Central Powers Invasion Of Ukraine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Operation Faustschlag ("Operation Fist Punch"), also known as the Eleven Days' War, Mawdsley (2007), p. 35 was a
 On 18 February, the German and Austro-Hungarian forces started a major three-pronged offensive against the Soviets with 53 divisions. The northern force advanced from
On 18 February, the German and Austro-Hungarian forces started a major three-pronged offensive against the Soviets with 53 divisions. The northern force advanced from
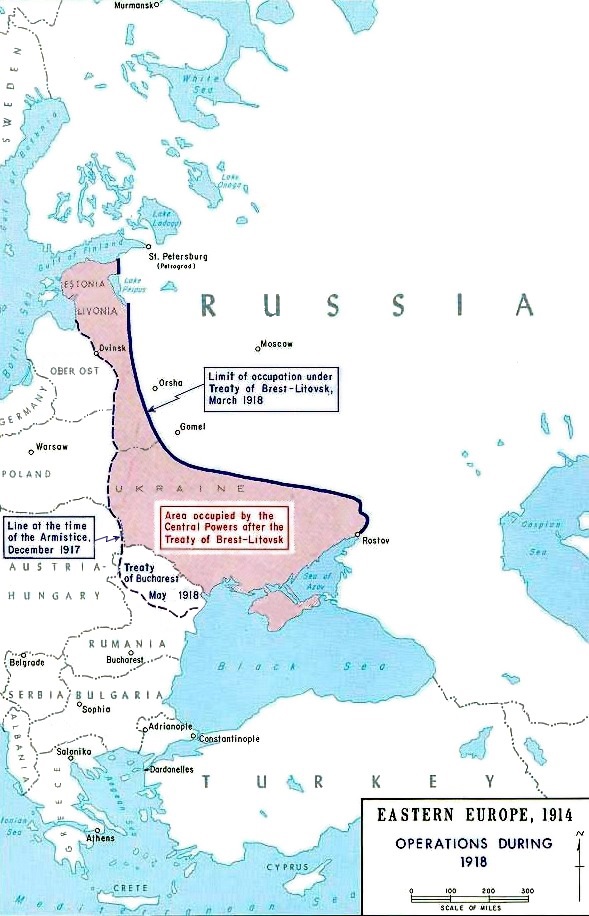 The Bolshevik capitulation on 3 March only ended the advance along a line from Narva to Northern Ukraine, as with the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk the Soviet government gave up all rights to Southern Russia. During the next few months, the southern Central Powers forces advanced over 500 miles further, capturing the whole of Ukraine and some territory beyond.
German operations also continued in the Caucasus and Finland, where Germany assisted the White Finnish forces in the
The Bolshevik capitulation on 3 March only ended the advance along a line from Narva to Northern Ukraine, as with the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk the Soviet government gave up all rights to Southern Russia. During the next few months, the southern Central Powers forces advanced over 500 miles further, capturing the whole of Ukraine and some territory beyond.
German operations also continued in the Caucasus and Finland, where Germany assisted the White Finnish forces in the Germany Takes Control of Crimea
Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
offensive in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. It was the last major action on the Eastern Front.
Russian forces were unable to put up any serious resistance due to the turmoil of the Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and ad ...
and subsequent Russian Civil War
, date = October Revolution, 7 November 1917 – Yakut revolt, 16 June 1923{{Efn, The main phase ended on 25 October 1922. Revolt against the Bolsheviks continued Basmachi movement, in Central Asia and Tungus Republic, the Far East th ...
. The armies of the Central Powers therefore captured huge territories in Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
, Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
, and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
, forcing the Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
government of Russia to sign the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace, separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russian SFSR, Russia and the Central Powers (German Empire, Germany, Austria-Hungary, Kingdom of ...
.
Background
Bolsheviks took power in Russia during theOctober Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key moment ...
and announced that Russia would be withdrawing from war. Talks with the Central Powers started in Brest-Litovsk
Brest ( be, Брэст / Берасьце, Bieraście, ; russian: Брест, ; uk, Берестя, Berestia; lt, Brasta; pl, Brześć; yi, בריסק, Brisk), formerly Brest-Litovsk (russian: Брест-Литовск, lit=Lithuanian Br ...
on 3 December 1917 and on the 17th a cease-fire went into effect. Peace talks soon followed, starting on 22 December. Tucker and Roberts (2005), p. 662
As negotiations began, the Central Powers presented demands for the territory that they had occupied during the 1914–1916 period, including Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
, Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
and western Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
. The Bolsheviks decided not to accept these terms and instead withdrew from the negotiations, eventually resulting in the breakdown of the ceasefire. Mawdsley (2007), p. 31–32 Leon Trotsky
Lev Davidovich Bronstein. ( – 21 August 1940), better known as Leon Trotsky; uk, link= no, Лев Давидович Троцький; also transliterated ''Lyev'', ''Trotski'', ''Trotskij'', ''Trockij'' and ''Trotzky''. (), was a Russian ...
, head of the Russian delegation, hoped to delay talks until a revolution occurred within Germany, which would force them out of the war. Tucker and Roberts (2005), p. 662-663
Trotsky was the leading advocate of the "neither war nor peace" policy and on 28 January 1918 announced that Soviet Russia considered the war over. Mawdsley (2007), p. 32 This was unacceptable to the Germans who were already transporting troops to the Western Front Western Front or West Front may refer to:
Military frontiers
*Western Front (World War I), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (World War II), a military frontier to the west of Germany
*Western Front (Russian Empire), a majo ...
. The German Chief of Staff, general Max Hoffmann, responded by signing the peace treaty
A peace treaty is an agreement between two or more hostile parties, usually countries or governments, which formally ends a state of war between the parties. It is different from an armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring ...
with Ukrainian People's Republic
The Ukrainian People's Republic (UPR), or Ukrainian National Republic (UNR), was a country in Eastern Europe that existed between 1917 and 1920. It was declared following the February Revolution in Russia by the First Universal. In March 1 ...
on 9 February and announced an end to the cease-fire with Russia in two-days time on 17 February, leading to the resumption of hostilities. Tucker and Roberts (2005), p. 663
While negotiations were ongoing, Soviet Commander-in-Chief Nikolai Krylenko oversaw the demobilization and democratization of the Russian army, introducing elected commanders, ending all ranks, and sending troops home. On 29 January, Krylenko ordered demobilization of the whole army. Mawdsley (2007), p. 34
Offensive
 On 18 February, the German and Austro-Hungarian forces started a major three-pronged offensive against the Soviets with 53 divisions. The northern force advanced from
On 18 February, the German and Austro-Hungarian forces started a major three-pronged offensive against the Soviets with 53 divisions. The northern force advanced from Pskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=pskov-ru.ogg, p=pskof; see also names in other languages) is a city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov Oblast, located about east of the Estonian border, on the Velikaya River. Population ...
towards Narva
Narva, russian: Нарва is a municipality and city in Estonia. It is located in Ida-Viru County, Ida-Viru county, at the Extreme points of Estonia, eastern extreme point of Estonia, on the west bank of the Narva (river), Narva river which ...
, the central force pushed towards Smolensk, and the southern force towards Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
. Woodward (2009), p. 295
The northern force, consisting of 16 divisions, captured the key Daugavpils
Daugavpils (; russian: Двинск; ltg, Daugpiļs ; german: Dünaburg, ; pl, Dyneburg; see other names) is a state city in south-eastern Latvia, located on the banks of the Daugava River, from which the city gets its name. The parts of the c ...
junction on the first day. This was soon followed by the capture of Pskov
Pskov ( rus, Псков, a=pskov-ru.ogg, p=pskof; see also names in other languages) is a city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov Oblast, located about east of the Estonian border, on the Velikaya River. Population ...
and securing Narva
Narva, russian: Нарва is a municipality and city in Estonia. It is located in Ida-Viru County, Ida-Viru county, at the Extreme points of Estonia, eastern extreme point of Estonia, on the west bank of the Narva (river), Narva river which ...
on 28 February. The central forces of the 10th Army and XLI corps advanced towards Smolensk. On 21 February Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach and the now subterranean Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative status in Belarus and is the admi ...
was captured together with the headquarters of the Western Army Group. The Southern forces broke through the remains of the Russian Southwestern Army Group, capturing Zhitomir on 24 February. Kiev
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
was secured on 2 March, one day after the Ukrainian Central Rada
The Central Council of Ukraine ( uk, Українська Центральна Рада, ) (also called the Tsentralna Rada or the Central Rada) was the All-Ukrainian council (soviet) that united deputies of soldiers, workers, and peasants deputie ...
troops had arrived there.
Central Powers armies had advanced over within a week, facing no serious Soviet resistance. German troops were now within of Petrograd
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
, forcing the Soviets to transfer their capital to Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
. The rapid advance was described as a "Railway War" (''der Eisenbahnfeldzug'') with German soldiers using Russian railways to advance eastward. Mawdsley (2007), p. 33 General Hoffmann wrote in his diary on 22 February:
It is the most comical war I have ever known. We put a handful of infantrymen with machine guns and one gun onto a train and rush them off to the next station; they take it, make prisoners of the Bolsheviks, pick up few more troops, and so on. This proceeding has, at any rate, the charm of novelty. Gilbert (2008), p. 399
Political impact
As the German offensive was ongoing, Trotsky returned to Petrograd. Most of the leadership still preferred continuing the war, even though Russia was in no position to do so, due to the destruction of its army. At this pointLenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 – 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 19 ...
intervened to push the Soviet leadership into acceptance of German terms, which by now had become even harsher. He was backed by other senior communists to include Kamenev
Lev Borisovich Kamenev. ('' né'' Rozenfeld; – 25 August 1936) was a Bolshevik revolutionary and a prominent Soviet politician.
Born in Moscow to parents who were both involved in revolutionary politics, Kamenev attended Imperial Moscow Un ...
, Zinoviev Zinoviev, Zinovyev, Zinovieff (russian: Зино́вьев), or Zinovieva (feminine; Зино́вьева), as a Russian surname, derives from the personal name Zinovi, from Greek '' Zenobios''.
Notable people with the surname include:
* Alexand ...
, and Stalin.
After a stormy session of Lenin's ruling council, during which the revolution's leader went so far as to threaten resignation, he obtained a 116 to 85 vote in favour of the new German terms. The vote in the Central Committee was even closer, seven in favour and six against. In the end, Trotsky switched his vote and German terms were accepted; on 3 March, the Bolsheviks signed the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace, separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russian SFSR, Russia and the Central Powers (German Empire, Germany, Austria-Hungary, Kingdom of ...
.
On 24 February, one day before the arrival of German troops to Tallinn
Tallinn () is the most populous and capital city of Estonia. Situated on a bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, Tallinn has a population of 437,811 (as of 2022) and administratively lies in the Harju ' ...
, the Estonian Salvation Committee
The Estonian Salvation Committee ( et, Eestimaa Päästekomitee or ''Päästekomitee'') was the executive body of the Estonian Provincial Assembly that issued the Estonian Declaration of Independence.
The Salvation Committee was created on Februa ...
declared
In the sport of cricket, a declaration occurs when a captain declares his team's innings closed and a forfeiture occurs when a captain chooses to forfeit an innings without batting. Declaration and forfeiture are covered in Law 15 of the ''Laws of ...
the independence of Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
. German occupation authorities refused to recognize the Estonian government and Germans were installed in positions of authority. Parrott (2002), p. 145
Aftermath
 The Bolshevik capitulation on 3 March only ended the advance along a line from Narva to Northern Ukraine, as with the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk the Soviet government gave up all rights to Southern Russia. During the next few months, the southern Central Powers forces advanced over 500 miles further, capturing the whole of Ukraine and some territory beyond.
German operations also continued in the Caucasus and Finland, where Germany assisted the White Finnish forces in the
The Bolshevik capitulation on 3 March only ended the advance along a line from Narva to Northern Ukraine, as with the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk the Soviet government gave up all rights to Southern Russia. During the next few months, the southern Central Powers forces advanced over 500 miles further, capturing the whole of Ukraine and some territory beyond.
German operations also continued in the Caucasus and Finland, where Germany assisted the White Finnish forces in the Finnish Civil War
The Finnish Civil War; . Other designations: Brethren War, Citizen War, Class War, Freedom War, Red Rebellion and Revolution, . According to 1,005 interviews done by the newspaper ''Aamulehti'', the most popular names were as follows: Civil W ...
. Under the treaty all Russian naval bases in the Baltic except Kronstadt were taken away, and the Russian Black Sea Fleet warships in Odessa
Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrativ ...
were to be disarmed and detained. The Bolsheviks also agreed to the immediate return of 630,000 Austrian prisoners-of-war. Gilbert (2008), p. 402
With the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, Soviet Russia had given up Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Belarus and Ukraine, enabling those territories to develop independently from Russian influence. Germany's intention was to turn these territories into political and territorial satellites, but this plan collapsed with Germany's own defeat within a year. Mawdsley (2007), p. 37 After the German surrender, the Soviets made an attempt to regain lost territories. They were successful in some areas like Ukraine, Belarus and the Caucasus, but were forced to recognize the independence of the Baltic States, Finland, and Poland. Raffass (2012), p. 43
In Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
, Ukrainian troops took control of the Donets Basin in April 1918. In the same month, Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
was also cleared of the Bolsheviks by Ukrainian troops and the Imperial German Army
The Imperial German Army (1871–1919), officially referred to as the German Army (german: Deutsches Heer), was the unified ground and air force of the German Empire. It was established in 1871 with the political unification of Germany under the l ...
.New York Herald
The ''New York Herald'' was a large-distribution newspaper based in New York City that existed between 1835 and 1924. At that point it was acquired by its smaller rival the ''New-York Tribune'' to form the '' New York Herald Tribune''.
His ...
(18 May 1918) On 13 March 1918 Ukrainian troops and the Austro-Hungarian Army had secured Odessa
Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrativ ...
. On 5 April 1918 the German army took control of Yekaterinoslav
Dnipro, previously called Dnipropetrovsk from 1926 until May 2016, is Ukraine's fourth-largest city, with about one million inhabitants. It is located in the eastern part of Ukraine, southeast of the Ukrainian capital Kyiv on the Dnieper Rive ...
, and 3 days later Kharkiv
Kharkiv ( uk, wikt:Харків, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest List of cities in Ukraine, city and List of hromadas of Ukraine, municipality in Ukraine.War Without Fronts: Atamans and Commissars in Ukraine, 1917-1919
by Mikhail Akulov,
by Mikhail Akulov,
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
, August 2013 (page 102 and 103) The German/Austro-Hungarian victories in Ukraine were due to the apathy of the locals and the inferior fighting skills of Bolsheviks troops compared to their Austro-Hungarian and German counterparts.
In the Bolshevik government, Lenin consolidated his power; however, fearing the possibility of a renewed German threat along the Baltic, he moved the capital from Petrograd to Moscow on 12 March. Debates became far more restrained, and he was never again so strongly challenged as he was regarding the Brest-Litovsk treaty. Mawdsley (2007), p. 36-37
See also
* Ober Ost *Finnish Civil War
The Finnish Civil War; . Other designations: Brethren War, Citizen War, Class War, Freedom War, Red Rebellion and Revolution, . According to 1,005 interviews done by the newspaper ''Aamulehti'', the most popular names were as follows: Civil W ...
* German Caucasus Expedition
*Soviet westward offensive of 1918–19
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Faustschlag, Operation 1918 in Russia Battles of the Eastern Front (World War I) Battles of World War I involving Austria-Hungary Battles of World War I involving Russia Battles of World War I involving Germany Conflicts in 1918 1918 in Belarus February 1918 events March 1918 events Ukraine in World War I