China–Russia border on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Chinese–Russian border or the Sino-Russian border is the
The Chinese–Russian border or the Sino-Russian border is the
 The eastern border section is over in length. According to a joint estimate published in 1999, it measured at .Sébastien Colin, ''Le développement des relations frontalières entre la Chine et la Russie'', études du CERI n°96, July 2003. (Note: this publication preceded the 2004 final settlement, and thus the estimate may slightly differ from the current number). It starts at the eastern China–
The eastern border section is over in length. According to a joint estimate published in 1999, it measured at .Sébastien Colin, ''Le développement des relations frontalières entre la Chine et la Russie'', études du CERI n°96, July 2003. (Note: this publication preceded the 2004 final settlement, and thus the estimate may slightly differ from the current number). It starts at the eastern China–
(The Agreement between the Government of the Russian Federation, the Government of the People's Republic of China, and the Government of Mongolia on the determination of the points of junction of the national borders of the three states) From the tripoint, the border line runs north-east, until it reaches the Argun River. The border follows the Argun and
(Protocol between the Government of the Russian Federation, the Government of Mongolia, and the Government of the People's Republic of China, describing the western junction point of the borders of the three states. Signed in Beijing, June 24, 1996) at the coordinates .Sovie
Topo map M45-104
scale 1:100,000,
 Today's Sino-Russian border line is mostly inherited by Russia (with minor adjustments) from the
Today's Sino-Russian border line is mostly inherited by Russia (with minor adjustments) from the
 Following the
Following the
 As with many other international borders, a bilateral treaty exists concerning the physical modalities of managing the China–Russia border. The currently valid agreement was signed in Beijing in 2006.Соглашение между Правительством Российской Федерации и Правительством Китайской Народной Республики о режиме российско-китайской государственной границы
As with many other international borders, a bilateral treaty exists concerning the physical modalities of managing the China–Russia border. The currently valid agreement was signed in Beijing in 2006.Соглашение между Правительством Российской Федерации и Правительством Китайской Народной Республики о режиме российско-китайской государственной границы
(Agreement between the Government of the Russian Federation and the Government of the People's Republic of China on the management of the Russia-China international border) The treaty requires the two states to clear trees in a -wide strip along the border (i.e. within from the border line on each side of it) (Article 6). Civil navigation is allowed on the border rivers and lakes, provided the vessels of each country stay on the appropriate side of the dividing line (Article 9); similar rules apply to fishing in these waters (Article 10). Each country's authorities will carry out appropriate measures to prevent grazing livestock from crossing into the other country and will endeavor to apprehend and return any livestock that wanders onto their territory from across the border (Article 17). Hunting using firearms is prohibited within from the borderline; hunters are prohibited from crossing the border in pursuit of a wounded animal (Article 19). Detained illegal border crossers are supposed to be normally returned to their country of origin within 7 days from their apprehension (Article 34).

(China), at the Rosgranitsa site At present three railway lines cross the border. The two railway border crossings at
(Kanas Pass) No roads suitable for wheeled vehicles exist over these two passes, although a difficult dirt road approaches from the Russian side to within from the Kanas Pass. Until the Soviet authorities closed the border in 1936, Kazakh nomads would occasionally use these passes.Перевал Бетсу-Канас
(Betsu-Kanas Pass) Proposals exist for the construction of a cross-border highway and the Altai gas pipeline from China to Russia, which would cross the western section of the Sino-Russian border.Перевал "Канас" станет пунктом сдачи газа РФ китайским партерам по "западному маршруту"
(Gas will be transferred to the Chinese partners over the Kanas Pass along the Western Route
File:Txu-oclc-6654394-nm-45-3rd-ed.jpg, western section
File:Txu-oclc-6654394-nm-50-3rd-ed.jpg,
File:Txu-oclc-6654394-nm-51-4th-ed.jpg,
File:Txu-oclc-6654394-nn-51-2nd-ed.jpg,
File:Txu-oclc-6654394-nn-52-4th-ed.jpg,
File:Txu-oclc-6654394-nm-52-4th-ed.jpg,
File:Txu-oclc-6654394-nl-52-4th-ed.jpg,
File:Txu-oclc-6654394-nm-53-4th-ed.jpg,
File:Txu-oclc-6654394-nl-53-2nd-ed.jpg,
File:Txu-oclc-6654394-nk-52-4th-ed.jpg,
online
* Humphrey, Caroline. "Loyalty and disloyalty as relational forms in Russia’s border war with China in the 1960s." ''History and Anthropology'' 28.4 (2017): 497–514
online
* Kuisong, Yang. "The Sino-Soviet Border Clash of 1969: From Zhenbao Island to Sino-American Rapprochement." ''Cold War History'' 1.1 (2000): 21–52. * Robinson, Thomas W. "The Sino-Soviet border dispute: Background, development, and the March 1969 clashes." ''American Political Science Review'' 66.4 (1972): 1175–1202
online
* Urbansky, Sören: ** ''Beyond the Steppe Frontier: A History of the Sino-Russian Border'' (2020) a comprehensive history
excerpt
** "A Very Orderly Friendship: The Sino-Soviet Border under the Alliance Regime, 1950-1960." ''Eurasia Border Review'' 3.Special Issue (2012): 33-5
online
** "The Unfathomable Foe. Constructing the Enemy in the Sino-Soviet Borderlands, ca. 1969–1982." ''Journal of Modern European History''10.2 (2012): 255–279
online
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20150707094121/http://www.rosgranitsa.ru/ru/activity/international/countries/china/pp The list of Russia's border crossing on the border with China(on the official site of Russia's Border Agency)
The Sino-Soviet Border Conflict; Deterrence, Escalation, and the Threat of Nuclear War in 1969
Michael S. Gerson CNA.org November 2010
International Boundary Study No. 64 (Revised) – February 13, 1978 China – U.S.S.R. Boundary
{{DEFAULTSORT:China-Russia borders China–Russia relations Borders of China Borders of Russia International borders
 The Chinese–Russian border or the Sino-Russian border is the
The Chinese–Russian border or the Sino-Russian border is the international border
Borders are usually defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political borders ...
between China and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
. After the final demarcation carried out in the early 2000s, it measures , and is the world's sixth-longest international border.
The China–Russian border consists of two non-contiguous sections separated: the long eastern section between Mongolia and North Korea and the much shorter western section between Kazakhstan and Mongolia.
Description
 The eastern border section is over in length. According to a joint estimate published in 1999, it measured at .Sébastien Colin, ''Le développement des relations frontalières entre la Chine et la Russie'', études du CERI n°96, July 2003. (Note: this publication preceded the 2004 final settlement, and thus the estimate may slightly differ from the current number). It starts at the eastern China–
The eastern border section is over in length. According to a joint estimate published in 1999, it measured at .Sébastien Colin, ''Le développement des relations frontalières entre la Chine et la Russie'', études du CERI n°96, July 2003. (Note: this publication preceded the 2004 final settlement, and thus the estimate may slightly differ from the current number). It starts at the eastern China–Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 millio ...
–Russia tripoint
A tripoint, trijunction, triple point, or tri-border area is a geographical point at which the boundaries of three countries or subnational entities meet. There are 175 international tripoints as of 2020. Nearly half are situated in rivers, l ...
(), marked by the border monument
A boundary marker, border marker, boundary stone, or border stone is a robust physical marker that identifies the start of a land boundary or the change in a boundary, especially a change in direction of a boundary. There are several other t ...
called Tarbagan-Dakh (Ta'erbagan Dahu, Tarvagan Dakh).Соглашением между Правительством Российской Федерации, Правительством Китайской Народной Республики и Правительством Монголии об определении точек стыков государственных границ трех государств (Заключено в г. Улан-Баторе 27 января 1994 года)(The Agreement between the Government of the Russian Federation, the Government of the People's Republic of China, and the Government of Mongolia on the determination of the points of junction of the national borders of the three states) From the tripoint, the border line runs north-east, until it reaches the Argun River. The border follows the Argun and
Amur
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeastern China ( Inner Manchuria). The Amur proper is long ...
river to the confluence of the latter with the Ussuri River. It
divides the Bolshoy Ussuriysky Island at the confluence of the two rivers, and then runs south along the Ussuri. The border crosses Lake Khanka, and finally runs to the south-west. The China–Russia border ends when it reaches the Tumen River
The Tumen River, also known as the Tuman River or Duman River (), is a long river that serves as part of the boundary between China, North Korea and Russia, rising on the slopes of Mount Paektu and flowing into the Sea of Japan. The river h ...
, which is the northern border of North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and ...
. The end point of the China–Russia border, and the China–North Korea–Russia tripoint, at (), is located only a few kilometers before the river flows into the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
, the other end of the North Korea–Russia border.
The much shorter (less than ) western border section is between Russia's Altai Republic
The Altai Republic (; russian: Респу́блика Алта́й, Respublika Altay, ; Altai: , ''Altay Respublika''), also known as Gorno-Altai Republic, and colloquially, and primarily referred to in Russian to distinguish from the neighbouri ...
and China's Xinjiang
Xinjiang, SASM/GNC: ''Xinjang''; zh, c=, p=Xīnjiāng; formerly romanized as Sinkiang (, ), officially the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (XUAR), is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China (PRC), located in the northwest ...
. It runs in the mostly snow-covered high elevation area of the Altai Mountains. Its western end point is the China–Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
–Russia tripoint, whose location is defined by the trilateral agreement as , elevation, 3327 m. Its eastern end is the western China–Mongolia–Russia tripoint, at the top of the peak Tavan Bogd Uul (Mt Kuitun),ПРОТОКОЛ-ОПИСАНИЕ ТОЧКИ ЗАПАДНОГО СТЫКА ГОСУДАРСТВЕННЫХ ГРАНИЦ ТРЕХ ГОСУДАРСТВ МЕЖДУ ПРАВИТЕЛЬСТВОМ Российской Федерации, ПРАВИТЕЛЬСТВОМ МОНГОЛИИ и ПРАВИТЕЛЬСТВОМ КИТАЙСКОЙ НАРОДНОЙ РЕСПУБЛИКИ (ПОДПИСАН в г. ПЕКИНЕ 24.06.1996)(Protocol between the Government of the Russian Federation, the Government of Mongolia, and the Government of the People's Republic of China, describing the western junction point of the borders of the three states. Signed in Beijing, June 24, 1996) at the coordinates .Sovie
Topo map M45-104
scale 1:100,000,
History
The Tsarist era (pre-1917)
 Today's Sino-Russian border line is mostly inherited by Russia (with minor adjustments) from the
Today's Sino-Russian border line is mostly inherited by Russia (with minor adjustments) from the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, while the Sino-Soviet border line was essentially the same as the border between the Russian and Qing
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-speak ...
Empires, settled by a number of treaties from the 17th through to the 19th centuries. Border issues first became an issue following Russia's rapid expansion into Siberia in the 17th century, with intermittent skirmishes occurring between them and Qing China. Below is a list of important border treaties, along with the indication as to which section of today's Sino-Russian border were largely set by them:
* Treaty of Nerchinsk (1689) - this covered the far eastern section of the border, creating a line along the Argun River and Shilka River, then proceeding overland via the Stanovoy Mountains, and then along the Uda river, terminating at the Tugur peninsula by the Sea of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk ( rus, Охо́тское мо́ре, Ohótskoye móre ; ja, オホーツク海, Ohōtsuku-kai) is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands ...
.
* Treaty of Kyakhta (1727)
The Treaty of Kyakhta (or Kiakhta),, ; , Xiao'erjing: بُلِيًاصِٿِ\ٿِاكْتُ تِيَوْيُؤ; mn, Хиагтын гэрээ, Hiagtiin geree, along with the Treaty of Nerchinsk (1689), regulated the relations between Imperia ...
, plus supplementary protocols of the same year - these were concerned mostly with the border line that is currently the Mongolia–Russia border (Mongolia then being part of China), this fixing a line from the river Irtysh
The Irtysh ( otk, 𐰼𐱅𐰾:𐰇𐰏𐰕𐰏, Ertis ügüzüg, mn, Эрчис мөрөн, ''Erchis mörön'', "erchleh", "twirl"; russian: Иртыш; kk, Ертіс, Ertis, ; Chinese: 额尔齐斯河, pinyin: ''É'ěrqísī hé'', Xiao'er ...
in the west to the Argun in the east.
* Treaty of Aigun
The Treaty of Aigun (Russian: Айгунский договор; ) was an 1858 treaty between the Russian Empire and the Qing dynasty that established much of the modern border between the Russian Far East and China by ceding much of Manchur ...
(1858) - this shifted the eastern border to run along the Amur River
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeastern China ( Inner Manchuria). The Amur proper is long ...
out to the Okhotsk.
* Convention of Peking
The Convention of Peking or First Convention of Peking is an agreement comprising three distinct treaties concluded between the Qing dynasty of China and Great Britain, France, and the Russian Empire in 1860. In China, they are regarded as amon ...
(1860) - this finalised the eastern stretch of the border, with China ceding to Russia the territory of modern Primorsky Krai
Primorsky Krai (russian: Приморский край, r=Primorsky kray, p=prʲɪˈmorskʲɪj kraj), informally known as Primorye (, ), is a federal subject (a krai) of Russia, located in the Far East region of the country and is a part of t ...
and southern Khabarovsk Krai.
* Treaty of Tarbagatai (1864) - this created the western section of the border in Central Asia, with the bulk of this border now forming China's borders with Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
, Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the ea ...
and Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
(with modifications). The border was modified via later treaties such as the Treaty of Saint Petersburg (1881)
The Treaty of Saint Petersburg (1881) (), also known as Treaty of Ili (), was a treaty between the Russian Empire and the Qing dynasty that was signed in Saint Petersburg, Russia, on . It provided for the return to China of the eastern part of th ...
, though the modern Russian section remained at the same place.
* Qiqihar Agreement (1911) - modified the eastern border along the Argun slightly, however China later repudiated the treaty.
The Sino-Soviet border (1917–1991)

 Following the
Following the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
in 1917 and the later formation of the Soviet Union, there have been a number of issues along the border:
* In 1911 Outer Mongolia
Outer Mongolia was the name of a territory in the Manchu-led Qing dynasty of China from 1691 to 1911. It corresponds to the modern-day independent state of Mongolia and the Russian republic of Tuva. The historical region gained ''de facto' ...
declared independence from China; the USSR recognised the country in 1921, thus removing a large part of the China-USSR border and splitting it into two sections. China later recognised Mongolian independence in 1946.
* Sino-Soviet conflict (1929)
The Sino-Soviet conflict of 1929 (, russian: Конфликт на Китайско-Восточной железной дороге) was an armed conflict between the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics and Chinese warlord Zhang Xueliang of ...
- a conflict largely centred on the Chinese Eastern Railway
The Chinese Eastern Railway or CER (, russian: Китайско-Восточная железная дорога, or , ''Kitaysko-Vostochnaya Zheleznaya Doroga'' or ''KVZhD''), is the historical name for a railway system in Northeast China (al ...
.
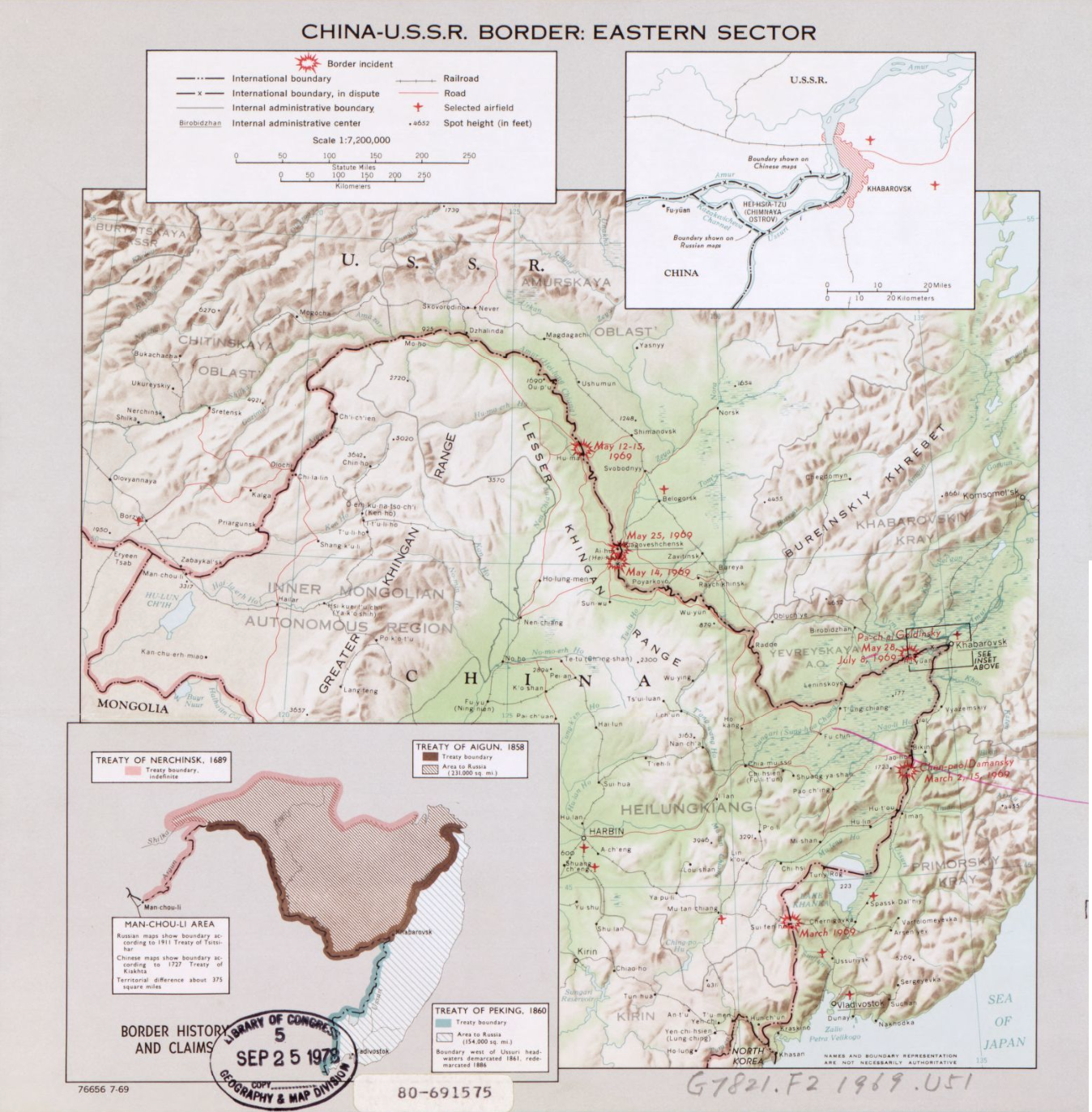
* Sino-Soviet border conflict (1969) - this was a serious seven-month undeclared military conflict
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regu ...
between the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
and China at the height of the Sino-Soviet split
The Sino-Soviet split was the breaking of political relations between the People's Republic of China and the Soviet Union caused by doctrinal divergences that arose from their different interpretations and practical applications of Marxism–Le ...
in 1969 (China having been taken over by Communists in 1949). Although military clashes ceased that year, the underlying issues were not resolved until the 1991 Sino-Soviet Border Agreement. The most serious of these border clashes, which brought the two countries to the brink of all-out war, occurred in March 1969 in the vicinity of Zhenbao (Damansky) Island on the Ussuri (Wusuli) River; as such, Chinese historians most commonly refer to the conflict as the Zhenbao Island Incident. Heavily militarised following the war, the border slowly opened after 1982, allowing the first exchange of goods between the two countries, though the territorial disputes remained unresolved. Between 1988 and 1992 the cross-border commerce between Russia and the Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang () formerly romanized as Heilungkiang, is a province in northeast China. The standard one-character abbreviation for the province is (). It was formerly romanized as "Heilungkiang". It is the northernmost and easternmost province ...
province increased threefold, with the number of legal Chinese workers in Russia increasing from 1,286 to 18,905.
Three countries bordered both China and the Soviet Union: Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bord ...
, Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 millio ...
and North Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and ...
. Both the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan
The Democratic Republic of Afghanistan (DRA),, renamed the Republic of Afghanistan, in 1987, was the Afghan state during the one-party rule of the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) from 1978 to 1992.
The PDPA came to powe ...
and Mongolian People's Republic
The Mongolian People's Republic ( mn, Бүгд Найрамдах Монгол Ард Улс, БНМАУ; , ''BNMAU''; ) was a socialist state which existed from 1924 to 1992, located in the historical region of Outer Mongolia in East Asia. It w ...
were pro-Soviet satellite states during the Cold War, while the Democratic People's Republic of Korea
North Korea, officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the northern half of the Korean Peninsula and shares borders with China and Russia to the north, at the Yalu (Amnok) and ...
was neutral.
Post-1991
The waning years of the Soviet Union saw a reduction of the tensions on the then heavily fortified Sino-Soviet border. In 1990–91, the two countries agreed to significantly reduce their military forces stationed along the border. To this day one can find numerous abandoned military facilities in Russia's border districts. Even though the Sino-Soviet border trade resumed as early as 1983–85, it accelerated in 1990–91; the rate of cross-border trade continue increasing as the USSR's former republics became separate states. To accommodate increasing volume of travel and private trade, a number of border crossings were re-opened. In early 1992, China announced border trade incentives and the creation of special economic zones (SEZs) along the Sino-Russian border, the largest of these being in Hunchun,Jilin
Jilin (; alternately romanized as Kirin or Chilin) is one of the three provinces of Northeast China. Its capital and largest city is Changchun. Jilin borders North Korea ( Rasŏn, North Hamgyong, Ryanggang and Chagang) and Russia (P ...
.
In 1991, China and USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
signed the 1991 Sino-Soviet Border Agreement, which was intended to start the process of resolving the border disputes held in abeyance since the 1960s. However, just a few months later the USSR was dissolved, and four former Soviet republics — Russia, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental coun ...
, Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the ea ...
, and Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
— inherited various sections of the former Sino–Soviet border.
It took more than a decade for Russia and China to fully resolve the border issues and to demarcate the border. On May 29, 1994, during Russian Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
Chernomyrdin's visit to Beijing, an "Agreement on the Sino-Russian Border Management System intended to facilitate border trade and hinder criminal activity" was signed. On September 3, a demarcation agreement was signed for the short () western section of the binational border; the demarcation of this section was completed in 1998.
In November 1997, at a meeting in Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
, Russian President
The president of the Russian Federation ( rus, Президент Российской Федерации, Prezident Rossiyskoy Federatsii) is the head of state of the Russian Federation. The president leads the executive branch of the federal ...
Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin ( rus, Борис Николаевич Ельцин, p=bɐˈrʲis nʲɪkɐˈla(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈjelʲtsɨn, a=Ru-Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin.ogg; 1 February 1931 – 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician wh ...
and General Secretary
Secretary is a title often used in organizations to indicate a person having a certain amount of authority, power, or importance in the organization. Secretaries announce important events and communicate to the organization. The term is derive ...
and Chinese President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
* President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese f ...
Jiang Zemin
Jiang Zemin (17 August 1926 – 30 November 2022) was a Chinese politician who served as general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) from 1989 to 2002, as chairman of the Central Military Commission from 1989 to 2004, and as pre ...
signed an agreement for the demarcation of the much longer (over ) eastern section of the border, in accordance with the provisions of the 1991 Sino-Soviet agreement.
The last unresolved territorial issue between the two countries was settled by the 2004 Complementary Agreement between China and Russia on the Eastern Section of the China–Russia Boundary. Pursuant to that agreement, Russia transferred to China a part of Abagaitu Islet, the entire Yinlong (Tarabarov) Island, about half of Bolshoy Ussuriysky Island, and some adjacent river islets. The transfer has been ratified by both the Chinese National People's Congress
The National People's Congress of the People's Republic of China (NPC; ), or simply the National People's Congress, is constitutionally the supreme state authority and the national legislature of the People's Republic of China.
With 2,9 ...
and the Russian State Duma
The State Duma (russian: Госуда́рственная ду́ма, r=Gosudárstvennaja dúma), commonly abbreviated in Russian as Gosduma ( rus, Госду́ма), is the lower house of the Federal Assembly of Russia, while the upper hous ...
in 2005, thus ending the decades-long border dispute. The official transfer ceremony was held on-site on October 14, 2008.
Border management
 As with many other international borders, a bilateral treaty exists concerning the physical modalities of managing the China–Russia border. The currently valid agreement was signed in Beijing in 2006.Соглашение между Правительством Российской Федерации и Правительством Китайской Народной Республики о режиме российско-китайской государственной границы
As with many other international borders, a bilateral treaty exists concerning the physical modalities of managing the China–Russia border. The currently valid agreement was signed in Beijing in 2006.Соглашение между Правительством Российской Федерации и Правительством Китайской Народной Республики о режиме российско-китайской государственной границы(Agreement between the Government of the Russian Federation and the Government of the People's Republic of China on the management of the Russia-China international border) The treaty requires the two states to clear trees in a -wide strip along the border (i.e. within from the border line on each side of it) (Article 6). Civil navigation is allowed on the border rivers and lakes, provided the vessels of each country stay on the appropriate side of the dividing line (Article 9); similar rules apply to fishing in these waters (Article 10). Each country's authorities will carry out appropriate measures to prevent grazing livestock from crossing into the other country and will endeavor to apprehend and return any livestock that wanders onto their territory from across the border (Article 17). Hunting using firearms is prohibited within from the borderline; hunters are prohibited from crossing the border in pursuit of a wounded animal (Article 19). Detained illegal border crossers are supposed to be normally returned to their country of origin within 7 days from their apprehension (Article 34).
Border crossings
Eastern section
According to the Russia's border agency, as of October 1, 2013, there are 26 border crossings on the China–Russia border; all of them are located on the eastern section of the border. Twenty-five of them are provided for by the bilateral agreement of January 27, 1994, and one more is designated by an additional special order of the Russian government. The 25 crossing points established by the treaty include four railway crossings, eleven as highway crossings, one as river crossing, and nine as "mixed" (mostly ferry crossings).Китай(China), at the Rosgranitsa site At present three railway lines cross the border. The two railway border crossings at
Zabaikalsk
Zabaykalsk (russian: Забайка́льск) is an urban locality (an urban-type settlement) and the administrative center of Zabaykalsky District of Zabaykalsky Krai, Russia, located on the Sino-Russian border just opposite the Chinese ...
/ Manzhouli and Suifenhe/ Grodekovo are over a century old, brought into existence by the original design of Russia's Transsiberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway (TSR; , , ) connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway line in the world. It runs from the city of Moscow in the west to the city of Vladivostok in the ea ...
that took a shortcut across Manchuria
Manchuria is an exonym (derived from the endo demonym "Manchu") for a historical and geographic region in Northeast Asia encompassing the entirety of present-day Northeast China (Inner Manchuria) and parts of the Russian Far East ( Outer ...
(the Chinese Eastern Railway
The Chinese Eastern Railway or CER (, russian: Китайско-Восточная железная дорога, or , ''Kitaysko-Vostochnaya Zheleznaya Doroga'' or ''KVZhD''), is the historical name for a railway system in Northeast China (al ...
). The third railway crossing, near Hunchun/Makhalino
Kraskino (russian: Кра́скино) is an urban locality (an urban-type settlement) in Khasansky District of Primorsky Krai, Russia, located on the shore of the Posyet Bay, southwest of Vladivostok, near the border with North Korea. Populatio ...
, operated between 2000 and 2004, was then closed for a few years, and only recently reopened. Construction was completed in 2022 of the Tongjiang-Nizhneleninskoye railway bridge
Tongjiang-Nizhneleninskoye railway bridge (Amur River Bridge) is an international Sino-Russian railroad bridge linking Nizhneleninskoye (in Russian: Нижнеленинское) in the Jewish Autonomous Oblast with Tongjiang (in Chinese: 同江 ...
near Tongjiang/Nizhneleninskoye
Nizhneleninskoye (russian: Нижнеле́нинское) is a rural locality (a '' selo'') in Leninsky District of the Jewish Autonomous Oblast. Located on the Amur River, Nizhneleninskoye is the location for the Tongjiang-Nizhneleninskoye rail ...
, which became the fourth railway border crossing.
Western section
As of 2018, there were no border crossings of any kind on the two countries' short and remote western border section. According to Russian topographic maps, the lowest mountain passes on the western section of the border are the Betsu-Kanas Pass (перевал Бетсу-Канас), elevation and Kanas (перевал Канас), elevation .Перевал Канас(Kanas Pass) No roads suitable for wheeled vehicles exist over these two passes, although a difficult dirt road approaches from the Russian side to within from the Kanas Pass. Until the Soviet authorities closed the border in 1936, Kazakh nomads would occasionally use these passes.Перевал Бетсу-Канас
(Betsu-Kanas Pass) Proposals exist for the construction of a cross-border highway and the Altai gas pipeline from China to Russia, which would cross the western section of the Sino-Russian border.
(Gas will be transferred to the Chinese partners over the Kanas Pass along the Western Route
f the pipeline
F, or f, is the sixth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ef'' (pronounced ), and the plural is ''efs''.
Hist ...
, 2015-05-08Historical maps
Historical maps of the border from west to east in the International Map of the World, mid-20th century:See also
*History of Sino-Russian relations
Prior to the 17th century China and Russia were on opposite ends of Siberia, which was populated by independent nomads. By about 1640 Russian settlers had traversed most of Siberia and founded settlements in the Amur River basin. From 1652 to 16 ...
* Sino-Russian relations since 1991
References
Further reading
* Burr, William. "Sino-American relations, 1969: the Sino-Soviet border war and steps towards rapprochement." ''Cold War History'' 1.3 (2001): 73-112. * Gerson, Michael S. ''The Sino-Soviet Border Conflict: Deterrence, Escalation, and the Threat of Nuclear War in 1969'' (2010online
* Humphrey, Caroline. "Loyalty and disloyalty as relational forms in Russia’s border war with China in the 1960s." ''History and Anthropology'' 28.4 (2017): 497–514
online
* Kuisong, Yang. "The Sino-Soviet Border Clash of 1969: From Zhenbao Island to Sino-American Rapprochement." ''Cold War History'' 1.1 (2000): 21–52. * Robinson, Thomas W. "The Sino-Soviet border dispute: Background, development, and the March 1969 clashes." ''American Political Science Review'' 66.4 (1972): 1175–1202
online
* Urbansky, Sören: ** ''Beyond the Steppe Frontier: A History of the Sino-Russian Border'' (2020) a comprehensive history
excerpt
** "A Very Orderly Friendship: The Sino-Soviet Border under the Alliance Regime, 1950-1960." ''Eurasia Border Review'' 3.Special Issue (2012): 33-5
online
** "The Unfathomable Foe. Constructing the Enemy in the Sino-Soviet Borderlands, ca. 1969–1982." ''Journal of Modern European History''10.2 (2012): 255–279
online
External links
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20150707094121/http://www.rosgranitsa.ru/ru/activity/international/countries/china/pp The list of Russia's border crossing on the border with China(on the official site of Russia's Border Agency)
The Sino-Soviet Border Conflict; Deterrence, Escalation, and the Threat of Nuclear War in 1969
Michael S. Gerson CNA.org November 2010
International Boundary Study No. 64 (Revised) – February 13, 1978 China – U.S.S.R. Boundary
{{DEFAULTSORT:China-Russia borders China–Russia relations Borders of China Borders of Russia International borders