Cairngorms on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Cairngorms ( gd, Am Monadh Ruadh) are a mountain range in the eastern Highlands of
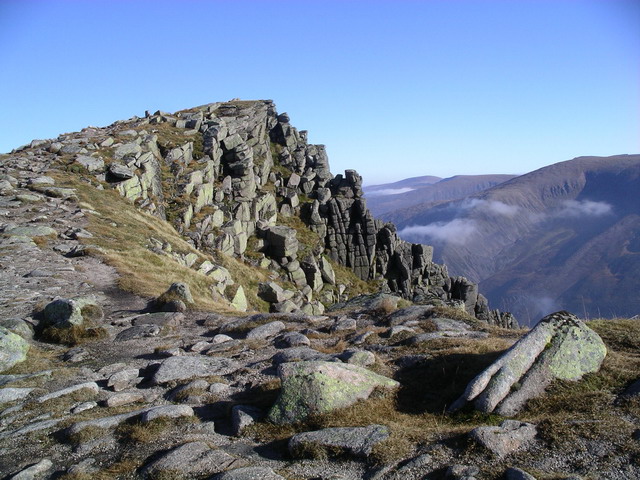 The original Gaelic name for the range is ''Am Monadh Ruadh'' (the red hills), distinguishing them from ''Am Monadh Liath'' (the grey hills), which lie to the west of the River Spey:
The
The original Gaelic name for the range is ''Am Monadh Ruadh'' (the red hills), distinguishing them from ''Am Monadh Liath'' (the grey hills), which lie to the west of the River Spey:
The
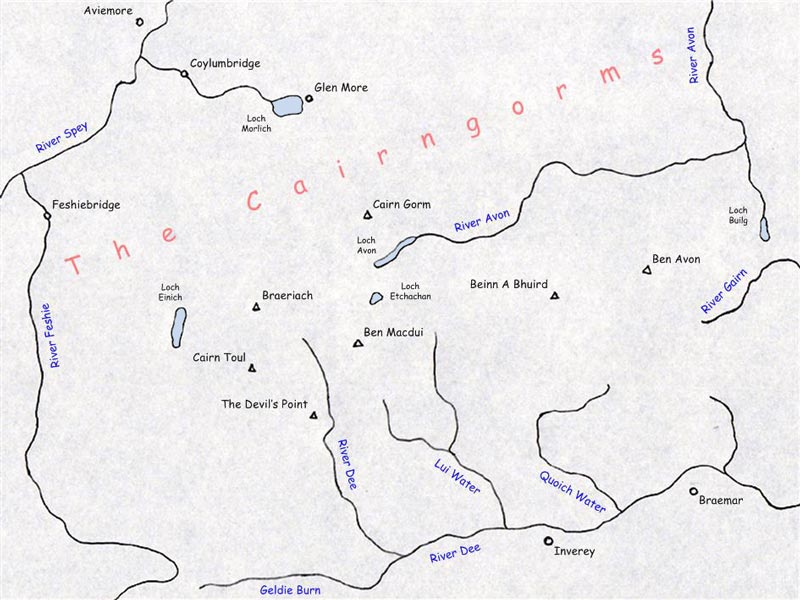 The Cairngorms consist of three large elevated plateaux adorned with low, rounded glacial mountains, and divided by the passes of the
The Cairngorms consist of three large elevated plateaux adorned with low, rounded glacial mountains, and divided by the passes of the
 In terms of height, remoteness and the severe and changeable weather, the Cairngorms are the most arduous area in the United Kingdom. in The plateau area has a
In terms of height, remoteness and the severe and changeable weather, the Cairngorms are the most arduous area in the United Kingdom. in The plateau area has a
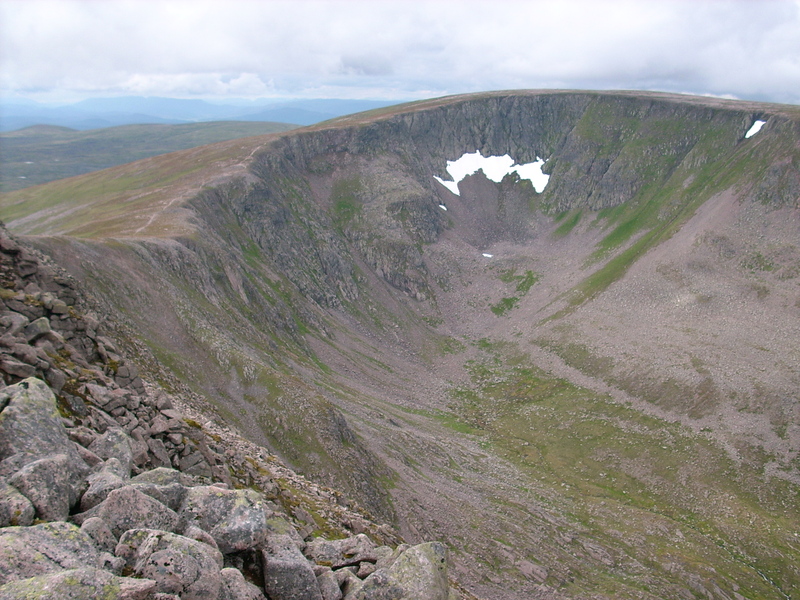 The Cairngorms hold some of the longest-lying snow patches in Scotland:
*On Ben Macdui, snow has been known to persist at a few locations from one winter to the next.
*Lying at the north-eastern shoulder of Cairn Gorm is Ciste Mhearad. This hollow contains a patch which, hitherto, was known to persist through many years, but has not done so since 2000.Royal Meteorological Society "Weather" October 2002, vol. 57; Adam Watson, Richard W Davison & John Pottie. Observations in 2007 and 2008 revealed that September was the month when final melting occurred for this patch. It sits at an altitude of and is located at approximately .
*
The Cairngorms hold some of the longest-lying snow patches in Scotland:
*On Ben Macdui, snow has been known to persist at a few locations from one winter to the next.
*Lying at the north-eastern shoulder of Cairn Gorm is Ciste Mhearad. This hollow contains a patch which, hitherto, was known to persist through many years, but has not done so since 2000.Royal Meteorological Society "Weather" October 2002, vol. 57; Adam Watson, Richard W Davison & John Pottie. Observations in 2007 and 2008 revealed that September was the month when final melting occurred for this patch. It sits at an altitude of and is located at approximately .
*
 The valleys between the individual plateaux were used as drove roads by cattle drovers who built rough protective shelters for their arduous journeys. At about the same time that droving was dying out towards the end of the 19th century, deer stalking estates were flourishing, and so the shelters were developed into bothies to provide improved, though still primitive, accommodation for gamekeepers. In modern times, these bothies have been taken over by the Mountain Bothies Association for use by walkers and climbers to provide shelter and rough sleeping accommodation. With the exception of the bothies, there are no buildings or settlements within the Cairngorms, nor is there evidence for historic settlement, except in the uppermost reaches of the Derry and Gairn rivers. In the surrounding areas, villages such as Aviemore and
The valleys between the individual plateaux were used as drove roads by cattle drovers who built rough protective shelters for their arduous journeys. At about the same time that droving was dying out towards the end of the 19th century, deer stalking estates were flourishing, and so the shelters were developed into bothies to provide improved, though still primitive, accommodation for gamekeepers. In modern times, these bothies have been taken over by the Mountain Bothies Association for use by walkers and climbers to provide shelter and rough sleeping accommodation. With the exception of the bothies, there are no buildings or settlements within the Cairngorms, nor is there evidence for historic settlement, except in the uppermost reaches of the Derry and Gairn rivers. In the surrounding areas, villages such as Aviemore and
File:Cairngorm mountains - geograph.org.uk - 1512462.jpg, Cairn Lochan (1215 m).
File:View north west from the summit of Beinn Bhreac - geograph.org.uk - 760977.jpg, View north-west from the summit of Beinn Bhreac (931 m).
File:South western slopes of Beinn Mheadhoin - geograph.org.uk - 532107.jpg, Loch Etchachan.
The Badenoch and Strathspey Conservation Group
The Cairngorm Club
Cairngorms National Park
Cairngorm Mountain
Cairngorms Climate Change
Walks in the Cairngorms
WinterHighland
{{Authority control Mountains and hills of the Eastern Highlands Mountains and hills of Aberdeenshire Mountains and hills of Highland (council area) Mountains and hills of Moray Ski areas and resorts in Scotland Rural Scotland Tourist attractions in Highland (council area) Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Badenoch and Strathspey Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Kincardine and Deeside Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Moray and Nairn Mountain ranges of Scotland National scenic areas of Scotland
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to th ...
closely associated with the mountain Cairn Gorm. The Cairngorms became part of Scotland's second national park
A national park is a natural park in use for conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individua ...
(the Cairngorms National Park
Cairngorms National Park ( gd, Pàirc Nàiseanta a' Mhonaidh Ruaidh) is a national park in northeast Scotland, established in 2003. It was the second of two national parks established by the Scottish Parliament, after Loch Lomond and The Tros ...
) on 1 September 2003. Although the Cairngorms give their name to, and are at the heart of, the Cairngorms National Park, they only form one part of the national park, alongside other hill ranges such as the Angus Glens and the Monadhliath, and lower areas like Strathspey.
The Cairngorms consists of high plateaux at about above sea level, above which domed summits (the eroded stumps of once much higher mountains ) rise to around . Many of the summits have tors, free-standing rock outcrops that stand on top of the boulder-strewn landscape. In places, the edges of the plateau form steep cliffs of granite and they are excellent for skiing
Skiing is the use of skis to glide on snow. Variations of purpose include basic transport, a recreational activity, or a competitive winter sport. Many types of competitive skiing events are recognized by the International Olympic Committee ...
, rock climbing and ice climbing. The Cairngorms form an arctic-alpine mountain environment, with tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mo ...
-like characteristics and long-lasting snow patches. This area is home to bird species such as ptarmigan, dotterel, snow bunting, curlew and red grouse
The red grouse (''Lagopus lagopus scotica'') is a medium-sized bird of the grouse family which is found in heather moorland in Great Britain and Ireland. It is usually classified as a subspecies of the willow ptarmigan but is sometimes consid ...
, as well as mammals such as mountain hare. The plateau also supports Britain's only herd of reindeer
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 subsp ...
(albeit semi-domesticated). Surrounding the central massif are many remnants of the Caledonian forest in straths and glens of the Rivers Spey Spey may refer to:
*Spey River (disambiguation)
*Spey casting, a fly fishing technique developed on the River Spey
*Rolls-Royce Spey, an early turbofan engine
* HMS ''Spey'', the name of seven ships of the Royal Navy
* For spey-wife -- see Völva a ...
and Dee. These forests support many species that are rare elsewhere in Britain, including red squirrels, pine marten, wood ants, Scottish crossbill
The Scottish crossbill (''Loxia scotica'') is a small passerine bird in the finch family Fringillidae. It is endemic to the Caledonian Forests of Scotland, and is the only terrestrial vertebrate species endemic to the United Kingdom. The ...
, capercaillie and crested tit.
There are no glaciers, but snow can fall in any month of the year, and snow patches usually persist all summer; for snow and ice climbing, the area is the most dependable in Britain. The mountains are also popular for hill-walking, ski touring and climbing
Climbing is the activity of using one's hands, feet, or any other part of the body to ascend a steep topographical object that can range from the world's tallest mountains (e.g. the eight thousanders), to small boulders. Climbing is done ...
, and there are three alpine ski centres in the range, at Cairn Gorm, The Lecht and Glenshee.
The range lies in the Scottish council areas
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
of Aberdeenshire
Aberdeenshire ( sco, Aiberdeenshire; gd, Siorrachd Obar Dheathain) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland.
It takes its name from the County of Aberdeen which has substantially different boundaries. The Aberdeenshire Council area incl ...
, Moray and Highland
Highlands or uplands are areas of high elevation such as a mountainous region, elevated mountainous plateau or high hills. Generally speaking, upland (or uplands) refers to ranges of hills, typically from up to while highland (or highlands) is ...
, and within the counties of Aberdeenshire
Aberdeenshire ( sco, Aiberdeenshire; gd, Siorrachd Obar Dheathain) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland.
It takes its name from the County of Aberdeen which has substantially different boundaries. The Aberdeenshire Council area incl ...
, Inverness-shire
Inverness-shire ( gd, Siorrachd Inbhir Nis) is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of Scotland. Covering much of the Highlands and Outer Hebrides, it is Scotland's largest county, though one of the smallest in populat ...
and Banffshire.
Etymology
 The original Gaelic name for the range is ''Am Monadh Ruadh'' (the red hills), distinguishing them from ''Am Monadh Liath'' (the grey hills), which lie to the west of the River Spey:
The
The original Gaelic name for the range is ''Am Monadh Ruadh'' (the red hills), distinguishing them from ''Am Monadh Liath'' (the grey hills), which lie to the west of the River Spey:
The English language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to t ...
name for the range is Cairngorms, and is derived from Cairn Gorm, which is prominent in the view of the mountains from Speyside. The earliest reference to this name appears to be from a Colonel T. Thornton, who visited the area in about 1786:
Cairn Gorm is generally translated as ''Blue Cairn'', although the Gaelic ''gorm'' is also used as an adjective and verb, meaning green or greening and is often seen in connection with growing grass. Thus, there is a contradiction or confusion, because the original Scottish Gaelic name of the mountains translates to English as the "red hills" whilst their English name is the "blue hills" or the "green hills".
Geography
 The Cairngorms consist of three large elevated plateaux adorned with low, rounded glacial mountains, and divided by the passes of the
The Cairngorms consist of three large elevated plateaux adorned with low, rounded glacial mountains, and divided by the passes of the Lairig an Laoigh
The Lairig an Laoigh ( ; gd, Làirig Laoigh) is a mountain pass through the Highlands of Scotland. In speech and sometimes in writing the name is reduced to "Lairig Laoigh". It is of glacial origin, dissecting the Cairngorm plateau, and it ru ...
and the Lairig Ghru.D. Bennet & R. Anderson. ''The Munros: Scottish Mountaineering Club Hillwalkers Guide'', pp. 127-147. Published 2016. The range gives the sense of being a single plateau, because the passes that cut through them are not very deep: the summit of Lairig an Laoigh lies at ,Ordnance Survey
Ordnance Survey (OS) is the national mapping agency for Great Britain. The agency's name indicates its original military purpose (see ordnance and surveying), which was to map Scotland in the wake of the Jacobite rising of 1745. There was ...
Landranger 1:50000, Sheet 36. whilst the summit of the Lairig Ghru is at above sea level at the Pools of Dee, where the water may be frozen over even in mid-summer. This means a walker could cross between the Cairntoul
Cairn Toul ( gd, Càrn an t-Sabhail, 'hill of the barn') is the fourth-highest mountain in Scotland and all of the British Isles, after Ben Nevis, Ben Macdui and Braeriach. The summit is 1,291 metres (4,236 feet) above sea level. It is in t ...
() – Braeriach
Braeriach or Brae Riach ( gd, Am Bràigh Riabhach, 'the brindled upland') is the third-highest mountain in Scotland and all of the British Isles, after Ben Nevis and Ben Macdui, rising above sea level. It is in the Scottish Highlands and is ...
() massif to the Ben Macdui () – Cairn Gorm () massif and thence onto the Beinn a' Bhùird
Beinn a' Bhùird is a Munro in the Cairngorm mountain range of Scotland.
In ''Watson'' (1975) the author suggests the mountain should be named ''Beinn Bòrd - table hill'', saying that local Scottish Gaelic speakers pronounced the mountain ''P ...
() – Ben Avon
Ben Avon ( gd, Beinn Athfhinn, 'mountain of the Avon') is a mountain in the Cairngorms of Scotland. It is a sprawling mountain with a broad summit plateau dotted with granite tors. One of these marks the summit, called ''Leabaidh an Daimh Bhuid ...
() massif without descending below the summit of the Lairig an Laoigh. The range is drained by the Rivers Dee and Spey Spey may refer to:
*Spey River (disambiguation)
*Spey casting, a fly fishing technique developed on the River Spey
*Rolls-Royce Spey, an early turbofan engine
* HMS ''Spey'', the name of seven ships of the Royal Navy
* For spey-wife -- see Völva a ...
; and the latter's two tributaries: the Rivers Feshie and Avon.
The approximate southern boundary of the Cairngorm range is generally reckoned to run from slightly east of Braemar
Braemar is a village in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, around west of Aberdeen in the Highlands. It is the closest significantly-sized settlement to the upper course of the River Dee sitting at an elevation of .
The Gaelic ''Bràigh Mhàrr'' pr ...
, west along the Dee and Glen Geldie to the head of Glen Feshie. The western edge of the range is defined by Glen Feshie and the River Spey as far as Aviemore, with the northern boundary running roughly eastward from Aviemore through Glenmore to Glen Avon. The eastern boundary is defined by Glen Avon and the Am Bealach Dearg, thus ending slightly east of Braemar.
The Cairngorms feature the highest, coldest and snowiest plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ...
s in the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles (O ...
and are home to five of the six highest mountains in Scotland:
* Ben Macdhui ()
* Braeriach
Braeriach or Brae Riach ( gd, Am Bràigh Riabhach, 'the brindled upland') is the third-highest mountain in Scotland and all of the British Isles, after Ben Nevis and Ben Macdui, rising above sea level. It is in the Scottish Highlands and is ...
()
* Cairn Toul ()
* Sgor an Lochain Uaine ()
* Cairn Gorm ()
There are no public roads through the Cairngorms, and all the public roads in the general area either skirt the Cairngorms or stop short, providing access to them only. From the south and south-east, motorised access ends at Linn of Dee, or Allanaquoich. From the north-west, a road passes Coylumbridge
Coylumbridge (Scottish Gaelic Drochaid na Cuingleum) is a small rural newly built hamlet), that lies 6 miles northeast of Dalnavert, Highland, and 3 miles southeast of Aviemore, in the valley of the River Spey, in the west Cairngorms National ...
, Glenmore and the Sugarbowl to end at the car park at the Cairngorm Mountain ski resort
Cairn Gorm ( gd, An Càrn Gorm) is a mountain in the Scottish Highlands. It is part of the Cairngorms range and wider Grampian Mountains. With a summit elevation of above sea level, Cairn Gorm is classed as a Munro and is the seventh-hi ...
. The majority of hill-walkers access the range from these road ends.
Climate
 In terms of height, remoteness and the severe and changeable weather, the Cairngorms are the most arduous area in the United Kingdom. in The plateau area has a
In terms of height, remoteness and the severe and changeable weather, the Cairngorms are the most arduous area in the United Kingdom. in The plateau area has a Tundra climate
The tundra climate is a polar climate sub-type located in high latitudes and high mountains. undra climate https://www.britannica.com/science/tundra-climateThe Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica, 2019 It is classified as ET according to Köppen ...
( Köppen ''ET''), and the shattered terrain is more like the high ground in high-arctic Canada or northern Norway than what is often observed in the European Alps or Rockies. The weather often deteriorates rapidly with altitude so that, when there are moderate conditions below the plateau, the top can be stormy or misty, and there can be icy or powdery snow. Even when no snow is falling, the wind can whip up lying snow to produce white-out conditions for a few metres above the surface, and snowdrifts can build up rapidly in sheltered places. Gravel can be blown through the air, and walking can be impossible.
The lowest recorded temperature in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
has twice been recorded in the Cairngorms, at Braemar
Braemar is a village in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, around west of Aberdeen in the Highlands. It is the closest significantly-sized settlement to the upper course of the River Dee sitting at an elevation of .
The Gaelic ''Bràigh Mhàrr'' pr ...
, where a temperature of , was recorded on 11 February 1895 and 10 January 1982. The greatest British wind speed of was measured at Cairngorm summit weather station in January 1993. The weather can be very hazardous at times, with dangerous and unpredictable conditions. What is often described as Britain's worst mountaineering tragedy, the Cairngorm Plateau Disaster, left five children and one adult dead in November 1971.
Cairn Gorm gets of snow annually according to snowforecast.com.
Snow patches
 The Cairngorms hold some of the longest-lying snow patches in Scotland:
*On Ben Macdui, snow has been known to persist at a few locations from one winter to the next.
*Lying at the north-eastern shoulder of Cairn Gorm is Ciste Mhearad. This hollow contains a patch which, hitherto, was known to persist through many years, but has not done so since 2000.Royal Meteorological Society "Weather" October 2002, vol. 57; Adam Watson, Richard W Davison & John Pottie. Observations in 2007 and 2008 revealed that September was the month when final melting occurred for this patch. It sits at an altitude of and is located at approximately .
*
The Cairngorms hold some of the longest-lying snow patches in Scotland:
*On Ben Macdui, snow has been known to persist at a few locations from one winter to the next.
*Lying at the north-eastern shoulder of Cairn Gorm is Ciste Mhearad. This hollow contains a patch which, hitherto, was known to persist through many years, but has not done so since 2000.Royal Meteorological Society "Weather" October 2002, vol. 57; Adam Watson, Richard W Davison & John Pottie. Observations in 2007 and 2008 revealed that September was the month when final melting occurred for this patch. It sits at an altitude of and is located at approximately .
*Braeriach
Braeriach or Brae Riach ( gd, Am Bràigh Riabhach, 'the brindled upland') is the third-highest mountain in Scotland and all of the British Isles, after Ben Nevis and Ben Macdui, rising above sea level. It is in the Scottish Highlands and is ...
's Garbh Choire Mòr is the location of Scotland's most persistent snow beds. Snow has been absent from this corrie just five times in the last century: 1933, 1959, 1996, 2003 and 2006. Sitting at an altitude of about 1140 m, these patches are located around ; the two most long-lasting patches are known as "the Pinnacles" and "the Sphinx" after the rock climbs lying above them. It has been claimed that Garbh Choire Mòr (as well as Coire an Lochain in the northern corries) may have contained a glacier as recently as the 19th century.
In 1994, the Cairngorms and surrounding mountains of north-east Scotland had 55 surviving patches, an exceptional number.
Geology
The Cairngorms were formed 40 million years before the last ice age, when slight uplift raised an eroded peneplain based on an exposedgranite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies und ...
pluton. The highest present-day peaks represent eroded monadnock hills. During the ice ages, the ice caps that covered most of northern Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to th ...
remained static—frozen to the ground for long periods—and actually protected the rounded summits and valleys and deep, weathered granite of the mountains of the area. Glacial erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is di ...
is represented in deep valleys which dissect the area. Many valleys are littered with glacial deposits from the period of glacial retreat. The most famous valley is the Lairig Ghru pass, a gouge through the centre of the mountains—a u-shaped valley, now partly filled with extensive scree
Scree is a collection of broken rock fragments at the base of a cliff or other steep rocky mass that has accumulated through periodic rockfall. Landforms associated with these materials are often called talus deposits. Talus deposits typically ha ...
produced by intense frost action during ice-free periods. Many parts of the Cairngorms exhibit classic periglacial weathering
Weathering is the deterioration of rocks, soils and minerals as well as wood and artificial materials through contact with water, atmospheric gases, and biological organisms. Weathering occurs '' in situ'' (on site, with little or no movemen ...
which occurred during cold periods in ice-free areas.
Tors are a common feature of the Cairngorm granite massif, being especially frequent on Ben Avon
Ben Avon ( gd, Beinn Athfhinn, 'mountain of the Avon') is a mountain in the Cairngorms of Scotland. It is a sprawling mountain with a broad summit plateau dotted with granite tors. One of these marks the summit, called ''Leabaidh an Daimh Bhuid ...
and Beinn Mheadhoin
Beinn Mheadhoin or Beinn Meadhain () is a mountain in the Highlands of Scotland. It is a Munro with a height of and by some counts it is the twelfth-highest mountain of Great Britain. It lies in the very heart of the Cairngorm mountains, and ...
and impressively high on Bynack More. They represent masses of granite which are less closely jointed than surrounding rock and which have therefore been less susceptible to underground weathering associated with fluid percolation along joints. The present tors have been exhumed over a long period of time, not least by periglacial processes associated with ice ages during the Quaternary period.
Nature and conservation
The Cairngorms provide a unique alpine semi-tundra moorland habitat, home to many rare plants, birds and animals. Speciality bird species on the plateaux include breeding ptarmigan, dotterel, snow bunting,golden eagle
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known birds ...
, ring ouzel and red grouse
The red grouse (''Lagopus lagopus scotica'') is a medium-sized bird of the grouse family which is found in heather moorland in Great Britain and Ireland. It is usually classified as a subspecies of the willow ptarmigan but is sometimes consid ...
, with snowy owl, twite, purple sandpiper and Lapland bunting seen on occasion. Mammal species include red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or hart, and a female is called a hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Iran, and parts of wes ...
and mountain hare, as well as the only herd of reindeer
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 subsp ...
in the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles (O ...
. They now roam the high Cairngorms, after being reintroduced in 1952 by a Swedish herdsman. The herd is now stable at around 150 individuals, some born in Scotland and some introduced from Sweden; since the individuals depend on humans for food and come from domesticated stock, they are not considered wild.
The surrounding areas feature an ancient woodland, one of the last major ones of its kind in the British Isles, known as the Caledonian forest. In the forests, capercaillie, black grouse, Scottish crossbill
The Scottish crossbill (''Loxia scotica'') is a small passerine bird in the finch family Fringillidae. It is endemic to the Caledonian Forests of Scotland, and is the only terrestrial vertebrate species endemic to the United Kingdom. The ...
, parrot crossbill and crested tit are found. Of particular fame is the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds ( RSPB) reserve at Abernethy Forest and Loch Garten
Loch Garten ( gd, Loch a' Ghartain) is a large Highland freshwater loch near Boat of Garten, in the Strathspey area of the Cairngorms National Park, in Scotland. It is surrounded by the tall pine trees of the Abernethy Forest, a large area (adjac ...
. A famous pair of osprey
The osprey (''Pandion haliaetus''), , also called sea hawk, river hawk, and fish hawk, is a diurnal, fish-eating bird of prey with a cosmopolitan range. It is a large raptor reaching more than in length and across the wings. It is brown o ...
s are present in the summer months, and they often attract large crowds to see them. The forest is home to the endangered capercaillie and endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found els ...
Scottish crossbill.
As well being included as part of the Cairngorms National Park the Cairngorm Mountains are designated as a national scenic area, one of 40 such areas in Scotland. Apart from a small area around the Cairngorm Ski Area, the whole of the mountain area is protected as both a Special Area of Conservation and a Special Protection Area, thus forming part of the Natura 2000 network of protected sites. The Cairngorms are classified as a Category IV protected area
Protected areas or conservation areas are locations which receive protection because of their recognized natural, ecological or cultural values. There are several kinds of protected areas, which vary by level of protection depending on the ena ...
by the International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natur ...
.
The Cairngorms were declared a national nature reserve (NNR) in 1954, being the largest NNR in Britain. In 2006 Scottish Natural Heritage (SNH) reviewed the Cairngorms NNR, and it was decided that the reserve should be broken up into separate, smaller reserves that reflected existing management units. There now are four NNRs within the core mountain area of the Cairngorms. Mar Lodge Estate, which covers the south side of the plateau and the watershed of the upper Dee has been classified as a national nature reserve since May 2017. The Abernethy Forest National Nature Reserve covers a stretch of land from the plateau down to Loch Garten
Loch Garten ( gd, Loch a' Ghartain) is a large Highland freshwater loch near Boat of Garten, in the Strathspey area of the Cairngorms National Park, in Scotland. It is surrounded by the tall pine trees of the Abernethy Forest, a large area (adjac ...
on the north side of the range, and Glenmore Forest Park, covering a remnant of the Caledonian Forest surrounding Loch Morlich, is also designated as a national nature reserve. The Invereshie and Inshriach National Nature Reserve lies on the western flanks of the range, and extends to the summit of Sgòr Gaoith
Sgòr Gaoith ( gd, Sgòr Gaoithe, 'windy peak') is a mountain peak in the far western massif of the Cairngorms in the Scottish Highlands. It is high, and is the highest point on a long north-south ridge. The ridge is separated from the Braer ...
.
Threats to the ecosystem
The Cairngorms represents an unusually cold area of mountains in a maritime climate at 57 degrees north. The climate is projected to warm—and precipitation patterns to change—under presentclimate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
models. This is an over-riding concern for the long-term conservation of this area. Ptarmigan has been considered as an indicator species for this process, although the natural population cycles of this bird do not seem to have been disrupted as yet.
Other man-made threats include the problems of popularity in a country with limited wilderness resources and a large, relatively affluent urban population. These include various types of recreation and the associated trampling damage and erosion, disturbance, litter and threats to water quality.
Human habitation and ownership
 The valleys between the individual plateaux were used as drove roads by cattle drovers who built rough protective shelters for their arduous journeys. At about the same time that droving was dying out towards the end of the 19th century, deer stalking estates were flourishing, and so the shelters were developed into bothies to provide improved, though still primitive, accommodation for gamekeepers. In modern times, these bothies have been taken over by the Mountain Bothies Association for use by walkers and climbers to provide shelter and rough sleeping accommodation. With the exception of the bothies, there are no buildings or settlements within the Cairngorms, nor is there evidence for historic settlement, except in the uppermost reaches of the Derry and Gairn rivers. In the surrounding areas, villages such as Aviemore and
The valleys between the individual plateaux were used as drove roads by cattle drovers who built rough protective shelters for their arduous journeys. At about the same time that droving was dying out towards the end of the 19th century, deer stalking estates were flourishing, and so the shelters were developed into bothies to provide improved, though still primitive, accommodation for gamekeepers. In modern times, these bothies have been taken over by the Mountain Bothies Association for use by walkers and climbers to provide shelter and rough sleeping accommodation. With the exception of the bothies, there are no buildings or settlements within the Cairngorms, nor is there evidence for historic settlement, except in the uppermost reaches of the Derry and Gairn rivers. In the surrounding areas, villages such as Aviemore and Braemar
Braemar is a village in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, around west of Aberdeen in the Highlands. It is the closest significantly-sized settlement to the upper course of the River Dee sitting at an elevation of .
The Gaelic ''Bràigh Mhàrr'' pr ...
provide a base for visitors to the core mountain area.
Much of the core mountain area is owned by conservation bodies, with the National Trust for Scotland
The National Trust for Scotland for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, commonly known as the National Trust for Scotland ( gd, Urras Nàiseanta na h-Alba), is a Scottish conservation organisation. It is the largest membership organi ...
owning Mar Lodge Estate, and the RSPB's Abernethy Estate stretching from the lower slopes up to the plateau. The main private landowners are the Glenavon Estate in the northeast, the Invercauld Estate in the southeast, the Glen Feshie Estate to the southwest and the Rothiemurchus
Rothiemurchus Forest is a remnant of the Caledonian Forest at near Aviemore, Inverness-shire, Scotland. It is in the Highland region.
The forest is popular for recreation and contains important independent wildlife, including the osprey, Scotti ...
Estate in the northwest.
Leisure
There is a funicular railway on Cairn Gorm serving the Cairn Gorm Ski Centre. Thefunicular
A funicular (, , ) is a type of cable railway system that connects points along a railway track laid on a steep slope. The system is characterized by two counterbalanced carriages (also called cars or trains) permanently attached to opposite e ...
opened in late 2001, and runs from a base station at 637 m up to the Ptarmigan Centre, situated at 1097 m, 150 m from the summit of Cairn Gorm. It was built amidst some controversy, with supporters of the scheme claiming that it would bring valuable tourist income into the area, whilst opponents argued that such a development was unsuitable for a supposedly protected area. A condition was therefore imposed under which walkers were not allowed outside the top station if arriving by funicular, although this did not apply to skiers and snowboarders in the winter. In 2010 the operating company proposed to modify this requirement to allow guided walks, whilst still preventing general access. Guided walks continued to be the only way for walkers and summer visitors to access the plateau if arriving via the funicular as of 2017.
The mountains are very popular for hill-walking, with eighteen Munros lying between Ben Avon
Ben Avon ( gd, Beinn Athfhinn, 'mountain of the Avon') is a mountain in the Cairngorms of Scotland. It is a sprawling mountain with a broad summit plateau dotted with granite tors. One of these marks the summit, called ''Leabaidh an Daimh Bhuid ...
in the east and Glen Feshie in the west. In winter these summits can often be reached by ski touring. The Cairngorms have excellent climbing
Climbing is the activity of using one's hands, feet, or any other part of the body to ascend a steep topographical object that can range from the world's tallest mountains (e.g. the eight thousanders), to small boulders. Climbing is done ...
, and has long attracted winter climbers, especially in the northern corries. This area boasts what was for a time probably the world's hardest traditionally protected mixed climb: "The Hurting", grade XI. As with all land in Scotland, there is a right of responsible access to the mountains for those wishing to participate in recreational pursuits, although the restriction on access via the funicular means walkers and climbers cannot use the railway to access the hills.
Angling
Angling is a fishing technique that uses a fish hook or "angle" (from Old English ''angol'') attached to a fishing line to tether individual fish in the mouth. The fishing line is usually manipulated via a fishing rod, although rodless techni ...
for trout
Trout are species of freshwater fish belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', '' Salmo'' and '' Salvelinus'', all of the subfamily Salmoninae of the family Salmonidae. The word ''trout'' is also used as part of the name of some non-sa ...
and salmon
Salmon () is the common name
In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of ...
is popular in the lochs and rivers that surround the mountains, and Loch Avon in the very heart of the range is noted for its Arctic charr. Other popular activities include birdwatching
Birdwatching, or birding, is the observing of birds, either as a recreational activity or as a form of citizen science. A birdwatcher may observe by using their naked eye, by using a visual enhancement device like binoculars or a telescope, b ...
and wildlife watching, whilst the Cairngorm Gliding Club (based in Glen Feshie) offers the opportunity for gliding.
Gallery
See also
*Ben Nevis
Ben Nevis ( ; gd, Beinn Nibheis ) is the highest mountain in Scotland, the United Kingdom and the British Isles. The summit is above sea level and is the highest land in any direction for . Ben Nevis stands at the western end of the Grampian ...
* Cairn Gorm
* Cairngorms National Park
Cairngorms National Park ( gd, Pàirc Nàiseanta a' Mhonaidh Ruaidh) is a national park in northeast Scotland, established in 2003. It was the second of two national parks established by the Scottish Parliament, after Loch Lomond and The Tros ...
* Caledonian Forest
* List of Munro mountains
* Mountains and hills of Scotland
Notes
References
Works cited
* John Allen joined the Cairngorm Mountain Rescue Team after the time of the disaster and went on to become its leader. * * Adam Watson is an academic and hill walker with very great experience of the Cairngorms.External links
The Badenoch and Strathspey Conservation Group
The Cairngorm Club
Cairngorms National Park
Cairngorm Mountain
Cairngorms Climate Change
Walks in the Cairngorms
WinterHighland
{{Authority control Mountains and hills of the Eastern Highlands Mountains and hills of Aberdeenshire Mountains and hills of Highland (council area) Mountains and hills of Moray Ski areas and resorts in Scotland Rural Scotland Tourist attractions in Highland (council area) Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Badenoch and Strathspey Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Kincardine and Deeside Sites of Special Scientific Interest in Moray and Nairn Mountain ranges of Scotland National scenic areas of Scotland