Chaadaev Portrait on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
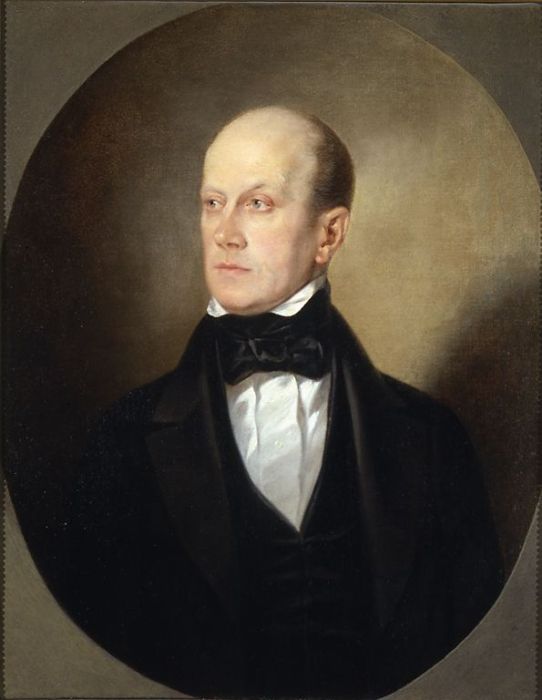 Pyotr or Petr Yakovlevich Chaadayev (russian: Пётр Я́ковлевич Чаада́ев; also spelled Chaadaev, or Čaadajev; 7 June 7 May Old Style">Old_Style.html" ;"title="7 May Old Style">7 May Old Style1794 – 26 April [14 April O.S.] 1856) was a Russian philosopher. He was one of the Russian Schellingians.
Chaadayev wrote eight "Philosophical Letters" about Russia in French between 1826 and 1831, which circulated among intellectuals in Russia in manuscript form for many years. They comprise an indictment of Russian culture for its laggard role far behind the leaders of Western civilization. He cast doubt on the greatness of the Russian past, and ridiculed Orthodoxy for failing to provide a sound spiritual basis for the Russian mind. He extolled the achievements of Europe, especially in rational and logical thought, its progressive spirit, its leadership in science, and indeed its leadership on the path to freedom. The Russian government saw his ideas as dangerous and unsound. After some were published, they were all banned by the censorship process. Because there was nothing to charge him with, Chaadayev was declared legally insane and put under constant medical supervision, though this was a formality rather than a real administrative abuse.
Pyotr or Petr Yakovlevich Chaadayev (russian: Пётр Я́ковлевич Чаада́ев; also spelled Chaadaev, or Čaadajev; 7 June 7 May Old Style">Old_Style.html" ;"title="7 May Old Style">7 May Old Style1794 – 26 April [14 April O.S.] 1856) was a Russian philosopher. He was one of the Russian Schellingians.
Chaadayev wrote eight "Philosophical Letters" about Russia in French between 1826 and 1831, which circulated among intellectuals in Russia in manuscript form for many years. They comprise an indictment of Russian culture for its laggard role far behind the leaders of Western civilization. He cast doubt on the greatness of the Russian past, and ridiculed Orthodoxy for failing to provide a sound spiritual basis for the Russian mind. He extolled the achievements of Europe, especially in rational and logical thought, its progressive spirit, its leadership in science, and indeed its leadership on the path to freedom. The Russian government saw his ideas as dangerous and unsound. After some were published, they were all banned by the censorship process. Because there was nothing to charge him with, Chaadayev was declared legally insane and put under constant medical supervision, though this was a formality rather than a real administrative abuse.
online
* M.A. Mendosa, ''Uno scrittore russo del primo ’800: Pëtr Jakovlevič Čaadaev'', Mantova: Universitas Studiorum, 2014,
"Philosophical Letters", by P. Chaadayev
at Runivers.ru in
"Philosophical Letters", by P. Chaadayev
* ttp://enriquecastanos.com/idea_rusa_chaadaev_soloviev_berdiaev.htm Principales ideas de la ''Carta filosófica a una dama'', de Piotr Chaadaev {{DEFAULTSORT:Chaadayev, Pyotr 1794 births 1856 deaths Writers from Moscow People from Moskovsky Uyezd Russian people of Tatar descent Russian nobility Decembrists Moscow State University alumni 19th-century philosophers from the Russian Empire
 Pyotr or Petr Yakovlevich Chaadayev (russian: Пётр Я́ковлевич Чаада́ев; also spelled Chaadaev, or Čaadajev; 7 June 7 May Old Style">Old_Style.html" ;"title="7 May Old Style">7 May Old Style1794 – 26 April [14 April O.S.] 1856) was a Russian philosopher. He was one of the Russian Schellingians.
Chaadayev wrote eight "Philosophical Letters" about Russia in French between 1826 and 1831, which circulated among intellectuals in Russia in manuscript form for many years. They comprise an indictment of Russian culture for its laggard role far behind the leaders of Western civilization. He cast doubt on the greatness of the Russian past, and ridiculed Orthodoxy for failing to provide a sound spiritual basis for the Russian mind. He extolled the achievements of Europe, especially in rational and logical thought, its progressive spirit, its leadership in science, and indeed its leadership on the path to freedom. The Russian government saw his ideas as dangerous and unsound. After some were published, they were all banned by the censorship process. Because there was nothing to charge him with, Chaadayev was declared legally insane and put under constant medical supervision, though this was a formality rather than a real administrative abuse.
Pyotr or Petr Yakovlevich Chaadayev (russian: Пётр Я́ковлевич Чаада́ев; also spelled Chaadaev, or Čaadajev; 7 June 7 May Old Style">Old_Style.html" ;"title="7 May Old Style">7 May Old Style1794 – 26 April [14 April O.S.] 1856) was a Russian philosopher. He was one of the Russian Schellingians.
Chaadayev wrote eight "Philosophical Letters" about Russia in French between 1826 and 1831, which circulated among intellectuals in Russia in manuscript form for many years. They comprise an indictment of Russian culture for its laggard role far behind the leaders of Western civilization. He cast doubt on the greatness of the Russian past, and ridiculed Orthodoxy for failing to provide a sound spiritual basis for the Russian mind. He extolled the achievements of Europe, especially in rational and logical thought, its progressive spirit, its leadership in science, and indeed its leadership on the path to freedom. The Russian government saw his ideas as dangerous and unsound. After some were published, they were all banned by the censorship process. Because there was nothing to charge him with, Chaadayev was declared legally insane and put under constant medical supervision, though this was a formality rather than a real administrative abuse.
Life
Chaadayev was born and died in Moscow. His surname is probably derived from the Turkic word ''Chaʿadai'', with the name deriving from Chagatay, the second son ofGenghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
. After leaving Moscow University
M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University (MSU; russian: Московский государственный университет имени М. В. Ломоносова) is a public research university in Moscow, Russia and the most prestigious ...
without completing his course in 1812, he entered the army and fought against the French invasion of Russia
The French invasion of Russia, also known as the Russian campaign, the Second Polish War, the Army of Twenty nations, and the Patriotic War of 1812 was launched by Napoleon Bonaparte to force the Russian Empire back into the continental block ...
.
Chaadaev's first hand observation of Tsar Alexander's reaction to a revolt in the Semenovsky regiment may have led to his resignation from service in 1820. From 1823 to 1826 he travelled in Europe, so that he was out of Russia during the Decembrist insurrection, though he was questioned on his return about his connections with many of the Decembrists. These connections may have contributed to his failure to find a position in the new government of Nicholas I.
He befriended Alexander Pushkin and was a model for Chatsky, the chief protagonist of Alexander Griboyedov
Alexander Sergeyevich Griboyedov (russian: Александр Сергеевич Грибоедов, ''Aleksandr Sergeevich Griboedov'' or ''Sergeevich Griboyedov''; 15 January 179511 February 1829), formerly romanized as Alexander Sergueevich Gri ...
's play '' Woe from Wit'' (1824). During the 1840s Chaadayev was an active participant in the Moscow literary circles.
Philosophy
The main thesis of his famous ''Philosophical Letters'' was that Russia had lagged behind Western countries and had contributed nothing to the world's progress and concluded that Russia must start de novo. As a result, they included criticism of Russia's intellectual isolation and social backwardness. When in 1836 the first edition (and only one published during his life) of the philosophical letters was published in the Russian magazine Telescope, its editor was exiled to the Far North of Russia. TheSlavophile
Slavophilia (russian: Славянофильство) was an intellectual movement originating from the 19th century that wanted the Russian Empire to be developed on the basis of values and institutions derived from Russia's early history. Slavoph ...
s at first mistook Chaadayev for one of them, but later, on realizing their mistake, bitterly denounced and disclaimed him. Chaadayev fought Slavophilism all of his life. His first Philosophical Letter has been labeled the "opening shot" of the Westernizer-Slavophile controversy which was dominant in Russian social thought of the nineteenth century. He wrote in his "first letter":
The strikingly uncomplimentary views of Russia in the first philosophical letter caused their author to be declared "clinically insane" because he criticized the regime of Tsar Nicholas I. The 1836 case of Pyotr is believed to be the first recorded incident where psychiatry was used in Russia to suppress dissent.
Living under house arrest following his declaration of insanity, Chaadayev next work was entitled, fittingly, "Apologie d'un Fou" Apology
Apology, The Apology, apologize/apologise, apologist, apologetics, or apologetic may refer to:
Common uses
* Apology (act), an expression of remorse or regret
* Apologia, a formal defense of an opinion, position, or action
Arts, entertainment, ...
of a Madman" but may better be translated as "Apologia of a Madman"] (1837). It opens with a quote from Samuel Coleridge stating "O my brethren! I have told/ Most bitter truth, but without bitterness."Peter Iakovlevich Chaadaev, Sochineniia i pis'ma, ed M. Gershenzon, Moscow, 1913
In this brilliant but uncompleted work he maintained that Russia must follow her inner lines of development if she was to be true to her historical mission.
His ideas influenced both the Westernizers (who supported bringing Russia into accord with developments in Europe by way of various degrees of liberal reform) and Slavophiles (who supported Russian Orthodoxy and national culture.)
Most of his works have been edited by his biographer, Mikhail Gershenzon
Mikhail Osipovich Gershenzon (russian: Михаи́л О́сипович Гершензо́н) ( Kishinev, - Moscow, 19 February 1925) was a Russian scholar, essayist and editor. He studied history, philosophy, and political science at Moscow ...
(two volumes, Moscow, 1913–14), whose study of the philosopher
A philosopher is a person who practices or investigates philosophy. The term ''philosopher'' comes from the grc, φιλόσοφος, , translit=philosophos, meaning 'lover of wisdom'. The coining of the term has been attributed to the Greek th ...
was published at St. Petersburg in 1908.
References
Sources
*''This article incorporates text from theNew International Encyclopedia
''The New International Encyclopedia'' was an American encyclopedia first published in 1902 by Dodd, Mead and Company. It descended from the ''International Cyclopaedia'' (1884) and was updated in 1906, 1914 and 1926.
History
''The New Intern ...
, a work which is now in the public domain.''
* lazov, Yuri. "Chaadaev and Russia's destiny." ''Studies in East European Thought'' 32.4 (1986): 281-301.
* McNally, Raymond T. "The Significance of Chaadayev's Weltanschauung." ''Russian Review'' 23.4 (1964): 352-361online
* M.A. Mendosa, ''Uno scrittore russo del primo ’800: Pëtr Jakovlevič Čaadaev'', Mantova: Universitas Studiorum, 2014,
External links
"Philosophical Letters", by P. Chaadayev
at Runivers.ru in
Djvu
DjVu ( , like French "déjà vu") is a computer file format designed primarily to store scanned documents, especially those containing a combination of text, line drawings, indexed color images, and photographs. It uses technologies such as ima ...
and PDF
Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, hardware, and operating systems. ...
format
"Philosophical Letters", by P. Chaadayev
* ttp://enriquecastanos.com/idea_rusa_chaadaev_soloviev_berdiaev.htm Principales ideas de la ''Carta filosófica a una dama'', de Piotr Chaadaev {{DEFAULTSORT:Chaadayev, Pyotr 1794 births 1856 deaths Writers from Moscow People from Moskovsky Uyezd Russian people of Tatar descent Russian nobility Decembrists Moscow State University alumni 19th-century philosophers from the Russian Empire