Calcium Metasilicate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Wollastonite is a
 Estimated world production of crude wollastonite ore was 1,200,000
Estimated world production of crude wollastonite ore was 1,200,000
''Mineral Commodity Summaries'' 2021 In the United States, wollastonite is mined in
Wollastonite
''USGS 2009 Minerals Yearbook'' (October 2010) The price of raw wollastonite in 2008 varied between US$80 and US$500 per tonne depending on the country and size and shape of the powder particles.
 The acicular nature of many wollastonite products allows it to compete with other acicular materials, such as ceramic fiber, glass fiber, steel fiber, and several organic fibers, such as
The acicular nature of many wollastonite products allows it to compete with other acicular materials, such as ceramic fiber, glass fiber, steel fiber, and several organic fibers, such as
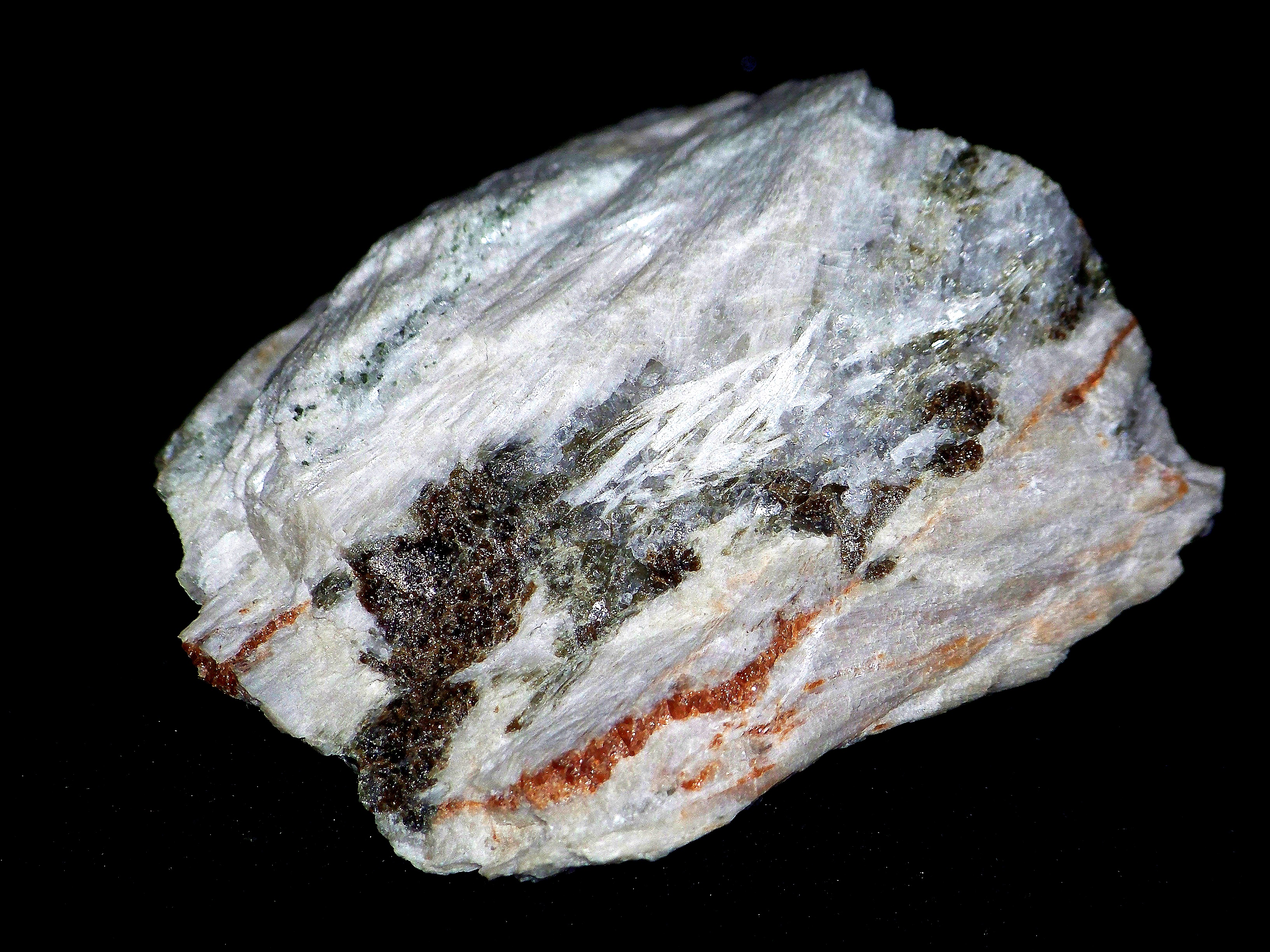 Wollastonite usually occurs as a common constituent of a thermally metamorphosed impure
Wollastonite usually occurs as a common constituent of a thermally metamorphosed impure

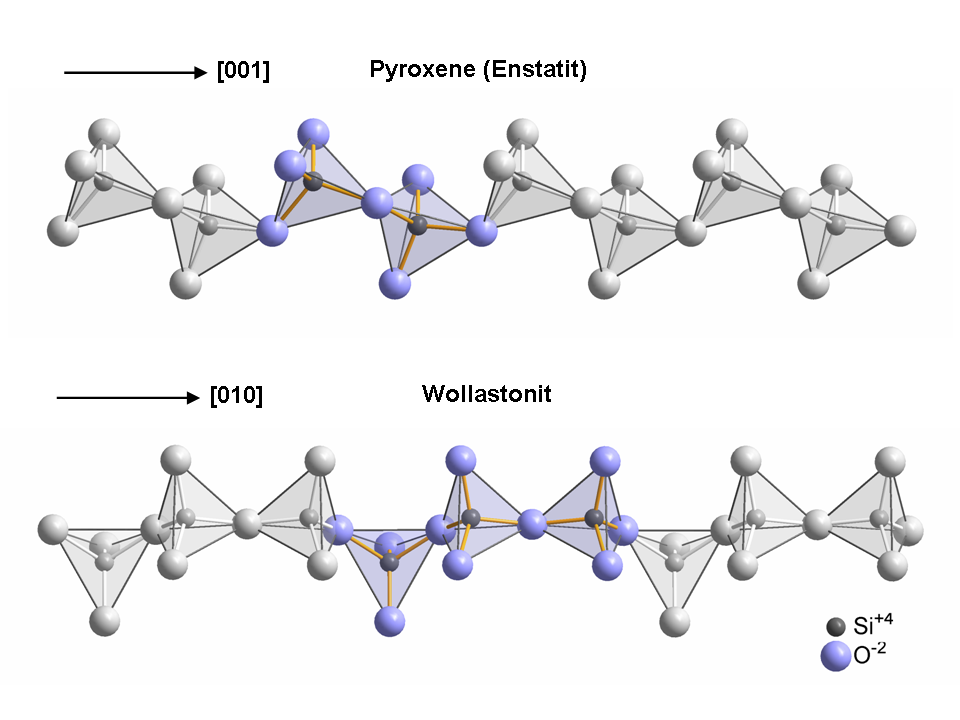 Wollastonite crystallizes triclinically in space group P with the lattice constants ''a'' = 7.94 Å, ''b'' = 7.32 Å, c = 7.07 Å; ''α'' = 90,03°, ''β'' = 95,37°, ''γ'' = 103,43° and six formula units per unit cell. Wollastonite was once classed structurally among the pyroxene group, because both of these groups have a ratio of Si:O = 1:3. In 1931, Warren and Biscoe showed that the crystal structure of wollastonite differs from minerals of the pyroxene group, and they classified this mineral within a group known as the pyroxenoids. It has been shown that the pyroxenoid chains are more kinked than those of pyroxene group, and exhibit longer repeat distance. The structure of wollastonite contains infinite chains of iO4tetrahedra sharing common vertices, running parallel to the ''b''-axis. The chain motif in wollastonite repeats after three tetrahedra, whereas in pyroxenes only two are needed. The repeat distance in the wollastonite chains is 7.32 Å and equals the length of the crystallographic ''b''-axis.
Molten CaSiO3 maintains a tetrahedral SiO4 local structure at temperatures up to 2000 ËšC. The nearest neighbor Ca-O coordination decreases from 6.0(2) in the room temperature glass to 5.0(2) in the 1700 ËšC liquid, coincident with an increasing number of longer Ca-O neighbors.
Wollastonite crystallizes triclinically in space group P with the lattice constants ''a'' = 7.94 Å, ''b'' = 7.32 Å, c = 7.07 Å; ''α'' = 90,03°, ''β'' = 95,37°, ''γ'' = 103,43° and six formula units per unit cell. Wollastonite was once classed structurally among the pyroxene group, because both of these groups have a ratio of Si:O = 1:3. In 1931, Warren and Biscoe showed that the crystal structure of wollastonite differs from minerals of the pyroxene group, and they classified this mineral within a group known as the pyroxenoids. It has been shown that the pyroxenoid chains are more kinked than those of pyroxene group, and exhibit longer repeat distance. The structure of wollastonite contains infinite chains of iO4tetrahedra sharing common vertices, running parallel to the ''b''-axis. The chain motif in wollastonite repeats after three tetrahedra, whereas in pyroxenes only two are needed. The repeat distance in the wollastonite chains is 7.32 Å and equals the length of the crystallographic ''b''-axis.
Molten CaSiO3 maintains a tetrahedral SiO4 local structure at temperatures up to 2000 ËšC. The nearest neighbor Ca-O coordination decreases from 6.0(2) in the room temperature glass to 5.0(2) in the 1700 ËšC liquid, coincident with an increasing number of longer Ca-O neighbors.
Oxford University MSDS sheet
{{Authority control Calcium minerals Inosilicates Triclinic minerals Minerals in space group 2
calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to ...
inosilicate mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. ( ...
( Ca Si O3) that may contain small amounts of iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
, magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
, and manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy use ...
substituting for calcium. It is usually white. It forms when impure limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
or dolomite Dolomite may refer to:
*Dolomite (mineral), a carbonate mineral
*Dolomite (rock), also known as dolostone, a sedimentary carbonate rock
*Dolomite, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community
*Dolomite, California, United States, an unincor ...
is subjected to high temperature and pressure, which sometimes occurs in the presence of silica-bearing fluids as in skarns or in contact with metamorphic rocks. Associated minerals include garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives.
All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different s ...
s, vesuvianite, diopside, tremolite
Tremolite is a member of the amphibole group of silicate minerals with composition: Ca2(Mg5.0-4.5Fe2+0.0-0.5)Si8O22(OH)2. Tremolite forms by metamorphism of sediments rich in dolomite and quartz. Tremolite forms a series with actinolite and ferro ...
, epidote
Epidote is a calcium aluminium iron sorosilicate mineral.
Description
Well developed crystals of epidote, Ca2Al2(Fe3+;Al)(SiO4)(Si2O7)O(OH), crystallizing in the monoclinic system, are of frequent occurrence: they are commonly prismatic in habi ...
, plagioclase feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feldsp ...
, pyroxene and calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
. It is named after the English chemist and mineralogist William Hyde Wollaston
William Hyde Wollaston (; 6 August 1766 – 22 December 1828) was an English chemist and physicist who is famous for discovering the chemical elements palladium and rhodium. He also developed a way to process platinum ore into malleable ingo ...
(1766–1828).
Despite its chemical similarity to the compositional spectrum of the pyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to ''Px'') are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe II) ...
group of minerals—where magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
(Mg) and iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
(Fe) substitution for calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to ...
ends with diopside and hedenbergite respectively—it is structurally very different, with a third tetrahedron in the linked chain (as opposed to two in the pyroxenes).
Production trends
tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
s in 2021. World reserves of wollastonite are estimated to exceed 100 million tonnes, though some existing deposits have not been surveyed.
Major producers of wollastonite include China, India, the United States, Mexico, and Finland.Wollastonite''Mineral Commodity Summaries'' 2021 In the United States, wollastonite is mined in
Willsboro, New York
Willsboro is a town in Essex County, New York, United States, and lies south of the city of Plattsburgh. As of the 2010 census, the town population was 2,025. The town is named after early landowner William Gilliland.
History
During the Amer ...
(first laboratory for local wollastonite research in Essex, New York by Koert Burnham in 1940s) and Gouverneur, New York. Deposits have also been mined commercially in North Western Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: MĂ©xico), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
.Robert L. VirtWollastonite
''USGS 2009 Minerals Yearbook'' (October 2010) The price of raw wollastonite in 2008 varied between US$80 and US$500 per tonne depending on the country and size and shape of the powder particles.
Uses
Wollastonite is among the fastest reacting silicates, but may have high costs associated with carbon storage.Ceramics
Wollastonite has industrial importance in ceramics manufacturing as an additive.Deer, Howie and Zussman. ''Rock Forming Minerals; Single Chain Silicates'', Vol. 2A, Second Edition, London, The Geological Society, 1997. In ceramics, wollastonite decreases shrinkage and gas evolution during firing, increasesgreen
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 Nanometre, nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by ...
and fired strength, maintains brightness during firing, permits fast firing, and reduces crazing, cracking, and glaze defects.
Construction
Wollastonite can serve as a substitute forasbestos
Asbestos () is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic "fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere b ...
in floor tiles, friction products, insulating board and panels, paint, plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be moulded, extruded or pressed into solid objects of various shapes. This adaptab ...
s, and roofing products. Similar to asbestos, wollastonite is resistant to chemical attack, stable at high temperatures, and improves flexural and tensile strength in composites. In some industries, wollastonite is used in different percentages of impurities, such as its use as a fabricator of mineral wool insulation, or as an ornamental building material.Andrews, R. W. (1970). ''Wollastonite''. London, Her Majesty's Stationery Office.
Wollastonite is used in a cement announced in 2019 which "reduces the overall carbon footprint
A carbon footprint is the total greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions caused by an individual, event, organization, service, place or product, expressed as carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e). Greenhouse gases, including the carbon-containing gases carbo ...
in precast concrete
Precast concrete is a construction product produced by casting concrete in a reusable molding (process), mold or "form" which is then cured in a controlled environment, transported to the construction site and maneuvered into place; examples i ...
by 70%."
Wollastonite has been studied for carbon mineralization for storage of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
(CO2) according to the following reaction:
:
Metallurgy
In metallurgical applications, wollastonite serves as a flux for welding, a source for calcium oxide, a slag conditioner, and to protect the surface of molten metal during the continuous casting of steel.Paint
As an additive in paint, wollastonite improves the durability of the paint film, acts as a pH buffer, improves its resistance to weathering, reduces gloss, reduces pigment consumption, and acts as a flatting and suspending agent.Plastic
In plastics, wollastonite improvestensile
In physics, tension is described as the pulling force transmitted axially by the means of a string, a rope, chain, or similar object, or by each end of a rod, truss member, or similar three-dimensional object; tension might also be described as t ...
and flexural strength, reduces resin consumption, and improves thermal and dimensional stability at elevated temperatures. Surface treatments are used to improve the adhesion between the wollastonite and the polymers to which it is added.
Plastics and rubber applications were estimated to account for 25% to 35% of U.S. sales in 2009, followed by ceramics with 20% to 25%; paint, 10% to 15%; metallurgical applications, 10% to 15%; friction products, 10% to 15%; and miscellaneous, 10% to 15%. Ceramic applications probably account for 30% to 40% of wollastonite sales worldwide, followed by polymers (plastics and rubber) with 30% to 35% of sales, and paint with 10% to 15% of sales. The remaining sales were for construction, friction products, and metallurgical applications.
Substitutes
 The acicular nature of many wollastonite products allows it to compete with other acicular materials, such as ceramic fiber, glass fiber, steel fiber, and several organic fibers, such as
The acicular nature of many wollastonite products allows it to compete with other acicular materials, such as ceramic fiber, glass fiber, steel fiber, and several organic fibers, such as aramid
Aramid fibers, short for aromatic polyamide, are a class of heat-resistant and strong synthetic fibers. They are used in aerospace and military applications, for ballistic-rated body armor fabric and ballistic composites, in marine cordage, ma ...
, polyethylene
Polyethylene or polythene (abbreviated PE; IUPAC name polyethene or poly(methylene)) is the most commonly produced plastic. It is a polymer, primarily used for packaging ( plastic bags, plastic films, geomembranes and containers including bo ...
, polypropylene
Polypropylene (PP), also known as polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in a wide variety of applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.
Polypropylene
belongs to the group of polyolefins and ...
, and polytetrafluoroethylene
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene that has numerous applications. It is one of the best-known and widely applied PFAS. The commonly known brand name of PTFE-based composition is Teflon by Chemour ...
in products where improvements in dimensional stability, flexural modulus, and heat deflection are sought.
Wollastonite also competes with several nonfibrous minerals or rocks, such as kaolin
Kaolinite ( ) is a clay mineral, with the chemical composition Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4. It is an important industrial mineral. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedral sheet of silica () linked through oxygen atoms to one octahedral ...
, mica
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into extremely thin elastic plates. This characteristic is described as perfect basal cleavage. Mica is ...
, and talc, which are added to plastics to increase flexural strength, and such minerals as barite, calcium carbonate, gypsum, and talc, which impart dimensional stability to plastics.
In ceramics, wollastonite competes with carbonates, feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feldsp ...
, lime
Lime commonly refers to:
* Lime (fruit), a green citrus fruit
* Lime (material), inorganic materials containing calcium, usually calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide
* Lime (color), a color between yellow and green
Lime may also refer to:
Botany ...
, and silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one ...
as a source of calcium and silicon. Its use in ceramics depends on the formulation of the ceramic body and the firing method.
Composition
In a pure CaSiO3, each component forms nearly half of the mineral by weight: 48.3% of CaO and 51.7% of SiO2. In some cases, small amounts of iron (Fe), and manganese (Mn), and lesser amounts of magnesium (Mg) substitute for calcium (Ca) in the mineral formula (''e.g.'', rhodonite). Wollastonite can form a series of solid solutions in the system CaSiO3-FeSiO3, orhydrothermal synthesis
Hydrothermal synthesis includes the various techniques of crystallizing substances from high-temperature aqueous solutions at high vapor pressures; also termed "hydrothermal method". The term "hydrothermal" is of geologic origin. Geochemists an ...
of phases in the system MnSiO3-CaSiO3.
Geologic occurrence
 Wollastonite usually occurs as a common constituent of a thermally metamorphosed impure
Wollastonite usually occurs as a common constituent of a thermally metamorphosed impure limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
, it also could occur when the silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
is due to metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chem ...
in contact altered calcareous sediments, or to contamination in the invading igneous rock
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main The three types of rocks, rock types, the others being Sedimentary rock, sedimentary and metamorphic rock, metamorphic. Igneous rock ...
. In most of these occurrences it is the result of the following reaction between calcite
Calcite is a Carbonate minerals, carbonate mineral and the most stable Polymorphism (materials science), polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on ...
and silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , most commonly found in nature as quartz and in various living organisms. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one ...
with the loss of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
:
:CaCO3 + SiO2 → CaSiO3 + CO2
Wollastonite may also be produced in a diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
reaction in skarn, it develops when limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
within a sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) ...
is metamorphosed by a dike
Dyke (UK) or dike (US) may refer to:
General uses
* Dyke (slang), a slang word meaning "lesbian"
* Dike (geology), a subvertical sheet-like intrusion of magma or sediment
* Dike (mythology), ''Dikē'', the Greek goddess of moral justice
* Dikes, ...
, which results in the formation of wollastonite in the sandstone as a result of outward migration of Ca.
Structure

 Wollastonite crystallizes triclinically in space group P with the lattice constants ''a'' = 7.94 Å, ''b'' = 7.32 Å, c = 7.07 Å; ''α'' = 90,03°, ''β'' = 95,37°, ''γ'' = 103,43° and six formula units per unit cell. Wollastonite was once classed structurally among the pyroxene group, because both of these groups have a ratio of Si:O = 1:3. In 1931, Warren and Biscoe showed that the crystal structure of wollastonite differs from minerals of the pyroxene group, and they classified this mineral within a group known as the pyroxenoids. It has been shown that the pyroxenoid chains are more kinked than those of pyroxene group, and exhibit longer repeat distance. The structure of wollastonite contains infinite chains of iO4tetrahedra sharing common vertices, running parallel to the ''b''-axis. The chain motif in wollastonite repeats after three tetrahedra, whereas in pyroxenes only two are needed. The repeat distance in the wollastonite chains is 7.32 Å and equals the length of the crystallographic ''b''-axis.
Molten CaSiO3 maintains a tetrahedral SiO4 local structure at temperatures up to 2000 ËšC. The nearest neighbor Ca-O coordination decreases from 6.0(2) in the room temperature glass to 5.0(2) in the 1700 ËšC liquid, coincident with an increasing number of longer Ca-O neighbors.
Wollastonite crystallizes triclinically in space group P with the lattice constants ''a'' = 7.94 Å, ''b'' = 7.32 Å, c = 7.07 Å; ''α'' = 90,03°, ''β'' = 95,37°, ''γ'' = 103,43° and six formula units per unit cell. Wollastonite was once classed structurally among the pyroxene group, because both of these groups have a ratio of Si:O = 1:3. In 1931, Warren and Biscoe showed that the crystal structure of wollastonite differs from minerals of the pyroxene group, and they classified this mineral within a group known as the pyroxenoids. It has been shown that the pyroxenoid chains are more kinked than those of pyroxene group, and exhibit longer repeat distance. The structure of wollastonite contains infinite chains of iO4tetrahedra sharing common vertices, running parallel to the ''b''-axis. The chain motif in wollastonite repeats after three tetrahedra, whereas in pyroxenes only two are needed. The repeat distance in the wollastonite chains is 7.32 Å and equals the length of the crystallographic ''b''-axis.
Molten CaSiO3 maintains a tetrahedral SiO4 local structure at temperatures up to 2000 ËšC. The nearest neighbor Ca-O coordination decreases from 6.0(2) in the room temperature glass to 5.0(2) in the 1700 ËšC liquid, coincident with an increasing number of longer Ca-O neighbors.
See also
* * *List of minerals
This is a list of minerals for which there are articles on Wikipedia.
Minerals are distinguished by various chemical and physical properties. Differences in chemical composition and crystal structure distinguish the various ''species''. Within a m ...
* List of minerals named after people
References
External links
Oxford University MSDS sheet
{{Authority control Calcium minerals Inosilicates Triclinic minerals Minerals in space group 2