
– over 2 million photographs dating back to the late 1800s
Greater Philadelphia GeoHistory Network
– historical maps and atlases
*
philly.com
– ''The Philadelphia Inquirer'' and ''Philadelphia Daily News, Daily News''
Convention & Visitors Bureau
Pennsylvania Convention Center
''10 Towns that Changed America''
– WTTW; segment from 7:23–12:00 of 56-minute video
{{Authority control
Philadelphia,
1682 establishments in Pennsylvania
Cities in Pennsylvania
Consolidated city-counties
County seats in Pennsylvania
Former capitals of the United States
Former state capitals in the United States, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania populated places on the Delaware River
Planned cities in the United States
Populated places established in 1682
Populated places on the Schuylkill River
Port cities and towns of the Pennsylvania Atlantic coast
Ukrainian communities in the United States

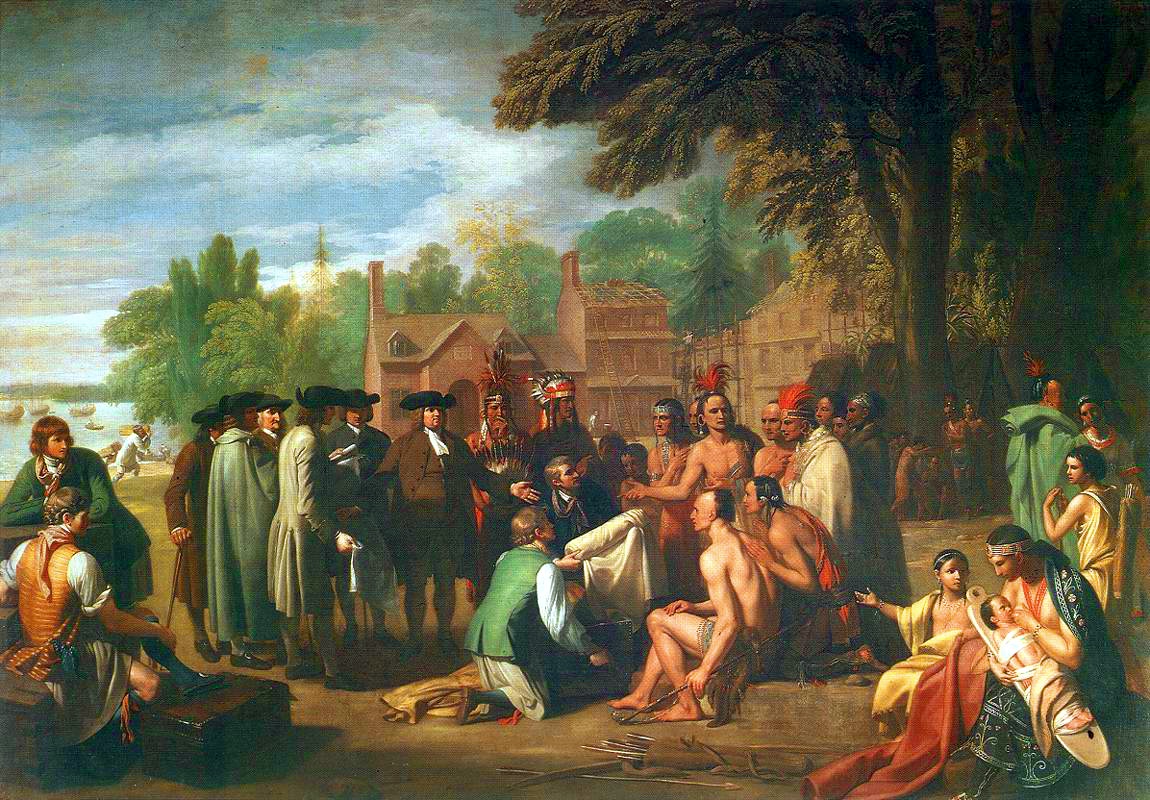 Europeans came to the
Europeans came to the  Philadelphia's importance and central location in the colonies made it a natural center for America's revolutionaries. By the 1750s, Philadelphia had surpassed
Philadelphia's importance and central location in the colonies made it a natural center for America's revolutionaries. By the 1750s, Philadelphia had surpassed  Throughout the 19th century, Philadelphia hosted a variety of industries and businesses, the largest being textile industry, textiles. Major corporations in the 19th and early 20th centuries included the Baldwin Locomotive Works, William Cramp & Sons, William Cramp & Sons Shipbuilding Company, and the Pennsylvania Railroad. Established in 1870, the Philadelphia Conveyancers' Association was chartered by the state in 1871. Industry, along with the U.S. Centennial, was celebrated in 1876 with the Centennial Exposition, the first official World's fair in the United States.
Immigrants, mostly from Ireland and Germany, settled in Philadelphia and the surrounding districts. These immigrants were largely responsible for the 1835 Philadelphia general strike, first general strike in North America in 1835, in which workers in the city won the ten-hour workday. The city was a destination for thousands of Irish immigrants fleeing the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine in the 1840s; housing for them was developed south of South Street (Philadelphia), South Street and later occupied by succeeding immigrants. They established a network of Catholic church, Catholic churches and schools and dominated the Catholic clergy for decades. Anti-Irish, anti-Catholic Nativism (politics), nativist Philadelphia nativist riots, riots erupted in Philadelphia in 1844. The rise in population of the surrounding districts helped lead to the Act of Consolidation, 1854, Act of Consolidation of 1854, which extended the city limits from the of Center City, Philadelphia, Center City to the roughly of
Throughout the 19th century, Philadelphia hosted a variety of industries and businesses, the largest being textile industry, textiles. Major corporations in the 19th and early 20th centuries included the Baldwin Locomotive Works, William Cramp & Sons, William Cramp & Sons Shipbuilding Company, and the Pennsylvania Railroad. Established in 1870, the Philadelphia Conveyancers' Association was chartered by the state in 1871. Industry, along with the U.S. Centennial, was celebrated in 1876 with the Centennial Exposition, the first official World's fair in the United States.
Immigrants, mostly from Ireland and Germany, settled in Philadelphia and the surrounding districts. These immigrants were largely responsible for the 1835 Philadelphia general strike, first general strike in North America in 1835, in which workers in the city won the ten-hour workday. The city was a destination for thousands of Irish immigrants fleeing the Great Famine (Ireland), Great Famine in the 1840s; housing for them was developed south of South Street (Philadelphia), South Street and later occupied by succeeding immigrants. They established a network of Catholic church, Catholic churches and schools and dominated the Catholic clergy for decades. Anti-Irish, anti-Catholic Nativism (politics), nativist Philadelphia nativist riots, riots erupted in Philadelphia in 1844. The rise in population of the surrounding districts helped lead to the Act of Consolidation, 1854, Act of Consolidation of 1854, which extended the city limits from the of Center City, Philadelphia, Center City to the roughly of  By the 20th century, Philadelphia had an entrenched Republican Party (United States), Republican political machine and a complacent population. The first major reform came in 1917 when outrage over the election-year murder of a police officer led to the shrinking of the Philadelphia City Council, City Council from two houses to just one. In July 1919, Philadelphia was one of more than 36 industrial cities nationally to suffer a Race riots in Philadelphia during the 1919 Red Summer, race riot of ethnic whites against blacks during Red Summer, in post-World War I unrest, as recent immigrants competed with blacks for jobs. In the 1920s, the public flouting of Prohibition in the United States, Prohibition laws, organized crime, mob violence, and police involvement in illegal activities led to the appointment of Brigadier general, Brig. Gen. Smedley Butler of the United States Marine Corps, U.S. Marine Corps as director of public safety, but political pressure prevented any long-term success in fighting crime and corruption.
In 1940, non-Hispanic whites constituted 86.8% of the city's population. The population peaked at more than two million residents in 1950, then began to decline with the restructuring of industry, which led to the loss of many middle-class union jobs. In addition, suburbanization had enticed many of the more affluent residents to outlying railroad commuting towns and newer housing. The resulting reduction in Philadelphia's tax base and the resources of local government caused the city to struggle through a long period of adjustment, with it approaching bankruptcy by the late 1980s.
Revitalization and gentrification of neighborhoods began in the late 1970s and continues into the 21st century, with much of the development occurring in the Center City, Philadelphia, Center City and University City, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, University City neighborhoods, while simultaneously exacerbating a shortage of affordable housing in Philadelphia. After many of the old manufacturers and businesses left Philadelphia or shut down, the city started attracting service businesses and began to market itself more aggressively as a tourist destination. Contemporary glass-and-granite
By the 20th century, Philadelphia had an entrenched Republican Party (United States), Republican political machine and a complacent population. The first major reform came in 1917 when outrage over the election-year murder of a police officer led to the shrinking of the Philadelphia City Council, City Council from two houses to just one. In July 1919, Philadelphia was one of more than 36 industrial cities nationally to suffer a Race riots in Philadelphia during the 1919 Red Summer, race riot of ethnic whites against blacks during Red Summer, in post-World War I unrest, as recent immigrants competed with blacks for jobs. In the 1920s, the public flouting of Prohibition in the United States, Prohibition laws, organized crime, mob violence, and police involvement in illegal activities led to the appointment of Brigadier general, Brig. Gen. Smedley Butler of the United States Marine Corps, U.S. Marine Corps as director of public safety, but political pressure prevented any long-term success in fighting crime and corruption.
In 1940, non-Hispanic whites constituted 86.8% of the city's population. The population peaked at more than two million residents in 1950, then began to decline with the restructuring of industry, which led to the loss of many middle-class union jobs. In addition, suburbanization had enticed many of the more affluent residents to outlying railroad commuting towns and newer housing. The resulting reduction in Philadelphia's tax base and the resources of local government caused the city to struggle through a long period of adjustment, with it approaching bankruptcy by the late 1980s.
Revitalization and gentrification of neighborhoods began in the late 1970s and continues into the 21st century, with much of the development occurring in the Center City, Philadelphia, Center City and University City, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, University City neighborhoods, while simultaneously exacerbating a shortage of affordable housing in Philadelphia. After many of the old manufacturers and businesses left Philadelphia or shut down, the city started attracting service businesses and began to market itself more aggressively as a tourist destination. Contemporary glass-and-granite 
 Philadelphia's architectural history dates back to
Philadelphia's architectural history dates back to  , the total city parkland, including municipal, state and federal parks within the city limits, amounts to . Philadelphia's largest park is
, the total city parkland, including municipal, state and federal parks within the city limits, amounts to . Philadelphia's largest park is 
 Apart from economic growth, another factor contributing to the population increase is Philadelphia's rising immigration rate. Like the millennial population, Philadelphia's immigrant population is also growing rapidly. According to research by The Pew Charitable Trusts, the city's foreign born, foreign-born population had increased by 69% between 2000 and 2016 to constitute nearly 20% of Philadelphia's work force, and had doubled between 1990 and 2017 to constitute 13.8% of the city's total population, with the top five countries of origin being China by a significant margin, followed by the Dominican Republic, Jamaica, India, and Vietnam.
Irish, Italian, German, Poles, Polish, English, Russian, Ukrainians, Ukrainian, and French constitute the largest European emigration, European ethnic groups in the city. Philadelphia has the second-largest Irish and Italian populations in the United States, after New York City. South Philadelphia remains one of the largest Italian-American, Italian neighborhoods in the country and is home to the Italian Market, Philadelphia, Italian Market.
The Pennsport, Philadelphia, Pennsport neighborhood and Grays Ferry, Philadelphia, Gray's Ferry section of South Philadelphia, home to many Mummers Parade, Mummer clubs, are well known as Irish-American, Irish neighborhoods. The Kensington, Philadelphia, Kensington, Port Richmond, Philadelphia, Port Richmond, and Fishtown neighborhoods have historically been heavily Irish and Polish. Port Richmond is well known in particular as the center of the Polish immigrant and Polish-American community in Philadelphia, and it remains a common destination for Polish immigrants. Northeast Philadelphia, although known for its Irish and Irish-American population, is also home to a large Jewish-American, Jewish and Russian population. Mount Airy, Philadelphia, Mount Airy in Northwest Philadelphia also contains a large Jewish community, while nearby Chestnut Hill, Philadelphia, Chestnut Hill is historically known as an White Anglo-Saxon Protestant, Anglo-Saxon Protestant community.
Philadelphia has a significant gay and lesbian population. Philadelphia's Gay village, Gayborhood, which is near Washington Square (Philadelphia), Washington Square, is home to a large concentration of gay and lesbian friendly businesses, restaurants, and bars.
The African Americans, Black American population in Philadelphia is the third-largest in the country, after New York City and Chicago. West Philadelphia and North Philadelphia are largely African-American neighborhoods, but many are leaving those areas in favor of the Northeast and Southwest sections of Philadelphia. A higher proportion of African-American Muslims reside in Philadelphia than in most other cities in America. West Philadelphia and Southwest Philadelphia are also home to various significant West Indian Americans, Afro-Caribbean and African immigration to the United States, African immigrant communities.
The Puerto Ricans in Philadelphia, Puerto Rican population in Philadelphia is the second-largest on the mainland United States after New York City, and the second-fastest growing after Orlando. Eastern North Philadelphia, particularly Fairhill, Philadelphia, Fairhill and surrounding areas to the north and east, has one of the highest concentrations of Puerto Ricans outside Puerto Rico, with many large swaths of blocks being close to 100% Puerto Rican. Large Puerto Rican and Dominican Americans, Dominican populations reside in North Philadelphia and the Northeast. In regard to other Latin American populations in Philadelphia, there are significant Mexican American, Mexican and Central American populations in South Philadelphia.
Philadelphia's Asian Americans, Asian American population originates mainly from China, India, Vietnam, South Korea, and the Philippines. Over 35,000 Chinese Americans lived in the city in 2015, including a large Fuzhounese Americans, Fuzhounese population. Center City hosts a growing Chinatown, Philadelphia, Chinatown accommodating heavily traveled Chinatown bus lines, Chinese-owned bus lines to and from Chinatown, Manhattan in Chinese in New York City, New York City, 95 miles to the north, as Philadelphia is experiencing significant Chinese emigration, Chinese immigration from New York City. A large Korean community initially settled in the North Philadelphia neighborhood of Olney, Philadelphia, Olney; however, the primary Koreatown, Philadelphia, Koreatown has subsequently shifted northward, straddling the border with the adjacent suburb of Cheltenham, Pennsylvania, Cheltenham in Montgomery County, Pennsylvania, Montgomery County, while also growing in nearby Cherry Hill, New Jersey. South Philadelphia is also home to large Cambodian Americans, Cambodian, Vietnamese-American, Vietnamese, Thai Americans, Thai, and Chinese communities.
Apart from economic growth, another factor contributing to the population increase is Philadelphia's rising immigration rate. Like the millennial population, Philadelphia's immigrant population is also growing rapidly. According to research by The Pew Charitable Trusts, the city's foreign born, foreign-born population had increased by 69% between 2000 and 2016 to constitute nearly 20% of Philadelphia's work force, and had doubled between 1990 and 2017 to constitute 13.8% of the city's total population, with the top five countries of origin being China by a significant margin, followed by the Dominican Republic, Jamaica, India, and Vietnam.
Irish, Italian, German, Poles, Polish, English, Russian, Ukrainians, Ukrainian, and French constitute the largest European emigration, European ethnic groups in the city. Philadelphia has the second-largest Irish and Italian populations in the United States, after New York City. South Philadelphia remains one of the largest Italian-American, Italian neighborhoods in the country and is home to the Italian Market, Philadelphia, Italian Market.
The Pennsport, Philadelphia, Pennsport neighborhood and Grays Ferry, Philadelphia, Gray's Ferry section of South Philadelphia, home to many Mummers Parade, Mummer clubs, are well known as Irish-American, Irish neighborhoods. The Kensington, Philadelphia, Kensington, Port Richmond, Philadelphia, Port Richmond, and Fishtown neighborhoods have historically been heavily Irish and Polish. Port Richmond is well known in particular as the center of the Polish immigrant and Polish-American community in Philadelphia, and it remains a common destination for Polish immigrants. Northeast Philadelphia, although known for its Irish and Irish-American population, is also home to a large Jewish-American, Jewish and Russian population. Mount Airy, Philadelphia, Mount Airy in Northwest Philadelphia also contains a large Jewish community, while nearby Chestnut Hill, Philadelphia, Chestnut Hill is historically known as an White Anglo-Saxon Protestant, Anglo-Saxon Protestant community.
Philadelphia has a significant gay and lesbian population. Philadelphia's Gay village, Gayborhood, which is near Washington Square (Philadelphia), Washington Square, is home to a large concentration of gay and lesbian friendly businesses, restaurants, and bars.
The African Americans, Black American population in Philadelphia is the third-largest in the country, after New York City and Chicago. West Philadelphia and North Philadelphia are largely African-American neighborhoods, but many are leaving those areas in favor of the Northeast and Southwest sections of Philadelphia. A higher proportion of African-American Muslims reside in Philadelphia than in most other cities in America. West Philadelphia and Southwest Philadelphia are also home to various significant West Indian Americans, Afro-Caribbean and African immigration to the United States, African immigrant communities.
The Puerto Ricans in Philadelphia, Puerto Rican population in Philadelphia is the second-largest on the mainland United States after New York City, and the second-fastest growing after Orlando. Eastern North Philadelphia, particularly Fairhill, Philadelphia, Fairhill and surrounding areas to the north and east, has one of the highest concentrations of Puerto Ricans outside Puerto Rico, with many large swaths of blocks being close to 100% Puerto Rican. Large Puerto Rican and Dominican Americans, Dominican populations reside in North Philadelphia and the Northeast. In regard to other Latin American populations in Philadelphia, there are significant Mexican American, Mexican and Central American populations in South Philadelphia.
Philadelphia's Asian Americans, Asian American population originates mainly from China, India, Vietnam, South Korea, and the Philippines. Over 35,000 Chinese Americans lived in the city in 2015, including a large Fuzhounese Americans, Fuzhounese population. Center City hosts a growing Chinatown, Philadelphia, Chinatown accommodating heavily traveled Chinatown bus lines, Chinese-owned bus lines to and from Chinatown, Manhattan in Chinese in New York City, New York City, 95 miles to the north, as Philadelphia is experiencing significant Chinese emigration, Chinese immigration from New York City. A large Korean community initially settled in the North Philadelphia neighborhood of Olney, Philadelphia, Olney; however, the primary Koreatown, Philadelphia, Koreatown has subsequently shifted northward, straddling the border with the adjacent suburb of Cheltenham, Pennsylvania, Cheltenham in Montgomery County, Pennsylvania, Montgomery County, while also growing in nearby Cherry Hill, New Jersey. South Philadelphia is also home to large Cambodian Americans, Cambodian, Vietnamese-American, Vietnamese, Thai Americans, Thai, and Chinese communities.

 Philadelphia's history attracts many tourists, with the Independence National Historical Park (which includes the Liberty Bell,
Philadelphia's history attracts many tourists, with the Independence National Historical Park (which includes the Liberty Bell, 
 Medical and research facilities of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine and the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
Philadelphia has the third-largest student concentration on the East Coast of the United States, East Coast, with more than 120,000 college and university students enrolled within the city and nearly 300,000 in the metropolitan area. More than 80 colleges, universities, trade, and specialty schools are in the Philadelphia region. One of the founding members of the Association of American Universities is in the city, the University of Pennsylvania, an Ivy League institution with claims to be the First university in the United States.
The city's largest university, as noted by number of students, is Temple University, followed by Drexel University. The University of Pennsylvania, Temple University, Drexel University, and Thomas Jefferson University comprise the city's nationally ranked research universities. Philadelphia is also home to five schools of medicine: Drexel University College of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine, Temple University School of Medicine, and Thomas Jefferson University's Thomas Jefferson University, Sidney Kimmel Medical College. Hospitals, universities, and higher education research institutions in Philadelphia's four congressional districts received more than $252 million in National Institutes of Health grants in 2015.
Other institutions of higher learning within the city's borders include:
* Chestnut Hill College
* Community College of Philadelphia
* Curtis Institute of Music
* Holy Family University
* La Salle University
* Moore College of Art and Design
* Peirce College
* Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts
* Saint Joseph's University
* Spells Writing Lab, Inc.
* The Art Institutes#Locations, The Art Institute of Philadelphia
* The Restaurant School at Walnut Hill College
* University of the Arts (Philadelphia), University of the Arts
* University of the Sciences
Medical and research facilities of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine and the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
Philadelphia has the third-largest student concentration on the East Coast of the United States, East Coast, with more than 120,000 college and university students enrolled within the city and nearly 300,000 in the metropolitan area. More than 80 colleges, universities, trade, and specialty schools are in the Philadelphia region. One of the founding members of the Association of American Universities is in the city, the University of Pennsylvania, an Ivy League institution with claims to be the First university in the United States.
The city's largest university, as noted by number of students, is Temple University, followed by Drexel University. The University of Pennsylvania, Temple University, Drexel University, and Thomas Jefferson University comprise the city's nationally ranked research universities. Philadelphia is also home to five schools of medicine: Drexel University College of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine, Temple University School of Medicine, and Thomas Jefferson University's Thomas Jefferson University, Sidney Kimmel Medical College. Hospitals, universities, and higher education research institutions in Philadelphia's four congressional districts received more than $252 million in National Institutes of Health grants in 2015.
Other institutions of higher learning within the city's borders include:
* Chestnut Hill College
* Community College of Philadelphia
* Curtis Institute of Music
* Holy Family University
* La Salle University
* Moore College of Art and Design
* Peirce College
* Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts
* Saint Joseph's University
* Spells Writing Lab, Inc.
* The Art Institutes#Locations, The Art Institute of Philadelphia
* The Restaurant School at Walnut Hill College
* University of the Arts (Philadelphia), University of the Arts
* University of the Sciences

 The city contains many art museums, such as the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts and the Rodin Museum, which holds the largest collection of work by Auguste Rodin outside France. The city's major art museum, the Philadelphia Museum of Art, is one of the List of largest art museums, largest art museums in the world. The long flight of Rocky Steps, steps to the Art Museum's main entrance became famous after the film ''Rocky'' (1976).
Areas such as South Street and Old City have a vibrant night life. The Avenue of the Arts (Philadelphia), Avenue of the Arts in Center City contains many restaurants and theaters, such as the Kimmel Center for the Performing Arts, home of the Philadelphia Orchestra, and the Academy of Music (Philadelphia), Academy of Music, home of Opera Philadelphia and the Pennsylvania Ballet. The Wilma Theater (Philadelphia), Wilma Theatre and the Philadelphia Theatre Company at the Suzanne Roberts Theatre produce a variety of new plays. Several blocks to the east are the Lantern Theater Company at St. Stephen's Episcopal Church (Philadelphia), St. Stephens Episcopal Church; and the Walnut Street Theatre, a National Historic Landmark stated to be the oldest and most subscribed-to theater (structure), theatre in the English-speaking world, founded in 1809."Walnut Street Theatre Historical Marker"
The city contains many art museums, such as the Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts and the Rodin Museum, which holds the largest collection of work by Auguste Rodin outside France. The city's major art museum, the Philadelphia Museum of Art, is one of the List of largest art museums, largest art museums in the world. The long flight of Rocky Steps, steps to the Art Museum's main entrance became famous after the film ''Rocky'' (1976).
Areas such as South Street and Old City have a vibrant night life. The Avenue of the Arts (Philadelphia), Avenue of the Arts in Center City contains many restaurants and theaters, such as the Kimmel Center for the Performing Arts, home of the Philadelphia Orchestra, and the Academy of Music (Philadelphia), Academy of Music, home of Opera Philadelphia and the Pennsylvania Ballet. The Wilma Theater (Philadelphia), Wilma Theatre and the Philadelphia Theatre Company at the Suzanne Roberts Theatre produce a variety of new plays. Several blocks to the east are the Lantern Theater Company at St. Stephen's Episcopal Church (Philadelphia), St. Stephens Episcopal Church; and the Walnut Street Theatre, a National Historic Landmark stated to be the oldest and most subscribed-to theater (structure), theatre in the English-speaking world, founded in 1809."Walnut Street Theatre Historical Marker" The city is known for its Submarine sandwich, hoagies, Stromboli (food), stromboli, roast pork sandwich, scrapple, pretzel#Pennsylvania, soft pretzels, Italian ice, water ice, Irish potato candy, tastykakes, and the cheesesteak sandwich which was developed by Italian immigrants. The Philadelphia area has many establishments that serve cheesesteaks, including restaurants, taverns, delicatessens and pizza parlors. The originator of the thinly-sliced steak sandwich in the 1930s, initially without cheese, is Pat's King of Steaks, which faces its rival Geno's Steaks, founded in 1966, across the intersection of 9th Street and Passyunk Avenue in the Italian Market, Philadelphia, Italian Market of South Philadelphia.
McGillin's Olde Ale House, opened in 1860 on Drury Street in Center City, Philadelphia, Center City, is the oldest continuously operated tavern in the city. The City Tavern is a replica of a historic 18th-century building first opened in 1773, demolished in 1854 after a fire, and rebuilt in 1975 on the same site as part of Independence National Historical Park. The tavern offers authentic 18th-century recipes, served in seven period dining rooms, three wine cellar rooms and an outdoor garden.
The Reading Terminal Market is a historic Marketplace, food market founded in 1893 in the Reading Terminal building, a designated National Historic Landmark. The enclosed market is one of the oldest and largest markets in the country, hosting over a hundred merchants offering Pennsylvania Dutch specialties, artisan cheese and meat, locally grown groceries, and specialty and ethnic foods.
The city is known for its Submarine sandwich, hoagies, Stromboli (food), stromboli, roast pork sandwich, scrapple, pretzel#Pennsylvania, soft pretzels, Italian ice, water ice, Irish potato candy, tastykakes, and the cheesesteak sandwich which was developed by Italian immigrants. The Philadelphia area has many establishments that serve cheesesteaks, including restaurants, taverns, delicatessens and pizza parlors. The originator of the thinly-sliced steak sandwich in the 1930s, initially without cheese, is Pat's King of Steaks, which faces its rival Geno's Steaks, founded in 1966, across the intersection of 9th Street and Passyunk Avenue in the Italian Market, Philadelphia, Italian Market of South Philadelphia.
McGillin's Olde Ale House, opened in 1860 on Drury Street in Center City, Philadelphia, Center City, is the oldest continuously operated tavern in the city. The City Tavern is a replica of a historic 18th-century building first opened in 1773, demolished in 1854 after a fire, and rebuilt in 1975 on the same site as part of Independence National Historical Park. The tavern offers authentic 18th-century recipes, served in seven period dining rooms, three wine cellar rooms and an outdoor garden.
The Reading Terminal Market is a historic Marketplace, food market founded in 1893 in the Reading Terminal building, a designated National Historic Landmark. The enclosed market is one of the oldest and largest markets in the country, hosting over a hundred merchants offering Pennsylvania Dutch specialties, artisan cheese and meat, locally grown groceries, and specialty and ethnic foods.

 Philadelphia County is a legal nullity. All county functions were assumed by the city in 1952. The city has been coterminous with the county since 1854.
Philadelphia's 1952 Home Rule Municipal charter, Charter was written by the City Charter Commission, which was created by the Pennsylvania General Assembly in an act of April 21, 1949, and a city ordinance of June 15, 1949. The existing city council received a proposed draft on February 14, 1951, and the electors approved it in an election held April 17, 1951. The first elections under the new Home Rule Charter were held in November 1951, and the newly elected officials took office in January 1952.
The city uses the Mayor–council government#Strong-mayor form, strong-mayor version of the mayor–council form of government, which is led by one mayor in whom executive (government), executive authority is vested. The mayor has the authority to appoint and dismiss members of all boards and commissions without the approval of the city council. Elected at-large, the mayor is limited to two consecutive four-year terms, but can run for the position again after an intervening term.
Philadelphia County is a legal nullity. All county functions were assumed by the city in 1952. The city has been coterminous with the county since 1854.
Philadelphia's 1952 Home Rule Municipal charter, Charter was written by the City Charter Commission, which was created by the Pennsylvania General Assembly in an act of April 21, 1949, and a city ordinance of June 15, 1949. The existing city council received a proposed draft on February 14, 1951, and the electors approved it in an election held April 17, 1951. The first elections under the new Home Rule Charter were held in November 1951, and the newly elected officials took office in January 1952.
The city uses the Mayor–council government#Strong-mayor form, strong-mayor version of the mayor–council form of government, which is led by one mayor in whom executive (government), executive authority is vested. The mayor has the authority to appoint and dismiss members of all boards and commissions without the approval of the city council. Elected at-large, the mayor is limited to two consecutive four-year terms, but can run for the position again after an intervening term.
 The current mayor is Jim Kenney who won the election in November 2015. Kenney's predecessor was Michael Nutter who had served two terms from 2009 to January 2016. Kenney is a member of the United States Democratic Party, Democratic Party as all List of mayors of Philadelphia#List of Mayors, Philadelphia mayors have been since 1952. Philadelphia City Council is the legislative branch which consists of ten council members representing individual districts and seven members elected at-large, all of whom are elected to four-year terms. Democrats are currently the majority and hold 14 seats including nine of the ten districts and five at-large seats. Republicans hold two seats: one at-large seat and the Northeast Philadelphia, Northeast-based Tenth District. The Working Families Party holds one at-large seat. The current council president is Darrell L. Clarke.
As of December 31, 2016, there were 1,102,620 registered voters in Philadelphia. Registered voters constitute 70.3% of the total population.
* Democratic Party (United States), Democratic: 853,140 (77.4%)
* Republican Party (United States), Republican: 125,530 (11.4%)
* Other parties and unaffiliated: 123,950 (11.2%)
Philadelphia had historically been a bastion of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party from the American Civil War until the mid-1930s. The city hosted the first Republican National Convention in 1856 Republican National Convention, 1856. Democratic registrations increased after the Great Depression; however, the city was not carried by Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt in his landslide victory of 1932 United States presidential election, 1932 as Pennsylvania was one of only six states won by Republican Herbert Hoover. Voter turnout surged from 600,000 in 1932 to nearly 900,000 in 1936 United States presidential election, 1936 and Roosevelt carried Philadelphia with over 60% of the vote. The city has voted Democratic in every presidential election since 1936. In 2008 United States presidential election, 2008, Democrat Barack Obama drew 83% of the city's vote. Obama's win was even greater in 2012 United States presidential election, 2012, capturing 85% of the vote. In 2016 United States presidential election, 2016, Democrat Hillary Clinton won 82% of the vote.
As a result of the previously declining population in the city and state, Philadelphia has only three congressional districts of the 18 districts in Pennsylvania, based on the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census apportionment: Pennsylvania's 2nd congressional district, the 2nd district, represented by Brendan Boyle; Pennsylvania's 3rd congressional district, the 3rd, represented by Dwight Evans (politician), Dwight Evans; and Pennsylvania's 5th congressional district, the 5th, represented by Mary Gay Scanlon. All three representatives are Democrats though Republicans still have some support in the city, primarily in the Northeast Philadelphia, Northeast. Sam Katz (Philadelphia), Sam Katz ran competitive mayoral races as the Republican nominee in Philadelphia mayoral election, 1999, 1999 and Philadelphia mayoral election, 2003, 2003, losing to Democrat John F. Street, John Street both times.
Pennsylvania's longest-serving List of United States Senators from Pennsylvania, Senator, Arlen Specter, was an alumnus of the University of Pennsylvania who opened his first law practice in Philadelphia."Specter, Arlen, (1930–2012)"
The current mayor is Jim Kenney who won the election in November 2015. Kenney's predecessor was Michael Nutter who had served two terms from 2009 to January 2016. Kenney is a member of the United States Democratic Party, Democratic Party as all List of mayors of Philadelphia#List of Mayors, Philadelphia mayors have been since 1952. Philadelphia City Council is the legislative branch which consists of ten council members representing individual districts and seven members elected at-large, all of whom are elected to four-year terms. Democrats are currently the majority and hold 14 seats including nine of the ten districts and five at-large seats. Republicans hold two seats: one at-large seat and the Northeast Philadelphia, Northeast-based Tenth District. The Working Families Party holds one at-large seat. The current council president is Darrell L. Clarke.
As of December 31, 2016, there were 1,102,620 registered voters in Philadelphia. Registered voters constitute 70.3% of the total population.
* Democratic Party (United States), Democratic: 853,140 (77.4%)
* Republican Party (United States), Republican: 125,530 (11.4%)
* Other parties and unaffiliated: 123,950 (11.2%)
Philadelphia had historically been a bastion of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party from the American Civil War until the mid-1930s. The city hosted the first Republican National Convention in 1856 Republican National Convention, 1856. Democratic registrations increased after the Great Depression; however, the city was not carried by Democrat Franklin D. Roosevelt in his landslide victory of 1932 United States presidential election, 1932 as Pennsylvania was one of only six states won by Republican Herbert Hoover. Voter turnout surged from 600,000 in 1932 to nearly 900,000 in 1936 United States presidential election, 1936 and Roosevelt carried Philadelphia with over 60% of the vote. The city has voted Democratic in every presidential election since 1936. In 2008 United States presidential election, 2008, Democrat Barack Obama drew 83% of the city's vote. Obama's win was even greater in 2012 United States presidential election, 2012, capturing 85% of the vote. In 2016 United States presidential election, 2016, Democrat Hillary Clinton won 82% of the vote.
As a result of the previously declining population in the city and state, Philadelphia has only three congressional districts of the 18 districts in Pennsylvania, based on the 2010 United States Census, 2010 census apportionment: Pennsylvania's 2nd congressional district, the 2nd district, represented by Brendan Boyle; Pennsylvania's 3rd congressional district, the 3rd, represented by Dwight Evans (politician), Dwight Evans; and Pennsylvania's 5th congressional district, the 5th, represented by Mary Gay Scanlon. All three representatives are Democrats though Republicans still have some support in the city, primarily in the Northeast Philadelphia, Northeast. Sam Katz (Philadelphia), Sam Katz ran competitive mayoral races as the Republican nominee in Philadelphia mayoral election, 1999, 1999 and Philadelphia mayoral election, 2003, 2003, losing to Democrat John F. Street, John Street both times.
Pennsylvania's longest-serving List of United States Senators from Pennsylvania, Senator, Arlen Specter, was an alumnus of the University of Pennsylvania who opened his first law practice in Philadelphia."Specter, Arlen, (1930–2012)" According to a 2015 report by the Pew Charitable Trusts, the Philadelphia Police Department#Districts, police districts with the highest rates of violent crime were Frankford, Philadelphia, Frankford (15th district) and Kensington, Philadelphia, Kensington (24th district) in the Near Northeast Philadelphia, Near Northeast, and districts to the North Philadelphia, North (22nd, 25th, and 35th districts), West Philadelphia, West (19th district) and Southwest Philadelphia, Southwest (12th district) of Center City, Philadelphia, Center City. Each of those seven districts recorded more than a thousand violent crimes in 2014. The lowest rates of violent crime occurred in Center City, South Philadelphia, the Far Northeast Philadelphia, Far Northeast, and Roxborough, Philadelphia, Roxborough districts, the latter of which includes Manayunk, Philadelphia, Manayunk.
Philadelphia had 500 (503 according to some sources) murders in 1990, a rate of 31.5 per 100,000. An average of about 400 murders occurred each year for most of the 1990s. The murder count dropped in 2002 to 288, then rose to 406 by 2006, before dropping slightly to 392 in 2007. A few years later, Philadelphia began to see a rapid decline in homicides and violent crime. In 2013, the city had 246 murders, which is a decrease of nearly 40% since 2006. In 2014, 248 homicides were committed. The homicide rate rose to 280 in 2015, then fell slightly to 277 in 2016, before rising again to 317 in 2017. Homicides increased dramatically in the late 2010s/early 2020s, reaching 499 homicides in 2020 and surpassing the 1990 "record" in 2021, with 501st murder on November 27 and 510 by the end of the month.
In 2006, Philadelphia's homicide rate of 27.7 per 100,000 people was the highest of the country's 10 most populous cities. In 2012, Philadelphia had the fourth-highest homicide rate among the country's most populous cities. The rate dropped to 16 homicides per 100,000 residents by 2014 placing Philadelphia as the sixth-highest city in the country.
The number of shootings in the city has declined significantly since the early years of the 21st century. Shooting incidents peaked at 1,857 in 2006 before declining nearly 44 percent to 1,047 shootings in 2014. Major crimes have decreased gradually since a peak in 2006 when 85,498 major crimes were reported. The number of reported major crimes fell 11 percent in three years to 68,815 occurrences in 2014. Violent crimes, which include homicide, rape, aggravated assault, and robbery, decreased 14 percent in three years to 15,771 occurrences in 2014.
Philadelphia was ranked as the 76th most dangerous city in a 2018 report based on Federal Bureau of Investigation, FBI data from 2016 for the rate of violent crimes per 1,000 residents in American cities with 25,000 or more people. The latest four years of reports indicate a steady reduction in violent crime as the city placed 67th in the 2017 report, 65th in 2016, and 54th in 2015.
In 2014, Philadelphia enacted an ordinance decriminalizing the possession of less than 30 grams of marijuana or 8 grams of hashish; the ordinance gave police officers the discretion to treat possession of these amounts as a civil infraction punishable by a $25 ticket, rather than a crime. Philadelphia was at the time the largest city to decriminalize the possession of marijuana. From 2013 to 2018, marijuana arrests in the city dropped by more than 85%. The purchase or sale of marijuana remains a criminal offense in Philadelphia.
According to a 2015 report by the Pew Charitable Trusts, the Philadelphia Police Department#Districts, police districts with the highest rates of violent crime were Frankford, Philadelphia, Frankford (15th district) and Kensington, Philadelphia, Kensington (24th district) in the Near Northeast Philadelphia, Near Northeast, and districts to the North Philadelphia, North (22nd, 25th, and 35th districts), West Philadelphia, West (19th district) and Southwest Philadelphia, Southwest (12th district) of Center City, Philadelphia, Center City. Each of those seven districts recorded more than a thousand violent crimes in 2014. The lowest rates of violent crime occurred in Center City, South Philadelphia, the Far Northeast Philadelphia, Far Northeast, and Roxborough, Philadelphia, Roxborough districts, the latter of which includes Manayunk, Philadelphia, Manayunk.
Philadelphia had 500 (503 according to some sources) murders in 1990, a rate of 31.5 per 100,000. An average of about 400 murders occurred each year for most of the 1990s. The murder count dropped in 2002 to 288, then rose to 406 by 2006, before dropping slightly to 392 in 2007. A few years later, Philadelphia began to see a rapid decline in homicides and violent crime. In 2013, the city had 246 murders, which is a decrease of nearly 40% since 2006. In 2014, 248 homicides were committed. The homicide rate rose to 280 in 2015, then fell slightly to 277 in 2016, before rising again to 317 in 2017. Homicides increased dramatically in the late 2010s/early 2020s, reaching 499 homicides in 2020 and surpassing the 1990 "record" in 2021, with 501st murder on November 27 and 510 by the end of the month.
In 2006, Philadelphia's homicide rate of 27.7 per 100,000 people was the highest of the country's 10 most populous cities. In 2012, Philadelphia had the fourth-highest homicide rate among the country's most populous cities. The rate dropped to 16 homicides per 100,000 residents by 2014 placing Philadelphia as the sixth-highest city in the country.
The number of shootings in the city has declined significantly since the early years of the 21st century. Shooting incidents peaked at 1,857 in 2006 before declining nearly 44 percent to 1,047 shootings in 2014. Major crimes have decreased gradually since a peak in 2006 when 85,498 major crimes were reported. The number of reported major crimes fell 11 percent in three years to 68,815 occurrences in 2014. Violent crimes, which include homicide, rape, aggravated assault, and robbery, decreased 14 percent in three years to 15,771 occurrences in 2014.
Philadelphia was ranked as the 76th most dangerous city in a 2018 report based on Federal Bureau of Investigation, FBI data from 2016 for the rate of violent crimes per 1,000 residents in American cities with 25,000 or more people. The latest four years of reports indicate a steady reduction in violent crime as the city placed 67th in the 2017 report, 65th in 2016, and 54th in 2015.
In 2014, Philadelphia enacted an ordinance decriminalizing the possession of less than 30 grams of marijuana or 8 grams of hashish; the ordinance gave police officers the discretion to treat possession of these amounts as a civil infraction punishable by a $25 ticket, rather than a crime. Philadelphia was at the time the largest city to decriminalize the possession of marijuana. From 2013 to 2018, marijuana arrests in the city dropped by more than 85%. The purchase or sale of marijuana remains a criminal offense in Philadelphia.
 Philadelphia's two major Newspaper, daily newspapers are ''The Philadelphia Inquirer'', first published in 1829—the third-oldest surviving daily newspaper in the country—and the ''Philadelphia Daily News'', first published in 1925. The ''Daily News'' has been published as an edition of the ''Inquirer'' since 2009. Recent owners of the ''Inquirer'' and ''Daily News'' have included Knight Ridder, The McClatchy Company, and Philadelphia Media Holdings, with the latter organization declaring bankruptcy in 2010. After two years of financial struggle, the newspapers were sold to Interstate General Media in 2012. The two newspapers had a combined daily circulation of 306,831 and a Sunday circulation of 477,313 —the eighteenth largest circulation in the country—while the website of the newspapers, Philly.com, was ranked thirteenth in popularity among online U.S. newspapers by Alexa Internet for the same year.
Smaller publications include the ''Philadelphia Tribune'' published five days each week for the African Americans, African-American community; ''Philadelphia (magazine), Philadelphia'' magazine, a monthly regional magazine; ''Philadelphia Weekly'', a weekly alternative newspaper; ''Philadelphia Gay News'', a weekly newspaper for the LGBT community; ''The Jewish Exponent'', a weekly newspaper for the Jewish community; ''Al Día (Philadelphia), Al Día'', a weekly newspaper for the Latinos, Latino community; and ''Philadelphia Metro'', a free daily newspaper.
Student-run newspapers include the University of Pennsylvania's ''The Daily Pennsylvanian'', Temple University's ''The Temple News'', and Drexel University's ''The Triangle (newspaper), The Triangle''.
Philadelphia's two major Newspaper, daily newspapers are ''The Philadelphia Inquirer'', first published in 1829—the third-oldest surviving daily newspaper in the country—and the ''Philadelphia Daily News'', first published in 1925. The ''Daily News'' has been published as an edition of the ''Inquirer'' since 2009. Recent owners of the ''Inquirer'' and ''Daily News'' have included Knight Ridder, The McClatchy Company, and Philadelphia Media Holdings, with the latter organization declaring bankruptcy in 2010. After two years of financial struggle, the newspapers were sold to Interstate General Media in 2012. The two newspapers had a combined daily circulation of 306,831 and a Sunday circulation of 477,313 —the eighteenth largest circulation in the country—while the website of the newspapers, Philly.com, was ranked thirteenth in popularity among online U.S. newspapers by Alexa Internet for the same year.
Smaller publications include the ''Philadelphia Tribune'' published five days each week for the African Americans, African-American community; ''Philadelphia (magazine), Philadelphia'' magazine, a monthly regional magazine; ''Philadelphia Weekly'', a weekly alternative newspaper; ''Philadelphia Gay News'', a weekly newspaper for the LGBT community; ''The Jewish Exponent'', a weekly newspaper for the Jewish community; ''Al Día (Philadelphia), Al Día'', a weekly newspaper for the Latinos, Latino community; and ''Philadelphia Metro'', a free daily newspaper.
Student-run newspapers include the University of Pennsylvania's ''The Daily Pennsylvanian'', Temple University's ''The Temple News'', and Drexel University's ''The Triangle (newspaper), The Triangle''.
 In the 1930s, the experimental station KYW-TV, W3XE, owned by Philco, became the first television station in Philadelphia. The station became NBC's first affiliate in 1939, and later became KYW-TV (currently a CBS affiliate). WCAU, WCAU-TV, WFIL-TV, and WHYY-TV were all founded by the 1960s. In 1952, WFIL (renamed WPVI-TV, WPVI) premiered the television show ''Bandstand'', which later became the nationally broadcast ''American Bandstand'' hosted by Dick Clark.
Each commercial network has an affiliate in Philadelphia: KYW-TV 3 (CBS), WPVI-TV 6 (ABC), WCAU 10 (NBC), WPHL-TV 17 (MyNetworkTV), WFPA-CD 28 (UniMás), WTXF-TV 29 (Fox), WPSG 57 (The CW), WWSI 62 (Telemundo), and WUVP-DT 65 (Univision). The region is served also by public broadcasting stations WPPT (TV), WPPT-TV (Philadelphia), WHYY-TV (Wilmington, Delaware and Philadelphia), WLVT-TV (Lehigh Valley), and NJTV (New Jersey).
Philadelphia has owned-and-operated stations for four major English-language broadcast networks: NBC – WCAU, WCAU-TV, CBS – KYW-TV, American Broadcasting Company, ABC – WPVI-TV, and Fox Broadcasting Company, Fox – WTXF-TV. The major Spanish-language networks are Univision – WUVP-DT, UniMás – WFPA-CD, and Telemundo – WWSI, WWSI-TV.
, the city is the nation's fourth-largest consumer in media market, as ranked by the Nielsen Media Research firm, with nearly 2.9 million TV households.
In the 1930s, the experimental station KYW-TV, W3XE, owned by Philco, became the first television station in Philadelphia. The station became NBC's first affiliate in 1939, and later became KYW-TV (currently a CBS affiliate). WCAU, WCAU-TV, WFIL-TV, and WHYY-TV were all founded by the 1960s. In 1952, WFIL (renamed WPVI-TV, WPVI) premiered the television show ''Bandstand'', which later became the nationally broadcast ''American Bandstand'' hosted by Dick Clark.
Each commercial network has an affiliate in Philadelphia: KYW-TV 3 (CBS), WPVI-TV 6 (ABC), WCAU 10 (NBC), WPHL-TV 17 (MyNetworkTV), WFPA-CD 28 (UniMás), WTXF-TV 29 (Fox), WPSG 57 (The CW), WWSI 62 (Telemundo), and WUVP-DT 65 (Univision). The region is served also by public broadcasting stations WPPT (TV), WPPT-TV (Philadelphia), WHYY-TV (Wilmington, Delaware and Philadelphia), WLVT-TV (Lehigh Valley), and NJTV (New Jersey).
Philadelphia has owned-and-operated stations for four major English-language broadcast networks: NBC – WCAU, WCAU-TV, CBS – KYW-TV, American Broadcasting Company, ABC – WPVI-TV, and Fox Broadcasting Company, Fox – WTXF-TV. The major Spanish-language networks are Univision – WUVP-DT, UniMás – WFPA-CD, and Telemundo – WWSI, WWSI-TV.
, the city is the nation's fourth-largest consumer in media market, as ranked by the Nielsen Media Research firm, with nearly 2.9 million TV households.

 Philadelphia is served by the Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) which operates buses, trains, rapid transit (as both subways and Elevated railway, elevated trains), Tram, trolleys, and Trolleybus, trackless trolleys (electric buses) throughout Philadelphia, the four Pennsylvania suburban counties of Bucks County, Pennsylvania, Bucks, Chester County, Pennsylvania, Chester, Delaware County, Pennsylvania, Delaware, and Montgomery County, Pennsylvania, Montgomery, in addition to service to Mercer County, New Jersey (Trenton, New Jersey, Trenton) and New Castle County, Delaware (Wilmington, Delaware, Wilmington and Newark, Delaware). The city's subway system consists of two routes: the subway section of the Market–Frankford Line running east–west under Market Street (Philadelphia), Market Street which opened in 1905 to the west and 1908 to the east of City Hall, and the Broad Street Line running north–south beneath Broad Street (Philadelphia), Broad Street which opened in stages from 1928 to 1938.
Beginning in the 1980s, large sections of the SEPTA Regional Rail service to the far suburbs of Philadelphia were discontinued due to a lack of funding for equipment and infrastructure maintenance.
Philadelphia's
Philadelphia is served by the Southeastern Pennsylvania Transportation Authority (SEPTA) which operates buses, trains, rapid transit (as both subways and Elevated railway, elevated trains), Tram, trolleys, and Trolleybus, trackless trolleys (electric buses) throughout Philadelphia, the four Pennsylvania suburban counties of Bucks County, Pennsylvania, Bucks, Chester County, Pennsylvania, Chester, Delaware County, Pennsylvania, Delaware, and Montgomery County, Pennsylvania, Montgomery, in addition to service to Mercer County, New Jersey (Trenton, New Jersey, Trenton) and New Castle County, Delaware (Wilmington, Delaware, Wilmington and Newark, Delaware). The city's subway system consists of two routes: the subway section of the Market–Frankford Line running east–west under Market Street (Philadelphia), Market Street which opened in 1905 to the west and 1908 to the east of City Hall, and the Broad Street Line running north–south beneath Broad Street (Philadelphia), Broad Street which opened in stages from 1928 to 1938.
Beginning in the 1980s, large sections of the SEPTA Regional Rail service to the far suburbs of Philadelphia were discontinued due to a lack of funding for equipment and infrastructure maintenance.
Philadelphia's  Two airports serve Philadelphia: the
Two airports serve Philadelphia: the 

 Since the early days of rail transportation in the United States, Philadelphia has served as a hub for several major rail companies, particularly the Pennsylvania Railroad and the Reading Company, Reading Railroad. The Pennsylvania Railroad first operated Broad Street Station (Philadelphia), Broad Street Station, then
Since the early days of rail transportation in the United States, Philadelphia has served as a hub for several major rail companies, particularly the Pennsylvania Railroad and the Reading Company, Reading Railroad. The Pennsylvania Railroad first operated Broad Street Station (Philadelphia), Broad Street Station, then  In 1815, Philadelphia began sourcing its water via the Fairmount Water Works on the
In 1815, Philadelphia began sourcing its water via the Fairmount Water Works on the  Philadelphia also has three partnership cities or regions:
Philadelphia has eight official Sister city, sister cities as designated by the Citizen Diplomacy International of Philadelphia: Philadelphia has dedicated landmarks to its sister cities. The Sister Cities Park, a site of at 18th and Benjamin Franklin Parkway within Logan Circle (Philadelphia), Logan Square, was dedicated in June 1976. The park was built to commemorate Philadelphia's first two sister city relationships, with Tel Aviv and Florence. The Toruń Triangle, honoring the sister city relationship with Toruń, Poland, was constructed in 1976, west of the United Way of America, United Way building at 18th Street and the Benjamin Franklin Parkway. Sister Cities Park was redesigned and reopened in 2012, featuring an interactive fountain honoring Philadelphia's sister and partnership cities, a café and visitor's center, children's play area, outdoor garden, and boat pond, as well as a pavilion built to environmentally friendly standards.
The Chinatown Gate, erected in 1984 and crafted by artisans of Tianjin, stands astride 10th Street, on the north side of its intersection with Arch Street (Philadelphia), Arch Street, as a symbol of the sister city relationship. The CDI of Philadelphia has participated in the United States Department of State, U.S. Department of State's "Partners for Peace" project with Mosul, Iraq,IVC of Philadelphia Partners with Mosul, Iraq in Groundbreaking Program
Philadelphia also has three partnership cities or regions:
Philadelphia has eight official Sister city, sister cities as designated by the Citizen Diplomacy International of Philadelphia: Philadelphia has dedicated landmarks to its sister cities. The Sister Cities Park, a site of at 18th and Benjamin Franklin Parkway within Logan Circle (Philadelphia), Logan Square, was dedicated in June 1976. The park was built to commemorate Philadelphia's first two sister city relationships, with Tel Aviv and Florence. The Toruń Triangle, honoring the sister city relationship with Toruń, Poland, was constructed in 1976, west of the United Way of America, United Way building at 18th Street and the Benjamin Franklin Parkway. Sister Cities Park was redesigned and reopened in 2012, featuring an interactive fountain honoring Philadelphia's sister and partnership cities, a café and visitor's center, children's play area, outdoor garden, and boat pond, as well as a pavilion built to environmentally friendly standards.
The Chinatown Gate, erected in 1984 and crafted by artisans of Tianjin, stands astride 10th Street, on the north side of its intersection with Arch Street (Philadelphia), Arch Street, as a symbol of the sister city relationship. The CDI of Philadelphia has participated in the United States Department of State, U.S. Department of State's "Partners for Peace" project with Mosul, Iraq,IVC of Philadelphia Partners with Mosul, Iraq in Groundbreaking Program