Chesapeake Bay Program on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
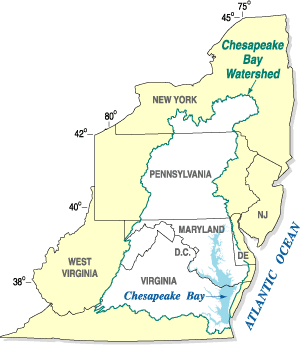 The Chesapeake Bay Program is the regional partnership that directs and conducts the restoration of the
The Chesapeake Bay Program is the regional partnership that directs and conducts the restoration of the
 In the late 1970s and early 1980s,
In the late 1970s and early 1980s,
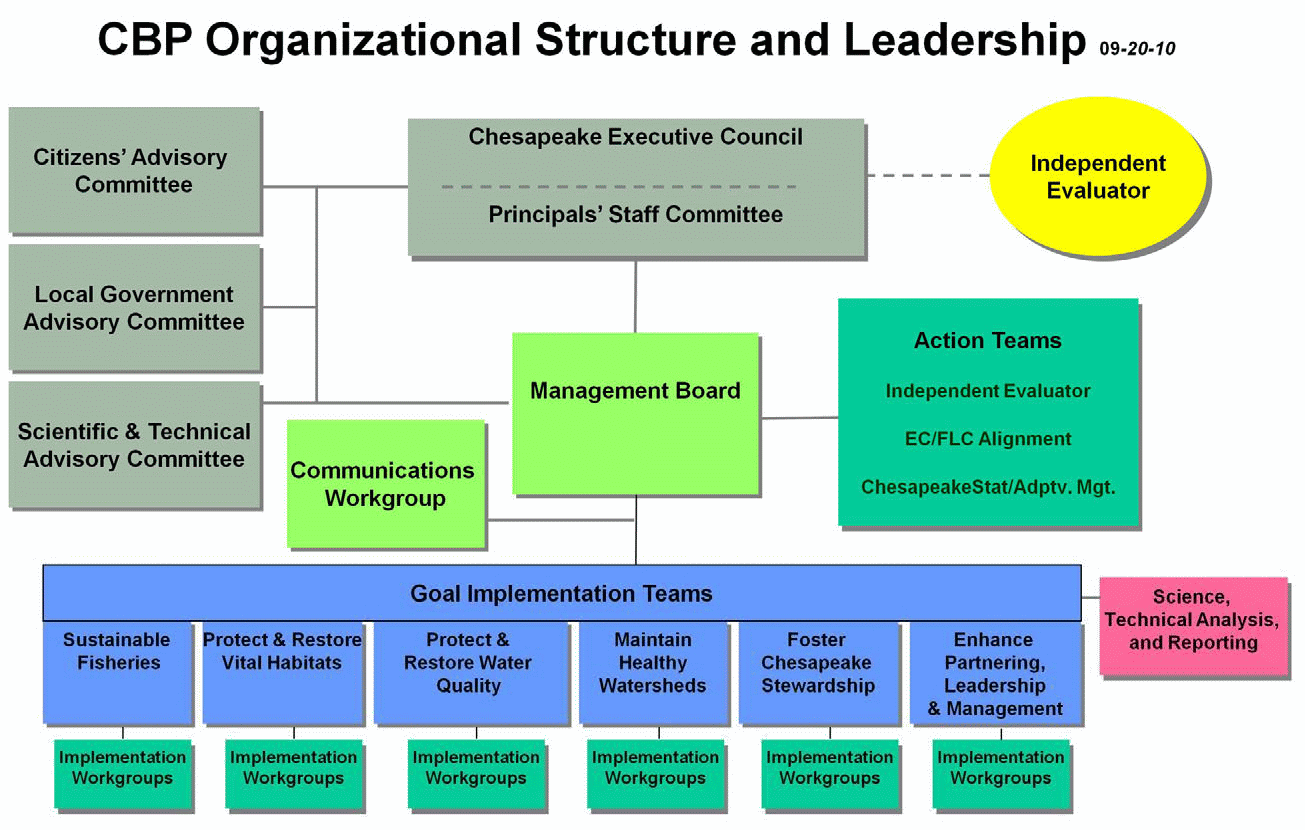 Since the signing of 1983 agreement, the Chesapeake Bay Program has adopted two additional agreements that provide overall guidance for Chesapeake Bay restoration:
* The ''1987 Chesapeake Bay Agreement'' established the Chesapeake Bay Program's goal to reduce the amount of
Since the signing of 1983 agreement, the Chesapeake Bay Program has adopted two additional agreements that provide overall guidance for Chesapeake Bay restoration:
* The ''1987 Chesapeake Bay Agreement'' established the Chesapeake Bay Program's goal to reduce the amount of
Chesapeake Bay Environmental Enforcement Coalition
*
Cornell Cooperative Extension
*
University of Delaware Cooperative Extension
*
University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science
*
Virginia Cooperative Extension
*
Anacostia Watershed SocietyCenter for Chesapeake CommunitiesCenter for Watershed Protection
*
Consortium for International Earth Science Information Network
*
Ecosystem Solutions
*
Interstate Commission on the Potomac River Basin
*
Low Impact Development Center
*
*
Potomac Conservancy
* Susquehanna River Basin Commission
Upper Susquehanna Coalition
Chesapeake Bay Program
- official site {{Authority control Chesapeake Bay watershed Environmental organizations based in the United States Local government in Delaware Local government in Maryland Local government in New York (state) Local government in Pennsylvania Local government in Virginia Government of the District of Columbia Local government in West Virginia Water organizations in the United States
 The Chesapeake Bay Program is the regional partnership that directs and conducts the restoration of the
The Chesapeake Bay Program is the regional partnership that directs and conducts the restoration of the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Ea ...
in the United States. As a partnership, the Chesapeake Bay Program brings together members of various state, federal, academic and local watershed organizations to build and adopt policies that support Chesapeake Bay restoration. By combining the resources and unique strengths of each individual organization, the Chesapeake Bay Program is able to follow a unified plan for restoration. The program office is located in Annapolis, Maryland
Annapolis ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of Maryland. It is the county seat of Anne Arundel County and its only incorporated city. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east ...
.
History
 In the late 1970s and early 1980s,
In the late 1970s and early 1980s, Congress
A congress is a formal meeting of the representatives of different countries, constituent states, organizations, trade unions, political parties, or other groups. The term originated in Late Middle English to denote an encounter (meeting of ...
funded scientific and estuarine
An estuary is a partially enclosed coastal body of brackish water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea. Estuaries form a transition zone between river environments and maritime environm ...
research of the Chesapeake Bay, which pinpointed three areas that required immediate attention:
* toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst ...
pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause harm. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the component ...
* nutrient over-enrichment
* dwindling underwater bay grasses.
The Environmental Protection Agency
Environmental Protection Agency may refer to the following government organizations:
* Environmental Protection Agency (Queensland), Australia
* Environmental Protection Agency (Ghana)
* Environmental Protection Agency (Ireland)
* Environmenta ...
(EPA) released a report in September 1983, based on seven years of research on the bay. The report stated that the bay was an "ecosystem in decline" and cited numerous instances of declines in the populations of oysters, crabs, freshwater fish and other wildlife.
In December 1983 the governor
A governor is an politician, administrative leader and head of a polity or Region#Political regions, political region, in some cases, such as governor-general, governors-general, as the head of a state's official representative. Depending on the ...
s of Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
, Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
and Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
; the mayor of the District of Columbia
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
; and the EPA Administrator signed ''The Chesapeake Bay Agreement of 1983.'' From this act, the Chesapeake Bay Program Executive Council was formed.
Evolution
 Since the signing of 1983 agreement, the Chesapeake Bay Program has adopted two additional agreements that provide overall guidance for Chesapeake Bay restoration:
* The ''1987 Chesapeake Bay Agreement'' established the Chesapeake Bay Program's goal to reduce the amount of
Since the signing of 1983 agreement, the Chesapeake Bay Program has adopted two additional agreements that provide overall guidance for Chesapeake Bay restoration:
* The ''1987 Chesapeake Bay Agreement'' established the Chesapeake Bay Program's goal to reduce the amount of nutrients
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
—primarily nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a Nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal and the lightest member of pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, often called the Pnictogen, pnictogens. ...
and phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol P and atomic number 15. All elemental forms of phosphorus are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive and are therefore never found in nature. They can nevertheless be prepared ar ...
—that enter the Chesapeake Bay by 40 percent by 2000. In 1992, the Chesapeake Bay Program partners agreed to continue the 40 percent reduction goal beyond 2000 and to attack nutrients at their source: upstream, in the Chesapeake Bay's tributaries
A tributary, or an ''affluent'', is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream ('' main stem'' or ''"parent"''), river, or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries, and the main stem river into which the ...
.
* In June 2000, the Chesapeake Bay Program adopted ''Chesapeake 2000,'' an agreement intended to guide restoration activities throughout the Chesapeake Bay watershed through 2010. ''Chesapeake 2000'' also provided the opportunity for the adjoining states of Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
, New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
New York may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* ...
and West Virginia
West Virginia is a mountainous U.S. state, state in the Southern United States, Southern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States.The United States Census Bureau, Census Bureau and the Association of American ...
to become more involved in the partnership. These headwater states now work with the Chesapeake Bay Program to reduce nutrients and sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
flowing into rivers from their jurisdictions. The renewed bay agreement was designed to guide restoration activities throughout the bay watershed through 2010. The members pledged to achieve over 100 specific actions all designed to restore the health of the bay. The agreement is organized into five categories, all dedicated to restoration and protection of different areas of the bay's health: living resources, vital habitat, water quality, sound land use, and stewardship and community engagement.
** The living resource section of the agreement states the goal of "restore, enhance and protect, the finfish
Fishery can mean either the Big business, enterprise of Animal husbandry#Aquaculture, raising or Fishing, harvesting fish and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place (wikt:AKA, a.k.a., fishing grounds). ...
, shellfish
Shellfish, in colloquial and fisheries usage, are exoskeleton-bearing Aquatic animal, aquatic invertebrates used as Human food, food, including various species of Mollusca, molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish ...
, and other living resources, their habitats and ecological relationship to sustain all fisheries
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a., fishing grounds). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farm ...
and provide for a balanced ecosystem." One of the specific goals for this is to help the blue crab Blue crab may refer to:
* Blue Crab 11, an American sailboat design
* ''Callinectes sapidus
''Callinectes sapidus'' (from the Ancient Greek language, Ancient Greek ,"beautiful" + , "swimmer", and Latin , "savory"), the blue crab, Atlantic blue ...
population by establishing harvest targets and begin implementing state fisheries management strategies and to manage the blue crab fishery to restore a healthy, size, age structure and biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
. This section also touches on multi-species management, a tenfold increase in the native oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but no ...
population, as well as resident and migratory fish passage.
** The vital habitat protection and restoration section aims to recommit to the existing goal of protecting of submerged aquatic vegetation which include specific levels of water clarity
Water clarity is a descriptive term for how deeply visible light penetrates through water. In addition to light penetration, the term water clarity is also often used to describe underwater visibility. Water clarity is one way that humans measure ...
to be met by 2010. It also touches on wetlands
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
, watershed, and forest preservation and conservation easement
In the United States, a conservation easement (also called conservation covenant, conservation restriction or conservation servitude) is a power invested in a qualified land conservation organization called a "land trust", or a governmental (muni ...
s.
** The water quality restoration and protection section states that the program plans on involving aid from stormwater management
Stormwater, also written storm water, is water that originates from precipitation (storm), including heavy rain and meltwater from hail and snow. Stormwater can soak into the soil (infiltration (hydrology), infiltrate) and become groundwater, be ...
, upgrading wastewater treatment plants
Wastewater treatment is a process which removes and eliminates contaminants from wastewater. It thus converts it into an effluent that can be returned to the water cycle. Once back in the water cycle, the effluent creates an acceptable impact on ...
to biological nutrient removal, upgrading managing sewage systems, and developing tributary strategies for each basin. It also states that by 2010, they want to correct the nutrient-relation problems associated with the bay and remove it from the list of impaired waters under the Clean Water Act
The Clean Water Act (CWA) is the primary federal law in the United States governing water pollution. Its objective is to restore and maintain the chemical, physical, and biological integrity of the nation's waters; recognizing the primary respo ...
.
** The sound land use
Land use is an umbrella term to describe what happens on a parcel of land. It concerns the benefits derived from using the land, and also the land management actions that humans carry out there. The following categories are used for land use: fo ...
portion of the agreement talks about permanently preserving 20 percent of the watershed from development
Development or developing may refer to:
Arts
*Development (music), the process by which thematic material is reshaped
* Photographic development
*Filmmaking, development phase, including finance and budgeting
* Development hell, when a proje ...
by 2010. Also, by 2002, each state will coordinate transportation policies to reduce the dependence on automobiles by encouraging travel alternatives such as biking and bus riding.
** Lastly, the stewardship section states that by 2001, they want to provide information to enhance the ability of citizen and community groups to participate in bay restoration. Also beginning in 2005, the Chesapeake Bay Program wants to provide an outdoor experience of the bay for every student before they graduate high school in order to encourage knowledge and awareness of the bay’s problems.
Budget
Since the creation of the program, Congress has provided annual appropriations, and the budgets of the Environmental Protection Agency andDepartment of Agriculture
An agriculture ministry (also called an agriculture department, agriculture board, agriculture council, or agriculture agency, or ministry of rural development) is a ministry charged with agriculture. The ministry is often headed by a minister f ...
have provided the majority of federal agency funds. Additional significant funding amounts from federal agencies have been provided by the Departments of Defense
Defense or defence may refer to:
Tactical, martial, and political acts or groups
* Defense (military), forces primarily intended for warfare
* Civil defense, the organizing of civilians to deal with emergencies or enemy attacks
* Defense industr ...
, Interior and Commerce
Commerce is the organized Complex system, system of activities, functions, procedures and institutions that directly or indirectly contribute to the smooth, unhindered large-scale exchange (distribution through Financial transaction, transactiona ...
. Funding has also been provided by the states of Maryland, Virginia, Delaware, New York, Pennsylvania and West Virginia; and the District of Columbia.
Partners
Signatories to the Chesapeake Bay Agreement
* Chesapeake Bay Commission (legislative assembly representing Maryland, Virginia and Pennsylvania) *Commonwealth of Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, Maryland to its south, West ...
*Commonwealth of Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
*District of Columbia
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and Federal district of the United States, federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from ...
*State of Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
* U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
Headwater State Partners
*New York State
New York, also called New York State, is a state in the northeastern United States. Bordered by New England to the east, Canada to the north, and Pennsylvania and New Jersey to the south, its territory extends into both the Atlantic Ocean and ...
*State of Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey to its northeast, and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state' ...
* State of West Virginia
Federal Agency Partners
Chesapeake Bay Environmental Enforcement Coalition
*
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the United States's civil space program, aeronautics research and space research. Established in 1958, it su ...
*National Capital Planning Commission
The National Capital Planning Commission (NCPC) is a United States government, U.S. government executive branch agency that provides Urban planning, planning guidance for Washington, D.C., and the surrounding National Capital Region. Through its pl ...
* U.S. Department of Agriculture
**Farm Service Agency
The Farm Service Agency (FSA) is the United States Department of Agriculture agency that was formed by merging the farm loan portfolio and staff of the Farmers Home Administration (FmHA) and the Agricultural Stabilization and Conservation Service ...
**Natural Resources Conservation Service
Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS), formerly known as the Soil Conservation Service (SCS), is an agency of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) that provides technical assistance to farmers and other private landowners and ...
** U.S. National Arboretum
*U.S. Department of Commerce
The United States Department of Commerce (DOC) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government. It is responsible for gathering data for business and governmental decision making, establishing industrial standards, catalyzing econo ...
*U.S. Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense (DoD, USDOD, or DOD) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government charged with coordinating and supervising the six U.S. armed services: the Army, Navy, Marines, Air Force, Space Force, t ...
*U.S. Department of Education
The United States Department of Education is a United States Cabinet, cabinet-level department of the federal government of the United States, United States government, originating in 1980. The department began operating on May 4, 1980, havin ...
* U.S. Department of the Interior
*U.S. Department of Transportation
The United States Department of Transportation (USDOT or DOT) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government. It is headed by the secretary of transportation, who reports directly to the president of the United States a ...
* U.S. General Services Administration
*U.S. Postal Service
The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or simply the Postal Service, is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the executive branch of the federal governmen ...
Academic Institution Partners
*Academy of Natural Sciences
The Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University, formerly the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, is the oldest natural science research institution and museum in the Americas. It was founded in 1812, by many of the leading natur ...
*Chesapeake Research Consortium
*College of William and Mary
The College of William & Mary (abbreviated as W&M) is a public research university in Williamsburg, Virginia, United States. Founded in 1693 under a royal charter issued by King William III and Queen Mary II, it is the second-oldest instit ...
Cornell Cooperative Extension
*
Old Dominion University
Old Dominion University (ODU) is a Public university, public research university in Norfolk, Virginia, United States. Established in 1930 as the two-year Norfolk Division of the College of William & Mary, it began by educating people with fewer ...
*Pennsylvania State University
The Pennsylvania State University (Penn State or PSU) is a Public university, public Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related Land-grant university, land-grant research university with campuses and facilities throughout Pennsyl ...
*Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase a ...
University of Delaware Cooperative Extension
*
University of the District of Columbia
The University of the District of Columbia (UDC) is a public historically black land-grant university in Washington, D.C., United States. The only public university in the city, it traces its origins to 1851 and opened in its current form in 1 ...
University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science
*
University of Maryland
The University of Maryland, College Park (University of Maryland, UMD, or simply Maryland) is a public land-grant research university in College Park, Maryland, United States. Founded in 1856, UMD is the flagship institution of the Univ ...
* University of Maryland, Eastern Shore
*University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (Penn or UPenn) is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. One of nine colonial colleges, it was chartered in 1755 through the efforts of f ...
*University of Virginia
The University of Virginia (UVA) is a Public university#United States, public research university in Charlottesville, Virginia, United States. It was founded in 1819 by Thomas Jefferson and contains his The Lawn, Academical Village, a World H ...
Virginia Cooperative Extension
*
Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University
The Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, commonly referred to as Virginia Tech (VT), is a Public university, public Land-grant college, land-grant research university with its main campus in Blacksburg, Virginia, United States ...
*West Virginia University
West Virginia University (WVU) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university with its main campus in Morgantown, West Virginia, United States. Its other campuses are those of the West Virginia University Ins ...
More Partners
* Alliance for the Chesapeake Bay *American Forests
American Forests is a 501(c)(3) non-profit conservation organization, established in 1875, and dedicated to protecting and restoring healthy forest ecosystems. The current headquarters are in Washington, D.C.
Activities
The mission of America ...
Anacostia Watershed Society
*
Chesapeake Bay Foundation
The Chesapeake Bay Foundation (CBF) is a non-profit organization devoted to the restoration and protection of the Chesapeake Bay in the United States. It was founded in 1967 and has headquarters offices in Annapolis, Maryland. The foundation has ...
* Chesapeake Bay TrustConsortium for International Earth Science Information Network
*
Ducks Unlimited
Ducks Unlimited (DU) is an American 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization dedicated to the conservation of wetlands and associated upland habitats for waterfowl, other wildlife, and people.
History and profile
In 1927, an offshoot of the Boone and ...
Ecosystem Solutions
*
International City/County Management Association
International City/County Management Association (ICMA; originally called the International City Managers' Association) is an association representing professionals in local government management. It is based in Washington, D.C.
Washington ...
Interstate Commission on the Potomac River Basin
*
Izaak Walton League
The Izaak Walton League of America, Inc. is an American environmental organization founded in 1922 that promotes natural resource protection and outdoor recreation. The organization was founded in Chicago, Illinois, by a group of sportsmen who wi ...
Low Impact Development Center
*
Metropolitan Washington Council of Governments
Metropolitan Washington Council of Governments (MWCOG) is an independent, nonprofit association designed to address regional issues confronting Washington, D.C., suburban Maryland, and Northern Virginia. It was founded in 1957.
MWCOG comprises 24 ...
* Montgomery Countybr>Department of Environmental Protection*
National Fish and Wildlife Foundation
The National Fish and Wildlife Foundation (NFWF) is an American foundation that was chartered by the United States Congress in 1984 to increase the resources available for the conservation of the nation's fish, wildlife, plants, and habitats.
A ...
Potomac Conservancy
* Susquehanna River Basin Commission
Upper Susquehanna Coalition
See also
* Clagett Farm - Project of the Chesapeake Bay FoundationReferences
External links
Chesapeake Bay Program
- official site {{Authority control Chesapeake Bay watershed Environmental organizations based in the United States Local government in Delaware Local government in Maryland Local government in New York (state) Local government in Pennsylvania Local government in Virginia Government of the District of Columbia Local government in West Virginia Water organizations in the United States