Capital Market Line on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
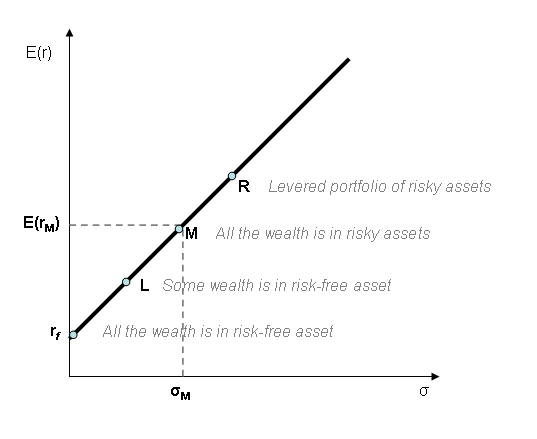 Capital market line (CML) is the tangent line drawn from the point of the risk-free asset to the
Capital market line (CML) is the tangent line drawn from the point of the risk-free asset to the
 Capital market line (CML) is the tangent line drawn from the point of the risk-free asset to the
Capital market line (CML) is the tangent line drawn from the point of the risk-free asset to the feasible region
In mathematical optimization, a feasible region, feasible set, search space, or solution space is the set of all possible points (sets of values of the choice variables) of an optimization problem that satisfy the problem's constraints, potent ...
for risky assets. The tangency point M represents the market portfolio
Market portfolio is a portfolio consisting of a weighted sum of every asset in the market, with weights in the proportions that they exist in the market, with the necessary assumption that these assets are infinitely divisible.
Richard Roll's c ...
, so named since all rational investors (minimum variance criterion) should hold their risky assets in the same proportions as their weights in the market portfolio.
Formula
: The CML results from the combination of the market portfolio and the risk-free asset (the point L). All points along the CML have superior risk-return profiles to any portfolio on theefficient frontier
In modern portfolio theory, the efficient frontier (or portfolio frontier) is an investment portfolio which occupies the "efficient" parts of the risk–return spectrum.
Formally, it is the set of portfolios which satisfy the condition that no o ...
, with the exception of the Market Portfolio, the point on the efficient frontier to which the CML is the tangent. From a CML perspective, the portfolio M is composed entirely of the risky asset, the market, and has no holding of the risk free asset, i.e., money is neither invested in, nor borrowed from the money market account. Points to the left of and above the CML are infeasible, whereas points to the right/below are attainable but inefficient.
Addition of leverage (the point R) creates levered portfolios that are also on the CML.
Capital market line, Sharpe ratio and alpha
All of the portfolios on the CML have the sameSharpe ratio
In finance, the Sharpe ratio (also known as the Sharpe index, the Sharpe measure, and the reward-to-variability ratio) measures the performance of an investment such as a security or portfolio compared to a risk-free asset, after adjusting for it ...
as that of the market portfolio, i.e.
:
In fact, the slope of the CML is the Sharpe ratio of the market portfolio.
A stock picking
In financial markets, stock valuation is the method of calculating theoretical values of companies and their stocks. The main use of these methods is to predict future market prices, or more generally, potential market prices, and thus to profit fr ...
rule of thumb is to buy assets whose Sharpe ratio will be above the CML and sell those whose Sharpe ratio will be below. Indeed, from the efficient market hypothesis
The efficient-market hypothesis (EMH) is a hypothesis in financial economics that states that asset prices reflect all available information. A direct implication is that it is impossible to "beat the market" consistently on a risk-adjusted bas ...
it follows that it's impossible to beat the market. Therefore, all portfolios should have a Sharpe ratio less than or equal to the market's. In consequence, if there is a portfolio (or asset) whose Sharpe ratio will be bigger than the market's then this portfolio (or asset) has a higher return per unit of risk (i.e. the volatility ), which contradicts the efficient market hypothesis
The efficient-market hypothesis (EMH) is a hypothesis in financial economics that states that asset prices reflect all available information. A direct implication is that it is impossible to "beat the market" consistently on a risk-adjusted bas ...
.
This ''abnormal'' extra return over the market's return at a given level of risk is what is called the alpha.
See also
* Capital allocation line *Efficient frontier
In modern portfolio theory, the efficient frontier (or portfolio frontier) is an investment portfolio which occupies the "efficient" parts of the risk–return spectrum.
Formally, it is the set of portfolios which satisfy the condition that no o ...
* Modern portfolio theory
Modern portfolio theory (MPT), or mean-variance analysis, is a mathematical framework for assembling a portfolio of assets such that the expected return is maximized for a given level of risk. It is a formalization and extension of diversificat ...
* Security characteristic line
* Security market line
Security market line (SML) is the representation of the capital asset pricing model. It displays the expected rate of return of an individual security as a function of systematic, non-diversifiable risk. The risk of an individual risky security re ...
References
{{stock market Investment