Caribbean Premier League Coaches on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of
/ref> The Oxford Online Dictionaries claim that the stress on the second syllable is the most common pronunciation in the Caribbean itself, but according to the Dictionary of Caribbean English Usage, the most common pronunciation in
 The word "Caribbean" has multiple uses. Its principal ones are geographical and political. The Caribbean can also be expanded to include territories with strong cultural and historical connections to Africa,
The word "Caribbean" has multiple uses. Its principal ones are geographical and political. The Caribbean can also be expanded to include territories with strong cultural and historical connections to Africa,
 The oldest evidence of humans in the Caribbean is in southern
The oldest evidence of humans in the Caribbean is in southern
 The Caribbean was known for pirates, especially between 1640 and 1680. The term "
The Caribbean was known for pirates, especially between 1640 and 1680. The term "
File:Attack near Playa Giron. April 19, 1961. - panoramio.jpg, Counter-attack by
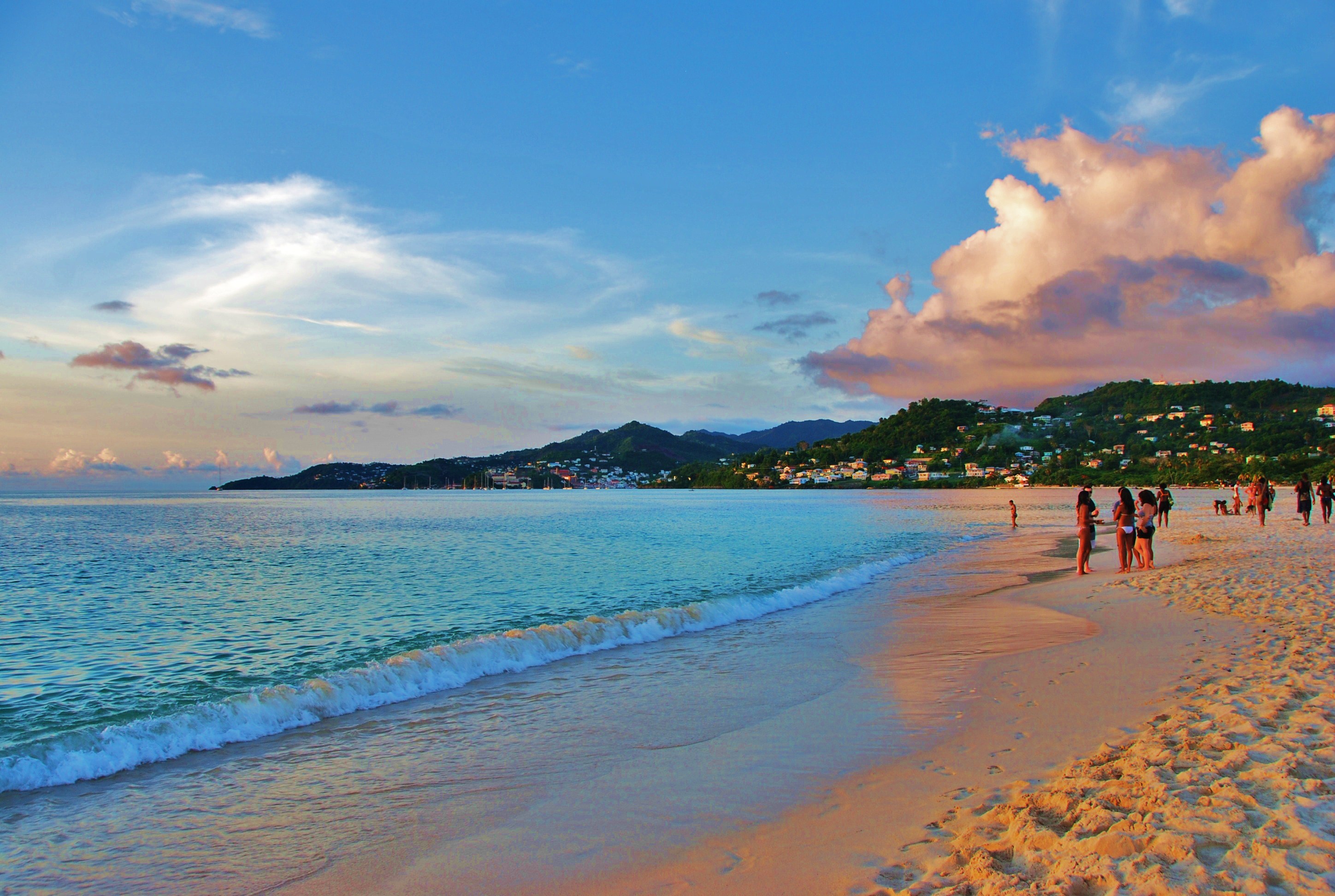
 The geography and climate in the Caribbean region varies: Some islands in the region have relatively flat terrain of non-volcanic origin. These islands include Aruba (possessing only minor volcanic features), Curaçao,
The geography and climate in the Caribbean region varies: Some islands in the region have relatively flat terrain of non-volcanic origin. These islands include Aruba (possessing only minor volcanic features), Curaçao,

 The climate of the area is
The climate of the area is 






 All islands at some point were, and a few still are,
All islands at some point were, and a few still are,



File:Epiphytes (Dominica).jpg, alt=Epiphytes (bromeliads, climbing palms) in the rainforest of Dominica., Epiphytes (bromeliads, climbing palms) in the rainforest of Dominica
File:Jumping frog.jpg, A green and black poison frog, ''
 At the time of European contact, the dominant ethnic groups in the Caribbean included the
At the time of European contact, the dominant ethnic groups in the Caribbean included the
Database documentation
Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) Population Database, version 3, International Center for Tropical Agriculture, 2005. Accessed on line February 20, 2008. In Haiti and most of the French,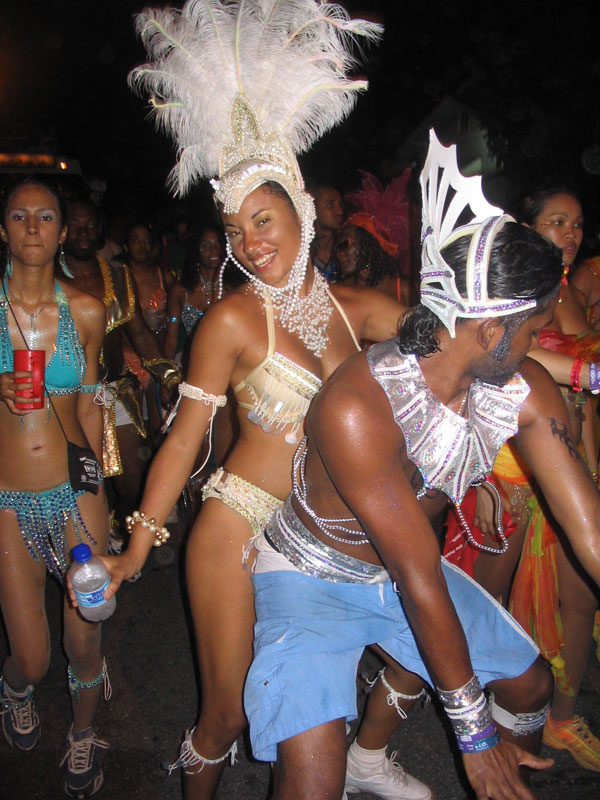




 Caribbean societies are very different from other Western societies in terms of size, culture, and degree of mobility of their citizens. The current economic and political problems the states face individually are common to all Caribbean states. Regional development has contributed to attempts to subdue current problems and avoid projected problems. From a political and economic perspective, regionalism serves to make Caribbean states active participants in current international affairs through collective coalitions. In 1973, the first political regionalism in the
Caribbean societies are very different from other Western societies in terms of size, culture, and degree of mobility of their citizens. The current economic and political problems the states face individually are common to all Caribbean states. Regional development has contributed to attempts to subdue current problems and avoid projected problems. From a political and economic perspective, regionalism serves to make Caribbean states active participants in current international affairs through collective coalitions. In 1973, the first political regionalism in the
 *
*
Digital Library of the Caribbean
Manioc, open access digital Library, books, images, conferences, articles about the Caribbean
Federal Research Division of the U.S. Library of Congress
Caribbean Islands (1987)
LANIC Caribbean country pages
* {{Authority control
the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
that consists of the Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean) and the surrounding coasts. The region is southeast of the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
and the North American mainland, east of Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
, and north of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...
.
Situated largely on the Caribbean Plate
The Caribbean Plate is a mostly oceanic tectonic plate underlying Central America and the Caribbean Sea off the north coast of South America.
Roughly 3.2 million square kilometers (1.2 million square miles) in area, the Caribbean Plate borders ...
, the region has more than 700 islands, islet
An islet is a very small, often unnamed island. Most definitions are not precise, but some suggest that an islet has little or no vegetation and cannot support human habitation. It may be made of rock, sand and/or hard coral; may be permanen ...
s, reef
A reef is a ridge or shoal of rock, coral or similar relatively stable material, lying beneath the surface of a natural body of water. Many reefs result from natural, abiotic processes— deposition of sand, wave erosion planing down rock o ...
s and cay
A cay ( ), also spelled caye or key, is a small, low-elevation, sandy island on the surface of a coral reef. Cays occur in tropical environments throughout the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans, including in the Caribbean and on the Great ...
s (see the list of Caribbean islands). Island arc
Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle alon ...
s delineate the eastern and northern edges of the Caribbean Sea: The Greater Antilles
The Greater Antilles ( es, Grandes Antillas or Antillas Mayores; french: Grandes Antilles; ht, Gwo Zantiy; jam, Grieta hAntiliiz) is a grouping of the larger islands in the Caribbean Sea, including Cuba, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, Jamaica, a ...
and the Lucayan Archipelago
The Lucayan Archipelago (named for the original native Lucayan people), also known as the Bahama Archipelago, is an island group comprising the Commonwealth of The Bahamas and the British Overseas Territory of the Turks and Caicos Islands. The ar ...
on the north and the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc bet ...
and the on the south and east (which includes the Leeward Antilles
The Leeward Antilles ( nl, Benedenwindse Eilanden) are a chain of islands in the Caribbean – specifically, the southerly islands of the Lesser Antilles (and, in turn, the Antilles and the West Indies) along the southeastern fringe of the C ...
). They form the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
with the nearby Lucayan Archipelago
The Lucayan Archipelago (named for the original native Lucayan people), also known as the Bahama Archipelago, is an island group comprising the Commonwealth of The Bahamas and the British Overseas Territory of the Turks and Caicos Islands. The ar ...
(the Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the ar ...
and Turks and Caicos Islands
The Turks and Caicos Islands (abbreviated TCI; and ) are a British Overseas Territory consisting of the larger Caicos Islands and smaller Turks Islands, two groups of tropical islands in the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean and n ...
), which are considered to be part of the Caribbean despite not bordering the Caribbean Sea. On the mainland, Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wate ...
, Cozumel
Cozumel (; yua, Kùutsmil) is an island and municipality in the Caribbean Sea off the eastern coast of Mexico's Yucatán Peninsula, opposite Playa del Carmen. It is separated from the mainland by the Cozumel Channel and is close to the Yucat� ...
, the Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula (, also , ; es, Península de Yucatán ) is a large peninsula in southeastern Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north ...
, Margarita Island
Margarita Island (, ) is the largest island in the States of Venezuela, Venezuelan state of Nueva Esparta, situated off the northeastern coast of the country, in the Caribbean Sea. The capital city of Nueva Esparta, La Asunción, is located on t ...
, and the Guianas
The Guianas, sometimes called by the Spanish loan-word ''Guayanas'' (''Las Guayanas''), is a region in north-eastern South America which includes the following three territories:
* French Guiana, an overseas department and region of France
* ...
( Guyana, Suriname, French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label=French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic coast of South America in the Guianas. ...
, Guayana Region
The Guayana Region is an administrative region of eastern Venezuela.
History
In the 1970s, after the process of forming the Political-Administrative Regions through CORDIPLAN in the government of Rafael Caldera, the Region of Guyana was f ...
, and Amapá in Brazil) are often included due to their political
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that stud ...
and cultural ties with the region.
Geopolitically, the islands of the Caribbean (the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
) are often regarded as a region of North America, though sometimes they are included in Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
or left as a region of their own and are organized into 30 territories including sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defined te ...
s, overseas departments
The overseas departments and regions of France (french: départements et régions d'outre-mer, ; ''DROM'') are departments of France that are outside metropolitan France, the European part of France. They have exactly the same status as mainlan ...
, and dependencies. From December 15, 1954, to October 10, 2010, there was a country known as the Netherlands Antilles composed of five states, all of which were Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
dependencies. From January 3, 1958, to May 31, 1962, there was also a short-lived political union called the West Indies Federation
The West Indies Federation, also known as the West Indies, the Federation of the West Indies or the West Indian Federation, was a short-lived political union that existed from 3 January 1958 to 31 May 1962. Various islands in the Caribbean that ...
composed of ten English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
-speaking Caribbean territories, all of which were then British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
dependencies. The West Indies cricket team
The West Indies cricket team, nicknamed the Windies, is a multi-national men's cricket team representing the mainly English-speaking countries and territories in the Caribbean region and administered by Cricket West Indies. The players on ...
continues to represent many of those nations.
Etymology and pronunciation
The region takes its name from that of theCaribs
“Carib” may refer to:
People and languages
*Kalina people, or Caribs, an indigenous people of South America
**Carib language, also known as Kalina, the language of the South American Caribs
*Kalinago people, or Island Caribs, an indigenous pe ...
, an ethnic group present in the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc bet ...
and parts of adjacent South America at the time of the Spanish conquest of the Americas
Spain began colonizing the Americas under the Crown of Castile and was spearheaded by the Spanish . The Americas were invaded and incorporated into the Spanish Empire, with the exception of Brazil, British America, and some small region ...
.
The two most prevalent pronunciations of "Caribbean" outside the Caribbean are (), with the primary stress on the third syllable, and (), with the stress on the second. Most authorities of the last century preferred the stress on the third syllable. This is the older of the two pronunciations, but the stressed-second-syllable variant has been established for over 75 years. It has been suggested that speakers of British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in ...
prefer () while North American speakers more typically use (), but major American dictionaries and other sources list the stress on the third syllable as more common in American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the most widely spoken language in the United States and in most circumstances i ...
too. According to the American version of Oxford Online Dictionaries, the stress on the second syllable is becoming more common in UK English and is increasingly considered "by some" to be more up to date and more "correct".Oxford Online Dictionaries/ref> The Oxford Online Dictionaries claim that the stress on the second syllable is the most common pronunciation in the Caribbean itself, but according to the Dictionary of Caribbean English Usage, the most common pronunciation in
Caribbean English
Caribbean English (CE, CarE) is a set of dialects of the English language which are spoken in the Caribbean and Liberia, most countries on the Caribbean coast of Central America, and Guyana and Suriname on the coast of South America. Carib ...
stresses the first syllable instead, ().
Definition
 The word "Caribbean" has multiple uses. Its principal ones are geographical and political. The Caribbean can also be expanded to include territories with strong cultural and historical connections to Africa,
The word "Caribbean" has multiple uses. Its principal ones are geographical and political. The Caribbean can also be expanded to include territories with strong cultural and historical connections to Africa, slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
, European colonisation and the plantation system
A plantation economy is an economy based on agricultural mass production, usually of a few commodity crops, grown on large farms worked by laborers or slaves. The properties are called plantations. Plantation economies rely on the export of cash ...
.
* The United Nations geoscheme for the Americas
The following is an alphabetical list of countries in the United Nations geoscheme for the Americas grouped by subregion and (if applicable) intermediate region. Note that the continent of North America comprises the intermediate regions of th ...
presents the Caribbean as a distinct region within the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
.
* Physiographically, the Caribbean region is mainly a chain of islands surrounding the Caribbean Sea. To the north, the region is bordered by the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United ...
, the Straits of Florida
The Straits of Florida, Florida Straits, or Florida Strait ( es, Estrecho de Florida) is a strait located south-southeast of the North American mainland, generally accepted to be between the Gulf of Mexico and the Atlantic Ocean, and between t ...
and the Northern Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
, which lies to the east and northeast. To the south lies the coastline of the continent of South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the sout ...
.
* Politically, the "Caribbean" may be centred
Countries and territories of the Caribbean today
History
 The oldest evidence of humans in the Caribbean is in southern
The oldest evidence of humans in the Caribbean is in southern Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmos ...
at Banwari Trace, where remains have been found from seven thousand years ago. These pre-ceramic sites, which belong to the Archaic (pre-ceramic) age, have been termed Ortoiroid
The Ortoiroid people were the second wave of human settlers of the Caribbean who began their migration into the Antilles around 2000 BCE. They were preceded by the Casimiroid peoples (~4190-2165 BCE). They are believed to have originated in the ...
. The earliest archaeological evidence of human settlement in Hispaniola dates to about 3600 BC, but the reliability of these finds is questioned. Consistent dates of 3100 BC appear in Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
. The earliest dates in the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc bet ...
are from 2000 BC in Antigua. A lack of pre-ceramic sites in the Windward Islands
french: Îles du Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Windward Islands. Clockwise: Dominica, Martinique, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and Grenada.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean Sea No ...
and differences in technology suggest that these Archaic settlers may have Central American origins. Whether an Ortoiroid colonization of the islands took place is uncertain, but there is little evidence of one.
DNA studies changed some of the traditional beliefs about pre-Columbian indigenous history. According to National Geographic, "studies confirm that a wave of pottery-making farmers—known as Ceramic Age people—set out in canoes from the northeastern coast of South America starting some 2,500 years ago and island-hopped across the Caribbean. They were not, however, the first colonizers. On many islands they encountered a foraging people who arrived some 6,000 or 7,000 years ago...The ceramicists, who are related to today's Arawak
The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, who historically lived in the Great ...
-speaking peoples, supplanted the earlier foraging inhabitants—presumably through disease or violence—as they settled new islands."
Between 400 BC and 200 BC the first ceramic-using agriculturalists, the Saladoid culture
The Saladoid culture is a pre-Columbian indigenous culture of territory in present-day Venezuela and the Caribbean that flourished from 500 BCE to 545 CE. The Saladoid were an Arawak people. Concentrated along the lowlands of the Orinoco River, the ...
, entered Trinidad from South America. They expanded up the Orinoco River to Trinidad, and then spread rapidly up the islands of the Caribbean. Some time after 250 AD another group, the Barancoid, entered Trinidad. The Barancoid society collapsed along the Orinoco around 650 AD and another group, the Arauquinoid, expanded into these areas and up the Caribbean chain. Around 1300 AD a new group, the Mayoid, entered Trinidad and remained the dominant culture until Spanish settlement.
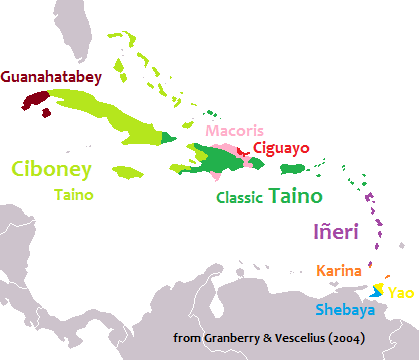
At the time of the European discovery of most of the islands of the Caribbean, three major Amerindian indigenous peoples lived on the islands: the Taíno
The Taíno were a historic indigenous people of the Caribbean whose culture has been continued today by Taíno descendant communities and Taíno revivalist communities. At the time of European contact in the late 15th century, they were the pri ...
in the Greater Antilles
The Greater Antilles ( es, Grandes Antillas or Antillas Mayores; french: Grandes Antilles; ht, Gwo Zantiy; jam, Grieta hAntiliiz) is a grouping of the larger islands in the Caribbean Sea, including Cuba, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, Jamaica, a ...
, the Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the ar ...
and the Leeward Islands, the Island Caribs and Galibi
The Kalina, also known as the Caribs or mainland Caribs and by several other names, are an indigenous people native to the northern coastal areas of South America. Today, the Kalina live largely in villages on the rivers and coasts of Venezuela, ...
in the Windward Islands, and the Ciboney
The Ciboney, or Siboney, were a Taíno people of western Cuba, Jamaica, and the Tiburon Peninsula of Haiti. A Western Taíno group living in central Cuba during the 15th and 16th centuries, they had a dialect and culture distinct from the Classi ...
in western Cuba. The Taínos are subdivided into Classic Taínos, who occupied Hispaniola and Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
, Western Taínos, who occupied Cuba, Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
, and the Bahamian archipelago, and the Eastern Taínos, who occupied the Leeward Islands. Trinidad was inhabited by both Carib speaking and Arawak-speaking groups.
European Contact
Soon afterChristopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
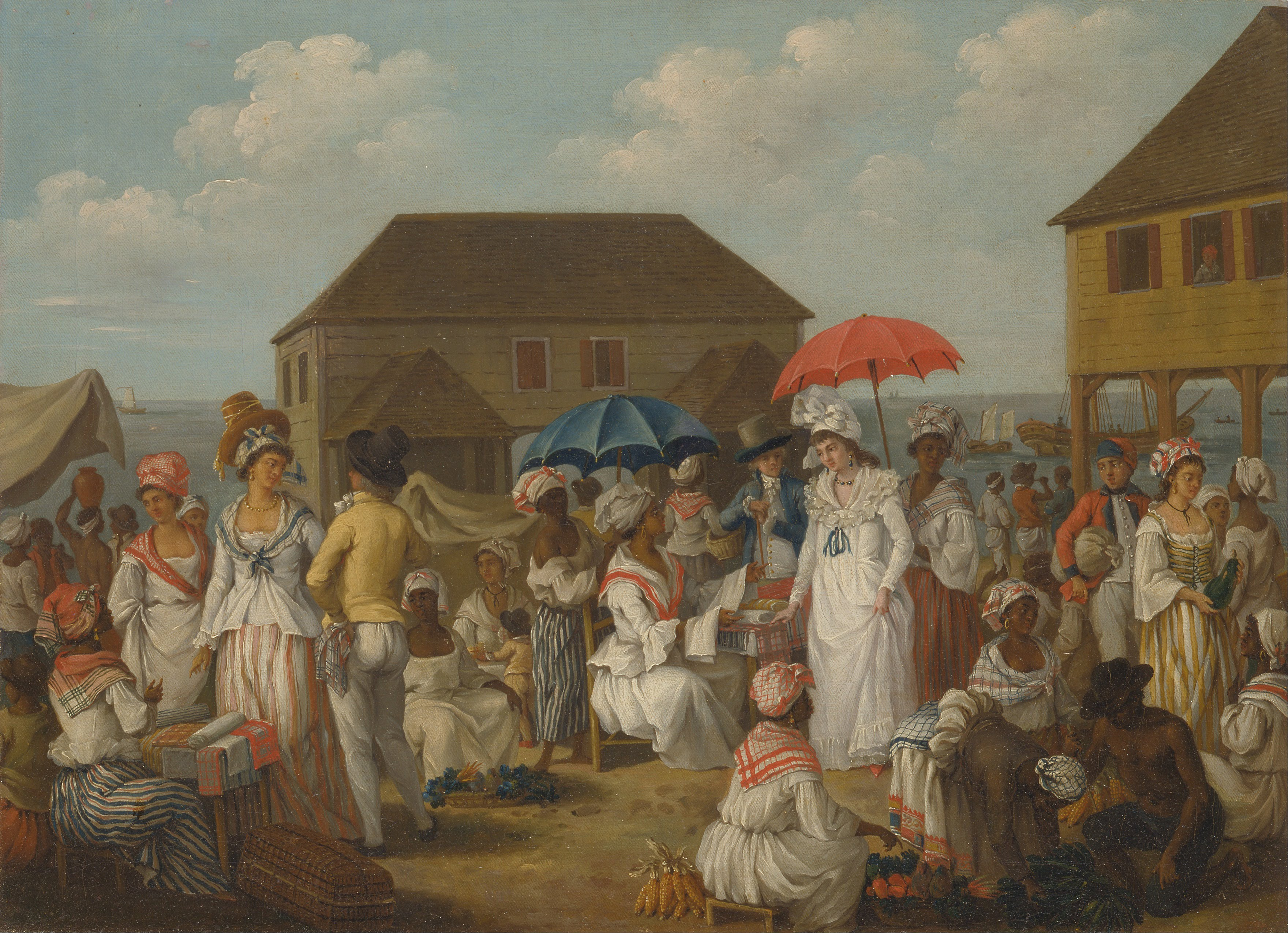
came to the Caribbean, both Portuguese and Spanish explorers began claiming territories in Central and South America. These early colonies brought gold to Europe; most specifically England, the Netherlands, and France. These nations hoped to establish profitable colonies in the Caribbean. Colonial rivalries made the Caribbean a cockpit for European wars for centuries.
Columbus, and the early colonists of Hispaniola, treated the indigenous peoples brutally, even enslaving children. In 1512, after pressure from Dominican friars, the Laws of Burgos
The Laws of Burgos ( es, Leyes de Burgos), promulgated on 27 December 1512 in Burgos, Crown of Castile (Spain), was the first codified set of laws governing the behavior of Spaniards in the Americas, particularly with regard to the Indigenous pe ...
were introduced by the Spanish Crown to better protect the rights of the New World natives. The Spanish used a form of slavery called the '' Encomienda'', where slaves would be awarded to the conquistadors, who were charged with protecting and converting their slaves. This had a devastating impact on the population, so starting in 1503, slaves from Africa were imported to the colony.
While early slave traders were Portuguese and Spanish, known as the First Atlantic System, by the 17th century the trade became dominated by British, French, and Dutch merchants. This was known as the Second Atlantic System. 5 million African slaves would be taken to the Caribbean, and around half would be traded to the British Caribbean islands. Slavery was abolished first in the Dutch Empire in 1814. Spain abolished slavery in its empire in 1811, with the exceptions of Cuba, Puerto Rico, and Santo Domingo. Slavery was not abolished in Cuba until 1886. Britain abolished the slave trade in 1807, and slavery proper in 1833. France abolished slavery in its colonies in 1848. The Caribbean was known for pirates, especially between 1640 and 1680. The term "
The Caribbean was known for pirates, especially between 1640 and 1680. The term "buccaneer
Buccaneers were a kind of privateers or free sailors particular to the Caribbean Sea during the 17th and 18th centuries. First established on northern Hispaniola as early as 1625, their heyday was from the Restoration in 1660 until about 168 ...
" is often used to describe a pirate operating in this region. The Caribbean region was war-torn throughout much of its colonial history, but the wars were often based in Europe, with only minor battles fought in the Caribbean. Some wars, however, were born of political turmoil in the Caribbean itself.
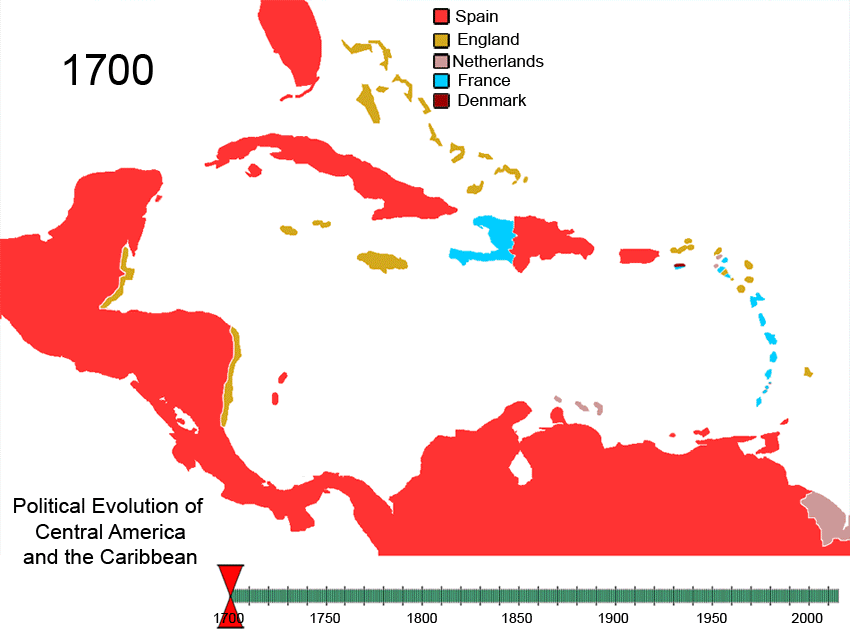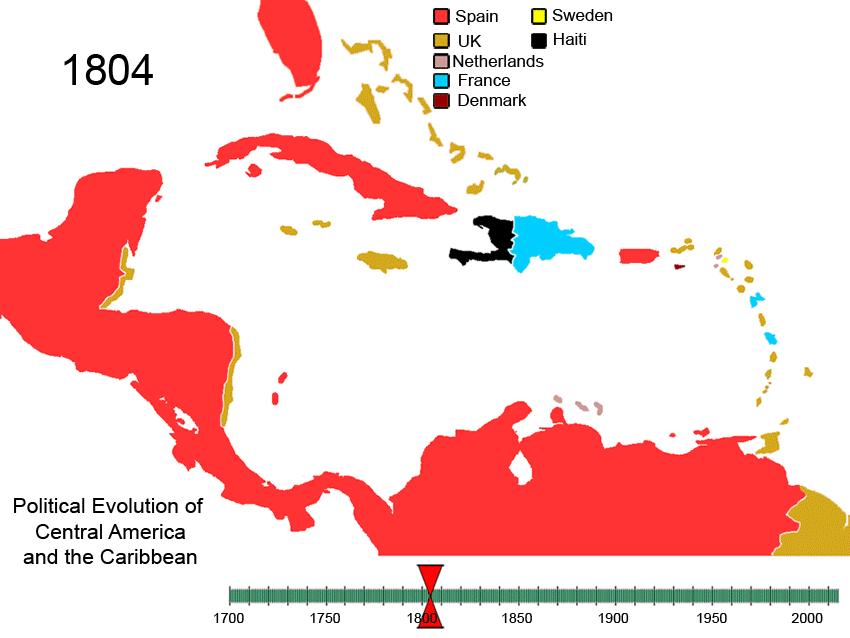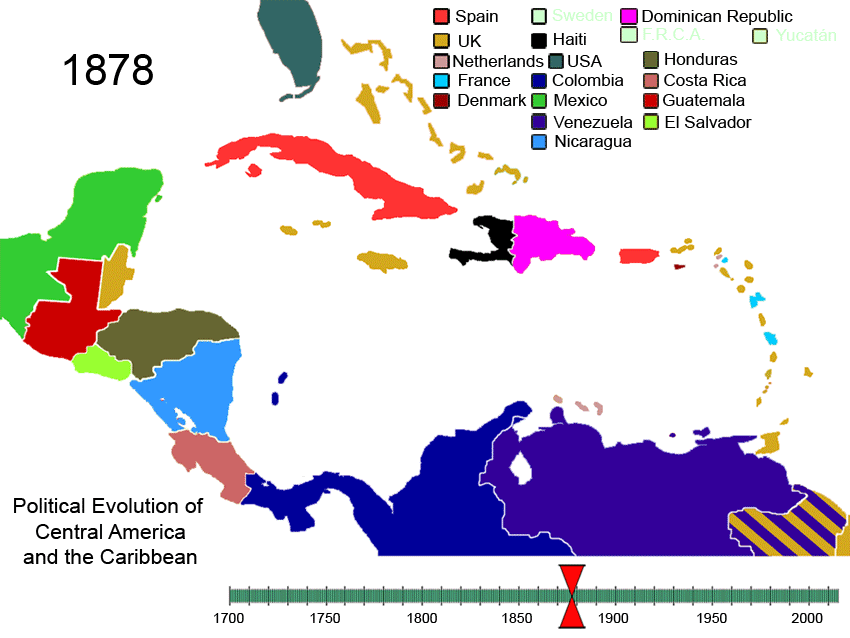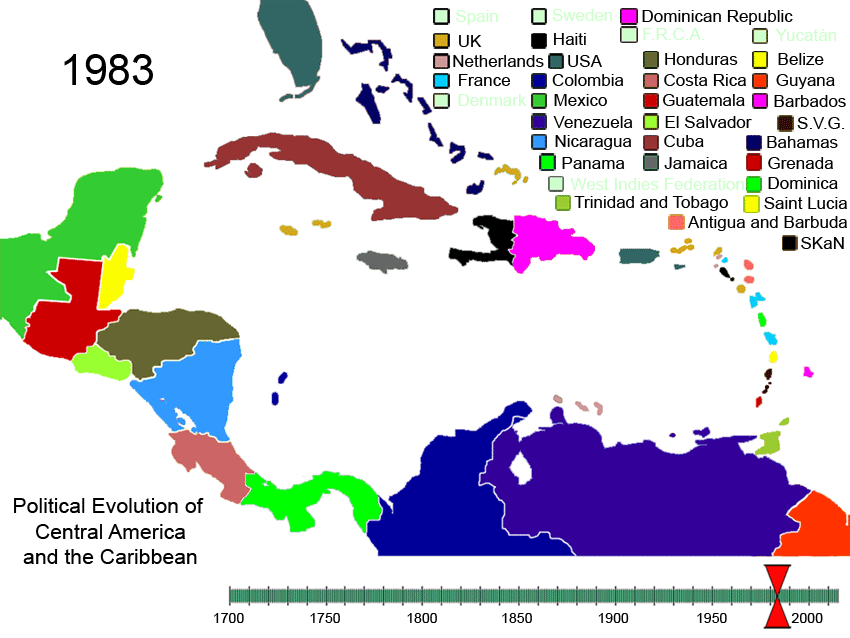
In 1791, a slave rebellion in the French colony of Saint-Domingue led to the establishment in 1804 of Haiti, the first republic in the Caribbean. Cuba became independent in 1898 following American intervention in the War of Independence
This is a list of wars of independence (also called liberation wars). These wars may or may not have been successful in achieving a goal of independence.
List
See also
* Lists of active separatist movements
* List of civil wars
* List o ...
during the Spanish-American war
Spanish Americans ( es, españoles estadounidenses, ''hispanoestadounidenses'', or ''hispanonorteamericanos'') are Americans whose ancestry originates wholly or partly from Spain. They are the longest-established European American group in th ...
. Following the war, Spain's last colony in the Americas, Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
, became an unincorporated territory of the United States.
Decolonisation and Modern period
Between the 1960s and 80s, most of the British holdings in the Caribbean achieved independence, starting with Jamaica in 1962, thenTrinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of ...
(1962), Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...
(1966), Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the ar ...
(1973), Grenada (1974), Dominica (1978), St. Lucia
Saint Lucia ( acf, Sent Lisi, french: Sainte-Lucie) is an island country of the West Indies in the eastern Caribbean. The island was previously called Iouanalao and later Hewanorra, names given by the native Arawaks and Caribs, two Amerin ...
(1979), St. Vincent (1979), Antigua and Barbuda (1981), St. Kitts and Nevis (1983). Presently, the United States, Britain, France and the Netherlands still have some Caribbean possessions.
The decline of the export industries meant a need to diversify the economies of the Caribbean territories. The tourism industry started developing in the early 20th century, rapidly developing in the 1960s when regular international flights made vacations affordable and is now a $50 billion industry. Another industry that developed in the early 20th century was offshore banking and financial services, particularly in The Bahamas and the Cayman Islands, as the proximity of the Caribbean islands to the United States made them an attractive location for branches of foreign banks seeking to avoid taxes.
US interventions
TheUnited States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
has conducted military operations in the Caribbean for at least 100 years.
Since the Monroe Doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine was a United States foreign policy position that opposed European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere. It held that any intervention in the political affairs of the Americas by foreign powers was a potentially hostile act ...
, the United States gained a major influence on most Caribbean nations. In the early part of the 20th century this influence was extended by participation in the Banana Wars
The Banana Wars were a series of conflicts that consisted of military occupation, police action, and intervention by the United States in Central America and the Caribbean between the end of the Spanish–American War in 1898 and the inceptio ...
. Victory in the Spanish–American War and the signing of the Platt Amendment
On March 2, 1901, the Platt Amendment was passed as part of the 1901 Army Appropriations Bill.Cuban Revolution
The Cuban Revolution ( es, Revolución Cubana) was carried out after the 1952 Cuban coup d'état which placed Fulgencio Batista as head of state and the failed mass strike in opposition that followed. After failing to contest Batista in co ...
of 1959, relations deteriorated rapidly leading to the Bay of Pigs Invasion
The Bay of Pigs Invasion (, sometimes called ''Invasión de Playa Girón'' or ''Batalla de Playa Girón'' after the Playa Girón) was a failed military landing operation on the southwestern coast of Cuba in 1961 by Cuban exiles, covertly fin ...
, the Cuban Missile Crisis, and successive US attempts to destabilize the island, based upon Cold War fears of the Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
threat. The US invaded and occupied Hispaniola for 19 years (1915–34), subsequently dominating the Haitian economy through aid and loan repayments. The US invaded Haiti again in 1994 and in 2004 were accused by CARICOM of arranging a coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
to remove elected Haitian leader Jean-Bertrand Aristide. In 1965, 23,000 US troops were sent to the Dominican Republic to quash a local uprising against military rule (see Dominican Civil War
The Dominican Civil War (), also known as the April Revolution (), took place between April 24, 1965, and September 3, 1965, in Santo Domingo, Dominican Republic. It started when civilian and military supporters of the overthrown democraticall ...
). President Lyndon Johnson had ordered the invasion to stem what he deemed to be a "Communist threat." However, the mission appeared ambiguous and was roundly condemned throughout the hemisphere as a return to gunboat diplomacy
In international politics, the term gunboat diplomacy refers to the pursuit of foreign policy objectives with the aid of conspicuous displays of naval power, implying or constituting a direct threat of warfare should terms not be agreeable to t ...
. In 1983, the US invaded Grenada to remove populist left-wing leader Maurice Bishop. The US maintains a naval military base in Cuba at Guantanamo Bay. The base is one of five unified commands whose "area of responsibility" is Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived f ...
and the Caribbean. The command is headquartered in Miami, Florida.
Cuban Revolutionary Armed Forces
The Cuban Revolutionary Armed Forces ( es, Fuerzas Armadas Revolucionarias; FAR) are the military forces of Cuba. They include ground forces, naval forces, air and air defence forces, and other paramilitary bodies including the Territorial T ...
supported by T-34
The T-34 is a Soviet medium tank introduced in 1940. When introduced its 76.2 mm (3 in) tank gun was less powerful than its contemporaries while its 60-degree sloped armour provided good protection against anti-tank weapons. The C ...
tanks near Playa Giron during the Bay of Pigs Invasion
The Bay of Pigs Invasion (, sometimes called ''Invasión de Playa Girón'' or ''Batalla de Playa Girón'' after the Playa Girón) was a failed military landing operation on the southwestern coast of Cuba in 1961 by Cuban exiles, covertly fin ...
, 19 April 1961.
File:DR1965-5 (8161964889).jpg, A Marine heavy machine gunner monitors a position along the international neutral corridor in Santo Domingo, 1965.
File:BTR-60PB Urgent Fury.jpg, A Soviet-made BTR-60
The BTR-60 is the first vehicle in a series of Soviet eight-wheeled armoured personnel carriers (APCs). It was developed in the late 1950s as a replacement for the BTR-152 and was seen in public for the first time in 1961. BTR stands for ''Brone ...
armored personnel carrier seized by US forces during Operation Urgent Fury (1983)
File:US Army helicopters on forward flight deck of USS Eisenhower (CVN-69) off Haiti in 1994.JPEG, US Army Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk
The Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk is a four-blade, twin-engine, medium-lift utility military helicopter manufactured by Sikorsky Aircraft. Sikorsky submitted the S-70 design for the United States Army's Utility Tactical Transport Aircraft System ( ...
, Bell AH-1 Cobra and Bell OH-58 Kiowa helicopters on deck of the US Navy aircraft carrier USS ''Dwight D. Eisenhower'' ( CVN-69) off Haiti, 1994.
Geography and geology
 The geography and climate in the Caribbean region varies: Some islands in the region have relatively flat terrain of non-volcanic origin. These islands include Aruba (possessing only minor volcanic features), Curaçao,
The geography and climate in the Caribbean region varies: Some islands in the region have relatively flat terrain of non-volcanic origin. These islands include Aruba (possessing only minor volcanic features), Curaçao, Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...
, Bonaire, the Cayman Islands, Saint Croix
Saint Croix; nl, Sint-Kruis; french: link=no, Sainte-Croix; Danish and no, Sankt Croix, Taino: ''Ay Ay'' ( ) is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincor ...
, the Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the ar ...
, and Antigua. Others possess rugged towering mountain-ranges like the islands of Saint Martin, Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
, Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
, Dominica, Montserrat, Saba Saba may refer to:
Places
* Saba (island), an island of the Netherlands located in the Caribbean Sea
* Şaba (Romanian for Shabo), a town of the Odesa Oblast, Ukraine
* Sabá, a municipality in the department of Colón, Honduras
* Saba (river), ...
, Sint Eustatius, Saint Kitts
Saint Kitts, officially the Saint Christopher Island, is an island in the West Indies. The west side of the island borders the Caribbean Sea, and the eastern coast faces the Atlantic Ocean. Saint Kitts and the neighbouring island of Nevis cons ...
, Saint Lucia, Saint Thomas, Saint John, Tortola
Tortola () is the largest and most populated island of the British Virgin Islands, a group of islands that form part of the archipelago of the Virgin Islands. It has a surface area of with a total population of 23,908, with 9,400 residents in ...
, Grenada, Saint Vincent, Guadeloupe, Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago: or ) is an island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of the French Republic, Martinique is located in ...
and Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of ...
.
Definitions of the terms Greater Antilles and Lesser Antilles often vary. The Virgin Islands as part of the Puerto Rican bank are sometimes included with the Greater Antilles. The term Lesser Antilles is often used to define an island arc that includes Grenada but excludes Trinidad and Tobago and the Leeward Antilles.
The waters of the Caribbean Sea host large, migratory schools of fish, turtles, and coral reef
A coral reef is an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals. Reefs are formed of colonies of coral polyps held together by calcium carbonate. Most coral reefs are built from stony corals, whose polyps cluster in groups.
C ...
formations. The Puerto Rico Trench
The Puerto Rico Trench is located on the boundary between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. The oceanic trench, the deepest in the Atlantic, is associated with a complex transition between the Lesser Antilles subduction zone to the sou ...
, located on the fringe of the Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea just to the north of the island of Puerto Rico, is the deepest point in all of the Atlantic Ocean.
The region sits in the line of several major shipping routes with the Panama Canal
The Panama Canal ( es, Canal de Panamá, link=no) is an artificial waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean and divides North and South America. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a condui ...
connecting the western Caribbean Sea with the Pacific Ocean.
Climate

tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
, varying from tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equa ...
in some areas to tropical monsoon and tropical savanna
Tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands is a terrestrial biome defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature. The biome is dominated by grass and/or shrubs located in semi-arid to semi-humid climate regions of subtropical and t ...
in others. There are also some locations that are arid
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most ...
climates with considerable drought in some years, and the peaks of mountains tend to have cooler temperate climate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
s.
Rainfall varies with elevation, size and water currents, such as the cool upwellings that keep the ABC islands arid. Warm, moist trade winds
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisp ...
blow consistently from the east, creating both rain forest and semi arid climates across the region. The tropical rainforest climates include lowland areas near the Caribbean Sea from Costa Rica north to Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wate ...
, as well as the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
and Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
, while the more seasonal dry tropical savanna climates are found in Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
, northern Colombia and Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, and southern Yucatán, Mexico. Arid climates are found along the extreme northern coast of Venezuela out to the islands including Aruba and Curacao, as well as the northwestern tip of Yucatán.
While the region generally is sunny much of the year, the wet season from May through November sees more frequent cloud cover (both broken and overcast), while the dry season from December through April is more often clear to mostly sunny. Seasonal rainfall is divided into 'dry' and 'wet' seasons, with the latter six months of the year being wetter than the first half. The air temperature is hot much of the year, varying from 25 to 33 C (77 F to 90 F) between the wet and dry seasons. Seasonally, monthly mean temperatures vary from only about 5 C (7 F) in the northern most regions, to less than 3 C in the southernmost areas of the Caribbean.
Hurricane season is from June to November, but they occur more frequently in August and September and more common in the northern islands of the Caribbean. Hurricanes
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
that sometimes batter the region usually strike northwards of Grenada and to the west of Barbados. The principal hurricane belt arcs to northwest of the island of Barbados in the Eastern Caribbean. A great example being recent events of Hurricane Irma devastating the island of Saint Martin during the 2017 hurricane season.
Sea surface temperatures change little annually, normally running from 30 °C (87 °F) in the warmest months to 26 °C (76 °F) in the coolest months. The air temperature is warm year round, in the 70s, 80s and 90s, and only varies from winter to summer about 2–5 degrees on the southern islands and about a 10–20 degrees difference on the northern islands of the Caribbean. The northern islands, like the Bahamas, Cuba, Puerto Rico and the Dominican Republic, may be influenced by continental masses during winter months, such as cold fronts.
Aruba: Latitude 12°N
Puerto Rico: Latitude 18°N
Cuba: at Latitude 22°N





Island groups
Lucayan Archipelago
The Lucayan Archipelago (named for the original native Lucayan people), also known as the Bahama Archipelago, is an island group comprising the Commonwealth of The Bahamas and the British Overseas Territory of the Turks and Caicos Islands. The ar ...
*
* (United Kingdom)
Greater Antilles
The Greater Antilles ( es, Grandes Antillas or Antillas Mayores; french: Grandes Antilles; ht, Gwo Zantiy; jam, Grieta hAntiliiz) is a grouping of the larger islands in the Caribbean Sea, including Cuba, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, Jamaica, a ...
* (United Kingdom)
*
* Hispaniola
**
**
*
* ( U.S. Commonwealth)
** Spanish Virgin Islands
Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc bet ...
* Leeward Islands
** (U.S.)
*** Saint Croix
Saint Croix; nl, Sint-Kruis; french: link=no, Sainte-Croix; Danish and no, Sankt Croix, Taino: ''Ay Ay'' ( ) is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincor ...
*** Saint Thomas
*** Saint John
*** Water Island
** (United Kingdom)
*** Tortola
Tortola () is the largest and most populated island of the British Virgin Islands, a group of islands that form part of the archipelago of the Virgin Islands. It has a surface area of with a total population of 23,908, with 9,400 residents in ...
*** Virgin Gorda
Virgin Gorda () is the third-largest island (after Tortola and Anegada) and second-most populous of the British Virgin Islands (BVI).
Geography
Located at about 18 degrees, 48 minutes North, and 64 degrees, 30 minutes West, it covers an area ...
*** Anegada
Anegada is the northernmost of the British Virgin Islands (BVI), a group of islands that form part of the archipelago of the Virgin Islands. It lies approximately north of Virgin Gorda. Anegada is the only inhabited British Virgin Island for ...
*** Jost Van Dyke
Jost Van Dyke (; sometimes colloquially referred to as JVD or Jost) is the smallest of the four main islands of the British Virgin Islands, measuring roughly . It rests in the northern portion of the archipelago of the Virgin Islands, loca ...
** (United Kingdom)
**
*** Antigua
*** Barbuda
Barbuda (), is an island located in the eastern Caribbean forming part of the sovereign state of Antigua and Barbuda. It is located north of the island of Antigua and is part of the Leeward Islands of the West Indies. The island is a popula ...
*** Redonda
Redonda is an uninhabited Caribbean island that is a part of Antigua and Barbuda, in the Leeward Islands, West Indies. The island is about long, wide, and is high at its highest point.
This small island lies between the islands of Nevis and ...
** Saint Martin, politically divided between
*** (France)
*** (Kingdom of the Netherlands
, national_anthem = )
, image_map = Kingdom of the Netherlands (orthographic projection).svg
, map_width = 250px
, image_map2 = File:KonDerNed-10-10-10.png
, map_caption2 = Map of the four constituent countries shown to scale
, capital = ...
)
** (Caribbean Netherlands
)
, image_map = BES islands location map.svg
, map_caption = Location of the Caribbean Netherlands (green and circled). From left to right: Bonaire, Saba, and Sint Eustatius
, elevation_max_m = 887
, elevation_max_footnotes =
, demographic ...
, Netherlands)
** (Caribbean Netherlands
)
, image_map = BES islands location map.svg
, map_caption = Location of the Caribbean Netherlands (green and circled). From left to right: Bonaire, Saba, and Sint Eustatius
, elevation_max_m = 887
, elevation_max_footnotes =
, demographic ...
, Netherlands)
** (French Antilles
The French West Indies or French Antilles (french: Antilles françaises, ; gcf, label= Antillean Creole, Antiy fwansez) are the parts of France located in the Antilles islands of the Caribbean:
* The two overseas departments of:
** Guadeloup ...
, France)
**
*** Saint Kitts
Saint Kitts, officially the Saint Christopher Island, is an island in the West Indies. The west side of the island borders the Caribbean Sea, and the eastern coast faces the Atlantic Ocean. Saint Kitts and the neighbouring island of Nevis cons ...
*** Nevis
Nevis is a small island in the Caribbean Sea that forms part of the inner arc of the Leeward Islands chain of the West Indies. Nevis and the neighbouring island of Saint Kitts constitute one country: the Federation of Saint Kitts and ...
** (United Kingdom)
** (French Antilles
The French West Indies or French Antilles (french: Antilles françaises, ; gcf, label= Antillean Creole, Antiy fwansez) are the parts of France located in the Antilles islands of the Caribbean:
* The two overseas departments of:
** Guadeloup ...
, France) including
*** Les Saintes
*** Marie-Galante
Marie-Galante ( gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Mawigalant) is one of the islands that form Guadeloupe, an overseas department of France. Marie-Galante has a land area of . It had 11,528 inhabitants at the start of 2013, but by the start of 2018 ...
*** La Désirade
La Désirade is an island in the French West Indies, in the Lesser Antilles of the Caribbean. It forms part of Guadeloupe, an overseas region of France.
History
Archaeological evidence has been discovered that suggests that an Amerindian p ...
* Windward Islands
french: Îles du Vent
, image_name =
, image_caption = ''Political'' Windward Islands. Clockwise: Dominica, Martinique, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, and Grenada.
, image_alt =
, locator_map =
, location = Caribbean Sea No ...
**
** (French Antilles
The French West Indies or French Antilles (french: Antilles françaises, ; gcf, label= Antillean Creole, Antiy fwansez) are the parts of France located in the Antilles islands of the Caribbean:
* The two overseas departments of:
** Guadeloup ...
, France)
**
**
*** Saint Vincent
*** The Grenadines
**
*** Grenada
*** Carriacou and Petite Martinique
**
**
*** Tobago
Tobago () is an List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, island and Regions and municipalities of Trinidad and Tobago, ward within the Trinidad and Tobago, Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located northeast of the larger island of Trini ...
*** Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmos ...
* Leeward Antilles
The Leeward Antilles ( nl, Benedenwindse Eilanden) are a chain of islands in the Caribbean – specifically, the southerly islands of the Lesser Antilles (and, in turn, the Antilles and the West Indies) along the southeastern fringe of the C ...
** (Kingdom of the Netherlands
, national_anthem = )
, image_map = Kingdom of the Netherlands (orthographic projection).svg
, map_width = 250px
, image_map2 = File:KonDerNed-10-10-10.png
, map_caption2 = Map of the four constituent countries shown to scale
, capital = ...
)
** (Kingdom of the Netherlands
, national_anthem = )
, image_map = Kingdom of the Netherlands (orthographic projection).svg
, map_width = 250px
, image_map2 = File:KonDerNed-10-10-10.png
, map_caption2 = Map of the four constituent countries shown to scale
, capital = ...
)
** (Caribbean Netherlands
)
, image_map = BES islands location map.svg
, map_caption = Location of the Caribbean Netherlands (green and circled). From left to right: Bonaire, Saba, and Sint Eustatius
, elevation_max_m = 887
, elevation_max_footnotes =
, demographic ...
, Netherlands)
** (Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
)
**
Historical groupings



colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
of European nations; a few are overseas or dependent territories:
* British West Indies
The British West Indies (BWI) were colonized British territories in the West Indies: Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grena ...
/ Anglophone Caribbean – Anguilla
Anguilla ( ) is a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Saint Martin. The terr ...
, Antigua and Barbuda, Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the ar ...
, Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...
, Bay Islands Bay Islands may refer to:
* Bay Islands Department, Honduras
* Southern Moreton Bay Islands, Queensland, Australia
See also
* Bay of Islands
* Bay of Isles
* Island Bay, Wellington
* Little Bay Islands
Little Bay Islands is a vacant town in ...
, Guyana, Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wate ...
, British Virgin Islands
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = Territorial song
, song = " Oh, Beautiful Virgin Islands"
, image_map = File:British Virgin Islands on the globe (Americas centered).svg
, map_caption =
, mapsize = 290px
, image_map2 = Bri ...
, Cayman Islands, Dominica, Grenada, Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
, Montserrat, Saint Croix
Saint Croix; nl, Sint-Kruis; french: link=no, Sainte-Croix; Danish and no, Sankt Croix, Taino: ''Ay Ay'' ( ) is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincor ...
(briefly), Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis (), officially the Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis, is an island country and microstate consisting of the two islands of Saint Kitts and Nevis, both located in the West Indies, in the Leeward Islands chain ...
, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines () is an island country in the Caribbean. It is located in the southeast Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, which lie in the West Indies at the southern end of the eastern border of the Caribbean Sea w ...
, Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of ...
(from 1797) and the Turks and Caicos Islands
The Turks and Caicos Islands (abbreviated TCI; and ) are a British Overseas Territory consisting of the larger Caicos Islands and smaller Turks Islands, two groups of tropical islands in the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean and n ...
* Danish West Indies
The Danish West Indies ( da, Dansk Vestindien) or Danish Antilles or Danish Virgin Islands were a Danish colony in the Caribbean, consisting of the islands of Saint Thomas with ; Saint John ( da, St. Jan) with ; and Saint Croix with . The ...
– Possession of Denmark-Norway before 1814
Events January
* January 1 – War of the Sixth Coalition – The Royal Prussian Army led by Gebhard Leberecht von Blücher crosses the Rhine.
* January 3
** War of the Sixth Coalition – Siege of Cattaro: French garrison ...
, then Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
, present-day United States Virgin Islands
The United States Virgin Islands,. Also called the ''American Virgin Islands'' and the ''U.S. Virgin Islands''. officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and an unincorporated and organized territory ...
* Dutch West Indies
The Dutch Caribbean (historically known as the Dutch West Indies) are the territories, colonies, and countries, former and current, of the Dutch Empire and the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Caribbean Sea. They are in the north and south-wes ...
– Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao, Saba Saba may refer to:
Places
* Saba (island), an island of the Netherlands located in the Caribbean Sea
* Şaba (Romanian for Shabo), a town of the Odesa Oblast, Ukraine
* Sabá, a municipality in the department of Colón, Honduras
* Saba (river), ...
, Sint Eustatius, Sint Maarten
Sint Maarten () is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Caribbean. With a population of 41,486 as of January 2019 on an area of , it encompasses the southern 44% of the divided island of Saint Martin, while the nort ...
, Bay Islands Bay Islands may refer to:
* Bay Islands Department, Honduras
* Southern Moreton Bay Islands, Queensland, Australia
See also
* Bay of Islands
* Bay of Isles
* Island Bay, Wellington
* Little Bay Islands
Little Bay Islands is a vacant town in ...
(briefly), Saint Croix
Saint Croix; nl, Sint-Kruis; french: link=no, Sainte-Croix; Danish and no, Sankt Croix, Taino: ''Ay Ay'' ( ) is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincor ...
(briefly), Tobago
Tobago () is an List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, island and Regions and municipalities of Trinidad and Tobago, ward within the Trinidad and Tobago, Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located northeast of the larger island of Trini ...
, Surinam and Virgin Islands
The Virgin Islands ( es, Islas Vírgenes) are an archipelago in the Caribbean Sea. They are geologically and biogeographically the easternmost part of the Greater Antilles, the northern islands belonging to the Puerto Rico Trench and St. Cro ...
* French West Indies – Anguilla
Anguilla ( ) is a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Saint Martin. The terr ...
(briefly), Antigua and Barbuda (briefly), Dominica, Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
(briefly), Grenada, Haiti (formerly Saint-Domingue), Montserrat (briefly), Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines () is an island country in the Caribbean. It is located in the southeast Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, which lie in the West Indies at the southern end of the eastern border of the Caribbean Sea w ...
, Sint Eustatius (briefly), Sint Maarten
Sint Maarten () is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Caribbean. With a population of 41,486 as of January 2019 on an area of , it encompasses the southern 44% of the divided island of Saint Martin, while the nort ...
, St. Kitts (briefly), Tobago
Tobago () is an List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, island and Regions and municipalities of Trinidad and Tobago, ward within the Trinidad and Tobago, Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located northeast of the larger island of Trini ...
(briefly), Saint Croix
Saint Croix; nl, Sint-Kruis; french: link=no, Sainte-Croix; Danish and no, Sankt Croix, Taino: ''Ay Ay'' ( ) is an island in the Caribbean Sea, and a county and constituent district of the United States Virgin Islands (USVI), an unincor ...
, the current French overseas ''départements'' of French Guiana
French Guiana ( or ; french: link=no, Guyane ; gcr, label=French Guianese Creole, Lagwiyann ) is an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France on the northern Atlantic coast of South America in the Guianas. ...
, Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago: or ) is an island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of the French Republic, Martinique is located in ...
and Guadeloupe (including Marie-Galante
Marie-Galante ( gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Mawigalant) is one of the islands that form Guadeloupe, an overseas department of France. Marie-Galante has a land area of . It had 11,528 inhabitants at the start of 2013, but by the start of 2018 ...
, La Désirade
La Désirade is an island in the French West Indies, in the Lesser Antilles of the Caribbean. It forms part of Guadeloupe, an overseas region of France.
History
Archaeological evidence has been discovered that suggests that an Amerindian p ...
and Les Saintes), the current French overseas collectivities
The French overseas collectivities (''collectivité d'outre-mer'' or ''COM'') are first-order administrative divisions of France, like the French regions, but have a semi-autonomous status. The COMs include some former French overseas colonies ...
of Saint Barthélemy
Saint Barthélemy (french: Saint-Barthélemy, ), officially the Collectivité territoriale de Saint-Barthélemy, is an overseas collectivity of France in the Caribbean. It is often abbreviated to St. Barth in French, and St. Barts in English ...
and Saint Martin
* Portuguese West Indies – present-day Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...
, known as ' in the 16th century when the Portuguese claimed the island en route to Brazil. The Portuguese left Barbados abandoned years before the British arrived.
* Spanish West Indies
The Spanish West Indies or the Spanish Antilles (also known as "Las Antillas Occidentales" or simply "Las Antillas Españolas" in Spanish) were Spanish colonies in the Caribbean. In terms of governance of the Spanish Empire, The Indies was the d ...
– Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
, Hispaniola (present-day Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
), Haiti (until 1659, lost to France), Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
, Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
(until 1655, lost to Great Britain), the Cayman Islands (until 1670 to Great Britain) Trinidad
Trinidad is the larger and more populous of the two major islands of Trinidad and Tobago. The island lies off the northeastern coast of Venezuela and sits on the continental shelf of South America. It is often referred to as the southernmos ...
(until 1797, lost to Great Britain) and Bay Islands Bay Islands may refer to:
* Bay Islands Department, Honduras
* Southern Moreton Bay Islands, Queensland, Australia
See also
* Bay of Islands
* Bay of Isles
* Island Bay, Wellington
* Little Bay Islands
Little Bay Islands is a vacant town in ...
(until 1643, lost to Great Britain), coastal islands of Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
(except Belize), and some Caribbean coastal islands of Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
, Colombia, Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
, and Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
.
* Swedish West Indies – present-day French Saint-Barthélemy, Guadeloupe (briefly) and Tobago
Tobago () is an List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, island and Regions and municipalities of Trinidad and Tobago, ward within the Trinidad and Tobago, Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located northeast of the larger island of Trini ...
(briefly).
* Courlander West Indies – Tobago
Tobago () is an List of islands of Trinidad and Tobago, island and Regions and municipalities of Trinidad and Tobago, ward within the Trinidad and Tobago, Republic of Trinidad and Tobago. It is located northeast of the larger island of Trini ...
(until 1691)
The British West Indies were united by the United Kingdom into a West Indies Federation
The West Indies Federation, also known as the West Indies, the Federation of the West Indies or the West Indian Federation, was a short-lived political union that existed from 3 January 1958 to 31 May 1962. Various islands in the Caribbean that ...
between 1958 and 1962. The independent countries formerly part of the B.W.I. still have a joint cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by str ...
team that competes in Test matches, One Day Internationals and Twenty20 International
A Twenty20 International (T20I) is a form of cricket, played between two of the international members of the International Cricket Council (ICC), in which each team faces a maximum of twenty overs. The matches have top-class status and are the ...
s. The West Indian cricket team
The West Indies cricket team, nicknamed the Windies, is a multi-national men's cricket team representing the mainly English-speaking countries and territories in the Caribbean region and administered by Cricket West Indies. The players on t ...
includes the South American nation of Guyana, the only former British colony on the mainland of that continent.
In addition, these countries share the University of the West Indies as a regional entity. The university consists of three main campuses in Jamaica, Barbados and Trinidad and Tobago, a smaller campus in the Bahamas and Resident Tutors in other contributing territories such as Trinidad.
Continental countries with Caribbean coastlines and islands
* **Ambergris Caye
Ambergris Caye ( ; Spanish: Cayo Ambergris), is the largest island of Belize, located northeast of the country's mainland, in the Caribbean Sea. It is about long from north to south, and about wide. Where it has not been modified by humans, it ...
** Caye Caulker
Caye Caulker (Spanish: Cayo Caulker) is a small limestone coral island off the coast of Belize in the Caribbean Sea measuring about (north to south) by less than (east to west). The town on the island is known by the name Caye Caulker Village. T ...
** Glover's Reef
Glover's Reef is a partially submerged atoll located off the southern coast of Belize, approximately 45 kilometres from the mainland. It forms part of the outermost boundary of the Belize Barrier Reef, and is one of its three atolls, besides Turn ...
** Hick's Cayes
Hick's Cayes (Spanish: ''Cayos Hicks'') are a group of uninhabited Islands in the South of Chetumal Bay, between St. George's Caye and Caye Chapel, about halfway between Belize City and San Pedro Town
San Pedro is a town on the southern part o ...
** Lighthouse Reef
Lighthouse Reef is an atoll in the Caribbean Sea, the easternmost part of the Belize Barrier Reef and one of its three atolls, the other two being Turneffe Atoll and Glover's Reef. Lighthouse Reef is located about southeast of Belize City. The at ...
** St. George's Caye
** Tobacco Caye
Tobacco Caye is a tiny island in Belize, about east of Dangriga.
It is approximately in area, shaped like an yam, with a north-south dimension of about and an east-west dimension of . It has a permanent population of about 20, and sees a re ...
** Turneffe Atoll
Turneffe Atoll is located southeast of Ambergris Caye and Caye Caulker, off the coast of Belize in Central America, from Belize City. It is one of three atolls of the Belize Barrier Reef, along with Glover's Reef and Lighthouse Reef. It is appr ...
*
** Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina
The Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina ( es, Archipiélago de San Andrés, Providencia y Santa Catalina, ), or San Andrés and Providencia, is one of the departments of Colombia, and the only one in North America. It consis ...
***Bajo Nuevo Bank
Bajo Nuevo Bank, also known as the Petrel Islands ( es, Bajo Nuevo, Islas Petrel), is a small, uninhabited reef with some small grass-covered islets, located in the western Caribbean Sea at , with a lighthouse on Low Cay at . The closest neighb ...
***Crab Cay
Crab Cay or Cayo Cangrejo is a small island in Old Providence McBean Lagoon National Natural Park within the municipality of Providencia and Santa Catalina Islands.
See also
*Caribbean Region, Colombia
*Providencia and Santa Catalina Islands
...
***Quita Sueño Bank
Quita Sueño Bank (claimed as Quitasueño) is a reef formation of Colombia which was once claimed by the United States, located 110 km north-northeast of Providencia Island.
History
In 1869, James Jennett claimed the bank for the United Stat ...
***Roncador Bank
Roncador Bank is a mostly-submerged atoll with several sandy cays. It lies in the west Caribbean Sea off the coast of Central America. Geography
It is about 15 by 6 kilometers in size, with an area of 65 km2 composed mostly of lago ...
*** Roncador Cay
***San Andrés (island)
, native_name_lang = icr
, sobriquet =
, image_name = San Andres Island Montage.jpg
, image_size = 300px
, image_caption = Top to bottom, left to right: A ...
***Santa Catalina Island (Colombia)
Santa Catalina Island is a small Colombian island in the Caribbean Sea. It belongs to the San Andrés y Providencia Department of Colombia and is the northernmost island in South America. The island has two bays: Old John Bay and Eliza Bay.
It i ...
***Serrana Bank
Serrana Bank is a Colombian-administered atoll in the western Caribbean Sea. It is a mostly underwater reef about 50 km long and 13 km wide and has six cays, or islets, the largest of which is Southwest Cay.
Geography
The cays fro ...
***Serranilla Bank
Serranilla Bank ( es, Isla Serranilla, Banco Serranilla and ''Placer de la Serranilla'') is a partially submerged reef, with small uninhabited islets, in the western Caribbean Sea. It is situated about northeast of Punta Gorda, Nicaragua, and ...
** Rosario Islands
The Rosario Islands (Islas del Rosario), also referred to as Corales Islas del Rosario (Coral Islands of Rosario), is an archipelago located off the coast of Colombia, approximately from Cartagena. It is one of the 46 Natural National Parks ...
*
** Brava Island, Costa Rica
**Isla Calero
Isla Calero (English: Calero Island) is the largest island in Costa Rica, as well as along the San Juan River, which marks the border between Nicaragua and Costa Rica. The island lies between the San Juan (to the north and west), the Río Colorad ...
**Uvita Island
Uvita Island, or Isla Uvita (Spanish: "little grape island"), officially Isla Quiribrí, is a small island offshore of the port at Limón on the Caribbean coast of Costa Rica. The island is long from north to south and wide, northwest to sou ...
*
*
*
*
** Islas de la Bahía
*** Cayos Cochinos
The Cayos Cochinos or Cochinos Cays consist of two small islands (''Cayo Menor'' and ''Cayo Grande'') and 13 smaller coral cays situated northeast of La Ceiba on the northern shores of Honduras. Although geographically separate, they belong to ...
*** Guanaja
Guanaja is one of the Bay Islands of Honduras and is in the Caribbean. It is about off the north coast of Honduras, and from the island of Roatan. One of the cays off Guanaja, also called Guanaja or Bonacca or Low Cay (or just simply, The C ...
*** Roatán
Roatán () is an island in the Caribbean, about off the northern coast of Honduras. It is located between the islands of Utila and Guanaja, and is the largest of the Bay Islands of Honduras. The island was formerly known in English as Ruatan ...
*** Swan Islands
*** Útila
***Cayos Cochinos
The Cayos Cochinos or Cochinos Cays consist of two small islands (''Cayo Menor'' and ''Cayo Grande'') and 13 smaller coral cays situated northeast of La Ceiba on the northern shores of Honduras. Although geographically separate, they belong to ...
*** Cayo Gorda
**Bobel Cay Bobel Cay is an island in Honduras, located around 500km off the east coast of the South American continent.
Location
Bobel Cay is of the most southerly islands under Honduras’ jurisdiction, and the cay is located close to the border of Nicarag ...
*
** Corn Islands
The Corn Islands are two islands about east of the Caribbean coast of Nicaragua, constituting one of 12 municipalities of the South Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region. The official name of the municipality is ''Corn Island'' (the English name is ...
** Miskito Cays
The Miskito Cays (Spanish: Cayos Miskitos) are an archipelago with an area of 27 km2 located off shore in the northeastern Caribbean coast of Nicaragua, part of the North Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region. The Miskito Cays are composed of 7 ...
** Pearl Cays The Pearl Cays (Spanish: ''Cayos Perlas'') is a group of 18 cays located about from Pearl Lagoon (Spanish: Laguna de Perlas) off the Caribbean coast of Nicaragua. They are part of the South Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region. The Pearl Cays are cov ...
***Calala Island
Calala Island is a private island located in the Caribbean Sea, forming part of an archipelago of islands known as the Pearl Cays, off the coast of Nicaragua.
Calala Island is privately owned by the Wickham family. The whole island operates as ...
**Rama Cay
Rama Cay is an island in the Bluefields Lagoon on the eastern coast of Nicaragua. During the 17th or 18th century, the more powerful Miskito awarded the island to the Rama people in recognition of their assistance in fighting off the Terraba
T ...
*
** Archipelago off Guna Yala
Guna Yala, formerly known as San Blas, is a '' comarca indígena'' (indigenous province) in northeast Panama. Guna Yala is home to the indigenous people known as the Gunas. Its capital is Gaigirgordub. It is bounded on the north by the Car ...
coast (including the San Blas Islands
The San Blas Islands of Panama is an archipelago comprising approximately 365 islands and cays, of which 49 are inhabited. They lie off the north coast of the Isthmus of Panama, east of the Panama Canal. A part of the ''comarca'' (district) Guna ...
)
** Bocas del Toro Archipelago
The Bocas del Toro Archipelago is a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea in the northwest of Panama. The archipelago separates Almirante Bay and Chiriquí Lagoon from the open Caribbean Sea. The archipelago is part of the Bocas del Toro Distric ...
(approximately 300 islands)
** Galeta Island (Panama)
** Isla Grande
**Soledad Miria
Soledad Miria (in the Kuna language Miria Ubigantupu or more recently Mirya Ubgigandub) is a small Caribbean island of Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a t ...
*** Cayos Limones
*
** Quintana Roo
Quintana Roo ( , ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Quintana Roo ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Quintana Roo), is one of the 31 states which, with Mexico City, constitute the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It is divided into 11 mu ...
*** Banco Chinchorro
Banco Chinchorro is an atoll reef lying off the southeast coast of the Municipality of Othón P. Blanco in Quintana Roo, Mexico, near Belize. It was featured throughout the 2009 semi-documentary film ''Alamar'' by Pedro González-Rubio.
Geograp ...
*** Cozumel
Cozumel (; yua, Kùutsmil) is an island and municipality in the Caribbean Sea off the eastern coast of Mexico's Yucatán Peninsula, opposite Playa del Carmen. It is separated from the mainland by the Cozumel Channel and is close to the Yucat� ...
*** Isla Blanca
*** Isla Contoy
Isla Contoy is a small island in the Mexican state of Quintana Roo, approximately 30 kilometers north of Isla Mujeres. The island is only in length and has an area of .
Since 1961, Isla Contoy is protected by the Mexican government and was decla ...
*** Isla Holbox
*** Isla Mujeres
Isla Mujeres (, Spanish for "Women Island" (formally “Isla de Mujeres”) is an island where the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea meet, about off the Yucatán Peninsula coast in the State of Quintana Roo, Mexico. It is approximately long ...
*
*
** Blanquilla Island
Blanquilla is an island, one of the Federal Dependencies of Venezuela, located in the southeastern Caribbean Sea about 293 km (182 miles) northeast of Caracas. It is a popular location for divers, as well as famous for its white sand beac ...
** Coche Island
Isla de Coche (''Coche Island'') is one of three islands forming the Nueva Esparta State of Venezuela, located in the Caribbean between Isla Margarita and the mainland. The other two islands are Isla Margarita, the main island of the state, and ...
** Cubagua Island
** Isla Aves
Isla de Aves (; Spanish for "Island of Birds" or "Birds Island"), or Aves Island, is a Federal Dependency of Venezuela. It has been the subject of numerous territorial disputes (now resolved) with the United States (through the Guano Islands A ...
** Islas Los Frailes
The Islas Los Frailes are an archipelago of rock islets with sparse scrub vegetation belonging to the Federal dependencies of Venezuela, part of Venezuela.Vargas, Francisco Alejandro. 1983: Nuestros héroes navales. Comandancia General de la Armad ...
** Isla Margarita
Margarita Island (, ) is the largest island in the Venezuelan state of Nueva Esparta, situated off the northeastern coast of the country, in the Caribbean Sea. The capital city of Nueva Esparta, La Asunción, is located on the island.
History
...
** La Orchila
La Orchila Island is an island and a military base off the coast of Venezuela, north of Caracas. It has numerous beaches, including one where the sand is markedly pink (Arena Rosada).
There is a presidential retreat on this island, and the re ...
** La Sola Island La Sola Island ( es, Isla La Sola) is a small island in the southeastern Caribbean Sea. The island is a part of the ''Dependencias Federales'' (Federal Dependencies) of Venezuela.
Geography
La Sola Island is located about northeast of Caracas, ab ...
** La Tortuga Island
La Tortuga Island (; "La Tortuga" means "the turtle") is an uninhabited island of Venezuela, the largest in the Federal Dependencies of Venezuela. It is part of a group of islands that include the Tortuguillos and Cayo Herradura. Isla La Tortu ...
** Las Aves archipelago
The Las Aves Archipelago is a pristine archipelago in the Caribbean Sea, and is part of the Federal Dependencies of Venezuela. It is located north of the Venezuelan states of Aragua and Carabobo, between the Dutch island Bonaire in the west, an ...
** Los Hermanos Archipelago
The Los Hermanos Archipelago is a chain of seven rocky barren islets that is part of the Federal Dependencies of Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), ...
** Los Monjes Archipelago
The Los Monjes islands (Spanish: ''Archipiélago Los Monjes'') is a federal dependency of Venezuela are located to the northwest of the Gulf of Venezuela, off the coast of Guajira Peninsula at the border between Colombia and the Venezuelan ...
** Los Roques archipelago
The Los Roques Archipelago (Spanish: ''Archipiélago de Los Roques'') is a federal dependency of Venezuela consisting of approximately 350 islands, cays, and islets in a total area of 40.61 square kilometers. The archipelago is located dir ...
** Los Testigos Islands
** Patos Island
Patos Island is a small island in the San Juan Islands of the U.S. state of Washington. Since 1893, it has been home to the Patos Island Lighthouse, guiding vessels through Boundary Pass between Canada and the United States. The name comes from ...


Biodiversity
The Caribbean islands have one of the most diverse eco systems in the world. The animals, fungi and plants, and have been classified as one of Conservation International'sbiodiversity hotspot
A biodiversity hotspot is a biogeographic region with significant levels of biodiversity that is threatened by human habitation. Norman Myers wrote about the concept in two articles in ''The Environmentalist'' in 1988 and 1990, after which the c ...
s because of their exceptionally diverse terrestrial and marine ecosystems, ranging from montane cloud forests
A cloud forest, also called a water forest, primas forest, or tropical montane cloud forest (TMCF), is a generally tropical or subtropical, evergreen, montane, moist forest characterized by a persistent, frequent or seasonal low-level cloud ...
, to tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equa ...
, to cactus
A cactus (, or less commonly, cactus) is a member of the plant family Cactaceae, a family comprising about 127 genera with some 1750 known species of the order Caryophyllales. The word ''cactus'' derives, through Latin, from the Ancient Gree ...
scrublands. The region also contains about 8% (by surface area) of the world's coral reefs along with extensive seagrass meadows, both of which are frequently found in the shallow marine waters bordering the island and continental coasts of the region.
For the fungi, there is a modern checklist based on nearly 90,000 records derived from specimens in reference collections, published accounts and field observations. That checklist includes more than 11,250 species of fungi recorded from the region. As its authors note, the work is far from exhaustive, and it is likely that the true total number of fungal species already known from the Caribbean is higher. The true total number of fungal species occurring in the Caribbean, including species not yet recorded, is likely far higher given the generally accepted estimate that only about 7% of all fungi worldwide have been discovered. Though the amount of available information is still small, a first effort has been made to estimate the number of fungal species endemic to some Caribbean islands. For Cuba, 2200 species of fungi have been tentatively identified as possible endemics of the island; for Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
, the number is 789 species; for the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
, the number is 699 species; for Trinidad and Tobago, the number is 407 species.
Many of the ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
s of the Caribbean islands have been devastated by deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated ...
, pollution, and human encroachment. The arrival of the first humans is correlated with extinction of giant
In folklore, giants (from Ancient Greek: ''gigas'', cognate giga-) are beings of human-like appearance, but are at times prodigious in size and strength or bear an otherwise notable appearance. The word ''giant'' is first attested in 1297 fr ...
owls and dwarf ground sloths. The hotspot contains dozens of highly threatened animals (ranging from birds, to mammals and reptiles), fungi and plants. Examples of threatened animals include the Puerto Rican amazon
The Puerto Rican amazon (''Amazona vittata''), also known as the Puerto Rican parrot (Puerto Rican Spanish: ''cotorra puertorriqueña'') or ''iguaca'', is the only extant parrot endemic to the archipelago of Puerto Rico, and belongs to the Neo ...
, two species of solenodon
Solenodons (from el, τέλειος , 'channel' or 'pipe' and el, ὀδούς , 'tooth') are venomous, nocturnal, burrowing, insectivorous mammals belonging to the family Solenodontidae . The two living solenodon species are the Cuban solen ...
(giant shrews) in Cuba and the Hispaniola island, and the Cuban crocodile
The Cuban crocodile (''Crocodylus rhombifer'') is a small-medium species of crocodile endemic to Cuba. Typical length is and typical weight . Large males can reach as much as in length and weigh more than . Despite its smaller size, it is a hig ...
.
The region's coral reefs, which contain about 70 species of hard corals and from 500 to 700 species of reef-associated fishes have undergone rapid decline in ecosystem integrity in recent years, and are considered particularly vulnerable to global warming and ocean acidification. According to a UNEP
The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) is responsible for coordinating responses to environmental issues within the United Nations system. It was established by Maurice Strong, its first director, after the United Nations Conference on ...
report, the Caribbean coral reefs might get extinct in next 20 years due to population explosion along the coast lines, overfishing, the pollution of coastal areas and global warming.
Some Caribbean islands have terrain that Europeans found suitable for cultivation for agriculture. Tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
was an important early crop during the colonial era, but was eventually overtaken by sugarcane production as the region's staple crop. Sugar was produced from sugarcane for export to Europe. Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
and Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...
were historically the largest producers of sugar. The tropical plantation system thus came to dominate Caribbean settlement. Other islands were found to have terrain unsuited for agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
, for example Dominica, which remains heavily forested. The islands in the southern Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc bet ...
, Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao, are extremely arid, making them unsuitable for agriculture. However, they have salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
pans that were exploited by the Dutch. Sea water was pumped into shallow ponds, producing coarse salt when the water evaporated.
The natural environmental diversity of the Caribbean islands has led to recent growth in eco-tourism
Ecotourism is a form of tourism involving responsible travel (using sustainable transport) to natural areas, conserving the environment, and improving the well-being of the local people. Its purpose may be to educate the traveler, to provide fund ...
. This type of tourism is growing on islands lacking sandy beaches and dense human populations.
Plants and animals
Dendrobates auratus
The green-and-black poison dart frog (''Dendrobates auratus''), also known as the green-and-black poison arrow frog and green poison frog (among others), is a brightly colored member of the order Anura native to Central America and northwestern ...
''
File:Caesalpinia pulcherrima, Guadeloupe.jpg, alt=Caesalpinia pulcherrima, Guadeloupe., ''Caesalpinia
''Caesalpinia'' is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. Historically, membership within the genus has been highly variable, with different publications including anywhere from 70 to 165 species, depending largely on the inclusion o ...
pulcherrima'', Guadeloupe
File:Costus speciosus Guadeloupe.JPG, alt=Costus speciosus, a marsh plant, Guadeloupe., '' Costus speciosus'', a marsh plant, Guadeloupe
File:Ocypode quadrata (Martinique).jpg, alt=An Atlantic ghost crab (Ocypode quadrata) in Martinique., An Atlantic ghost crab (''Ocypode quadrata'') in Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago: or ) is an island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of the French Republic, Martinique is located in ...
File:Calebassier.jpg, alt=Crescentia cujete, or calabash fruit, Martinique., ''Crescentia cujete
''Crescentia cujete'', commonly known as the calabash tree, is a species of flowering plant native to the Americas, that is grown in Africa, Central America, South America, the West Indies and extreme southern Florida. It is the national tree ...
'', or calabash fruit, Martinique
Martinique ( , ; gcf, label=Martinican Creole, Matinik or ; Kalinago: or ) is an island and an overseas department/region and single territorial collectivity of France. An integral part of the French Republic, Martinique is located in ...
File:Thalassoma bifasciatum (Bluehead Wrasse) juvenile yellow stage over Bispira brunnea (Social Feather Duster Worms).jpg, alt=Thalassoma bifasciatum (bluehead wrasse fish), over Bispira brunnea (social feather duster worms)., ''Thalassoma bifasciatum
''Thalassoma bifasciatum'', the bluehead, bluehead wrasse or blue-headed wrasse, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a wrasse from the family Labridae. It is native to the coral reefs of the tropical waters of the western Atlantic Ocean ...
'' (bluehead wrasse fish), over '' Bispira brunnea'' (social feather duster worms)
File:Stenopus hispidus (Banded cleaner shrimp).jpg, alt=Two Stenopus hispidus (banded cleaner shrimp) on a Xestospongia muta (giant barrel sponge)., Two ''Stenopus hispidus
''Stenopus hispidus'' is a shrimp-like decapod crustacean belonging to the infraorder Stenopodidea. Common names include coral banded shrimp and banded cleaner shrimp.
Distribution
''Stenopus hispidus'' has a pan-tropical distribution, extendi ...
'' (banded cleaner shrimp) on a '' Xestospongia muta'' (giant barrel sponge)
File:Cyphoma signata (Fingerprint Cowry) pair.jpg, alt=A pair of Cyphoma signatum (fingerprint cowry), off coastal Haiti., A pair of '' Cyphoma signatum'' (fingerprint cowry), off coastal Haiti
File:Extinctbirds1907 P18 Amazona martinicana0317.png, The Martinique amazon
The Martinique amazon (''Amazona martinicana'') is a hypothetical extinct species of Caribbean parrot in the family Psittacidae. It is not known from any material remains, but was said to be similar to the red-necked amazon (''A. arausiaca'') f ...
, ''Amazona martinicana'', is an extinct species of parrot in the family Psittacidae.
File:Anastrepha suspensa 5193019.jpg, alt=Anastrepha suspensa, a Caribbean fruit fly., ''Anastrepha
''Anastrepha'' is the most diverse genus in the Americas, American tropics and subtropics. Currently, it comprises more than 300 described species, including nine major pest species, such as the Mexican fruit fly (''A. ludens''), the South Americ ...
suspensa'', a Caribbean fruit fly
File:Hemidactylus mabouia (Dominica).jpg, alt=Hemidactylus mabouia, a tropical gecko, in Dominica Edited by: Taniya Brooks., ''Hemidactylus
__NOTOC__
''Hemidactylus'' is a genus of the common gecko family, Gekkonidae. It has 189 described species, newfound ones being described every few years. These geckos are found in all the tropical regions of the world, extending into the subtrop ...
mabouia'', a tropical gecko, in Dominica. Edited by: Taniya Brooks
Demographics
Indigenous groups
* Arawak peoples **Igneri
The Igneri were an indigenous Arawak people of the southern Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. Historically, it was believed that the Igneri were conquered and displaced by the Island Caribs in an invasion some time before European contact. Howev ...
** Taíno
The Taíno were a historic indigenous people of the Caribbean whose culture has been continued today by Taíno descendant communities and Taíno revivalist communities. At the time of European contact in the late 15th century, they were the pri ...
* Caquetio people
Caquetio, Caiquetio, or Caiquetia are natives of northwestern Venezuela, living along the shores of Lake Maracaibo at the time of the Spanish conquest. They moved inland to avoid enslavement by the Spaniards, while their numbers were drastically ...
* Ciboney
The Ciboney, or Siboney, were a Taíno people of western Cuba, Jamaica, and the Tiburon Peninsula of Haiti. A Western Taíno group living in central Cuba during the 15th and 16th centuries, they had a dialect and culture distinct from the Classi ...
* Ciguayo
At the time of first contact between Europe and the Americas, the indigenous peoples of the Caribbean included the Taíno of the northern Lesser Antilles, most of the Greater Antilles and the Bahamas, the Kalinago of the Lesser Antilles, the Cigua ...
* Garifuna
The Garifuna people ( or ; pl. Garínagu in Garifuna) are a people of mixed free African and indigenous American ancestry that originated in the Caribbean island of Saint Vincent and speak Garifuna, an Arawakan language, and Vincentian ...
* Kalina
Kalina may refer to:
People
* Kalina people, or Caribs, an indigenous people of the northern coastal areas of South America
* Kalina language, or Carib, the language of the Kalina people
* Kalina (given name)
* Kalina (surname)
* Noah Kalina, ...
* Kalinago
The Kalinago, also known as the Island Caribs or simply Caribs, are an indigenous people of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean. They may have been related to the Mainland Caribs (Kalina) of South America, but they spoke an unrelated langua ...
* Lucayan
* Macorix
* Raizal
The Raizal are an Afro-Caribbean ethnic group from the Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina, off of Colombia's Caribbean coast. They are recognized by the Colombian authorities as one of the Afro-Colombian ethnic groups ...
 At the time of European contact, the dominant ethnic groups in the Caribbean included the
At the time of European contact, the dominant ethnic groups in the Caribbean included the Taíno
The Taíno were a historic indigenous people of the Caribbean whose culture has been continued today by Taíno descendant communities and Taíno revivalist communities. At the time of European contact in the late 15th century, they were the pri ...
of the Greater Antilles
The Greater Antilles ( es, Grandes Antillas or Antillas Mayores; french: Grandes Antilles; ht, Gwo Zantiy; jam, Grieta hAntiliiz) is a grouping of the larger islands in the Caribbean Sea, including Cuba, Hispaniola, Puerto Rico, Jamaica, a ...
and northern Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc bet ...
, the Island Caribs of the southern Lesser Antilles, and smaller distinct groups such as the Guanajatabey
The Guanahatabey (also spelled Guanajatabey) were an indigenous people of western Cuba at the time of European contact. Archaeological and historical studies suggest the Guanahatabey were archaic hunter-gatherers with a distinct language and cu ...
of western Cuba and the Ciguayo
At the time of first contact between Europe and the Americas, the indigenous peoples of the Caribbean included the Taíno of the northern Lesser Antilles, most of the Greater Antilles and the Bahamas, the Kalinago of the Lesser Antilles, the Cigua ...
of eastern Hispaniola. The population of the Caribbean is estimated to have been around 750,000 immediately before European contact, although lower and higher figures are given. After contact, social disruption and epidemic diseases such as smallpox and measles (to which they had no natural immunity) led to a decline in the Amerindian population. such as the Kongo
Congo or The Congo may refer to either of two countries that border the Congo River in central Africa:
* Democratic Republic of the Congo, the larger country to the southeast, capital Kinshasa, formerly known as Zaire, sometimes referred to a ...
, Igbo
Igbo may refer to:
* Igbo people, an ethnic group of Nigeria
* Igbo language, their language
* anything related to Igboland, a cultural region in Nigeria
See also
* Ibo (disambiguation)
* Igbo mythology
* Igbo music
* Igbo art
*
* Igbo-Ukwu, a ...
, Akan Akan may refer to:
People and languages
*Akan people, an ethnic group in Ghana and Côte d'Ivoire
*Akan language, a language spoken by the Akan people
*Kwa languages, a language group which includes Akan
* Central Tano languages, a language group ...
, Fon and Yoruba
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute ...
as well as military prisoners from Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
, who were deported during the Cromwellian reign in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
. Immigrants from Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* The United Kingdom, a sovereign state in Europe comprising the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland and many smaller islands
* Great Britain, the largest island in the United King ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
, Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
and Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
also arrived, although the mortality rate was high for both groups.
The population is estimated to have reached 2.2 million by 1800. Immigrants from India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
, China, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
, and other countries arrived in the mid-19th century as indentured servants. After the ending of the Atlantic slave trade, the population increased naturally. The total regional population was estimated at 37.5 million by 2000.Table A.2Database documentation
Latin America and the Caribbean (LAC) Population Database, version 3, International Center for Tropical Agriculture, 2005. Accessed on line February 20, 2008. In Haiti and most of the French,
Anglophone
Speakers of English are also known as Anglophones, and the countries where English is natively spoken by the majority of the population are termed the ''Anglosphere''. Over two billion people speak English , making English the largest language ...
and Dutch Caribbean
The Dutch Caribbean (historically known as the Dutch West Indies) are the territories, colonies, and countries, former and current, of the Dutch Empire and the Kingdom of the Netherlands in the Caribbean Sea. They are in the north and south-wes ...
, the population is predominantly of African origin; on many islands there are also significant populations of mixed racial origin (including Mulatto- Creole, Dougla
Dougla people (plural ''Douglas'') are Caribbean people who are of mixed African and Indian descent. The word ''Dougla'' (also Dugla or Dogla) is used throughout the Dutch and English-speaking Caribbean.
Definition
The word ''Dougla'' origin ...
, Mestizo, Quadroon
In the colonial societies of the Americas and Australia, a quadroon or quarteron was a person with one quarter African/ Aboriginal and three quarters European ancestry.
Similar classifications were octoroon for one-eighth black (Latin root ''o ...
, Cholo
''Cholo'' () is a loosely defined Spanish term that has had various meanings. Its origin is a somewhat derogatory term for people of mixed-blood heritage in the Spanish Empire in Latin America and its successor states as part of ''castas' ...
, Castizo, Criollo
Criollo or criolla (Spanish for creole) may refer to:
People
* Criollo people, a social class in the Spanish race-based colonial caste system (the European descendants)
Animals
* Criollo duck, a species of duck native to Central and South Ameri ...
, Zambo
Zambo ( or ) or Sambu is a racial term historically used in the Spanish Empire to refer to people of mixed Indigenous and African ancestry. Occasionally in the 21st century, the term is used in the Americas to refer to persons who are of mixe ...
, Pardo
''Pardos'' (feminine ''pardas'') is a term used in the former Portuguese and Spanish colonies in the Americas to refer to the triracial descendants of Southern Europeans, Amerindians and West Africans. In some places they were defined as ne ...
, Asian Latin Americans
Asian Latin Americans or Latinasians are Latin Americans of Asian descent. Asian immigrants to Latin America have largely been from East Asia or West Asia. Historically, Asians in Latin America have a centuries-long history in the region, star ...
, Chindian
Chindian ( zh, c=中印人, p=Zhōngyìnrén, cy=Jūngyanyàn; ta, சிந்தியன்; is an informal term used to refer to a person of mixed Chinese and Indian ancestry; i.e. from any of the host of ethnic groups native to modern Ch ...
, Cocoa panyols
The Panyols are a pardo (tri-racial) ethnic group in Trinidad and Tobago of Afro-Indigenous descent, primarily of mixed South American Amerindian, Trinidad and Tobago Amerindian, Afro-Trinidadian and Spanish descent. The name is a derivat ...
, and Eurasian
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Ja ...
), as well as populations of European ancestry: Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
, French, Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
, Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
and Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
ancestry. Asians, especially those of Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
descent, and Javanese Indonesians, form a significant minority in parts of the region. Indians form a plurality of the population in Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of ...
, Guyana, and Suriname. Most of their ancestors arrived in the 19th century as indentured laborers.
The Spanish-speaking Caribbean populations are primarily of European, African, or racially mixed origins. Puerto Rico has a European majority with a mixture of European-African-Native American (tri-racial), and a large Mulatto (European-West African) and West African minority. Cuba also has a European majority, along with a significant population of African ancestry. The Dominican Republic has the largest mixed-race population, primarily descended from Europeans, West African
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations geoscheme for Africa#Western Africa, United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, ...
s, and Amerindians.

Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
has a large African majority, in addition to a significant population of mixed racial background, and has minorities of Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, Europeans, Indians, Latino
Latino or Latinos most often refers to:
* Latino (demonym), a term used in the United States for people with cultural ties to Latin America
* Hispanic and Latino Americans in the United States
* The people or cultures of Latin America;
** Latin A ...
s, Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, and Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
s. This is a result of years of importation of slaves and indentured laborers, and migration. Most multi-racial Jamaicans refer to themselves as either mixed race or brown. Similar populations can be found in the Caricom states of Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wate ...
, Guyana and Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of ...
. Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of ...
has a multi-racial cosmopolitan society due to the arrivals of Africans, Indians, Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, Latino
Latino or Latinos most often refers to:
* Latino (demonym), a term used in the United States for people with cultural ties to Latin America
* Hispanic and Latino Americans in the United States
* The people or cultures of Latin America;
** Latin A ...
s, and Europeans along with the native indigenous Amerindians population. This multi-racial mix of the Caribbean has created sub-ethnicities that often straddle the boundaries of major ethnicities and include Mulatto- Creole, Mestizo, Pardo
''Pardos'' (feminine ''pardas'') is a term used in the former Portuguese and Spanish colonies in the Americas to refer to the triracial descendants of Southern Europeans, Amerindians and West Africans. In some places they were defined as ne ...
, Zambo
Zambo ( or ) or Sambu is a racial term historically used in the Spanish Empire to refer to people of mixed Indigenous and African ancestry. Occasionally in the 21st century, the term is used in the Americas to refer to persons who are of mixe ...
, Dougla
Dougla people (plural ''Douglas'') are Caribbean people who are of mixed African and Indian descent. The word ''Dougla'' (also Dugla or Dogla) is used throughout the Dutch and English-speaking Caribbean.
Definition
The word ''Dougla'' origin ...
, Chindian
Chindian ( zh, c=中印人, p=Zhōngyìnrén, cy=Jūngyanyàn; ta, சிந்தியன்; is an informal term used to refer to a person of mixed Chinese and Indian ancestry; i.e. from any of the host of ethnic groups native to modern Ch ...
, Afro-Asians
Afro-Asians, African Asians or simply Black Asians, often referred to as Blasians, are persons of mixed Asian and African ancestry. Historically, Afro-Asian populations have been marginalised as a result of human migration and social conflict ...
, Eurasian
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Ja ...
, Cocoa panyols
The Panyols are a pardo (tri-racial) ethnic group in Trinidad and Tobago of Afro-Indigenous descent, primarily of mixed South American Amerindian, Trinidad and Tobago Amerindian, Afro-Trinidadian and Spanish descent. The name is a derivat ...
, and Asian Latinos.
Language
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
(64%), French (25%), English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
(14%), Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, Haitian Creole, and Papiamento are the predominant official languages of various countries in the region, although a handful of unique creole language
A creole language, or simply creole, is a stable natural language that develops from the simplifying and mixing of different languages into a new one within a fairly brief period of time: often, a pidgin evolved into a full-fledged language. ...
s or dialects can also be found in virtually every Caribbean country. Other languages such as Caribbean Hindustani
Caribbean Hindustani is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by Indo-Caribbeans and the Indo-Caribbean diaspora. It is mainly based on the Bhojpuri and Awadhi dialects. These Hindustani dialects were the most spoken dialects by the Indians who came as i ...
, Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, Javanese, Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
, Hmong
Hmong may refer to:
* Hmong people, an ethnic group living mainly in Southwest China, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand
* Hmong cuisine
* Hmong customs and culture
** Hmong music
** Hmong textile art
* Hmong language, a continuum of closely related to ...
, Amerindian languages
Over a thousand indigenous languages are spoken by the Indigenous peoples of the Americas. These languages cannot all be demonstrated to be related to each other and are classified into a hundred or so language families (including a large numbe ...
, other African languages
The languages of Africa are divided into several major language families:
* Niger–Congo or perhaps Atlantic–Congo languages (includes Bantu and non-Bantu, and possibly Mande and others) are spoken in West, Central, Southeast and Souther ...
, other European languages
Most languages of Europe belong to the Indo-European language family. Out of a total European population of 744 million as of 2018, some 94% are native speakers of an Indo-European language. Within Indo-European, the three largest phyla are Ro ...
, and other Indian languages can also be found.
Religion




Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
is the predominant religion in the Caribbean (84.7%). Other religions in the region are Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, Islam, Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in t ...
, Rastafari, Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religions, Indian religion or Indian philosophy#Buddhist philosophy, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha. ...
, Chinese folk religion
Chinese folk religion, also known as Chinese popular religion comprehends a range of traditional religious practices of Han Chinese, including the Chinese diaspora. Vivienne Wee described it as "an empty bowl, which can variously be filled ...
(incl. Taoism
Taoism (, ) or Daoism () refers to either a school of philosophical thought (道家; ''daojia'') or to a religion (道教; ''daojiao''), both of which share ideas and concepts of Chinese origin and emphasize living in harmony with the '' Ta ...
and Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or a ...
), Bahá'í, Jainism
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle bein ...
, Sikhism
Sikhism (), also known as Sikhi ( pa, ਸਿੱਖੀ ', , from pa, ਸਿੱਖ, lit=disciple', 'seeker', or 'learner, translit=Sikh, label=none),''Sikhism'' (commonly known as ''Sikhī'') originated from the word ''Sikh'', which comes fro ...
, Kebatinan, Traditional African religions
The traditional beliefs and practices of African people are highly diverse beliefs that include various ethnic religions.Encyclopedia of African Religion (Sage, 2009) Molefi Kete Asante Generally, these traditions are oral rather than scriptura ...
, Yoruba
The Yoruba people (, , ) are a West African ethnic group that mainly inhabit parts of Nigeria, Benin, and Togo. The areas of these countries primarily inhabited by Yoruba are often collectively referred to as Yorubaland. The Yoruba constitute ...
(incl. Trinidad Orisha
Trinidad Orisha, also known as Shango, is a syncretic religion in Trinidad and Tobago and the Caribbean, originally from West Africa ( Yoruba religion). Trinidad Orisha incorporates elements of Spiritual Baptism, and the closeness between Orisha ...
), Afro-American religions
African diaspora religions are a number of related Pagan beliefs that developed in the Americas in various nations of the Caribbean, Latin America and the Southern United States. They derive from Pagan traditional African religions with some influ ...
, (incl. Santería, Palo
Palo may refer to:
Places
* Palo, Argentina, a village in Argentina
* Palo, Estonia, village in Meremäe Parish, Võru County, Estonia
* Palo, Huesca, municipality in the province of Huesca, Spain
* Palo, Iowa, United States, a town located wit ...
, Umbanda
Umbanda () is a syncretic Afro-Brazilian religion that blends traditional African religions with Roman Catholicism, Spiritism, and Indigenous American beliefs. Although some of its beliefs and most of its practices existed in the late 19th ce ...
, Brujería
Various types of witchcraft and occult religious practices exist in Latin American and Afro-Caribbean cultures, known in Spanish as (pronounced ). Influenced by indigenous religion, Catholicism, and European witchcraft, the purpose may range ...
, Hoodoo, Candomblé, Quimbanda
Quimbanda () is an Afro-Brazilian religion practiced primarily in the urban city centers of Brazil. Quimbanda practices are typically associated with magic, rituals with Exus, and Pombagiras spirits. Quimbanda was originally contained under the ...
, Orisha, Xangô de Recife, Xangô do Nordeste, Comfa, Espiritismo
''Espiritismo'' (Portuguese language, Portuguese and Spanish language, Spanish for "Spiritism") is a term used in Latin America and the Caribbean to refer to the folk religions, popular belief that Goodness and evil, good and evil spirits can af ...
, Santo Daime
Santo Daime () is a syncretic religion founded in the 1930s in the Brazilian Amazonian state of Acre by Raimundo Irineu Serra, known as Mestre Irineu. Santo Daime incorporates elements of several religious or spiritual traditions including Folk ...
, Obeah
Obeah, or Obayi, is an ancestrally inherited tradition of Akan witches of Ghana, Ivory Coast, and Togo and their descendants in the African diaspora of the Caribbean. Inheritors of the tradition are referred to as "obayifo" (Akan/Ghana-region ...
, Candomblé, Abakuá
Abakuá, also sometimes known as Ñañiguismo, is an Afro-Cuban men's initiatory fraternity or secret society, which originated from fraternal associations in the Cross River region of southeastern Nigeria and southwestern Cameroon.
Abakuá ...
, Kumina
Kumina is an Afro-Jamaican religion. Kumina has practices that include secular ceremonies, dance and music that developed from the beliefs and traditions brought to the island by Kongo enslaved people and indentured labourers, from the Congo r ...
, Winti
Winti is an Afro-Surinamese traditional religion that originated in the colony Suriname, part of the Dutch Empire. It is a syncretization of the different African religious beliefs and practices brought in mainly by Akan and Fon slaves durin ...
, Sanse, Cuban Vodú, Dominican Vudú
Dominican ''Vudú'', or Dominican Voodoo, popularly known as ''Las 21 Divisiones'' (The 21 Divisions), is a heavily Catholicized syncretic shaman
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what ...
, Louisiana Voodoo
Louisiana Voodoo (french: Vaudou louisianais, es, Vudú de Luisiana), also known as New Orleans Voodoo, is an African diasporic religion which originated in Louisiana, now in the southern United States. It arose through a process of syncreti ...
, Haitian Vodou, and Vodun
Vodun (meaning ''spirit'' in the Fon, Gun and Ewe languages, with a nasal high-tone ''u''; also spelled Vodon, Vodoun, Vodou, Vudu, Voudou, Voodoo, etc.) is a religion practiced by the Aja, Ewe, and Fon peoples of Benin, Togo, Ghana, and ...
).
Politics
Regionalism
Caribbean Basin
In Geography, the Caribbean Basin is generally defined as the area running from Florida westward along the Gulf coast, then south along the Mexican coast through Central America and then eastward across the northern coast of South America. This ...
was created by advances of the English-speaking Caribbean nations through the institution known as the Caribbean Common Market and Community ( CARICOM) which is located in Guyana.
Certain scholars have argued both for and against generalizing the political structures of the Caribbean. On the one hand the Caribbean states are politically diverse, ranging from communist systems such as Cuba toward more capitalist Westminster-style parliamentary systems as in the Commonwealth Caribbean. Other scholars argue that these differences are superficial, and that they tend to undermine commonalities in the various Caribbean states. Contemporary Caribbean systems seem to reflect a "blending of traditional and modern patterns, yielding hybrid systems that exhibit significant structural variations and divergent constitutional traditions yet ultimately appear to function in similar ways." The political systems of the Caribbean states share similar practices.
The influence of regionalism in the Caribbean is often marginalized. Some scholars believe that regionalism cannot exist in the Caribbean because each small state is unique. On the other hand, scholars also suggest that there are commonalities amongst the Caribbean nations that suggest regionalism exists. "Proximity as well as historical ties among the Caribbean nations has led to cooperation as well as a desire for collective action." These attempts at regionalization reflect the nations' desires to compete in the international economic system.
Furthermore, a lack of interest from other major states promoted regionalism in the region. In recent years the Caribbean has suffered from a lack of U.S. interest. "With the end of the Cold War, U.S. security and economic interests have been focused on other areas. As a result there has been a significant reduction in U.S. aid and investment to the Caribbean." The lack of international support for these small, relatively poor states, helped regionalism prosper.
Following the Cold War another issue of importance in the Caribbean has been the reduced economic growth of some Caribbean States due to the United States and European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
's allegations of special treatment toward the region by each other.
United States-EU trade dispute
The United States under PresidentBill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton ( né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and agai ...
launched a challenge in the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and ...
against the EU over Europe's preferential program, known as the Lomé Convention
The Lomé Convention is a trade and aid agreement between the European Economic Community (EEC) and 71 African, Caribbean, and Pacific (ACP) countries, first signed in February 1975 in Lomé, Togo.
History
The first Lomé Convention (Lomé I) ...
, which allowed banana exports from the former colonies of the Group of African, Caribbean and Pacific states (ACP) to enter Europe cheaply. The World Trade Organization sided in the United States' favour and the beneficial elements of the convention to African, Caribbean and Pacific states has been partially dismantled and replaced by the Cotonou Agreement
The Cotonou Agreement is a treaty between the European Union and the African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States ("ACP countries"). It was signed in June 2000 in Cotonou, Benin's largest city, by 78 ACP countries (Cuba did not sign) and the t ...
.
During the US/EU dispute, the United States imposed large tariffs on European Union goods (up to 100%) to pressure Europe to change the agreement with the Caribbean nations in favour of the Cotonou Agreement.
Farmers in the Caribbean have complained of falling profits and rising costs as the Lomé Convention weakens. Some farmers have faced increased pressure to turn towards the cultivation of illegal drugs, which has a higher profit margin and fills the sizable demand for these illegal drugs in North America and Europe.
Caribbean Financial Action Task Force and Association of Caribbean States
Caribbean nations have also started to more closely cooperate in theCaribbean Financial Action Task Force The Caribbean Financial Action Task Force (CFATF) is an organization of states and territories of the Caribbean Basin that have agreed to implement common counter-measures against money laundering. CFATF has associate status within the Financial A ...
and other instruments to add oversight of the offshore industry. One of the most important associations that deal with regionalism amongst the nations of the Caribbean Basin
In Geography, the Caribbean Basin is generally defined as the area running from Florida westward along the Gulf coast, then south along the Mexican coast through Central America and then eastward across the northern coast of South America. This ...
has been the Association of Caribbean States
The Association of Caribbean States (ACS; es, Asociación de Estados del Caribe; french: Association des États de la Caraïbe) is an advisory association of nations centered on the Caribbean Basin. It was formed with the aim of promoting cons ...
(ACS). Proposed by CARICOM in 1992, the ACS soon won the support of the other countries of the region. It was founded in July 1994. The ACS maintains regionalism within the Caribbean on issues unique to the Caribbean Basin. Through coalition building, like the ACS and CARICOM, regionalism has become an undeniable part of the politics and economics of the Caribbean. The successes of region-building initiatives are still debated by scholars, yet regionalism remains prevalent throughout the Caribbean.
Bolivarian Alliance
The President ofVenezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, Hugo Chavez
Hugo or HUGO may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Hugo'' (film), a 2011 film directed by Martin Scorsese
* Hugo Award, a science fiction and fantasy award named after Hugo Gernsback
* Hugo (franchise), a children's media franchise based on a ...
launched an economic group called the Bolivarian Alliance for the Americas
''Alba'' ( , ) is the Scottish Gaelic name for Scotland. It is also, in English language historiography, used to refer to the polity of Picts and Scots united in the ninth century as the Kingdom of Alba, until it developed into the Kin ...
(ALBA), which several eastern Caribbean islands joined. In 2012, the nation of Haiti, with 9 million people, became the largest CARICOM nation that sought to join the union.
Regional institutions
Here are some of the bodies that several islands share in collaboration: *African, Caribbean and Pacific Group of States
The Organisation of African, Caribbean and Pacific States (OACPS) is a group of countries in Africa, the Caribbean, and the Pacific that was created by the Georgetown Agreement in 1975. Formerly known as African, Caribbean and Pacific Group o ...
* Association of Caribbean States
The Association of Caribbean States (ACS; es, Asociación de Estados del Caribe; french: Association des États de la Caraïbe) is an advisory association of nations centered on the Caribbean Basin. It was formed with the aim of promoting cons ...
(ACS), Trinidad and Tobago
* Caribbean Association of Industry and Commerce (CAIC), Trinidad and Tobago
* Caribbean Association of National Telecommunication Organizations (CANTO), Trinidad and Tobago
* Caribbean Community
The Caribbean Community (CARICOM or CC) is an intergovernmental organization that is a political and economic union of 15 member states (14 nation-states and one dependency) throughout the Caribbean. They have primary objectives to promote econo ...
(CARICOM), Guyana
* Caribbean Development Bank
The Caribbean Development Bank (CDB) is a financial institution that helps Caribbean nations finance social and economic programs in its member countries. CDB was established by an Agreement signed on October 18, 1969, in Kingston, Jamaica, and ent ...
(CDB), Barbados
* Caribbean Disaster Emergency Management Agency
The Caribbean Disaster Emergency Management Agency (CDEMA) is an inter-regional supportive network of independent emergency units throughout the Caribbean region. Formed on September 1, 2005, as the Caribbean Disaster Emergency Response Agency ( ...
(CDERA), Barbados
* Caribbean Educators Network
* Caribbean Electric Utility Services Corporation (CARILEC), Saint Lucia
* Caribbean Examinations Council
The Caribbean Examinations Council (CXC) is an examination board in the Caribbean. It was established in 1972 under agreement by the participating governments in the Caribbean Community to conduct such examinations as it may think appropriate an ...
(CXC), Barbados and Jamaica
* Caribbean Financial Action Task Force The Caribbean Financial Action Task Force (CFATF) is an organization of states and territories of the Caribbean Basin that have agreed to implement common counter-measures against money laundering. CFATF has associate status within the Financial A ...
(CFATF), Trinidad and Tobago
* Caribbean Food Crops Society
The Caribbean Food Crop Society is the regional trade association serving agronomists and agriculture for countries bordering on the Caribbean Sea. Agriculture is the largest sector of the economy of the Caribbean and it affects every nation and t ...
, Puerto Rico
* Caribbean Football Union (CFU), Jamaica
* Caribbean Hotel & Tourism Association (CHTA), Florida and Puerto Rico
* Caribbean Initiative (Initiative of the IUCN)
* Caribbean Programme for Economic Competitiveness The Caribbean Regional Human Resource Development Program for Economic Competitiveness known as (CPEC) for short is a programme funded by the Canadian International Development Agency (Canadian International Development Agency, CIDA). The agency is ...
(CPEC), Saint Lucia
* Caribbean Regional Environmental Programme (CREP), Barbados
* Caribbean Regional Fisheries Mechanism (CRFM), Belize
* Caribbean Regional Negotiating Machinery (CRNM), Barbados and Dominican Republic
* Caribbean Telecommunications Union (CTU), Trinidad and Tobago
* Caribbean Tourism Organization
The Caribbean Tourism Organizations main objective is the development of sustainable tourism for the economic and social benefit of Caribbean people.
Operations
The CTO, with headquarters in Barbados, is the Caribbean’s tourism development age ...
(CTO), Barbados
* Community of Latin American and Caribbean States
A community is a social unit (a group of living things) with commonality such as place, norms, religion, values, customs, or identity. Communities may share a sense of place situated in a given geographical area (e.g. a country, village, tow ...
(CELAC)
* Foundation for the Development of Caribbean Children, Barbados
* Latin America and Caribbean Network Information Centre (LACNIC), Brazil and Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
* Latin American and the Caribbean Economic System, Venezuela
* Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States
The Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS; French: ''Organisation des États de la Caraïbe orientale'', OECO) is an inter-governmental organisation dedicated to economic harmonisation and integration, protection of human and legal ri ...
(OECS), Saint Lucia
* United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean
The United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean, known as ECLAC, UNECLAC or in Spanish and Portuguese CEPAL, is a United Nations regional commission to encourage economic cooperation. ECLAC includes 46 member States (2 ...
(ECLAC), Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
and Trinidad and Tobago
* University of the West Indies, Jamaica, Barbados, Trinidad and Tobago. In addition, the fourth campus, the Open Campus was formed in June 2008 as a result of an amalgamation of the Board for Non-Campus Countries and Distance Education, Schools of Continuing Studies, the UWI Distance Education Centres and Tertiary Level Units. The Open Campus has 42 physical sites in 16 Anglophone caribbean countries.
* West Indies Cricket Board
Cricket West Indies (CWI) is the governing body for cricket in the West Indies (a sporting confederation of over a dozen mainly English-speaking Caribbean countries and dependencies that once formed the British West Indies). It was originally ...
, Antigua and Barbuda
Cuisine
Favourite or national dishes

 *
* Anguilla
Anguilla ( ) is a British Overseas Territory in the Caribbean. It is one of the most northerly of the Leeward Islands in the Lesser Antilles, lying east of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands and directly north of Saint Martin. The terr ...
– rice, peas and fish
* Antigua and Barbuda – fungee and pepperpot
* Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the ar ...
– Guava duff
Duff is a Bahamian cuisine dessert dish made with fruit (especially guava) in a dough. Fruit is folded into the dough and boiled, then served with a sauce. Ingredients include fruit, butter, sugar, eggs, nutmeg, cinnamon, cloves, flour, rum, peppe ...
, Conch Salad, Peas n' Rice, and Conch Fritters
* Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate) ...
– cou-cou
Cou-cou, coo-coo (as it is known in the Windward Islands), or fungie (as it is known in the Leeward Islands and Dominica) makes up part of the national dishes of Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, British Virgin Islands and the U.S. Virgin Islands. ...
and flying fish
The Exocoetidae are a family of marine fish in the order Beloniformes class Actinopterygii, known colloquially as flying fish or flying cod. About 64 species are grouped in seven to nine genera. While they cannot fly in the same way a bird d ...
* Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wate ...
– rice and beans, stew chicken with potato salad; white rice, stew beans and fry fish with cole slaw
* British Virgin Islands
)
, anthem = "God Save the King"
, song_type = Territorial song
, song = " Oh, Beautiful Virgin Islands"
, image_map = File:British Virgin Islands on the globe (Americas centered).svg
, map_caption =
, mapsize = 290px
, image_map2 = Bri ...
– fish and fungee
* Cayman Islands – turtle stew, turtle steak, grouper
Groupers are fish of any of a number of genera in the subfamily Epinephelinae of the family Serranidae, in the order Perciformes.
Not all serranids are called "groupers"; the family also includes the sea basses. The common name "grouper" is ...
* Colombian Caribbean – rice with coconut milk, arroz con pollo
''Arroz con pollo'' (Spanish for ''rice with chicken'') is a traditional dish of Latin America, closely related to paella. It typically consists of chicken cooked with rice, onions, saffron, and a potential plethora of other grains or vegetables ...
, sancocho
Sancocho (from the Spanish verb ''sancochar'', "to parboil") is a traditional soup in several Latin American cuisines. Variations represent popular national dishes in Dominican Republic, Colombia, Cuba, Honduras, Ecuador, Panama, Puerto Rico, Tri ...
, Arab cuisine
Arab cuisine ( ar, المطبخ العربي) is the cuisine of the Arabs, defined as the various regional cuisines spanning the Arab world, from the Maghreb to the Fertile Crescent and the Arabian Peninsula. These cuisines are centuries old an ...
(due to the large Arab population)
* Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
– platillo Moros y Cristianos
is a traditional Cuban dish served both in homes and in restaurants. It is the Cuban version of rice and beans, a dish found throughout Latin America, the Caribbean, and in the Southern United States.
Etymology
means 'Moors and Christians'. ...
, ropa vieja
Ropa vieja (; "old clothes") is a dish with regional variations in Latin America, the Philippines, and Spain. It normally includes some form of stewed beef and tomatoes with a sofrito base.
, lechon
A suckling pig is a piglet fed on its mother's milk (i.e., a piglet which is still a " suckling"). In culinary contexts, a suckling pig is slaughtered between the ages of two and six weeks. It is traditionally cooked whole, often roasted, ...
, maduros, ajiaco
Ajiaco () is a soup common to Colombia, Cuba, and Peru.Clark, Melissa (October 28, 2011)"From Colombia, the Ultimate One-Pot Meal" ''The New York Times''. Accessed April 2016. Scholars have debated the origin of the dish. The dish is especially p ...
* Dominica – mountain chicken
''Leptodactylus fallax'', commonly known as the mountain chicken or giant ditch frog, is a critically endangered species of frog that is native to the Caribbean islands of Dominica and Montserrat. The population declined by at least 80% from ...
, rice and peas, dumplings, saltfish, dashin, bakes (fried dumplings), coconut confiture, curry goat, cassava farine
Flour is a Powder (substance), powder made by Mill (grinding), grinding raw grains, List of root vegetables, roots, beans, Nut (fruit), nuts, or seeds. Flours are used to make many different foods. Cereal flour, particularly wheat flour, ...
, oxtail
* Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
– arroz con pollo
''Arroz con pollo'' (Spanish for ''rice with chicken'') is a traditional dish of Latin America, closely related to paella. It typically consists of chicken cooked with rice, onions, saffron, and a potential plethora of other grains or vegetables ...
with stewed red kidney beans, pan fried
Pan frying or pan-frying is a form of frying food characterized by the use of minimal cooking oil or fat (compared to shallow frying or deep frying), typically using just enough to lubricate the pan. In the case of a greasy food such as bacon, ...
or braised beef, salad/ ensalada de coditos, empanadas
An empanada is a type of baked or fried turnover consisting of pastry and filling, common in Spanish, other Southern European, Latin American, and Iberian-influenced cultures around the world. The name comes from the Spanish (to bread, i.e., ...
, mangú, sancocho
* Grenada – oil down
Oil down is a salted meat and vegetable stew that is the national dish of Grenada.
Description
Oil down is a stew of breadfruit, salted meat, chicken, dumplings, callaloo, and other vegetables stewed in coconut milk, herbs, and spices. The name ...
, Roti and rice & chicken
* Guyana – roti
Roti (also known as chapati) is a round flatbread native to the Indian subcontinent. It is popular in India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Maldives, Myanmar, Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore, Thailand, Guyana, Suriname, Jamaica, Trini ...
and curry
A curry is a dish with a sauce seasoned with spices, mainly associated with South Asian cuisine. In southern India, leaves from the curry tree may be included.
There are many varieties of curry. The choice of spices for each dish in trad ...
, pepperpot, cookup rice, methem, pholourie
Pholourie (), also spelled ''phulourie'' or ''phoulourie'', is a snack food of Indo-Caribbean origin that is commonly eaten in Trinidad and Tobago as well as in Guyana, Suriname and other parts of the Caribbean. It consists of fried, spiced ...
* Haiti – griot (fried pork) served with du riz a pois or diri ak pwa (rice and beans
Rice and beans, or beans and rice, is a category of dishes from many cultures around the world, whereby the staple foods of rice and beans are combined in some manner. The grain and legume combination provides several important nutrients and man ...
)
* Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
– ackee and saltfish
Ackee and saltfish is the Jamaican national dish prepared with ackee and salted codfish.
Background
The ackee fruit (''Blighia sapida'') is the national fruit of Jamaica. It was imported to the Caribbean from Ghana before 1725 as 'Ackee' or ' ...
, callaloo
Callaloo (many spelling variants, such as kallaloo, calaloo, calalloo, calaloux or callalloo; ) is a popular Caribbean vegetable dish. There are many variants across the Caribbean, depending on the availability of local vegetables. The main in ...
, jerk chicken
Jerk, The Jerk, Jerks, or Jerking may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film, stage, and television
* ''Jerk'' (play), a 2008 puppet play by Dennis Cooper
* ''Jerk'' (TV series), a 2019 British sitcom
* ''The Jerk'', a 1979 American film
* "Jerk ...
, curry chicken
Chicken curry is a dish originating from the Indian subcontinent. It is common in the Indian subcontinent, Southeast Asia, Great Britain, Caribbean, and Japan. A typical curry from the Indian subcontinent consists of chicken stewed in an onion- ...
* Montserrat – Goat water
Goat water, also referred to as kiddy stew, is a stew that is a part of the national cuisine of the Caribbean island of Montserrat It has been described as a national dish of Montserrat. It has also been described as a national stew.
Goat water i ...
* Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and unincorporated ...
– yellow rice with green pigeon pea
The pigeon pea (''Cajanus cajan'') is a perennial legume from the family Fabaceae native to the Old World. The pigeon pea is widely cultivated in tropical and semitropical regions around the world, being commonly consumed in South Asia, South ...
s, saltfish stew, roasted pork shoulder, chicken fricassée, mofongo, tripe soup, alcapurria, coconut custard, rice pudding, guava turnovers, Mallorca bread
* Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Kitts and Nevis (), officially the Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis, is an island country and microstate consisting of the two islands of Saint Kitts and Nevis, both located in the West Indies, in the Leeward Islands chain ...
– goat water
Goat water, also referred to as kiddy stew, is a stew that is a part of the national cuisine of the Caribbean island of Montserrat It has been described as a national dish of Montserrat. It has also been described as a national stew.
Goat water i ...
, coconut dumplings, spicy plantain
Plantain may refer to:
Plants and fruits
* Cooking banana, banana cultivars in the genus ''Musa'' whose fruits are generally used in cooking
** True plantains, a group of cultivars of the genus ''Musa''
* ''Plantaginaceae'', a family of flowerin ...
, saltfish
Dried and salted cod, sometimes referred to as salt cod or saltfish or salt dolly, is cod which has been preserved by drying after salting. Cod which has been dried without the addition of salt is stockfish. Salt cod was long a major export o ...
, breadfruit
* Saint Lucia – callaloo
Callaloo (many spelling variants, such as kallaloo, calaloo, calalloo, calaloux or callalloo; ) is a popular Caribbean vegetable dish. There are many variants across the Caribbean, depending on the availability of local vegetables. The main in ...
, dal
In Indian cuisine, ''dal'' (also spelled ''daal'' or ''dhal''; pronunciation: , Hindi: दाल, Urdu: ) are dried, split pulses (e.g., lentils, peas, and beans) that do not require soaking before cooking. India is the largest producer of pu ...
roti
Roti (also known as chapati) is a round flatbread native to the Indian subcontinent. It is popular in India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Maldives, Myanmar, Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore, Thailand, Guyana, Suriname, Jamaica, Trini ...
, dried and salted cod
Dried and salted cod, sometimes referred to as salt cod or saltfish or salt dolly, is cod which has been preserved by drying after salting. Cod which has been dried without the addition of salt is stockfish. Salt cod was long a major export ...
, green bananas, rice and beans
Rice and beans, or beans and rice, is a category of dishes from many cultures around the world, whereby the staple foods of rice and beans are combined in some manner. The grain and legume combination provides several important nutrients and man ...
* Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines () is an island country in the Caribbean. It is located in the southeast Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, which lie in the West Indies at the southern end of the eastern border of the Caribbean Sea w ...
– roasted breadfruit and fried jackfish
* Suriname – brown beans and rice, roti
Roti (also known as chapati) is a round flatbread native to the Indian subcontinent. It is popular in India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Maldives, Myanmar, Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore, Thailand, Guyana, Suriname, Jamaica, Trini ...
and curry
A curry is a dish with a sauce seasoned with spices, mainly associated with South Asian cuisine. In southern India, leaves from the curry tree may be included.
There are many varieties of curry. The choice of spices for each dish in trad ...
, peanut soup
Peanut soup or groundnut soup is a soup made from peanuts, often with various other ingredients. It is a staple of African cuisine but is also eaten in East Asia (Taiwan), the United States (mainly in Virginia) and other areas around the world. ...
, battered fried plantain
Fried plantain is a dish cooked wherever plantains grow, from West Africa to East Africa as well as Central America, the tropical region of northern South America and the Caribbean countries like Haiti to Cuba and in many parts of Southeast As ...
with peanut sauce
Peanut sauce, satay sauce (saté sauce), ''bumbu kacang'', ''sambal kacang'', or ''pecel '' is an Indonesian sauce made from ground roasted or fried peanuts, widely used in Indonesian cuisine and many other dishes throughout the world.
Peanut ...
, nasi goreng
''Nasi goreng'' (English pronunciation: ) is a Southeast Asian fried rice dish, usually cooked with pieces of meat and vegetables. One of Indonesia's national dishes, it is also eaten in Malay-speaking communities in countries such as Malaysi ...
, moksie alesi, bara, pom
* Trinidad and Tobago
Trinidad and Tobago (, ), officially the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago, is the southernmost island country in the Caribbean. Consisting of the main islands Trinidad and Tobago, and numerous much smaller islands, it is situated south of ...
– doubles, curry
A curry is a dish with a sauce seasoned with spices, mainly associated with South Asian cuisine. In southern India, leaves from the curry tree may be included.
There are many varieties of curry. The choice of spices for each dish in trad ...
with roti
Roti (also known as chapati) is a round flatbread native to the Indian subcontinent. It is popular in India, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Nepal, Bangladesh, Maldives, Myanmar, Malaysia, Indonesia, Singapore, Thailand, Guyana, Suriname, Jamaica, Trini ...
or dal bhat
Dal bhat ( ne, दालभात, ur, دال بھات, bn, ডাল ভাত, gu, દાળ ભાત, mr, डाळ भात, as, দাইল ভাত ''dail bhat'' / ডালি ভাত ''dali bhat'') is a traditional meal from th ...
, aloo pie
An aloo pie is a fried dumpling popular in the cuisine of Trinidad and Tobago. It is a soft, fried pastry made from flour and water, and filled with boiled, spiced and mashed potatoes (''aloo'' being the Hindi word for "potato") and other vegetabl ...
, phulourie, callaloo
Callaloo (many spelling variants, such as kallaloo, calaloo, calalloo, calaloux or callalloo; ) is a popular Caribbean vegetable dish. There are many variants across the Caribbean, depending on the availability of local vegetables. The main in ...
, bake and shark, curry crab and dumpling
* United States Virgin Islands
The United States Virgin Islands,. Also called the ''American Virgin Islands'' and the ''U.S. Virgin Islands''. officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and an unincorporated and organized territory ...
– stewed goat, oxtail or beef, seafood, callaloo
Callaloo (many spelling variants, such as kallaloo, calaloo, calalloo, calaloux or callalloo; ) is a popular Caribbean vegetable dish. There are many variants across the Caribbean, depending on the availability of local vegetables. The main in ...
, fungee
See also
* African diaspora *Anchor coinage
The anchor coinage was a series of four denominations of silver coins issued for use in some British colonies in 1820 and 1822. The name comes from the crowned anchor that appears on the obverse of the coins. The denominations were sixteenth, eigh ...
* British African-Caribbean people
British African-Caribbean people are an ethnic group in the United Kingdom. They are British citizens whose ancestry originates from the Caribbean or they are nationals of the Caribbean who reside in the UK. There are some self-identified Afro-C ...
* British Indo-Caribbean people
British Indo-Caribbean people are residents of the United Kingdom who were born in the Caribbean and whose ancestors are indigenous to India. The UK has a large population of Indo-Caribbean people.
Background
Indian people were first introduced ...
* Caribbean people
* Climate change in the Caribbean
* CONCACAF
The Confederation of North, Central America and Caribbean Association Football,, ; french: Confédération de football d'Amérique du Nord, d'Amérique centrale et des Caraïbes, . Dutch language, Dutch uses the English name. abbreviated as CON ...
* Council on Hemispheric Affairs
The Council on Hemispheric Affairs (COHA) is a Washington, D.C.-based non-governmental organization (NGO) founded in 1975. The organization can draw on a large number of interns of graduate and undergraduate students, who gain experience in diffe ...
* Culture of the Caribbean
The term Caribbean culture summarizes the artistic, musical, literary, culinary, political and social elements that are representative of Caribbean people all over the world.
As a collection of settler nations, the contemporary Caribbean has b ...
* Economy of the Caribbean
The 'Economy of the Caribbean' is varied, but depends heavily on natural resources, agriculture and travel and tourism.
Main trading partners
Natural resources
By international standards, minerals most valuable on the international market are fo ...
* Indian diaspora
Overseas Indians (IAST: ), officially Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) and Overseas Citizens of India (OCIs) are Indians who live outside of the Republic of India. According to the Government of India, ''Non-Resident Indians'' are citizens of Indi ...
* Indo-Caribbean
* Indo-Caribbean American
Indo-Caribbean Americans or Indian-Caribbean Americans, are Americans who trace their ancestry ultimately to India, though whose recent ancestors lived in the Caribbean, where they migrated beginning in 1838 as indentured laborers. There are l ...
* List of Caribbean music genres
Caribbean music genres are very diverse. They are each synthesis of African, European, Arab, Asian, and Indigenous influences, largely created by descendants of African slaves (see Afro-Caribbean music), along with contributions from other com ...
* List of sovereign states and dependent territories in the Caribbean
* NECOBELAC Project
* Non-resident Indian and person of Indian origin
Overseas Indians ( IAST: ), officially Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) and Overseas Citizens of India (OCIs) are Indians who live outside of the Republic of India. According to the Government of India, ''Non-Resident Indians'' are citizens of In ...
* Piracy in the Caribbean
]The era of piracy in the Caribbean began in the 1500s and phased out in the 1830s after the navies of the nations of Western Europe and North America with colonies in the Caribbean began combating pirates. The period during which pirates were ...
* Politics of the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean S ...
* Tourism in the Caribbean
Tourism is one of the Caribbean's major economic sectors, with 25 million visitors contributing $49 billion towards the area's gross domestic product in 2013, which represented 14% of its total GDP. It is often described as, "the most tourism-dep ...
Geography:
* Americas (terminology)
The Americas, also known as America,"America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 33: " 6c: from the feminine of ''Americus'', the Latinized first name of the expl ...
* List of archipelagos by number of islands
* List of Caribbean islands
* List of indigenous names of Eastern Caribbean islands
* List of mountain peaks of the Caribbean
* List of Ultras of the Caribbean
* Middle America (Americas)
* Latin America and the Caribbean (region)
Notes
References
Bibliography
* Engerman, Stanley L. "A Population History of the Caribbean", pp. 483–528 in ''A Population History of North America'' Michael R. Haines and Richard Hall Steckel (Eds.), Cambridge University Press, 2000, . * Hillman, Richard S., and Thomas J. D'agostino, eds. ''Understanding the Contemporary Caribbean'', London: Lynne Rienner, 2003 .Further reading
* Develtere, Patrick R. 1994. "Co-operation and development: With special reference to the experience of the Commonwealth Caribbean" ACCO, * Gowricharn, Ruben. ''Caribbean Transnationalism: Migration, Pluralization, and Social Cohesion''. Lanham: Lexington Books, 2006. * Henke, Holger, and Fred Reno, eds. ''Modern Political Culture in the Caribbean''. Kingston:University of West Indies
The University of the West Indies (UWI), originally University College of the West Indies, is a public university system established to serve the higher education needs of the residents of 17 English-speaking countries and territories in th ...
Press, 2003.
* Heuman, Gad. ''The Caribbean: Brief Histories''. London: A Hodder Arnold Publication, 2006.
* de Kadt, Emanuel, (editor). ''Patterns of foreign influence in the Caribbean'', Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books ...
, 1972.
* Knight, Franklin W. ''The Modern Caribbean'' (University of North Carolina Press, 1989).
* Kurlansky, Mark. 1992. ''A Continent of Islands: Searching for the Caribbean Destiny''. Addison-Wesley Publishing.
* Langley, Lester D. ''The United States and the Caribbean in the Twentieth Century''. London: University of Georgia Press
The University of Georgia Press or UGA Press is the university press of the University of Georgia, a public land-grant research university with its main campus in Athens, Georgia. It is the oldest and largest publishing house in Georgia and a ...
, 1989.
* Maingot, Anthony P. ''The United States and the Caribbean: Challenges of an Asymmetrical Relationship''. Westview Press, 1994.
* Palmie, Stephan, and Francisco A. Scarano, eds. ''The Caribbean: A History of the Region and Its Peoples'' (University of Chicago Press; 2011); 660 pp.; writings on the region since the pre-Columbia era.
* Ramnarine, Tina K. ''Beautiful Cosmos: Performance and Belonging in the Caribbean Diaspora''. London, Pluto Press, 2007.
* Rowntree, Lester/Martin Lewis/Marie Price/William Wyckoff. ''Diversity Amid Globalization: World Regions, Environment, Development'', 4th edition, 2008.
External links
*Digital Library of the Caribbean
Manioc, open access digital Library, books, images, conferences, articles about the Caribbean
Federal Research Division of the U.S. Library of Congress
Caribbean Islands (1987)
LANIC Caribbean country pages
* {{Authority control