Camelus Bactrianus-sil on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A camel (from: la, camelus and grc-gre, κάμηλος (''kamēlos'') from Hebrew or Phoenician: גָמָל ''gāmāl''.) is an
 Camels have a series of physiological adaptations that allow them to withstand long periods of time without any external source of water. The dromedary camel can drink as seldom as once every 10 days even under very hot conditions, and can lose up to 30% of its body mass due to dehydration. Unlike other mammals, camels'
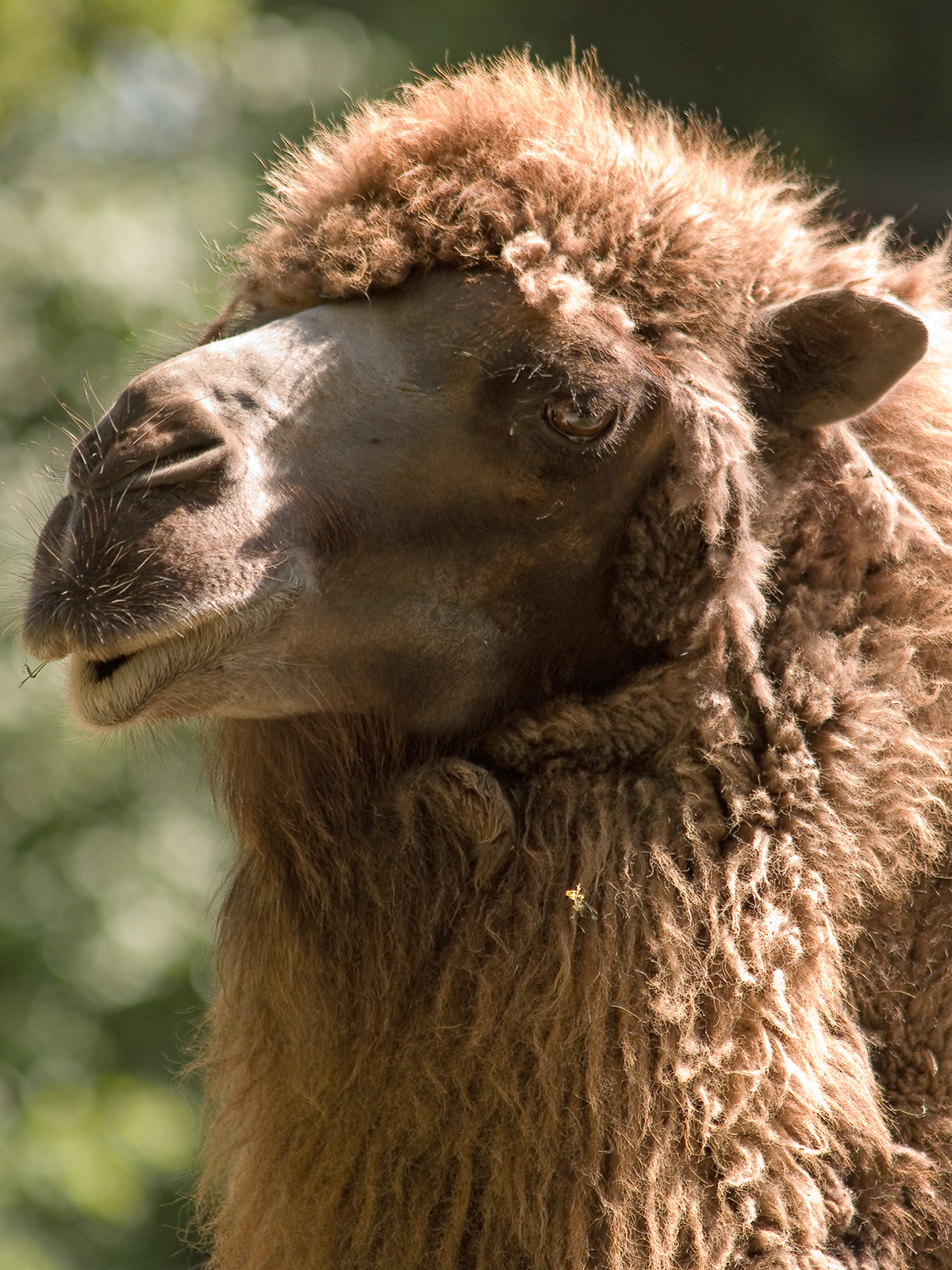
Camels have a series of physiological adaptations that allow them to withstand long periods of time without any external source of water. The dromedary camel can drink as seldom as once every 10 days even under very hot conditions, and can lose up to 30% of its body mass due to dehydration. Unlike other mammals, camels'  The camel's thick coat insulates it from the intense heat radiated from desert sand; a shorn camel must sweat 50% more to avoid overheating. During the summer the coat becomes lighter in color, reflecting light as well as helping avoid sunburn. The camel's long legs help by keeping its body farther from the ground, which can heat up to . Dromedaries have a pad of thick tissue over the
The camel's thick coat insulates it from the intense heat radiated from desert sand; a shorn camel must sweat 50% more to avoid overheating. During the summer the coat becomes lighter in color, reflecting light as well as helping avoid sunburn. The camel's long legs help by keeping its body farther from the ground, which can heat up to . Dromedaries have a pad of thick tissue over the
 The
The
File:Stenomylus.jpg, alt=A drawing of two early camels, Stenomylus illustration
File:NMNH-USNMV16601Stenomylus.tif, Stenomylus skeleton
File:NMNH-USNMV15917Poebrotherium.jpg,
File:Camel cart.JPG, alt= A camel harnessed to a cart loaded with branches and twigs, A camel serving as a
 By at least 1200 BC the first camel saddles had appeared, and
By at least 1200 BC the first camel saddles had appeared, and
 The
The

 Camel milk is a
Camel milk is a

 They provide food in the form of meat and milk. Approximately 3.3 million camels and camelids are slaughtered each year for meat worldwide. A camel carcass can provide a substantial amount of meat. The male dromedary carcass can weigh , while the carcass of a male Bactrian can weigh up to . The carcass of a female dromedary weighs less than the male, ranging between . The brisket, ribs and loin are among the preferred parts, and the hump is considered a delicacy. The hump contains "white and sickly fat", which can be used to make the ''khli'' (preserved meat) of mutton, beef, or camel. On the other hand, camel milk and meat are rich in protein, vitamins, glycogen, and other nutrients making them essential in the diet of many people. From chemical composition to meat quality, the dromedary camel is the preferred breed for meat production. It does well even in arid areas due to its unusual physiological behaviors and characteristics, which include tolerance to extreme temperatures, radiation from the sun, water paucity, rugged landscape and low vegetation. Camel meat is reported to taste like coarse beef, but older camels can prove to be very tough, although camel meat becomes tenderer the more it is cooked.
Camel is one of the animals that can be ritually slaughtered and divided into three portions (one for the home, one for extended family/social networks, and one for those who cannot afford to slaughter an animal themselves) for the
They provide food in the form of meat and milk. Approximately 3.3 million camels and camelids are slaughtered each year for meat worldwide. A camel carcass can provide a substantial amount of meat. The male dromedary carcass can weigh , while the carcass of a male Bactrian can weigh up to . The carcass of a female dromedary weighs less than the male, ranging between . The brisket, ribs and loin are among the preferred parts, and the hump is considered a delicacy. The hump contains "white and sickly fat", which can be used to make the ''khli'' (preserved meat) of mutton, beef, or camel. On the other hand, camel milk and meat are rich in protein, vitamins, glycogen, and other nutrients making them essential in the diet of many people. From chemical composition to meat quality, the dromedary camel is the preferred breed for meat production. It does well even in arid areas due to its unusual physiological behaviors and characteristics, which include tolerance to extreme temperatures, radiation from the sun, water paucity, rugged landscape and low vegetation. Camel meat is reported to taste like coarse beef, but older camels can prove to be very tough, although camel meat becomes tenderer the more it is cooked.
Camel is one of the animals that can be ritually slaughtered and divided into three portions (one for the home, one for extended family/social networks, and one for those who cannot afford to slaughter an animal themselves) for the
File:Shadda (detail), Karabagh region, southwest Caucasus.jpeg, Shadda (cover,detail), Karabagh region, southwest Caucasus, early 19th century
File:Vessel in the Form of a Recumbent Camel with Jugs, 2015.65.15.jpg, Vessel in the form of a recumbent camel with jugs, 250 BC – 224 AD,
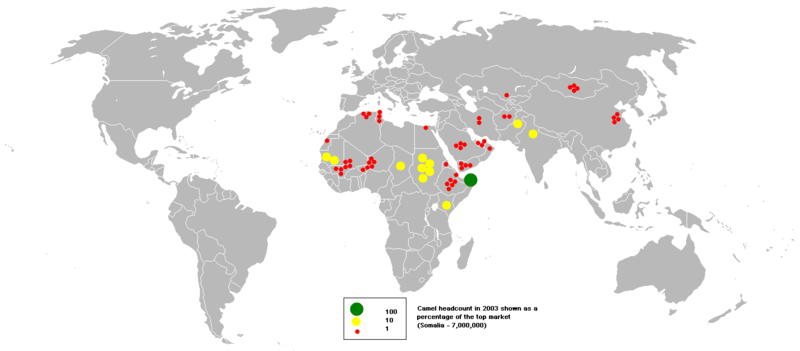
 There are approximately 14 million camels alive , with 90% being dromedaries. Dromedaries alive today are
There are approximately 14 million camels alive , with 90% being dromedaries. Dromedaries alive today are
 Over one million dromedary camels are estimated to be feral in Australia, descended from those introduced as a method of transport in the 19th and early 20th centuries. This population is growing about 8% per year; it was estimated at around 700,000 in 2008. Representatives of the Australian government have culled more than 100,000 of the animals in part because the camels use too much of the limited resources needed by sheep farmers.
A small population of introduced camels, dromedaries and Bactrians, wandered through
Over one million dromedary camels are estimated to be feral in Australia, descended from those introduced as a method of transport in the 19th and early 20th centuries. This population is growing about 8% per year; it was estimated at around 700,000 in 2008. Representatives of the Australian government have culled more than 100,000 of the animals in part because the camels use too much of the limited resources needed by sheep farmers.
A small population of introduced camels, dromedaries and Bactrians, wandered through
Camels and Camel Milk. Report Issued by Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. (1982)
* * * *
Six Green Reasons to Drink Camel's Milk
The Camel as a pet
"Could Emirati camels hold the key to treating venomous snake bites?"
{{Authority control African cuisine Arab cuisine Camelids Domesticated animals Halal meat Livestock Middle Eastern cuisine Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus
even-toed ungulate
The even-toed ungulates (Artiodactyla , ) are ungulates—hoofed animals—which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes: the third and fourth. The other three toes are either present, absent, vestigial, or pointing poster ...
in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. Camels have long been domesticated and, as livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animals ...
, they provide food (milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digestion, digest solid food. Immune factors and immune ...
and meat) and textiles (fiber and felt from hair
Hair is a protein filament that grows from follicles found in the dermis. Hair is one of the defining characteristics of mammals.
The human body, apart from areas of glabrous skin, is covered in follicles which produce thick terminal and f ...
). Camels are working animal
A working animal is an animal, usually domesticated, that is kept by humans and trained to perform tasks instead of being slaughtered to harvest animal products. Some are used for their physical strength (e.g. oxen and draft horses) or for t ...
s especially suited to their desert habitat and are a vital means of transport for passengers and cargo. There are three surviving species of camel. The one-humped dromedary
The dromedary (''Camelus dromedarius'' or ;), also known as the dromedary camel, Arabian camel, or one-humped camel, is a large even-toed ungulate, of the genus ''Camelus'', with one hump on its back.
It is the tallest of the three species of ...
makes up 94% of the world's camel population, and the two-humped Bactrian camel
The Bactrian camel (''Camelus bactrianus''), also known as the Mongolian camel or domestic Bactrian camel, is a large even-toed ungulate native to the steppes of Central Asia. It has two humps on its back, in contrast to the single-humped dro ...
makes up 6%. The Wild Bactrian camel
The wild Bactrian camel (''Camelus ferus'') is a critically endangered species of camel living in parts of northwestern China and southwestern Mongolia. It is closely related to the Bactrian camel (''Camelus bactrianus''). Both are large, doub ...
is a separate species and is now critically endangered.
The word ''camel'' is also used informally in a wider sense, where the more correct term is "camelid", to include all seven species of the family Camelidae
Camelids are members of the biological family Camelidae, the only currently living family in the suborder Tylopoda. The seven extant members of this group are: dromedary camels, Bactrian camels, wild Bactrian camels, llamas, alpacas, vicuñas, ...
: the true camels (the above three species), along with the "New World" camelids: the llama
The llama (; ) (''Lama glama'') is a domesticated South American camelid, widely used as a List of meat animals, meat and pack animal by Inca empire, Andean cultures since the Pre-Columbian era.
Llamas are social animals and live with othe ...
, the alpaca
The alpaca (''Lama pacos'') is a species of South American camelid mammal. It is similar to, and often confused with, the llama. However, alpacas are often noticeably smaller than llamas. The two animals are closely related and can successfu ...
, the guanaco
The guanaco (; ''Lama guanicoe'') is a camelid native to South America, closely related to the llama. Guanacos are one of two wild South American camelids, the other being the vicuña, which lives at higher elevations.
Etymology
The guanaco ...
, and the vicuña
The vicuña (''Lama vicugna'') or vicuna (both , very rarely spelled ''vicugna'', its former genus name) is one of the two wild South American camelids, which live in the high alpine areas of the Andes, the other being the guanaco, which live ...
, which belong to the separate tribe Lamini
Lamini (members are called ''laminoids'') is a tribe of the subfamily Camelinae. It contains one extant genus with four species, all exclusively from South America: llamas, alpacas, vicuñas, and guanacos. The former two are domesticated specie ...
. Camelids originated in North America during the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
, with the ancestor of modern camels, ''Paracamelus
''Paracamelus'' is an extinct genus of camel in the family Camelidae. It originated in North America during the Middle Miocene but crossed the Beringian land bridge into Eurasia during the Late Miocene, approximately 7.5–6.5 million years ...
'', migrating across the Bering land bridge
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of ...
into Asia during the late Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
, around 6 million years ago.
Taxonomy
Extant species
3 species are extant:Biology
The averagelife expectancy
Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average time an organism is expected to live, based on the year of its birth, current age, and other demographic factors like sex. The most commonly used measure is life expectancy at birth ...
of a camel is 40 to 50 years. A full-grown adult dromedary camel stands at the shoulder and at the hump. Bactrian camels can be a foot taller. Camels can run at up to in short bursts and sustain speeds of up to . Bactrian camels weigh and dromedaries . The widening toes on a camel's hoof provide supplemental grip for varying soil sediments.
The male dromedary camel has an organ called a dulla in his throat, a large, inflatable sac he extrudes from his mouth when in rut to assert dominance and attract females. It resembles a long, swollen, pink tongue hanging out of the side of his mouth. Camels mate by having both male and female sitting on the ground, with the male mounting from behind. The male usually ejaculates
Ejaculation is the discharge of semen (the ''ejaculate''; normally containing sperm) from the male reproductory tract as a result of an orgasm. It is the final stage and natural objective of male sexual stimulation, and an essential componen ...
three or four times within a single mating session. Camelids are the only ungulates to mate in a sitting position.
Ecological and behavioral adaptations
Camels do not directly store water in their humps; they are reservoirs of fatty tissue. When this tissue is metabolized, it yields more than one gram of water for every gram of fat processed. This fat metabolization, while releasing energy, causes water to evaporate from the lungs duringrespiration
Respiration may refer to:
Biology
* Cellular respiration, the process in which nutrients are converted into useful energy in a cell
** Anaerobic respiration, cellular respiration without oxygen
** Maintenance respiration, the amount of cellul ...
(as oxygen is required for the metabolic process): overall, there is a net decrease in water.
 Camels have a series of physiological adaptations that allow them to withstand long periods of time without any external source of water. The dromedary camel can drink as seldom as once every 10 days even under very hot conditions, and can lose up to 30% of its body mass due to dehydration. Unlike other mammals, camels'
Camels have a series of physiological adaptations that allow them to withstand long periods of time without any external source of water. The dromedary camel can drink as seldom as once every 10 days even under very hot conditions, and can lose up to 30% of its body mass due to dehydration. Unlike other mammals, camels' red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
s are oval rather than circular in shape. This facilitates the flow of red blood cells during dehydration and makes them better at withstanding high osmotic
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region o ...
variation without rupturing when drinking large amounts of water: a camel can drink of water in three minutes.
Camels are able to withstand changes in body temperature
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature ...
and water consumption that would kill most other mammals. Their temperature ranges from at dawn and steadily increases to by sunset, before they cool off at night again. In general, to compare between camels and the other livestock, camels lose only 1.3 liters of fluid intake every day while the other livestock lose 20 to 40 liters per day. Maintaining the brain temperature within certain limits is critical for animals; to assist this, camels have a rete mirabile
A rete mirabile (Latin for "wonderful net"; plural retia mirabilia) is a complex of arteries and veins lying very close to each other, found in some vertebrates, mainly warm-blooded ones. The rete mirabile utilizes countercurrent blood flow within ...
, a complex of arteries and veins lying very close to each other which utilizes countercurrent blood flow to cool blood flowing to the brain.Inside Nature's Giants
''Inside Nature's Giants'' is a British science documentary, first broadcast in June 2009 by Channel 4. The documentary shows experts performing dissection on some of nature's largest animals, including whales and elephants.
The programme is ...
. Channel 4 (UK) documentary. Transmitted 30 August 2011 Camels rarely sweat, even when ambient temperatures reach . Any sweat that does occur evaporates at the skin level rather than at the surface of their coat; the heat of vaporization
The enthalpy of vaporization (symbol ), also known as the (latent) heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance to transform a quantity of that substance into a gas. T ...
therefore comes from body heat rather than ambient heat. Camels can withstand losing 25% of their body weight in water, whereas most other mammals can withstand only about 12–14% dehydration before cardiac failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, an ...
results from circulatory disturbance.
When the camel exhales, water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous pha ...
becomes trapped in their nostrils
A nostril (or naris , plural ''nares'' ) is either of the two orifices of the nose. They enable the entry and exit of air and other gasses through the nasal cavities. In birds and mammals, they contain branched bones or cartilages called turbi ...
and is reabsorbed into the body as a means to conserve water. Camels eating green herbage can ingest sufficient moisture in milder conditions to maintain their bodies' hydrated state without the need for drinking.
 The camel's thick coat insulates it from the intense heat radiated from desert sand; a shorn camel must sweat 50% more to avoid overheating. During the summer the coat becomes lighter in color, reflecting light as well as helping avoid sunburn. The camel's long legs help by keeping its body farther from the ground, which can heat up to . Dromedaries have a pad of thick tissue over the
The camel's thick coat insulates it from the intense heat radiated from desert sand; a shorn camel must sweat 50% more to avoid overheating. During the summer the coat becomes lighter in color, reflecting light as well as helping avoid sunburn. The camel's long legs help by keeping its body farther from the ground, which can heat up to . Dromedaries have a pad of thick tissue over the sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Sh ...
called the ''pedestal''. When the animal lies down in a sternal recumbent position, the pedestal raises the body from the hot surface and allows cooling air to pass under the body.
Camels' mouths have a thick leathery lining, allowing them to chew thorny desert plants. Long eyelashes and ear hairs, together with nostrils that can close, form a barrier against sand. If sand gets lodged in their eyes, they can dislodge it using their transparent third eyelid (also known as the nictitating membrane). The camels' gait and widened feet help them move without sinking into the sand.
The kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood ...
s and intestines
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans ...
of a camel are very efficient at reabsorbing water. Camels' kidneys have a 1:4 cortex
Cortex or cortical may refer to:
Biology
* Cortex (anatomy), the outermost layer of an organ
** Cerebral cortex, the outer layer of the vertebrate cerebrum, part of which is the ''forebrain''
*** Motor cortex, the regions of the cerebral cortex i ...
to medulla ratio. Thus, the medullary part of a camel's kidney occupies twice as much area as a cow's kidney. Secondly, renal corpuscles
A renal corpuscle (also called malpighian body) is the blood-filtering component of the nephron of the kidney. It consists of a glomerulus - a tuft of capillaries composed of endothelial cells, and a glomerular capsule known as Bowman's capsul ...
have a smaller diameter, which reduces surface area for filtration. These two major anatomical characteristics enable camels to conserve water and limit the volume of urine in extreme desert conditions.Rehan S and AS Qureshi, 2006. Microscopic evaluation of the heart, kidneys and adrenal glands of one-humped camel calves (Camelus dromedarius) using semi automated image analysis system. J Camel Pract Res. 13(2): 123
Camel urine
Camel urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in a camel's anatomy. Urine from Arabian camels has been used in the Arabian Peninsula as prophetic medicine for centuries, being a part of ancient Bedouin practices. After the spread of MERS-CoV ...
comes out as a thick syrup, and camel faeces are so dry that they do not require drying when the Bedouins
The Bedouin, Beduin, or Bedu (; , singular ) are nomadic Arabs, Arab tribes who have historically inhabited the desert regions in the Arabian Peninsula, North Africa, the Levant, and Mesopotamia. The Bedouin originated in the Syrian Desert ...
use them to fuel fires.
The camel immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
differs from those of other mammals. Normally, the Y-shaped antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
molecules consist of two heavy (or long) chains along the length of the Y, and two light (or short) chains at each tip of the Y. Camels, in addition to these, also have antibodies made of only two heavy chains, a trait that makes them smaller and more durable. These "heavy-chain-only" antibodies, discovered in 1993, are thought to have developed 50 million years ago, after camelids split from ruminants and pigs. Camels suffer from surra caused by ''Trypanosoma evansi
''Trypanosoma evansi'' is a parasitic species of excavate trypanosome in the genus ''Trypanosoma'' that causes one form of surra in animals. Discovered by Griffith Evans in 1880 at Dera Ismail Khan (British India), it is the first known tryp ...
'' wherever camels are domesticated in the world, and resultantly camels have evolved trypanolytic antibodies as with many mammals. In the future, nanobody/single-domain antibody
A single-domain antibody (sdAb), also known as a nanobody, is an antibody fragment consisting of a single monomeric variable antibody domain. Like a whole antibody, it is able to bind selectively to a specific antigen. With a molecular weight of ...
therapy will surpass natural camel antibodies by reaching locations currently unreachable due to natural antibodies' larger size. Such therapies may also be suitable for other mammals. Tran ''et al.'' 2009 provides a new reference test
A medical test is a medical procedure performed to detect, diagnose, or monitor diseases, disease processes, susceptibility, or to determine a course of treatment. Medical tests such as, physical and visual exams, diagnostic imaging, genetic te ...
for surra (''T. evansi'') of camel. They use recombinant (rISG75, an Invariant Surface Glycoprotein) and ELISA
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (, ) is a commonly used analytical biochemistry assay, first described by Eva Engvall and Peter Perlmann in 1971. The assay uses a solid-phase type of enzyme immunoassay (EIA) to detect the presence ...
. The Tran test has high test specificity
''Sensitivity'' and ''specificity'' mathematically describe the accuracy of a test which reports the presence or absence of a condition. Individuals for which the condition is satisfied are considered "positive" and those for which it is not are ...
and appears likely to work just as well for ''T. evansi'' in other hosts, and for a pan-''Trypanozoon
''Trypanosoma'' is a genus of kinetoplastids (class Trypanosomatidae), a monophyletic group of unicellular parasitic flagellate protozoa. Trypanosoma is part of the phylum Sarcomastigophora. The name is derived from the Greek ''trypano-'' ( ...
'' test, which would also be useful for '' T. b. brucei'', '' T. b. gambiense'', '' T. b. rhodesiense'', and '' T. equiperdum''.
Genetics
Thekaryotype
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of metaphase chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is disce ...
s of different camelid species have been studied earlier by many groups, but no agreement on chromosome nomenclature of camelids has been reached. A 2007 study flow sorted camel chromosomes, building on the fact that camels have 37 pairs of chromosomes (2n=74), and found that the karyotype consisted of one metacentric
Metacentric may refer to:
* Metacentric height
The metacentric height (GM) is a measurement of the initial static stability of a floating body. It is calculated as the distance between the centre of gravity of a ship and its metacentre. A larger ...
, three submetacentric, and 32 acrocentric autosomes. The Y is a small metacentric chromosome, while the X is a large metacentric chromosome.
 The
The hybrid camel
A hybrid camel is a hybrid between a Bactrian camel (''Camelus bactrianus'') and dromedary (''Camelus dromedarius'').
Names
Hybrid camels have different names depending on zone and language. Some names include turkoman, tülu, bukht, nar, in ...
, a hybrid between Bactrian and dromedary camels, has one hump, though it has an indentation deep that divides the front from the back. The hybrid is at the shoulder and tall at the hump. It weighs an average of and can carry around , which is more than either the dromedary or Bactrian can.
According to molecular data, the wild Bactrian camel (''C. ferus'') separated from the domestic Bactrian camel (''C. bactrianus'') about 1 million years ago. New World and Old World camelids diverged about 11 million years ago. In spite of this, these species can hybridize and produce viable offspring. The cama is a camel-llama hybrid bred by scientists to see how closely related the parent species are. Scientists collected semen
Semen collection refers to the process of obtaining semen from human males or other animals with the use of various methods, for the purposes of artificial insemination, or medical study (usually in fertility clinics). Semen can be collected via ...
from a camel via an artificial vagina and inseminated a llama after stimulating ovulation with gonadotrophin
Gonadotropins are glycoprotein hormones secreted by gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary of vertebrates. This family includes the mammalian hormones follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), the placental/chorionic ...
injections. The cama is halfway in size between a camel and a llama and lacks a hump. It has ears intermediate between those of camels and llamas, longer legs than the llama, and partially cloven hooves
A cloven hoof, cleft hoof, divided hoof or split hoof is a hoof split into two toes. This is found on members of the mammalian order Artiodactyla. Examples of mammals that possess this type of hoof are cattle, deer, pigs, antelopes, gazelles, ...
. Like the mule
The mule is a domestic equine hybrid between a donkey and a horse. It is the offspring of a male donkey (a jack) and a female horse (a mare). The horse and the donkey are different species, with different numbers of chromosomes; of the two pos ...
, camas are sterile, despite both parents having the same number of chromosomes.
Evolution
The earliest known camel, called ''Protylopus
''Protylopus'' is an extinct genus of camel that lived during middle to late Eocene some 50-40 million years ago in North America.
Along with being the oldest camel known, it was also the smallest, reaching a length of , and probably weighing a ...
'', lived in North America 40 to 50 million years ago (during the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
). It was about the size of a rabbit and lived in the open woodlands of what is now South Dakota
South Dakota (; Sioux language, Sioux: , ) is a U.S. state in the West North Central states, North Central region of the United States. It is also part of the Great Plains. South Dakota is named after the Lakota people, Lakota and Dakota peo ...
. By 35 million years ago, the ''Poebrotherium
''Poebrotherium'' ( ) is an extinct genus of camelid, endemic to North America. They lived from the Eocene to Miocene epochs, 46.3—13.6 mya, existing for approximately .
Discovery and history
''Poebrotherium'' was first named by scientist J ...
'' was the size of a goat and had many more traits similar to camels and llamas. The hoofed '' Stenomylus'', which walked on the tips of its toes, also existed around this time, and the long-necked ''Aepycamelus
''Aepycamelus'' is an extinct genus of camelids that lived during the Miocene 20.6–4.9 million years ago, existing for about . Its name is derived from the Homeric Greek , "high and steep" and κάμηλος – "camel"; thus, "high camel"; ''a ...
'' evolved in the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recen ...
.
The ancestor of modern camels, ''Paracamelus
''Paracamelus'' is an extinct genus of camel in the family Camelidae. It originated in North America during the Middle Miocene but crossed the Beringian land bridge into Eurasia during the Late Miocene, approximately 7.5–6.5 million years ...
'', migrated into Eurasia from North America via Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip ...
during the late Miocene, between 7.5 and 6.5 million years ago. During the Pleistocene, around 3 to 1 million years ago, the North American Camelidae spread to South America as part of the Great American Interchange
The Great American Biotic Interchange (commonly abbreviated as GABI), also known as the Great American Interchange and the Great American Faunal Interchange, was an important late Cenozoic paleozoogeographic biotic interchange event in which lan ...
via the newly formed Isthmus of Panama
The Isthmus of Panama ( es, Istmo de Panamá), also historically known as the Isthmus of Darien (), is the narrow strip of land that lies between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, linking North and South America. It contains the country ...
, where they gave rise to guanacos
The guanaco (; ''Lama guanicoe'') is a camelid native to South America, closely related to the llama. Guanacos are one of two wild South American camelids, the other being the vicuña, which lives at higher elevations.
Etymology
The guanaco g ...
and related animals. Populations of ''Paracamelus'' continued to exist in the North American Arctic into the Early Pleistocene
The Early Pleistocene is an unofficial sub-epoch in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, being the earliest division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. It is currently estimated to span the time ...
. This creature is estimated to have stood around tall. The Bactrian camel diverged from the dromedary about 1 million years ago, according to the fossil record.
The last camel native to North America was ''Camelops hesternus
''Camelops''Being occasionally called ''Western Camel'' or ''Yesterday's Camel''. is an extinct genus of camels that lived in North and Central America, ranging from Alaska to Guatemala, from the middle Pliocene to the end of the Pleistocene. It ...
'', which vanished along with horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million y ...
s, short-faced bear
The Tremarctinae or short-faced bears is a subfamily of Ursidae that contains one living representative, the spectacled bear (''Tremarctos ornatus'') of South America, and several extinct species from four genera: the Florida spectacled bear ('' ...
s, mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus'', one of the many genera that make up the order of trunked mammals called proboscideans. The various species of mammoth were commonly equipped with long, curved tusks and, ...
s and mastodon
A mastodon ( 'breast' + 'tooth') is any proboscidean belonging to the extinct genus ''Mammut'' (family Mammutidae). Mastodons inhabited North and Central America during the late Miocene or late Pliocene up to their extinction at the end of th ...
s, ground sloth
Ground sloths are a diverse group of extinct sloths in the mammalian superorder Xenarthra. The term is used to refer to all extinct sloths because of the large size of the earliest forms discovered, compared to existing tree sloths. The Caribbe ...
s, sabertooth cat
Machairodontinae is an extinct subfamily of carnivoran mammals of the family Felidae (true cats). They were found in Asia, Africa, North America, South America, and Europe from the Miocene to the Pleistocene, living from about 16 million ...
s, and many other megafauna, coinciding with the migration of humans from Asia at the end of the Pleistocene, around 15–11,000 years ago.
Poebrotherium
''Poebrotherium'' ( ) is an extinct genus of camelid, endemic to North America. They lived from the Eocene to Miocene epochs, 46.3—13.6 mya, existing for approximately .
Discovery and history
''Poebrotherium'' was first named by scientist J ...
skeleton
File:NMNH-USNM244271 2.jpg, Procamelus
''Procamelus'' is an extinct genus of Camelini, camel endemic to North America. It lived from the Middle to Late Miocene 16.0—5.3 Annum, mya, existing for approximately . The name is derived from the Greek πρό, meaning "before" or denoting p ...
skull
File:Camelops hesternus.jpg, alt=, ''Camelops hesternus
''Camelops''Being occasionally called ''Western Camel'' or ''Yesterday's Camel''. is an extinct genus of camels that lived in North and Central America, ranging from Alaska to Guatemala, from the middle Pliocene to the end of the Pleistocene. It ...
'', the last true camel native to North America
Domestication
Likehorse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million y ...
s, camels originated in North America and eventually spread across Beringia
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip ...
to Asia. They survived in the Old World, and eventually humans domesticated them and spread them globally. Along with many other megafauna in North America, the original wild camels were wiped out during the spread of the first indigenous peoples of the Americas
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the A ...
from Asia into North America, 10 to 12,000 years ago; although fossils have never been associated with definitive evidence of hunting.
Most camels surviving today are domesticated. Although feral
A feral () animal or plant is one that lives in the wild but is descended from domesticated individuals. As with an introduced species, the introduction of feral animals or plants to non-native regions may disrupt ecosystems and has, in some ...
populations exist in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, India and Kazakhstan, wild camels survive only in the wild Bactrian camel
The wild Bactrian camel (''Camelus ferus'') is a critically endangered species of camel living in parts of northwestern China and southwestern Mongolia. It is closely related to the Bactrian camel (''Camelus bactrianus''). Both are large, doubl ...
population of the Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert (Chinese: 戈壁 (沙漠), Mongolian: Говь (ᠭᠣᠪᠢ)) () is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia, and is the sixth largest desert in the world.
Geography
The Gobi measures from southwest to northeast an ...
.
History
When humans first domesticated camels is disputed. Dromedaries may have first been domesticated by humans inSomalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
or South Arabia
South Arabia () is a historical region that consists of the southern region of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia, mainly centered in what is now the Republic of Yemen, yet it has also historically included Najran, Jizan, Al-Bahah, and 'Asi ...
sometime during the 3rd millennium BC
The 3rd millennium BC spanned the years 3000 through 2001 BC. This period of time corresponds to the Early to Middle Bronze Age, characterized by the early empires in the Ancient Near East. In Ancient Egypt, the Early Dynastic Period is followe ...
, the Bactrian in central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
around 2,500 BC, as at Shar-i Sokhta (also known as the Burnt City), Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
.
Martin Heide's 2010 work on the domestication of the camel tentatively concludes that humans had domesticated the Bactrian camel by at least the middle of the third millennium somewhere east of the Zagros Mountains
The Zagros Mountains ( ar, جبال زاغروس, translit=Jibal Zaghrus; fa, کوههای زاگرس, Kuh hā-ye Zāgros; ku, چیاکانی زاگرۆس, translit=Çiyakani Zagros; Turkish: ''Zagros Dağları''; Luri: ''Kuh hā-ye Zāgro ...
, with the practice then moving into Mesopotamia. Heide suggests that mentions of camels "in the patriarchal narratives may refer, at least in some places, to the Bactrian camel", while noting that the camel is not mentioned in relationship to Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
.
Recent excavations in the Timna Valley
The Timna Valley (תִּמְנָע, ) is located in southern Israel in the southwestern Arava/Arabah, approximately north of the Gulf of Aqaba and the city of Eilat. The area is rich in copper ore and has been mined since the 5th millennium ...
by Lidar Sapir-Hen and Erez Ben-Yosef discovered what may be the earliest domestic camel bones yet found in Israel or even outside the Arabian Peninsula
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate ...
, dating to around 930 BC. This garnered considerable media coverage, as it is strong evidence that the stories of Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Jew ...
, Jacob
Jacob (; ; ar, يَعْقُوب, Yaʿqūb; gr, Ἰακώβ, Iakṓb), later given the name Israel, is regarded as a patriarch of the Israelites and is an important figure in Abrahamic religions, such as Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. J ...
, Esau
Esau ''Ēsaû''; la, Hesau, Esau; ar, عِيسَوْ ''‘Īsaw''; meaning "hairy"Easton, M. ''Illustrated Bible Dictionary'', (, , 2006, p. 236 or "rough".Mandel, D. ''The Ultimate Who's Who in the Bible'', (.), 2007, p. 175 is the elder son o ...
, and Joseph
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the mo ...
were written after this time.
The existence of camels in Mesopotamia—but not in the eastern Mediterranean lands—is not a new idea. The historian Richard Bulliet
Richard W. Bulliet (born 1940) is a professor of history at Columbia University who specializes in the history of Islamic society and institutions, the history of technology, and the history of the role of animals in human society.
Early life ...
did not think that the occasional mention of camels in the Bible meant that the domestic camels were common in the Holy Land at that time. The archaeologist William F. Albright
William Foxwell Albright (May 24, 1891– September 19, 1971) was an American archaeologist, biblical scholar, philologist, and expert on ceramics. He is considered "one of the twentieth century's most influential American biblical scholars."
...
, writing even earlier, saw camels in the Bible as an anachronism
An anachronism (from the Ancient Greek, Greek , 'against' and , 'time') is a chronology, chronological inconsistency in some arrangement, especially a juxtaposition of people, events, objects, language terms and customs from different time per ...
.
The official report by Sapir-Hen and Ben-Joseph notes:
The introduction of the dromedary camel (Camelus dromedarius) as a pack animal to theand concludes:southern Levant The Southern Levant is a Region, geographical region encompassing the southern half of the Levant. It corresponds approximately to modern-day Israel, State of Palestine, Palestine, and Jordan; some definitions also include southern Lebanon, southe ...... substantially facilitated trade across the vast deserts of Arabia, promoting both economic and social change (e.g., Kohler 1984; Borowski 1998: 112–116; Jasmin 2005). This ... has generated extensive discussion regarding the date of the earliest domestic camel in the southern Levant (and beyond) (e.g., Albright 1949: 207; Epstein 1971: 558–584; Bulliet 1975; Zarins 1989; Köhler-Rollefson 1993; Uerpmann and Uerpmann 2002; Jasmin 2005; 2006; Heide 2010; Rosen and Saidel 2010; Grigson 2012). Most scholars today agree that the dromedary was exploited as a pack animal sometime in the earlyIron Age The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...(not before the 12th century C
Current data from copper smelting sites of the Aravah Valley enable us to pinpoint the introduction of domestic camels to the southern Levant more precisely based on stratigraphic contexts associated with an extensive suite of radiocarbon dates. The data indicate that this event occurred not earlier than the last third of the 10th century Cand most probably during this time. The coincidence of this event with a major reorganization of the copper industry of the region—attributed to the results of the campaign of PharaohShoshenq I Hedjkheperre Setepenre Shoshenq I (Egyptian ''ššnq''; reigned c. 943–922 BC)—also known as Shashank or Sheshonk or Sheshonq Ifor discussion of the spelling, see Shoshenq—was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the founder of the Twenty-secon ...—raises the possibility that the two were connected, and that camels were introduced as part of the efforts to improve efficiency by facilitating trade.
draft animal
A working animal is an animal, usually domesticated, that is kept by humans and trained to perform tasks instead of being slaughtered to harvest animal products. Some are used for their physical strength (e.g. oxen and draft horses) or for t ...
in Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
(2009)
File:A camel with its rider playing kettle drums..jpg, alt= A painting of a man sitting on a camel and playing the drums, A camel in a ceremonial procession, its rider playing kettledrum
Timpani (; ) or kettledrums (also informally called timps) are musical instruments in the percussion family. A type of drum categorised as a hemispherical drum, they consist of a membrane called a head stretched over a large bowl traditionally ...
s, Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
(c. 1840)
File:Negev camel petroglyph.jpg, Petroglyph of a camel, Negev
The Negev or Negeb (; he, הַנֶּגֶב, hanNegév; ar, ٱلنَّقَب, an-Naqab) is a desert and semidesert region of southern Israel. The region's largest city and administrative capital is Beersheba (pop. ), in the north. At its southe ...
, southern Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
(prior to c. 5300 BC)
File:Bartholomeus Breenbergh 002.jpg, ''Joseph Sells Grain'' by Bartholomeus Breenbergh
Bartholomeus Breenbergh (before 13 November 1598 – after 3 October 1657) was a Dutch Golden Age painter of Italian and Italianate landscapes, in Rome (1619-1630) and Amsterdam (1630-1657).
Biography
Little is known of his early life. In his ...
(1655), showing camel with rider at left
Textiles
Desert tribes and Mongolian nomads use camel hair for tents,yurt
A yurt (from the Turkic languages) or ger ( Mongolian) is a portable, round tent covered and insulated with skins or felt and traditionally used as a dwelling by several distinct nomadic groups in the steppes and mountains of Central Asia. ...
s, clothing, bedding and accessories. Camels have outer guard hairs and soft inner down, and the fibers are sorted by color and age of the animal. The guard hairs can be felted for use as waterproof coats for the herdsmen, while the softer hair is used for premium goods. The fiber can be spun for use in weaving or made into yarns for hand knitting or crochet. Pure camel hair is recorded as being used for western garments from the 17th century onwards, and from the 19th century a mixture of wool and camel hair was used.
Military uses

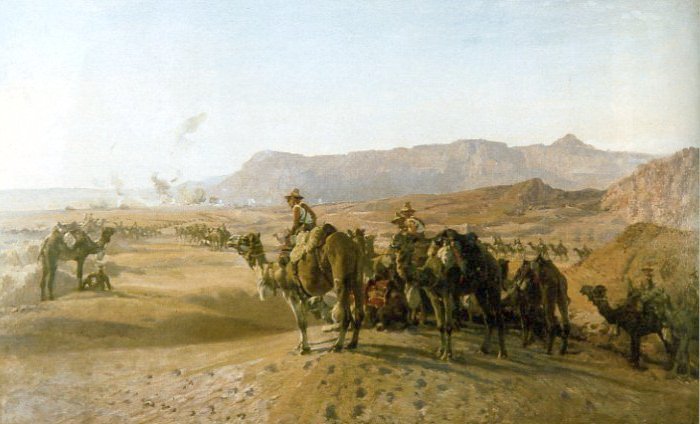
 By at least 1200 BC the first camel saddles had appeared, and
By at least 1200 BC the first camel saddles had appeared, and Bactrian camels
The Bactrian camel (''Camelus bactrianus''), also known as the Mongolian camel or domestic Bactrian camel, is a large even-toed ungulate native to the steppes of Central Asia. It has two humps on its back, in contrast to the single-humped drome ...
could be ridden. The first saddle was positioned to the back of the camel, and control of the Bactrian camel was exercised by means of a stick. However, between 500 and 100 BC, Bactrian camels came into military use. New saddles, which were inflexible and bent, were put over the humps and divided the rider's weight over the animal. In the seventh century BC the military Arabian saddle evolved, which again improved the saddle design slightly.
Military forces have used camel cavalries in wars throughout Africa, the Middle East, and into the modern-day Border Security Force
The Border Security Force (BSF) is India's border guarding organisation on its border with Pakistan and Bangladesh. It is one of the seven Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF) of India, and was raised in the wake of the 1965 war on 1 December 1 ...
(BSF) of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
(though as of July 2012, the BSF planned the replacement of camels with ATVs). The first documented use of camel cavalries occurred in the Battle of Qarqar
The Battle of Qarqar (or Ḳarḳar) was fought in 853 BC when the army of the Neo-Assyrian Empire led by Emperor Shalmaneser III encountered an allied army of eleven kings at Qarqar led by Hadadezer, called in Assyrian ''Adad-idir'' and possi ...
in 853 BC. Armies have also used camels as freight animals instead of horses and mules.
The East Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
used auxiliary
Auxiliary may refer to:
* A backup site or system
In language
* Auxiliary language (disambiguation)
* Auxiliary verb
In military and law enforcement
* Auxiliary police
* Auxiliaries, civilians or quasi-military personnel who provide support of ...
forces known as ''dromedarii
Dromedarii were camel-riding auxiliary forces recruited in the desert provinces of the Late Roman Empire in Syria.
They were developed to take the place of horses, where horses were not common. They were also successful against enemy horses, as ...
'', whom the Romans recruited in desert provinces. The camels were used mostly in combat because of their ability to scare off horses at close range (horses are afraid of the camels' scent), a quality famously employed by the Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, wikt:𐎧𐏁𐏂𐎶, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an History of Iran#Classical antiquity, ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Bas ...
Persians when fighting Lydia
Lydia (Lydian language, Lydian: 𐤮𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣𐤠, ''Śfarda''; Aramaic: ''Lydia''; el, Λυδία, ''Lȳdíā''; tr, Lidya) was an Iron Age Monarchy, kingdom of western Asia Minor located generally east of ancient Ionia in the mod ...
in the Battle of Thymbra
The Battle of Thymbra was the decisive battle in the war between Croesus of the Lydian Kingdom and Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid Empire. Cyrus, after he had pursued Croesus into Lydia after the drawn Battle of Pteria, met the remains of ...
(547 BC).
19th and 20th centuries
 The
The United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
established the U.S. Camel Corps
The United States Camel Corps was a mid-19th-century experiment by the United States Army in using camels as pack animals in the Southwestern United States. Although the camels proved to be hardy and well suited to travel through the region, th ...
, stationed in California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
, in the 19th century. One may still see stables at the Benicia Arsenal in Benicia, California
Benicia ( , ) is a waterside city in Solano County, California, located in the North Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area. It served as the capital of California for nearly thirteen months from 1853 to 1854. The population was 26,997 at the ...
, where they nowadays serve as the Benicia Historical Museum. Though the experimental use of camels was seen as a success (John B. Floyd
John Buchanan Floyd (June 1, 1806 – August 26, 1863) was the 31st Governor of Virginia, U.S. Secretary of War, and the Confederate general in the American Civil War who lost the crucial Battle of Fort Donelson.
Early family life
John Buchan ...
, Secretary of War
The secretary of war was a member of the U.S. president's Cabinet, beginning with George Washington's administration. A similar position, called either "Secretary at War" or "Secretary of War", had been appointed to serve the Congress of the ...
in 1858, recommended that funds be allocated towards obtaining a thousand more camels), the outbreak of the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
in 1861 saw the end of the Camel Corps: Texas became part of the Confederacy, and most of the camels were left to wander away into the desert.
France created a ''méhariste
Méhariste is a French word that roughly translates to camel cavalry. The word is most commonly used as a designation of military units.
French camel corps
Origins
France created a corps of méhariste camel companies (''Compagnies Méharistes ...
'' camel corps in 1912 as part of the Armée d'Afrique in the Sahara in order to exercise greater control over the camel-riding Tuareg
The Tuareg people (; also spelled Twareg or Touareg; endonym: ''Imuhaɣ/Imušaɣ/Imašeɣăn/Imajeɣăn'') are a large Berber ethnic group that principally inhabit the Sahara in a vast area stretching from far southwestern Libya to southern A ...
and Arab insurgents, as previous efforts to defeat them on foot had failed. The Free French Camel Corps fought during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, and camel-mounted units remained in service until the end of French rule over Algeria in 1962.
In 1916, the British created the Imperial Camel Corps
The Imperial Camel Corps Brigade (ICCB) was a camel-mounted infantry brigade that the British Empire raised in December 1916 during the First World War for service in the Middle East.
From a small beginning the unit eventually grew to a brigad ...
. It was originally used to fight the Senussi
The Senusiyya, Senussi or Sanusi ( ar, السنوسية ''as-Sanūssiyya'') are a Muslim political-religious tariqa (Sufi order) and clan in colonial Libya and the Sudan region founded in Mecca in 1837 by the Grand Senussi ( ar, السنوسي ...
, but was later used in the Sinai and Palestine Campaign in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. The Imperial Camel Corps comprised infantrymen mounted on camels for movement across desert, though they dismounted at battle sites and fought on foot. After July 1918, the Corps began to become run down, receiving no new reinforcements, and was formally disbanded in 1919.
In World War I, the British Army also created the Egyptian Camel Transport Corps
The Egyptian Camel Transport Corps (known as the CTC, Camel Corps or Camel Transport) were a group of Egyptian camel drivers who supported the British Army in Egypt during the First World War's Sinai and Palestine Campaign. The work done by the 17 ...
, which consisted of a group of Egyptian camel drivers and their camels. The Corps supported British war operations in Sinai
Sinai commonly refers to:
* Sinai Peninsula, Egypt
* Mount Sinai, a mountain in the Sinai Peninsula, Egypt
* Biblical Mount Sinai, the site in the Bible where Moses received the Law of God
Sinai may also refer to:
* Sinai, South Dakota, a place ...
, Palestine, and Syria by transporting supplies to the troops.
The Somaliland Camel Corps
The Somaliland Camel Corps (SCC) was a Rayid unit of the British Army based in British Somaliland. It lasted from the early 20th century until 1944.
Beginnings and the Dervish rebellion
In 1888, after signing successive treaties with the then r ...
was created by colonial authorities in British Somaliland
British Somaliland, officially the Somaliland Protectorate ( so, Dhulka Maxmiyada Soomaalida ee Biritishka), was a British Empire, British protectorate in present-day Somaliland. During its existence, the territory was bordered by Italian Soma ...
in 1912; it was disbanded in 1944.
Bactrian camels were used by Romanian forces during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
in the Caucasian region. At the same period the Soviet units operating around Astrakhan
Astrakhan ( rus, Астрахань, p=ˈastrəxənʲ) is the largest city and administrative centre of Astrakhan Oblast in Southern Russia. The city lies on two banks of the Volga, in the upper part of the Volga Delta, on eleven islands of the ...
in 1942 adopted local camels as draft animals due to shortage of trucks and horses, and kept them even after moving out of the area. Despite severe losses, some of these camels ended up as far west as to Berlin itself.
The Bikaner Camel Corps
The Bikaner Camel Corps was a unit of Imperial Service Troops from India that fought for the Allies in World War I and World War II.
The Corps was founded by Maharaja Ganga Singh of the Indian state of Bikaner, as the Ganga Risala after the Bri ...
of British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance on the Indian subcontinent. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one ...
fought alongside the British Indian Army
The British Indian Army, commonly referred to as the Indian Army, was the main military of the British Raj before its dissolution in 1947. It was responsible for the defence of the British Indian Empire, including the princely states, which co ...
in World Wars I and II.
The ''Tropas Nómadas The (Nomad Troops) were an auxiliary regiment to the colonial army in Spanish Sahara (today Western Sahara), from the 1930s until the end of the Spanish presence in the territory in 1975. Composed of Sahrawi tribesmen, the Tropas Nómadas were equ ...
'' (Nomad Troops) were an auxiliary regiment of Sahrawi tribesmen serving in the colonial army in Spanish Sahara (today Western Sahara
Western Sahara ( '; ; ) is a disputed territory on the northwest coast and in the Maghreb region of North and West Africa. About 20% of the territory is controlled by the self-proclaimed Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR), while the r ...
). Operational from the 1930s until the end of the Spanish presence in the territory in 1975, the ''Tropas Nómadas'' were equipped with small arms and led by Spanish officers. The unit guarded outposts and sometimes conducted patrols on camelback.
21st century competition
At the King Abdulaziz Camel Festival, in Saudi Arabia, thousands of camels are paraded and are judged on their lips and humps. The festival also features camel racing and camel milk tasting and has combined prize money of $57m (£40m). In 2018, 12 camels were disqualified from the beauty contest after it was discovered their owners had tried to improve their camel's good looks with injections ofbotox
Botulinum toxin, or botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT), is a neurotoxic protein produced by the bacterium '' Clostridium botulinum'' and related species. It prevents the release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine from axon endings at the neuromus ...
, into the animals' lips, noses and jaws. In 2021 over 40 camels were disqualified for acts of tampering and deception in beautifying camels.
Food uses
Dairy

 Camel milk is a
Camel milk is a staple food
A staple food, food staple, or simply a staple, is a food that is eaten often and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard diet for a given person or group of people, supplying a large fraction of energy needs and ...
of desert nomad tribes and is sometimes considered a meal itself; a nomad can live on only camel milk for almost a month.
Camel milk can readily be made into yogurt
Yogurt (; , from tr, yoğurt, also spelled yoghurt, yogourt or yoghourt) is a food produced by bacterial Fermentation (food), fermentation of milk. The bacteria used to make yogurt are known as ''yogurt cultures''. Fermentation of sugars in t ...
, but can only be made into butter
Butter is a dairy product made from the fat and protein components of churned cream. It is a semi-solid emulsion at room temperature, consisting of approximately 80% butterfat. It is used at room temperature as a spread, melted as a condiment ...
if it is soured first, churned, and a clarifying agent Clarifying agents are used to remove suspended solids from liquids by inducing flocculation, causing the solids to form larger aggregates that can be easily removed after they either float to the surface or sink to the bottom of the containment vess ...
is then added. Until recently, camel milk could not be made into camel cheese because rennet
Rennet () is a complex set of enzymes produced in the stomachs of ruminant mammals. Chymosin, its key component, is a protease enzyme that curdles the casein in milk. In addition to chymosin, rennet contains other enzymes, such as pepsin and a ...
was unable to coagulate the milk proteins to allow the collection of curd
Curd is obtained by coagulating milk in a sequential process called curdling. It can be a final dairy product or the first stage in cheesemaking. The coagulation can be caused by adding rennet or any edible acidic substance such as lemon ...
s. Developing less wasteful uses of the milk, the FAO
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)french: link=no, Organisation des Nations unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture; it, Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite per l'Alimentazione e l'Agricoltura is an intern ...
commissioned Professor J.P. Ramet of the École Nationale Supérieure d'Agronomie et des Industries Alimentaires, who was able to produce curdling by the addition of calcium phosphate
The term calcium phosphate refers to a family of materials and minerals containing calcium ions (Ca2+) together with inorganic phosphate anions. Some so-called calcium phosphates contain oxide and hydroxide as well. Calcium phosphates are white ...
and vegetable rennet in the 1990s. The cheese produced from this process has low levels of cholesterol and is easy to digest, even for the lactose intolerant.
Camel milk can also be made into ice cream
Ice cream is a sweetened frozen food typically eaten as a snack or dessert. It may be made from milk or cream and is flavoured with a sweetener, either sugar or an alternative, and a spice, such as cocoa or vanilla, or with fruit such as str ...
.
Meat

qurban
''Qurbanī'' ( ar, قربانى), ''Qurban'', or ''uḍḥiyah'' () as referred to in Islamic law, is a ritual animal sacrifice of a livestock animal during Eid al-Adha.
The concept and definition of the word is derived from the Qur'an, the s ...
of Eid al-Adha
Eid al-Adha () is the second and the larger of the two main holidays celebrated in Islam (the other being Eid al-Fitr). It honours the willingness of Ibrahim (Abraham) to sacrifice his son Ismail (Ishmael) as an act of obedience to Allah's co ...
.
The Abu Dhabi
Abu Dhabi (, ; ar, أَبُو ظَبْيٍ ' ) is the capital and second-most populous city (after Dubai) of the United Arab Emirates. It is also the capital of the Emirate of Abu Dhabi and the centre of the Abu Dhabi Metropolitan Area.
...
Officers' Club serves a camel burger mixed with beef or lamb fat in order to improve the texture and taste. In Karachi, Pakistan
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former cap ...
, some restaurants prepare nihari
Nihari (; bn, নিহারী; ); is a stew originating in Lucknow, the capital of 18th-century Awadh under the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. It consists of slow-cooked meat, mainly a shank cut of beef, lamb and mutton, or goa ...
from camel meat. Specialist camel butchers provide expert cuts, with the hump considered the most popular.
Camel meat has been eaten for centuries. It has been recorded by ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
writers as an available dish at banquets in ancient Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, usually roasted whole. The Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
emperor Heliogabalus enjoyed camel's heel. Camel meat is mainly eaten in certain regions, including Eritrea
Eritrea ( ; ti, ኤርትራ, Ertra, ; ar, إرتريا, ʾIritriyā), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of Eastern Africa, with its capital and largest city at Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia ...
, Somalia
Somalia, , Osmanya script: 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒕𐒖; ar, الصومال, aṣ-Ṣūmāl officially the Federal Republic of SomaliaThe ''Federal Republic of Somalia'' is the country's name per Article 1 of thProvisional Constituti ...
, Djibouti
Djibouti, ar, جيبوتي ', french: link=no, Djibouti, so, Jabuuti officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red ...
, Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the A ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
, Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
, Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya bo ...
, Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t ...
, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, , om, Itiyoophiyaa, so, Itoobiya, ti, ኢትዮጵያ, Ítiyop'iya, aa, Itiyoppiya officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, and other arid regions where alternative forms of protein may be limited or where camel meat has had a long cultural history. Camel blood is also consumable, as is the case among pastoralists in northern Kenya
)
, national_anthem = "Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Nairobi
, coordinates =
, largest_city = Nairobi
, ...
, where camel blood is drunk with milk and acts as a key source of iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
, vitamin D
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (c ...
, salts and minerals.
A 2005 report issued jointly by the Saudi Ministry of Health and the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency, under the Department of Health and Human Services, and is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgi ...
details four cases of human bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the plague bacterium (''Yersinia pestis''). One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as well a ...
resulting from the ingestion of raw camel liver.
Australia
Camel meat is also occasionally found inAustralian cuisine
Australian(s) may refer to:
Australia
* Australia, a country
* Australians, citizens of the Commonwealth of Australia
** European Australians
** Anglo-Celtic Australians, Australians descended principally from British colonists
** Aboriginal Au ...
: for example, a camel lasagna
Lasagna (, also , also known as lasagne, ) is a type of pasta, possibly one of the oldest types, made of very wide, flat sheets. Either term can also refer to an Italian dish made of stacked layers of lasagna alternating with fillings such as ...
is available in Alice Springs
Alice Springs ( aer, Mparntwe) is the third-largest town in the Northern Territory of Australia. Known as Stuart until 31 August 1933, the name Alice Springs was given by surveyor William Whitfield Mills after Alice, Lady Todd (''née'' Al ...
. Australia has exported camel meat, primarily to the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
but also to Europe and the US, for many years. The meat is very popular among East African Australians, such as Somalis
The Somalis ( so, Soomaalida 𐒈𐒝𐒑𐒛𐒐𐒘𐒆𐒖, ar, صوماليون) are an ethnic group native to the Horn of Africa who share a common ancestry, culture and history. The Lowland East Cushitic Somali language is the shared ...
, and other Australians have also been buying it. The feral nature of the animals means they produce a different type of meat to farmed camels in other parts of the world, and it is sought after because it is disease-free, and a unique genetic group. Demand is outstripping supply, and governments are being urged not to cull the camels, but redirect the cost of the cull into developing the market. Australia has seven camel dairies, which produce milk, cheese and skincare products in addition to meat.
Religion
Islam
Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraha ...
consider camel meat ''halal
''Halal'' (; ar, حلال, ) is an Arabic word that translates to "permissible" in English. In the Quran, the word ''halal'' is contrasted with ''haram'' (forbidden). This binary opposition was elaborated into a more complex classification kno ...
'' ( ar, حلال, 'allowed'). However, according to some Islamic schools of thought, a state of impurity is brought on by the consumption of it. Consequently, these schools hold that Muslims must perform ''wudhu
Wuḍūʾ ( ar, الوضوء ' ) is the Islamic procedure for cleansing parts of the body, a type of ritual purification, or ablution. The 4 Fardh (Mandatory) acts of ''Wudu'' consists of washing the face, arms, then wiping the head and the fee ...
'' (ablution) before the next time they pray
Prayer is an invocation or act that seeks to activate a rapport with an object of worship through deliberate communication. In the narrow sense, the term refers to an act of supplication or intercession directed towards a deity or a deified an ...
after eating camel meat. Also, some Islamic schools of thought consider it ''haram
''Haram'' (; ar, حَرَام, , ) is an Arabic term meaning 'Forbidden'. This may refer to either something sacred to which access is not allowed to the people who are not in a state of purity or who are not initiated into the sacred knowle ...
'' ( ar, حرام, 'forbidden') for a Muslim to perform ''Salat
(, plural , romanized: or Old Arabic ͡sˤaˈloːh, ( or Old Arabic ͡sˤaˈloːtʰin construct state) ), also known as ( fa, نماز) and also spelled , are prayers performed by Muslims. Facing the , the direction of the Kaaba wit ...
'' in places where camels lie, as it is said to be a dwelling place of the ''Shaytan
' (; ''devils'' or ''demons''), singular: (شَيْطَان) are evil spirits in Islam, inciting humans (and jinn) to sin by "whispering" (وَسْوَسَة, “waswasah”) to their hearts (قَلْب ''qalb''). Folklore suggests that they a ...
'' ( ar, شيطان, 'Devil
A devil is the personification of evil as it is conceived in various cultures and religious traditions. It is seen as the objectification of a hostile and destructive force. Jeffrey Burton Russell states that the different conceptions of t ...
'). According to Abu Yusuf
Ya'qub ibn Ibrahim al-Ansari () better known as Abu Yusuf ( ar, أبو يوسف, Abū Yūsuf) (d.798) was a student of jurist Abu Hanifa (d.767) who helped spread the influence of the Hanafi school of Islamic law through his writings and the gove ...
(d.798), the urine of camel may be used for medical treatment if necessary, but according to Abū Ḥanīfa
Nuʿmān ibn Thābit ibn Zūṭā ibn Marzubān ( ar, نعمان بن ثابت بن زوطا بن مرزبان; –767), commonly known by his '' kunya'' Abū Ḥanīfa ( ar, أبو حنيفة), or reverently as Imam Abū Ḥanīfa by Sunni Musl ...
h, the drinking of camel urine is discouraged.
The Islamic texts contain several stories featuring camels. In the story of the people of Thamud
The Thamud ( ar, ثَمُوْد, translit=Ṯamūd) were an ancient Arabian tribe or tribal confederation that occupied the northwestern Arabian peninsula between the late-eighth century BCE, when they are attested in Assyrian sources, and the ...
, the Prophet Salih
Salih (; ar, صَالِحٌ, Ṣāliḥ, lit=Pious), also spelled Saleh (), is an Arab prophet mentioned in the Quran who prophesied to the tribe of Thamud in ancient Arabia, before the lifetime of Muhammad. The story of Salih is linked to the ...
miraculously brings forth a '' naqat'' ( ar, ناقة, 'milch-camel
Camel milk has supported nomad and pastoral cultures since the domestication of camels millennia ago. Herders may for periods survive solely on the milk when taking the camels on long distances to graze in desert and arid environments, especially i ...
') out of a rock. After the Prophet Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 Common Era, CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Muhammad in Islam, Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet Divine inspiration, di ...
migrated from Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red ...
to Medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the Holiest sites in Islam, second-holiest city in Islam, ...
, he allowed his she-camel to roam there; the location where the camel stopped to rest determined the location where he would build his house in Medina.
Judaism
According toJewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
tradition, camel meat and milk are not kosher
(also or , ) is a set of dietary laws dealing with the foods that Jewish people are permitted to eat and how those foods must be prepared according to Jewish law. Food that may be consumed is deemed kosher ( in English, yi, כּשר), fro ...
. Camels possess only one of the two kosher criteria; although they chew their cud, they do not possess cloven hooves
A cloven hoof, cleft hoof, divided hoof or split hoof is a hoof split into two toes. This is found on members of the mammalian order Artiodactyla. Examples of mammals that possess this type of hoof are cattle, deer, pigs, antelopes, gazelles, ...
: "But these you shall not eat among those that bring up the cud and those that have a cloven hoof: the camel, because it brings up its cud, but does not have a ompletelycloven hoof; it is unclean for you."
Cultural depictions
What may be the oldest carvings of camels were discovered in 2018 in Saudi Arabia. They were analysed by researchers from several scientific disciplines and, in 2021, were estimated to be 7,000 to 8,000 years old. The dating ofrock art
In archaeology, rock art is human-made markings placed on natural surfaces, typically vertical stone surfaces. A high proportion of surviving historic and prehistoric rock art is found in caves or partly enclosed rock shelters; this type also ...
is made difficult by the lack of organic material in the carvings that may be tested, so the researchers attempting to date them tested animal bones found associated with the carvings, assessed erosion patterns, and analysed tool marks in order to determine a correct date for the creation of the sculptures. This Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts ...
dating would make the carvings significantly older than Stonehenge (5,000 years old) and the Egyptian pyramids at Giza (4,500 years old) and it predates estimates for the domestication of camels.
Brooklyn Museum
The Brooklyn Museum is an art museum located in the New York City borough of Brooklyn. At , the museum is New York City's second largest and contains an art collection with around 1.5 million objects. Located near the Prospect Heights, Crown H ...
File:Brooklyn Museum - Maru Ragini (Dhola and Maru riding on a Camel).jpg, ''Maru Ragini'' (''Dhola and Maru Riding on a Camel)'', c. 1750, Brooklyn Museum
The Brooklyn Museum is an art museum located in the New York City borough of Brooklyn. At , the museum is New York City's second largest and contains an art collection with around 1.5 million objects. Located near the Prospect Heights, Crown H ...
File:Brooklyn Museum - The Magi Journeying (Les rois mages en voyage) - James Tissot - overall.jpg, ''The Magi Journeying'' (''Les rois mages en voyage'')—James Tissot, c. 1886, Brooklyn Museum
The Brooklyn Museum is an art museum located in the New York City borough of Brooklyn. At , the museum is New York City's second largest and contains an art collection with around 1.5 million objects. Located near the Prospect Heights, Crown H ...
File:KiplingCamel3.gif, ''How the Camel Got His Hump'' (From Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)''The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British India, which inspired much of his work.
...
's ''Just So Stories
''Just So Stories for Little Children'' is a 1902 collection of origin stories by the British author Rudyard Kipling. Considered a classic of children's literature, the book is among Kipling's best known works.
Kipling began working on the ...
'')
Distribution and numbers
 There are approximately 14 million camels alive , with 90% being dromedaries. Dromedaries alive today are
There are approximately 14 million camels alive , with 90% being dromedaries. Dromedaries alive today are domesticated animals
This page gives a list of domesticated animals, also including a list of animals which are or may be currently undergoing the process of domestication and animals that have an extensive relationship with humans beyond simple predation. This includ ...
(mostly living in the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
, the Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid c ...
, Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
, Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
and South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;;;;; ...
). The Horn region alone has the largest concentration of camels in the world, where the dromedaries constitute an important part of local nomadic life. They provide nomadic people in Somalia and Ethiopia with milk, food, and transportation.Plain text version.Southwestern United States
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado, Ne ...
after having been imported in the 19th century as part of the U.S. Camel Corps
The United States Camel Corps was a mid-19th-century experiment by the United States Army in using camels as pack animals in the Southwestern United States. Although the camels proved to be hardy and well suited to travel through the region, th ...
experiment. When the project ended, they were used as draft animals in mines and escaped or were released. Twenty-five U.S. camels were bought and exported to Canada during the Cariboo Gold Rush
The Cariboo Gold Rush was a gold rush in the Colony of British Columbia, which later joined the Canadian province of British Columbia. The first gold discovery was made at Hills Bar in 1858, followed by more strikes in 1859 on the Horsefly River, ...
.
The Bactrian camel is, , reduced to an estimated 1.4 million animals, most of which are domesticated. The Wild Bactrian camel
The wild Bactrian camel (''Camelus ferus'') is a critically endangered species of camel living in parts of northwestern China and southwestern Mongolia. It is closely related to the Bactrian camel (''Camelus bactrianus''). Both are large, doub ...
is a separate species and is the only truly wild (as opposed to feral) camel in the world. The wild camels are critically endangered and number approximately 1400, inhabiting the Gobi and Taklamakan Deserts in China and Mongolia.
See also
*Afghan cameleers in Australia
Afghan cameleers in Australia, also known as "Afghans" ( ps, افغانان) or "Ghans" ( ps, غانز), were camel drivers who worked in Outback Australia from the 1860s to the 1930s. Small groups of cameleers were shipped in and out of ...
* Australian feral camel
Australian feral camels are feral populations of dromedaries (''Camelus dromedarius'') in Australia. Imported from British India and Afghanistan during the 19th century for transport and construction during the colonisation of the central and ...
* Camel howdah
* Camel milk
Camel milk has supported nomad and pastoral cultures since the domestication of camels millennia ago. Herders may for periods survive solely on the milk when taking the camels on long distances to graze in desert and arid environments, especially ...
* Camel racing
Camel racing is a popular sport in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Pakistan, Mongolia and Australia. Professional camel racing, like horse racing, is an event for betting and tourist attraction. Camels can run at speeds up ...
* Camel train
A camel train or caravan is a series of camels carrying passengers and goods on a regular or semi-regular service between points. Despite rarely travelling faster than human walking speed, for centuries camels' ability to withstand harsh cond ...
(caravan)
* Camel urine
Camel urine is a liquid by-product of metabolism in a camel's anatomy. Urine from Arabian camels has been used in the Arabian Peninsula as prophetic medicine for centuries, being a part of ancient Bedouin practices. After the spread of MERS-CoV ...
* Camel wrestling
Camel wrestling ( Turkish ''deve güreşi'') is a sport in which two male Tülü camels wrestle, typically in response to a female camel in heat being led before them. It is most common in the Aegean region of Turkey, but is also practiced in oth ...
* Camelops
''Camelops''Being occasionally called ''Western Camel'' or ''Yesterday's Camel''. is an extinct genus of camels that lived in North and Central America, ranging from Alaska to Guatemala, from the middle Pliocene to the end of the Pleistocene. It ...
* ''Camelus moreli
The Syrian camel (''Camelus moreli''), is an extinct species of camel from Syria. It has been discovered in the Hummal area of the western Syrian desert. Found to have existed around 100,000 years ago, the camel was up to tall at the shoulder, ...
''
* Dromedary
The dromedary (''Camelus dromedarius'' or ;), also known as the dromedary camel, Arabian camel, or one-humped camel, is a large even-toed ungulate, of the genus ''Camelus'', with one hump on its back.
It is the tallest of the three species of ...
* List of animals with humps
* Xerocole
A xerocole (), is a general term referring to any animal that is adapted to live in a desert. The main challenges xerocoles must overcome are lack of water and excessive heat. To conserve water they avoid evaporation and concentrate excretions (i ...
Citations
General and cited references
Camels and Camel Milk. Report Issued by Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. (1982)
* * * *
Further reading
*External links
Six Green Reasons to Drink Camel's Milk
The Camel as a pet
"Could Emirati camels hold the key to treating venomous snake bites?"
{{Authority control African cuisine Arab cuisine Camelids Domesticated animals Halal meat Livestock Middle Eastern cuisine Taxa named by Carl Linnaeus