Capital Of Uzbekistan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also historically known as Chach is the
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
and largest city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or their metropo ...
of Uzbekistan. It is the most populous city in Central Asia, with a population of 2,909,500 (2022). It is in northeastern Uzbekistan, near the border with Kazakhstan. Tashkent comes from the Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
''tash'' and ''kent'', literally translated as "Stone City" or "City of Stones".
Before Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
ic influence started in the mid-8th century AD, Tashkent was influenced by the Sogdian and Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
cultures. After Genghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
destroyed it in 1219, it was rebuilt and profited from the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
. From the 18th to the 19th century, the city became an independent city-state, before being re-conquered by the Khanate of Kokand. In 1865, Tashkent fell to the Russian Empire; it became the capital of Russian Turkestan. In Soviet times, it witnessed major growth and demographic changes due to forced deportations from throughout the Soviet Union. Much of Tashkent was destroyed in the 1966 Tashkent earthquake
The 1966 Tashkent earthquake ( uz, Toshkent zilzilasi; russian: Ташкентское землетрясение) occurred on 26 April in the Uzbek SSR. It had a moment magnitude of 5.2 with an epicenter in central Tashkent at a depth of . The e ...
, but it was rebuilt as a model Soviet city. It was the fourth-largest city in the Soviet Union at the time, after Moscow, Leningrad and Kyiv.
Today, as the capital of an independent Uzbekistan, Tashkent retains a multiethnic population, with ethnic Uzbeks as the majority. In 2009, it celebrated its 2,200 years of written history.
History
Etymology
During its long history, Tashkent has had various changes in names and political and religious affiliations. Abu Rayhan Biruni wrote that the city's name Tashkent comes from the Turkic ''tash'' and ''kent'', literally translated as "Stone City" or "City of Stones".Ilya Gershevitch
Ilya Gershevitch (1914 in Zürich – 2001 in Cambridge) was a noted Iranologist.
Gershevitch was born to Russian parents fleeing from Germany to Switzerland at the outbreak of World War I.
He enrolled in the University of Rome in 1933, and mov ...
(1974:55, 72) (apud Livshits, 2007:179) traces the city's old name Chach back to Old Iranian *''čāiča-'' "area of water, lake" (cf. Lake ''Čaēčista'' mentioned in the Avesta) (whence Middle Chinese transcription *''źiäk'' > standard Chinese
Standard Chinese ()—in linguistics Standard Northern Mandarin or Standard Beijing Mandarin, in common speech simply Mandarin, better qualified as Standard Mandarin, Modern Standard Mandarin or Standard Mandarin Chinese—is a modern Standar ...
''Shí'' with Chinese character 石 for "stone"), and *''Čačkand'' ~ ''Čačkanθ'' was the basis for Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
adaption Tashkent, popularly etymologized as "stone city".
Early history
Tashkent was first settled some time between the 5th and 3rd centuries BC by ancient people as anoasis
In ecology, an oasis (; ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environment'ksar''with its surrounding feeding source, the palm grove, within a relational and circulatory nomadic system.”
The location of oases has been of critical imp ...
on the Chirchik River, near the foothills of the West Tian Shan Mountains. In ancient times, this area contained Beitian, probably the summer "capital" of the Kangju
Kangju (; Eastern Han Chinese: ''kʰɑŋ-kɨɑ'' < *''khâŋ-ka'' (c. 140 BCE)) was the Chinese name of a kingdom in
 In pre-Islamic and early Islamic times, the town and the province were known as ''Chach''. The Shahnameh of
In pre-Islamic and early Islamic times, the town and the province were known as ''Chach''. The Shahnameh of
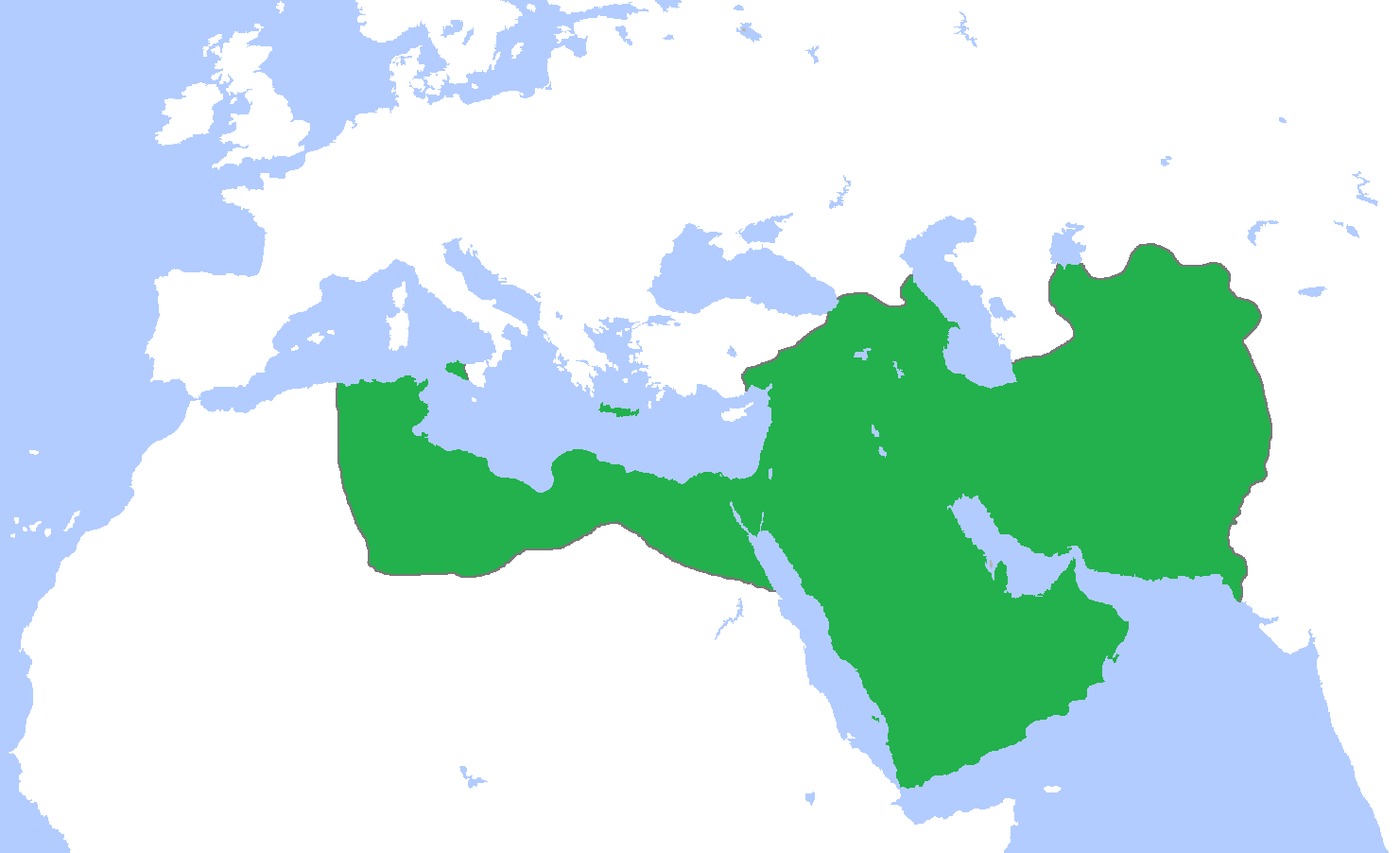 Tashkent was conquered by the Arabs at the beginning of the 8th century.
According to the descriptions of the authors of the 10th century, Shash was structurally divided into a citadel, an inner city (madina) and two suburbs - an inner (rabad-dahil) and an outer (rabad-harij). The citadel, surrounded by a special wall with two gates, contained the ruler's palace and the prison.
Tashkent was conquered by the Arabs at the beginning of the 8th century.
According to the descriptions of the authors of the 10th century, Shash was structurally divided into a citadel, an inner city (madina) and two suburbs - an inner (rabad-dahil) and an outer (rabad-harij). The citadel, surrounded by a special wall with two gates, contained the ruler's palace and the prison.

 The most famous saint Sufi of Tashkent was Sheikh Khovendi at-Takhur (13th to the first half of the 14th century). According to legend, Amir Timur, who was treating his wounded leg in Tashkent with the healing water of the Zem-Zem spring, ordered to build a mausoleum for the saint. By order of Timur, the Zangiata mausoleum was built.
The most famous saint Sufi of Tashkent was Sheikh Khovendi at-Takhur (13th to the first half of the 14th century). According to legend, Amir Timur, who was treating his wounded leg in Tashkent with the healing water of the Zem-Zem spring, ordered to build a mausoleum for the saint. By order of Timur, the Zangiata mausoleum was built.
 Shaybanid Suyunchkhoja Khan was an enlightened Uzbek ruler; following the traditions of his ancestors Mirzo
Shaybanid Suyunchkhoja Khan was an enlightened Uzbek ruler; following the traditions of his ancestors Mirzo
 The Tsar liberally rewarded Chernyayev and his men with medals and bonuses, but regarded the impulsive general as a loose cannon, and soon replaced him with General Konstantin Petrovich von Kaufman. Far from being granted independence, Tashkent became the capital of the new territory of Russian Turkistan, with Kaufman as first Governor-General. A
The Tsar liberally rewarded Chernyayev and his men with medals and bonuses, but regarded the impulsive general as a loose cannon, and soon replaced him with General Konstantin Petrovich von Kaufman. Far from being granted independence, Tashkent became the capital of the new territory of Russian Turkistan, with Kaufman as first Governor-General. A
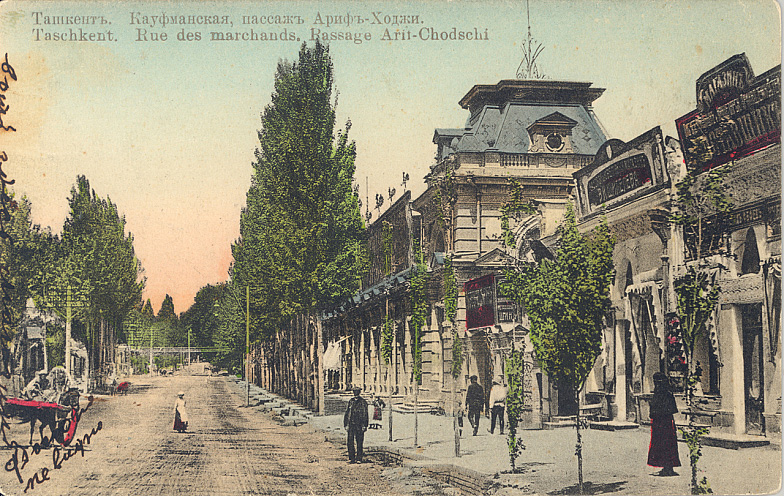 With the fall of the Russian Empire, the Russian Provisional Government removed all civil restrictions based on religion and nationality, contributing to local enthusiasm for the
With the fall of the Russian Empire, the Russian Provisional Government removed all civil restrictions based on religion and nationality, contributing to local enthusiasm for the
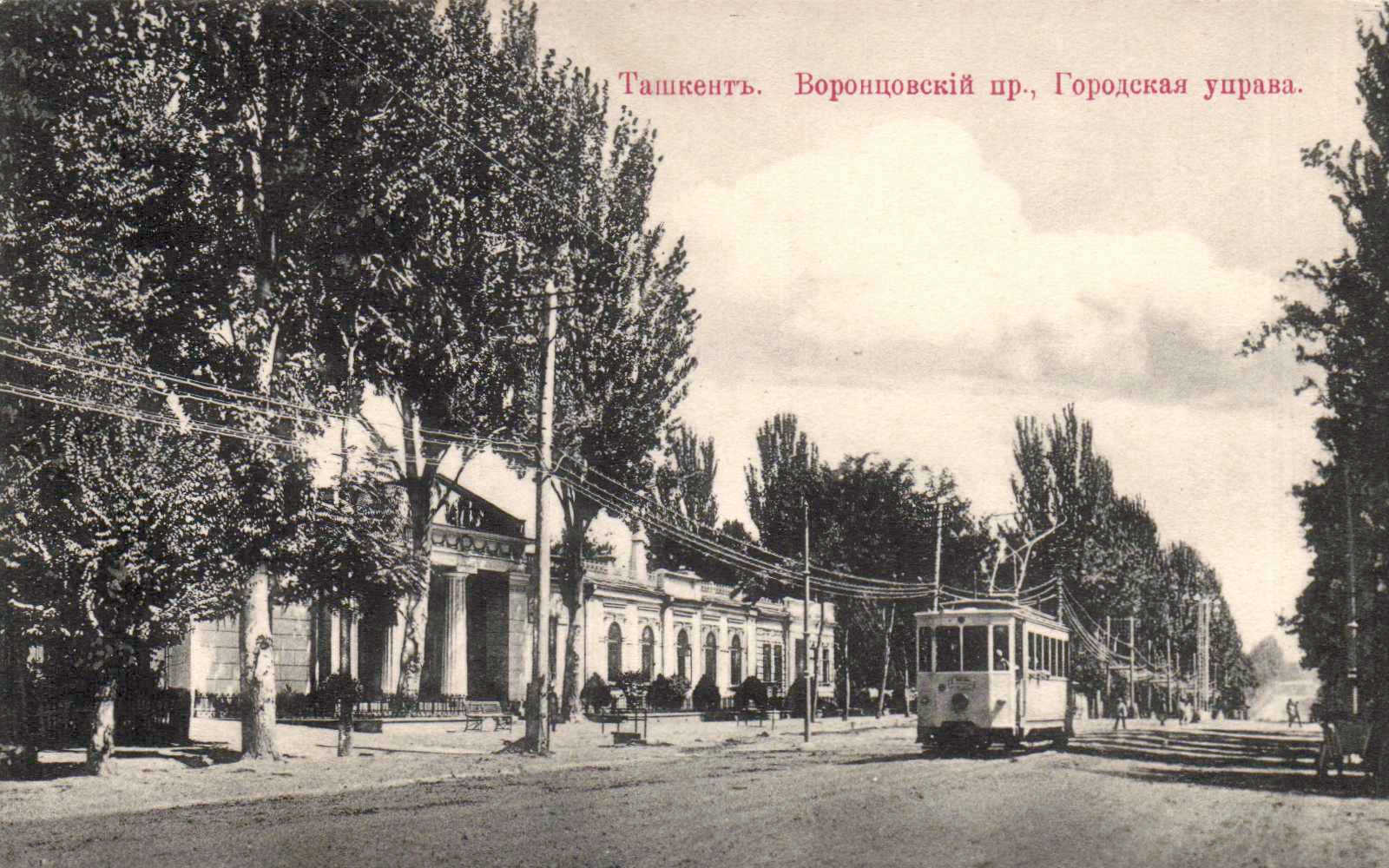

 The city began to industrialize in the 1920s and 1930s.
Violating the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union in June 1941. The government worked to relocate factories from western Russia and Ukraine to Tashkent to preserve the Soviet industrial capacity. This led to great increase in industry during World War II.
It also evacuated most of the German communist emigres to Tashkent.Robert K. Shirer, "Johannes R. Becher 1891–1958"
The city began to industrialize in the 1920s and 1930s.
Violating the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union in June 1941. The government worked to relocate factories from western Russia and Ukraine to Tashkent to preserve the Soviet industrial capacity. This led to great increase in industry during World War II.
It also evacuated most of the German communist emigres to Tashkent.Robert K. Shirer, "Johannes R. Becher 1891–1958"
, ''Encyclopedia of German Literature'', Chicago and London: Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers, 2000, by permission at Digital Commons, University of Nebraska, accessed 3 February 2013 The Russian population increased dramatically; evacuees from the war zones increased the total population of Tashkent to well over a million. Russians and Ukrainians eventually comprised more than half of the total residents of Tashkent. Many of the former refugees stayed in Tashkent to live after the war, rather than return to former homes. During the postwar period, the Soviet Union established numerous scientific and engineering facilities in Tashkent. On 10 January 1966, then Indian Prime Minister Lal Bahadur Shastri and
 Since 1991, the city has changed economically, culturally, and architecturally. New development has superseded or replaced icons of the Soviet era. The largest statue ever erected for Lenin was replaced with a globe, featuring a geographic map of Uzbekistan. Buildings from the Soviet era have been replaced with new modern buildings. The "Downtown Tashkent" district includes the 22-story NBU Bank building, international hotels, the International Business Center, and the Plaza Building.
Since 1991, the city has changed economically, culturally, and architecturally. New development has superseded or replaced icons of the Soviet era. The largest statue ever erected for Lenin was replaced with a globe, featuring a geographic map of Uzbekistan. Buildings from the Soviet era have been replaced with new modern buildings. The "Downtown Tashkent" district includes the 22-story NBU Bank building, international hotels, the International Business Center, and the Plaza Building.
 The Tashkent Business district is a special district, established for the development of small, medium and large businesses in Uzbekistan. In 2018, was started to build a Tashkent city (new Downtown) which would include a new business district with skyscrapers of local and foreign companies, world hotels such as Hilton Tashkent Hotel, apartments, biggest malls, shops and other entertainments. The construction of the International Business Center is planned to be completed by the end of 2021. Fitch assigns “BB-” rating to Tashkent city, “Stable” forecast.
In 2007, Tashkent was named a "cultural capital of the Islamic world" by '' Moscow News'', as the city has numerous historic mosques and significant Islamic sites, including the Islamic University. Tashkent holds the
The Tashkent Business district is a special district, established for the development of small, medium and large businesses in Uzbekistan. In 2018, was started to build a Tashkent city (new Downtown) which would include a new business district with skyscrapers of local and foreign companies, world hotels such as Hilton Tashkent Hotel, apartments, biggest malls, shops and other entertainments. The construction of the International Business Center is planned to be completed by the end of 2021. Fitch assigns “BB-” rating to Tashkent city, “Stable” forecast.
In 2007, Tashkent was named a "cultural capital of the Islamic world" by '' Moscow News'', as the city has numerous historic mosques and significant Islamic sites, including the Islamic University. Tashkent holds the
File:Tashkent History 1860.jpg, c. 1865
File:Tashkent History 1913.jpg, 1913
File:Tashkent History 1940.jpg, 1940
File:Tashkent History 1965.jpg, 1965
File:Tashkent History 1967.jpg, 1966: earthquake and subsequent redevelopment
File:Tashkent History 1981.jpg, 1981
File:Tashkent History 2000.jpg, 2000
 In 1983, the population of Tashkent amounted to 1,902,000 people living in a municipal area of . By 1991, (
In 1983, the population of Tashkent amounted to 1,902,000 people living in a municipal area of . By 1991, (


 Since 2020, when the
Since 2020, when the
At the time of the Tsarist take over it had four districts (Uzbek ''daha''): #Beshyoghoch #Kukcha #Shaykhontokhur #Sebzor In 1940 it had the following districts (Russian ''район''): # Oktyabr # Kirov # Stalin # Frunze # Lenin # Kuybishev By 1981 they were reorganized into: #Bektemir #Akmal-Ikramov (Uchtepa) #Khamza (Yashnobod) #Lenin (Mirobod) #Kuybishev (Mirzo Ulugbek) #Sergeli #Oktober (Shaykhontokhur) #Sobir Rakhimov (Olmazar) #Chilanzar #Frunze (Yakkasaray) #Kirov (Yunusabad)
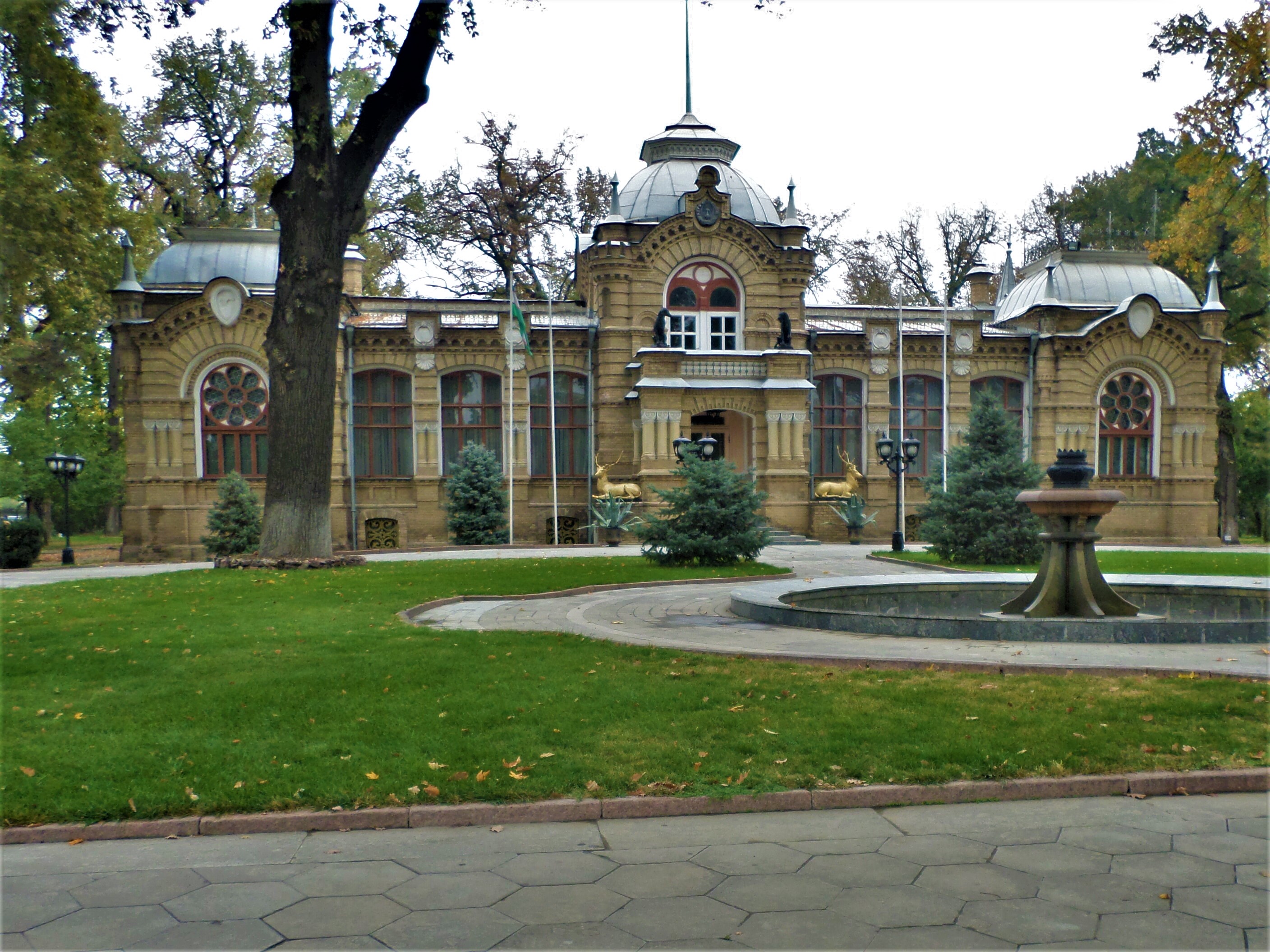



 Due to the destruction of most of the ancient city during the
Due to the destruction of most of the ancient city during the
 * Metro system
*
* Metro system
*

Museum of Fine Arts
All about capital of Uzbekistan – TashkentPhotos of historical monuments and modern buildings in TashkentRecent photos of Tashkent with comments in EnglishDisability Information Resource Centre in Tashkent
{{Authority control Capitals in Asia Cities in Central Asia Populated places along the Silk Road Populated places in Uzbekistan Syr-Darya Oblast Populated places established in the 1st millennium BC 1st-millennium BC establishments
Central Asia< ...
confederacy. Some scholars believe that a "Stone Tower" mentioned by Ptolemy in his famous treatise ''Geography'', and by other early accounts of travel on the old Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
, referred to this settlement (due to its etymology). This tower is said to have marked the midway point between Europe and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. Other scholars, however, disagree with this identification, though it remains one of four most probable sites for the Stone Tower.
History as Chach
 In pre-Islamic and early Islamic times, the town and the province were known as ''Chach''. The Shahnameh of
In pre-Islamic and early Islamic times, the town and the province were known as ''Chach''. The Shahnameh of Ferdowsi
Abul-Qâsem Ferdowsi Tusi ( fa, ; 940 – 1019/1025 CE), also Firdawsi or Ferdowsi (), was a Persians, Persian poet and the author of ''Shahnameh'' ("Book of Kings"), which is one of the world's longest epic poetry, epic poems created by a sin ...
also refers to the city as Chach.
The principality of Chach had a square citadel built around the 5th to 3rd centuries BC, some south of the Syr Darya
The Syr Darya (, ),, , ; rus, Сырдарья́, Syrdarjja, p=sɨrdɐˈrʲja; fa, سيردريا, Sirdaryâ; tg, Сирдарё, Sirdaryo; tr, Seyhun, Siri Derya; ar, سيحون, Seyḥūn; uz, Sirdaryo, script-Latn/. historically known ...
River. By the 7th century AD, Chach had more than 30 towns and a network of over 50 canals, forming a trade center between the Sogdians and Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
nomads. The Buddhist monk Xuanzang (602/603? – 664 AD), who travelled from China to India through Central Asia, mentioned the name of the city as (). The Chinese chronicles '' History of Northern Dynasties'', '' Book of Sui'', and ''Old Book of Tang
The ''Old Book of Tang'', or simply the ''Book of Tang'', is the first classic historical work about the Tang dynasty, comprising 200 chapters, and is one of the Twenty-Four Histories. Originally compiled during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdo ...
'' mention a possession called ("stone") or with a capital of the same name since the fifth century AD.
In 558–603, Chach was part of the Turkic Khaganate. At the beginning of the 7th century, the Turkic Kaganate, as a result of internecine wars and wars with its neighbors, disintegrated into the Western and Eastern Kaganates. The Western Turkic ruler Tong Yabghu Qaghan (618-630) set up his headquarters in the Ming-bulak area to the north of Chach. Here he received embassies from the emperors of the Tang Empire and Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ...
. In 626, the Indian preacher Prabhakaramitra arrived with ten companions to the Khagan. In 628, a Buddhist Chinese monk Xuanzang arrived in Ming Bulak.
The Turkic rulers of Chach minted their coins with the inscription on the obverse side of the "lord of the Khakan money" (mid-8th century); with an inscription in the ruler Turk (VII century), in Nudjket in the middle of the VIII century, coins were issued with the obverse inscription “Nanchu (Banchu) Ertegin sovereign".
Islamic Caliphate
 Tashkent was conquered by the Arabs at the beginning of the 8th century.
According to the descriptions of the authors of the 10th century, Shash was structurally divided into a citadel, an inner city (madina) and two suburbs - an inner (rabad-dahil) and an outer (rabad-harij). The citadel, surrounded by a special wall with two gates, contained the ruler's palace and the prison.
Tashkent was conquered by the Arabs at the beginning of the 8th century.
According to the descriptions of the authors of the 10th century, Shash was structurally divided into a citadel, an inner city (madina) and two suburbs - an inner (rabad-dahil) and an outer (rabad-harij). The citadel, surrounded by a special wall with two gates, contained the ruler's palace and the prison.

Post Caliphate rule
Under the Samanid Empire, whose founder Ismail Samani was a descendant of Persian Zoroastrian convert toIslam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, the city came to be known as Binkath. However, the Arabs retained the old name of ''Chach'' for the surrounding region, pronouncing it ''ash-Shāsh'' () instead. Kand, qand, kent, kad, kath, kud—all meaning a city—are derived from the Persian/ Sogdian کنده (kanda), meaning a town or a city. They are found in city names such as Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, Yarkand
Yarkant County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also Shache County,, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency also transliterated from Uyghur as Yakan County, is a county in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous ...
, Panjakent
, image_skyline = Pajakent Bazaar1.jpg
, imagesize =
, image_caption = Panjakent Bazaar
, image_flag =
, image_seal =
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, pushpin_map = Tajikistan#West Asia
, pushpin_relief = yes
, pushpin_label_position =
, pushp ...
, Khujand etc.).
Abu Bakr Muhammad ibn Ali ash-Shashi, known as al-Kaffal ash-Shashi (904-975), was born in Tashkent - an Islamic theologian, scholar, jurist of the Shafi'i madhhab, hadith scholar and linguist.
After the 11th century, the name evolved from Chachkand/Chashkand to Tashkand. The modern spelling of "Tashkent" reflects Russian orthography and 20th-century Soviet influence.
At the end of the 10th century, Tashkent became part of the possessions of the Turkic state of the Karakhanids. In 998/99 the Tashkent oasis went to the Karakhanid Ahmad ibn Ali, who ruled the north-eastern regions of Mavarannahr. In 1177/78, a separate khanate was formed in the Tashkent oasis. Its center was Banakat, where dirhams Mu'izz ad-dunya wa-d-din Qilich-khan were minted, in 1195-1197 - Jalal ad-dunya wa-d-din Tafgach-khakan, in 1197-1206 - 'Imad ad-dunya va-d-din Ulug Egdish Chagry-khan.
Mongol conquest
The city was destroyed byGenghis Khan
''Chinggis Khaan'' ͡ʃʰiŋɡɪs xaːŋbr />Mongol script: ''Chinggis Qa(gh)an/ Chinggis Khagan''
, birth_name = Temüjin
, successor = Tolui (as regent)Ögedei Khan
, spouse =
, issue =
, house = Borjigin
, ...
in 1219 and lost much of its population as a result of the Mongols' destruction of the Khwarezmid Empire in 1220.
Timurid period
Under theTimurid Timurid refers to those descended from Timur (Tamerlane), a 14th-century conqueror:
* Timurid dynasty, a dynasty of Turco-Mongol lineage descended from Timur who established empires in Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent
** Timurid Empire of C ...
and subsequent Shaybanid dynasties, the city's population and culture gradually revived as a prominent strategic center of scholarship, commerce and trade along the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
.
During the reign of Amir Timur (1336-1405), Tashkent was restored and in the 14th-15th centuries Tashkent was part of Timur's empire. For Timur, Tashkent was considered a strategic city. In 1391 Timur set out in the spring from Tashkent to Desht-i-Kipchak to fight the Khan of the Golden Horde Tokhtamysh Khan. Timur returned from this victorious campaign through Tashkent.
Uzbek Shaybanid's dynasty period
In the 16th century, Tashkent was ruled by the Shaybanid dynasty. Shaybanid Suyunchkhoja Khan was an enlightened Uzbek ruler; following the traditions of his ancestors Mirzo
Shaybanid Suyunchkhoja Khan was an enlightened Uzbek ruler; following the traditions of his ancestors Mirzo Ulugbek
Mīrzā Muhammad Tāraghay bin Shāhrukh ( chg, میرزا محمد طارق بن شاہ رخ, fa, میرزا محمد تراغای بن شاہ رخ), better known as Ulugh Beg () (22 March 1394 – 27 October 1449), was a Timurid Empire, Tim ...
and Abul Khair Khan
Mirza Abū'l-Khair Mūhammed Khan bin Qājı Abdūllah Sultan ( kk, Мырза Әбілқайыр Мұхаммед хан бин Қажы Абдұллаh Сұлтан, , romanized: ''Myrza Äbılqaiyr Mūhammed Han bin Qajy Abdūllah Sūltan''), ...
, he gathered famous scientists, writers and poets at his court, among them: Vasifi, Abdullah Nasrullahi, Masud bin Osmani Kuhistani. Since 1518 Vasifi was the educator of the son of Suyunchhoja Khan Keldi Muhammad, with whom, after the death of his father in 1525, he moved to Tashkent. After the death of his former pupil, he became the educator of his son, Abu-l-Muzaffar Hasan-Sultan.
Later the city was subordinated to Shaybanid Abdullah Khan II
Abdullah Khan (''Abdollah Khan Ozbeg'') (1533/4–1598), known as "The old Khan (title), Khan", was an Uzbeks, Uzbek ruler of the Khanate of Bukhara (1500–1785). He was the last Shaybanid Dynasty, Shaybanid Khan of Bukhara from 1583 until his ...
(the ruler actually from 1557, officially in 1583–1598), who issued his coins here
From 1598 to 1604 Tashkent was ruled by the Shaybanid Keldi Muhammad, who issued silver and copper coins on his behalf.
Kazakh ruled period
In 1598, Kazakh Taukeel Khan was at war with the Khanate of Bukhara. The Bukhara troops sent against him were defeated by Kazakhs in the battle between Tashkent and Samarkand. During the reign of Yesim-Khan, a peace treaty was concluded between Bukhara and Kazakhs, according to which Kazakhs abandoned Samarkand, but left behind Tashkent, Turkestan and a number of Syr Darya cities. Yesim-Khan ruled theKazakh Khanate
The Kazakh Khanate ( kk, Қазақ Хандығы, , ), in eastern sources known as Ulus of the Kazakhs, Ulus of Jochi, Yurt of Urus, was a Kazakh state in Central Asia, successor of the Golden Horde existing from the 15th to 19th century, ...
from 1598 to 1628, his main merit was that he managed to unite the Kazakh khanate.
Tashkent state
In 1784, Yunus Khoja, the ruler of the dakha (district) Shayhantahur, united the entire city under his rule and created an independent Tashkent state (1784-1807), which by the beginning of the 19th century seized vast lands.Kokand Khanate
In 1809, Tashkent was annexed to the Khanate of Kokand. At the time, Tashkent had a population of around 100,000 and was considered the richest city in Central Asia. Under the Kokand domination, Tashkent was surrounded by a moat and an adobe battlement (about 20 kilometers long) with 12 gates. It prospered greatly through trade with Russia but chafed under Kokand's high taxes. The Tashkent clergy also favored the clergy ofBukhara
Bukhara (Uzbek language, Uzbek: /, ; tg, Бухоро, ) is the List of cities in Uzbekistan, seventh-largest city in Uzbekistan, with a population of 280,187 , and the capital of Bukhara Region.
People have inhabited the region around Bukhara ...
over that of Kokand. However, before the Emir of Bukhara could capitalize on this discontent, the Russian army arrived.
Colonial period
In May 1865,Mikhail Grigorevich Chernyayev
Mikhail Grigoryevich Chernyaev (Russian: Михаил Григорьевич Черняев) (3 November / 22 October 1828, Bender, Bessarabia Governorate – 16 August 1898) was a Russian major general, who, together with Konstantin Kaufman and ...
(Cherniaev), acting against the direct orders of the Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" i ...
and outnumbered at least 15–1, staged a daring night attack against a city with a wall long with 11 gates and 30,000 defenders. While a small contingent staged a diversionary attack, the main force penetrated the walls, led by a Russian Orthodox priest. Although the defense was stiff, the Russians captured the city after two days of heavy fighting and the loss of only 25 dead as opposed to several thousand of the defenders (including Alimqul `Alimqul (also spelt Alymkul, Alim quli, Alim kuli) (ca. 1833 – 1865) was a warlord in the Kokand Khanate, and its ''de facto'' ruler from 1863 to 1865.
Alimqul was born in Budjun Batken, 1833, into a family of a Kyrgyz- Kipchak ''beys''. ...
, the ruler of the Kokand Khanate). Chernyayev, dubbed the "Lion of Tashkent" by city elders, staged a hearts-and-minds campaign to win the population over. He abolished taxes for a year, rode unarmed through the streets and bazaars meeting common people, and appointed himself "Military Governor of Tashkent", recommending to Tsar Alexander II that the city become an independent khanate
A khaganate or khanate was a polity ruled by a khan, khagan, khatun, or khanum. That political territory was typically found on the Eurasian Steppe and could be equivalent in status to tribal chiefdom, principality, kingdom or empire.
Mong ...
under Russian protection.
 The Tsar liberally rewarded Chernyayev and his men with medals and bonuses, but regarded the impulsive general as a loose cannon, and soon replaced him with General Konstantin Petrovich von Kaufman. Far from being granted independence, Tashkent became the capital of the new territory of Russian Turkistan, with Kaufman as first Governor-General. A
The Tsar liberally rewarded Chernyayev and his men with medals and bonuses, but regarded the impulsive general as a loose cannon, and soon replaced him with General Konstantin Petrovich von Kaufman. Far from being granted independence, Tashkent became the capital of the new territory of Russian Turkistan, with Kaufman as first Governor-General. A cantonment
A cantonment (, , or ) is a military quarters. In Bangladesh, India and other parts of South Asia, a ''cantonment'' refers to a permanent military station (a term from the British India, colonial-era). In military of the United States, United Stat ...
and Russian settlement were built across the Ankhor Canal from the old city, and Russian settlers and merchants poured in. Tashkent was a center of espionage in the Great Game rivalry between Russia and the United Kingdom over Central Asia. The Turkestan Military District was established as part of the military reforms of 1874. The Trans-Caspian Railway arrived in 1889, and the railway workers who built it settled in Tashkent as well, bringing with them the seeds of Bolshevik Revolution.
Effect of the Russian Revolution
 With the fall of the Russian Empire, the Russian Provisional Government removed all civil restrictions based on religion and nationality, contributing to local enthusiasm for the
With the fall of the Russian Empire, the Russian Provisional Government removed all civil restrictions based on religion and nationality, contributing to local enthusiasm for the February Revolution
The February Revolution ( rus, Февра́льская револю́ция, r=Fevral'skaya revolyutsiya, p=fʲɪvˈralʲskəjə rʲɪvɐˈlʲutsɨjə), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and somet ...
. The Tashkent Soviet of Soldiers' and Workers' Deputies was soon set up, but primarily represented Russian residents, who made up about a fifth of the Tashkent population. Muslim leaders quickly set up the Tashkent Muslim Council (''Tashkand Shura-yi-Islamiya'') based in the old city. On 10 March 1917, there was a parade with Russian workers marching with red flags, Russian soldiers singing '' La Marseillaise'' and thousands of local Central Asians. Following various speeches, Governor-General Aleksey Kuropatkin closed the events with words "Long Live a great free Russia".
The First Turkestan Muslim Conference was held in Tashkent 16–20 April 1917. Like the Muslim Council, it was dominated by the Jadid
The Jadids were Muslim modernist reformers within the Russian Empire in the late 19th and early 20th century. They normally referred to themselves by the Turkic terms ''Taraqqiparvarlar'' ('progressives'), ''Ziyalilar'' ('intellectuals') or simpl ...
, Muslim reformers. A more conservative faction emerged in Tashkent centered around the Ulema. This faction proved more successful during the local elections of July 1917. They formed an alliance with Russian conservatives, while the Soviet became more radical. The Soviet attempt to seize power in September 1917 proved unsuccessful.
In April 1918, Tashkent became the capital of the Turkestan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (Turkestan ASSR
The Turkestan Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (initially, the Turkestan Socialist Federative Republic; 30 April 191827 October 1924) was an autonomous republic of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic located in Soviet Central As ...
). The new regime was threatened by White forces, '' basmachi;'' revolts from within, and purges ordered from Moscow.
Soviet period

 The city began to industrialize in the 1920s and 1930s.
Violating the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union in June 1941. The government worked to relocate factories from western Russia and Ukraine to Tashkent to preserve the Soviet industrial capacity. This led to great increase in industry during World War II.
It also evacuated most of the German communist emigres to Tashkent.Robert K. Shirer, "Johannes R. Becher 1891–1958"
The city began to industrialize in the 1920s and 1930s.
Violating the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union in June 1941. The government worked to relocate factories from western Russia and Ukraine to Tashkent to preserve the Soviet industrial capacity. This led to great increase in industry during World War II.
It also evacuated most of the German communist emigres to Tashkent.Robert K. Shirer, "Johannes R. Becher 1891–1958", ''Encyclopedia of German Literature'', Chicago and London: Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers, 2000, by permission at Digital Commons, University of Nebraska, accessed 3 February 2013 The Russian population increased dramatically; evacuees from the war zones increased the total population of Tashkent to well over a million. Russians and Ukrainians eventually comprised more than half of the total residents of Tashkent. Many of the former refugees stayed in Tashkent to live after the war, rather than return to former homes. During the postwar period, the Soviet Union established numerous scientific and engineering facilities in Tashkent. On 10 January 1966, then Indian Prime Minister Lal Bahadur Shastri and
Pakistan President
The president of Pakistan ( ur, , translit=s̤adr-i Pākiṣṭān), officially the President of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is the ceremonial head of state of Pakistan and the commander-in-chief of the Pakistan Armed Forces.Ayub Khan
Ayub Khan is a compound masculine name; Ayub is the Arabic version of the name of the Biblical figure Job, while Khan or Khaan is taken from the title used first by the Mongol rulers and then, in particular, their Islamic and Persian-influenced s ...
signed a pact in Tashkent with Soviet Premier
The Premier of the Soviet Union (russian: Глава Правительства СССР) was the head of government of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR). The office had four different names throughout its existence: Chairman of the ...
Alexei Kosygin as the mediator to resolve the terms of peace after the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965
The Indo-Pakistani War of 1965 or the Second Kashmir War was a culmination of skirmishes that took place between April 1965 and September 1965 between Pakistan and India. The conflict began following Pakistan's Operation Gibraltar, which was d ...
. On the next day, Shastri died suddenly, reportedly due to a heart attack. It is widely speculated that Shastri was killed by poisoning the water he drank.
Much of Tashkent's old city was destroyed by a powerful earthquake on 26 April 1966. More than 300,000 residents were left homeless, and some 78,000 poorly engineered homes were destroyed, mainly in the densely populated areas of the old city where traditional adobe
Adobe ( ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for ''mudbrick''. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is used to refer to any kind of e ...
housing predominated. The Soviet republics, and some other countries, such as Finland, sent "battalions of fraternal peoples" and urban planners to help rebuild devastated Tashkent.
Tashkent was rebuilt as a model Soviet city with wide streets planted with shade trees, parks, immense plazas for parades, fountains, monuments, and acres of apartment blocks. The Tashkent Metro
The Tashkent Metro ( uz, Toshkent metropoliteni, Тошкент метрополитени) is the rapid transit system serving the city of Tashkent, the capital of Uzbekistan. It was the seventh metro to be built in the former USSR, opening in 1 ...
was also built during this time. About 100,000 new homes were built by 1970, but the builders occupied many, rather than the homeless residents of Tashkent. Further development in the following years increased the size of the city with major new developments in the Chilonzor area, north-east and south-east of the city.
At the time of the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, Tashkent was the fourth-largest city in the USSR and a center of learning in the fields of science and engineering.
Due to the 1966 earthquake and the Soviet redevelopment, little architectural heritage has survived of Tashkent's ancient history. Few structures mark its significance as a trading point on the historic Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and reli ...
.
Capital of Uzbekistan
Tashkent is the capital of and the most cosmopolitan city in Uzbekistan. It was noted for its tree-lined streets, numerous fountains, and pleasant parks, at least until the tree-cutting campaigns initiated in 2009 by the local government. Since 1991, the city has changed economically, culturally, and architecturally. New development has superseded or replaced icons of the Soviet era. The largest statue ever erected for Lenin was replaced with a globe, featuring a geographic map of Uzbekistan. Buildings from the Soviet era have been replaced with new modern buildings. The "Downtown Tashkent" district includes the 22-story NBU Bank building, international hotels, the International Business Center, and the Plaza Building.
Since 1991, the city has changed economically, culturally, and architecturally. New development has superseded or replaced icons of the Soviet era. The largest statue ever erected for Lenin was replaced with a globe, featuring a geographic map of Uzbekistan. Buildings from the Soviet era have been replaced with new modern buildings. The "Downtown Tashkent" district includes the 22-story NBU Bank building, international hotels, the International Business Center, and the Plaza Building.
 The Tashkent Business district is a special district, established for the development of small, medium and large businesses in Uzbekistan. In 2018, was started to build a Tashkent city (new Downtown) which would include a new business district with skyscrapers of local and foreign companies, world hotels such as Hilton Tashkent Hotel, apartments, biggest malls, shops and other entertainments. The construction of the International Business Center is planned to be completed by the end of 2021. Fitch assigns “BB-” rating to Tashkent city, “Stable” forecast.
In 2007, Tashkent was named a "cultural capital of the Islamic world" by '' Moscow News'', as the city has numerous historic mosques and significant Islamic sites, including the Islamic University. Tashkent holds the
The Tashkent Business district is a special district, established for the development of small, medium and large businesses in Uzbekistan. In 2018, was started to build a Tashkent city (new Downtown) which would include a new business district with skyscrapers of local and foreign companies, world hotels such as Hilton Tashkent Hotel, apartments, biggest malls, shops and other entertainments. The construction of the International Business Center is planned to be completed by the end of 2021. Fitch assigns “BB-” rating to Tashkent city, “Stable” forecast.
In 2007, Tashkent was named a "cultural capital of the Islamic world" by '' Moscow News'', as the city has numerous historic mosques and significant Islamic sites, including the Islamic University. Tashkent holds the Samarkand Kufic Quran
The Samarkand Kufic Quran (also known as the Uthman Quran, Samarkand codex, Samarkand manuscript and Tashkent Quran) is an 8th or 9th century manuscript Quran written in the territory of modern Iraq in the Kufic script. Today it is kept in the ...
, one of the earliest written copies of the Quran, which has been located in the city since 1924.
Tashkent is the most visited city in the country, and has greatly benefited from increasing tourism as a result of reforms under president Shavkat Mirziyoyev and opening up by abolishing visas for visitors from the European Union and other developing countries or making visas easier for foreigners.
Tashkent over the years
The city and the origin of television
The first demonstration of a fully electronic TV set to the public was made in Tashkent in summer 1928 byBoris Grabovsky
Boris Pavlovich Grabovsky ( ua, Бори́с Па́влович Грабо́вський, 26 May 1901 – 13 January 1966) was a Soviet engineer of Ukrainian descent who invented a first fully electronic TV set (video transmitting tube and video ...
and his team. In his method that had been patented in Saratov
Saratov (, ; rus, Сара́тов, a=Ru-Saratov.ogg, p=sɐˈratəf) is the largest city and administrative center of Saratov Oblast, Russia, and a major port on the Volga River upstream (north) of Volgograd. Saratov had a population of 901,36 ...
in 1925, Boris Grabovsky proposed a new principle of TV imaging based on the vertical and horizontal electron beam sweeping under high voltage. Nowadays this principle of the TV imaging is used practically in all modern cathode-ray tubes. Historian and ethnographer Boris Golender (Борис Голендер in Russian), in a video lecture, described this event. This date of demonstration of the fully electronic TV set is the earliest known so far. Despite this fact, most modern historians disputably consider Vladimir Zworykin
Vladimir Kosma Zworykin; or with the patronymic as ''Kosmich''; or russian: Кузьмич, translit=Kuz'mich, label=none. Zworykin anglicized his name to ''Vladimir Kosma Zworykin'', replacing the patronymic with the name ''Kosma'' as a middle na ...
and Philo Farnsworth as inventors of the first fully electronic TV set. In 1964, the contribution made to the development of early television by Grabovsky was officially acknowledged by the Uzbek government and he was awarded the prestigious degree "Honorable Inventor of the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic".
Geography and climate
Geography
Tashkent is situated in a well-watered plain on the road betweenSamarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, Uzbekistan's second city, and Shymkent across the border. Tashkent is just 13 km from two border crossings into Kazakhstan.
Closest geographic cities with populations of over 1 million are: Shymkent (Kazakhstan), Dushanbe (Tajikistan), Bishkek
Bishkek ( ky, Бишкек), ), formerly Pishpek and Frunze, is the capital and largest city of Kyrgyzstan. Bishkek is also the administrative centre of the Chüy Region. The region surrounds the city, although the city itself is not part of ...
(Kyrgyzstan), Kashgar
Kashgar ( ug, قەشقەر, Qeshqer) or Kashi ( zh, c=喀什) is an oasis city in the Tarim Basin region of Southern Xinjiang. It is one of the westernmost cities of China, near the border with Afghanistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Pakistan ...
(China), Almaty
Almaty (; kk, Алматы; ), formerly known as Alma-Ata ( kk, Алма-Ата), is the List of most populous cities in Kazakhstan, largest city in Kazakhstan, with a population of about 2 million. It was the capital of Kazakhstan from 1929 to ...
(Kazakhstan), Kabul (Afghanistan) and Peshawar (Pakistan).
Tashkent sits at the confluence of the Chirchiq River
The Chirchiq or Chirchik ( uz, Chirchiq, Чирчиқ, russian: Чирчик) is a river of Uzbekistan, a major right tributary of the Syr Darya. It is in length and its basin has an area of . The principal tributary is the Ugom (right).
The ri ...
and several of its tributaries and is built on deep alluvial deposits up to . The city is located in an active tectonic area suffering large numbers of tremors and some earthquakes.
The local time in Tashkent is UTC/GMT +5 hours.
Climate
Tashkent features a Mediterranean climate ( Köppen: ''Csa'') bordering a humid continental climate ( Köppen: ''Dsa''). /upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/f0/Asia_K%C3%B6ppen_Map.png Updated Asian map of the Köppen climate classification system/ref> As a result, Tashkent experiences cold and often snowy winters not typically associated with most Mediterranean climates and long, hot and dry summers. Most precipitation occurs during winter, which frequently falls as snow. The city experiences two peaks of precipitation in the early winter and spring. The slightly unusual precipitation pattern is partially due to its altitude. Summers are long in Tashkent, usually lasting from May to September. Tashkent can be extremely hot during the months of July and August. The city also sees very little precipitation during the summer, particularly from June through September.Demographics
 In 1983, the population of Tashkent amounted to 1,902,000 people living in a municipal area of . By 1991, (
In 1983, the population of Tashkent amounted to 1,902,000 people living in a municipal area of . By 1991, (Dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
) the number of permanent residents of the capital had grown to approximately 2,136,600. Tashkent was the fourth most populated city in the former USSR, after Moscow, Leningrad ( St. Petersburg), and Kyiv. Nowadays, Tashkent remains the fourth most populous city in the CIS. The population of the city was 2,716,176 people in 2020.
*78.0% – Uzbeks
*5% – Russians
*4.5% – Tatars
*2.2% – Koryo-saram (Koreans)
*2.1% – Tajiks
*1.2% – Uighurs
The Uyghurs; ; ; ; zh, s=, t=, p=Wéiwú'ěr, IPA: ( ), alternatively spelled Uighurs, Uygurs or Uigurs, are a Turkic ethnic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the general region of Central and East Asia. The Uyghu ...
*7.0% – other ethnic backgrounds
Uzbek is the main spoken language as well as Russian for inter-ethnic communication. As with most of Uzbekistan, street signs and other things are often a mix of Latin and Cyrillic scripts.
Districts



 Since 2020, when the
Since 2020, when the Yangihayot
Yangihayot is one of 12 Districts of Tashkent, city districts (''tuman'') of Tashkent, the capital of Uzbekistan. It was created in 2020 from parts of the city districts Sergeli and Bektemir, and parts of the districts Zangiota District, Zangiota, ...
district was created, Tashkent is divided into the following 12 districts ( uz, tumanlar):At the time of the Tsarist take over it had four districts (Uzbek ''daha''): #Beshyoghoch #Kukcha #Shaykhontokhur #Sebzor In 1940 it had the following districts (Russian ''район''): # Oktyabr # Kirov # Stalin # Frunze # Lenin # Kuybishev By 1981 they were reorganized into: #Bektemir #Akmal-Ikramov (Uchtepa) #Khamza (Yashnobod) #Lenin (Mirobod) #Kuybishev (Mirzo Ulugbek) #Sergeli #Oktober (Shaykhontokhur) #Sobir Rakhimov (Olmazar) #Chilanzar #Frunze (Yakkasaray) #Kirov (Yunusabad)
Main sights

 Due to the destruction of most of the ancient city during the
Due to the destruction of most of the ancient city during the 1917 revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
and, later, the 1966 earthquake, little remains of Tashkent's traditional architectural heritage. Tashkent is, however, rich in museums and Soviet-era monuments. They include:
* Kukeldash Madrasah. Dating back to the reign of Abdullah Khan II
Abdullah Khan (''Abdollah Khan Ozbeg'') (1533/4–1598), known as "The old Khan (title), Khan", was an Uzbeks, Uzbek ruler of the Khanate of Bukhara (1500–1785). He was the last Shaybanid Dynasty, Shaybanid Khan of Bukhara from 1583 until his ...
(1557–1598) it is being restored by the provincial Religious Board of Mawarannahr Moslems. There is talk of making it into a museum, but it is currently being used as a madrassah.
*Chorsu Bazaar
Chorsu Bazaar ( fa, بازار چارسو, ), also called charsu bazaar, is the traditional bazaar located in the center of the old town of Tashkent, the capital city of Uzbekistan. Under its blue-colored domed building and the adjacent areas, a ...
, located near the Kukeldash Madrassa. This huge open air bazaar
A bazaar () or souk (; also transliterated as souq) is a marketplace consisting of multiple small Market stall, stalls or shops, especially in the Middle East, the Balkans, North Africa and India. However, temporary open markets elsewhere, suc ...
is the center of the old town of Tashkent. Everything imaginable is for sale. It is one of the major tourist attractions of the city.
*Hazrati Imam Complex. It includes several mosques, shrine, and a library which contains a manuscript Qur'an in Kufic script, considered to be the oldest extant Qur'an in the world. Dating from 655 and stained with the blood of murdered caliph, Uthman, it was brought by Timur to Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, seized by the Russians as a war trophy and taken to Saint Petersburg. It was returned to Uzbekistan in 1924.
*Yunus Khan Mausoleum. It is a group of three 15th-century mausoleums, restored in the 19th century. The biggest is the grave of Yunus Khan, grandfather of Mughal Empire founder Babur
Babur ( fa, , lit= tiger, translit= Bābur; ; 14 February 148326 December 1530), born Mīrzā Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad, was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his ...
.
*Palace of Prince Romanov. During the 19th century Grand Duke
Grand duke (feminine: grand duchess) is a European hereditary title, used either by certain monarchs or by members of certain monarchs' families. In status, a grand duke traditionally ranks in order of precedence below an emperor, as an approxi ...
Nikolai Konstantinovich, a first cousin of Alexander III of Russia was banished to Tashkent for some shady deals involving the Russian Crown Jewels. His palace still survives in the centre of the city. Once a museum, it has been appropriated by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.
*Alisher Navoi Opera and Ballet Theatre Ali Sher may refer to:
People
*Ali Sher Bengali, 16th-century Muslim theologian
* Ali Sher Hyderi, 20th-century political leader from Sindh, Pakistan
* Ali Sher Khalji, 13th-century governor of Bengal
*Ali Sher Khan Anchan, 17th-century king from ...
, built by the same architect who designed Lenin's Tomb
Lenin's Mausoleum (from 1953 to 1961 Lenin's & Stalin's Mausoleum) ( rus, links=no, Мавзолей Ленина, r=Mavzoley Lenina, p=məvzɐˈlʲej ˈlʲenʲɪnə), also known as Lenin's Tomb, situated on Red Square in the centre of Moscow, is ...
in Moscow, Aleksey Shchusev, with Japanese prisoner of war labor in World War II. It hosts Russian ballet and opera.
*Fine Arts Museum of Uzbekistan. It contains a major collection of art from the pre-Russian period, including Sogdian murals, Buddhist statues and Zoroastrian art, along with a more modern collection of 19th and 20th century applied art, such as suzani embroidered hangings. Of more interest is the large collection of paintings "borrowed" from the Hermitage by Grand Duke Romanov to decorate his palace in exile in Tashkent, and never returned. Behind the museum is a small park, containing the neglected graves of the Bolsheviks who died in the Russian Revolution of 1917 and to Osipov's treachery in 1919, along with first Uzbekistani President Yuldosh Akhunbabayev.
*Museum of Applied Arts. Housed in a traditional house originally commissioned for a wealthy tsarist diplomat, the house itself is the main attraction, rather than its collection of 19th and 20th century applied arts.
*State Museum of History of Uzbekistan
The State Museum of History of Uzbekistan ( Uzbek: ''Oʻzbekiston tarixi davlat muzeyi''; russian: Государственный музей истории Узбекистана), previously known as the National Museum of Turkestan, was founded i ...
the largest museum in the city. It is housed in the ex-Lenin Museum.
*Amir Timur Museum
The Amir Timur Museum is located in Tashkent, the capital of Uzbekistan. It opened in 1996, and is dedicated to the Turco-Mongol warlord Amir Timur (Tamerlane).
Origin
After Uzbekistan became independent in 1991, much attention was given to th ...
, housed in a building with brilliant blue dome and ornate interior. It houses exhibits of Timur and of President Islam Karimov. To adjacent south of the museum is Amir Timur Square
The Amir Timur Square () is the main town square in Tashkent, Uzbekistan.
History
The predecessor of the square is a park built during the first governor-general of the Russian Turkestan era. The square was at the intersection of two main streets ...
where there is a statue of Timur on horseback, surrounded by some of the nicest gardens and fountains in the city.
*Navoi Literary Museum, commemorating Uzbekistan's adopted literary hero, Alisher Navoi
'Ali-Shir Nava'i (9 February 1441 – 3 January 1501), also known as Nizām-al-Din ʿAli-Shir Herawī ( Chagatai: نظام الدین علی شیر نوایی, fa, نظامالدین علیشیر نوایی) was a Timurid poet, writer ...
, with replica manuscripts, Islamic calligraphy and 15th century miniature paintings.
*The Tashkent Metro
The Tashkent Metro ( uz, Toshkent metropoliteni, Тошкент метрополитени) is the rapid transit system serving the city of Tashkent, the capital of Uzbekistan. It was the seventh metro to be built in the former USSR, opening in 1 ...
is known for extravagant design and architecture in the buildings. Taking photos in the system was banned until 2018.
The Russian Orthodox church in Amir Temur Square, built in 1898, was demolished in 2009. The building had not been allowed to be used for religious purposes since the 1920s due to the anti-religious campaign conducted across the former Soviet Union by the Bolshevik (communist) government in Moscow. During the Soviet period the building was used for different non-religious purposes; after independence it was a bank.
Tashkent also has a World War II memorial park and a Defender of Motherland monument.
Education
Most important scientific institutions of Uzbekistan, such as theAcademy of Sciences of Uzbekistan
The Academy of Sciences of Uzbekistan ( uz, Oʻzbekiston Respublikasi Fanlar akademiyasi, Ўзбекистон Республикаси Фанлар академияси) is the main scientific organization of the Republic of Uzbekistan. It coordi ...
, are located in Tashkent. There are several universities and institutions of higher education:
* TEAM University
*The Branch of the Russian State University of Oil and Gas (NRU) named after I.M. Gubkin
* Tashkent Automobile and Road Construction Institute
* Tashkent State Technical University
*Tashkent Institute of Architecture and Construction
* Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Melioration
*International Business School Kelajak Ilmi
* Tashkent University of Information Technologies
* Westminster International University in Tashkent
* Turin Polytechnic University in Tashkent
* National University of Uzbekistan
* University of World Economy and Diplomacy
* Tashkent State Economic University
*Tashkent State Institute of Law
Tashkent State University of Law (TSUL) is a public higher educational institution. It is one of the leading Uzbek legal research centers, located in the capital city Tashkent.
The university is one of the leading universities in Uzbekistan, re ...
* Tashkent Financial Institute
*State Conservatory of Uzbekistan
*Tashkent Pediatric Medical Institute
*Tashkent State Medicine Academy
*Tashkent State University of Oriental Studies
The Tashkent State University of Oriental Studies ( uz, Toshkent davlat sharqshunoslik instituti) is a state institution of higher education in Tashkent, the capital of Uzbekistan. Founded in November 1918, the school is the only Oriental-studi ...
*Tashkent Islamic University
* Management Development Institute of Singapore in Tashkent
*Tashkent Institute of Textile and Light Industry
* Tashkent Institute of Railway Transport Engineers
*National Institute of Arts and Design named after Kamaleddin Bekhzod
* Inha University Tashkent
*Uzbekistan State University of World Languages
, native_name_lang =
, image = OʻzDJTU.jpg
, image_size = 200 px
, image_alt =
, caption = A front side of Uzbekistan State World Languages University
, latin_name =
, other_name = russian: Узбекский государствен ...
*AKFA UNIVERSITY
Media
*Nine Uzbek language newspapers, four in English, and nine in Russian. *Several television and cable television facilities, including Tashkent Tower, the second tallest structure in Central Asia. *Moreover, there are digital broadcasting systems available in Tashkent which is unique in Central Asia.Transportation
 * Metro system
*
* Metro system
*Tashkent International Airport
Islam Karimov Tashkent International Airport ( uz, Islom Karimov Toshkent Xalqaro Aeroporti) is the main international airport of Uzbekistan and the 3rd busiest airport in Central Asia (after Almaty International Airport and Astana Internation ...
is the largest in the country, connecting the city to Asia, Europe and North American continents.
* Tashkent–Samarkand high-speed rail line
*Trolleybus system was closed down in 2010.
* Tram transport ended at 1 May 2016.
Entertainment and shopping
There are several shopping malls in Tashkent. These include Next, Samarqand Darvoza and Kontinent shopping malls. Most of the malls, including Riviera and Compass mall, were built and are operated by the Tower Management Group. This is part of the Orient Group of Companies. The capital's most established theatre is the Alisher Navoi Theater, that has regular ballet and opera performances. Ilkhom Theater, founded by Mark Weil in 1976, was the first independent theater in the Soviet Union. In 2007 Mark Weil was murdered in Tashkent by 3 people, who under investigation claimed that he has "misinterpreted" the Qu'ran in a production he had directed. The theater operates and has a strong reputation in Tashkent.Sport

Football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
is the most popular sport in Tashkent, with the most prominent football clubs being Pakhtakor Tashkent FK, FC Bunyodkor, and PFC Lokomotiv Tashkent
PFC Lokomotiv Tashkent ( uz, Lokomotiv Toshkent Professional Futbol Klubi) is an Uzbekistan, Uzbek professional association football, football club based in Tashkent.
The owner and main sponsor of the club is a state-owned company Uzbek Railways. ...
, all three of which compete in the Uzbekistan Super League
Uzbekistan Super League ( uz, O'zbekiston Superligasi), also called Coca-Cola Uzbekistan Super League due to sponsorship reasons ( uz, Coca-Cola O'zbekiston Superligasi / Coca-Cola Ўзбекистон Суперлигаси), is the top division ...
. Footballers Maksim Shatskikh
Maksim Aleksandrovich Shatskikh (russian: Максим Александрович Шацких; born 30 August 1978) is an Uzbek professional football coach of Pakhtakor Tashkent and a former player.
He is widely regarded as one of the best ...
, Peter Odemwingie
Peter Osaze Odemwingie (born 15 July 1981) is a retired Nigerian professional footballer who played as a forward and winger.
Odemwingie grew up in Uzbekistan and Russia and began his career with Bendel Insurance in the Nigeria Premier League. ...
and Vasilis Hatzipanagis were born in the city.
Humo Tashkent
Humo Hockey Club, also known as Humo Tashkent, are a professional ice hockey team based in Tashkent, Uzbekistan. Originally a member of the Uzbekistan Ice Hockey League, Humo joined the Kazakhstan Hockey Championship for the 2022–23 Season. Hu ...
, a professional ice hockey team was established in 2019 with the aim of joining Kontinental Hockey League (KHL), a top level Eurasian league in future. Humo joined the second-tier Supreme Hockey League (VHL) for the 2019–20 season. Humo play their games at the Humo Ice Dome
The Humo Arena or Ice Dome Tashkent ( uz, «Humo Arena» muz majmuasi) is a multifunctional indoor arena located in Tashkent, Uzbekistan. Humo Arena is the biggest hockey arena in Central Asia with a capacity of 12,500 and the second after the Be ...
; both the team and arena derive their name from the mythical Huma bird.
Humo Tashkent was a member of the reformed Uzbekistan Ice Hockey League which began play in February 2019. Humo finished in first place at the end of the regular season.
Cyclist Djamolidine Abdoujaparov was born in the city, while tennis player Denis Istomin was raised there.
Akgul Amanmuradova and Iroda Tulyaganova
Iroda Tulyaganova ( uz, Ирода Тўлаганов, translit=Iroda To'laganova; born 7 January 1982) is a former professional tennis player from Uzbekistan.
Tulyaganova has career-high WTA rankings of 16 in singles (reached in June 2002) and ...
are notable female tennis players from Tashkent.
Gymnasts Alina Kabaeva and Israeli Olympian Alexander Shatilov were also born in the city.
Former world champion and Israeli Olympic bronze medalist sprint canoer in the K-1 500 m event Michael Kolganov
Michael "Misha" Kolganov (or Kalganov, he, מיכאל (מישה) קולגנוב, russian: Михаил Калганов; born October 24, 1974) is a USSR-born Israeli sprint kayaker and former world champion (1998–99). Competing in th ...
was also born in Tashkent.
In Weightlifting, Uzbekistan won the heavyweight class in both the Rio. and Tokyo Olympic Games. Tashkent is hosting the 2021 Weightlifting World Championships.
Notable people
* Behzod Abduraimov, Uzbek classical pianist *, Uzbek novelist * Ismoilkhuja Akhmedkhodjaev, Uzbek racing driver *Turgun Alimatov
Turgun Alimatov ( uz, Turgʻun Alimatov; 20 January 1922 – 17 December 2008) was a leading Uzbek classic music and shashmaqam player and composer of 20th century folk and classic music. He was a master performer of tanbur
The term ''Tanbur ...
, Uzbek classic music and shashmaqam player and composer
*Natasha Alam
Natasha Alam (Russian: Наталья Анатольевна Шиманчук; born Natalia Anatolievna Shimanchuk, born March 10, 1973) is an Uzbekistani–American actress and model. Alam has starred on ''True Blood'' and been a cover model for ...
, Uzbekistani–American actress and model
* Abdulla Aripov, Uzbek politician and Prime Minister of Uzbekistan
This is a list of prime ministers of Uzbekistan ( uz, O‘zbekiston bosh vaziri), from the establishment of the office in 1925 as the chairman of the Council of Ministers of the Uzbek SSR to the present day.
The current prime minister, Abdulla ...
* Artour 'Arteezy' Babaev, Uzbek-born Canadian Dota 2
''Dota 2'' is a 2013 multiplayer online battle arena (MOBA) video game by Valve. The game is a sequel to ''Defense of the Ancients'' (''DotA''), a community-created mod for Blizzard Entertainment's '' Warcraft III: Reign of Chaos.'' ''Dota 2' ...
professional player for Evil Geniuses
* Lola Astanova, Russian-American pianist
*Vera Bulatova
Vera Andreevna Bulatova (Russian: Вера Андреевна Булатова; September 30, 1915 in Moscow – December 11, 2014 in Tashkent) was a Russian–born Uzbekistani archaeologist, architectural historian and museologist. She authored ov ...
, archaeologist
* Vlada Ekshibarova (now Vlada Katic; born 1989), Israeli-Uzbekistani tennis player
*Sogdiana Fedorinskaya
Sogdiana (Russian language, Russian: Согдиана), also known as Sogdiana Fedorinskaya (Russian language, Russian: Согдиана Федоринская), born as Oksana Vladimirovna Nechitaylo (Russian language, Russian: Оксана В ...
, Uzbekistani singer and actress
*Gʻafur Gʻulom
Gʻafur Gʻulom or Gafur Gulom (Russified form Gafur Gulyam) ( uz, Gʻafur Gʻulom, Ғафур Ғулом) (May 10, 1903 – July 10, 1966) was an Uzbek poet, writer, and literary translator. He is best remembered for his stories ''Shum Bola'' (' ...
, poet
* Vasilis Hatzipanagis, Greek international footballer
* Ravshan Irmatov, football referee
*Arthur Kaliyev
Arthur Kaliyev (russian: Артур Калиев; born June 26, 2001) is an Uzbekistani-born American professional ice hockey forward for the Los Angeles Kings of the National Hockey League (NHL). He was drafted 33rd overall by the Kings in the ...
, born in Tashkent raised in Staten Island
Staten Island ( ) is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Richmond County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located in the city's southwest portion, the borough is separated from New Jersey by the Arthur Kill and the Kill Van Kull an ...
, New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
, American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
ice hockey player for the Los Angeles Kings of the NHL
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockey—LNH, ) is a professional ice hockey league in North America comprising 32 teams—25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranked professional ...
* Rustam Kasimdzhanov, chess player, former FIDE World Champion
*Moshe Kaveh
Moshe Kaveh (משה קוה; born 1943) is an Israeli physicist and former President of Bar-Ilan University.
Biography
Kaveh was born in Tashkent, Uzbek SSR, Soviet Union where his parents sought safety after fleeing from Poland. All of his fathe ...
(born 1943), Israeli physicist and former President of Bar-Ilan University
* Vladimir Kozlov, Ukrainian-American professional wrestler
* Varvara Lepchenko, Uzbekistani-born American professional tennis player
*Olena Lytovchenko
Olena Oleksiivna Lytovchenko (1 May 1963 – 28 October 2021) was a Ukrainian writer and a metallurgical engineer by education. She wrote and co-authored with her husband Timur Litovchenko adventures, historical fiction, and detective fiction wh ...
, writer
*Tohir Malik
Tohir Malik (27 December 1946 – 16 May 2019) was an Uzbek novelist and story writer. He was awarded Uzbek National Writer in 2000. Multiple films were made based on his novels and fictions, such as ''Last bullet'' (Uzbek language, Uzbek: '' ...
, novelist
*Boris Mavashev
Boris Mavashev ( he, בוריס מבשב, born 9 May 1939 in Tashkent) is an Israeli seismologist, doctor of geology and ecology, specializing in the geochemical and meteorological precursors of earthquakes.
Early life
Boris Mavashev was born on ...
, Israeli seismologist
*Eson Kandov
Eson Kandov (*October 31, 1941 in Tashkent) was an singer and musician from Uzbekistan with a successful career during the 1960-80s. He was awarded the distinction as Honored Artist of the Uzbek SSR in 1974 and is considered the first artist who ...
, singer and musician
*Abdulla Qodiriy
Abdulla Qodiriy ( uz, Abdulla Qodiriy, Абдулла Қодирий; russian: link=no, Абдулла́ Кадыри́) (April 10, 1894 – October 4, 1938), also spelt Abdullah Qodiriy and Abdullah Kadiri in English, was an Uzbek people, Uzbek ...
, writer
*Mirjalol Qosimov
Mirjalol Kushakovich Qosimov ( uz, Mirjalol Qoʻshoqovich Qosimov, russian: Мирджалол Кушакович Касымов; in English also: Mirdjalal Kasimov or Kasymov) (born 17 September 1970) is a former head coach of the Uzbekistan na ...
, former player and head coach of the Uzbekistan national football team
*Igor Povalyayev
Igor Stanislavovich Povalyayev (russian: Игорь Станиславович Поваляев; born 16 November 1962) is a former Russian-Uzbekistani professional footballer.
Club career
He made his professional debut in the Soviet Top League ...
, former Russian-Uzbekistani professional footballer
*Svetlana Radzivil
Svetlana Mikhaylovna Radzivil (russian: Светлана Михайловна Радзивил; born 17 January 1987 in Tashkent, Uzbek SSR) is an Uzbekistani high jumper. She is among Asia's top female high jumpers. She won the Asian Games tit ...
, Uzbekistani high jumper
*Artur Rozyyev
Artur Geldymuratovich Rozyyev (russian: Артур Гельдымуратович Розыев; born 25 October 1982) is a former Russian professional football player.
Club career
He played 5 seasons in the Russian Football National League
...
, former Russian professional football player
*Tursunoy Saidazimova Tursunoy Saidazimova (russian: Турсуной Саидазимова; 1911 – 10 May 1928), occasionally transliterated as Tursunoi Saidazimova, was one of the first Uzbek actresses in the Uzbek SSR and one of the first to sing onstage without ...
, singer
*Shakhida Shaimardanova
Shakhida Shaimardanova (born 1938) is an Uzbek composer who is best known for her ''Symphony in C Major''.
Shaimardanova was born in Tashkent
Tashkent (, uz, Toshkent, Тошкент/, ) (from russian: Ташкент), or Toshkent (; ), also ...
, composer
*Iroda Tulyaganova
Iroda Tulyaganova ( uz, Ирода Тўлаганов, translit=Iroda To'laganova; born 7 January 1982) is a former professional tennis player from Uzbekistan.
Tulyaganova has career-high WTA rankings of 16 in singles (reached in June 2002) and ...
, former tennis player
* Alisher Usmanov, born in Chust, Uzbekistan
Chust ( uz, Chust/Чуст; russian: Чуст) is a city in eastern Uzbekistan. It is the administrative center of Chust District. The City of Chust is located in the northern corner of the Fergana Valley along the river Chustsoy.
Chust is one ...
, spent his childhood in Tashkent
* Milana Vayntrub, Uzbek-born American actress and comedian
*Rita Volk
Margarita Volkovinskaya (russian: Маргарита Волковинская, born September 3, 1990), known professionally as Rita Volk, is an Uzbekistani–American actress. She is known for her role as Amy Raudenfeld in the MTV romantic com ...
, Uzbekistani–American actress
*Hakim Karimovich Zaripov
Hakim Karimovich Zaripov (variously Zaripov Khakim Karimovich; 17 September 1924 – 18 January 2023) was a Soviet and Uzbek circus performer, trick rider, and horse trainer.
Early life
Zaripov was born on 17 September 1924 in Tashkent, Turkesta ...
, circus performer
* Farrukh Zokirov, Uzbek and Soviet singer
* Zulfiya, writer and poet
Twin towns – sister cities
Tashkent is twinned with: * Ankara, Turkey * Ashgabat, Turkmenistan * Astana, Kazakhstan * Berlin, Germany *Bishkek
Bishkek ( ky, Бишкек), ), formerly Pishpek and Frunze, is the capital and largest city of Kyrgyzstan. Bishkek is also the administrative centre of the Chüy Region. The region surrounds the city, although the city itself is not part of ...
, Kyrgyzstan
* Cairo, Egypt
* Dnipro
Dnipro, previously called Dnipropetrovsk from 1926 until May 2016, is Ukraine's fourth-largest city, with about one million inhabitants. It is located in the eastern part of Ukraine, southeast of the Ukrainian capital Kyiv on the Dnieper Rive ...
, Ukraine
* Kyiv, Ukraine
* Moscow, Russia
* Nagoya, Japan
* Riga
Riga (; lv, Rīga , liv, Rīgõ) is the capital and largest city of Latvia and is home to 605,802 inhabitants which is a third of Latvia's population. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava river where it meets the Ba ...
, Latvia
* Seattle, United States
* Seoul, South Korea
* Shanghai, China
* Sverdlovsk, Ukraine
See also
*Gates of Tashkent
The Gates of Tashkent, in present-day Uzbekistan, were built around the town at the close of the 10th century, but did not survive to the present. The last gate was destroyed in 1890 as a result of the growth of the city, but some of the districts ...
* Tashkent Declaration
References
Museum of Fine Arts
Further reading
*Stronski, Paul, ''Tashkent: Forging a Soviet City, 1930–1966'' (Pittsburgh, University of Pittsburgh Press, 2010). *Jeff Sahadeo, ''Russian Colonial Society in Tashkent, 1865–1923'' (Bloomington, IN, Indiana University Press, 2010).External links
* *All about capital of Uzbekistan – Tashkent
{{Authority control Capitals in Asia Cities in Central Asia Populated places along the Silk Road Populated places in Uzbekistan Syr-Darya Oblast Populated places established in the 1st millennium BC 1st-millennium BC establishments