Cinnamon (desktop environment) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cinnamon is a

 In 2016, Cinnamon started to use X-Apps, which are a collection of applications developed by the Linux Mint team as an alternative to
In 2016, Cinnamon started to use X-Apps, which are a collection of applications developed by the Linux Mint team as an alternative to
Timeshift
is a system restore utility used to undo undesired system changes through the use of snapshots via
Blueberry
is a graphical frontend for the CLI
Xviewer
is an image viewer based on Eye of GNOME
Xreader
is a document viewer based on Atril
Xplayer
is a media player based on GNOME Videos (Totem)
Pix
is angnome-online-accounts-gtk
/code> is a graphical online account manager for GTK-based desktop environments other than GNOME, due to recent changes in the GNOME Online Accounts package that now requires other desktop environments to be based on GTK4 rather than GTK3. *
/code> is a Python and C-based
 Cinnamon can be modified by themes, applets, desklets, actions, and extensions. Themes can customize the look of aspects of Cinnamon, including but not limited to the menu, panel, calendar and run dialog. Applets are icons or texts that appear on the panel. Five applets are shipped by default, and developers are free to create their own. A tutorial for creating simple applets is available. Desklets are miniature applications that one can place and run on the desktop, providing quick access to information and functionality. Actions are tasks that can be executed from the context menu of the Nemo file manager. Extensions can modify the functionalities of Cinnamon, such as providing an alternative menu to launch applications or altering the look of the window switcher.
Users can find themes, applets, desklets, actions, and extensions from Cinnamon Spices, the official repository where developers can share their creations for users to download and rate.
Cinnamon can be modified by themes, applets, desklets, actions, and extensions. Themes can customize the look of aspects of Cinnamon, including but not limited to the menu, panel, calendar and run dialog. Applets are icons or texts that appear on the panel. Five applets are shipped by default, and developers are free to create their own. A tutorial for creating simple applets is available. Desklets are miniature applications that one can place and run on the desktop, providing quick access to information and functionality. Actions are tasks that can be executed from the context menu of the Nemo file manager. Extensions can modify the functionalities of Cinnamon, such as providing an alternative menu to launch applications or altering the look of the window switcher.
Users can find themes, applets, desklets, actions, and extensions from Cinnamon Spices, the official repository where developers can share their creations for users to download and rate.
It's FOSS
praised Cinnamon 6.0 by stating "Linux Mint complements its name as a refreshing offering in the world of Linux distributions. It does not fail to provide useful features while trying to add modern components to the desktop experience."
File:Linux Mint 19.1 "Tessa" (Cinnamon).png, Cinnamon 4.0 Menu showing on Linux Mint 19.1 Tessa.
File:Cinnamon 1.6 Alt-Tab Window Previews.png, Cinnamon 1.6 showing an Alt-Tab thumbnails and window previews.
File:Cinnamon 1.6 Notifications Applet.png, Cinnamon 1.6 showing a Notification Applet.
File:Cinnamon 1.6 Workspace OSD.png, Cinnamon 1.6 showing a Workspace OSD.
File:Cinnamon System Settings 4.0.10 screenshot.png, Cinnamon Control Center in Cinnamon 4.0.10
File:Cinnamon on LMDE Demonstration.webm, Demonstration of Cinnamon running on LMDE 6
free and open-source
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is software available under a Software license, license that grants users the right to use, modify, and distribute the software modified or not to everyone free of charge. FOSS is an inclusive umbrella term ...
desktop environment
In computing, a desktop environment (DE) is an implementation of the desktop metaphor made of a bundle of programs running on top of a computer operating system that share a common graphical user interface (GUI), sometimes described as a graphi ...
for Linux
Linux ( ) is a family of open source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an kernel (operating system), operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically package manager, pac ...
and other Unix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X, *nix or *NIX) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Uni ...
operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
s, which was originally based on GNOME 3
GNOME 3 is the third major release of the GNOME desktop environment. A major departure from technologies implemented by its predecessors, GNOME 3 introduced a dramatically different user interface. It was the first GNOME release to utilize a unif ...
, but follows traditional desktop metaphor
In computing, the desktop metaphor is an interface metaphor which is a set of unifying concepts used by graphical user interfaces to help users interact more easily with the computer. The desktop metaphor treats the computer monitor as if it is ...
conventions.
The development of Cinnamon began by the Linux Mint
Linux Mint is a community-developed Linux distribution. It is based on Ubuntu and designed for x86-64 based computers; another variant is based on Debian which is named Linux Mint Debian Edition (LMDE) and has both 64-bit and IA-32 support. T ...
team as the result of the April 2011 release of GNOME 3, in which the conventional desktop metaphor of GNOME 2 was discarded in favor of GNOME Shell. Following several attempts to extend GNOME 3
GNOME 3 is the third major release of the GNOME desktop environment. A major departure from technologies implemented by its predecessors, GNOME 3 introduced a dramatically different user interface. It was the first GNOME release to utilize a unif ...
so that it would suit the Linux Mint design goals through "Mint GNOME Shell Extensions", the Linux Mint team eventually forked several GNOME 3 components to build an independent desktop environment. This separation from GNOME was finished with the release of Cinnamon 2.0.0 on 9 October 2013. Applet
In computing, an applet is any small application that performs one specific task that runs within the scope of a dedicated widget engine or a larger program, often as a plug-in. The term is frequently used to refer to a Java applet, a program ...
s, extensions
Extension, extend or extended may refer to:
Mathematics
Logic or set theory
* Axiom of extensionality
* Extensible cardinal
* Extension (model theory)
* Extension (proof theory)
* Extension (predicate logic), the set of tuples of values t ...
, actions, and desklets made explicitly for Cinnamon are no longer compatible with GNOME Shell.
As the distinctive factor and preeminent desktop environment for Linux Mint, Cinnamon has generally received favorable coverage by the press, in particular for its ease of use and gentle learning curve
A learning curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between how proficient people are at a task and the amount of experience they have. Proficiency (measured on the vertical axis) usually increases with increased experience (the ...
. In regard to its conservative design model, Cinnamon is similar to the Xfce
Xfce or XFCE (pronounced as four individual letters, ) is a Free and open-source software, free and open-source desktop environment for Linux and other Unix-like operating systems.
Xfce aims to be fast and Lightweight software, lightweight whil ...
, MATE, GNOME 2, and GNOME Flashback desktop environments.
History
As with many other desktop environments based on GNOME, including Canonical's Unity, Cinnamon was the result of disapproval and dissatisfaction of the GNOME team's abandonment of a traditional desktop experience in April 2011. Until then, GNOME 2 had included the traditional desktop metaphor, but in GNOME 3, this was entirely replaced with GNOME Shell, which by default lacked a taskbar-like panel and other features of a conventional desktop like those ofMicrosoft Windows
Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating systems developed and marketed by Microsoft. It is grouped into families and subfamilies that cater to particular sec ...
and GNOME 2. The elimination of these basic features was unacceptable to the developers of distributions such as Mint
Mint or The Mint may refer to:
Plants
* Lamiaceae, the mint family
** ''Mentha'', the genus of plants commonly known as "mint"
Coins and collectibles
* Mint (facility), a facility for manufacturing coins
* Mint condition, a state of like-new ...
and Ubuntu
Ubuntu ( ) is a Linux distribution based on Debian and composed primarily of free and open-source software. Developed by the British company Canonical (company), Canonical and a community of contributors under a Meritocracy, meritocratic gover ...
, which are geared to users who wanted interfaces that are familiar and easy-to-use.
To overcome these differences, the Linux Mint team initially set out to develop extensions for GNOME Shell to replace the abandoned features. The results of this effort were known as the "Mint GNOME Shell Extensions" or MGSE. Meanwhile, the MATE desktop environment had also been forked from GNOME 2. Linux Mint 12, released in November 2011, subsequently included both, thereby giving users a choice of either GNOME 3 with the MGSE or a MATE desktop that closely resembled GNOME 2.
However, even with MGSE, GNOME 3 was still largely missing the comforts of GNOME 2 and was not well received by the user community. At the time, some of the missing features could not be replaced by extensions, and it seemed that extensions would not be viable in the long run due to concerns of significant changes upstream from the GNOME team. Moreover, the GNOME developers were not willing to cooperate with the wishes of the Mint developers. To give the Mint developers finer control over the development process, GNOME Shell was forked as "Project Cinnamon" in January 2012.
Gradually, the Mint developers adapted various core applications. Beginning with version 1.2, released in January 2012, the window manager of Cinnamon is called Muffin
A muffin or bun is an individually portioned baked product; however, the term can refer to one of two distinct items: a part-raised flatbread (like a crumpet) that is baked and then cooked on a griddle (typically unsweetened), or a (often sw ...
, which was originally a fork of GNOME 3's Mutter. Similarly, since September 2012 (version 1.6 onwards), Cinnamon includes the Nemo file manager which was forked from Nautilus
A nautilus (; ) is any of the various species within the cephalopod family Nautilidae. This is the sole extant family of the superfamily Nautilaceae and the suborder Nautilina.
It comprises nine living species in two genera, the type genus, ty ...
. Nemo was created in response to disapproval of some upstream changes in Nautilus 3.6 that significantly altered the functionality and user interface of the file manager. Cinnamon-Settings, included since May 2013 (version 1.8 onwards), combines the functionality of GNOME-Control-Center with that of Cinnamon-Settings, and made it possible to manage and update applets, extensions, desklets, actions, and themes through Cinnamon-Settings. Gnome-Screensaver was also forked into what is now called Cinnamon-Screensaver.
Since 9 October 2013 (version 2.0.0 onwards), Cinnamon is no longer a frontend of GNOME like Unity or GNOME Shell, but rather a completely independent desktop environment. Although Cinnamon is still heavily built on GNOME technologies and utilizes GTK
GTK (formerly GIMP ToolKit and GTK+) is a free software cross-platform widget toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces (GUIs). It is licensed under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License, allowing both Free software, free and ...
, it no longer requires GNOME as a dependency in order to be installed.
Further improvements in later versions include a desktop grid, wildcard support in file searches, multi-process settings daemon, desktop actions in the panel launcher, separate processes for desktop handling and file manager in Nemo; an additional desktop panel layout option that offers a more modern looking theme and grouped windows; improved naming for duplicate applications in the menu (i.e. Flatpak vs. deb packages), pinned files in Nemo, touchpad gestures, bulk file rename of multiple files and folders using bulky, customizable context menu items in Nemo called "Actions", the ability to display user profile pictures on the panel, improved multi-monitor support in regard to open windows, better visual indicators in the system notifications tray for VPN connections, and an emphasis on performance improvements.
On 30 November 2023, version 6.0.0 of the Cinnamon desktop was released. This is the first release of Cinnamon to include an experimental Wayland session implementation, along with fractional scaling and AVIF background image support, among other improvements. On 16 June 2024, version 6.2.0 of Cinnamon was released. This release introduced the ability to add the user profile picture to the panel, along with other improvements. On 28 November 2024, version 6.4.0 of Cinnamon was released. This release introduced redesigned dialog prompts using the Clutter toolkit rather than GTK. In addition, A "Night Light" blue light filter was introduced to potentially reduce eye strain and improve sleep quality when an end user is using Cinnamon during night time.
Software components

X-Apps
 In 2016, Cinnamon started to use X-Apps, which are a collection of applications developed by the Linux Mint team as an alternative to
In 2016, Cinnamon started to use X-Apps, which are a collection of applications developed by the Linux Mint team as an alternative to GNOME Core Applications
The GNOME Core Applications (also known as Apps for GNOME) are a software suite of software applications that are packaged as part of the standard free and open-source GNOME desktop environment. GNOME Core Applications have a consistent look and ...
but intended to work across different GTK-based desktop environments such as but not limited to Cinnamon, Budgie, Pantheon, Unity, MATE, and XFCE; most of these applications have a traditional user interface (UI), for example, using a menu bar instead of a header-bar. The Linux Mint team is currently in the process of transitioning development for X-Apps applications from being part of the Linux Mint development process to being a completely independent project. Most of them are forks
In cutlery or kitchenware, a fork (from 'pitchfork') is a Eating utensil, utensil, now usually made of metal, whose long handle terminates in a head that branches into several narrow and often slightly curved tine (structural), tines with whic ...
of GNOME Core Applications:
Timeshift
is a system restore utility used to undo undesired system changes through the use of snapshots via
BTRFS
Btrfs (pronounced as "better F S", "butter F S", "b-tree F S", or "B.T.R.F.S.") is a computer storage format that combines a file system based on the copy-on-write (COW) principle with a logical volume manager (distinct from Linux's LVM), d ...
or rsync
rsync (remote sync) is a utility for transferring and synchronizing files between a computer and a storage drive and across networked computers by comparing the modification times and sizes of files. It is commonly found on Unix-like opera ...
.
Blueberry
is a graphical frontend for the CLI
gnome-bluetooth library.
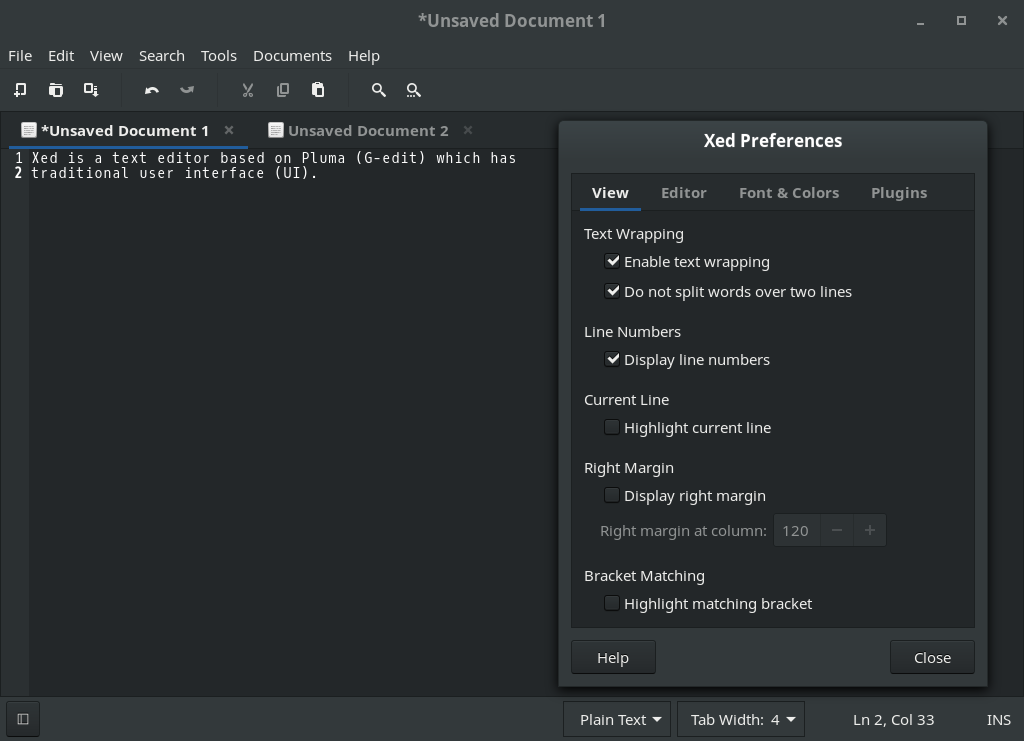
* Xed is a text editor based on Pluma
Xviewer
is an image viewer based on Eye of GNOME
Xreader
is a document viewer based on Atril
Xplayer
is a media player based on GNOME Videos (Totem)
Pix
is an
image organizer
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a proje ...
based on gThumb
gThumb is a free and open-source image viewer and image organizer with options to edit images. It is designed to have a clean and simple user interface and follows the GNOME Human Interface Guidelines and integrates well with the GNOME deskt ...
* /code> is a graphical online account manager for GTK-based desktop environments other than GNOME, due to recent changes in the GNOME Online Accounts package that now requires other desktop environments to be based on GTK4 rather than GTK3. *
/code> is a Python and C-based
software library
In computing, a library is a collection of resources that can be leveraged during software development to implement a computer program. Commonly, a library consists of executable code such as compiled functions and classes, or a library can ...
that provides the resources needed for applications in the X-Apps project to work across different desktop environments.
Features
Features provided by Cinnamon include * Desktop effects, including animations, transition effects and transparency using composition; * Panels equipped with a main menu, launchers, a window list and the system tray can be adjusted on left, right, upper or lower edge of the screen * Various extensions; * Applets that appear on the panel * Overview with functions similar to that in GNOME Shell; and * Settings editor for easy customization. It can customize: ** The panel ** Thecalendar
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A calendar date, date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is ...
** Themes
** Desktop effects
** Applets
** Actions
** Extensions
* Volume and brightness adjustment using scroll wheel
A scroll wheel is a wheel used for scrolling. The term usually refers to such wheels found on computer mouse, computer mice (where they can also be called a mouse wheel). It is often made of hard plastic with a rubbery surface, centred around a ...
while pointing at the respective taskbar icon.
* Hot corners on the screen
, there is no official documentation for Cinnamon itself. The 2016 documentation for the Cinnamon edition of Linux Mint does have a small chapter on the Cinnamon desktop.
Extensibility
 Cinnamon can be modified by themes, applets, desklets, actions, and extensions. Themes can customize the look of aspects of Cinnamon, including but not limited to the menu, panel, calendar and run dialog. Applets are icons or texts that appear on the panel. Five applets are shipped by default, and developers are free to create their own. A tutorial for creating simple applets is available. Desklets are miniature applications that one can place and run on the desktop, providing quick access to information and functionality. Actions are tasks that can be executed from the context menu of the Nemo file manager. Extensions can modify the functionalities of Cinnamon, such as providing an alternative menu to launch applications or altering the look of the window switcher.
Users can find themes, applets, desklets, actions, and extensions from Cinnamon Spices, the official repository where developers can share their creations for users to download and rate.
Cinnamon can be modified by themes, applets, desklets, actions, and extensions. Themes can customize the look of aspects of Cinnamon, including but not limited to the menu, panel, calendar and run dialog. Applets are icons or texts that appear on the panel. Five applets are shipped by default, and developers are free to create their own. A tutorial for creating simple applets is available. Desklets are miniature applications that one can place and run on the desktop, providing quick access to information and functionality. Actions are tasks that can be executed from the context menu of the Nemo file manager. Extensions can modify the functionalities of Cinnamon, such as providing an alternative menu to launch applications or altering the look of the window switcher.
Users can find themes, applets, desklets, actions, and extensions from Cinnamon Spices, the official repository where developers can share their creations for users to download and rate.
Overview mode
New overview modes have been added to Cinnamon 1.4. These two modes are "Expo" and "Scale", which can be configured in Cinnamon Settings.Adoption
Reception
In their review of Linux Mint 17, ''Ars Technica
''Ars Technica'' is a website covering news and opinions in technology, science, politics, and society, created by Ken Fisher and Jon Stokes in 1998. It publishes news, reviews, and guides on issues such as computer hardware and software, sci ...
'' described Cinnamon 2.2 as "being perhaps the most user-friendly and all-around useful desktop available on any platform."
In their review of Linux Mint 18, ZDNet said "You can turn the Linux Mint Cinnamon desktop into the desktop of your dreams."
In their review of Linux Mint 22It's FOSS
praised Cinnamon 6.0 by stating "Linux Mint complements its name as a refreshing offering in the world of Linux distributions. It does not fail to provide useful features while trying to add modern components to the desktop experience."
Gallery
See also
* GNOME Shell * MATE desktop environment - fork of GNOME 2References
External links
* {{GTK 2011 software Desktop environments based on GTK Free desktop environments GNOME Graphical shells that use GTK Software forks X Window System