Calgary Winter Olympics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
)
, nations = 57
, athletes = 1,423 (1,122 men, 301 women)
, events = 46 in 6 sports (10 disciplines)
, opening = February 13, 1988
, closing = February 28, 1988
, opened_by = Governor General Jeanne Sauvé
, cauldron =
 Bill Pratt was a former
Bill Pratt was a former
 The design of the Olympic Torch for the Calgary games was a reproduction of the main landmark building of the Calgary skyline, the Calgary Tower. The National Research Council Canada developed the design for the Torch, the base of the torch is made of maple wood, the national tree of Canada, aluminum, and hardened steel, all 100% collected in Canadian territory. The torch was designed to remain lit despite the extreme conditions of Canadian winters. The Torch had to be light enough for relay runners to carry comfortably, and the final design came in at 60 centimetres in length and 1.7 kilograms in weight. The maple handle portion included laser-incised pictograms of the 10 official Olympic Winter sports, and lettering was engraved on the steel caldron portion. The torch used a mixed type of three fuels (gasoline, kerosene and alcohol) to allow a continuous burn during the unpredictable Canadian winter. Approximately 100 torches were manufactured for the Games.
The design of the Olympic Torch for the Calgary games was a reproduction of the main landmark building of the Calgary skyline, the Calgary Tower. The National Research Council Canada developed the design for the Torch, the base of the torch is made of maple wood, the national tree of Canada, aluminum, and hardened steel, all 100% collected in Canadian territory. The torch was designed to remain lit despite the extreme conditions of Canadian winters. The Torch had to be light enough for relay runners to carry comfortably, and the final design came in at 60 centimetres in length and 1.7 kilograms in weight. The maple handle portion included laser-incised pictograms of the 10 official Olympic Winter sports, and lettering was engraved on the steel caldron portion. The torch used a mixed type of three fuels (gasoline, kerosene and alcohol) to allow a continuous burn during the unpredictable Canadian winter. Approximately 100 torches were manufactured for the Games.
 The weather was a dominant story throughout much of the Games, as strong chinook winds that brought daily temperatures as high as wreaked havoc on the schedules for outdoor events. Events were delayed when winds were deemed unsafe for competitors and organizers used artificial snow making equipment to ensure skiing venues were properly prepared. It was the first time in Olympic history that alpine events were held on artificial snow. The Games were also marred by the death of the Austrian ski team's doctor, Joerg Oberhammer, on February 25 after a collision with another skier threw him underneath a working snow grooming machine at Nakiska, crushing and killing him instantly. The incident was ruled an accident.
The top individual competitors at the Olympics were Finnish ski jumper Matti Nykänen and Dutch speed skater
The weather was a dominant story throughout much of the Games, as strong chinook winds that brought daily temperatures as high as wreaked havoc on the schedules for outdoor events. Events were delayed when winds were deemed unsafe for competitors and organizers used artificial snow making equipment to ensure skiing venues were properly prepared. It was the first time in Olympic history that alpine events were held on artificial snow. The Games were also marred by the death of the Austrian ski team's doctor, Joerg Oberhammer, on February 25 after a collision with another skier threw him underneath a working snow grooming machine at Nakiska, crushing and killing him instantly. The incident was ruled an accident.
The top individual competitors at the Olympics were Finnish ski jumper Matti Nykänen and Dutch speed skater  One of the most popular athletes from the games was British ski jumper Michael Edwards, who gained infamy by placing last in both the 70 and 90 metre events finishing 70 and 53 points behind his next closest competitor, respectively. Edwards' "heroic failure" made him an instant celebrity; he went from earning £6,000 per year as a plasterer before the Games to making £10,000 per hour per appearance afterward. Left embarrassed by the spectacle he created, the IOC altered the rules following Calgary to eliminate each nation's right to send at least one athlete and set minimum competition standards for future events. Regardless, the President of the Organizing Committee, Frank King, playfully saluted Edwards' unorthodox sporting legacy, which would also be commemorated with a 2016 feature film, ''
One of the most popular athletes from the games was British ski jumper Michael Edwards, who gained infamy by placing last in both the 70 and 90 metre events finishing 70 and 53 points behind his next closest competitor, respectively. Edwards' "heroic failure" made him an instant celebrity; he went from earning £6,000 per year as a plasterer before the Games to making £10,000 per hour per appearance afterward. Left embarrassed by the spectacle he created, the IOC altered the rules following Calgary to eliminate each nation's right to send at least one athlete and set minimum competition standards for future events. Regardless, the President of the Organizing Committee, Frank King, playfully saluted Edwards' unorthodox sporting legacy, which would also be commemorated with a 2016 feature film, ''

 Prior to 1988, the Winter Olympics were viewed as a second-rate event, in comparison to the Summer Olympics. The
Prior to 1988, the Winter Olympics were viewed as a second-rate event, in comparison to the Summer Olympics. The
 In light of the
In light of the
''Olympic Review'', March 1988 – Official results
{{Good article Sports competitions in Calgary Winter Olympics, 1988 Winter multi-sport events in Canada Olympic Games in Canada Winter Olympics by year 1988 in multi-sport events Winter Olympics February 1988 sports events in Canada 1980s in Calgary
Robyn Perry Robyn Ainsworth (born Robyn Perry in 1975) is a former figure skater who lit the Olympic Flame, as a 12-year-old schoolgirl, in the opening ceremony for the 1988 Winter Olympics.
Biography
On February 13, 1988, she was the final runner in the Olym ...
, stadium = McMahon Stadium
, winter_prev = Sarajevo 1984
, winter_next = Albertville 1992
)
, nations = 64
, athletes = 1,801 (1313 men, 488 women)
, events = 57 in 6 sports (12 disciplines)
, opening = 8 February 1992
, closing = 23 February 1992
, opened_by = President François Mitterrand
, cauldron ...
, summer_prev = Los Angeles 1984
The 1984 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXIII Olympiad and also known as Los Angeles 1984) were an international multi-sport event held from July 28 to August 12, 1984, in Los Angeles, California, United States. It marked the secon ...
, summer_next = Seoul 1988
The 1988 Summer Olympics (), officially known as the Games of the XXIV Olympiad () and commonly known as Seoul 1988 ( ko, 서울 1988, Seoul Cheon gubaek palsip-pal), was an international multi-sport event held from 17 September to 2 October ...
The 1988 Winter Olympics, officially known as the XV Olympic Winter Games (french: XVes Jeux olympiques d'hiver) and commonly known as Calgary 1988 ( bla, Mohkínsstsisi 1988; sto, Wîchîspa Oyade 1988 or ; cr, Otôskwanihk 1998/; srs, Guts’ists’i 1988; kut, ʔaknuqtapȼik’ 1988; den, Klincho-tinay-indihay 1988), was a multi-sport event held from February 13 to 28, 1988, in Calgary
Calgary ( ) is the largest city in the western Canadian province of Alberta and the largest metro area of the three Prairie Provinces. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806, makin ...
, Alberta, Canada. It was the first Winter Olympic Games to be held for 15 days, like the counterpart Summer Olympic Games
The Summer Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'été), also known as the Games of the Olympiad, and often referred to as the Summer Olympics, is a major international multi-sport event normally held once every four years. The inau ...
. The majority of the contested events took place in Calgary itself. However, the skiing events were held west of the city at the Nakiska ski resort in Kananaskis Country and the Canmore Nordic Centre Provincial Park
Canmore Nordic Centre Provincial Park is a provincial park in Alberta, Canada, located immediately west of Canmore, west of Calgary.
This provincial park is situated at the foot of Mount Rundle within the Canadian Rocky Mountains along Bow V ...
in the town of Canmore Canmore may refer to:
* Canmore (database), a Scottish national online database of ancient monuments;
*Canmore, Alberta, a town in Canada;
*the House of Dunkeld, a royal house that ruled Scotland in the 11th, 12th and 13th centuries, including
**Mal ...
.
In 1988, a record 57 National Olympic Committee
A National Olympic Committee (NOC) is a national constituent of the worldwide Olympic movement. Subject to the controls of the International Olympic Committee, NOCs are responsible for organizing their people's participation in the Olympic Games ...
s (NOC) sent a total of 1,423 athletes to these Games. These Winter Olympics would be the last attended one for both the Soviet Union and East Germany NOCs. Just like the 1976 Summer Olympics
Events January
* January 3 – The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force.
* January 5 – The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea.
* January 11 – The 1976 Phi ...
, Canada failed again to win a gold medal in an official medal event on home soil. The Finnish ski jumper, Matti Nykänen, and the Dutch speed skater, Yvonne van Gennip
Yvonne Maria Therèse van Gennip (born 1 May 1964) is one of the most successful female Dutch all-round speed skaters. Her main success dates from the 1988 Winter Olympics in Calgary, where she unexpectedly won three gold medals. She was the ...
, won three individual gold medals each. The 1988 Winter Olympics were also remembered for the "heroic failure" of both the British ski jumper, Michael Edwards, and the debut of the Jamaica national bobsleigh team
The Jamaica national bobsleigh team represents Jamaica in international bobsleighing competitions. The men's team debut in the 1988 Winter Olympic Games four-man bobsleigh in Calgary, Alberta, was received as underdogs in a cold weather sport ...
. Both of them became subjects of major feature films about their participation in these Games: ''Cool Runnings
''Cool Runnings'' is a 1993 American sports film directed by Jon Turteltaub and starring Leon Robinson, Doug E. Doug, Malik Yoba, and John Candy. It is loosely based on the true story of the Jamaica national bobsleigh team's debut in competition ...
'' by Disney in 1993 and ''Eddie the Eagle
Michael David Edwards (born 5 December 1963), better known as Eddie the Eagle, is an English ski-jumper and Olympian who in 1988 became the first competitor since 1928 to represent Great Britain in Olympic ski jumping, finishing last in the ...
'' by 20th Century Studios
20th Century Studios, Inc. (previously known as 20th Century Fox) is an American film production company headquartered at the Fox Studio Lot in the Century City area of Los Angeles. As of 2019, it serves as a film production arm of Walt Disn ...
in 2016.
At approximately C$829 million, the Calgary Games were one of the most expensive Olympics ever held at the time. The facilities that were built for these Winter Olympics helped the Calgary region turn into the heart of Canada's elite winter sports program, under the tutelage of WinSport
The Calgary Olympic Development Association (CODA), operating as WinSport, is a non-profit organization based in Calgary, Alberta, Canada whose mandate is to provide training and development to Canada's Olympic athletes, and to maintain the facil ...
. The five purpose-built venues for those Games continued to be used mostly for training and hosting various winter sporting events every year. These experiences helped Canada develop into one of the top nations in Winter Olympics competition. The climax of this effort was the overall first-place finish at the 2010 Winter Olympics
)''
, nations = 82
, athletes = 2,626
, events = 86 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, opening = February 12, 2010
, closing = February 28, 2010
, opened_by = Governor General Michaëlle Jean
, cauldron = Catriona Le May DoanNancy GreeneWayne Gretz ...
in Vancouver, British Columbia.
Host city selection
Calgary's bid for the 1988 Winter Olympic Games was Canada's seventh and Calgary's fourth attempt at hosting the Winter Games. The first Canadian bid for Winter Games belonged to Montreal in1956
Events
January
* January 1 – The Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, Anglo-Egyptian Condominium ends in Sudan.
* January 8 – Operation Auca: Five U.S. evangelical Christian Missionary, missionaries, Nate Saint, Roger Youderian, Ed McCully, Jim ...
, while Vancouver bid for both the 1976
Events January
* January 3 – The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force.
* January 5 – The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea.
* January 11 – The 1976 Phila ...
and 1980
Events January
* January 4 – U.S. President Jimmy Carter proclaims a grain embargo against the USSR with the support of the European Commission.
* January 6 – Global Positioning System time epoch begins at 00:00 UTC.
* January 9 – ...
Games, while Calgary (and neighbouring Banff) under the Calgary Olympic Development Association
The Calgary Olympic Development Association (CODA), operating as WinSport, is a non-profit organization based in Calgary, Alberta, Canada whose mandate is to provide training and development to Canada's Olympic athletes, and to maintain the facili ...
(CODA) submitted bids for the 1964
Events January
* January 1 – The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland is dissolved.
* January 5 - In the first meeting between leaders of the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches since the fifteenth century, Pope Paul VI and Patriarch ...
, 1968
The year was highlighted by protests and other unrests that occurred worldwide.
Events January–February
* January 5 – "Prague Spring": Alexander Dubček is chosen as leader of the Communist Party of Czechoslovakia.
* Januar ...
, and 1972
Within the context of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) it was the longest year ever, as two leap seconds were added during this 366-day year, an event which has not since been repeated. (If its start and end are defined using Solar time, me ...
Winter Games. CODA was laid dormant in 1966, after losing three consecutive bids in a row. However, CODA was later revived in 1978, when Frank King and Bob Niven of Calgary's Booster Club took over the organization's leadership. King and Niven brought some members from previous bids back including former Olympic Sprinter and CODA founder Ernie McCullough
Ernie McCullough (3 December 1925 – 21 July 2015) was a Canadian sprinter. He competed in the men's 400 metres at the 1948 Summer Olympics
The 1948 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XIV Olympiad and also known as London ...
, and politician Arthur Ryan Smith
Captain Arthur Ryan Smith Jr. OC AOE DFC (May 16, 1919 – June 30, 2008) was a Canadian oilfield worker, fighter pilot, executive business man, philanthropist, magazine editor, advertising executive and politician on the municipal, provincia ...
to consult on the project.
In October 1979, CODA was able to secure the Canadian Olympic Association's (COA) support as Canada's official bid for the 1988 Winter Olympics over a competing bid by Vancouver by a vote of 27–9. Calgary's bid was bold because no one infrastructure existed there and everything would have to be built from scratch. CODA proposed constructing all new venues to overcome the city's lack of winter sports facilities with the argument that Canada's inventory of training facilities would grow significantly if Calgary was awarded the Games. The defeated Vancouver organizing group lamented that they lost to Calgary's "Big-ticket Games" idea, which was estimated to cost nearly three times what Vancouver was expected to pay to host the Winter Olympics. Vancouver's bid was based on already developed infrastructure, including the Pacific Coliseum and Whistler Blackcomb
Whistler Blackcomb is a ski resort located in Whistler, British Columbia, Canada. By many measures it is the largest ski resort in North America and has the greatest uphill lift capacity. It features the Peak 2 Peak Gondola for moving between ...
that would again serve as the basis for bids for the successful 2010 Winter Olympics bid and later the 2030 Winter Olympics
The 2030 Winter Olympics, officially known as the XXVI Olympic Winter Games, is an upcoming international multi-sport event. The host city was initially set to be elected at the 140th IOC Session in Mumbai in 2023, but IOC officials declared in ...
Next, CODA spent two years building local support for the megaproject, selling memberships to approximately 80,000 of Calgary's 600,000 residents. Calgary had further secured million in funding from the federal ( million) and Alberta's governments while some civic leaders, including then- mayor Ralph Klein, crisscrossed the world to favour IOC
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss ...
delegates. Driven by the arrival of the National Hockey League's (NHL) newly renamed Calgary Flames from Atlanta in 1980, the city had already begun constructing a new NHL arena that would be later named the Olympic Saddledome. That course of action demonstrated to the IOC Calgary's determination in wanting to host the Winter Olympics.
The Olympic bid itself emphasized the cultural and natural beauty of Calgary, Alberta and surrounding areas, as a perfect asset for hosting the Winter Olympics. The city was marketed as a capitalist, oil-driven, and modern economy that also had mountain playgrounds, extensive wilderness
Wilderness or wildlands (usually in the plural), are natural environments on Earth that have not been significantly modified by human activity or any nonurbanized land not under extensive agricultural cultivation. The term has traditionally re ...
, and rodeo
Rodeo () is a competitive equestrian sport that arose out of the working practices of cattle herding in Spain and Mexico, expanding throughout the Americas and to other nations. It was originally based on the skills required of the working va ...
culture. The two seemingly contradictory images were brought together, as part of an extensive and diverse lobbying program.
Calgary was one of three cities and towns that bid officially for the 1988 Winter Olympics. The other two were Falun, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
, and Cortina d'Ampezzo
Cortina d'Ampezzo (; lld, Anpezo, ; historical de-AT, Hayden) is a town and ''comune'' in the heart of the southern (Dolomitic) Alps in the Province of Belluno, in the Veneto region of Northern Italy. Situated on the Boite river, in an alp ...
, Italy. The Italian town ( comune) had before hosted the 1956 Winter Olympics
The 1956 Winter Olympics, officially known as the VII Olympic Winter Games ( it, VII Giochi Olimpici invernali) and commonly known as Cortina d'Ampezzo 1956 ( lld, Anpezo 1956 or ), was a multi-sport event held in Cortina d'Ampezzo, Italy, from ...
. The vote was held on September 30, 1981, in Baden-Baden, West Germany, during the 84th IOC Session and 11th Olympic Congress
An Olympic Congress is a large gathering of representatives from the different constituencies of the Olympic Movement, organised by the International Olympic Committee (IOC). As detailed in chapter 1, rule 4 of the Olympic Charter, the IOC Pres ...
. After Cortina d'Ampezzo was eliminated in the first round of balloting, Calgary won in the second and final round of balloting over Falun, by a margin of 17 votes. The announcement of CODA's victory sent the delegates in Baden-Baden and Calgary residents into singing and dancing. It also made then Alberta premier, Peter Lougheed, burst openly into tears in front of the cameras. Later, Ralph Klein sang a rendition of Mac Davis
Morris Mac Davis (January 21, 1942 – September 29, 2020) was an American country music singer, songwriter, and actor. A native of Lubbock, Texas, he enjoyed success as a crossover artist, and during his early career he wrote for Elvis Presley, ...
' ''It's Hard to Be Humble
"It's Hard to be Humble" is a song written and recorded by American country music artist Mac Davis from his LP, ''Hard To Be Humble''. It became an international hit in the spring of 1980.
A version by T.R. Dallas became a Top 20 hit in Ireland ...
''. It was the first Winter Olympics awarded to Canada and the second Olympic Games overall, following the 1976 Summer Olympics
Events January
* January 3 – The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force.
* January 5 – The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea.
* January 11 – The 1976 Phi ...
in Montreal. Cortina d'Ampezzo, along with Milan, would get to host the 2026 Winter Olympics
)
, nations =
, athletes =
, events = 116 in 8 sports
, opening = 6 February 2026
, closing = 22 February 2026
, opened_by =
, cauldron =
, stadium = San Siro Verona Arena
, wint ...
. The town will be the fourth to host the Winter Olympics twice, along with St. Moritz
St. Moritz (also german: Sankt Moritz, rm, , it, San Maurizio, french: Saint-Moritz) is a high Alpine resort town in the Engadine in Switzerland, at an elevation of about above sea level. It is Upper Engadine's major town and a municipality in ...
(1928
Events January
* January – British bacteriologist Frederick Griffith reports the results of Griffith's experiment, indirectly proving the existence of DNA.
* January 1 – Eastern Bloc emigration and defection: Boris Bazhanov, J ...
and 1948
Events January
* January 1
** The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is inaugurated.
** The Constitution of New Jersey (later subject to amendment) goes into effect.
** The railways of Britain are nationalized, to form British ...
), Lake Placid (1932
Events January
* January 4 – The British authorities in India arrest and intern Mahatma Gandhi and Vallabhbhai Patel.
* January 9 – Sakuradamon Incident (1932), Sakuradamon Incident: Korean nationalist Lee Bong-chang fails in his effort ...
and 1980
Events January
* January 4 – U.S. President Jimmy Carter proclaims a grain embargo against the USSR with the support of the European Commission.
* January 6 – Global Positioning System time epoch begins at 00:00 UTC.
* January 9 – ...
), and Innsbruck
Innsbruck (; bar, Innschbruck, label=Bavarian language, Austro-Bavarian ) is the capital of Tyrol (state), Tyrol and the List of cities and towns in Austria, fifth-largest city in Austria. On the Inn (river), River Inn, at its junction with the ...
(1964
Events January
* January 1 – The Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland is dissolved.
* January 5 - In the first meeting between leaders of the Roman Catholic and Orthodox churches since the fifteenth century, Pope Paul VI and Patriarch ...
and 1976
Events January
* January 3 – The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force.
* January 5 – The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea.
* January 11 – The 1976 Phila ...
).
Olympic historians, John E. Findling and Kimberly D. Pelle noted that once the Games were awarded to Calgary, the cultural and community aspects of the bid were pushed aside by the newly formed Calgary Olympic organizing committee called the ''Olympiques Calgary Olympics '88'' (OCO'88). It then proceeded to take on a "vigorous, resilient, and impersonal corporate business strategy" toward the planning and operation of the Games.
Venues
 Bill Pratt was a former
Bill Pratt was a former general contractor
A general contractor, main contractor or prime contractor is responsible for the day-to-day oversight of a construction site, management of vendors and trades, and the communication of information to all involved parties throughout the course of ...
who took over as OCO'88 president in 1983. He was the main manager
Management (or managing) is the administration of an organization, whether it is a business, a nonprofit organization, or a government body. It is the art and science of managing resources of the business.
Management includes the activities o ...
that oversaw the construction of the Olympic megaproject. Donald Jacques, a former general manager of the Calgary Exhibition and Stampede, once said, "Because of him, everything was built on time and on budget." However, Bill Pratt was controversial by rubbing many of his colleagues the wrong way. One former co-worker once predicted back in 1983: "He will get everything built. There may not be many (of us) left around to enjoy it, but he'll get it done." His relations with the news media were also strained at times. He had barely settled into his new position when the Calgary press media began criticizing OCO'88 for excessive secrecy
Secrecy is the practice of hiding information from certain individuals or groups who do not have the "need to know", perhaps while sharing it with other individuals. That which is kept hidden is known as the secret.
Secrecy is often controvers ...
and for awarding Olympic contracts to Calgary's PR firm Francis Williams and Johnson Ltd. Pratt was a director of that firm, before accepting the organizing committee job. OCO'88 had insisted that there was no conflict of interest involved in the whole process. Therefore, Pratt declared: "I have been nailed for a lot, but that does not bother me. The record stands". After the 1988 Winter Olympics bid was won in 1981, OCO'88 made a new technical assessment and had to re-plan all the originally proposed competition venues except for the few that already existed and were within the campus of the University of Calgary.
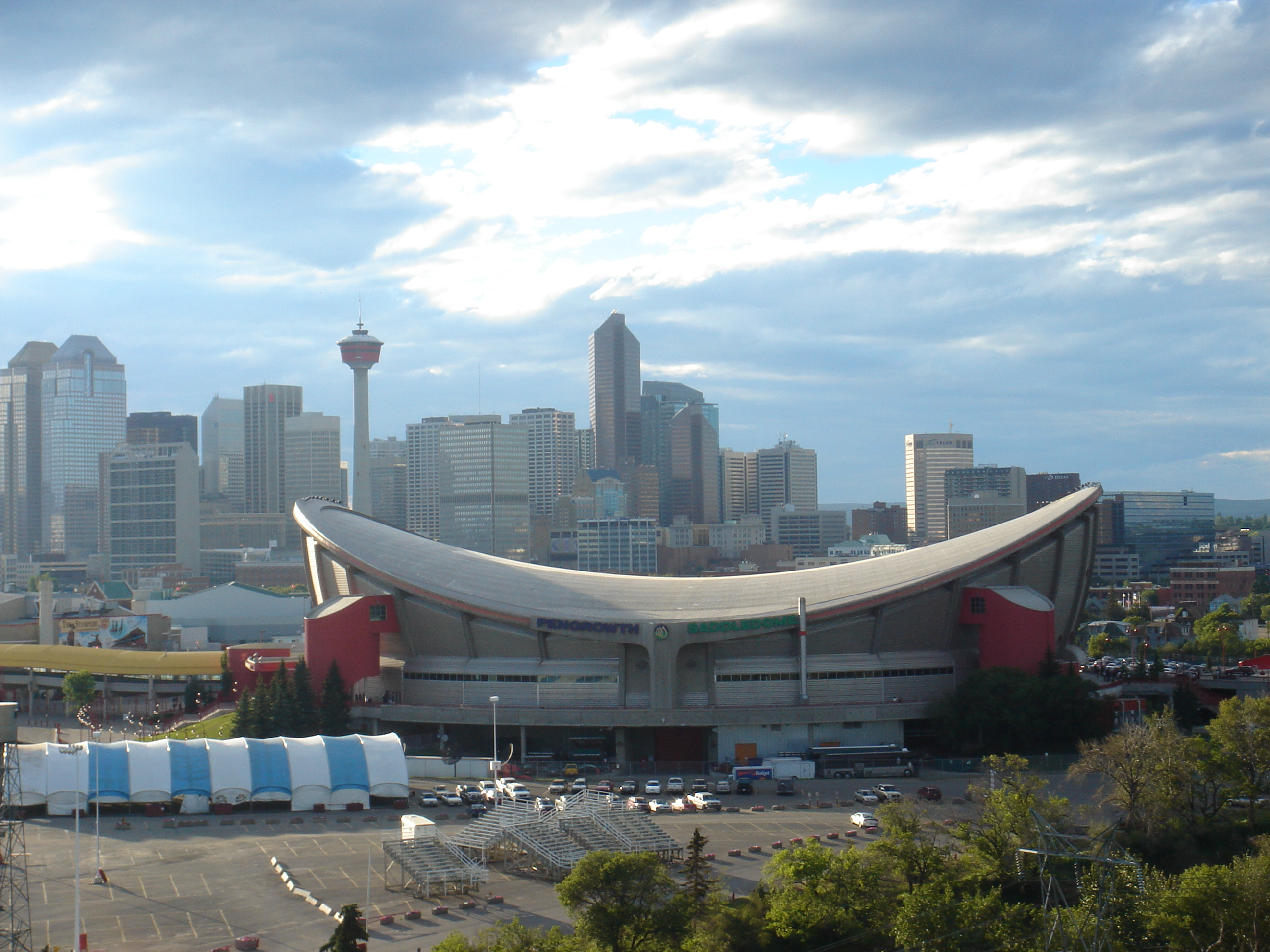
McMahon Stadium, the primary outdoor facility used mainly by the Canadian Football League's (CFL) Calgary Stampeders and inside of the University of Calgary and had originally been chosen to host only the opening ceremonies and the Saddledome was chosen to be the place of the closing ceremonies
Closing may refer to:
Business and law
* Closing (law), a closing argument, a summation
* Closing (real estate), the final step in executing a real estate transaction
* Closing (sales), the process of making a sale
* Closing a business, the proc ...
. But due to the huge demand for tickets, the Organizing Committee decided to move the closing ceremony to the Stadium which held twice the capacity of the Saddledome. The last time that the two Winter Olympic ceremonies were held at the same venue was at the 1960 Winter Olympics
The 1960 Winter Olympics (officially the VIII Olympic Winter Games and also known as Squaw Valley 1960) were a winter multi-sport event held from February 18 to 28, 1960, at the Squaw Valley Resort (now known as Palisades Tahoe) in Squaw Vall ...
in Squaw Valley, California.
The 1988 Winter Olympics' five main all-purpose venues were created at a significant cost at that time. Three of them are located within Calgary and the other two are located west of the city. First, the Olympic Saddledome was the venue for the men's ice hockey final and the figure skating finals. It is located at Stampede Park and this facility was expected to cost C$83 million, but a cost overrun pushed it to nearly C$100 million. Second, the Olympic Oval was built on the campus of the University of Calgary for C$40 million. It was the first fully enclosed 400-metre long track speed skating in the world, to protect the athletes from bitterly cold weather and the Chinook winds. Third, Canada Olympic Park (formerly called the ''Paskapoo Ski Hill'') was renovated for C$200 million and is located on the western outskirts of Calgary. This most expensive venue of these Winter Olympics hosted the men's bobsleigh, luge
A luge is a small one- or two-person sled on which one sleds supine (face up) and feet-first. A luger steers by using the calf muscles to flex the sled's runners or by exerting opposite shoulder pressure to the seat. Racing sleds weigh for s ...
, and men's ski jumping and its portion of the Nordic combined events. Also, it hosted some events of the demonstration sport
A demonstration sport, or exhibition sport, is a sport which is played to promote it, rather than as part of standard medal competition. This occurs commonly during the Olympic Games, but may also occur at other sporting events.
Demonstration spor ...
of freestyle skiing
Freestyle skiing is a skiing discipline comprising aerials, Mogul Skiing, moguls, Ski Cross, cross, Half-pipe skiing, half-pipe, slopestyle and big air as part of the Freestyle skiing at the Winter Olympics, Winter Olympics. It can consist of a ...
.
From the west of Calgary, the other two main all-purpose venues were built at the foothills of the Rocky Mountains. First, the Canmore Nordic Centre
Canmore Nordic Centre Provincial Park is a provincial park in Alberta, Canada, located immediately west of Canmore, west of Calgary.
This provincial park is situated at the foot of Mount Rundle within the Canadian Rocky Mountains along Bow ...
was 90% funded by the province of Alberta, for C$17.3 million. It is located beside the town of Canmore Canmore may refer to:
* Canmore (database), a Scottish national online database of ancient monuments;
*Canmore, Alberta, a town in Canada;
*the House of Dunkeld, a royal house that ruled Scotland in the 11th, 12th and 13th centuries, including
**Mal ...
and it hosted cross-country skiing
Cross-country skiing is a form of skiing where skiers rely on their own locomotion to move across snow-covered terrain, rather than using ski lifts or other forms of assistance. Cross-country skiing is widely practiced as a sport and recreation ...
, plus its men's portion of the Nordic combined, and the men's biathlon events. After the Games were over, there was the intention that it would become a year-round destination for Albertans, by facilitating Canmore's economic transition away from coal mining
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from ...
to tourist attractions. However, the Nakiska (''Cree
The Cree ( cr, néhinaw, script=Latn, , etc.; french: link=no, Cri) are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada ...
'' meaning "to meet") ski resort was the most controversial venue built for these Winter Olympics. It is located on Mount Allan (inside Kananaskis Country) and it hosted the alpine skiing
Alpine skiing, or downhill skiing, is the pastime of sliding down snow-covered slopes on skis with fixed-heel bindings, unlike other types of skiing ( cross-country, Telemark, or ski jumping), which use skis with free-heel bindings. Whether for ...
events for C$25 million by the Alberta government. The venue site drew criticism because of the various environmental concerns, the building of adequate ski slopes, and the need to use artificial snow, a result of the lower snow quantity that fell that season. Also, the International Ski Federation
The ''Fédération internationale de ski et de snowboard'' (FIS; en, International Ski and Snowboard Federation) is the highest international governing body for skiing and snowboarding. Founded on 2 February 1924 in Chamonix, France during the ...
(FIS) officials noted the venue's lack of technical difficulties needed for the Olympic competition. Therefore, these FIS officials proposed some major changes in the paths and that caused great and greater difficulties. These modifications were met with praise from Olympic alpine skiing competitors. Like at Canada Olympic Park, this venue also hosted some freestyle skiing events as a demonstration sport.
Three other existing facilities served as secondary competition venues for the Games. The first one, was the Max Bell Centre hosted the demonstration sports of curling and short track speed skating. The Father David Bauer Olympic Arena
The Father David Bauer Olympic Arena is an ice hockey arena in Calgary, Alberta, Canada. It seats about 1,750 for hockey with a standing room capacity of over 2,000. It is named after David Bauer (ice hockey), Father David Bauer.
Canada's defunct ...
and the Stampede Corral shared the functions of secondary venues for the ice hockey tournament and the figure skating preliminaries. Though the Stampede Corral did not support the International Ice Hockey Federation's (IIHF) standard-sized Olympic ice surface, OCO'88 was able to convince the IIHF to sanction the ice rink for Olympic competition, in exchange for a C$1.2 million payment.
Participating National Olympic Committees
A record 57National Olympic Committee
A National Olympic Committee (NOC) is a national constituent of the worldwide Olympic movement. Subject to the controls of the International Olympic Committee, NOCs are responsible for organizing their people's participation in the Olympic Games ...
s (NOCs) entered athletes at the 1988 Winter Olympics, with eight more NOCs than any other previous Olympic Winter Games. 1,122 men and 301 women, for a total of 1,423 athletes, participated in these Games. Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
, Guam, Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, República de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
, Jamaica, the Netherlands Antilles
nl, In vrijheid verenigd"Unified by freedom"
, national_anthem =
, common_languages = Dutch English Papiamento
, demonym = Netherlands Antillean
, capital = Willemstad
, year_start = 1954
, year_end = 2010
, date_start = 15 December
, ...
and the Virgin Islands had their Winter Olympics debut in 1988.

Sports
There were 46 events contested in 6 sports (10 disciplines). In addition, there were 4 demonstration disciplines that have no official status in the overall medal tally.Calendar
:''All dates are in Mountain Time Zone ( UTC-7)''Weather conditions
The weather conditions were a problem facing OCO'88 during the Games, with temperatures ranging from -28° to +22° Celsius. After an unexpectedly freezing opening ceremony, the outdoor competitions scheduled to start the next day had to be postponed. This ended up affecting the men's downhill skiing event at Nakiska which was postponed for one day, due to Chinook winds blowing up to 160 km/h. The women's downhill event also experienced the same scenario. With the ski jumping venue facing north at Canada Olympic Park (COP), the same winds also disrupted those events, with the large hill event being postponed four times. It also disrupted the Nordic combined events, in which the ski jumping part had to be postponed as well. This situation ended up causing something unprecedented in the history of the Winter Olympics, as for the first time both the ski jumping and Nordic combined cross-country skiing events were contested in a single day. Despite using artificial cooling, the bobsleigh andluge
A luge is a small one- or two-person sled on which one sleds supine (face up) and feet-first. A luger steers by using the calf muscles to flex the sled's runners or by exerting opposite shoulder pressure to the seat. Racing sleds weigh for s ...
events did not need to be rescheduled; however, several races had to be postponed because of the high temperatures recorded and also because of the dirt that was carried away by these winds.
Preparations
Olympic organizing committee (OCO'88)
TheCalgary Olympic Development Association
The Calgary Olympic Development Association (CODA), operating as WinSport, is a non-profit organization based in Calgary, Alberta, Canada whose mandate is to provide training and development to Canada's Olympic athletes, and to maintain the facili ...
(CODA) Board of Directors had originally 25 members. It was chaired by Frank King, followed by former Mayors
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a Municipal corporation, municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities ...
Ralph Klein and Ross Alger Ross or ROSS may refer to:
People
* Clan Ross, a Highland Scottish clan
* Ross (name), including a list of people with the surname or given name Ross, as well as the meaning
* Earl of Ross, a peerage of Scotland
Places
* RoSS, the Republic of Sout ...
, and other prominent Calgarians. The executive committee president was Robert Niven. The Olympic Organizing Committee (OOC) was formed by utilizing many of the original board of directors members. It was initially started with 11 members and was grown to 25 members by October 1983. It grew further to 29 members by 1985, when former Alberta premier, Peter Lougheed, was added to the list. An Olympic biographer, Kevin Wamsley, noted that the CEO
A chief executive officer (CEO), also known as a central executive officer (CEO), chief administrator officer (CAO) or just chief executive (CE), is one of a number of corporate executives charged with the management of an organization especially ...
Frank King, President Bill Pratt, Ralph Klein, and former COA President Roger Jackson had collectively the most influence on all aspects of these Winter Olympics. This organizing committee took a hierarchical
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important ...
form for planning these Olympics, which caused consternation from some staff, volunteers, and people in executive roles. The original staff, who were at odds with the current management structure, were either fired or willingly resigned. Also, there were claims that some of the volunteers were verbally abused. As a result, David Leighton resigned as OOC President in 1982, after only five months on the job. Therefore, Bill Pratt, a former general manager of the Calgary Stampede, became the new OCOG's president shortly afterwards. The City of Calgary and the Canadian Olympic Association (COA) delegated officially all Olympic responsibilities, including staging the Winter Olympics under the Olympic Charter
The Olympic Charter is a set of rules and guidelines for the organisation of the Olympic Games, and for governing the Olympic movement. Its last revision was on the 17th of July 2020 during the 136th IOC Session, held by video conference. Adop ...
, to the newly formed OCO'88 in February and September 1983 respectively.
However, conflicts within OCO'88 grew in the public eye and a review of the entire management structure was conducted after Ralph Klein threatened it with a public inquiry in 1986. Thus, Frank King remained as CEO, but with the addition of more full-time staff. Also, more than 9,000 volunteers were registered who were allocated to the most diverse areas. Despite these changes, there was still some animosity within OCO'88. Kevin Walmsley noted that Bill Pratt and Frank King continued to have a very tense relationship and that any movement caused sparks with each other. Some members of the media commented that the changes made further alienated the general public, with a host broadcaster producer, Ralph Mellanby
Ralph Mellanby (August 22, 1934 – January 29, 2022) was a Canadian sportscaster and television producer, who was the executive producer of ''Hockey Night in Canada'' broadcasts from 1966 to 1985 and on the production team for various Olympic G ...
, describing it as "an oilman's and cattleman's Calgary thing." Long-time IOC member
This is a list of members of the International Olympic Committee. According to the Olympic Charter, the members of the IOC "represent and promote the interests of the IOC and of the Olympic Movement in their countries and in the organisations of ...
Dick Pound, on behalf of the International Olympic Committee (IOC), went on record to say that the IOC grew increasingly frustrated, as it saw the actions of OCO'88 as a refusal to collaborate with them.
Television
The 1988 Winter Olympic Games coincided with a shift in television policy by the International Olympic Committee and growing enthusiasm by broadcasters in the United States. Amendments to the ''Olympic Charter'' in 1977 established a policy mandating joint television rights involving the IOC and the local organizing committee and was enshrined in the 1981 bid agreement for the Calgary games. The joint negotiating committee convened in 1984 late-January, some weeks before the Sarajevo 1984 Winter Games at the IOC's president residency at theLausanne Palace
The Lausanne Palace is a historic luxury hotel in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is located in the city centre, near the Esplanade of Montbenon and has a view on Le Flon on one side and on the Lake Léman on the other. It is owned by the Sandoz Fam ...
were held to negotiate the Calgary television contracts with American broadcasters. The negotiating committee was represented by Dick Pound for the IOC, Bill Wardle for OCO'88 and consultant Barry Frank. The co-negotiating committee designed a new tender process for the television rights bid with an emphasis on creating a level playing field for all broadcasters. For the first time, the negotiations were based on a series of sealed bids and representatives from ABC
ABC are the first three letters of the Latin script known as the alphabet.
ABC or abc may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Broadcasting
* American Broadcasting Company, a commercial U.S. TV broadcaster
** Disney–ABC Television ...
, CBS and NBC vied for the opportunity to broadcast the Games.
After six rounds of sealed bids, the ABC delegation led by producer Roone Arledge was successful with an agreement paying a record million ( million Canadian at the time) in exchange for exclusive rights for the games. CBS exited the bidding process after the second round with a final offer of $257 million, while ABC and NBC both reached the fifth round with an offer of $300 million. In the sixth and final stage, the IOC and OCO'88 decided a coin flip
Coin flipping, coin tossing, or heads or tails is the practice of throwing a coin in the air and checking which side is showing when it lands, in order to choose between two alternatives, heads or tails, sometimes used to resolve a dispute betwe ...
would determine which of ABC or NBC had the right to submit the first bid or defer, a decision neither network supported. NBC's president of sports Arthur A. Watson elected to call the coin-flip, although he remained silent on the first flip, so a second coinflip was required, and NBC won with a choice of "heads", and after 30 minutes of deliberation submitted a $304 million bid. ABC's representative Arledge made a quick phone call to executive Fred Pierce, and ABC submitted a $309 million bid, exceeding NBC's bid by $5 million. ABC's record-setting bid was immediately controversial, first Arledge had exceeded the maximum allowable bid set by ABC's executives by $34 million, and in the coming weeks ABC's coverage of the 1984 Winter Olympics
The 1984 Winter Olympics, officially known as the XIV Olympic Winter Games (Serbo-Croatian and Slovene: ''XIV. Zimske olimpijske igre''; Cyrillic: XIV Зимске олимпијске игре; mk, XIV Зимски олимписки игр ...
which cost $91.5 million returned poor Nielsen ratings
Nielsen Media Research (NMR) is an American firm that measures media audiences, including television, radio, theatre, films (via the AMC Theatres MAP program), and newspapers. Headquartered in New York City, it is best known for the Nielsen rat ...
. Early estimates speculated the network would lose $50-$60 million televising the games. The '' Wall Street Journal'' described the NBC agreement as the "biggest prize of the Winter Olympics". The deal which was at the time the highest amount ever paid for a sporting event, allowed OCO'88 to announce the Games would be debt-free.
The negotiations with American television broadcasters were in sharp contrast to negotiations for Western European rights with the European Broadcasting Union
The European Broadcasting Union (EBU; french: Union européenne de radio-télévision, links=no, UER) is an alliance of Public broadcasting, public service media organisations whose countries are within the European Broadcasting Area or who ar ...
quickly closing an exclusive deal with the IOC for million led by Juan Antonio Samaranch and Marc Hodler on behalf of the IOC. The ''Calgary Herald'' headline after the announcement negatively reflected on the "bargain" the European network received, and OCO'88 chairman Frank King publicly expressed his disappointment with the IOC. Samaranch's argument for providing for a privileged negotiation with EBU was ensuring European viewers had equal access and coverage of the games, something he did not believe would occur if private networks from each nation were provided with the opportunity to bid. Dick Pound was also critical of the decision and argued more revenue could be brought in from BBC and RAI alone and the privileged status suppressed the willingness of the EBU to make a market-value bid on the games.
The CTV Television Network
The CTV Television Network, commonly known as CTV, is a Canadian English-language terrestrial television network. Launched in 1961 and acquired by BCE Inc. in 2000, CTV is Canada's largest privately owned television network and is now a divis ...
won the bid to broadcast the Games in Canada in December 1983, paying million for the exclusive rights. CTV also won the $23.5 million contract to serve as the host broadcaster, responsible for the manpower and equipment to televise the games. In 1978, while the bid was strengthened, CBC and CTV signed an agreement that if Calgary were the eventual winner, the two broadcasters would create a consortium in which the purchase of television rights would take place jointly. The previous arrangement had CBC provide full coverage for Summer Games with CTV broadcasting a nightly summary, while CTV had the rights to Winter Games with CBC broadcasting a nightly summary. The nightly summary of the Games was also televised on CBC.
The Asian broadcast rights were awarded to NHK in July 1986 for million.
OCO'88 made several alterations to the Olympic program as part of efforts to ensure value for its broadcast partners. Now, the premier and main events, including ice hockey and figure skating, were scheduled for prime time
Prime time or the peak time is the block of broadcast programming taking place during the middle of the evening for a television show. It is mostly targeted towards adults (and sometimes families). It is used by the major television networks to ...
and the Games were lengthened to 15 days from the previous 12 to ensure three weekends of coverage. However, a significant downturn in advertising revenue for sporting events resulted in ABC forecasting significant financial losses on the Games. Calgary organizers appreciated their fortunate timing in signing the deal. King described the timing of the contract with ABC as "the passing of the sun and the moon at the right time for Calgary". The revenue growth from broadcasting was significant for the Calgary Games, the 1980 Lake Placid Games generated million, while OCO'88 generated $324.9 million in broadcast rights. ABC had net losses of more than $60 million, and broadcast rights to the 1992 Winter Olympics
)
, nations = 64
, athletes = 1,801 (1313 men, 488 women)
, events = 57 in 6 sports (12 disciplines)
, opening = 8 February 1992
, closing = 23 February 1992
, opened_by = President François Mitterrand
, cauldron ...
were later sold to the CBS network for $243 million, a 20 per cent reduction compared to Calgary.
Ticketing controversies
A series of ticket-related scandals plagued the organizing committee as the Games approached, resulting in widespread public anger. Demand for tickets was high, particularly for the main events which had sold out a year in advance. Residents had been promised that only 10 per cent of tickets would go to "Olympic insiders", IOC officials and sponsors, but OCO'88 was later forced to admit that up to 50 percent of seats to top events had gone to insiders. The organizing committee, which was subsequently chastised by mayor Klein for running a "closed shop", admitted that it had failed to properly communicate the obligations it had to supply IOC officials and sponsors with priority tickets. These events were preceded by the ticketing manager for OCO'88 being charged with theft and fraud after he sent modified ticket request forms to Americans that asked them to pay in United States funds rather than Canadian and to return them to his company's post office box rather than the office of the organizing committee. At that time, the American dollar was trading 40 cents higher than the Canadian dollar, resulting in significantly higher than anticipated revenue through currency conversion. The ticket manager maintained his innocence claiming he was used as a scapegoat and sponsor credit card Visa was responsible for the error, despite his claims, the ticketing manager was convicted offraud
In law, fraud is intentional deception to secure unfair or unlawful gain, or to deprive a victim of a legal right. Fraud can violate civil law (e.g., a fraud victim may sue the fraud perpetrator to avoid the fraud or recover monetary compens ...
, theft, and forgery
Forgery is a white-collar crime that generally refers to the false making or material alteration of a legal instrument with the specific intent to defraud anyone (other than themself). Tampering with a certain legal instrument may be forbidd ...
, and sentenced to 5 years in prison.
Organizers attempted to respond to public concern by asking sponsors to consider reducing their orders and by paying $1.5 million to add 2,600 seats to the Saddledome, as well as increase capacity for ski jumping, alpine skiing and the opening ceremonies. This led to a change of the venue of the closing ceremonies from Saddledome to McMahon Stadium, as the stadium capacity was about two times bigger than the indoor venue. King also noted that the Calgary Games offered a then-record 1.9 million tickets for sale, three times the amount available at Sarajevo or Lake Placid and that 79 percent of them were to be allocated to Calgarians. By the start of the 1988 Winter Games, a record of over 1.4 million tickets had been sold, a figure that eclipsed the previous three Winter Games combined. In the OCO'88's final report, the Committee admits the culmination of fraud charges, a large portion of premier tickets requested by Olympic insiders, and poor communications led to a negative public reaction to the ticketing process.
For the first time in the history of the Olympics, both summer and winter, the Organizing Committee worked with a refund policy for returned or unused tickets. When an event was postponed by at least 24 hours, the ticketholder was eligible for a refund. Due to weather issues, the 8 events that were scheduled for the first 24 hours had to be rescheduled, resulting in 130,000 ticket refunds totalling million, with transactions handled by the Royal Bank of Canada
Royal Bank of Canada (RBC; french: Banque royale du Canada) is a Canadian multinational financial services company and the largest bank in Canada by market capitalization. The bank serves over 17 million clients and has more than 89,000& ...
.
Community
The city of Calgary is world-renowned for the enthusiasm of its population for volunteer work which is reflected in the annual Calgary Stampede, which also relied heavily on volunteers to run the Olympics. Over 22,000 people signed up for more than 9,400 positions, no matter how inglorious: doctors, lawyers and executives even offered to collect the waste generated during the opening ceremony. Also, for the first time, a "Homestay" program was created and several local families opened their homes to visitors from around the world, and others were renting their rooms or houses to those who could not stay in pay a reserve in a hotel. Klein was among those who felt it necessary that the event be community driven, a decision which allowed the city's welcoming spirit to manifest. The Games' mascots,Hidy and Howdy
Hidy and Howdy were the official mascots of the 1988 Winter Olympics in Calgary, Alberta, Canada. They were anthropomorphic twin polar bears who wore western/cowboy style outfits. Students of Bishop Carroll High School in Calgary were used as ...
, were designed to evoke images of "western hospitality". The smiling, cowboy-themed polar bear
The polar bear (''Ursus maritimus'') is a hypercarnivorous bear whose native range lies largely within the Arctic Circle, encompassing the Arctic Ocean, its surrounding seas and surrounding land masses. It is the largest extant bear specie ...
s were popular across Canada. Played by a team of 150 students from Bishop Carroll High School, the sister-brother pair made up to 300 appearances per month in the lead-up to the Games. From their introduction at the closing ceremonies of the Sarajevo Games in 1984 until their retirement at the conclusion of the Calgary Games, the pair made about 50,000 appearances. The iconic mascots graced signs welcoming travellers to Calgary for nearly two decades until they were replaced in 2007. The mascot's names "Hidy" and "Howdy" were chosen by a public contest.
Finances
The 1988 Winter Olympic Games were the most expensive Games, summer or winter, to be held at that time, with total expenses exceeding million. The high cost was anticipated, as organizers were aware at the outset of their bid that most facilities would have to be constructed. The venues, constructed primarily with public money, were designed to have lasting use beyond the Games and were planned to become the home of several of Canada's national winter sports teams. The record-breaking cost of the Calgary Olympics came in stark contrast to the original projections during the 1981 bid, which estimated a total cost of million, split between million in capital costs and million in operating costs. The significant growth in capital expenditures came despite the three levels of government taking over projects which constituted nearly half of the original budgeted capital projects. The primary source of revenue for OCO'88 was the lucrative television contracts, bringing in million (58.3 per cent of revenue), followed by corporate sponsorships at million (15.8 per cent of revenue), and ticket sales of million (7.5 per cent of revenue). Of the total expenses for the Games ( million), the Government of Canada contributed million (22.7 per cent), the Government of Alberta contributed million (14.8 per cent), and the City of Calgary contributed million (4.9 per cent). The million of government capital contributions not directly included in OCO'88's revenue statements included the Government of Canada constructing the million Canada Olympic Park, and million for the Olympic Oval. Provincial expenses included million to build theCanmore Nordic Centre
Canmore Nordic Centre Provincial Park is a provincial park in Alberta, Canada, located immediately west of Canmore, west of Calgary.
This provincial park is situated at the foot of Mount Rundle within the Canadian Rocky Mountains along Bow ...
, and million to build Nakiska. All three governments contributed to the million Olympic Saddledome. Of OCO'88's reported revenue of million, million was paid to the IOC as a share of television and market rights, and an additional million was paid to the United States Olympic Committee for rights to broadcast the Games in the United States, and million was reimbursed to NOC's for accommodation fees at the Games.
The Games were a major economic boom for the city, which had fallen into its worst recession in 40 years following the collapse of both oil and grain prices three years before the games. A report prepared for the city in January 1985 estimated the games would create 11,100 man-years of employment and generate million in salaries and wages. In its post-Games report, OCO'88 estimated the Olympics created billion in economic benefits across Canada during the 1980s, 70 percent within Alberta, as a result of capital spending, increased tourism and new sporting opportunities created by the facilities.
Torch relay
The 1988 Olympic torch relay began on November 15, 1987, when the torch was lit atOlympia
The name Olympia may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Olympia'' (1938 film), by Leni Riefenstahl, documenting the Berlin-hosted Olympic Games
* ''Olympia'' (1998 film), about a Mexican soap opera star who pursues a career as an athlet ...
and Greek runner Stelios Bisbas
Stylianos "Stelios" Bisbas (Greek: Στυλιανός "Στέλιος" Μπίσμπας; born 9 November 1968 in Athens) is a retired Greek athlete who specialised in the sprint hurdles. He represented his country at the 1996 Summer Olympics witho ...
began what was called "the longest torch run in history". The flame arrived in St. John's, Newfoundland
St. John's is the capital and largest city of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador, located on the eastern tip of the Avalon Peninsula on the island of Newfoundland.
The city spans and is the easternmost city in North America ...
on the Atlantic Ocean two days later and over 88 days, travelled west across the then 10 Canadian provinces and two territories. It passed through most major cities, north to the Arctic Ocean at Inuvik, Northwest Territories
Inuvik (''place of man'') is the only town in the Inuvik Region, and the third largest community in Canada's Northwest Territories. Located in what is sometimes called the Beaufort Delta Region, it serves as its administrative and service cen ...
, then west to the Pacific Ocean at Victoria, British Columbia before returning east to Alberta, and finally Calgary. The torch covered a distance of , the greatest distance for a torch relay in Olympic history until the 2000 Sydney Games
The 2000 Summer Olympics, officially the Games of the XXVII Olympiad and also known as Sydney 2000 (Dharug: ''Gadigal 2000''), the Millennium Olympic Games or the Games of the New Millennium, was an international multi-sport event held from 1 ...
, and a sharp contrast to the 1976 Montreal Games when the relay covered only .
The identity of the final torchbearer who would light the Olympic cauldron was one of the Organizing Committee's most closely guarded secrets. The relay began at St. John's with Barbara Ann Scott
Barbara Ann Scott (May 9, 1928 – September 30, 2012) was a Canadian figure skater. She was the 1948 Olympic champion, a two-time World champion (1947–1948), and a four-time Canadian national champion (1944–46, 48) in ladies' singles. Kn ...
and Ferd Hayward representing Canada's past Olympians and ended with Ken Read and Cathy Priestner
Catherine Ann Priestner (born May 27, 1956 in Windsor, Ontario) is a Canadian who won a silver medal in Speed skating at the 1976 Winter Olympics, where she was Canada's flag bearer in the closing ceremonies. She also competed in the 1972 ...
carrying the torch into McMahon Stadium representing the nation's current Olympians. They then stopped to acknowledge the contribution of parathlete Rick Hansen and his "Man in Motion" tour before handing the torch to 12-year-old Robyn Perry Robyn Ainsworth (born Robyn Perry in 1975) is a former figure skater who lit the Olympic Flame, as a 12-year-old schoolgirl, in the opening ceremony for the 1988 Winter Olympics.
Biography
On February 13, 1988, she was the final runner in the Olym ...
, an aspiring figure skater who was selected to represent the future of the Olympic Movement three years before the IOC's changed the year of the Winter Games, to light the cauldron.
Olympic Torch
 The design of the Olympic Torch for the Calgary games was a reproduction of the main landmark building of the Calgary skyline, the Calgary Tower. The National Research Council Canada developed the design for the Torch, the base of the torch is made of maple wood, the national tree of Canada, aluminum, and hardened steel, all 100% collected in Canadian territory. The torch was designed to remain lit despite the extreme conditions of Canadian winters. The Torch had to be light enough for relay runners to carry comfortably, and the final design came in at 60 centimetres in length and 1.7 kilograms in weight. The maple handle portion included laser-incised pictograms of the 10 official Olympic Winter sports, and lettering was engraved on the steel caldron portion. The torch used a mixed type of three fuels (gasoline, kerosene and alcohol) to allow a continuous burn during the unpredictable Canadian winter. Approximately 100 torches were manufactured for the Games.
The design of the Olympic Torch for the Calgary games was a reproduction of the main landmark building of the Calgary skyline, the Calgary Tower. The National Research Council Canada developed the design for the Torch, the base of the torch is made of maple wood, the national tree of Canada, aluminum, and hardened steel, all 100% collected in Canadian territory. The torch was designed to remain lit despite the extreme conditions of Canadian winters. The Torch had to be light enough for relay runners to carry comfortably, and the final design came in at 60 centimetres in length and 1.7 kilograms in weight. The maple handle portion included laser-incised pictograms of the 10 official Olympic Winter sports, and lettering was engraved on the steel caldron portion. The torch used a mixed type of three fuels (gasoline, kerosene and alcohol) to allow a continuous burn during the unpredictable Canadian winter. Approximately 100 torches were manufactured for the Games.
Event highlights
The 1988 Winter Games began on afternoon of February 13 with a $10 million opening ceremony in front of 60,000 spectators at McMahon Stadium that featured 5,500 performers, an aerial flyover by the Royal Canadian Air Force's Snowbirds, the parade of nations and the release of 1,000 homing pigeons. Canadian composer David Foster performed the instrumental theme song ("Winter Games") and its vocal version ("Can't You Feel It?"), while internationally recognized Canadian folk/country musicians Gordon Lightfoot singing '' Four Strong Winds'' and Ian Tyson performing '' Alberta Bound'' were among the featured performers. Governor General Jeanne Sauvé opened the Games on behalf of Queen Elizabeth II as an estimated 1.5 billion people watched the ceremony. The weather was a dominant story throughout much of the Games, as strong chinook winds that brought daily temperatures as high as wreaked havoc on the schedules for outdoor events. Events were delayed when winds were deemed unsafe for competitors and organizers used artificial snow making equipment to ensure skiing venues were properly prepared. It was the first time in Olympic history that alpine events were held on artificial snow. The Games were also marred by the death of the Austrian ski team's doctor, Joerg Oberhammer, on February 25 after a collision with another skier threw him underneath a working snow grooming machine at Nakiska, crushing and killing him instantly. The incident was ruled an accident.
The top individual competitors at the Olympics were Finnish ski jumper Matti Nykänen and Dutch speed skater
The weather was a dominant story throughout much of the Games, as strong chinook winds that brought daily temperatures as high as wreaked havoc on the schedules for outdoor events. Events were delayed when winds were deemed unsafe for competitors and organizers used artificial snow making equipment to ensure skiing venues were properly prepared. It was the first time in Olympic history that alpine events were held on artificial snow. The Games were also marred by the death of the Austrian ski team's doctor, Joerg Oberhammer, on February 25 after a collision with another skier threw him underneath a working snow grooming machine at Nakiska, crushing and killing him instantly. The incident was ruled an accident.
The top individual competitors at the Olympics were Finnish ski jumper Matti Nykänen and Dutch speed skater Yvonne van Gennip
Yvonne Maria Therèse van Gennip (born 1 May 1964) is one of the most successful female Dutch all-round speed skaters. Her main success dates from the 1988 Winter Olympics in Calgary, where she unexpectedly won three gold medals. She was the ...
as they each won three gold medals. Italy's Alberto Tomba won gold in two skiing events, his first of five career Olympic medals en route to becoming the first alpine skier to win medals at three Winter Games. East Germany's Katarina Witt defended her 1984 gold medal in women's figure skating, capturing a second gold in Calgary. Her compatriot Christa Rothenburger won the gold medal in the 1000 metre race in speed skating, then went on to win a silver medal in the team sprint cycling event at the 1988 Summer Games to become the only person in Olympic history to win medals at both Olympic Games in the same year. The Soviet Union won gold in hockey as Scandinavian neighbours Finland and Sweden took silver and bronze, respectively.
As it had in 1976, Canada again failed to win an official gold medal as the host of an Olympic Games. Canadians won two gold medals in demonstration events, including by Sylvie Daigle
Sylvie Daigle (born December 1, 1962) is a Canadian speed skater. She is a member of the Canadian short track relay team that won gold at the 1992 Winter Olympics and silver at the 1994 Winter Olympics. She is also a five-time O ...
as one of her five medals in short-track speed skating. Canada's top official performances came in figure skating where Brian Orser and Elizabeth Manley each won silver medals. Promoted by the media as the " Battle of the Brians"—the competition between Orser and American rival Brian Boitano—and the " Battle of the Carmens"—between Witt and American rival Debi Thomas, who had both elected to skate to Bizet
Georges Bizet (; 25 October 18383 June 1875) was a French composer of the Romantic era. Best known for his operas in a career cut short by his early death, Bizet achieved few successes before his final work, ''Carmen'', which has become on ...
's ''Carmen
''Carmen'' () is an opera in four acts by the French composer Georges Bizet. The libretto was written by Henri Meilhac and Ludovic Halévy, based on the Carmen (novella), novella of the same title by Prosper Mérimée. The opera was first perfo ...
'' in their long programs—were the marquee events of the Games. Boitano won the gold medal over Orser by only one-tenth of a point. Witt won the gold while Thomas won the bronze medal. Manley was not viewed as a medal contender, but skated the greatest performance of her career to come within a fraction of Witt's gold medal-winning score.
American speed skater Dan Jansen's personal tragedy was one of the more poignant events of the Games as he skated the 500 metre race mere hours after his sister Jane died of leukemia. A gold medal favourite, Jansen chose to compete as he felt it is what his sister would have wanted. Viewers around the world witnessed his heartbreak as he fell and crashed into the outer wall in the first quarter of his heat. In the 1000 metre race four days later, Jansen was on a world record pace when he again fell. After failing again in Albertville, Jansen finally won a gold medal at the 1994 Lillehamer Games.
 One of the most popular athletes from the games was British ski jumper Michael Edwards, who gained infamy by placing last in both the 70 and 90 metre events finishing 70 and 53 points behind his next closest competitor, respectively. Edwards' "heroic failure" made him an instant celebrity; he went from earning £6,000 per year as a plasterer before the Games to making £10,000 per hour per appearance afterward. Left embarrassed by the spectacle he created, the IOC altered the rules following Calgary to eliminate each nation's right to send at least one athlete and set minimum competition standards for future events. Regardless, the President of the Organizing Committee, Frank King, playfully saluted Edwards' unorthodox sporting legacy, which would also be commemorated with a 2016 feature film, ''
One of the most popular athletes from the games was British ski jumper Michael Edwards, who gained infamy by placing last in both the 70 and 90 metre events finishing 70 and 53 points behind his next closest competitor, respectively. Edwards' "heroic failure" made him an instant celebrity; he went from earning £6,000 per year as a plasterer before the Games to making £10,000 per hour per appearance afterward. Left embarrassed by the spectacle he created, the IOC altered the rules following Calgary to eliminate each nation's right to send at least one athlete and set minimum competition standards for future events. Regardless, the President of the Organizing Committee, Frank King, playfully saluted Edwards' unorthodox sporting legacy, which would also be commemorated with a 2016 feature film, ''Eddie the Eagle
Michael David Edwards (born 5 December 1963), better known as Eddie the Eagle, is an English ski-jumper and Olympian who in 1988 became the first competitor since 1928 to represent Great Britain in Olympic ski jumping, finishing last in the ...
''.
The Jamaican bobsleigh team, making their nation's Winter Olympic debut, was also popular in Calgary. The team was the brainchild of a pair of Americans who recruited individuals with strong sprinting ability from the Jamaican military to form the team. Dudley Stokes and Michael White finished the two-man event in 30th place out of 41 competitors and launched the Jamaican team into worldwide fame. The pair, along with Devon Harris and Chris Stokes, crashed in the four-man event, but were met with cheers from the crowd as they pushed their sled across the finish line. Their odyssey was made into the 1993 movie ''Cool Runnings
''Cool Runnings'' is a 1993 American sports film directed by Jon Turteltaub and starring Leon Robinson, Doug E. Doug, Malik Yoba, and John Candy. It is loosely based on the true story of the Jamaica national bobsleigh team's debut in competition ...
'', a largely fictionalized comedy by Walt Disney Pictures.
Medal table
Podium sweeps
Records in speed skating
All of the long track world (WR) and Olympic records (OR) that occurred during these Games were later broken at succeeding Winter Olympics and other world events.Legacy
 Prior to 1988, the Winter Olympics were viewed as a second-rate event, in comparison to the Summer Olympics. The
Prior to 1988, the Winter Olympics were viewed as a second-rate event, in comparison to the Summer Olympics. The IOC
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss ...
had, at one point, considered eliminating it altogether. First, there are only a few mountainous areas in the world that would be able to host the Winter Olympics. Second, there were major challenges in generating revenues for the host city and the IOC from such Games. However, CODA
Coda or CODA may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* Movie coda, a post-credits scene
* ''Coda'' (1987 film), an Australian horror film about a serial killer, made for television
*''Coda'', a 2017 American experimental film from Na ...
convinced the IOC that it could not only generate enough revenues to make a profit but have enough money left over to ensure a lasting legacy of winter sports development. OCO'88 followed mainly the example of LAOOC which organized the 1984 Summer Olympics
The 1984 Summer Olympics (officially the Games of the XXIII Olympiad and also known as Los Angeles 1984) were an international multi-sport event held from July 28 to August 12, 1984, in Los Angeles, California, United States. It marked the secon ...
. Under LAOOC's president, Peter Ueberroth, he was able to attract a large United States television contract and Los Angeles became the first Olympic host city to benefit from a change in the IOC's strategy on corporate sponsorship. For the 1988 Winter Olympics, OCO'88 attracted financial support from over two dozen major Canadian and multinational corporations, in order to generate millions of dollars in revenues.
For OCO'88, it foresaw some winter sports, like the debut of the Super-G and other new winter sports events, as a way to increase the audience
An audience is a group of people who participate in a show or encounter a work of art, literature (in which they are called "readers"), theatre, music (in which they are called "listeners"), video games (in which they are called "players"), or ...
's appeal of the Winter Olympics. Thus, for the sponsors, the Games' length of time to 15 days provided an extra weekend of Olympic media coverage to the world. This additional programming time was filled mainly by TV-friendly demonstration events that are popular in Canada. The 1988 Winter Olympics' exposure to curling, freestyle skiing
Freestyle skiing is a skiing discipline comprising aerials, Mogul Skiing, moguls, Ski Cross, cross, Half-pipe skiing, half-pipe, slopestyle and big air as part of the Freestyle skiing at the Winter Olympics, Winter Olympics. It can consist of a ...
, and short track speed skating events in Calgary influenced the worldwide popularity of all of them. So much so that all these events became the new and official Olympic finals in the period between the 1992 Winter Olympics
)
, nations = 64
, athletes = 1,801 (1313 men, 488 women)
, events = 57 in 6 sports (12 disciplines)
, opening = 8 February 1992
, closing = 23 February 1992
, opened_by = President François Mitterrand
, cauldron ...
to the 2002 Winter Olympics
The 2002 Winter Olympics, officially the XIX Olympic Winter Games and commonly known as Salt Lake 2002 ( arp, Niico'ooowu' 2002; Gosiute Shoshoni: ''Tit'-so-pi 2002''; nv, Sooléí 2002; Shoshoni: ''Soónkahni 2002''), was an internation ...
.
Impact on Calgary
Hosting the Winter Olympics helped fuel a significant increase in Calgary's reputation on the world stage. Crosbie Cotton, a reporter for the ''Calgary Herald
The ''Calgary Herald'' is a daily newspaper published in Calgary, Alberta, Canada. Publication began in 1883 as ''The Calgary Herald, Mining and Ranche Advocate, and General Advertiser''. It is owned by the Postmedia Network.
History
''The ...
'' who covered the city's Olympic odyssey from its 1979 initiative to the closing ceremonies, noted an increased positive outlook of the city's population over time. He believed that the populace began to outgrow its "giant inferiority complex
In psychology, an inferiority complex is an intense personal feeling of inadequacy, often resulting in the belief that one is in some way deficient, or inferior, to others.
According to Alfred Adler, a feeling of inferiority may be brought ab ...
" that is "typically Canadian", by replacing it with a new level of confidence as the Games approached. This outcome helped the city grow from a regional oil and gas centre, best known for the Calgary Stampede, to a destination for international political, economic, and sporting events. A study prepared for the organizing committee of the 2010 Winter Olympics
)''
, nations = 82
, athletes = 2,626
, events = 86 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, opening = February 12, 2010
, closing = February 28, 2010
, opened_by = Governor General Michaëlle Jean
, cauldron = Catriona Le May DoanNancy GreeneWayne Gretz ...
, (VANOC
The Vancouver Organizing Committee for the 2010 Olympic and Paralympic Winter Games (VANOC) (french: Comité d’organisation des Jeux olympiques et paralympiques d’hiver de 2010 à Vancouver - COVAN) was the non-profit organization responsible ...
), claimed that Calgary hosted over 200 national and international sporting competitions between 1987 and 2007, due to the facilities it had constructed for these Olympic Games.
The Games' enduring popularity within Calgary has been attributed to efforts in making them "everybody's Games." Aside from the sense of community fostered by the high level of volunteer support, OCO'88 included the general public in other ways. For example, the citizens were given an opportunity to purchase a brick
A brick is a type of block used to build walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Properly, the term ''brick'' denotes a block composed of dried clay, but is now also used informally to denote other chemically cured cons ...
with their names engraved on it. Those bricks were used to build the Olympic Plaza ''Olympic Plaza'' may refer to one of the following:
*Olympic Plaza (Calgary) – A downtown city park and gathering place in Calgary, Alberta, Canada
*Pyeongchang Olympic Plaza – Public square situated on the site of the former Olympic Stadium i ...
, where the medal ceremonies were held in 1988. It remains a popular public park and event site in the city's downtown core today.
After the success of these Olympic Games, Calgary was wanting to bring back the Olympic experience again. It offered, to the IOC
The International Olympic Committee (IOC; french: link=no, Comité international olympique, ''CIO'') is a non-governmental sports organisation based in Lausanne, Switzerland. It is constituted in the form of an association under the Swiss ...
, in becoming a possible alternate host city of the 2002 Winter Olympics
The 2002 Winter Olympics, officially the XIX Olympic Winter Games and commonly known as Salt Lake 2002 ( arp, Niico'ooowu' 2002; Gosiute Shoshoni: ''Tit'-so-pi 2002''; nv, Sooléí 2002; Shoshoni: ''Soónkahni 2002''), was an internation ...
, after a bidding scandal resulted in speculation that Salt Lake City would not be able to remain the host city. Next, the city was attempting to be Canada's bid for the 2010 Winter Olympics
)''
, nations = 82
, athletes = 2,626
, events = 86 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, opening = February 12, 2010
, closing = February 28, 2010
, opened_by = Governor General Michaëlle Jean
, cauldron = Catriona Le May DoanNancy GreeneWayne Gretz ...
, but the COC decided to give it to Vancouver and Whistler. Later, a 2013 '' Calgary Sun'' online poll found that 81% of respondents said they would support the idea of hosting another Winter Olympics. On November 13, 2018, Calgary held a public non-binding plebiscite on whether it should bid to host the 2026 Olympic and Paralympic Winter Games. On November 19, 2018, the results of the plebiscite showed that 56.4% (171,750) of eligible voters said "No", while 43.6% (132,832) of them said "Yes." Therefore, the city council concluded that the bid would be withdrawn.
Canada's development as a winter sport nation
 In light of the
In light of the 1976 Summer Olympics
Events January
* January 3 – The International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights enters into force.
* January 5 – The Pol Pot regime proclaims a new constitution for Democratic Kampuchea.
* January 11 – The 1976 Phi ...
' disastrous financial legacy, the Calgary Olympic organizing committee, OCO'88, parlayed its ability to generate television and sponsorship revenues, along with the three levels of government support, into what was ultimately a C$170 million surplus. While OCO'88 reported officially a surplus after the Games were over, the accounting practices of the final report did not include federal, provincial, and municipal capital and operations funding infrastructures.
The overall surplus was turned into endowment funds that were split between Canada Olympic Park (C$110 million) and CODA
Coda or CODA may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* Movie coda, a post-credits scene
* ''Coda'' (1987 film), an Australian horror film about a serial killer, made for television
*''Coda'', a 2017 American experimental film from Na ...
. They were subsequently reformed later, in order to manage the Olympic facilities with a trust fund that had grown steadily to be worth over C$200 million by 2013. Consequently, all five primary facilities built for the 1988 Winter Olympics remained operational for their intended purposes, 25 years after the Games concluded. Calgary and Canmore Canmore may refer to:
* Canmore (database), a Scottish national online database of ancient monuments;
*Canmore, Alberta, a town in Canada;
*the House of Dunkeld, a royal house that ruled Scotland in the 11th, 12th and 13th centuries, including
**Mal ...
became the heart of winter sports in Canada, as CODA (now known as WinSport) established itself as the nation's leader in developing elite winter athletes. For the 2006 Winter Olympics
The 2006 Winter Olympics, officially the XX Olympic Winter Games ( it, XX Giochi olimpici invernali) and also known as Torino 2006, were a winter multi-sport event held from 10 to 26 February 2006 in Turin, Italy. This marked the second t ...
, a quarter of Canada's Olympic winter athletes were from the Calgary region and three-quarters of its medalists were from or trained in Alberta.
Before 1988, Canada was not a winter sports power. The nation's five overall medals won in Calgary was its second-best total at a Winter Olympics, behind the seven overall medals it won at the 1932 Winter Olympics
The 1932 Winter Olympics, officially known as the III Olympic Winter Games and commonly known as Lake Placid 1932, were a winter multi-sport event in the United States, held in Lake Placid, New York, United States. The games opened on February ...
in Lake Placid, New York. After 1988, Canada won an increasing number of gold and overall medals at each successive Winter Olympics. It culminated in an overall performance of 26 medals won at the 2010 Winter Olympics
)''
, nations = 82
, athletes = 2,626
, events = 86 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, opening = February 12, 2010
, closing = February 28, 2010
, opened_by = Governor General Michaëlle Jean
, cauldron = Catriona Le May DoanNancy GreeneWayne Gretz ...
, which included the previous Olympic record of 14 gold medals. Until 2010, Norway won the most Olympic gold medals on home soil at the 1952 Winter Olympics
The 1952 Winter Olympics, officially known as the VI Olympic Winter Games ( no, De 6. olympiske vinterleker; nn, Dei 6. olympiske vinterleikane) and commonly known as Oslo 1952, was a winter multi-sport event held from 14 to 25 February 195 ...
. However, Norway recaptured the record of winning the most Olympic gold medals at a single Winter Olympics, at 16. At the 2018 Winter Olympics
, nations = 93
, athletes = 2,922 (1,680 men and 1,242 women)
, events = 102 in 7 sports (15 disciplines)
, opening =
, closing =
, opened_by = President Moon Jae-in
, cauldron = Kim Yun-a
, stadium = Pyeongchang Olympic Stadium
, winte ...
, Canada earned its highest overall medal count in the Winter Olympics to date, with a total of 29 medals.
See also
References
Notes CitationsOfficial reports
* * * * *Works cited
* * * * * *Further reading
* *External links
*''Olympic Review'', March 1988 – Official results
{{Good article Sports competitions in Calgary Winter Olympics, 1988 Winter multi-sport events in Canada Olympic Games in Canada Winter Olympics by year 1988 in multi-sport events Winter Olympics February 1988 sports events in Canada 1980s in Calgary