Cannabis Intoxication on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The effects of cannabis are caused by
The effects of cannabis are caused by



 When smoked, the short-term effects of cannabis manifest within seconds and are fully apparent within a few minutes, typically lasting for 1–3 hours, varying by the person and the strain of cannabis. After oral ingestion of cannabis, the onset of effect is delayed relative to smoking, taking 30 minutes to 2 hours, but the duration is prolonged due to continued slow absorption. The duration of noticeable effects has been observed to diminish after prolonged, repeated use and the development of increased tolerance to cannabinoids.
Cannabis use can decrease blood pressure, which increases the risk of
When smoked, the short-term effects of cannabis manifest within seconds and are fully apparent within a few minutes, typically lasting for 1–3 hours, varying by the person and the strain of cannabis. After oral ingestion of cannabis, the onset of effect is delayed relative to smoking, taking 30 minutes to 2 hours, but the duration is prolonged due to continued slow absorption. The duration of noticeable effects has been observed to diminish after prolonged, repeated use and the development of increased tolerance to cannabinoids.
Cannabis use can decrease blood pressure, which increases the risk of
 The psychoactive effects of cannabis, known as a "
The psychoactive effects of cannabis, known as a "
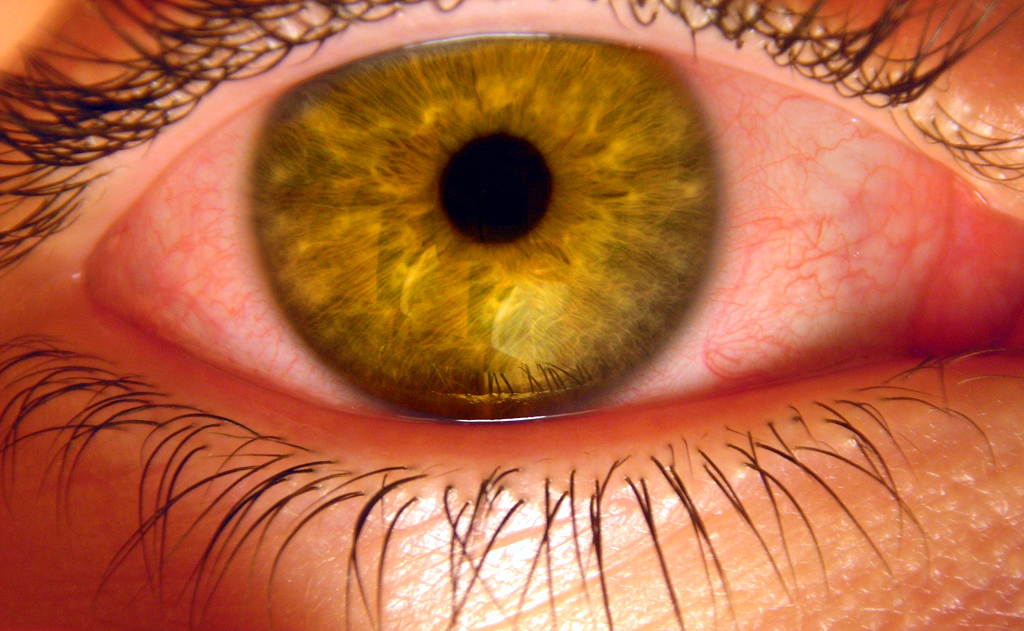 Some of the short-term physical effects of cannabis use include increased heart rate, dry mouth, reddening of the eyes (congestion of the
Some of the short-term physical effects of cannabis use include increased heart rate, dry mouth, reddening of the eyes (congestion of the
How Marijauan Works: Other Physiological Effects
. HowStuffWorks. Retrieved on 3 November 2007 A 2015 study suggests that cannabis triggers uncharacteristic behaviour in
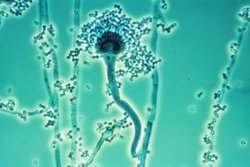 The fungi ''
The fungi ''
 The effects of cannabis are caused by
The effects of cannabis are caused by chemical compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element ...
s in the cannabis plant, including 113 different cannabinoids such as tetrahydrocannabinol
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term ''THC'' ...
(THC) and 120 terpenes, which allow its drug to have various psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries between t ...
and physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
effects on the human body. Different plants of the genus Cannabis contain different and often unpredictable concentrations of THC and other cannabinoids and hundreds of other molecules that have a pharmacological effect, so that the final net effect cannot reliably be foreseen.
Acute effects while under the influence can sometimes include euphoria
Euphoria ( ) is the experience (or affect) of pleasure or excitement and intense feelings of well-being and happiness. Certain natural rewards and social activities, such as aerobic exercise, laughter, listening to or making music and da ...
. Although some assert that cannabidiol (CBD), another cannabinoid found in cannabis in varying amounts, may alleviate the adverse effects of THC that some users experience, little is known about CBD effects on humans. Cannabinoid receptor antagonists have previously been tested as antidotes for cannabis intoxication with success, reducing or eliminating the physiological and psychological effects of intoxication. Some of these products are currently in development as cannabis antidotes.
In the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, medical cannabis
Medical cannabis, or medical marijuana (MMJ), is cannabis and cannabinoids that are prescribed by physicians for their patients. The use of cannabis as medicine has not been rigorously tested due to production and governmental restrictions ...
research is limited by federal restrictions. Smoking any substance could possibly carry similar risks as smoking tobacco due to carcinogens present in all smoke,
and the ultimate conclusions on these factors are disputed.
Cannabis use disorder is defined as a medical diagnosis in the fifth revision of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM; latest edition: DSM-5-TR, published in March 2022) is a publication by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) for the classification of mental disorders using a common langua ...
(DSM-5
The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition'' (DSM-5), is the 2013 update to the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'', the taxonomic and diagnostic tool published by the American Psychiatric ...
).
Chemistry






Cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors
The most prevalentpsychoactive
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior.
Th ...
substances in cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: ''Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternatively ...
are cannabinoids
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tet ...
, particularly THC. Some varieties, having undergone careful selection and growing techniques, can yield as much as 34% THC. Another psychoactive cannabinoid present in ''Cannabis sativa'' is tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV), but it is only found in small amounts and is a cannabinoid antagonist
A cannabinoid receptor antagonist, also known simply as a cannabinoid antagonist or as an anticannabinoid, is a type of cannabinoidergic drug that binds to cannabinoid receptors (CBR) and prevents their activation by endocannabinoids. They include ...
.
There are similar compounds in cannabis that do not exhibit psychoactive response but are obligatory for functionality: cannabidiol (CBD), an isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulae – that is, same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers.
Iso ...
of THC; cannabivarin (CBV), an analog
Analog or analogue may refer to:
Computing and electronics
* Analog signal, in which information is encoded in a continuous variable
** Analog device, an apparatus that operates on analog signals
*** Analog electronics, circuits which use analo ...
of cannabinol
Cannabinol (CBN) is a mildly psychoactive cannabinoid that acts as a low affinity partial agonist at both CB1 and CB2 receptors. This activity at CB1 and CB2 receptors constitutes interaction of CBN with the endocannabinoid system (ECS).
CBN w ...
(CBN) with a different side chain, cannabidivarin (CBDV), an analog of CBD with a different side chain, and cannabinolic acid. CBD is believed to regulate the metabolism of THC by inactivating cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a Protein superfamily, superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are ...
enzymes that metabolize drugs; one such mechanism is via generation of carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simple ...
(a pharmacologically active neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell.
Neuro ...
) by upon metabolism of CBD. THC is converted rapidly to 11-hydroxy-THC
11-Hydroxy-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (11-OH-Δ9-THC, alternatively numbered as 7-OH-Δ1-THC), usually referred to as 11-hydroxy-THC, is the main active metabolite of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is formed in the body after THC is consumed.
A ...
, which is also pharmacologically active, so the euphoria outlasts measurable THC levels in blood.
Biochemical mechanisms in the brain
Cannabinoids usually contain a 1,1'-di-methyl-pyran ring, a variedly derivatizedaromatic ring
In chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property of cyclic ( ring-shaped), ''typically'' planar (flat) molecular structures with pi bonds in resonance (those containing delocalized electrons) that gives increased stability compared to saturat ...
and a variedly unsaturated cyclohexyl ring and their immediate chemical precursors, constituting a family of about 60 bi-cyclic and tri-cyclic compounds. Like most other neurological processes, the effects of cannabis on the brain follow the standard protocol of signal transduction
Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellula ...
, the electrochemical system of sending signals through neurons
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. N ...
for a biological response. It is now understood that cannabinoid receptors appear in similar forms in most vertebrates
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, ...
and invertebrates
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chordate ...
and have a long evolutionary history of 500 million years. The binding of cannabinoids to cannabinoid receptors decrease adenylyl cyclase
Adenylate cyclase (EC 4.6.1.1, also commonly known as adenyl cyclase and adenylyl cyclase, abbreviated AC) is an enzyme with systematic name ATP diphosphate-lyase (cyclizing; 3′,5′-cyclic-AMP-forming). It catalyzes the following reaction:
:A ...
activity, inhibit calcium N channels, and disinhibit K+A channels. There are at least two types of cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2).
Sustainability in the body
Mostcannabinoids
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tet ...
are lipophilic (fat soluble) compounds that are easily stored in fat, thus yielding a long elimination half-life
Biological half-life (also known as elimination half-life, pharmacologic half-life) is the time taken for concentration of a biological substance (such as a medication) to decrease from its maximum concentration ( Cmax) to half of Cmax in the bl ...
relative to other recreational drug
Recreational drug use indicates the use of one or more psychoactive drugs to induce an altered state of consciousness either for pleasure or for some other casual purpose or pastime by modifying the perceptions and emotions of the user. When a ...
s. The THC molecule, and related compounds, are usually detectable in drug tests from 3 days up to 10 days according to Redwood Laboratories. Long-term users can produce positive tests for two to three months after ceasing cannabis use (see drug test
A drug test is a technical analysis of a biological specimen, for example urine, hair, blood, breath, sweat, or oral fluid/saliva—to determine the presence or absence of specified parent drugs or their metabolites. Major applications of drug ...
).
Toxicities
When cannabis is smoked, blood levels of THC peak rapidly after a few minutes and then decline, although the psychotropic effects persist for longer. Edible forms of cannabis often contain several hundred milligrams of THC, much more than the 32 mg of a typical cannabis cigarette. The rise of edible cannabis products has been responsible for a large increase of poisoning of children and young people: in American states which have legalized cannabis, emergency room admissions of such cases have typically doubled. Symptoms in children can include lethargy, sedation andseizure
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with los ...
.
Cannabis is suspected of being a potential contributory factor or direct cause of sudden death, due to the strain it can place on the cardiovascular system
The blood circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, tha ...
, or because of cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome
Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (CHS) is recurrent nausea, vomiting, and cramping abdominal pain that can occur due to prolonged, high-dose cannabis use. These symptoms may be relieved temporarily by taking a hot shower or bath. Complications ...
.
Related to cannabinoids
THC, the principal psychoactive constituent of the cannabis plant, has an extremely lowtoxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst ...
and the amount that can enter the body through the consumption of cannabis plants poses no threat of death. In dogs, the minimum lethal dose of THC is over 3000 mg/kg. According to ''The Merck Index
''The Merck Index'' is an encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs and biologicals with over 10,000 monograph on single substances or groups of related compounds published online by the Royal Society of Chemistry.
History
The first edition of the Merc ...
'',1996. ''The Merck Index'', 12th ed., Merck & Co., Rahway, New Jersey the of THC (the dose which causes the death of 50% of individuals) is 1270 mg/kg for male rats and 730 mg/kg for female rats from oral consumption in sesame oil, and 42 mg/kg for rats from inhalation.
Cannabinoids and other molecules present in cannabis can alter the metabolism of other drugs, especially due to competition for clearing metabolic pathways such as cytochromes CYP450
Cytochromes P450 (CYPs) are a superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor that functions as monooxygenases. In mammals, these proteins oxidize steroids, fatty acids, and xenobiotics, and are important for the clearance of various compo ...
, thus leading to drug toxicities by medications that the person consuming cannabis may be taking.
Related to smoking
A 2007 study found that whiletobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
and cannabis smoke are quite similar, cannabis smoke contained higher amounts of ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
, hydrogen cyanide
Hydrogen cyanide, sometimes called prussic acid, is a chemical compound with the formula HCN and structure . It is a colorless, extremely poisonous, and flammable liquid that boils slightly above room temperature, at . HCN is produced on an ...
, and nitrogen oxides, but lower levels of carcinogenic
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substan ...
polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). This study found that directly inhaled cannabis smoke contained as much as 20 times as much ammonia and 5 times as much hydrogen cyanide as tobacco smoke and compared the properties of both mainstream and sidestream (smoke emitted from a smouldering 'joint' or 'cone') smoke. Mainstream cannabis smoke was found to contain higher concentrations of selected polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) than sidestream tobacco smoke. However, other studies have found much lower disparities in ammonia and hydrogen cyanide between cannabis and tobacco, and that some other constituents (such as polonium-210, lead, arsenic, nicotine, and tobacco-specific nitrosamines) are either lower or non-existent in cannabis smoke. A 2021 longitudinal study conducted among populations of HIV-positive and HIV-negative adults found that smoke-related carcinogenic
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substan ...
toxicants and biomarkers detected in tobacco smokers were also detected in exclusive marijuana smokers, including carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simple ...
(CO), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), aldehydes (such as acrolein
Acrolein (systematic name: propenal) is the simplest unsaturated aldehyde. It is a colorless liquid with a piercing, acrid smell. The smell of burnt fat (as when cooking oil is heated to its smoke point) is caused by glycerol in the burning fa ...
), acrylonitrile
Acrylonitrile is an organic compound with the formula and the structure . It is a colorless, volatile liquid although commercial samples can be yellow due to impurities. It has a pungent odor of garlic or onions. In terms of its molecular ...
and acrylamide
Acrylamide (or acrylic amide) is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH2=CHC(O)NH2. It is a white odorless solid, soluble in water and several organic solvents. From the chemistry perspective, acrylamide is a vinyl-substituted primary ...
metabolites, but exposures are lower compared with tobacco or dual smokers. Increased levels of acrolein exposure by tobacco smoking but not exclusive marijuana smoking were detected both in HIV-positive and HIV-negative adults, and contribute to increased diagnoses of cardiovascular diseases and respiratory diseases
Respiratory diseases, or lung diseases, are pathological conditions affecting the organs and tissues that make gas exchange difficult in air-breathing animals. They include conditions of the respiratory tract including the trachea, bronchi, br ...
among tobacco smokers.
Cannabis smoke contains thousands of organic and inorganic chemical compounds. This tar
Tar is a dark brown or black viscous liquid of hydrocarbons and free carbon, obtained from a wide variety of organic materials through destructive distillation. Tar can be produced from coal, wood, petroleum, or peat. "a dark brown or black bit ...
is chemically similar to that found in tobacco smoke or cigars. Over fifty known carcinogen
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substan ...
s have been identified in cannabis smoke. These include nitrosamines, reactive aldehydes, and polycylic hydrocarbons, including benz yrene. Marijuana smoke was listed as a cancer agent in California in 2009. A study by the British Lung Foundation published in 2012 identifies cannabis smoke as a carcinogen and also finds awareness of the danger is low compared with the high awareness of the dangers of smoking tobacco particularly among younger users. Other observations include possible increased risk from each cigarette; lack of research on the effect of cannabis smoke alone; low rate of addiction compared to tobacco; and episodic nature of cannabis use compared to steady frequent smoking of tobacco. Professor David Nutt, a UK drug expert, points out that the study cited by the British Lung Foundation has been accused of both "false reasoning" and "incorrect methodology". Further, he notes that other studies have failed to connect cannabis with lung cancer, and accuses the BLF of "scaremongering over cannabis".
Short-term effects
fainting
Syncope, commonly known as fainting, or passing out, is a loss of consciousness and muscle strength characterized by a fast onset, short duration, and spontaneous recovery. It is caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain, typically from ...
. Combining alcohol with cannabis greatly increases the level of impairment and the risk of injury or death from accidents.
Psychological effects
high
High may refer to:
Science and technology
* Height
* High (atmospheric), a high-pressure area
* High (computability), a quality of a Turing degree, in computability theory
* High (tectonics), in geology an area where relative tectonic uplift ...
", are subjective and vary among persons and the method of use.
When THC enters the blood stream and reaches the brain, it binds to cannabinoid receptors. The endogenous ligand
In biochemistry and pharmacology, a ligand is a substance that forms a complex with a biomolecule to serve a biological purpose. The etymology stems from ''ligare'', which means 'to bind'. In protein-ligand binding, the ligand is usually a m ...
of these receptors is anandamide, the effects of which THC emulates. This agonism
Agonism (from Greek ἀγών '' agon'', "struggle") is a political and social theory that emphasizes the potentially positive aspects of certain forms of conflict. It accepts a permanent place for such conflict in the political sphere, but seeks ...
of the cannabinoid receptors results in changes in the levels of various neurotransmitters, especially dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine const ...
and norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as both a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline" (from Latin '' ad'', ...
; neurotransmitters which are closely associated with the acute effects of cannabis ingestion, such as euphoria
Euphoria ( ) is the experience (or affect) of pleasure or excitement and intense feelings of well-being and happiness. Certain natural rewards and social activities, such as aerobic exercise, laughter, listening to or making music and da ...
and anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
.
Some effects may include a general altered state of consciousness, euphoria
Euphoria ( ) is the experience (or affect) of pleasure or excitement and intense feelings of well-being and happiness. Certain natural rewards and social activities, such as aerobic exercise, laughter, listening to or making music and da ...
, relaxation or stress reduction, increased appreciation of the arts, including humor and music, joviality, metacognition
Metacognition is an awareness of one's thought processes and an understanding of the patterns behind them. The term comes from the root word '' meta'', meaning "beyond", or "on top of".Metcalfe, J., & Shimamura, A. P. (1994). ''Metacognition: knowi ...
and introspection, enhanced recollection (episodic memory
Episodic memory is the memory of everyday events (such as times, location geography, associated emotions, and other contextual information) that can be explicitly stated or conjured. It is the collection of past personal experiences that occurred ...
), and increased sensuality, sensory awareness, libido, and creativity. Abstract or philosophical thinking, disruption of linear memory and paranoia
Paranoia is an instinct or thought process that is believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety or fear, often to the point of delusion and irrationality. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of conspiracy concer ...
or anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
are also typical. Anxiety
Anxiety is an emotion which is characterized by an unpleasant state of inner turmoil and includes feelings of dread over anticipated events. Anxiety is different than fear in that the former is defined as the anticipation of a future threat wh ...
is the most commonly reported negative side effect of smoking marijuana. Up to 30 percent of recreational users experience intense anxiety and/or panic attacks after smoking cannabis. Some report anxiety only after not smoking cannabis for a prolonged period of time. Inexperience and use in an unfamiliar environment are major contributing factors to this anxiety. Cannabidiol (CBD), another cannabinoid found in cannabis, has been shown to improve the adverse effects of THC, including anxiety.
Cannabis produces many other subjective effects, including an increased enjoyment of food taste and aroma, and marked distortions in the perception of time. At higher doses, effects can include altered body image
Body image is a person's thoughts, feelings and perception of the aesthetics or sexual attractiveness of their own body. The concept of body image is used in a number of disciplines, including neuroscience, psychology, medicine, psychiatry, ps ...
, auditory and/or visual illusions, pseudohallucinations, and ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements that can include gait abnormality, speech changes, and abnormalities in eye movements. Ataxia is a clinical manifestation indicating dysfunction of ...
from selective impairment of polysynaptic reflexes. In some cases, cannabis can lead to acute psychosis
Psychosis is a condition of the mind that results in difficulties determining what is real and what is not real. Symptoms may include delusions and hallucinations, among other features. Additional symptoms are incoherent speech and behavior ...
and dissociative states such as depersonalization and derealization.
Furthermore, even in those with no family history of psychosis, the administration of pure THC in clinical settings has been demonstrated to elicit transient psychotic symptoms. Any episode of acute psychosis that accompanies cannabis use usually abates after six hours, but in rare instances, heavy users may find the symptoms continuing for many days.
While psychoactive drugs are typically categorized as stimulant
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and inv ...
s, depressants, or hallucinogens, cannabis exhibits a mix of all of these effects. Scientific studies have suggested that other cannabinoids like CBD may also play a significant role in its psychoactive effects.
Somatic effects
 Some of the short-term physical effects of cannabis use include increased heart rate, dry mouth, reddening of the eyes (congestion of the
Some of the short-term physical effects of cannabis use include increased heart rate, dry mouth, reddening of the eyes (congestion of the conjunctiva
The conjunctiva is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium ...
l blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s), a reduction in intra-ocular pressure
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is the fluid pressure inside the eye. Tonometry is the method eye care professionals use to determine this. IOP is an important aspect in the evaluation of patients at risk of glaucoma. Most tonometers are calibrated to ...
, muscle relaxation and a sensation of cold or hot hands and feet.
Electroencephalography
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a method to record an electrogram of the spontaneous electrical activity of the brain. The biosignals detected by EEG have been shown to represent the postsynaptic potentials of pyramidal neurons in the neocortex ...
(EEG) shows somewhat more persistent alpha waves of slightly lower frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
than usual. Cannabinoids produce a marked depression of motor activity via activation of neuronal cannabinoid receptors belonging to the Cannabinoid receptor type 1.
Duration
Peak levels of cannabis-associated intoxication occur approximately 20 minutes after smoking it and last for several hours. The total short-term duration of cannabis use when smoked depends on the potency, method of smoking – e.g. whether pure or in conjunction with tobacco – and how much is smoked. Peak levels of intoxication typically last an average of three to four hours. When taken orally (in the form of capsules, food, or drink), the psychoactive effects take longer to manifest and generally last longer, typically lasting for an average of four to six hours after consumption. Oral ingestion use eliminates the need to inhale toxic combustion products created by smoking and therefore negates the risk of respiratory harm associated with cannabis smoking.Effects on driving
While several studies have shown increased risk associated with cannabis use by drivers, other studies have not found increased risk. Cannabis usage has been shown in some studies to have a negative effect on driving ability. The British Medical Journal indicated that "drivers who consume cannabis within three hours of driving are nearly twice as likely to cause a vehicle collision as those who are not under the influence of drugs or alcohol". In ''Cannabis and driving: a review of the literature and commentary'', the United Kingdom'sDepartment for Transport
The Department for Transport (DfT) is a department of His Majesty's Government responsible for the English transport network and a limited number of transport matters in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland that have not been devolved. The d ...
reviewed data on cannabis and driving, finding although impaired, "subjects under cannabis treatment appear to perceive that they are indeed impaired. Where they can compensate, they do". In a review of driving simulator studies, researchers note that "even in those who learn to compensate for a drug's impairing effects, substantial impairment in performance can still be observed under conditions of general task performance (i.e. when no contingencies are present to maintain compensated performance)."
A 2012 meta-analysis found that acute cannabis use increased the risk of an automobile crash. An extensive 2013 review of 66 studies regarding crash risk and drug use found that cannabis was associated with minor, but not statistically significant increased odds of injury or fatal accident.
In the largest and most precisely controlled study of its kind carried out by the U.S. Department of Transportation's National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA ) is an agency of the U.S. federal government, part of the Department of Transportation. It describes its mission as "Save lives, prevent injuries, reduce vehicle-related crashes" rela ...
, it was found that other "studies that measure the presence of THC in the drivers' blood or oral fluid, rather than relying on self-report tend to have much lower (or no) elevated crash risk estimates. Likewise better controlled studies have found lower (or no) elevated crash risk estimates". The study found that "after adjusting for age, gender, race and alcohol use, drivers who tested positive for marijuana were no more likely to crash than those who had not used any drugs or alcohol prior to driving". A 2018 study indicated that the number of fatal crashes involving marijuana after the recreational marijuana legalization or decriminalization increased in Colorado, Washington, and Massachusetts.
Cardiovascular effects
Short-term (one to two hours) effects on the cardiovascular system can include increased heart rate, dilation of blood vessels, and fluctuations in blood pressure. There are medical reports of occasional heart attacks ormyocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may ...
, stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
and other cardiovascular side effects. Marijuana's cardiovascular effects are not associated with serious health problems for most young, healthy users. Researchers reported in the ''International Journal of Cardiology
The ''International Journal of Cardiology'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal that publishes research articles about the study and management of cardiac diseases. The journal is affiliated with the International Society for Adult Congenital Cardia ...
'', "Marijuana use by older people, particularly those with some degree of coronary artery
The coronary arteries are the arterial blood vessels of coronary circulation, which transport oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. The heart requires a continuous supply of oxygen to function and survive, much like any other tissue or organ of ...
or cerebrovascular disease, poses greater risks due to the resulting increase in catecholamines, cardiac workload, and carboxyhemoglobin levels, and concurrent episodes of profound postural hypotension
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the dias ...
. Indeed, marijuana may be a much more common cause of myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which may ...
than is generally recognized. In day-to-day practice, a history of marijuana use is often not sought by many practitioners, and even when sought, the patient's response is not always truthful".
A 2013 analysis of 3,886 myocardial infarction survivors over an 18-year period showed "no statistically significant association between marijuana use and mortality".
A 2008 study by the National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ...
Biomedical Research Centre in Baltimore found that heavy, chronic smoking of marijuana (138 joints per week) changed blood proteins
Blood-proteins, also termed plasma proteins, are proteins present in blood plasma. They serve many different functions, including transport of lipids, hormones, vitamins and minerals in activity and functioning of the immune system. Other blood pr ...
associated with heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, hea ...
and stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
.
A 2000 study by researchers at Boston's Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) in Boston, Massachusetts is a teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School. It was formed out of the 1996 merger of Beth Israel Hospital (founded in 1916) and New England Deaconess Hospital (founded ...
, Massachusetts General Hospital
Massachusetts General Hospital (Mass General or MGH) is the original and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School located in the West End neighborhood of Boston, Massachusetts. It is the third oldest general hospital in the United Stat ...
and Harvard School of Public Health found that a middle age person's risk of heart attack rises nearly fivefold in the first hour after smoking marijuana, "roughly the same risk seen within an hour of sexual activity".
Cannabis arteritis is a very rare peripheral vascular disease similar to Buerger's disease
Thromboangiitis obliterans, also known as Buerger disease (English ; ) or Winiwarter-Buerger disease, is a recurring progressive inflammation and thrombosis (clotting) of small and medium arteries and veins of the hands and feet. It is strongly a ...
. There were about 50 confirmed cases from 1960 to 2008, all of which occurred in Europe.
Combination with other drugs
A confounding factor in cannabis research is the prevalent usage of other recreational drugs, especiallyalcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
and nicotine. Such complications demonstrate the need for studies on cannabis that have stronger controls, and investigations into alleged symptoms of cannabis use that may also be caused by tobacco. Some critics question whether agencies doing the research make an honest effort to present an accurate, unbiased summary of the evidence, or whether they "cherry-pick" their data to please funding sources which may include the tobacco industry or governments dependent on cigarette tax revenue; others caution that the raw data, and not the final conclusions, are what should be examined.
The Australian National Household Survey of 2001 showed that cannabis in Australia is rarely used without other drugs. 95% of cannabis users also drank alcohol; 26% took amphetamines; 19% took ecstasy and only 2.7% reported not having used any other drug with cannabis. While research has been undertaken on the combined effects of alcohol and cannabis on performing certain tasks, little research has been conducted on the reasons why this combination is so popular. Evidence from a controlled experimental study undertaken by Lukas and Orozco suggests that alcohol causes THC to be absorbed more rapidly into the blood plasma of the user. Data from the Australian National Survey of Mental Health and Wellbeing found that three-quarters of recent cannabis users reported using alcohol when cannabis was not available, this suggests that the two are substitutes.
Memory and learning
Studies on cannabis and memory are hindered by small sample sizes, confounding drug use, and other factors. The strongest evidence regarding cannabis and memory focuses on its temporary negative effects on short-term and working memory. In a 2001 study looking at neuropsychological performance in long-term cannabis users, researchers found "some cognitive deficits appear detectable at least 7 days after heavy cannabis use but appear reversible and related to recent cannabis exposure rather than irreversible and related to cumulative lifetime use". On his studies regarding cannabis use, lead researcher and Harvard professorHarrison Pope
Harrison Graham "Skip" Pope, Jr. (born 1947, in Massachusetts), is an American professor and physician, currently Professor of Psychiatry at Harvard Medical School and an attending physician at McLean Hospital. He is also the DirectorBiological Ps ...
said he found marijuana is not dangerous over the long term, but there are short-term effects. From neuropsychological tests, Pope found that chronic cannabis users showed difficulties, with verbal memory in particular, for "at least a week or two" after they stopped smoking. Within 28 days, memory problems vanished and the subjects "were no longer distinguishable from the comparison group".
Researchers from the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine
The University of California San Diego School of Medicine is the graduate medical school of the University of California, San Diego. It was the third medical school in the University of California system, after those established at UCSF and UCLA, ...
failed to show substantial, systemic neurological effects from long-term recreational use of cannabis. Their findings were published in the July 2003 issue of the ''Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society''. The research team, headed by Dr Igor Grant, found that cannabis use did affect perception, but did not cause permanent brain damage
Neurotrauma, brain damage or brain injury (BI) is the destruction or degeneration of brain cells. Brain injuries occur due to a wide range of internal and external factors. In general, brain damage refers to significant, undiscriminating t ...
. Researchers looked at data from 15 previously published controlled studies involving 704 long-term cannabis users and 484 nonusers. The results showed long-term cannabis use was only marginally harmful on memory and learning. Other functions such as reaction time, attention, language, reasoning ability, perceptual and motor skills were unaffected. The observed effects on memory and learning, they said, showed long-term cannabis use caused "selective memory defects", but that the impact was "of a very small magnitude". A study by Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine showed that heavy use of marijuana is associated with decrements in neurocognitive performance even after 28 days of abstinence.
Appetite
The feeling of increased appetite following the use ofcannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: ''Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternatively ...
has been documented for hundreds of years, and is known colloquially as the "munchies". Clinical studies and survey data have found that cannabis increases food enjoyment and interest in food.Bonsor, Kevin.How Marijauan Works: Other Physiological Effects
. HowStuffWorks. Retrieved on 3 November 2007 A 2015 study suggests that cannabis triggers uncharacteristic behaviour in
proopiomelanocortin
Pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) is a precursor polypeptide with 241 amino acid residues. POMC is synthesized in corticotrophs of the anterior pituitary from the 267-amino-acid-long polypeptide precursor pre-pro-opiomelanocortin (pre-POMC), by the r ...
(POMC) neurons, which are usually associated with decreasing hunger.
Endogenous cannabinoids, more commonly known as endocannabinoids, exist in cow and human milk. It is widely accepted that the neonatal survival of many species is largely dependent upon their suckling behavior and research has identified the endogenous cannabinoid system to be the first neural system to display complete control over milk ingestion and neonatal survival.
Pathogens and microtoxins
Mostmicroorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s found in cannabis only affect plants and not humans, but some microorganisms, especially those that proliferate when the herb is not correctly dried and stored, can be harmful to humans. Some users may store marijuana in an airtight bag or jar in a refrigerator
A refrigerator, colloquially fridge, is a commercial and home appliance consisting of a thermally insulated compartment and a heat pump (mechanical, electronic or chemical) that transfers heat from its inside to its external environment so th ...
to prevent fungal and bacterial growth.
 The fungi ''
The fungi ''Aspergillus flavus
''Aspergillus flavus'' is a saprotrophic and pathogenic fungus with a cosmopolitan distribution. It is best known for its colonization of cereal grains, legumes, and tree nuts. Postharvest rot typically develops during harvest, storage, and/or t ...
'', ''Aspergillus fumigatus
''Aspergillus fumigatus'' is a species of fungus in the genus ''Aspergillus'', and is one of the most common ''Aspergillus'' species to cause disease in individuals with an immunodeficiency.
''Aspergillus fumigatus'', a saprotroph widespread in ...
'', '' Aspergillus niger'', ''Aspergillus parasiticus
''Aspergillus parasiticus'' is a fungus belonging to the genus ''Aspergillus''. This species is an unspecialized saprophytic mold, mostly found outdoors in areas of rich soil with decaying plant material as well as in dry grain storage facilities ...
'', ''Aspergillus tamarii
''Aspergillus tamarii'' is a species of fungus in the genus ''Aspergillus''. It is from the ''Flavi'' section. The species was first described in 1913.Kita, G. 1913, Centralbl. Bakteriol., Abt. 2 37: 433 ''A. tamarii'' has been used in the produc ...
'', '' Aspergillus sulphureus'', '' Aspergillus repens'', ''Mucor hiemalis
''Mucor hiemalis'' is among the zygosporic fungi found in unspoiled foods. It has different industrial importance as biotransforming agents of pharmacological and chemical compounds.
Morphology and cell structure
''Mucor hiemalis'' grows in ex ...
'' (not a human pathogen), '' Penicillium chrysogenum'', ''Penicillium italicum
''Penicillium italicum'' is a plant pathogen. It is a common post harvest disease commonly associated with citrus fruits.
Management
Inoculation of healthy fruit can be diminished and controlled by careful picking, handling, and packaging of the ...
'' and ''Rhizopus nigricans
''Rhizopus stolonifer'' is commonly known as white bread mold. It is a member of ''Zygomycota'' and considered the most important species in the genus ''Rhizopus''. It is one of the most common fungi in the world and has a global distribution al ...
'' have been found in moldy cannabis. '' Aspergillus'' mold species can infect the lungs via smoking or handling of infected cannabis and cause opportunistic and sometimes deadly aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is a fungal infection of usually the lungs, caused by the genus ''Aspergillus'', a common mould that is breathed in frequently from the air around, but does not usually affect most people. It generally occurs in people with lung dise ...
. Some of the microorganisms found create aflatoxins, which are toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst ...
and carcinogenic
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substan ...
. Mold is also found in smoke from mold-infected cannabis, and the lungs and nasal passages are a major means of contracting fungal infections. Levitz and Diamond (1991) suggested baking marijuana in home ovens at 150 °C 02 °F for five minutes before smoking. Oven treatment killed conidia
A conidium ( ; ), sometimes termed an asexual chlamydospore or chlamydoconidium (), is an asexual, non-motile spore of a fungus. The word ''conidium'' comes from the Ancient Greek word for dust, ('). They are also called mitospores due to the ...
of ''A. fumigatus'', ''A. flavus'' and ''A. niger'', and did not lower THC levels. Cannabis contaminated with ''Salmonella muenchen'' was correlated with dozens of cases of salmonellosis in 1981. Thermophilic actinomycete
The Actinomycetales is an order of Actinomycetota. A member of the order is often called an actinomycete. Actinomycetales are generally gram-positive and anaerobic and have mycelia in a filamentous and branching growth pattern. Some actinomycete ...
s were also found in cannabis.
Long-term effects
Exposure to marijuana may have biologically based physical, mental, behavioral, and social health consequences and is "associated with diseases of the liver (particularly with co-existing hepatitis C), lungs, heart, eyesight, and vasculature" according to a 2013 literature review by Gordon and colleagues. The association with these diseases has only been reported in cases where people have smoked cannabis. The authors cautioned that "evidence is needed, and further research should be considered, to prove causal associations of marijuana with many physical health conditions". Cannabis use disorder is defined in the fifth revision of the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM; latest edition: DSM-5-TR, published in March 2022) is a publication by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) for the classification of mental disorders using a common langua ...
'' (DSM-5
The ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition'' (DSM-5), is the 2013 update to the ''Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'', the taxonomic and diagnostic tool published by the American Psychiatric ...
) as a condition requiring treatment. Several drugs have been investigated in an attempt to ameliorate the symptoms of stopping cannabis use. Such drugs include bupropion
Bupropion, sold under the brand names Wellbutrin and Zyban among others, is an atypical antidepressant primarily used to treat major depressive disorder and to support smoking cessation. It is also popular as an add-on medication in the case ...
, divalproex
Valproate (VPA) and its valproic acid, sodium valproate, and valproate semisodium forms are medications primarily used to treat epilepsy and bipolar disorder and prevent migraine headaches. They are useful for the prevention of seizures in thos ...
, nefazodone
Nefazodone, sold formerly under the brand names Serzone, Dutonin, and Nefadar among others, is an atypical antidepressant which was first marketed by Bristol-Myers Squibb (BMS) in 1994 but has since largely been discontinued. BMS withdrew it from ...
, lofexidine, and dronabinol. Of these, dronabinol (a trade name for THC) has proven the most effective. The drugs buspirone and rimonabant
Rimonabant (also known as SR141716; trade names Acomplia, Zimulti) is an anorectic antiobesity drug that was first approved in Europe in 2006 but was withdrawn worldwide in 2008 due to serious psychiatric side effects; it was never approved in t ...
have shown some success in helping maintain cannabis abstinence.
There is evidence that long-term use of cannabis increases the risk of psychosis, regardless of confounding
In statistics, a confounder (also confounding variable, confounding factor, extraneous determinant or lurking variable) is a variable that influences both the dependent variable and independent variable, causing a spurious association. Con ...
factors, and particularly for people who have genetic risk factors. A 2019 meta-analysis found that 34% of people with cannabis-induced psychosis transitioned to schizophrenia. This was found to be comparatively higher than hallucinogens (26%) and amphetamines (22%).
Long-term cannabis users are at risk for developing cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome
Cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome (CHS) is recurrent nausea, vomiting, and cramping abdominal pain that can occur due to prolonged, high-dose cannabis use. These symptoms may be relieved temporarily by taking a hot shower or bath. Complications ...
(CHS), characterized by recurrent bouts of intense vomiting. The mechanism behind CHS is poorly understood and is contrary to the antiemetic properties of cannabis and cannabinoids. Of those who went to the emergency department (ED) with recurrent vomiting in one institution in the United States from 2005 to 2010, about 6% had the condition.
Effects in pregnancy
Cannabis consumption in pregnancy might be associated with restrictions in growth of the fetus, miscarriage, and cognitive deficits in offspring based on animal studies, although there is limited evidence for this in humans at this time. A 2012systematic review
A systematic review is a Literature review, scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from publ ...
found although it was difficult to draw firm conclusions, there was some evidence that prenatal exposure to cannabis was associated with "deficits in language, attention, areas of cognitive performance, and delinquent behavior in adolescence". A report prepared for the Australian National Council on Drugs
The Australian National Council on Drugs (ANCD) describes itself as "the principal advisory body to Government on drug policy and plays a critical role in ensuring the voice of the community is heard in relation to drug related policies and s ...
concluded cannabis and other cannabinoids are contraindicated in pregnancy as it may interact with the endocannabinoid system.
Effects in pediatrics
Children can become exposed to cannabis, typically through accidental exposure which can lead to very high doses, especially in the case of edibles. Unlike in adults, these levels of exposure can lead to major complications in children. These complications include encephalopathy, hypotension, respiratory depression severe enough to require ventilation, somnolence, coma, and there have been case reports of death. Pediatric exposure to edibles is of increasing concern because these products are typically sweets (gummies, cookies, etc.), and their prevalence is increasing as cannabis is legalized or decriminalized in many territories.See also
*Cannabis smoking
Cannabis smoking (or colloquially smoking pot) is the inhalation of smoke or vapor released by heating the flowers, leaves, or extracts of cannabis and releasing the main psychoactive chemical, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which is absorbe ...
* Psychoactive drug
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, psychoactive agent or psychotropic drug is a chemical substance, that changes functions of the nervous system, and results in alterations in perception, mood, consciousness, cognition or behavior. ...
References
Further reading
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Effects Of Cannabis Cannabis and health Cannabis smoking Effects of psychoactive drugs